This page contains example call flows showing how calls to the primary device’s IMPU are forked to both primary and companion devices under various configurations.
|
|
These call flows just show the path of the initial INVITE request up to when it is forked. From that point all scenarios would be identical to typical forking scenarios, so these parts have been omitted as they do not convey any new information. |
- Example with +sip.instance routing disabled
- Example with +sip.instance routing enabled
- Example with +sip.instance routing enabled and Voice Over PS support required
- Example with primary and companion devices on CS
- Example of hiding undisclosed identity
- Example of barring call to undisclosed identity
- Example of call using per-device routing
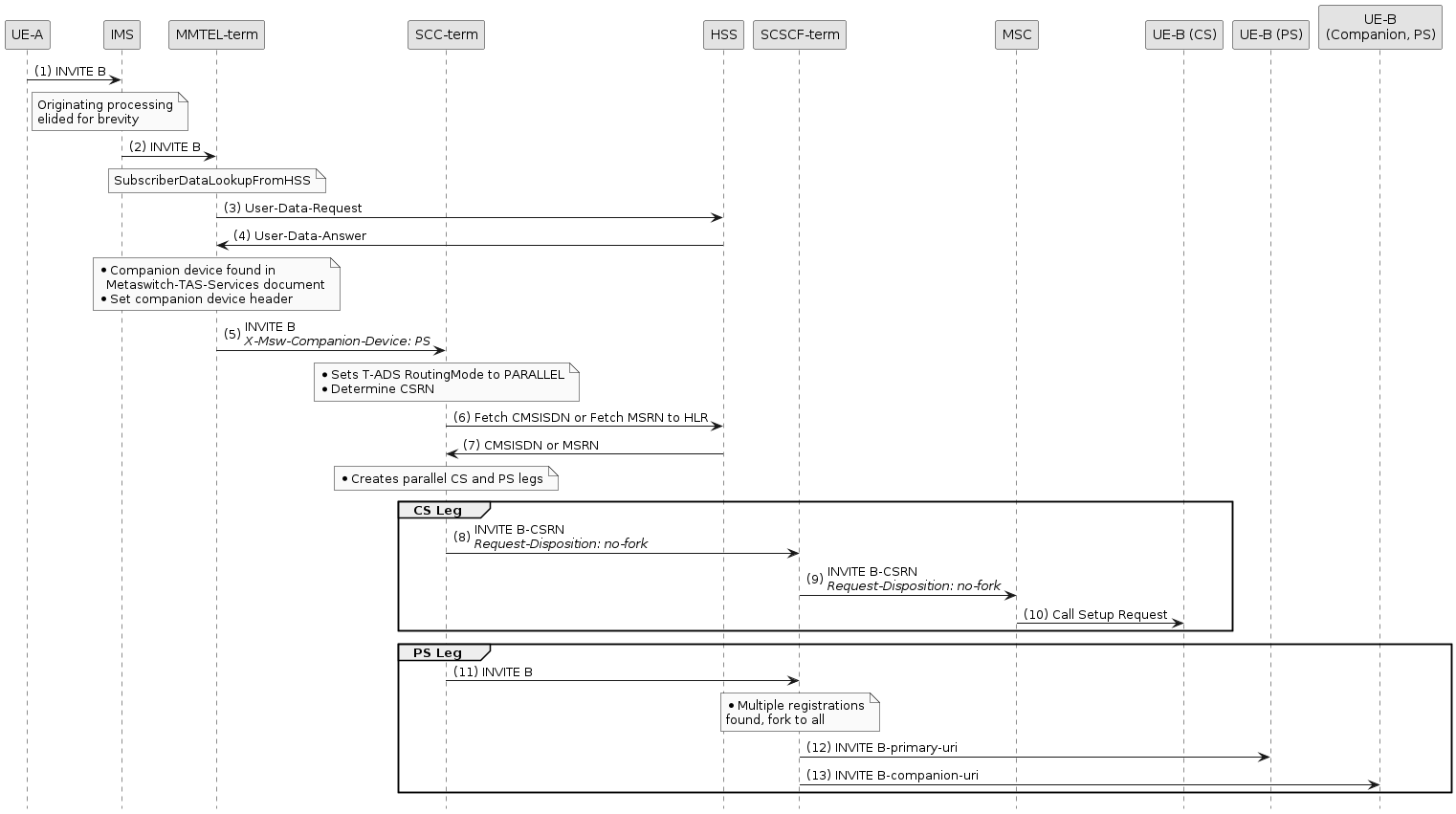
Example with +sip.instance routing disabled
In this flow, T-ADS is configured with EnableSipInstanceRouting = false.
This means that for the PS leg, T-ADS will forward the INVITE normally to the S-CSCF.
The S-CSCF sees that there are multiple registrations for the user, so forks the INVITE to both devices.
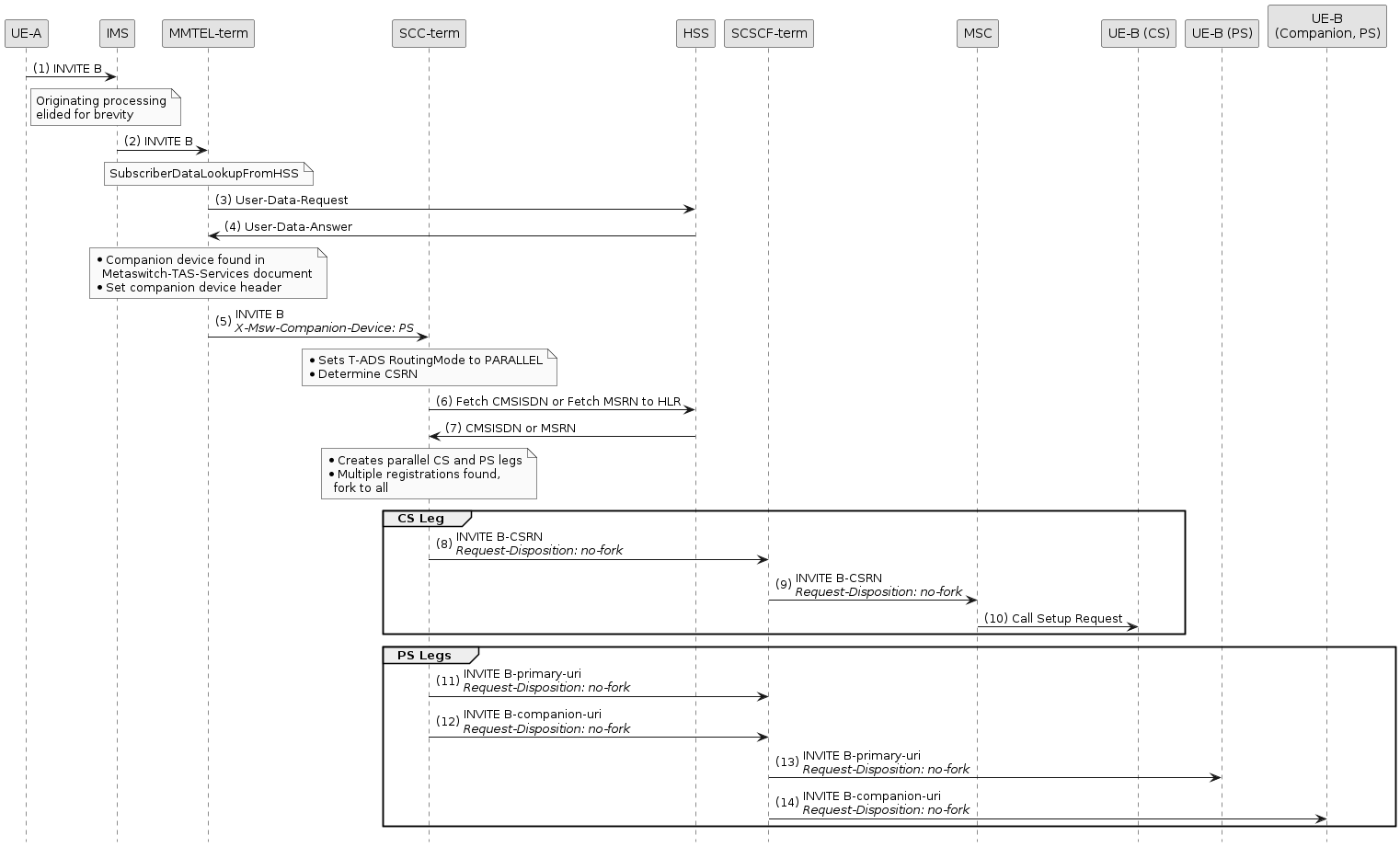
Example with +sip.instance routing enabled
In this flow, T-ADS is configured with EnableSipInstanceRouting = true.
This means that T-ADS will perform the forking itself, and create separate PS legs towards each registered device.
The Request-Disposition: no-fork header is added to the outbound INVITEs so that downstream nodes do not attempt to fork.
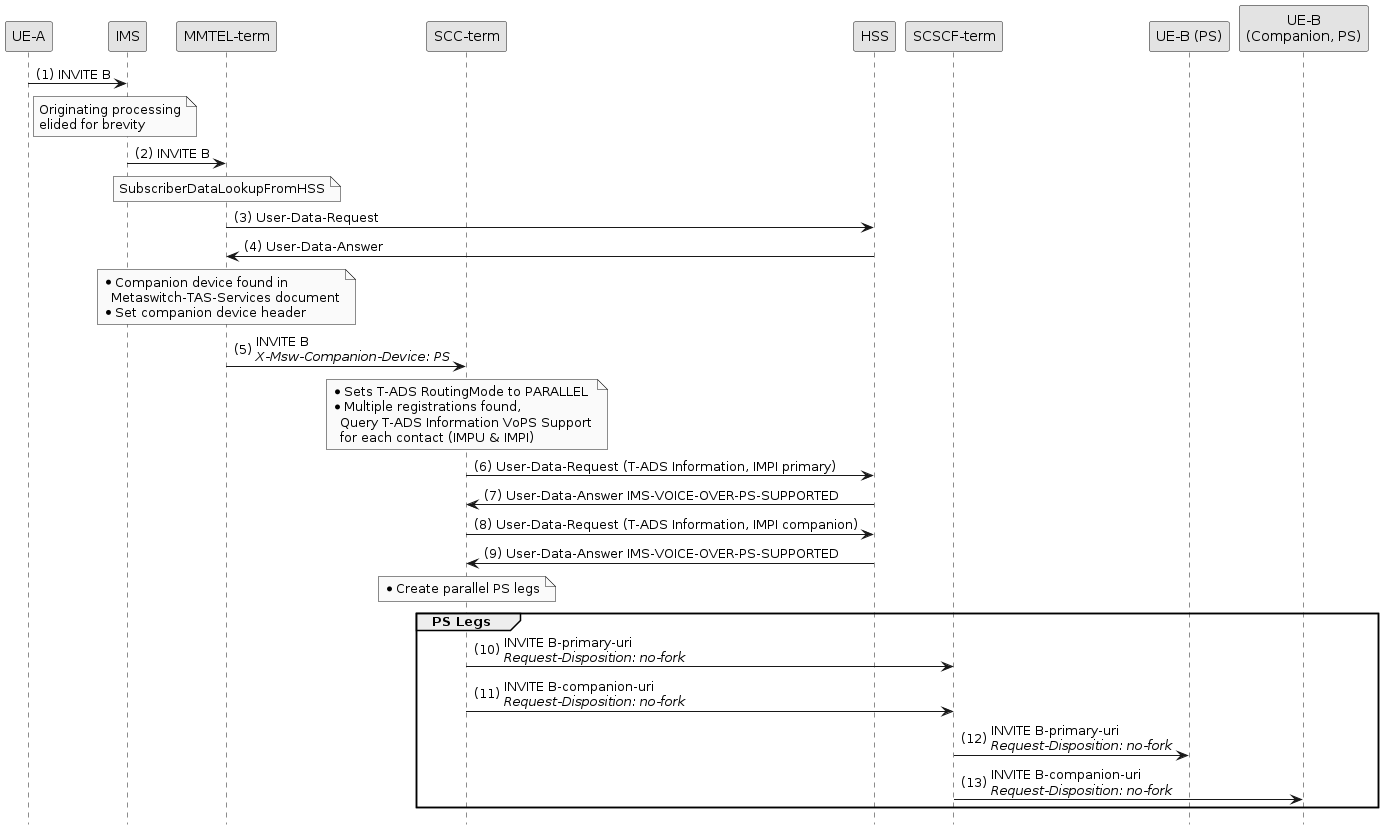
Example with +sip.instance routing enabled and Voice Over PS support required
In this flow, T-ADS is configured with EnableSipInstanceRouting = true and VoiceOverPSSupportRequired = true.
This means that T-ADS will perform the forking itself, but will only create an outbound PS leg if the HSS
can detect that the device is currently attached to the PS network.
The Request-Disposition: no-fork header is added to the outbound INVITEs so that downstream nodes do not attempt to fork.
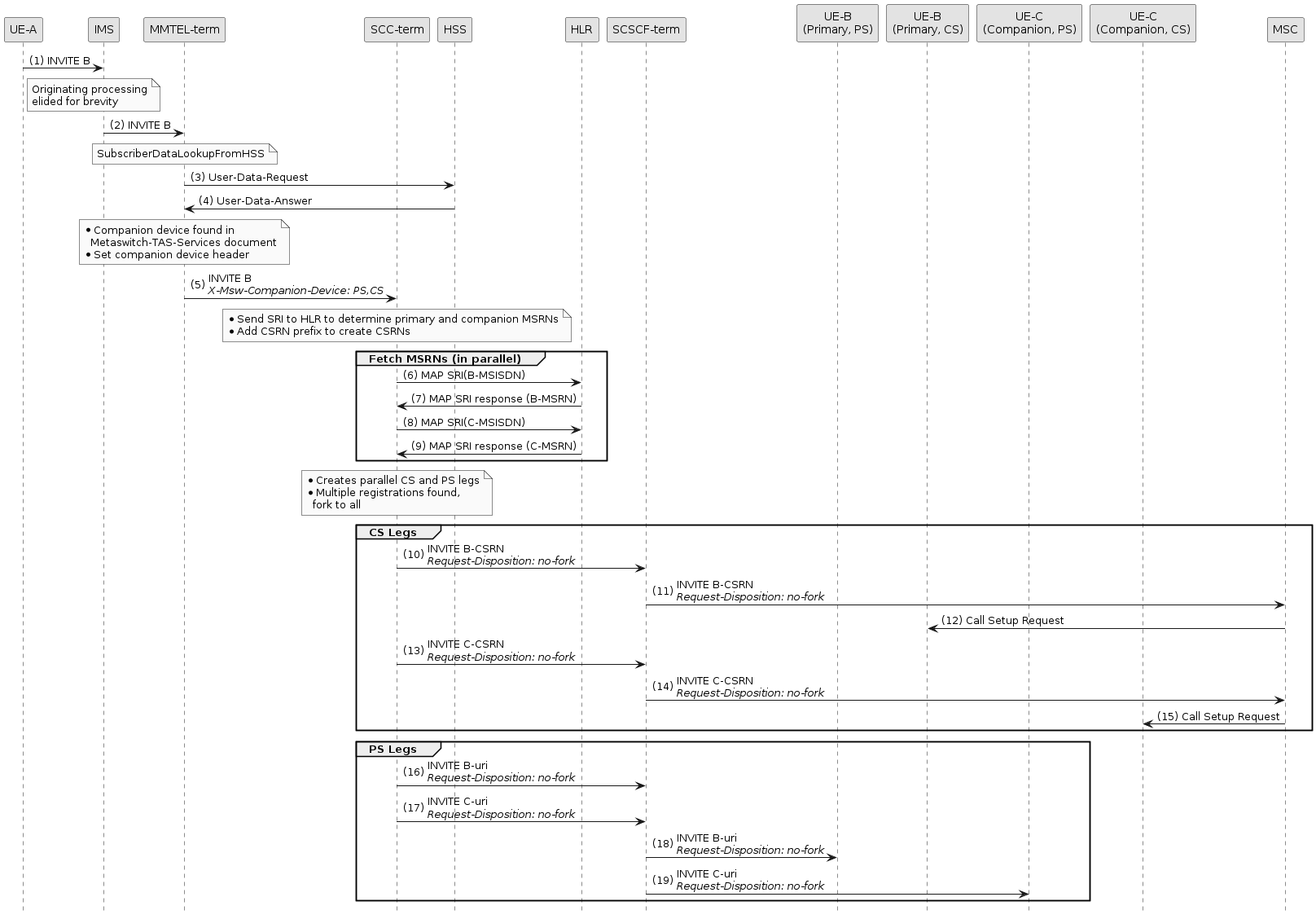
Example with primary and companion devices on CS
In this example, the called party (B) has a Metaswitch-TAS-Services document that indicates they have a companion device with CS support,
by the presence of the device/radio-access/CS element as shown in the XML fragment below:
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-companion-device>
<operator-companion-device authorized="true">
<shared-identity-sip>sip:+641234567@example.com</shared-identity-sip>
<shared-identity-tel>tel:+641234567</shared-identity-tel>
<devices>
<device active="true">
<model>Acme Watch</model>
<radio-access>
<PS/>
<CS msisdn="641234568"/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>
</operator-companion-device>
</complete-companion-device>
</metaswitch-services>T-ADS is configured to query the HLR to determine CSRNs (UseHLRBasedCSRN = true).
T-ADS sends a MAP SendRoutingInfo request to the HLR to determine the CSRNs for the primary and companion device.
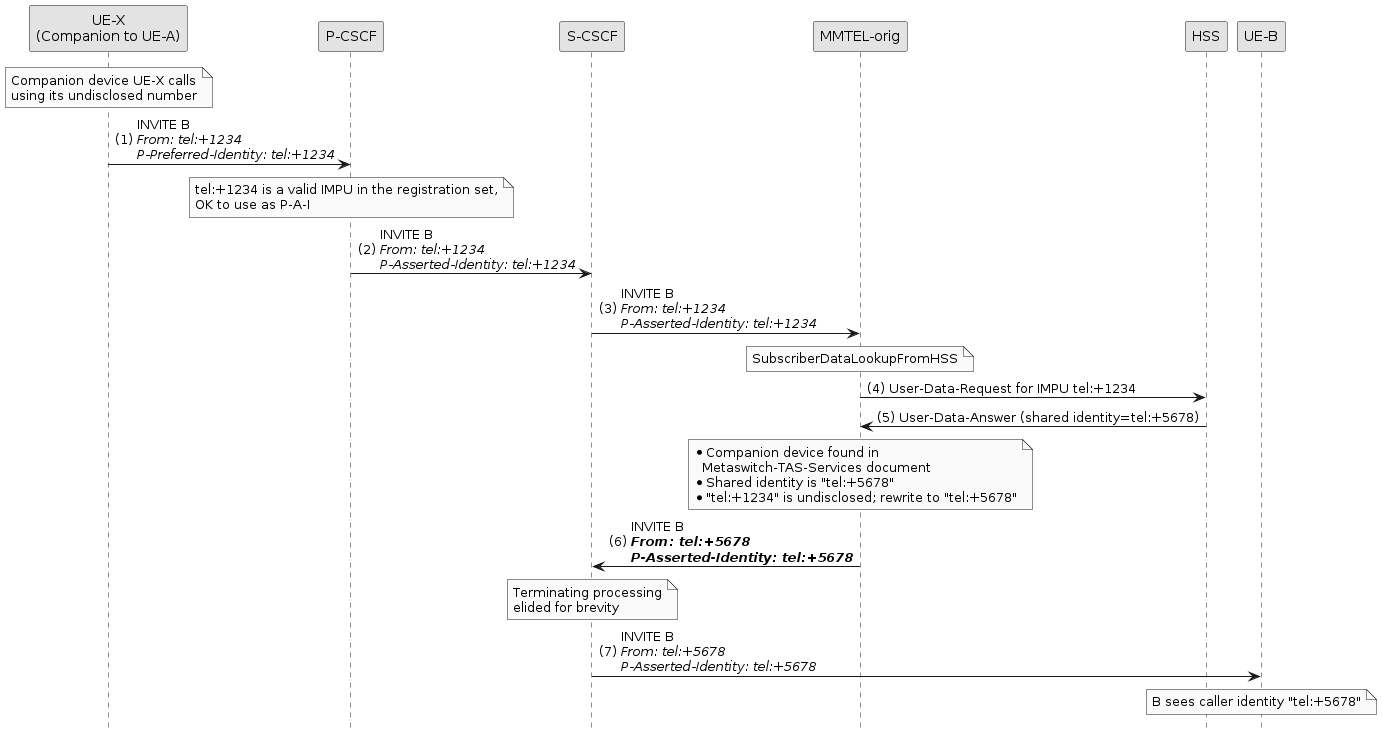
Example of hiding undisclosed identity
A companion device ("UE-X") is making a call, but is using its own undisclosed identity ("tel:+1234") as the calling party address.
The originating MMTel instance retrieves the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document and sees that an undisclosed identity is being used.
MMTel corrects the calling party address so that downstream devices see the shared identity ("tel:+5678")
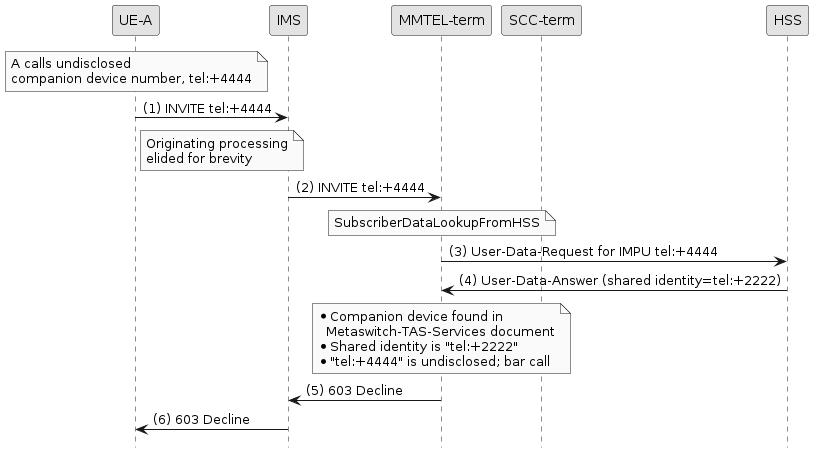
Example of barring call to undisclosed identity
In this example, the subscriber’s Metaswitch-TAS-Services document indicates that they have a companion device,
and the shared identity is "sip:+2222@example.com"/"tel:+2222", which may be used to call the primary or companion device.
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-companion-device>
<operator-companion-device authorized="true">
<shared-identity-sip>sip:+2222@example.com</shared-identity-sip>
<shared-identity-tel>tel:+2222</shared-identity-tel>
<devices>
<device active="true">
<radio-access>
<PS/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>
</operator-companion-device>
</complete-companion-device>
</metaswitch-services>However, subscriber A attempts a call to the companion device’s undisclosed identity, "tel:+4444". This will be barred by the terminating MMTel instance.
|
|
When matching an identity with the shared identity in Metaswitch-TAS-Services, the identity is normalised
using the Normalization Component.
|
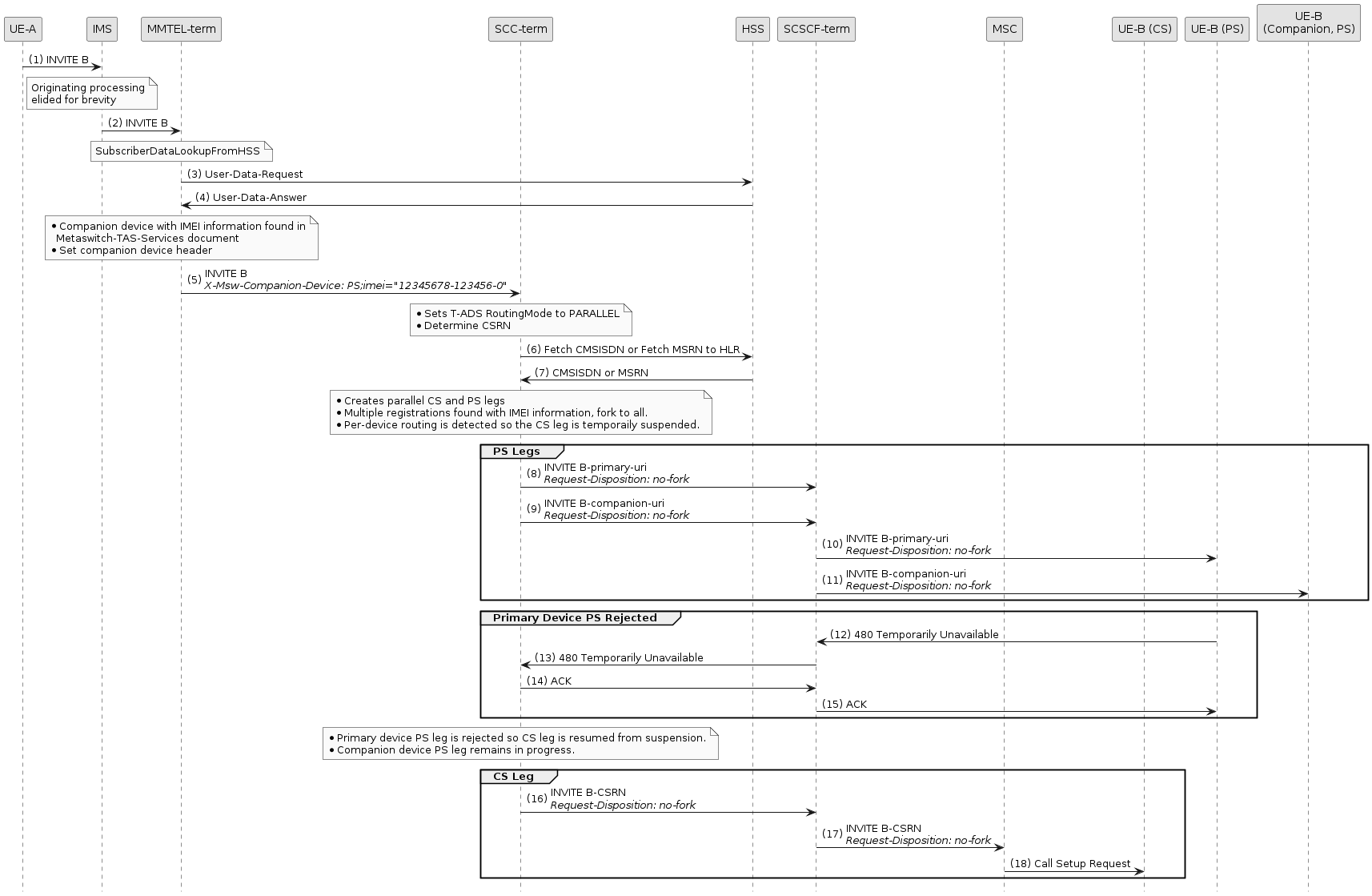
Example of call using per-device routing
In this flow, T-ADS is configured with EnableSipInstanceRouting = true.
This means that T-ADS will perform the forking itself, and create separate PS legs towards each registered device.
The Request-Disposition: no-fork header is added to the outbound INVITEs so that downstream nodes do not attempt to fork.
In this example, the subscriber’s Metaswitch-TAS-Services document indicates that they have a companion device,
and provides the companion device’s IMEI.
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-companion-device>
<operator-companion-device authorized="true">
<shared-identity-sip>sip:+2222@example.com</shared-identity-sip>
<shared-identity-tel>tel:+2222</shared-identity-tel>
<devices>
<device active="true">
<radio-access>
<PS/>
<imei>12345678-123456-0</imei>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>
</operator-companion-device>
</complete-companion-device>
</metaswitch-services>T-ADS is also configured with PerDeviceRoutingMode = AUTO.
This means that if T-ADS is able to correlate PS routes with companion device IMEI information from the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document,
then the CS routing attempt will be delayed until after PS routes to the primary device have been exhausted.