The following is an example SBB that uses an sbbpart written using the generated sbbpart super class for the Ping Pong API.
There are two aspects to this example:
-
A root SBB that defines an SBB local interface.
-
An sbb-part that extends the generated sbb-part superclass. The sbb-part will interact with the root SBB via the root SBB local interface.
|
|
Advantages of using the generated sbb-part superclass
|
|
|
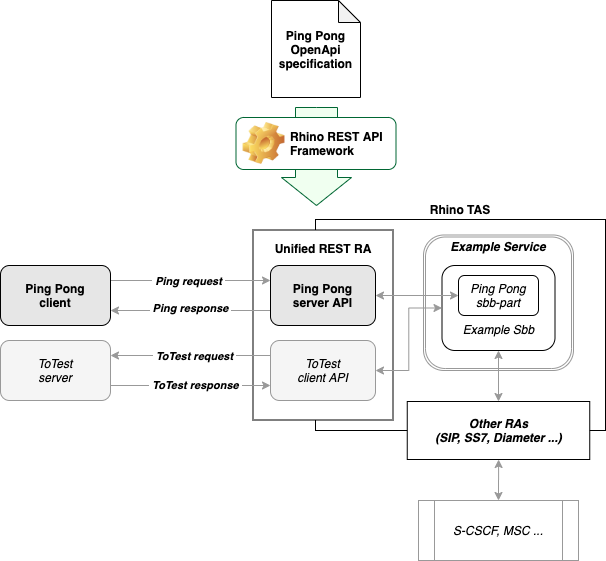
Learn about Rhino TAS - Telecom Application Server and the JAIN SLEE (JSR 240). |
Create an SBB class and SBB local interface
SBB local interface
The sbb-part will interact with the root SBB by invoking methods on its SBB local interface.
In this example, the root SBB local interface includes a single operation triggerScenario().
public interface TriggerScenario {
boolean triggerScenario(String api, String scenario);
}@Library(
id = @ComponentId(name = "@component.name@",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@")
)
public interface ExampleRestApiSbbLocal extends TriggerScenario, SbbLocalObject {
}SBB class
The root SBB implements the business logic of the service.
The slee-annotations on the root SBB define the service, root SBB and a dependency on our Ping Pong SBB-Part.
In this simple example, the root SBB will write a trace message in response to triggerScenario().
@SleeService(  id = @ComponentId(name = "@component.name@",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"),
rootSbb = @RootSBB(sbb = @ComponentId(name = "example-rest-api-sbb",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"))
)
@SBB(
id = @ComponentId(name = "@component.name@",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"),
rootSbb = @RootSBB(sbb = @ComponentId(name = "example-rest-api-sbb",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"))
)
@SBB(  vendorExtensionID = "example-rest-api-sbb-id",
id = @ComponentId(name = "example-rest-api-sbb",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"),
sbbClasses = @SBBClasses(
localInterface = @SBBLocalInterface(
interfaceName = "com.exampleco.slee.rest.ExampleRestApiSbbLocal"),
abstractClass = @SBBAbstractClass(reentrant = true)
),
libraryRefs = {
@LibraryReference(library = @ComponentId(name = "example-service-sbblocal",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"))
}
)
@OcSBB(
vendorExtensionID = "example-rest-api-sbb-id",
sbbParts = {
@SBBPartReference(id = @ComponentId(name = "example-pingpong-api-sbbpart",
vendorExtensionID = "example-rest-api-sbb-id",
id = @ComponentId(name = "example-rest-api-sbb",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"),
sbbClasses = @SBBClasses(
localInterface = @SBBLocalInterface(
interfaceName = "com.exampleco.slee.rest.ExampleRestApiSbbLocal"),
abstractClass = @SBBAbstractClass(reentrant = true)
),
libraryRefs = {
@LibraryReference(library = @ComponentId(name = "example-service-sbblocal",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"))
}
)
@OcSBB(
vendorExtensionID = "example-rest-api-sbb-id",
sbbParts = {
@SBBPartReference(id = @ComponentId(name = "example-pingpong-api-sbbpart",  vendor = "@component.vendor@",
ersion = "@component.version@"))
},
sbbClasses = @OcSBBClasses()
)
public abstract class ExampleRestApiSbb implements javax.slee.Sbb, TriggerScenario {
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
ersion = "@component.version@"))
},
sbbClasses = @OcSBBClasses()
)
public abstract class ExampleRestApiSbb implements javax.slee.Sbb, TriggerScenario {-
defines the service and identifies the root SBB
-
the example SBB (the root SBB for the service)
-
the sbb-part annotation links the root SBB to our Ping Pong sbb-part
@Override
public boolean triggerScenario(String api, String scenario) {
tracer.fine("Triggering: api={}, scenario={}", api, scenario);
return true;
}Create an sbb-part
SBB-Part class
The PingpongSbbpart class extends the generated sbb-part superclass (PingpongApiServerSbbpart).
@LibraryReferences(
libraryRefs = {
@LibraryReference(library=@ComponentId(name="example-service-sbblocal",
vendor="@component.vendor@",
version="@component.version@"))
}
)
public class PingpongSbbpart extends PingpongApiServerSbbpart {Implement sbb-part constructor
The PingpongSbbpart calls the superclass constructor and creates a Ping API object.
public PingpongSbbPart(SbbPartContext context) {
super(context);
this.pingApi = getApiProvider().getApiClient(
ApiConfiguration.standardConfiguration()).getPingApi();
}Override protected methods from the generated sbb-part superclass
The generated superclass defines protected methods that our sbb-part overrides to implement the service logic of the service.
protected final void handlePingRequest(PingRequest request,
ActivityContextInterface aci,
EventContext eventContext) throws IOException
{
getTracer().finest("Ping! {}", request);
// defer to the root sbb; call triggerScenario() on its sbb-local interface
final PingContext context = request.getPingContext();
final TriggerScenario testsbb = (TriggerScenario) getSbbPartContext().getSbbLocalObject();
testsbb.triggerScenario(context.getApi(), context.getScenario());
// send a success response
RestResponseBuilder response = request.create_200_SuccessResponse("text/plain", "Pong!");
pingApi.sendResponse(response, aci);
}
protected final void rejectPingRequest(PingRequest request, ActivityContextInterface aci) {
try {
final RestResponseBuilder errorResponse = request.createDefaultResponse(
501,"application/json",
new Error().code(501)
.message("Failed to process Ping request: " + request.getPingContext()));
pingApi.sendResponse(errorResponse, aci);
}
catch (IOException e) {
getTracer().finest("Failed to send 501 error response", e);
}
}Implement handlePingRequest by calling triggerScenario() on the sbb-local interface,
passing the api and scenario values from the PingReqest.
Understanding the Generated Code in PingpongApiServerSbbpart
The generated sbb-part superclass handles all the necessary wiring code required to access the PingPong REST API.
-
@SBBPart,@RATypeBindingsand @SBBPartDeployableUnit slee annotations -
SBB Part constuctor that does required JNDI lookups for the
PingPongREST API provider -
implements event handlers for each event supported by the
PingPongREST API -
defines protected methods that developers override to implement service logic
@SBBPart(
id = @ComponentId(name = "@component.name@",
vendor = "@component.vendor@",
version = "@component.version@"),
sbbPartClasses = @SBBPartClasses(
sbbPartClass = @SBBPartClass(
className="@sbbpart.class.name@"
),
activityContextInterface = @SBBPartActivityContextInterface(interfaceName = "@sbbpart.class.aci@")
),
libraryRefs = {
@LibraryReference(library = @ComponentId(name = "@guava-library.name@",
vendor = "@guava-library.vendor@",
version = "@guava-library.version@")),
@LibraryReference(library =
@ComponentId(name = "@rest-api-common.LibraryID.rest-api-common.name@",
vendor = "@rest-api-common.LibraryID.rest-api-common.vendor@",
version = "@rest-api-common.LibraryID.rest-api-common.version@"))
}
)
@RATypeBindings(
raTypeBindings = {
@RATypeBinding(
raType = @ComponentId(name = "pingpong-api-server",
vendor = "ExampleCo",
version = "1.0"),
resourceAdaptorObjectName
= PingpongApiServerSbbpart.pingpong_PROVIDER_JNDI_NAME,
resourceAdaptorEntityLink = "unified-rest-ra",
activityContextInterfaceFactoryName
= PingpongApiServerSbbpart.pingpong_ACI_FACTORY_JNDI_NAME
)
}
)
@SBBPartDeployableUnit(
securityPermissions =
@SecurityPermissions(securityPermissionSpec = "grant { permission java.security.AllPermission; };")
)
public class PingpongApiServerSbbpart { public static final String pingpong_PROVIDER_JNDI_NAME = "api/pingpong-api-server/provider";
public static final String pingpong_ACI_FACTORY_JNDI_NAME = "api/pingpong-api-server/acifactory";
public PingpongApiServerSbbpart(SbbPartContext context) {
this.sbbPartContext = context;
this.tracer = (ExtendedTracer) sbbPartContext.getTracer(context.getSbbPart().getName());
try {
final Context env = (Context) new InitialContext().lookup("java:comp/env");
this.apiProvider = (PingpongApiServerProvider)
env.lookup(pingpong_PROVIDER_JNDI_NAME);
this.apiAciFactory = (PingpongApiServerACIFactory)
env.lookup(pingpong_ACI_FACTORY_JNDI_NAME);
}
catch (NamingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("NamingException trying to locate PingpongApiServerProvider", e);
}
} @EventMethod(  eventType = @ComponentId(name = "com.exampleco.openapi.pingpong.api.PingRequest",
vendor = "ExampleCo",
version = "1.0"),
initialEvent = true,
initialEventSelectVariable = IESVariableType.ActivityContext
)
public void onPingRequest(PingRequest request,
eventType = @ComponentId(name = "com.exampleco.openapi.pingpong.api.PingRequest",
vendor = "ExampleCo",
version = "1.0"),
initialEvent = true,
initialEventSelectVariable = IESVariableType.ActivityContext
)
public void onPingRequest(PingRequest request,  ActivityContextInterface aci,
EventContext eventContext)
{
// handle PingRequest event
tracer.finest("Received: {}", request);
try {
handlePingRequest(request, aci, eventContext);
}
catch(IOException e) {
tracer.finest("Failed to handle: {}", request, e);
rejectPingRequest(request, aci);
}
}
protected void handlePingRequest(PingRequest request,
ActivityContextInterface aci,
EventContext eventContext)
{
// handle PingRequest event
tracer.finest("Received: {}", request);
try {
handlePingRequest(request, aci, eventContext);
}
catch(IOException e) {
tracer.finest("Failed to handle: {}", request, e);
rejectPingRequest(request, aci);
}
}
protected void handlePingRequest(PingRequest request,  ActivityContextInterface aci,
EventContext eventContext) throws IOException
{
throw new IOException("handlePingRequest() is not implemented.");
}
protected void rejectPingRequest(PingRequest request, ActivityContextInterface aci) {
ActivityContextInterface aci,
EventContext eventContext) throws IOException
{
throw new IOException("handlePingRequest() is not implemented.");
}
protected void rejectPingRequest(PingRequest request, ActivityContextInterface aci) {  tracer.info("rejectPingRequest() is not implemented.");
}
tracer.info("rejectPingRequest() is not implemented.");
}-
slee-annotation for the
PingRequestevent handler -
implementation of the
PingRequestevent handler -
developer overrides this method to define normal behaviour for handling a
PingRequest -
developer overides this method to define the behaviour when handling a
PingRequestfails.
