This page describes the information shared by components that implement reorigination for GSM and CDMA networks .
For GSM networks:
For CDMA networks:
-
CDMA Reorigination service and SCCCDMAReOrigination feature
These components use:
-
shared network operation configuration, and
-
a shared Correlation RA entity for reorigination information.
-
(GSM reorigination) a Cassandra CQL RA entity to store call information data in a cassandra DB.
Network operator configuration
Network configuration data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile table named SCCCommonReOriginationConfigProfileTable.
| Attribute name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
UsePrefix |
boolean |
If set to true, prepends |
NetworkPrefix |
String |
See |
SkipHSSLookup |
boolean |
This decides whether the SIP feature will do a query to the HSS for the S-CSCF address or not |
DirectRoutingURI |
String |
The value to use for the address to add to the route header that will be added to the |
GeneratedPVNITemplate |
String |
A template string for the P-Visited-Network-Information header generated in the reorigination, where |
PoliceOriginatingRequests |
boolean |
Police incoming originating requests, and reject attempts to hijack the call. Enabled by default. |
ImsUserStateSourceForMtBypass |
String |
The source used to determine the IMS user state of the subscriber, during MT bypass. One of: |
(CAMEL Only) Visited Network ID Address List
Both the IN and SIP Reorigination features, in a GSM deployment, make use of an address list for mapping a given VLR address to a Visited Network ID. This is used as a fallback if the InitialDP does not contain suitable location information.
The SIP feature uses this address list in order to populate headers on the outgoing INVITE message.
The IN feature uses the address list purely as an early failure measure.
It checks that there exists a matching Visited Network ID for the VLR address; this prevents network resources from being wasted establishing a SIP dialog that will
ultimately fail at the SIP Reorigination feature anyway.
|
|
Currently, we require that the VLR address’s nature is International and its numbering plan is ISDN.
|
There are two profile tables associated with this address list:
-
<PlatformOperatorName>_SCCReorigination_AddressListConfigurationTable
-
<PlatformOperatorName>_SCCReorigination_AddressListEntryTable
The configuration table is a standard address list configuration table, see Address List Configuration Profile
for more information. The list entry table is an extended version of the standard address list entry table (details
here: Address List Entry Profile)
with one additional field, a String called VisitedNetworkId. Profiles in this table must use a standard format for their
names, made up of three fields: the Sentinel Selection Key,
a fixed String VisitedNetworks, and the VLR address prefix to be matched when searching for a Visited Network ID.
The name should be formatted like this:
-
<SelectionKey>:VisitedNetworks:<AddressPrefix>
Here’s an example:
-
OpenCloud:OpenCloud::::VisitedNetworks:6421
See the respective behaviour sections of the IN and SIP Reorigination feature pages for details on how each feature uses the address list.
For an overview of how address lists work in general, see: Address Lists.
|
|
We recommend that the visited network is formatted according to GSMA IR.65 section 6.2.1. I.e. is of the format epc.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org or ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org, depending on the version used |
Use of the Correlation RA
The IN feature/CDMA reorigination service and their SIP counterparts share (and communicate) correlation information through
the Correlation RA. The resource adaptor entity used has the resource-adaptor-entity-link name sentinel-correlation-reorigination.
|
|
See Correlation Resource Adaptor for more information about the correlation RA. |
The reorigination addresses allocated by the Correlation RA must route through to the IMS, and allow the I-CSCF to trigger the SCC-AS. Typically this is done by configuring a range of numbers that correspond to one or more IMS public service identifiers.
The sentinel-correlation-reorigination RA entity has one or more correlation ID pools.
-
a default ID pool (optional)
-
a set of named ID pools.
Choosing the Correlation ID Pool
Each named ID pool is identified by the NodeID and a set of prefixes for choosing/selecting the ID pool. From the Correlation RA standpoint, the prefixes can be any address string. The client to the RA provides an address that the RA uses:
In GSM Volte, the IN reorigination feature uses the MobileCountryCode extracted from LocationInformation in the triggering InitialDP
In CDMA Volte, the CDMA reorigination service uses the LocationAreaID extracted from the OriginationRequest or AnalyzedInformation
The Correlation RA performs a longestPrefix match address list search on pools with a matching NodeID for the current node. If no pool is matched by the search or no address is provided by the client to the RA, then the default pool is selected. If multiple pools match the longestPrefix address list search, the first pool in the result set is selected.
Storing Call Information in Cassandra
Call information data is stored in cassandra for two reasons:
-
A reorigination session can be processed successfully if the SCC-AS node that received and processed the
InitialDP,OriginationRequestorAnalyzedInformationtrigger fails before the re-originated SIPINVITEis received by the SCC-AS. -
A reorigination session can be processed successfully during an SCC-AS upgrade, even if the SCC-AS node that processed the
InitialDP,OriginationRequestorAnalyzedInformationtrigger, and the SCC-AS node that received the re-originated SIPINVITEare members of different SCC-AS clusters.
|
|
The SCC Re-Origination features use the cassandra-general resource adaptor entity. |
GSM Re-Origination
Call information data is stored in Cassadandra with keyspace opencloud_scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination,
and table scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination_data.
A sample command for creating the opencloud_scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination keyspace in a production environment is:
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS opencloud_scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 3};Replication may not be necessary for testing purposes. A sample CQL command for creating such a keyspace is:
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS opencloud_scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 1};The following CQL statements creates the scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination_data table:
USE opencloud_scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS scc_camel_to_ims_reorigination_data (
correlation_id text,
correlation_id_expire_time timestamp,
node_uri text,
correlation_data blob,
PRIMARY KEY (correlation_id)
)
WITH gc_grace_seconds = 600; // 10 minutes| Field | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
correlation_id |
text |
The correlation ID related to the |
correlation_id_expire_time |
timestamp |
Represents the maximum time, after which the correlation ID allocation is considered to have expired |
node_uri |
text |
The URI of the SCC-AS node that assigned the correlation ID |
correlation_data |
blob |
Call information that is stored on the |
The correlation_id is the primary key.
CDMA Re-Origination
Call information data is stored in Cassadandra with keyspace opencloud_scc_cdma_to_ims_reorigination,
and table scc_cdma_to_ims_reorigination_data.
| Field | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
correlation_id |
text |
The correlation ID related to the |
correlation_id_expire_time |
timestamp |
Represents the maximum time, after which the correlation ID allocation is considered to have expired |
node_uri |
text |
The URI of the SCC-AS node that assigned the correlation ID |
correlation_data |
blob |
Call information that is stored on the |
The correlation_id is the primary key.
Reorigination basic flow
The following diagrams cover some basic reorigination scenarios for GSM and CDMA networks.
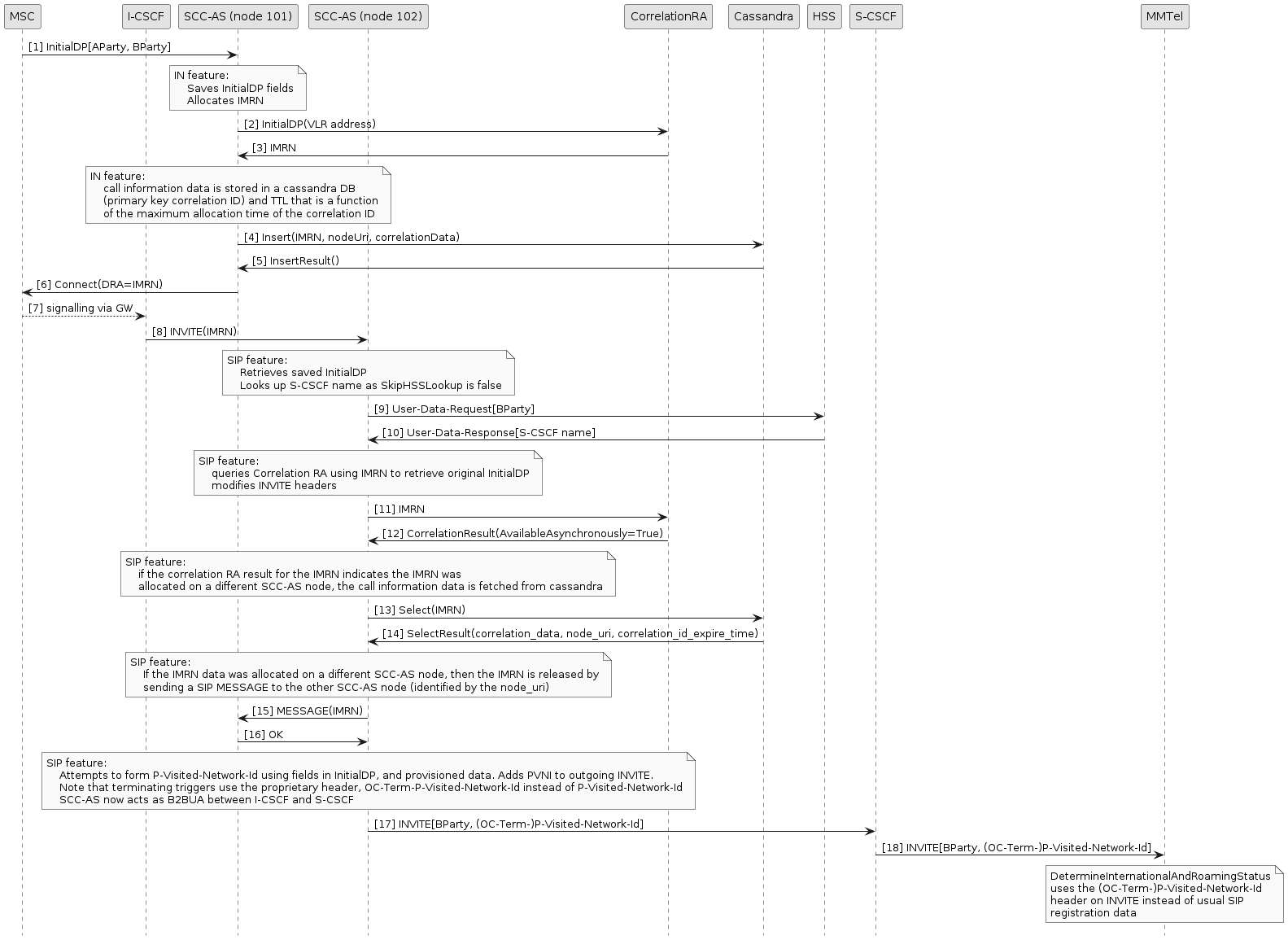
GSM Reorigination Scenario 1
In the following diagram:
-
Sentinel VoLTE acts as the SCC-AS (node 101 and node 102).
-
The “IN feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature.
-
The “SIP feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP feature.
-
Correlation data is stored in an external cassandra DB. The Sentinel SCC-AS reads call information data from cassandra when the re-originated SIP
INVITEis received on a different SCC-AS node that received theInitialDP. -
The User-Data-Request and Answer will not occur if the SkipHSSLookup flag is set to true and instead the value in the DirectRoutingURI will be used.
This flow diagram shows a configuration where the SkipHSSLookup flag is set to false, so that the SCC-AS looks up the HSS
and acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the S-CSCF after B number restoration.
The InitialDP is received on SCC-AS (node 101), and the SIP INVITE is received in a different SCC-AS (node 102).
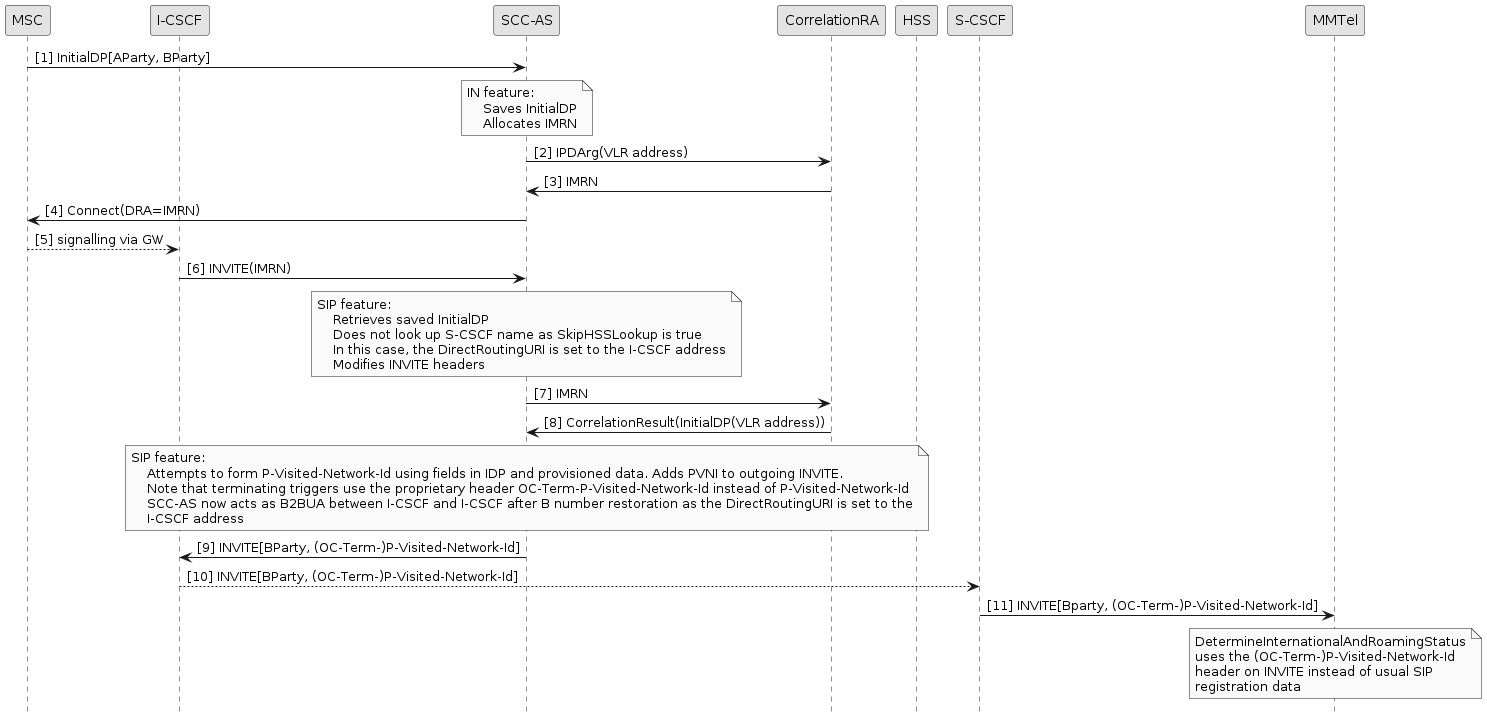
GSM Reorigination Scenario 2
As a variation to the above diagram, the following shows the effect of configuring:
-
SkipHSSLookup flag set to true
-
DirectRoutingURI set to the I-CSCF
CDMA Reorigination Scenario
In the following diagram:
-
Sentinel VoLTE acts as the SCC-AS.
-
The “CDMA Service” is the CDMA ReOrigination service.
-
The “SIP feature” is the SCCCDMAReOrigination feature.
-
Correlation data is stored in an external cassandra DB. The Sentinel SCC-AS reads call information data from cassandra when the re-originated SIP INVITE is received on a different SCC-AS node that received the
OriginationRequestorAnalyzedInformation. -
The User-Data-Request and Answer will not occur if the SkipHSSLookup flag is set to true and instead the value in the DirectRoutingURI will be used.
This flow diagram shows a configuration where:
-
SkipHSSLookup flag set to true
-
DirectRoutingURI set to the I-CSCF
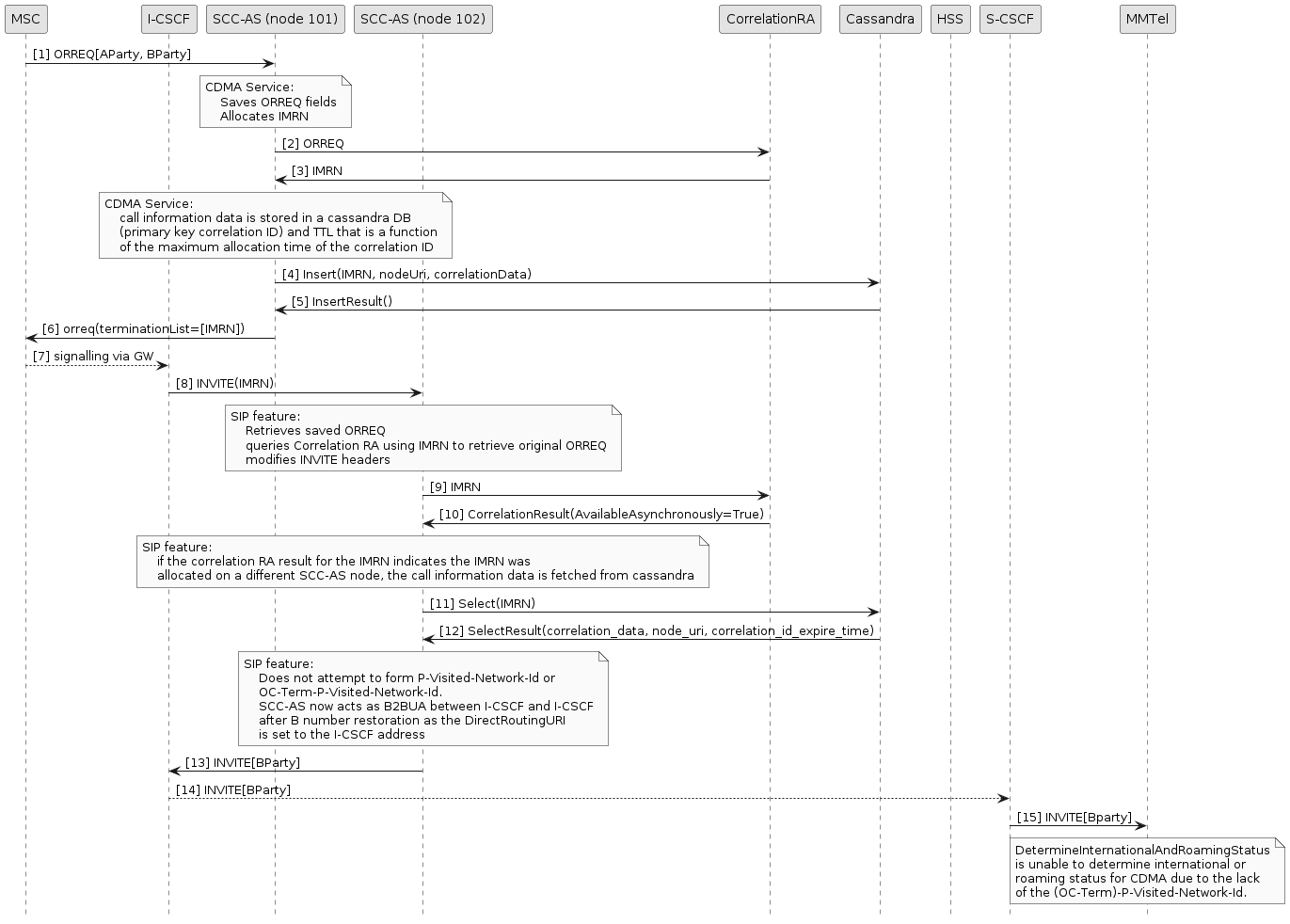
For further information related to headers set in the outgoing SIP INVITE, please refer to SIP headers in the outgoing INVITE.
Reorigination MT Bypass flow
The following diagrams show an MT scenario where the served user is not registered in the IMS and the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature bypasses terminating reorigination.
The difference between each scenario is the method used to determine if the served user is registered in the IMS.
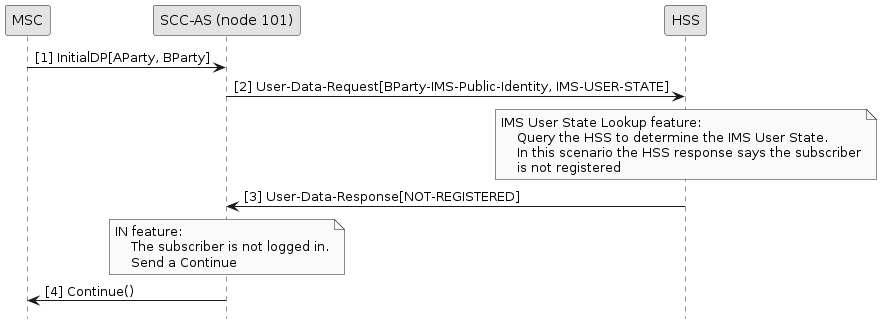
GSM MT Bypass, Query HSS for IMS User State
In the following diagram:
-
Sentinel VoLTE acts as the SCC-AS (node 101 and node 102).
-
The “IMS User State Lookup feature” is the IMSUserStateLookupFromHSS feature.
-
The “IN feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature.
-
The SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature is configured with
BypassTermReorIfNotRegistered == true
-
The InitialDP is received on SCC-AS (node 101).
The IMSUserStateLookupFromHSS feature queries the HSS for the IMS user state of the served user
(as identified by the IMS public identity derived from the InitialDP).
In this scenario the served user is not registered in the IMS, so the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN
sends a Continue and closes the dialog with the MSC.
GSM MT Bypass, Derive IMS User State by Querying Third Party Registration Data in Cassandra
In the following diagram:
-
Sentinel VoLTE acts as the SCC-AS (node 101 and node 102).
-
The “IMSID Lookup Cassandra IN feature” is the IMSIDLookupFromCassandraIN feature.
-
The “IN feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature.
-
The SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature is configured with
BypassTermReorIfNotRegistered == true
-
The InitialDP is received on SCC-AS (node 101).
The IMSIDLookupFromCassandraIN feature checks the Associated URIs table in the Cassandra database
for entries related to the served user (as identified by the IMS public identity derived from the InitialDP).
In this scenario there are no entries in the Associated URIs table (therefore the served user is not registered in the IMS).
The SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN sends a Continue and closes the dialog with the MSC.

