OpenCloud’s Rhino Sentinel VoLTE product implements the Service Centralisation and Continuity Application Server (SCC-AS) and Multimedia Telephony Application Server (MMTel-AS).
|
|
Sentinel VoLTE is based on OpenCloud’s Sentinel architecture and frameworks, and automatically gains from all benefits of Sentinel, including:
|
Major components
In the diagram below, the components OpenCloud provides are in green.
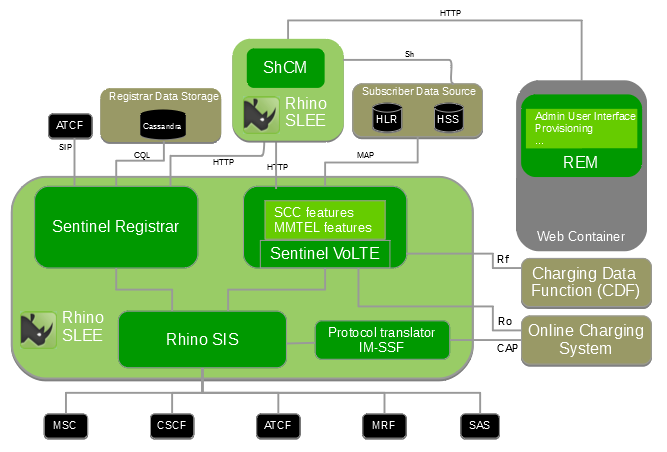
VoLTE includes the ‘session processing’ parts:
-
an extensible Third Party Registrar with support for either HSS or Cassandra as Storage system for Registrar Subscriber Data
-
an extensible IN SCP
-
an extensible SIP session processing framework.
It provides web-server based infrastructure for:
-
the administration web user interface (Rhino Element Manager)
-
RESTful Provisioning Services
-
JSLEE services.
It also provides Online Charging Support by either using the Ro interface or CAP interface with IM-SSF Protocol Translator and Offline Charging Support via Rf interface and CDRs. For more information see the Charging Support.
JSLEE services
Sentinel VoLTE’s JSLEE services are based on OpenCloud’s Sentinel architecture and frameworks.
It includes four JSLEE services:
-
Sentinel-based SIP Third Party Registrar (for SCC and MMTEL)
-
Sentinel-based SIP based Service — hosting the ‘main session processing logic’ (for SCC and MMTEL)
-
Sentinel-based IN SCP Service (for SCC)
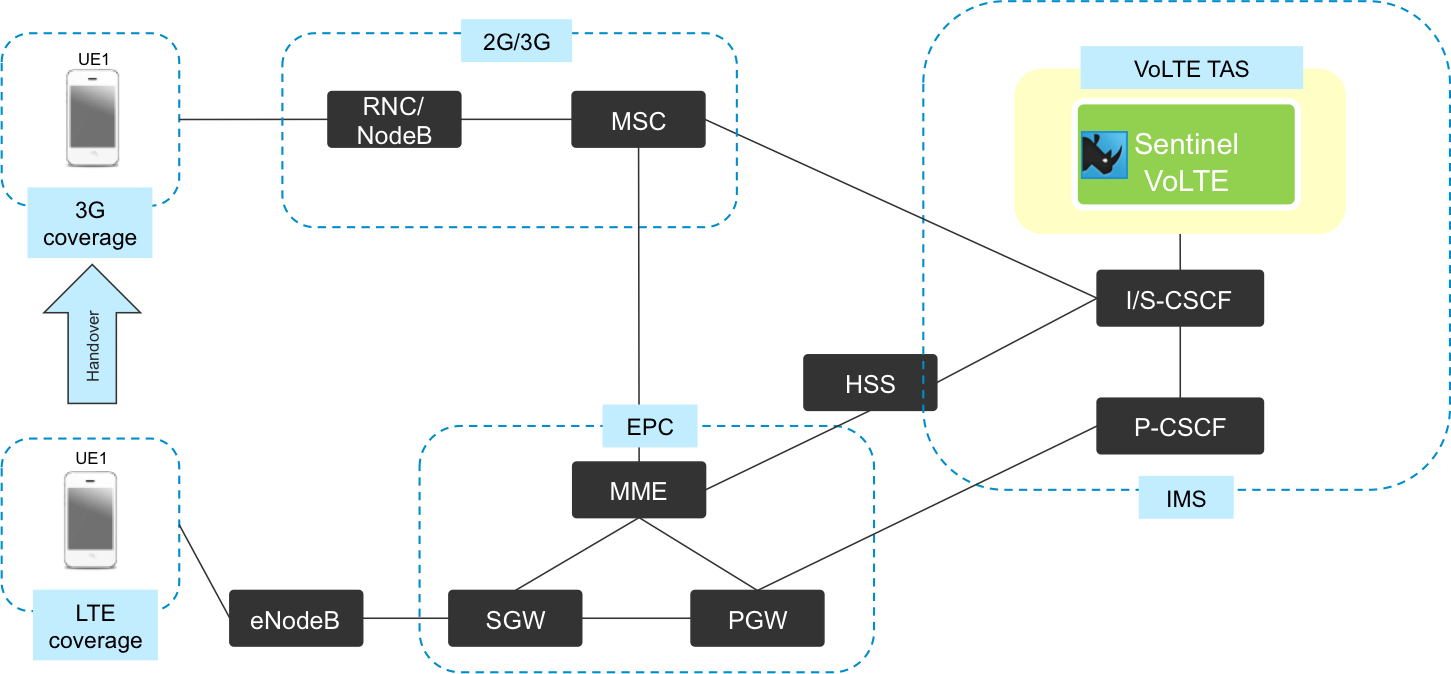
Sentinel VoLTE in an LTE network
The diagram below shows where Sentinel VoLTE fits into an LTE network.
B2BUA architecture
The B2BUA architecture includes:
iFC Triggering Chaining and the SCC and MMTEL
3GPP defines that the SCC-AS is the first TAS invoked in the Originating iFC treatment, and the last in the Terminating iFC treatment.
The following diagrams represent a session where the SCC-AS and the MMTEL-AS are the only two TAS invoked, and MMTEL is used for both Originating and Terminating treatment.
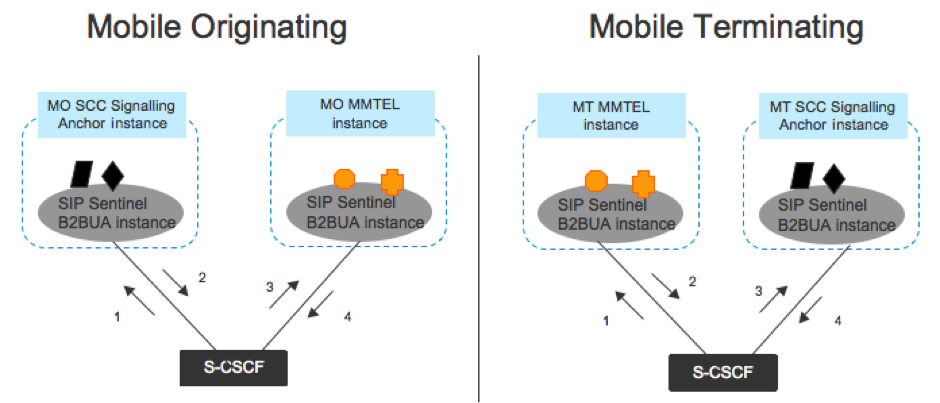
Note that for simplicity, both the Originating and Terminating Served-Users are in the same network, and happen to be assigned to the same Serving CSCF.
Sentinel VoLTE TAS implements both the SCC-AS and the MMTEL-AS. In this Session there are four Back-to-Back User Agent instances:
-
Mobile Originating SCC-AS
-
Mobile Originating MMTEL
-
Mobile Terminating MMTEL
-
Mobile Terminating SCC-AS.
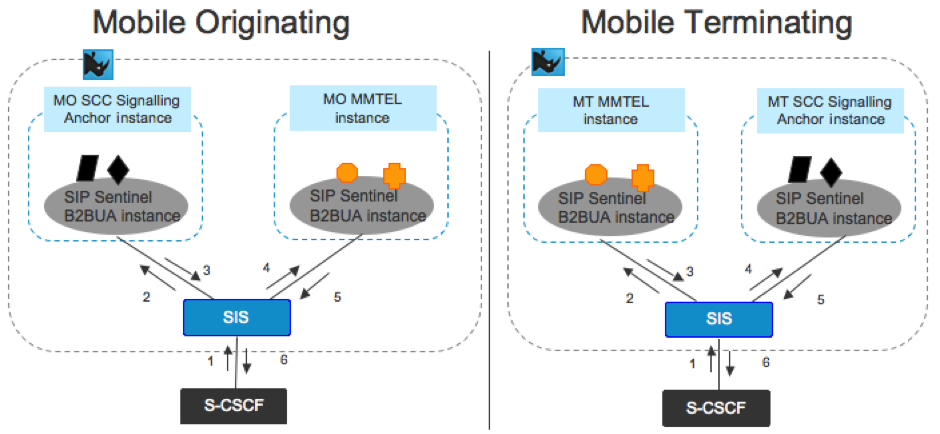
Co-location using the Rhino SIS
OpenCloud supports co-location of the B2BUA instances in the same cluster, and even Unix process/JVM instance. The co-location and signalling interaction can be achieved using the Rhino SIS to orchestrate the session.
Therefore, the S-CSCF does not need to be configured for iFC trigger chaining as shown in the first case. This is an optional configuration and is represented below.
Subscriber Data Storage
VoLTE supports either HSS or HLR for storing Subscriber Data. The data from the HLR and HSS is normalized in VoLTE and used by MMTEL and SCC services. This means that the Operator can use either data source without changing the service logic.
Supplementary services database
The subscriber’s supplementary services data is stored in the HSS as transparent data. Sentinel VoLTE TAS queries the HSS via the Sh interface to read and store the data.
The data is stored in XML format and can have the standard service data and extensions or even proprietary data sets.
Media resource function
The Media Resource Function (MRF) is responsible for providing multimedia-related functions, such as mixing of streams of audio and audio/video conferences, controlling Interactive Voice Response (IVR) sessions, and playing back multimedia.
The MRF can be invoked by single-purpose protocols, such as NETANN, when the TAS does not need to have further control of the session. This is useful for actions such as post-call announcements where the TAS hands over the control of the session to the MRF. The single-purpose protocols can be used together with the VoiceXML protocol to specify the interaction script that the MRF executes for the call (TAS forwards the SIP INVITE message with the VoiceXML URI in a SIP URI parameter).
For more complex scenarios, the TAS uses other XML-based protocols to control the MRF, such as MSML. The TAS forwards the SIP INVITE with the SDP information to the MRF. The MRF establishes a RTP stream with the UE. After that, the TAS sends MSML documents inside SIP INFO messages with the actions that MRF should execute (for example, play announcement).
Sentinel VoLTE supports NETANN and the MSML interface. A H.248 interface is not supported, so the MRF is expected to provide both the MRFC and MRFP elements.
An MRF is not included within Sentinel VoLTE; however, Rhino TAS has been integrated multiple times with MRFs and media servers from all major vendors (including RadiSys, Dialogic, and Alcatel-Lucent).
Cloud and virtualisation
Sentinel VoLTE is well-suited to cloud deployment. Find out more at the cloud and virtualisation page.
