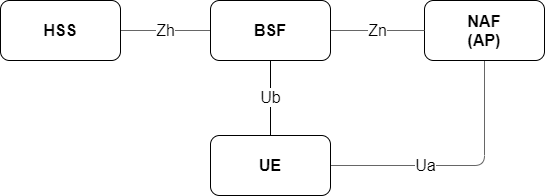
The diagram below shows a simplified view of the main roles and their interfaces involved in GAA.
| Role name | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
UE |
User Equipment |
The device that needs to securely access an application in the network. |
NAF |
Networked Application Function |
An application server. |
BSF |
Bootstrapping Security Function |
The BSF communicates with the UE and its HSS to create a security association based on the shared secret K. |
HSS |
Home Subscriber Server |
The HSS knows the UE’s shared secret K, and uses this to generate new authentication vectors (AVs) when requested by the BSF. The HSS also stores the subscriber’s GBA bootstrap security settings (GUSS), an XML document describing how the shared keys may be used with various service types. |
| Interface name | Description |
|---|---|
Ua |
Specifies how the UE authenticates with the NAF. Authentication is based on HTTP Digest authentication over HTTPS. Other application-specific interfaces may be defined on top of Ua. For example, Ut defines the interface between the UE and its XCAP server. |
Ub |
Specifies how the UE communicates with the BSF to create a NAF-specific shared key that the UE will use to authenticate over Ua. Based on AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement, RFC 3310) over HTTP. |
Zh |
A Diameter (RFC 6733) interface between the BSF and the HSS. The BSF uses Zh to request a new authentication vector (AV) from the HSS. The AV contains values that will be used to generate the NAF-specific shared key. The BSF also uses Zh to obtain the subscriber’s GUSS document. |
Zn |
The NAF uses Zn to obtain the NAF-specific shared key from the BSF, to authenticate the UE. This interface may be realized using Diameter or SOAP/HTTP. |
