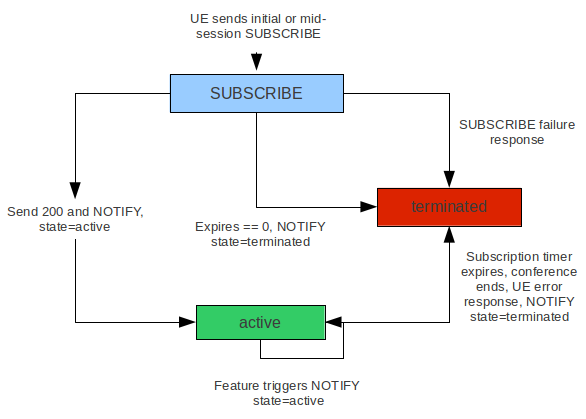
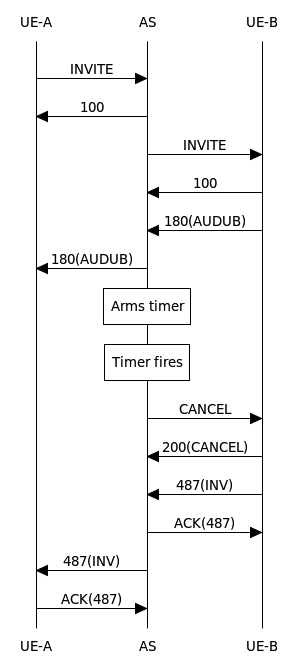
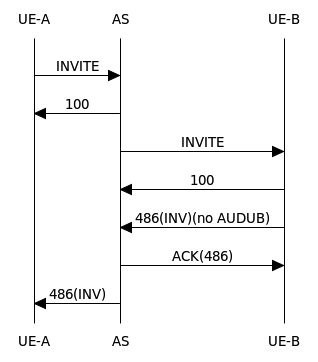
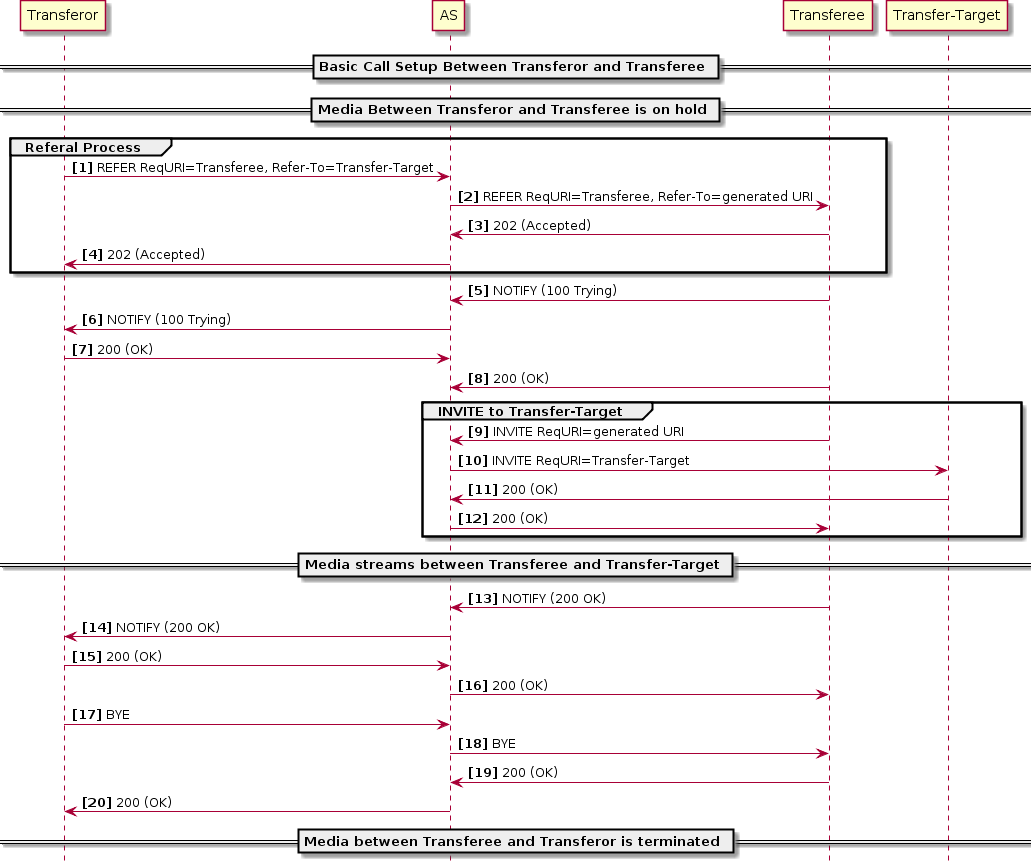
This document covers procedures for deploying, configuring, and managing Sentinel VoLTE:
-
Getting Started — how to install the product
-
Features — the behaviour and configuration of each feature
-
Mappers — the behaviour of mappers
-
Mapping of GSMA IR.92 to Sentinel VoLTE Features — features that provide support for GSMA’s IR.92 specification
-
Provisioning — how to provision and configure the Sentinel VoLTE product
-
Sentinel VoLTE and Data — the various data sources for Sentinel VoLTE and how VoLTE is configured to use them
-
Session Processing — how Sentinel VoLTE processes sessions, including Initial Filter Criteria, use of the HSS via Sh, and related topics
-
Charging Information — describes the format and content of CDRs, and AVPs present in the Diameter Ro interface
-
XCAP Server — how to configure the XCAP server
-
Manual Upgrade Procedure — how to manually upgrade your Sentinel VoLTE version
-
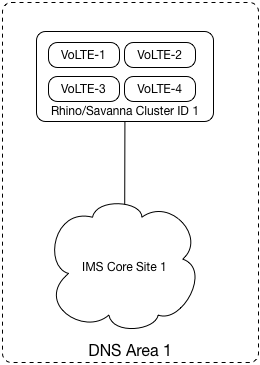
DNS Redundancy — how to configure DNS to provide a redundant configuration
-
Feature Source — list of features that have source code available through the SDK
-
Resource Adaptors — interfaces used by Sentinel VoLTE to communicate with external systems
-
System Statistics — statistics defined for Sentinel VoLTE features
-
License Requirements — license requirements for running Sentinel VoLTE
| |
Read this document in conjunction with the Sentinel VoLTE Architecture document. |
Getting Started
This section explains how to set up a standalone version Sentinel VoLTE on a Rhino SDK.
Preparing to Install Sentinel VoLTE
Before you install Sentinel VoLTE, you need to download the SDK package, get other required software.
You can then either:
-
let the built-in installer install both the Rhino SDK and Sentinel VoLTE, or
-
install and configure Rhino and the JVM manually, then use the installer to install Sentinel VoLTE into your Rhino
In both cases you need to get a license.
Allowing the installer to install both the Rhino SDK and Sentinel VoLTE software is recommended for functional testing or experimentation with Sentinel VoLTE. For production installs and/or load testing it is recommended to manually install and configure Rhino and the JVM.
Finally, if you are planning to install Sentinel VoLTE on an existing OpenCloud Rhino installation, it makes sense to refer to other OpenCloud product dependencies
Download the Sentinel VoLTE SDK package
To get the latest Sentinel VoLTE SDK package go to https://repo.opencloud.com/artifactory/opencloud-sentinel-volte-2.7.0/opencloud/volte/2.7.0/sentinel-volte-sdk/ Choose the version with the highest release number.
The SDK package contains an installer, that can install Sentinel VoLTE as an out-of-the-box system. It is also an SDK allowing customisation of the product.
| |
You will need OpenCloud-supplied credentials to download the package. |
Get required software
You’ll need the following software to run Sentinel VoLTE:
| Software | Download Link | Documentation Link |
|---|---|---|
Java JDK 7 |
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk7-downloads-1880260.html |
|
Apache Tomcat 7.0.39 or greater (7.0.x series or 8.5.x series, not 9.x.x series) |
||
Rhino 2.5.0.0 or later - optional - to be used when installing and configuring Rhino manually |
||
Rhino Element Manager 1.5.0.4 or later |
||
Sentinel VoLTE SDK including out of the box installer |
||
Cassandra Database, version 2.1.17 or later version from the 2.1.x series. Cassandra is required for SCC-AS functionality |
http://cassandra.apache.org/doc/latest/getting_started/index.html |
Note that it is not necessary to configure auto-start (e.g. systemctl or init.d) for Cassandra or Tomcat.
Install and configure Rhino and the JVM
Optionally you can install and configure Rhino and the JVM for use with Sentinel VoLTE. This is recommended for production deployments, and clustered setups.
Alternatively for Proof of Concept and lab functional testing it is recommended to use the Installer documented in Installing Sentinel VoLTE Services
Install Rhino
1 |
Start by choosing a location to extract the contents of the Rhino package. We’ll refer to this directory as |
|---|---|
2 |
Rhino must be started at least once to generate the necessary configuration files. To start Rhino, in the ./start-rhino.sh |
3 |
Wait until Rhino is ready. It prints the following message in its log when ready: SLEE successfully started on node(s) [101] |
4 |
Stop Rhino by executing in the ./stop-rhino.sh --node 101 (specifying the node ID of the local node) |
| |
For more about installing and configuring the Rhino TAS, please see the Rhino v2.5 Documentation. |
Configure Rhino and the JVM
If you want to install Sentinel VoLTE in top of an already running Rhino then this step must be performed. If you are letting the installer configure the Rhino SDK for you, this step can be skipped.
The following settings are needed:
| Setting | Configuration |
|---|---|
|
Management database size |
For a full Sentinel VoLTE install, the default Rhino 2.5 management database size is insufficient and should be increased to at least 400MB. To do this, edit <memdb>
<jndi-name>ManagementDatabase</jndi-name>
<message-id>10003</message-id>
<group-name>rhino-db</group-name>
<committed-size>400M</committed-size>
<stripe-count>1</stripe-count>
...
</memdb>
|
|
JVM |
You’ll also need to configure the JVM: For RhinoSDK: * The Rhino All of these settings can be found in For Rhino Production: The configuration will depend on the expected traffic characteristics and the hardware configuration. There is no rule of thumb for production setup and each project installation will require specific analysis. The only requirement is the |
|
Socket permissions |
If running the installer remotely, you will need to add the host address where the installer is running to the mlet configuration file. In addition, you’ll need to add the address of any Rhino Element Manager hosts and any remote hosts from which you might access the Rhino console.
<mlets>
<mlet enabled="true">
<classpath>
<jar-url>$${rhino.dir.base.url}/lib/jmxr-adaptor.jar</jar-url>
<security-permission-spec>
.... other entries
permission java.net.SocketPermission "<IP ADDRESS>", "accept,resolve";
.... other entries
</security-permission-spec>
</classpath>
</mlet>
</mlets>
|
| |
Start Rhino to load the new configuration
To start Rhino, in the This applies the Rhino and JVM configuration. |
Get a license
| |
To install Sentinel VoLTE you need a license to run SIS, CGIN, and Sentinel VoLTE from OpenCloud. In order to obtain a license file, please contact OpenCloud. A full overview of license requirements can be found of this page: License Requirements. |
If you allow the installer to install both Rhino SDK and Sentinel VoLTE for you, it will prompt you for the location of the license file.
If you prefer to set up Rhino manually, then you need to install the license file prior to installing Sentinel VoLTE.
To install your license file:
1 |
Make sure Rhino is started and running. |
|---|---|
2 |
Go to the |
3 |
In this directory, start the Rhino Console with the |
4 |
In the Rhino Console execute, this command: installlicense [PATH_TO_LICENSE_FILE] ( |
Ports
If using the standard configuration, the following ports need to be open on the VoLTE TAS host’s firewall.
| Port | Purpose |
|---|---|
5060 |
SIP traffic |
5061 |
Secure SIP traffic |
8080 |
REM GUI |
1199-1203 |
RMI Access |
If using other configuration the firewall should be configured for those non-standard ports. Other ports may be opened as needed. For example if ssh is used to administer a node, then port 22 would be opened
OpenCloud product dependencies
Sentinel VoLTE is built on top of other OpenCloud products. The 2.7.0.x series depends on the following series:
| Product | Series |
|---|---|
Rhino |
2.5.0.x |
REM |
1.5.0.4 or later |
SIP |
2.4.1.x |
CGIN |
1.5.4.x |
SIS |
2.5.4.x |
SIS-EM |
1.2.0.1 or later |
Diameter |
3.1.0.x |
IM-SSF |
1.4.6.x |
CDR-RA |
2.3.0.x |
HTTP-RA |
2.2.0.x |
DB-Query-RA |
1.4.0.x |
FSM Tool |
1.1.0.x |
CQL-RA |
1.1.0.1 |
Installing Sentinel VoLTE Services
Sentinel VoLTE is installed through the use of an installer program.
The installer can run in interactive and non-interactive modes - suitable for manual and automated installs respectively. When running in interactive mode it will prompt you for various necessary settings and save them.
| |
The installer will offer to install the Rhino SDK for you, or allow you to specify an existing Rhino installation. Once either a new Rhino SDK install, or an existing installation is selected the installer will install Sentinel VoLTE into your Rhino or Rhino SDK. |
The installer prepares configures for a single node Sentinel VoLTE system, with a single peer for various other network elements such as:
-
Media Resource Function (MRF)
-
Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF)
-
Home Subscriber Server (HSS)
-
Online Charging System (OCS), and/or Prepaid Service Control Point (SCP)
-
Alternative options for storage of the Third Party Registration data
For more advanced configurations, such as clustering, or multiple signalling peers, it is recommended becoming familiar with the Rhino platform, SIS and Sentinel VoLTE products.
To install Sentinel VoLTE services in interactive mode:
For further information on installation read:
1. Unzip sentinel-volte-sdk.zip
To unzip sentinel-volte-sdk.zip:
1 |
Copy the downloaded install zip file to a machine where Rhino and Sentinel VoLTE will run.
user@machine$ mkdir ~/sentinel-volte |
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Unzip. user@machine$ cp ~/sentinel-volte-sdk.zip ~/sentinel-volte user@machine$ cd ~/sentinel-volte user@machine$ unzip sentinel-volte-sdk.zip |
2. Run the installer
| |
The installer prompts you for various configuration settings, such as the SIP URI for the MRF. You can review and change settings prior to installation so don’t worry if you got something wrong first time. |
The install program is split into several "phases".
These are:
-
initialisation of the environment
-
question and answer (in interactive mode)
-
review settings (in interactive mode)
-
execution of installation
NB: the installer captures full logging from the various tools that it uses, and writes these logs into the sentinel-volte-sdk/build/target/log directory.
NB: Before installing, if the host requires a proxy to access Artifactory then it must be configured in sdk.properties. sdk.properties can be found in the top-level directory of the unzipped package. Find the section marked with # Proxy settings and change it to the following:
# Proxy settings # sdk.http.proxyHost=<proxy hostname here> sdk.http.proxyPort=<proxy port here> sdk.https.proxyHost<proxy hostname here> sdk.https.proxyPort=<proxy port here> # # These properties are used for both http and https. sdk.http.nonProxyHosts=localhost|127.0.0.1
To run the installer:
1 |
The testuser@machine$ cd ~/sentinel-volte/sentinel-volte-sdk testuser@machine$ build/bin/installer The installer first initialises the environment. It typically shows output similar to the following Initialising the SDK ... Retrieving Installer dependencies ... done. You may be prompted for Artifactory credentials, which should have been supplied to you by OpenCloud. |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Question and answer to determine necessary settings The installer will prompt the user for various values. A value inside square brackets, if present, is the default answer for that question. When the user presses the Explanations of all of the questions the installer will ask are laid out over the next few steps. Note that some of the questions will only appear under certain circumstances, so not all of them will be seen in a given installer run. |
||||
3 |
Taking the SDK offline The user is prompted whether or not they want to take the SDK offline. You can optionally take the SDK offline by creating a local repository. This will take several minutes depending on connection speed, but will make subsequent retrievals much faster and remove the need for an internet connection. Do you want to take the SDK offline? y/[N] > If the user presses the The user is then presented with progress information related to the downloading of artifacts necessary to take the SDK offline. This process can take more than 30 minutes. |
||||
4 |
HSS or HLR The user can choose to use the HSS or HLR for various functionality. You can choose to use the HSS or the HLR. If you select HSS, then supplementary service data will be read from the HSS, and the CMSISDN will be used for SCC TADS Routing. If you select HLR, then supplementary service data will be read from the HLR, and the MSRN will be used for SCC TADS Routing. Use HSS or HLR? [hss] > If the user enters |
||||
5 |
Option for use of an external Prepaid Service Control Point for Online Charging You can have the option of using CAP-based online charging instead of Diameter Ro-based online charging in your installation. This will deploy additional components. Deploy optional CAP-based online charging components? y/[N] > If the user press the key |
||||
6 |
Creation of a deployment module The installer will now create a suitable deployment module. This may take several minutes. |
||||
7 |
Basic SDK Questions Your organization's name, e.g. Rocket Communications Inc. sdk.component.vendor [UNSET] > This value will be used for the sdk.component.version [1.0] > This value will be used for the The name of the platform operator, e.g. Rocket. sdk.platform.operator.name [UNSET] > The name of the platform operator for the system. It is used extensively throughout configuration profiles. An Ivy organization field, recommended lower case with no whitespace e.g. "rocket". sdk.ivy.org [UNSET] > This value is used as the sdk.ivy.publish.revision [1.0.0] > This value is used as the base of the |
||||
8 |
Install Rhino Questions You can either have the installer set up a Rhino SDK for you or point it at an existing Rhino installation, SDK or production. Note: If you want to use an existing Rhino installation it has to be running and a proper license has to be installed when finishing the installation after the configuration. Also make sure that you have adjusted the memory settings and created a tcapsim-gt-table.txt file as detailed in the documentation. Set up a Rhino SDK installation automatically? y/[N] > If you allow the installer to set up a new Rhino SDK installation, it will prompt for a license file. Enter the path to your Rhino license file > /home/testuser/Downloads/opencloud.license It then installs the Rhino SDK and starts it. If you instruct the installer to use an existing Rhino, the installer will prompt for the path to the Rhino client directory. Enter the path to your Rhino client directory > /home/testuser/rhino/2.4/client If the associated installation is a Rhino production then additional information is required to complete configuration. You can either have the installer deploy against Rhino SDK or production. Does the specified client point to a production installation? y/[N] > If you choose Yes, then the installer prompts for details of the cluster nodes and hosts. Enter your Rhino node setup.
It has to be formatted like this: {nodeId,nodeId}host,{nodeId}host
Examples:
{101}localhost
{101,102}host1,{103}host2
Node setup [{101}localhost] > {101}hostname1,{102}hostname2
|
||||
9 |
International and Roaming Network Questions Home domain [example.com] > A domain name for a home network. Home network prefix [65] > A corresponding network prefix for that home domain. Home network MCC [525] > The MCC for the home network
Comma separated list of home network MNCs eg 01,02 Home network MNC list [01,02,07] > A list of MNCs for the home network.
Roaming domain [roaming.com] > A domain name for a visited network. Roaming network prefix [65] > A corresponding network prefix for that roaming domain. Note that additional home and roaming networks can be specified through the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature configuration profile once setup is complete. |
||||
10 |
Play Announcement Questions Media server URI [sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060] > The URI of the Media Resource Function (MRF). The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the MRF. |
||||
11 |
Online Charging Questions Online charging involves realtime communication with an external charging system, e.g. to an OCS via Diameter Ro Enable online charging? [Y]/n > y If the user enters This install allows online charging using either Diameter Ro or CAP. Enter the type you want with "ro" or "cap". Charging type [ro] > The installer uses Diameter Ro by default if the user does NOT select CAP-based online charging in step 5. This installation will use Diameter Ro for online charging. If the user chooses Yes and |
||||
12 |
Diameter Ro and CCA Questions - if This value is placed into the Origin-Host AVP. Host [diameterclient] > The Diameter hostname for Sentinel VoLTE. It is used in the Origin-Host AVP of outgoing diameter messages. The Diameter Ro release used for online charging can be configured to one of the following release versions: V8d0, V960, Va00, Vb80, Vcb0 Diameter Ro release [Vcb0] > The Diameter release e.g (rel 12.11.0,Vcb0) used for online charging. This installer allows setting up a simple configuration with a single peer for the OCS. If you need a configuration with multiple peers, you can either do so after the installation finishes by following the Diameter documentation, or editing the following file now: [path-to-config-file]/DiameterConfig.xml Do you want to set up a simple configuration? [Y]/n > If yes, the installer will provide a series of prompts for setting up a basic diameter configuration (where there is a single OCS server); if no, you will need to manually configure diameter peers for the charging system. Peer URI [aaa://diameterserver:3868;transport=tcp] > URI of the online charging server. Diameter peer address [diameterserver] > Diameter address of the online charging server. Realm name [example.com] > Diameter Realm for the online charging system. |
||||
13 |
Diameter Rf The Rf Control RA is used by interim CDR features to send accounting data to the CDF during offline charging interactions. Enabling this RA will implicitly enable interim CDRs. Disabling the Rf Control RA will prevent interim CDR features from interacting with the CDF, but they may still be configured to write interim CDRs to disk. Enable Rf Control RA? [Y]/n > This value is placed into the Origin-Host AVP. Host [diameterclient] > The Diameter hostname for Sentinel VoLTE. It is used in the Origin-Host AVP of outgoing diameter messages. The Diameter Rf release used for offline charging can be configured to one of the following release versions: V8d0, V960, Va00, Vb80, Vcb0 Diameter Rf release [Vcb0] > The Diameter release e.g (rel 12.11.0,Vcb0) used for Rf. This installer allows setting up a simple configuration with a single peer for the CDF. If you need a configuration with multiple peers, you can either do so after the installation finishes by following the Diameter documentation, or editing the following file now: /home/user/akendall/repos/sentinel-volte/sentinel-volte-sdk/target/artifacts/sentinel-volte-sdk/deploy-volte/config/sentinel-rf-control-ra-deploy/rf-control-ra-config.yaml Do you want to set up a simple configuration? [Y]/n > If yes, the installer will provide a series of prompts for setting up a basic diameter configuration (where there is a single CDF); if no, you will need to manually configure diameter peers for the Rf system. Peer URI [aaa://RfCDF:5898;transport=tcp] > URI of the CDF. This address is only necessary if the host in the peer URI specified above is not resolvable. If it is then you can just accept the default value here. Peer address [RfCDF] > Peer address of the CDF. Realm name [opencloud] > Realm of the CDF. |
||||
14 |
Call Detail Records (CDRs) Enabling interim CDRs implicitly due to Rf Control RA being enabled Session CDRs are written to disk only at the end of a session. Enable session CDRs? y/[N] > If Rf was not enabled in step 13 then an additional question will be asked regarding enabling Interim CDRs |
||||
15 |
CAP Charging (IM-SSF) - if Country code [65] > The country code for the home network. Default media server address [sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060]> Address of the media server (MRF) to be used by the IM-SSF. |
||||
16 |
Sh Cache Diameter Questions This value is placed into the Origin-Host AVP. Host [diameterclient] > The Diameter host for Sentinel VoLTE. It is used in the Origin-Host AVP of outgoing diameter messages. This installer allows setting up a simple configuration with a single peer for the HSS. If you need a configuration with multiple peers, you can either do so after the installation finishes by following the Diameter documentation, or editing the following file now: [path-to-config-file]/sh-cache-ra-config.yaml Do you want to set up a simple configuration? [Y]/n > If yes, the installer will provide a series of prompts for setting up a basic diameter configuration (where there is a single HSS server); if no, you will need to manually configure diameter peers for the HSS. Peer URI [aaa://diameterserver:3888;transport=tcp] > URI of the HSS. This address is only necessary if the host in the peer URI specified above is not resolvable. If it is then you can just accept the default value here. Peer address [diameterserver] > Diameter address of the HSS. Realm name [example.com] > Diameter Realm for the HSS. |
||||
17 |
Sentinel Registrar Questions The registrar allows configuration to be specific to a particular node, which may be necessary for some settings like the ATU-STI. If a certain property is not found in a node-specific profile, or no profile exists for the current node, the registrar will fall back on the standard profile. This installer will configure the standard profile and add a node-specific profile for node 101. If you are using more than one node then you can edit the file [path-to-config-file]/RegistrarConfigurationTable.yaml after finishing the configuration in the installer, but before proceeding with the actual installation. Destination realm [example.com] > Diameter realm for the Home Subscriber Server (HSS) ATU-STI [sip:localhost:5060] > The Access Transfer Update - Session Transfer Identifier. Registration Data Storage can use either the HSS, or a Cassandra database. Specify the type you want with either "HssCache" or "Cassandra". Registration Data Storage type [HssCache] > Determines where the registrar will store third party registration data. Data can be stored in either the HSS, or a Cassandra database. Please enter a comma separated list of Cassandra hosts in the form "host1,host2" Cassandra Hosts [localhost] > Comma separated list of hostnames for the Cassandra database. Please enter the port Cassandra is listening on Cassandra Port [9042] > The destination port for the Cassandra database server. |
||||
18 |
Sentinel VoLTE Shared Config Questions Sentinel VoLTE shared configuration can be specific to a particular node, which may be necessary for some settings like the MMTel and SCC AS URI's. If a certain property is not found in a node-specific profile, or no profile exists for the current node, then Sentinel VoLTE shared config will fall back on the standard profile. This installer will configure the standard profile and add a node-specific profile for node 101. If you are using more than one node then you can edit the file [path-to-config-file]/VoLTESharedConfigProfileTable.yaml after finishing the configuration in the installer, but before proceeding with the actual installation. MMTel AS URI [sip:mmtel@127.0.0.1:5060] > The URI that identifies this MMTel AS SCC AS URI [sip:scc@127.0.0.1:5060] > The URI that identifies this SCC AS |
||||
19 |
External Session Tracking Questions External Session Tracking uses Cassandra to save session information that can be shared across nodes. Please enter a comma separated list of Cassandra hosts in the form "host1,host2" Cassandra Hosts [localhost] > Comma separated list of hostnames for the Cassandra database. Please enter the port Cassandra is listening on Cassandra Port [9042] > The destination port for the Cassandra database server. |
||||
20 |
SIP SIS RA Questions SIP SIS RA Host [localhost] > The hostname for the server hosting Sentinel VoLTE. |
||||
21 |
MMTel Conferencing Questions The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function. The Conf and ECT features will automatically add an "lr" parameter to it. The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the I-CSCF. Example: sip:127.0.0.1:5054;transport=tcp I-CSCF URI [sip:icscf@icscfhost.example:5060] > The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF). The URI of the Media Resource Function. The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the MRF. Example: sip:msml@127.0.0.1:5060 MRF URI [sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060] > The URI of the Media Resource Function (MRF) to be used as the conference bridge. Conference Factory PSI [sip:conf-factory@example.com] > A Public Service Identifier that can be used by a subscriber to establish a conference call. The Conference MSML Schema Vendor Name. Used by the Conf feature to determine mapper selection when creating MSML documents for interaction with the MRF. Conference MSML Schema Vendor Name [Dialogic] > The name of the vendor providing the conference MSML schema. |
||||
22 |
ODB Questions Enable HSS IMS-ODB-Information query ==================================== The SubscriberDataLookupFromHss feature does NOT query the Operator Determined Barring information (IMS-ODB-Information) by default. Enable HSS query for IMS-ODB-Information: y/[N] Answering |
||||
23 |
HLR Configuration The following questions concern the HLR configuration. They are only asked if the user has chosen to use the HLR - a question asked near the beginning of the install. The SCCP address of the HLR. Example: type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=143,national=false HLR address [type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=143,national=false] > The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS. Example: type=C7,ri=gt,digits=653333333,gti=4,nature=international,numbering=isdn,tt=0,national=true Originating Sentinel address [type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=7,ssn=157] > The address of the MLC (Sentinel). Example: address=222,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN MLC address [address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN] > The timeout value for opening the MAP dialog with the HLR (in milliseconds). Invoke timeout [5000] > |
||||
24 |
T-ADS Questions LTE (E-UTRAN) is an allowed PS access network technology. You can also configure WLAN to be an allowed access network. Allow WLAN access? y/[N] > Answering 'yes' will allow subscribers to use WiFi as an access network. |
||||
25 |
Review settings Once all questions have been answered, the user is provided the opportunity to review and if happy, accept the settings. TIP: settings are saved to disk, so that they can be read later. Review settings *************** Basic SDK properties ==================== sdk.component.vendor: Rocket Communications Inc sdk.component.version: 1.0 sdk.platform.operator.name: Rocket sdk.ivy.org: rocket sdk.ivy.publish.revision: 1.0.0 ... edited for brevity MMTel Conferencing ================== I-CSCF URI: sip:192.168.10.1:5054;transport=tcp MRF URI: sip:192.168.10.17 Conference Factory PSI: sip:conf-factory@example.com Play Announcements ================== Media server URI: sip:annc@192.168.10.17:5060 Accept these values? [Y]/n > y ... edited for brevity Configuration changes written. If the user presses the |
||||
26 |
Execution phase Now that the installer has gathered all necessary information it provides the user with the option to install the VoLTE TAS now. Install now? [Y]/n > If the user wants to install at a later time, they can press the Installing Rhino ... done.
Starting Rhino in the background ... done.
Publishing deployment module deploy-volte ... done.
Deploying; this is going to take a while ... done.
Binding; this is going to take a while ... done.
Configuring; this is going to take a while ... done.
Running post-installation tasks ... done.
Installation completed successfully in 32 minutes and 19 seconds. Rhino has been left running to finish applying configuration changes.
The configuration has been saved to the file {sdk-path}/install.properties. This file can be used to re-run the installation non-interactively with the same settings.
The installation has now completed successfully. |
| |
A properties file is automatically created when the interactive installer is run. This file is located in the sentinel-volte-sdk directory and named install.properties. In this way an interactive installations settings are saved, and can be distributed through the install.properties file. You can later use this file for a new installation using the Non-interactive mode. Save this file for future upgrade procedure as instructed here and here. |
Non-interactive mode
To run the installer in non-interactive mode a properties file is passed to the installer program
testuser@machine$ cd ~/sentinel-volte/sentinel-volte-sdk testuser@machine$ ./build/bin/installer -p my-install.properties
SIS and CGIN
During installation SIS and CGIN versions are extracted into the SDK directory structure. This is so that SIS can be configured as necessary.
The CGIN connectivity pack is extracted into the sentinel-volte-sdk/cgin/cgin-connectivity-full-CGIN_VERSION directory. The SIS is extracted into the sentinel-volte-sdk/sis/SIS_VERSION directory. Here CGIN_VERSION and SIS_VERSION are the release versions for each product respectively (e.g. 1.5.2.8 and 2.5.2.7)
The SIS console command is located at sentinel-volte-sdk/sis/SIS_VERSION/admin/sis-console.
Background information
The installer sits on top of the Sentinel VoLTE SDK infrastructure
The installer works by creation of a "deployment module" for Sentinel VoLTE. This module name is "deploy-volte" and it is located in the root of the Sentinel VoLTE SDK directory.
A deployment module can be created through the use of the sdkadm create-deployment-module command. The values that the user enters (or passes in when using non-interactive mode) are written into the various configuration files in this deployment module.
The deployment module is then published, and the deployer, binder and configurer are invoked in order to install/bind/configure the application in Rhino.
This means that the the installer is part of the Sentinel VoLTE SDK, and that there is no technology difference between the SDK and an "off the shelf install". Therefore custom configurations can easily be made through modification of the deployment module, and publishing it, and running the configurer.
Installer log files
The installer captures full logging from the various tools that it uses, and writes these logs into the sentinel-volte-sdk/build/target/log directory. This output is more verbose than the user sees when running the installer.
Each time an install is done, a file called install.log is created in this directory. If there is a previous install.log file, that it is moved to install_date.log. The value of "date" is the time of the last write timestamp in the file.
Therefore running the installer three times results in three installer log files.
Post-Installation Instructions
Update XCAP server
To configure the XCAP Server for Sentinel VoLTE, you can change the Diameter peer connection to the HSS and populate XCAP server settings and MMTel service data. You may optionally enable XCAP authentication using Sentinel AGW.
Diameter peer connection to the HSS
For the Diameter peer connection to the HSS, a file called VolteHssDiameterConfig.xml must be present in a folder called rem_home in Tomcat. If this folder does not exist, create it:
1 |
|
|---|---|
2 |
Change the values for the HSS hostname and port. There are two
|
Populate XCAP server settings and MMTel service data
There are several configuration pages in REM for XCAP connectivity and MMTel service data mappings that must be populated. This can either be done manually following the admin guide, or more easily using the script volte-sentinel-mappings-config. This file is located in the build/bin directory of the Sentinel VoLTE SDK.
This can be executed from your VoLTE TAS’s command line, provided the Java Runtime Environment (v 7+) is installed. The command must be given these arguments:
| Mandatory Arguments | What it specifies |
|---|---|
-u (--username) |
Your Rhino Element Manager (REM) username. |
-pw (--password) |
Your Rhino Element Manager (REM) password. |
-h (--hostname) |
The hostname or IP address of your Rhino Element Manager (REM). |
-p (--port) |
The port of your Rhino Element Manager (REM). |
-n (--network-operator) |
The network operator name. |
-r (--rhino-instance-id) |
The Rhino Instance ID. |
-dh (--hss-destination-host) |
The destination host of the HSS. |
-dr (--hss-destination-realm) |
The destination realm of the HSS. |
Optional Arguments |
What it specifies |
-x (--xcap-mapping) |
Must be in the format Can be specified multiple times. e.g. |
Here is an example command:
cd ~/sentinel-volte/sentinel-volte-sdk ./build/bin/volte-sentinel-mappings-config -u emadm -pw password -h localhost -p 8080 -r Local -n OpenCloud -dh hss-instance -dr example.com -x "extensions/operator-flexible-alerting-group;complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group" -x "extensions/flexible-alerting-group-members;complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/members"
| |
To see a listing of the required arguments, from the command line, execute the JAR file without any arguments. |
Enable XCAP authentication using Sentinel AGW
By default the XCAP Server assumes that requests will be authenticated externally using an Authentication Proxy (AP). If this is the case, no further configuration is required.
If an AP is not suitable or available, the XCAP server can be configured to authenticate requests itself using OpenCloud Sentinel AGW. Sentinel AGW provides an implementation of 3GPP GAA (Generic Authentication Architecture) procedures.
For more information, and instructions on configuring the XCAP Server with Sentinel AGW, see the Sentinel AGW Guide.
OpenIMS HSS
If you’re using the OpenIMS HSS, you’ll need to specify the interface (IP address and port values) that it uses:
1 |
Edit the |
|---|---|
2 |
Find the |
3 |
Change its |
4 |
Change its |
Create init.d scripts
There are two init.d scripts for Ubuntu Linux which make starting and stopping Rhino and REM easier (linked below):
Note: These are illustrative and useful for Proof of concept rather than production environments.
To set these up:
1 |
Copy the script to the host server’s sudo cp rhino /etc/init.d |
|---|---|
2 |
Make the script executable: |
3 |
Refresh, with the sudo update-rc.d rhino defaults 99 |
Init.d Sample Scripts for VoLTE
| |
These sample scripts are illustrative init.d scripts for Rhino and REM |
For production installations use production Rhino’s own init.d scripts rather than these.
Sample Rhino script
#!/bin/bash
#
# Manage the Rhino SLEE.
# Put this file in /etc/init.d and symlink that in /etc/rc?.d
RHINO_HOME=/home/ubuntu/sentinel-volte-sdk/rhino-sdk/RhinoSDK
RHINO_USER=ubuntu
case "$1" in
start)
# This command will fail nicely if that file is not there, so
# checking for that file's existence is not necessary.
echo "Starting the Rhino SLEE"
sudo su - ${RHINO_USER} -c ${RHINO_HOME}/start-rhino.sh > /dev/null 2>&1 &
# logs will be in ${RHINO_HOME}/work/log
;;
stop)
echo "Stopping the Rhino SLEE"
[ -d ${RHINO_HOME} ] && [ -x ${RHINO_HOME}/stop-rhino.sh ] \
&& ${RHINO_HOME}/stop-rhino.sh --nice
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 { start | stop }"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
Sample REM script
#!/bin/sh
#
# Rhino Element Manager start/stop script.
#
#
# Location of the Rhino Element Manager
REM_HOME=/home/ubuntu/sentinel-volte-sdk/rhino-sdk/RhinoSDK/apache-tomcat-*
RHINO_USER=ubuntu
usage()
{
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop}"
exit 1
}
#
# Main
#
# Parameter check
[ $# -gt 0 ] || usage
case "$1" in
start)
# Start REM
sudo su - "$RHINO_USER" -c "$REM_HOME/bin/catalina.sh start"
echo "REM Starting"
;;
stop)
# Stop REM
sudo su - "$RHINO_USER" -c "$REM_HOME/bin/catalina.sh stop"
echo "REM Stopping"
;;
*)
usage
exit 2
;;
esac
exit 0
Sample VolteHssDiameterConfig XML for VoLTE
| |
This sample script is for updating the XCAP server configuration when carrying out post install instructions for Sentinel VoLTE. |
<exported-profile-data table="VolteHssDiameterConfiguration">
<attributes>
<attribute-desc name="productVendorId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="applicationVendorId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="host" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="applicationId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="realm" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="peerTable" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="realmTable" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="product" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="version" type="int" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="enableMultiNodeConfig" type="boolean" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="nodeIDs" type="int[]" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="perNodeHosts" type="java.lang.String[]" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="perNodeListenAddresses" type="java.lang.String[]" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="perNodePorts" type="int[]" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="perNodeSecondaryAddresses" type="java.lang.String[]" serialised="false"/>
</attributes>
<profile name="xcapserver" action="create">
<attribute-value name="productVendorId">19808</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="applicationVendorId">0</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="host">xcapserver</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="applicationId">0</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="realm">example</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="peerTable">
<![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE peer-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Peer Table Configuration 1.1.0//EN"
"http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-peer-table-1.1.0.dtd">
<peer-table>
<default-options>
<option>
<option-name>TCP_NODELAY</option-name>
<option-type>java.lang.Boolean</option-type>
<option-value>true</option-value>
</option>
</default-options>
<peer connectAtStartup="true">
<uri>aaa://hss-instance:3868;transport=tcp</uri>
<address>hss-instance</address>
<option>
<option-name>TCP_NODELAY</option-name>
<option-type>java.lang.Boolean</option-type>
<option-value>false</option-value>
</option>
</peer>
</peer-table>]]>
</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="realmTable">
<![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE realm-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Realm Table Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-realm-table-1.0.dtd">
<realm-table>
<realm>
<realm-name>example.com</realm-name>
<application-route>
<application>
<application-id>4</application-id>
<vendor-id>0</vendor-id> <!-- optional, default is zero -->
</application>
<action>LOCAL</action>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>hss-instance</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</application-route>
</realm>
<default-route>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>hss-instance</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</default-route>
</realm-table>]]>
</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="product">OpenCloud Diameter</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="version">1</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="enableMultiNodeConfig">false</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="nodeIDs" content-type="null"/>
<attribute-value name="perNodeHosts" content-type="null"/>
<attribute-value name="perNodeListenAddresses" content-type="null"/>
<attribute-value name="perNodePorts" content-type="null"/>
<attribute-value name="perNodeSecondaryAddresses" content-type="null"/>
</profile>
</exported-profile-data>Installing the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning Module
The Sentinel VoLTE provisioning module is distributed as a Rhino Element Manager (REM) plugin.
It requires REM 1.5.0 or compatible. REM can be installed with Jetty or Apache Tomcat. For Sentinel VoLTE, the Apache Tomcat method is required.
To install the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning module you will need:
-
the REM distribution package —
rhino-element-manager-<version>.zip; expanded to a location of your choice -
an Apache Tomcat installation — either downloaded and configured manually, or installed via a package manager; minimum supported version is
7.0.39 -
the Sentinel VoLTE REM plugin —
volte-sentinel-element-manager-<version>.em.jar-
download for your release version from https://repo.opencloud.com/artifactory/opencloud-sentinel-volte-2.7.0/opencloud/volte/2.7.0/volte-sentinel-element-manager
-
-
(optional) the SIS REM plugin —
sis-em-<version>.em.jar-
download for your release version from https://repo.opencloud.com/artifactory/opencloud-sentinel-volte-2.7.0/opencloud/sis-em/1.2.0/sis-em
-
Below are the procedures to:
| |
REM restart required
After installing and configuring the plugin, you will need to restart REM, for example by restarting the Tomcat webapp it is running in: ${CATALINA_BASE}/bin/catalina.sh stop
${CATALINA_BASE}/bin/catalina.sh start
|
Set up Tomcat
To set up Apache Tomcat for the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning module:
1 |
Follow the instructions for running REM on Apache Tomcat in the REM Guide. |
|---|---|
2 |
Create the cd apache-tomcat-<version> mkdir -p rem_home/plugins |
3 |
If running Apache Tomcat using Java 1.7, you will need to increase the PermGen size. Add JAVA_OPTS="-XX:PermSize=512m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m" This step should be skipped if running Apache Tomcat on Java 1.8 or higher. |
Install the REM plugin
To install the REM plugin for the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning Module:
1 |
Copy cd apache-tomcat-<version> cp /full/path/to/volte-sentinel-element-manager-<version>.em.jar rem_home/plugins/ |
|---|---|
2 |
(Optional) Copy cd apache-tomcat-<version> cp /full/path/to/sis-em-<version>.em.jar rem_home/plugins/ |
Customize plugin logging
1 |
Unzip cd apache-tomcat-<version> mkdir rem-tmp cd rem-tmp unzip ../webapps/rem.war WEB-INF/classes/log4j2.properties |
|---|---|
2 |
Edit log4j.rootLogger=INFO, FILE, CONSOLE
log4j.appender.CONSOLE=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %-5p <%t> [%c] %m%n
log4j.appender.FILE=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.FILE.File=${rem.home}/rem.log
log4j.appender.FILE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.FILE.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p <%t> [%c] %m%n
log4j.logger.rem=INFO
log4j.logger.openjpa=INFO
log4j.logger.org.apache.wink=INFO
# Uncomment for subscriberdata cache eviction logging
#log4j.logger.rem.server.sentinel.subscriberdata.cache=TRACE
log4j.logger.sentinel.audit=INFO, AUDIT
log4j.additivity.sentinel.audit=false
log4j.appender.AUDIT=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.AUDIT.File=${rem.home}/sentinel-audit.log
log4j.appender.AUDIT.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.AUDIT.layout.ConversionPattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}", "%c{1}", %m%n
|
3 |
Replace zip ../webapps/rem.war WEB-INF/classes/log4j2.properties |
4 |
Remove temporary files: cd .. rm -rf rem-tmp |
Import Rhino trust certificate
This can also be done using the REM web UI.
1 |
Import a Rhino Trust Certificate into REM: "${JAVA_HOME}/bin/keytool" -importcert -file ${RHINO_HOME}/rhino-trust.cert -keystore "${TOMCAT_HOME}/rem_home/rhino-ems.ks" -storepass changeit -noprompt
|
|---|
Security considerations
Below are recommendations for securely running the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning Module.
Use https
Be aware that the Sentinel VoLTE machine API uses HTTP BASIC authentication. This passes the username and password with every request.
To prevent your credentials going over the network unencrypted, run REM over https.
Set up SSL
See the Tomcat 7 - SSL How-To docs for help setting up SSL in Apache Tomcat 7.
Virtualized Deployment Requirements
Sentinel VoLTE is supported in a virtualized environment, details presented here provide a guide to the scope of that support and how Sentinel VoLTE should be setup in that environment.
VMWare Supported
VMWare vSphere ESXi 5.1 and 6 is supported and certified. vCenter is not a mandatory requirement. |
Operating System Support
Please refer to the Platforms section of the Rhino Compatibility Guide for supported operating systems. |
Dedicated Storage Array Required
Sentinel VoLTE does not require dedicated storage. CDR files and Rhino logs should be partitioned separately and managed to avoid failure or data loss due to space utilization. |
CPU Contention Supported
CPU Contention is supported, however %ready numbers should be kept below 5% to avoid significant impact on overall application performance. It is strongly recommended that VMs are bound to physical CPU sockets to ensure predictable latency. |
Fault Tolerance
A rhino cluster provides support for both high availability and fault tolerance internally. Sentinel VoLTE does not make use of the Rhino replication but does use the high availability systems. The cluster as a whole can tolerate failure of individual nodes with no support from the virtual machine. Live replication of virtual machines (FT Model) will interfere with Rhino’s internal clustering mechanisms. |
VMWare vSphere High Availability
Sentinel VoLTE provides is own HA clustering based upon the Rhino SLEE Architecture. |
Test Lab Minimum Virtual Host Requirements
1 vCPU, 8Gb RAM, 30Gb HD, 0 IOPS (Disk I/O is not normally a significant requirement as it’s not used except for logging and installation/configuration changes. Under normal operation a rhino node produces very little logging, but can use > 100Mb/s during severe error conditions under load). |
Production Minimum Virtual Host Requirements
1 Rhino node per VM, 1 CPU (bound) @2.4+Ghz, 12Gb java heap, 30Gb HD, 0 IOPS. A quorum node is much lighter weight, and would require a vm with 1 vcpu, 512Mb ram, 0 IOPS. |
Scalability
Linear to 2.4Ghz, No scaling improvement over 2.4Ghz. (At Maximum load @ 2.4GHz, we reach saturation of Java CMS collector). |
Virtual host resource changes while running
Sentinel VoLTE does not support host resource changes while running. |
Features
This page presents summaries and links to more detailed descriptions of features installed with the Sentinel VoLTE product.
SIP features
The SIP features can be thought of as building blocks for any SIP-AS functionality, regardless of whether it is MMTel-AS, SCC-AS or any other SIP-AS.
General VoLTE features
The General VoLTE Features are used by both the MMTel-AS and SCC-AS functionality of the Sentinel VoLTE product. They can be thought of as building blocks for MMTel-AS and SCC-AS.
MMTel features
The MMTel Features implement MMTel-AS functionality.
SCC features
The SCC Features implement SCC-AS functionality.
Third Party Registration features
The Third Party Registration features implement the necessary Third Party Registration functionality for the MMTel-AS and SCC-AS.
External Session Tracking features
The External Session Tracking Features are used to track sessions in a cassandra database
CAMEL features
The CAMEL features can be thought of as building blocks for SCP functionality.
General features
The General Features are essentially utility features that are installed out-of-the-box.
The Sentinel VoLTE product does not use the Subscriber Data Lookup and Subscriber Validity features as the General VoLTE features are used instead. These features may be used when customising Sentinel VoLTE.
SIP features
The SIP Features are not specific to SCC or MMTel or even VoLTE installations. They are installed out-of-the-box with Sentinel VoLTE.
General VoLTE Features
These features are neither MMTel specific nor SCC specific.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
The set of features used for External Session Tracking in Cassandra |
|
|
uses information from the incoming INVITE request to determine whether Ro Online charging should be applied to the session, |
|
|
uses the Leg Manager to get the names of the original SIP legs established during call set up, and saves the values |
|
|
uses information from an incoming |
|
|
reads Third Party Registration information stored in the HSS as Transparent Data, and writes it into session state. |
|
|
reads Third Party Registration information stored in the Cassandra Database, and writes it into session state. |
|
|
is responsible for reading data from the HSS and writing it into Sentinel session state fields. |
|
|
is responsible for reading data from the HSS and writing it into Sentinel session state variables fields. |
|
|
is responsible for reading subscriber data from the HLR and writing it into Sentinel session state variable fields. |
|
|
is responsible for building a Call Detail Record that reflects the actions taken whilst processing a session. |
|
|
is a system feature which prevents SDP-change initiated CDRs from being written by the |
|
|
is a system feature that is responsible for writing interim Call Detail Records throughout the session. |
|
|
is responsible for building a Call Detail Record that reflects the actions taken whilst processing a session. |
|
|
sets values for the Feature-Caps header on outgoing messages based on data from the session’s FeatureCapsManager |
|
|
is responsible for reading subscriber location data from the HLR and writing it into Sentinel session state variable fields. |
|
|
schedules configurable announcements to the subscriber based on indicators in OCS answers |
External Session Tracking Features
The set of features for External Session Tracking. All of these features make use of the external session tracking Cassandra schema. For an overview of External Session Tracking refer to Session Tracking.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
creates the cassandra entries for external session tracking before the call is answered |
|
|
deletes the cassandra entries for forked sessions once the dialog is confirmed |
|
|
keeps entries updated in the external session tracking database |
|
|
removes entries in the external session tracking database |
|
|
updates session state when a session’s held status changes |
|
|
performance testing results for SCC External Session Tracking |
TrackSessionPreAnswer
This feature creates the cassandra entries for external session tracking before the call is answered .
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Any and All |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ExternalSessionTrackingActive |
boolean |
Set by SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking. If this is not true the feature will not execute |
ExternalSessionTrackingKeys |
Set<String> |
The list of tracking keys to save the current session against |
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
PreAlertingLegs |
Set<String> |
A list of legs that are in the Pre-Alerting state |
AlertingLegs |
Set<String> |
A list of legs that are in the Alerting state |
Statistics
TrackSessionPreAnswer statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → TrackSessionPreAnswer
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.TrackSessionPreAnswer"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
AddedTrackedDialog |
Incremented when the feature adds a TrackedDialog insert statement to the cassandra batch query |
AddedTrackedDialogKeys |
Incremented when the feature adds a TrackedDialogKeys insert statement to the cassandra batch query |
SentQueryToCassandra |
Incremented when the feature executes an asynchronous query to cassandra |
CassandraSuccess |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra success result |
CassandraError |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra error result |
CassandraTimeout |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra timeout result |
SavedDialogStatePartialDialog |
Incremented when the feature receives the initial INVITE, and the partial dialog-ID is written to Cassandra |
SavedDialogStatePreAlerting |
Incremented when the feature receives a dialog-creating non-180 provisional response, and updates Cassandra |
SavedDialogStateAlerting |
Incremented when the feature receives the first 180 Ringing response, and updates Cassandra |
SavedDialogStateActiveAwaitingAck |
Incremented when the feature receives the 2xx response to the initial INVITE, and updates Cassandra |
DeletedPartialDialog |
Incremented when the full dialog-ID is known and the partial dialog entry is deleted from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a success response arriving from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a failure response arriving from Cassandra |
Behaviour
This feature runs on 18x responses to the initial INVITE, it saves information about the current session to the cassandra database. It writes the following:
| Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Established Dialog Id |
String |
A normalised string that identifies the current session, in the form of '<call-id>;local-tag=<to-tag>;remote-tag=<from-tag>' for Originating calls, and '<call-id>;local-tag=<from-tag>;remote-tag=<to-tag>' for Terminating calls |
State |
DialogState (enum) |
The current state of the session. Values are PreAlerting or Alerting |
AS URI |
String |
The URI of the serving AS |
Associated Dialog Id |
String |
A normalised sting that identifies the associated dialog for the current session, in the form of '<call-id>;local-tag=<from-tag>;remote-tag=<to-tag>' for Originating calls, and '<call-id>;local-tag=<to-tag>;remote-tag=<from-tag>' for Terminating calls |
Tracking Keys |
Set<String> |
The set of tracking keys to save against the current session |
TrackSessionClearForks
This feature deletes the cassandra entries for forked sessions once the dialog is confirmed .
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Any and All |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ExternalSessionTrackingActive |
boolean |
Set by SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking. If this is not true the feature will not execute |
Statistics
TrackSessionClearForks statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → TrackSessionClearForks
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.TrackSessionClearForks"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
DeletedTrackedDialog |
Incremented when the feature adds a TrackedDialog delete statement to the cassandra batch query |
DeletedTrackedDialogKeys |
Incremented when the feature adds a TrackedDialogKeys delete statement to the cassandra batch query |
SentQueryToCassandra |
Incremented when the feature executes an asynchronous query to cassandra |
CassandraSuccess |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra success result |
CassandraError |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra error result |
CassandraTimeout |
Incremented when the feature receives a cassandra timeout result |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a success response arriving from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a failure response arriving from Cassandra |
TrackSessionRefresh
This feature keeps entries updated in the external session tracking database .
The external session tracking database entries for an access leg are set to expire automatically. To guard against expiring entries too soon, this feature periodically refreshes the entries when SIP activity is detected on the leg. This feature also updates the database entries when the session’s held status changes.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SIP Access PartyRequest, SIP Mid Session Party Request, SIP Mid Session Party Response, |
None |
None |
Stateful |
POJO |
Sets a session output variable. |
Prerequisite features
-
-
The configuration of the SessionRefresh feature is used to determine when to refresh the database entries.
-
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ExternalSessionTrackingActive |
Boolean |
Set by the SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking feature |
ASURI |
String |
Set by the SCCDetermineSessionType feature |
ExternalSessionTrackingKeys |
Set<String> |
Set by the SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking feature |
AccessLegMediaFeatureTags |
Set<String> |
Set by the SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC or TrackSessionPreAnswer features |
HeldStatusChanged |
Boolean |
Set by the DetectHoldResume feature, triggers a database update if |
LastHeldTime |
Long |
Set by the DetectHoldResume feature |
SessionIsHeld |
Boolean |
Set by the DetectHoldResume feature |
Statistics
TrackSessionRefresh statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → TrackSessionRefresh
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.TrackSessionRefresh"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
TrackedDialogRefreshStarted |
Incremented when the feature starts a TrackedDialog Cassandra refresh |
TrackedDialogRefreshSuccess |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog refresh returns successfully from Cassandra |
TrackedDialogRefreshError |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog refresh fails with a Cassandra error |
TrackedDialogRefreshTimeout |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog refresh fails with a Cassandra timeout |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a success response arriving from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a failure response arriving from Cassandra |
Behaviour
The TrackSessionRefresh feature keeps entries updated in the Cassandra external session tracking table. These entries are added with a Time-To-Live (TTL), so will automatically expire at some point, ensuring the table does not fill up with out of date sessions. This feature ensures the Cassandra TTLs are refreshed on access leg sessions that are still active, so they don’t expire too soon.
In addition, the feature also updates the tracked session entries when the call’s held status changes. See Hold and resume procedures below.
The feature only runs when the session state variable ExternalSessionTrackingActive is true, as determined by the SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking feature.
Determining the Cassandra TTL to use
The Cassandra TTL for tracked sessions is derived from the SessionRefresh feature’s configuration. The SessionRefresh feature’s RefreshPeriod parameter specifies the time (in seconds) after which feature will send a session refresh request (re-INVITE) to keep the session open. So a request will be sent on the session at least this often.
The TrackSessionRefresh feature uses the value RefreshPeriod ✕ 1.5 as the Cassandra TTL.
Call setup procedures
The feature is first triggered by the initial ACK request during call setup (originating and terminating), at the SipAccess_PartyRequest execution point. It updates the tracked dialog entries (created by TrackSessionPreAnswer) with state=ACTIVE and a new TTL. The LastTrackSessionRefreshTime and TrackedSessionDialogID session state variables are set at this point.
Mid-call procedures
The feature is triggered on the SipMidSession_PartyRequest and SipMidSession_PartyResponse execution points. However no action will be performed if the tracked session database entries have been refreshed recently, to avoid unnecessary database queries.
To determine if a refresh is necessary, the feature calculates how much time has passed since LastTrackSessionRefreshTime. If the elapsed time is more than halfway through the TTL period, or within 60s of the TTL expiry time, then a refresh is initiated.
The refresh operation reads the access leg’s entry in the trackeddialog table, then updates this entry and any related trackeddialogkeys entries with a new TTL, but otherwise unchanged.
Hold and resume procedures
If the DetectHoldResume feature indicates that the call’s held status has changed, this triggers an immediate refresh of the tracked session entries. The TrackSessionRefresh feature checks if the HeldStatusChanged flag is set in session state, and if so, updates the tracked session entries with the current held status.
End-of-call procedures
The feature takes no action at the end of the call. A separate feature, DeleteTrackedSession, runs at the SipEndSession execution point to remove the database entries. If this feature was not triggered for any reason, the entries would expire naturally at the end of the TTL period.
DeleteTrackedSession
This feature removes entries in the external session tracking database at the end of a session.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SIP End Session |
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ExternalSessionTrackingActive |
Boolean |
Set by the SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking feature |
TrackedSessionDialogID |
String |
Set by the TrackSessionRefresh |
Statistics
DeleteTrackedSession statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DeleteTrackedSession
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DeleteTrackedSession"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
TrackedDialogDeleteStarted |
Incremented when the feature starts a TrackedDialog Cassandra delete |
TrackedDialogDeleteSuccess |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog delete returns successfully from Cassandra |
TrackedDialogDeleteError |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog delete fails with a Cassandra error |
TrackedDialogDeleteTimeout |
Incremented when a TrackedDialog delete fails with a timeout |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a success response arriving from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a failure response arriving from Cassandra |
Behaviour
The DeleteTrackedSession feature runs at the SipEndSession execution point, and removes any tracked session database entries for the access leg.
The feature looks up the access leg’s trackeddialog entry using the dialog ID from the TrackedSessionDialogID session state variable. If found, the trackeddialog and all related trackeddialogkeys entries are removed.
The feature only runs when the session state variable ExternalSessionTrackingActive is true, as determined by the SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking feature.
DetectHoldResume
This feature updates session state when a session’s held status changes .
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SIP Mid Session Party Request, SIP Mid Session Party Response |
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input and output variables
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
HeldStatusChanged |
Boolean |
Indicates that the current message has changed the held status of the session. |
SessionIsHeld |
Boolean |
Indicates whether the session is currently on hold. |
LastActiveTime |
Long |
The time that the session last changed from held to active. |
LastHeldTime |
Long |
The time that the session last changed from active to held. |
Statistics
DetectHoldResume statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetectHoldResume
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetectHoldResume"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
DetectSessionHold |
Incremented when the feature detects a transition from active to held |
DetectSessionResume |
Incremented when the feature detects a transition from held to active |
Behaviour
The DetectHoldResume feature updates session state when the session’s held status changes.
The feature runs on the SIP Mid-Session Party Request and SIP Mid-Session Party Response execution points. If a message containing an SDP offer arrives, the SDP is compared to the session’s previous SDP.
The feature looks for changes in directionality attribute in the session description, for example a=sendrecv or a=sendonly, to determine if the session is being put on hold or resumed. If the held status has changed, session state is updated with the new held status.
External Session Tracking Cassandra Schema
Overview
External session tracking saves all of the relevant information to track a session across multiple nodes. It saves the information in a Cassandra database. For an architectural view please refer to Session Tracking.
For further information related to use of Cassandra for production purposes please refer to Cassandra Database Configuration.
Data Schema
Cassandra’s tables exist in a 'keyspace', which, for illustrative purposes, can be thought of as a 'database' in SQL implementations. Creating a keyspace is simple, but some considerations are present.
-
The keyspace must be named
opencloud_external_session_tracking -
For a production environment, and for non-functional testing prior to production, the keyspace can be created such that it is replicated. A sample CQL command for creating such a keyspace is:
CREATE KEYSPACE opencloud_external_session_tracking WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy' ,'replication_factor' : 3 };-
When developing features using the SDK against Cassandra, replication may not be necessary. A sample CQL command for creating such a keyspace is:
CREATE KEYSPACE opencloud_external_session_tracking WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy' ,'replication_factor' : 1 };Once a keyspace is created, the required tables can be created. The following CQL statements provide both the structure and insight into the tables that are required.
USE opencloud_external_session_tracking;
//This table contains tracked dialogs
//tracked dialogs may be found by establisheddialogid
//there is one row for each tracked dialog
CREATE TABLE trackeddialog(
establisheddialogid text, //The established dialog ID, in form of Target-Dialog header value
//e.g. fa77as7dad8-sd98ajzz@host.example.com;local-tag=kkaz-;remote-tag=6544
state text, //The state of the call. One of:
//"PARTIAL_DIALOG", "PRE_ALERTING", "ALERTING", "ACTIVE", or "HELD"
asuri text, //The SIP URI of the tracking AS.
//e.g In SCC, the SCC-AS URI of the signalling anchor for this dialog
lastactivetime timestamp, //The last time the call moved into state "active"
lastheldtime timestamp, //The last time the call moved into state "held"
committedsdp text, //The committed SDP for this dialog
committedsdptimestamp timestamp, //The time that the SDP was committed
associateddialogid text, //The associated dialog ID, e.g. in a routing B2BUA this should be set to the
//the other dialog ID
mediafeaturetags set<text>, //The UE's media feature tags received in the initial INVITE (originating)
//or in the dialog-creating response (terminating)
primary key(establisheddialogid)
);
//This table provides a mapping from a trackingkey to the established dialog IDs for that tracking key
//I.e. one tracking key may track multiple dialogs
CREATE TABLE trackeddialogkeys(
trackingkey text, //A tracking key for the tracked dialog
// example 1: cmsisdn=16505550425
// example 2: impu=sip:+16505550386@example.com;user=phone
// example 3: +sip.instance="<urn:uuid:f81d4fae-7dec-11d0-a765-00a0c91e6bf6>"
// example 4: impi=john.doe@example.com
establisheddialogid text, //The established dialog ID, in form of Target-Dialog header value
//e.g. fa77as7dad8-sd98ajzz@host.example.com;local-tag=kkaz-;remote-tag=6544
state text, //The state of the call. One of:
//"PARTIAL_DIALOG", "PRE_ALERTING", "ALERTING", "ACTIVE", or "HELD"
asuri text, //The SIP URI of the tracking AS
//e.g. in SCC, the SCC-AS URI of the signalling anchor for this dialog
lastactivetime timestamp, //The last time the call moved into state "active"
lastheldtime timestamp, //The last time the call moved into state "held"
committedsdp text, //The committed SDP for this dialog
committedsdptimestamp timestamp, //The time that the SDP was committed
associateddialogid text, //The associated dialog ID, e.g. in a routing B2BUA this should be set to the
//the other dialog ID
mediafeaturetags set<text>, //The UE's media feature tags received in the initial INVITE (originating)
//or in the dialog-creating response (terminating)
primary key(trackingkey,establisheddialogid)
);|NOTE Setting the tombstone deletion strategy to a shorter interval than the default is strongly recommended for third-party registration tables. The default interval causes increased load on the Cassandra servers during compaction, and particularly during recovery after failover. 1 hour is sufficient for proper management of registration and session data.
External Session Tracking Performance
Overview
This page details performance testing results for SCC External Session Tracking . The cassandra database activity involved in session tracking results in an increase in CPU usage for the Rhino host.
Two scenarios - SCC Simple and SCC Provisional - were both run twice with session tracking (SRVCC) enabled or disabled to demonstrate the change in CPU usage.
Cassandra Activity
| Test | Cassandra Record Created |
|---|---|
|
SCC Simple - No SRVCC |
None |
|
SCC Simple - With SRVCC |
|
|
SCC Provisional - No SRVCC |
None |
|
SCC Provisional - With SRVCC |
PRE-ALERTING and ACTIVE |
External Session Tracking Performance Scenarios
Test Scenarios
SCC-Simple - No SRVCC
This scenario mimics a simple SCC call. SRVCC is disabled, so no external session tracking occurs.
SCC-Simple - With SRVCC
This scenario is identical to SCC-Simple - No SRVCC, except SRVCC is enabled, so external session tracking occurs when the call set-up is complete (message 7).
DetermineChargeMode
This feature uses information from the incoming INVITE request to determine whether Ro Online charging should be applied to the session, by setting the MonitorCallOnly session state variable. The MonitorCallOnly variable affects whether Sentinel VoLTE should perform online charging through Diameter Ro, or only monitor the call. Online Charging through CAP is handled by a separate service composition, see Service Compositions for more details about this.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Any and All |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MonitorCallOnly |
boolean |
True if the feature finds the Route Header “oc-charge-mode” Parameter set to |
ChargeMode |
ChargeMode (enum) |
The charge mode determined by the feature. |
Statistics
DetermineChargeMode statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineChargeMode
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineChargeMode"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
MonitorOnly |
Incremented when the feature has set the MonitorCallOnly Session State field to true |
NonMonitorOnly |
Incremented when the feature has set the MonitorCallOnly Session State field to false |
Error |
Incremented when the feature was unable to determine the charge mode |
Behaviour
This feature checks information from the incoming SIP request in order to set a Session State variable which affects Sentinel VoLTE’s charging behaviour.
Values examined
| Value Name | Source | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Route Header “oc-charge-mode” Parameter |
Incoming SIP request |
This is a custom parameter on the URI of the top-most route header. It is expected that this will be added by the S-CSCF based on iFCs. |
Charge mode selection circumstances
| Route Header “oc-charge-mode” Parameter | Resulting Charging behaviour |
|---|---|
|
oc-charge-mode=ro |
MonitorCallOnly set to false, Diameter Ro charging will be applied, ChargeMode set to |
|
oc-charge-mode=cap |
MonitorCallOnly set to true, Diameter Ro charging will not be applied, ChargeMode set to |
|
oc-charge-mode=offline |
MonitorCallOnly set to true, Diameter Ro charging will not be applied, ChargeMode set to |
|
oc-charge-mode has any other value |
MonitorCallOnly set to false, Diameter Ro charging will be applied, ChargeMode set to |
|
oc-charge-mode parameter absent |
MonitorCallOnly set to false, Diameter Ro charging will be applied, ChargeMode set to |
DetermineInitialLegNames
This feature uses the Leg Manager to get the names of the original SIP legs established during call set up, and saves the values to a set of session state fields that may be used by other VoLTE features when they need to access a specific leg by name.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input and output variables
Session output variables
| Session state variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CurrentLocalLegName |
String |
The name of the leg towards the local UE (that is, the calling party on an originating instance, or the called party on a terminating instance) |
CurrentRemoteLegName |
String |
The name of the leg towards the remote UE (that is, the called party on an originating instance, or the calling party on a terminating instance) |
CurrentCallingLegName |
String |
The name of the leg towards the calling party |
CurrentCalledLegName |
String |
The name of the leg towards the called party |
Statistics
DetermineInitialLegNames statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureStarted |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureFailedToStart |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureIssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureTimedOut |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureCallingLegNameSet |
Incremented when calling leg name is found |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureCalledLegNameSet |
Incremented when called leg name is found |
Behaviour
Network pre-credit check
When invoked at the SipAccess_NetworkPreCreditCheck execution point the feature will do the following:
-
Retrieve the leg that the initial INVITE arrived on and get its name.
-
Set the
CurrentCallingLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name. -
On an originating instance, set the
CurrentLocalLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name;
on a terminating instance, set theCurrentRemoteLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name.
SIP access party response
When invoked at the SipAccess_PartyResponse execution point the feature will do the following:
-
Retrieve the leg that the response arrived on and get its name.
-
Verify that the response is to an INVITE and has a 2XX status. (If it isn’t, the feature will stop here.)
-
Set the
CurrentCalledLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name. -
On an originating instance, set the
CurrentRemoteLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name;
on a terminating instance, set theCurrentLocalLegNamesession variable to the leg’s name.
DetermineRoamingFromHlr
DetermineRoamingFromHlr is responsible for reading subscriber location data from the HLR and writing it into Sentinel session state variable fields.
The data it reads from the HLR is accessed through the AnyTimeInterrogation MAP operation. The Application Context used is anyTimeInfoEnquiryContext_v3_ac
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC. |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-determine-roaming-from-hlr module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-hlr-module opencloud#volte-determine-roaming-from-hlr#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new module; once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new module.
The module-pack consists of a single module, volte-determine-roaming-from-hlr, containing the feature’s code. It does rely on the volte-map-event-handler which contains the shared event handler for MAP features and also publishes a module pack, however the event handler will not require modification unless a new feature name is introduced.
Session state output variables
| Attribute Name | Type |
|---|---|
Description |
RoamingStatus |
Enum |
|
RoamingIndicator |
boolean |
Note: The default values for both RoamingStatus and RoamingIndicator are UNKNOWN and false respectively. If this feature is unable to determine the roaming status for any reason, it will leave the pre-set values.
Configuration
The feature uses configuration data from both the HLR CGIN MAP Configuration and SIP Sentinel Configuration.
Statistics
DetermineRoamingFromHlr statistics are tracked by the DetermineRoamingFromHlr feature and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID ▶ DetermineRoamingFromHlr.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature issues a warning |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
RequestSent |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature receives subscriber data from the HLR |
RequestSuccessful |
Counter |
Incremented after the feature successfully processes the data it received, and loads it into session state fields |
RequestFailed |
Counter |
Incremented when absent configuration data prevents the feature from running |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between sending the request to the HLR and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
InternationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the subscriber is roaming internationally |
NotRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the subscriber is not roaming |
NationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the subscriber is national roaming |
RoamingDataMissingFromHlrResponse |
Counter |
Incremented whenever an ATI result comes back from Hlr with missing or invalid location information |
DialogOpenRefuseEvent |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the ATI fails due to a dialog open refuse |
DialogUserAbortEvent |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the ATI fails due to a dialog user abort |
DialogProviderAbortEvent |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the ATI fails due to a dialog provider abort |
OperationErrorEvent |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the ATI fails due to an operation error |
Behaviour
This feature uses the CGIN MAP RA to query the HLR with an ATI for subscriber location information.
Each time the feature is invoked, it checks the call type and determines the subscriber number that it should use to query the HLR.
The feature attempts to extract "phone number digits" from the CMSISDN session state field set by FetchCMSISDN, and if it cannot, from the Subscriber field set by SubscriberDetermination. If the feature cannot form a MSISDN it raises a Feature Error and finishes execution.
The feature then requests subscriber location info by sending a AnyTimeInterrogation request to the configured HLR.
In order to form the ATI request the feature:
-
sets the GSM SCF address to the
SentinelSCCPAddressconfiguration value -
sets the destination SCCP address to the
HlrSCCPAddressconfiguration value -
sets the
RequestedInfoindicator field to request Location Information
If a successful result is received, it retrieves location information from the ATI result. The location information can be in either of the CellGlobalIdOrServiceAreaIdFixedLength or LaiFixedLength fields. If neither field is present, the feature increments the RoamingDataMissingFromHlrResponse stat and finishes.
If the location information is found, the MCC and MNC are compared against the configured home network information to determine whether the subscriber is roaming or not. The RoamingStatus and RoamingIndicator session state fields are then set accordingly. Their default values in the case of incomplete information or feature failure are UNKNOWN and false respectively.
DetermineVoltePlanId
This feature uses information from an incoming INVITE, MESSAGE or SUBSCRIBE request, and from session state to set the plan ID in the Sentinel selection key . The plan ID affects which features will run for the call on the current AS instance. It also will set some Session State fields.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Any and All |
Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Prerequisite features
These features must run before DetermineVoltePlanId:
-
DetermineCallType
-
SCCDetermineSessionType (Only required on SCC AS)
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-determine-plan-id module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-planid-module opencloud#volte-determine-plan-id#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-determine-plan-id |
Contains all of the code for this feature. |
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type |
|---|---|
CallType |
Enum |
SCCSessionType |
Enum |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Updated by the feature based on factors described in the Behaviour section. |
RequestIsForMmtelTransfer |
Boolean |
Set to true if request is targeted at configured Session-Transfer-To-Own-Device special URI. |
Network operator data
This feature reads part of the feature configuration profile table for MMTel Conference to determine the PSI for the conferencing service.
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
ConfFactoryPSI |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for conferencing service PSI |
none |
MmtelTransferNumber |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for special Session-Transfer-To-Own-Device |
none |
Statistics
DetermineVoltePlanId statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineVoltePlanId
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineVoltePlanId"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
NoPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature fails to select an appropriate plan ID |
MmtelOriginatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-orig” |
MmtelTerminatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-term” |
MmtelConferencingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-conf” |
SccOriginatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-orig” |
SccTerminatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term” |
SccTerminatingTadsOnlyPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term-tads” |
SccTerminatingAnchorOnlyPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term-anchor” |
SccReoriginationPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-reorigination” |
SccAccessTransferPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-access-transfer” |
ConferenceConfigurationNotFound |
Incremented when the feature is unable to find a valid conference PSI from configuration profiles |
Behaviour
This feature checks a series of values from session state, feature configuration, and the incoming SIP request in order to select the appropriate session plan to run, and possibly set some Session State fields.
Values examined
| Value Name | Source | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Custom Route Header |
Incoming SIP request |
These are custom parameters on the URI of the top-most route header. It is expected that these will be added by the S-CSCF based on iFCs. |
SCCSessionType |
Session State |
This is set by the SCCDetermineSessionType feature when it detects the incoming request is for Access Transfer or Reorigination, as these requests do not come from the S-CSCF there should never be a oc-mode parameter on the route header. |
Call Type |
Session State |
Set by the DetermineCallType feature. |
Request URI |
Incoming SIP request |
Matched against the configured conference PSI to determine when a conference call is being requested. |
Custom Route Header Parameters
Sentinel VoLTE supports specific custom headers and header parameters to indicate or propagate certain conditions between nodes in the network.
Plan ID selection circumstances
Route Header oc-mode Parameter |
SCCSessionType | Call Type | SIP Request-URI Matches Conference PSI | Resulting Plan ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(Not Present) |
Access Transfer |
(Ignored) |
(Ignored) |
scc-access-transfer |
|
(Not Present) |
Reorigination |
(Ignored) |
(Ignored) |
scc-reorigination |
|
oc-mode=mmtel |
(Ignored) |
Originating |
(Ignored) |
mmtel-orig |
|
oc-mode=mmtel |
(Ignored) |
Terminating |
No |
mmtel-term |
|
oc-mode=mmtel |
(Ignored) |
Terminating |
Yes |
mmtel-conf |
|
oc-mode=scc |
(Ignored) |
Originating |
(Ignored) |
scc-orig |
|
oc-mode=scc |
(Ignored) |
Terminating |
(Ignored) |
scc-term |
|
oc-mode=scc-tads |
(Ignored) |
Terminating |
(Ignored) |
scc-term-tads |
|
oc-mode=scc-anchor |
(Ignored) |
Terminating |
(Ignored) |
scc-term-anchor |
| |
|
FeatureCapsManagement
This feature sets values for the Feature-Caps header on outgoing messages based on data from the session’s FeatureCapsManager
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SCC |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Contains information about which Feature-Caps header values should be applied to outgoing messages on each SIP leg |
Statistics
FeatureCapsManagement statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → FeatureCapsManagement
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.FeatureCapsManagement"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
StrippedValuesFromMessage |
Incremented when the feature removes Feature-Caps parameter values from a message |
AddedValuesToMessage |
Incremented when the feature adds Feature-Caps parameter values to a message |
Behaviour
This feature interacts with the session’s FeatureCapsManager interface and its associated LegFeatureCapsHandler interfaces. These interfaces are documented in the Sentinel VoLTE SPI Javadoc.
When invoked, the FeatureCapsManagement feature iterates over all SIP legs associated with the current session. For each leg, the feature will check if there is a LegFeatureCapsHandler for that leg in the session’s FeatureCapsManager. If there is a LegFeatureCapsHandler for the leg, the feature will look for SIP INVITE requests and responses in the leg’s outgoing message queue. Each INVITE request or response found in the queue will be processed as described below. Each individual message in the queue will only be processed once (i.e. if the feature is invoked multiple times before a given message is sent, that message will only be processed on the first time that it is seen).
Values to Strip
When a message is processed, the feature will first determine if the LegFeatureCapsHandler has any Feature-Caps values to strip. If so, the feature will look for those values on any existing Feature-Caps header on the message. If the values are found, they will be removed from the given header.
Values to Add
After stripping values, the feature will check the LegFeatureCapsHandler for Feature-Caps values to add to the message. If values are found, then a new Feature-Caps header will be appended to the message. The new header will contain all of the values to add.
It is possible for the LegFeatureCapsHandler to indicate that new Feature-Caps values are currently suppressed for the leg. If this is the case, the feature will forgo adding any new Feature-Caps values to the outgoing message.
IMSIDLookup
This feature reads Third Party Registration information stored in the HSS as Transparent Data, and writes it into session state. Information is read during INVITE processing. It reads the Third Party Registration information via the Sh Cache RA. For more information refer to Data Stored by the Third Party Registrar in HSS.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
SIP Access Session Pre-Credit Check |
No |
No |
Stateless |
SBB |
Prerequisite features
These features must run before IMSIDLookup:
-
SIP Subscriber Determination — in order to know who the subscriber is for the call.
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-imsid-lookup module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-imsid-module opencloud#volte-imsid-lookup#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes a single module:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-imsid-lookup |
Contains the feature’s code. |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type |
|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
| |
This is the IMS Public Identity for the Served User, and is extracted from the SIP INVITE. |
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
The list of registration records for the subscriber |
IsLoggedIn |
boolean |
True, if the feature was able to set both IDs |
CMSISDN |
String |
The correlation MSISDN registered for the subscriber |
HasCMSISDN |
boolean |
True if the CMSISDN is set |
Statistics
IMSIDLookup statistics are tracked by the IMSIDLookup SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ IMSIDLookup SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Invoked |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature runs. |
FeatureError |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution. |
NoSubscriberSpecified |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine which subscriber to retrieve IDs for. |
IMSIDRetrieveSuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when IDs are successfully retrieved and decoded. |
IMSIDRetrieveFail |
Counter |
Incremented when ID retrieval or decoding fails. |
CacheQueried |
Counter |
Incremented when a query is made to the Sh-Cache. |
CacheIndicatedQuerySuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when a success response is received from the Sh-Cache. |
CacheIndicatedQueryFailure |
Counter |
Incremented when a failure response is received from the Sh-Cache. |
SubscriberNotRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber is not present in the Sh-Cache or has no valid registration. |
RegistrationOutOfSync |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber information is not consistent between the network and the Sh-Cache. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between requesting data from the Sh-Cache RA and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
The feature queries the HSS using an Access Key of the IMS Public Identity of the Served User and the Service Indication of opencloud-3rd-party-registrar.
User logged in
The RegistrationRecords session state field is set to a List of RegistrationRecord. Each element in the list indicates a device, with public and private IDs, that the subscriber is registered on. If the subscriber is registered on only one device, there is only one element in the list. If the subscriber is simultaneously registered on (say) four devices, there will be four elements in the list.
The CMSISDN field will be set if it is present in the data registered for the user. If the subscriber is simultaneously registered on multiple devices, this value will not be set.
IMSIDLookupFromCassandra
This feature reads Third Party Registration information stored in the Cassandra Database, and writes it into session state. Information is read during INVITE processing. It reads the Third Party Registration information via the Cassandra CQL RA. For more information refer to Cassandra storage.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
SIP Access Session Pre-Credit Check |
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Prerequisite features
These features must run before IMSIDLookupFromCassandra:
-
SIP Subscriber Determination — in order to know who the subscriber is for the call.
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-imsid-lookup-cassandra module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-imsid-cassandra-module opencloud#volte-imsid-lookup-cassandra#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes a single module:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-imsid-lookup-cassandra |
Contains the feature’s code. |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type |
|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
| |
This is the IMS Public Identity for the Served User, and is extracted from the SIP INVITE. |
Session output variables
| Session State variable name | Variable type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
The list of registration records for the subscriber |
IsLoggedIn |
boolean |
True, if the feature was able to set both IDs |
CMSISDN |
String |
The correlation MSISDN registered for the subscriber |
HasCMSISDN |
boolean |
True if the CMSISDN is set |
Statistics
IMSIDLookupFromCassandra statistics are tracked by the IMSIDLookupFromCassandra feature and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID ▶ IMSIDLookupFromCassandra.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature runs. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
NoSubscriberSpecified |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine which subscriber to retrieve IDs for. |
IMSIDRetrieveSuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when IDs are successfully retrieved and decoded. |
IMSIDRetrieveFail |
Counter |
Incremented when ID retrieval or decoding fails. |
CassandraQueried |
Counter |
Incremented when a query is made to Cassandra. |
MultipleDevicesRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when multiple registered devices have been detected. |
SubscriberNotRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when could not find an active subscriber. |
RegistrationOutOfSync |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber information is not consistent between the network and the database. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between querying the Cassandra database and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
The feature queries the Cassandra Database using a Primary Key of the IMS Public Identity of the Served User.
User logged in
The RegistrationRecords session state field is set to a List of RegistrationRecord. Each element in the list indicates a device, with public and private IDs, that the subscriber is registered on. If the subscriber is registered on only one device, there is only one element in the list. If the subscriber is simultaneously registered on (say) four devices, there will be four elements in the list.
The CMSISDN field will be set if it is present in the data registered for the user. If the subscriber is simultaneously registered on multiple devices, this value will not be set.
SetOcsAnnouncementID
SetOcsAnnouncementID schedules configurable announcements to the subscriber based on indicators in OCS answers
The feature enqueues OCS announcements for out-of-credit (4012 CCA result code), low balance (Low-Balance-Indicator AVP) and general use (OC-Play-Announcement-Id) including welcome announcements.
The feature runs on every credit check result and checks if the CCA meets certain criteria (i.e.presence of OC-Play-Announcement-Id AVP, low balance AVP or on 4012 result). If the CCA matches the criteria the feature schedules announcements based off of them. The feature also runs on each party request for a terminating call to determine whether the session has been established and so if a reauthorization request should be triggered.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC. |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Behaviour
Announcement IDs set in the OC-Play-Announcement-Id AVP are always played. Configured announcement IDs for out-of-credit (4012 CCA result code) or low balance (Low-Balance-Indicator AVP) are only played if no OC-Play-Announcement-Id AVPs were present.
Call phase |
OC-Play-Announcement-Id-AVP |
Low Balance Indicator AVP |
4012 Out-of- Credit |
Behaviour |
Early media |
Present |
Not present |
Not present |
OCS announcement played, call continues |
Early media |
Present |
Present |
Not present |
OCS announcement played, call continues (configured low balance announcement not played) |
Early media |
Present |
Not present |
Present |
OCS announcement played, call ends |
Early media |
Not present |
Present |
Not present |
Low balance feature configured announcement played, call continues |
Early media |
Not present |
Present |
Present |
Out of credit feature configured announcement played, call ends |
Mid call |
Present |
Not present |
Not present |
OCS announcement played, call continues |
Mid call |
Present |
Present |
Not present |
OCS announcement played, call continues (configured low balance announcement not played) |
Mid call |
Present |
Not present |
Present |
OCS announcement played, call ends |
Mid call |
Not present |
Present |
Not present |
Low balance feature configured announcement played, call continues |
Mid call |
Not present |
Present |
Present |
Out of credit feature configured announcement played, call ends |
Announcements for terminating calls
It is not possible to play announcements to the terminating subscriber after the initial credit check as the session has not yet been established. If the initial credit check requested announcements then a reauthorization request will be sent once the session is established. Any announcements in the response to this subsequent reauthorization request will be played. The reauthorization request can be delayed for a number of milliseconds using the ChargingReauthDelayMillis configuration field.
Mid call announcements to the terminating subscriber will be played immediately.
Low Balance Announcements
If the LowBalanceIndicator AVP is set in a successful CCA-I or CCA-U then a low balance announcement will be played (either configured or via the OC-Play-Announcement-Id-AVP) and a session state field is set to mark that a low balance announcement has been played. Subsequent credit checks will not trigger another low balance announcement unless the previous credit check response did not have the LowBalanceIndicator AVP set.
Out of Credit Announcements
If a credit check response contains a 4012 result code then:
-
For early originating sessions, the feature will schedule the configured early dialog announcement if an announcement was not supplied in the CCA and then end the session with the appropriate sip error response according to the CCA result code.
-
For early terminating and forwarding sessions, the feature will not schedule an announcement and will end the session with a 480 Temporarily Unavailable response.
-
For confirmed originating and terminating sessions, the feature will schedule the configured mid session announcement if an announcement was not supplied in the CCA and then end the session.
Session state input variables
| Attribute Name | Type |
|---|---|
LatestOcsAnswer |
org.jainslee.resources.diameter.ro.types.vcb0.CreditControlAnswer |
LegForCdrs |
String |
CallType |
com.opencloud.sentinel.common.CallType |
Session state output variables
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AnnouncementID |
int |
The ID of the early dialog announcement to play, if any |
EarlyMediaAnnouncementQueue |
List |
A List of early dialog announcements to play, if any |
MidCallAnnouncementId |
int |
The ID of the mid call announcement to play, if any |
MidCallAnnouncementQueue |
List |
A list of the mid call announcements to play, if any |
EndSessionAfterAnnouncement |
int |
The Sip response error code for the SipPlayAnnouncement feature to use on endSession. |
EndSessionWithAnnouncement |
boolean |
Set to true if session should end after announcement is played. |
MidCallAnnouncementPlayedParty |
String |
Leg name indicating which party the announcement will be played to |
MidCallEndSessionWithAnnouncement |
boolean |
Set to true if session should end after announcement is played. |
UserEndSessionCause |
int |
The Sip response error code to use on endSession, if applicable. |
LowBalanceAnnouncementPlayed |
boolean |
Set to true when a low balance announcement has been scheduled. Set to false when a CCA is received without a |
OcsAnnouncementPlayed |
boolean |
Set to true when |
Configuration
SetOcsAnnouncementID uses two JSLEE configuration profile tables: LowBalanceAnnouncementConfigProfileTable and SetOutOfCreditAnnouncementIDConfigProfileTable.
| Attribute Name | Profile Table | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
EarlyDialogLowBalanceAnnouncementID |
LowBalanceAnnouncementConfigProfileTable |
int |
The ID of the early dialog announcement to play, if any |
MidSessionLowBalanceAnnouncementID |
LowBalanceAnnouncementConfigProfileTable |
int |
The ID of the mid call announcement to play, if any |
ChargingReauthDelayMillis |
LowBalanceAnnouncementConfigProfileTable |
long |
When a terminating call is ACKed and the latest CCA indicates a low balance, a delayed credit check will be performed to postpone playing an announcement. The reauth will be delayed by the amount specified here (0 triggers an immediate reauth.) This allows time for the ACK to propagate through the network to ensure the played party is fully connected before triggering the announcement after receiving another CCA-U with low balance indicator. |
OutOfCreditAnnouncementID |
SetOutOfCreditAnnouncementIDConfigProfileTable |
int |
The ID of the early dialog announcement to play, if any |
MidSessionOutOfCreditAnnouncementID |
SetOutOfCreditAnnouncementIDConfigProfileTable |
int |
The ID of the mid call announcement to play, if any |
Statistics
SetOcsAnnouncementID statistics are tracked by the SetOcsAnnouncementID feature and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID ▶ SetOcsAnnouncementID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
TimerEventReceived |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a ChargingReauthDelay timer event is received. |
InvalidExecutionPoint |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the feature is invoked in an invalid execution point. Indicates misconfigured feature scripts. |
IgnoringRepeatLowBalance |
Counter |
The feature will not trigger a second announcement for ongoing low balance indicators. |
ClearLowBalancePlayed |
Counter |
If a CCA is received with no low balance indicator, any subsequent low balance will trigger another announcement. |
StartReauthTimer |
Counter |
Incremented when a terminating call is ACKed but the latest CCA indicates an announcement is requested. |
LowBalanceReauthTimerEventReceived |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a reauthorization timer event is received. |
DoCreditReauth |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the feature issues a credit reauth. |
ScheduledOcPlayAnnouncementId |
Counter |
Incremented whenever an OC-Play-Announcement-Id announcement is enqueued. |
EarlyDialogLowBalanceAnnouncementIDSet |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a configured early media Low Balance Announcement ID is enqueued. |
MidSessionLowBalanceAnnouncementIDSet |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a configured mid call Low Balance Announcement ID is enqueued. |
EarlyDialogOutOfCreditAnnouncementIDSet |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a configured early media Out of Credit Announcement ID is enqueued. |
MidSessionOutOfCreditAnnouncementIDSet |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a configured mid call Out of Credit Announcement ID is enqueued. |
EndSessionCauseSet |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a session is terminated due to running out of credit. |
NoOutOfCreditAnnouncementID |
Counter |
Incremented whenever an early media Out of Credit Announcement cannot be played as there is no configured announcement ID. |
NoMidSessionOutOfCreditAnnouncementID |
Counter |
Incremented whenever a mid call Out of Credit Announcement cannot be played as there is no configured announcement ID. |
UnableToDetermineEndSessionCause |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the end of session cause code could not be determined. |
MissingLegForCdrs |
Counter |
Incremented whenever the leg to play announcements too could not be determined. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR
SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR is responsible for reading subscriber data from the HLR and writing it into Sentinel session state variable fields.
The data it reads from the HLR is accessed through the AnyTimeSubscriberInterrogation MAP operation. The Application Context used is anyTimeInfoHandlingContext_v3_ac
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC. |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-hlr-subscriber-data-lookup module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-hlr-module opencloud#volte-hlr-subscriber-data-lookup#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new module, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new module.
The module-pack consists of a single module, volte-hlr-subscriber-data-lookup, containing the feature’s code. It does rely on the volte-map-event-handler which contains the shared event handler for MAP features and also publishes a module pack, however the event handler will not require modification unless a new feature name is introduced.
Session input variables
| Attribute Name | Type |
|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
Configuration
The feature uses the HLRConfigProfileTable to access its configuration. For more information refer to HLR CGIN MAP Configuration.
Statistics
SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR statistics are tracked by the SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR feature and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature issues a warning |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
RequestSent |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature receives subscriber data from the HLR |
RequestSuccessful |
Counter |
Incremented after the feature successfully processes the data it received, and loads it into session state fields |
RequestFailed |
Counter |
Incremented when absent configuration data prevents the feature from running |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between sending the request to the HLR and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
This feature uses the CGIN MAP RA to access the HLR.
Each time the feature is invoked, it checks the call type and determines the subscriber number that it should use to query the HLR.
The feature attempts to extract "phone number digits" from the Default Public ID, and if it cannot, from any other registered IMS Public User Identity. The first IMS Public User Identity that has "phone number digits" has its digits extracted to form the MSISDN for the AnytimeSubscriptionInterrogation query. If the feature cannot form an MSISDN it raises a Feature Error and finishes execution.
The feature requests the subscriber data by sending a AnyTimeSubscriptionInterrogation request for all Supplementary Services. If the triggering attempt is a terminating trigger, the feature sends two queries in order to gather the Call Forwarding information.
In order to form the ATSI request the feature:
-
sets the GSM SCF address to the
SentinelSCCPAddressconfiguration value -
sets the destination SCCP address to the
HlrSCCPAddressconfiguration value -
sets the indicator fields to request CLIP, CLIR, CW, ODB and may request Forwarding information for unconditional forwarding
If the session is a terminating session, a second request is sent where Forwarding information is requested for conditional forwarding.
Once the query(s) are successful, it sets the session state fields for the supplementary services according the mapping below.
Supplementary Service Session State Mappings
| GSM Service | MMTel Service |
|---|---|
CLIP |
|
COLP |
|
CLIR |
|
COLR |
|
ODB |
|
ODB |
|
Call Forwarding |
|
Call Waiting |
|
Call Hold |
GSM ASN.1 Schema to Session-State Fields
The mapping below describes how the AnyTimeSubscriptionInterrogation result is mapped into the MMTel Subscriber Data Representation.
ss-Status ASN.1 field
The field ss-Status is used by almost all supplementary services and defines the service state. Each service defines a set of possible values based on ss-Status, so called State Vectors. A state vector is formed of 4 variables: Provisioning State, Registration State, Activation State and HLR Induction State. This feature only reads the Activation State, i.e. "A and Q" bits.
For more information see 3GPP TS 23.011 - Technical realization of Supplementary Services.
CLIP
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
ClipData.ss-Status |
MMTelOIPServiceData.active |
|
OverrideCategory |
MTelOIPServiceData.override |
No default value. It is an obligatory field from HLR response. |
CLIR
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
ClirData.ss-Status |
MMTelOIRServiceData.active |
|
n/a |
MMTelOIRServiceData.mode |
the same default for IMS OIR |
ClirData.CliRestrictionOption |
MMTelOIRServiceData.defaultBehaviourType |
No default value. It is an obligatory field from HLR response. |
COLP
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
n/a |
MMTelTIPServiceData.active |
|
n/a |
MMTelTIPServiceData.override |
the same default for IMS TIP |
COLR
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
n/a |
MMTelTIRServiceData.active |
|
n/a |
MMTelTIRServiceData.mode |
the same default for IMS TIR |
ODB - Incoming calls
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
n/a |
MMTelICBServiceData.active |
|
ODB-Info.ODB-Data.ODB-GeneralData |
MMTelICBServiceData.ruleset |
see Ruleset Conditions for barring incoming calls |
Ruleset Conditions for barring incoming calls
| ODB Data Value | Condition |
|---|---|
allIC-CallsBarred |
Unconditional |
n/a |
Anonymous |
roamingOutsidePLMNIC-CallsBarred |
Roaming |
roamingOutsidePLMNICountryIC-CallsBarred |
Roaming and International ExHC |
ODB - Outgoing calls
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
n/a |
MMTelOCBServiceData.active |
|
ODB-Info.ODB-Data.ODB-GeneralData |
MMTelOCBServiceData.ruleset |
see Ruleset Conditions for barring outgoing calls |
Ruleset Conditions for barring outgoing calls
| ODB Data Value | Condition |
|---|---|
allOG-CallsBarred |
Unconditional |
internationalOGCallsBarred |
International |
internationalOGCallsNotToHPLMN-CountryBarred |
International-exHC |
roamingOutsidePLMNOG-CallsBarred |
Roaming |
Call Forwarding
| ASN.1 Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Mapping Rules |
|---|---|---|
callForwardingData.forwardingFeatureList[x].ss-Status |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.active |
|
callForwardingData.forwardingFeatureList.forwardingOptions |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.ruleset |
No default value defined. |
callForwardingData.forwardingFeatureList.noReplyConditionTime |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.noreplytimeout |
No default value defined. |
Ruleset Conditions for Call Forwarding
| ASN.1 value in bits 4 and 3 of Octet 1 of Ext-ForwardOptions | Condition | 00 |
|---|---|---|
Not Reachable |
01 |
Busy |
10 |
No reply |
11 |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS
SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS is responsible for reading data from the HSS and writing it into Sentinel session state fields.
The data it reads from the HSS must be accessed from TransparentUserData in the HSS.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
SBB |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-2 module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-hss2-module opencloud#volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-2#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-2 |
Contains the feature’s code. |
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-2-service-indication-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
Session input variables
| Attribute Name | Type |
|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
Configuration
This feature has an out-of-the-box configuration ensuring the MMTel features work. The configuration may be extended to
-
support additional MMTel features that use the MMTel services XML schema
-
support additional features that use a different XML schema
This configuration extensibility is supported through the profile table named ${PlatformOperatorName}_SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2ServiceIndicationProfileTable. If the platform operator name is RocketInc then the profile table name is RocketInc_SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2ServiceIndicationProfileTable.
The profile table contains one profile for each Service Indication that shall be queried in the HSS. Each profile defines:
-
the Service-Indication
-
the fully qualified class name of the Transparent Data Codec class - used to parse the returned XML into a Java Object
-
a list of adaptor class names (fully qualified class names)
-
an option to enable or disable the query
This table, by the default, has entries for MMTEL-Services and the IMS-ODB-Information. The MMTEL-Services query is enabled by default, while IMS-ODB-Information is disabled. The query can be enabled or disabled by setting the value of DisableQuery field to true or false. A value of true disables the query.
Statistics
SubscriberDataLookupFromHss statistics are tracked by the SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2 SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2 SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Invoked |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs. |
Failed |
Counter |
Incremented if a fatal error occurs while the feature is running. |
SubscriberDataRetrieved |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature receives subscriber data from the HSS or Sh-Cache. |
SessionStatePopulated |
Counter |
Incremented after the feature successfully processes the data it received, and loads it into session state fields. |
AdaptorClassError |
Counter |
Incremented when Adaptor class is not of type SimservsSessionAdaptor or the feature fails to retrieve adaptor class. |
CodecClassError |
Counter |
Incremented when Codec class is not of type ServiceDataCodec or the feature fails to retrieve codec class. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when absent configuration data prevents the feature from running. |
SessionStateNotFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the session state field the feature requires for operation is missing. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between sending the request to the HSS and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
This feature uses the Sh Cache RA to access the HSS.
Each time the feature is invoked, it determines the IMS public identity that it should use to query the HSS.
If the session input variable DefaultPublicID of the first RegistrationRecord in the RegistrationRecords list is present, this field is used as the IMS public identity in the HSS query. Otherwise, the the session input variable subscriber is used as the IMS public identity in the HSS query.
The feature requests the Sh Cache RA to fetch the transparent user data for the IMS Public Identifier and Service Indication. This data is stored in the corresponding session-state fields.
The feature can be configured to fetch multiple Service Indications, i.e. to retrieve different documents. The out-of-the-box configuration looks for the MMTel Services document.
For each profile in the feature’s configuration
-
the feature requests the Sh Cache RA to fetch the transparent user data document
-
Once a result is available, each adaptor in the list of adaptors is invoked in order to populate session state
MMTel Schema to Session-State Fields
The MMTel Services schema is configured into this feature in all out-of-the-box installations. This section describes the source of a variable (from within the returned document), and the destination session state field name and attribute for the out-of-the-box configuration.
OIP
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-originating-identity-presentation/originating-identity-presentation/active |
MMTelOIPServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-originating-identity-presentation/operator-originating-identity-presentation/restriction-override |
MMTelOIPServiceData.override |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL OIP see MMTelOIP.
OIR
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-originating-identity-restriction/originating-identity-presentation-restriction/active |
MMTelOIRServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-originating-identity-restriction/operator-originating-identity-presentation-restriction/mode |
MMTelOIRServiceData.mode |
If not specified the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-originating-identity-restriction/originating-identity-presentation-restriction/default-behaviour |
MMTelOIRServiceData.defaultBehaviourType |
If not specified the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL OIR see MMTelOIR.
TIP
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-terminating-identity-presentation/terminating-identity-presentation/active |
MMTelTIPServiceData.active |
If not specified the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-terminating-identity-presentation/operator-terminating-identity-presentation/restriction-override |
MMTelTIPServiceData.override |
If not specified the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL TIP see MMTelTIP.
TIR
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-terminating-identity-restriction/terminating-identity-presentation-restriction/active |
MMTelTIRServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-terminating-identity-restriction/operator-terminating-identity-presentation-restriction/mode |
MMTelTIRServiceData.mode |
If not specified the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL TIR see MMTelTIR.
ICB
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/active |
MMTelICBServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete/communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/ruleset |
MMTelICBServiceData.ruleset |
No default value specified. |
For more information on MMTEL ICB see MMTelICB.
OCB
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-communication-barring/outgoing-communication-barring/active |
MMTelOCBServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-communication-barring/outgoing-communication-barring/ruleset |
MMTelOCBServiceData.ruleset |
No default value specified. |
For more information on MMTEL OCB see MMTelOCB.
Operator Determined Barring
For more information see Operator Determined Barring.
CDIV
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-communication-diversion/active |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
MMTELServices/complete-communication-diversion/NoReplyTimer |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.noReplyTimeOut |
No default value specified. |
MMTELServices/complete-communication-diversion/ruleset |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.rules |
The default value is specified in Network operator data for MMTEL CDIV |
Ruleset Conditions for CDIV. Ruleset is a collection of rules.
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/common-policy/conditions |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.rules[].conditions |
No default value specified. |
MMTELServices/complete-communication-diversion/forward-to |
MMTelCDIVServiceData.rules[].forwardToAction |
No default value specified. |
For more information on MMTEL CDIV see MMTelCDIV.
CW
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-communication-waiting/communication-waiting/active |
MMTelCWServiceData |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL CW see MMTelCW.
HOLD
| Sh Field (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
n/a |
MMTelHOLDServiceData.active |
If not present in the XML document, the field is set to |
For more information on MMTEL Hold see MMTelHold.
Flexible-Alerting
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTELServices/complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/group-type |
MMTelFAGroup |
|
MMTELServices/complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/membership |
MMTelFAMembership |
|
MMTELServices/complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/members |
MMTelFAServiceData.members[] |
No default value. |
MMTELServices/complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/identity |
MMTelFAServiceData.identity |
The |
MMTELServices/complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group/@authorized |
MMTelFAServiceData.authorized |
Default value true. |
For more information on MMTEL FA see Flexible Alerting.
ECT
| XPath in document (From) | Session-State Field (To) | Default values |
|---|---|---|
MMTelServices/complete-explicit-communication-transfer/operator-explicit-communication-transfer/@authorized |
MMTelECTServiceData.authorized |
Default value false. |
For more information on MMTEL ECT see MMTelECT
SubscriberDataLookupFromHSSOld
SubscriberDataLookupFromHSSOld is responsible for reading data from the HSS and writing it into Sentinel session state variables fields.
Note: this feature is deprecated in favour of the new SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS feature. This deprecated feature is installed by default, but is not referenced in any feature execution script. The feature remains in case external developers used it as an extensibility mechanism. All out-of-the-box product features have been migrated away from this feature. In previous releases of the Sentinel VoLTE product, this feature was named SubscriberDataLookupFromHss, but it has now been renamed to SubscriberDataLookupFromHssOld. I.e. there is a new feature with the name SubscriberDataLookupFromHss.
The data it reads from the HSS must be accessed from TransparentUserData in the HSS.
The session state fields that are written to, and the locations in the XML documents retrieved from the HSS, are configurable.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Both or either of MMTEL or SCC |
Originating, Forwarding, and Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
SBB |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-hss-module opencloud#volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup |
Contains the feature’s code. |
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-service-indication-profile |
Contains the profile specification for configuring the service indications the feature should request. |
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-field-mapping-profile |
Contains the profile specification for configuring the session state fields the feature should populate. |
Network operator data
This data is stored in two JSLEE configuration profile tables. Both are scoped by Sentinel selection key. (However, unlike various other features, each operator has a profile table with multiple profiles within the table.)
-
The first is for mapping transparent user data service indications to Java codec classes.
-
The second configures the mapping between sections of the decoded document and session state variables/fields.
Service indications and codecs
Different applications use transparent user data in the HSS. To distinguish the format of the data, individual applications get unique service indications.
To enable flexibility, this feature allows a new XML schema to be introduced, alongside Java classes to parse (turn the XML into Java objects) and generated XML (turn Java objects back into XML for storage in the HSS).
The Java classes are called “codecs”, as they encode and decode between XML and Java.
This is stored in the profile table named $NetworkOperator_SubscriberDataLookupFromHssServiceIndicationProfileTable.
For example, if the network operator is “OpenCloud”, then the profile table name is OpenCloud_SubscriberDataLookupFromHssServiceIndicationProfileTable.
Each profile in the table has the following attributes.
| Attribute Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ServiceIndication |
String |
This is the value of the Service Indication. For example, for MMTEL this is |
CodecFQCN |
String |
This is the fully qualified class name of the codec class. For example, for Sentinel VoLTE MMTEL, this is |
Field definition profile
For the XML document to be entered into session state (so that other features can read these variables), the XML document must be broken down into relevant variables.
This is fulfilled by use of a field definition profile. Each field definition profile defines one session state variable, and where it comes from in the XML document.
| Attribute Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SessionStateFieldName |
String |
The name of the session state field to write to. |
XPath |
String |
The location in the XML document to read from. |
ServiceIndication |
String |
The service indication in transparent user data in the HSS. |
RootElementName |
String |
The name of the root element of the document; if non-empty it is chopped off the XPath. |
This is stored in the profile table $NetworkOperator_SubscriberDataLookupFromHssFieldDefinitionProfileTable; for example, if the network operator is “OpenCloud” then the profile table name is OpenCloud_SubscriberDataLookupFromHssFieldDefinitionProfileTable.
Communication diversion active example
As an example, MMTEL supplementary service settings are read by using the “MMTEL-Services” service indication.
Within the returned document, the XPath for the CDIV feature being active is /complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/@active.
The session state variable name is determined by the feature in question. In this case, the MMTelCDIV feature looks for a session input variable called CDIVActive.
So we end up with the following configuration for this field:
| Attribute Name | Value |
|---|---|
SessionStateFieldName |
CDIVActive |
XPath |
/complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/@active |
ServiceIndication |
MMTEL-Services |
RootElementName |
An alternative (using RootElementName) is:
| Attribute Name | Value |
|---|---|
SessionStateFieldName |
CDIVActive |
XPath |
MMTelServices/complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/@active |
ServiceIndication |
MMTEL-Services |
RootElementName |
MMTelServices |
Session input variables
| Attribute Name | Type |
|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
Statistics
SubscriberDataLookupFromHss statistics are tracked by the SubscriberDataLookupFromHss SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SubscriberDataLookupFromHss SBB ID.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssInvoked |
Incremented each time the feature runs. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssFailed |
Incremented if a fatal error occurs while the feature is running. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssSubscriberDataRetrieved |
Incremented when the feature receives subscriber data from the HSS or Sh-Cache. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssSessionStatePopulated |
Incremented after the feature successfully processes the data it received, and loads it into session state fields. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssMisconfigured |
Incremented when absent configuration data prevents the feature from running. |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHssSessionStateNotFound |
Incremented when the session state field the feature requires for operation is missing. |
Behaviour
This feature uses the Sh Cache RA to access the HSS.
Each time the feature is invoked, it checks the call type and determines the IMS public identity that it should use to query the HSS.
If the session input variable DefaultPublicID of the first RegistrationRecord in the RegistrationRecords list is present, this field is used as the IMS public identity in the HSS query. Otherwise, the the session input variable subscriber is used as the IMS public identity in the HSS query.
For each service indication profile, the feature requests the Sh Cache RA to return the transparent user data for the IMS public identifier and service indication.
Next, the document is queried once for each field definition profile. The results of each XPath query are written into the session state variable. If any error occurs, the session state variable is not modified.
Examples of errors include:
-
Cannot decode the XML document.
-
The session state variable name does not correspond to a session state variable (for example, it was mistyped).
-
The Java type for the session state variable, and the type of the object returned by the XPath query are incompatible.
-
The XPath query did not return any data.
Recommended minimum configuration for MMTEL
In order to provide MMTEL, according to IR.92 it is recommended that:
-
the service indication profile includes the pre-built MMTel codec
-
all session input variables for the out-of-the-box MMTel features are included.
Minimum service indication profiles for MMTEL
| ServiceIndication | CodecFQCN |
|---|---|
MMTEL-Services |
com.opencloud.mmtel.feature.hssdata.MmtelServiceDataCodec |
Minimum field definition profiles for MMTEL
| SessionStateFieldName | XPath | ServiceIndication | RootElementName |
|---|---|---|---|
CDIVActive |
/complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
CDIVRuleset |
/complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/ruleset |
MMTEL-Services |
|
CDIVSubscriberNoReplyTimeout |
/complete-communication-diversion/communication-diversion/NoReplyTimer |
MMTEL-Services |
|
CWActive |
/complete-communication-waiting/communication-waiting/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
ICBActive |
/complete-communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
ICBRuleset |
/complete-communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/ruleset |
MMTEL-Services |
|
OCBActive |
/complete-communication-barring/outgoing-communication-barring/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
OCBRuleset |
/complete-communication-barring/outgoing-communication-barring/ruleset |
MMTEL-Services |
|
OIPActive |
/complete-originating-identity-presentation/originating-identity-presentation/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
OIRActive |
/complete-originating-identity-restriction/originating-identity-presentation-restriction/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
OIRDefaultBehaviourType |
/complete-originating-identity-restriction/originating-identity-presentation-restriction/default-behaviour |
MMTEL-Services |
|
TIPActive |
/complete-terminating-identity-presentation/terminating-identity-presentation/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
TIRActive |
/complete-terminating-identity-restriction/terminating-identity-presentation-restriction/@active |
MMTEL-Services |
|
TIRDefaultBehaviourType |
/complete-terminating-identity-restriction/terminating-identity-presentation-restriction/default-behaviour |
MMTEL-Services |
SuppressSdpCdr
SuppressSdpCdr is a system feature which prevents SDP-change initiated CDRs from being written by the VolteInterimCdr feature for non-roaming Mobile Terminating calls.
Statistics
SuppressSdrCdr statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SuppressSdpCdr
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SuppressSdpCdr"
Name |
Description |
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
NoPendingSdpCdr |
Incremented when the feature runs but there is no pending SDP CDR to suppress |
SdpCdrWriteSuppressed |
Incremented each time an SDP CDR is suppressed |
SdpCdrWriteAllowed |
Incremented each time the feature runs but doesn’t suppress a pending SDP CDR |
Functionality
This feature uses information available in session state to suppress interim CDRs from being written in response to SDP changes for non-roaming Mobile Terminating calls. The mechanism it uses to suppress the CDRs from being written by the VolteInterimCdr feature is to unset the WriteCdrOnSDPChange session state field.
When this feature runs, if the session state variable RoamingIndicator is False, and CallType is MobileTerminating, the WriteCdrOnSDPChange session state field will be set to False.
VoLTE Interim CDR Feature
VolteInterimCdr is a system feature that is responsible for writing interim Call Detail Records throughout the session.
VolteInterimCdr runs at various key points throughout a session and if any of its write conditions are met, it will create a new interim CDR based on session state, and write it out using the cdr-ra.
| |
By default, Sentinel runs featurescript SipEndSession-SysPost-Default {
run VolteInterimCdr
run MaxCallDuration
run SessionRefresh
}
|
Details
Feature script name |
VolteInterimCdr |
|---|---|
Applicable contexts |
SIP service |
Prerequisite features |
None, but information from various features is used if available |
Session state inputs and outputs
Inputs
If any of these fields are unset the feature will skip writing them to the CDR file.
This feature uses the same session state fields as the Sentinel Interim CDR feature. This page will only discuss the additions to the fields described there.
| Name | Type | Description | Where set |
|---|---|---|---|
TerminatingDomain |
String |
The accepted terminating domain in a T-ADS scenario |
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation feature, SCCTADSParallelRouting feature |
MMTelInformation |
org.jainslee.resources.diameter .ro.types.vcb0.MmtelInformation |
The MMTel-Information Diameter AVP |
|
RegistrationRecords |
List<com.opencloud.sentinel.state.RegistrationRecord> |
Contains subscriber information retrieved from the Registrar and HSS or Cassandra |
|
CallReferenceNumber |
byte[] |
Contains the Call Reference Number used in queries to the HLR |
Functionality
This features uses the information from the session state fields mentioned above and constructs a protobuf message out of it for output. See AVP CDR Format for the format of these messages.
Also see Charging Information for general information about the contents of CDRs and CCRs.
| |
This feature only supports writing binary CDRs. If the cdr-ra is configured to write string CDRs the feature will fail to execute. |
VoLTE SIP AVP CDR Feature
This feature is responsible for building a Call Detail Record that reflects the actions taken whilst processing a session.
It runs once when a session is ending and creates a CDR based on information gathered from session state, and then writes it out using the cdr-ra.
| |
By default, Sentinel runs featurescript SipEndSession-SysPost-Default {
run VolteSipAvpCdr
run MaxCallDuration
run SessionRefresh
}
|
Details
Feature script name |
VolteSipAvpCdr |
|---|---|
Applicable contexts |
SIP service |
Prerequisite features |
None, but information from various features is used if available |
Session state inputs and outputs
Inputs
If any of these fields are unset the feature will skip writing them to the CDR file.
This feature uses the same session state fields as the Sentinel SIP AVP CDR feature. This page will only discuss the additions to the fields described there.
| Name | Type | Description | Where set |
|---|---|---|---|
TerminatingDomain |
String |
The accepted terminating domain in a T-ADS scenario |
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation feature, SCCTADSParallelRouting feature |
MMTelInformation |
org.jainslee.resources.diameter .ro.types.vcb0.MmtelInformation |
The MMTel-Information Diameter AVP |
|
RegistrationRecords |
List<com.opencloud.sentinel.state.RegistrationRecord> |
Contains subscriber information retrieved from the Registrar and HSS or Cassandra |
|
CallReferenceNumber |
byte[] |
Contains the Call Reference Number used in queries to the HLR |
Functionality
This features uses the information from the session state fields mentioned above and constructs a protobuf message out of it for output. See AVP CDR Format for the format of these messages.
Also see Charging Information for general information about the contents of CDRs and CCRs.
| |
This feature only supports writing binary CDRs. If the cdr-ra is configured to write string CDRs the feature will fail to execute. |
VoLTE SIP Legacy CDR Feature
This feature is responsible for building a Call Detail Record that reflects the actions taken whilst processing a session.
It runs once when a session is ending and creates a CDR based on information gathered from session state, and then writes it out using the cdr-ra.
| |
This feature is deprecated and not enabled by default. It has been superseded by the VoLTE SIP AVP CDR feature |
Details
Feature script name |
VolteSipLegacyCdr |
|---|---|
Applicable contexts |
SIP service |
Prerequisite features |
None, but information from various features is used if available |
Session state inputs and outputs
Inputs
If any of these fields are unset the feature will skip writing them to the CDR file.
This feature uses the same session state fields as the Sentinel SIP Legacy CDR feature. This page will only discuss the additions to the fields described there.
| Name | Type | Description | Where set |
|---|---|---|---|
TerminatingDomain |
String |
The accepted terminating domain in a T-ADS scenario |
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation feature, SCCTADSParallelRouting feature |
Statistics
VolteSipLegacyCdr statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → VolteSipLegacyCdr
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.VolteSipLegacyCdr"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssueWarning |
Incremented when a non fatal error occurs while the feature is executing |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs while the feature is executing |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
CDRwritten |
Incremented when a CDR is written successfully |
CDRnotWritten |
Incremented when a CDR is not written successfully due to an error |
Functionality
This features uses the information from the session state fields mentioned above and constructs a protobuf message out of it for output. See Legacy CDR Format for the format of these messages.
Also see Charging Information for general information about the contents of CDRs and CCRs.
| |
This feature only supports writing binary CDRs. If the cdr-ra is configured to write string CDRs the feature will fail to execute. |
MMTel Features
These features are MMTel specific.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
a logical representation of supplementary service data as a group of POJO objects. It allows MMTel services/features to execute independently of any concrete schema for the supplementary service data. Therefore it can be loaded from the HSS or the HLR using the MMTel-Services XML schema or 3GPP MAP ASN.1 schema. |
|
|
lets users create multi-party sessions between two or more parties |
|
|
provides a means for UEs to subscribe to “conference” event package notifications for a conference |
|
|
enables a ‘diverting user’ to divert communications addressed to the ‘diverting user’ to another destination |
|
|
lets a UE be informed that no resources are available for an incoming communication |
|
|
determines if the SIP session is roaming and if it represents an international, or international ex HC call, based on the location of the calling party and the destination address |
|
|
lets a user suspend reception of the media stream(s) of an established IP multimedia session, and resume the media stream(s) at a later time |
|
|
implements incoming communication barring and anonymous communication rejection |
|
|
implements outgoing communication barring |
|
|
are barring conditions determined by the operator that takes precedence over MMTelICB and MMTelOCB |
|
|
implements the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) service |
|
|
implements the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) service |
|
|
implements the Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) service |
|
|
implements the Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) service |
|
|
handles the finalisation of charging when a call is answered over WiFi. |
|
|
records charging information about MMTel supplementary services invoked on a call. |
|
|
determines if and how the Flexible Alerting features will execute based on feature configuration and the HSS Subscriber Data. |
|
|
implements the Flexible Alerting service, by alerting the group members in parallel |
|
|
implements the Flexible Alerting service, by sequentially alerting the group members. |
|
|
connects the IMPU acquired from the subscriber registration to the existing ACI for the session transfer |
|
|
checks if the subscriber has the STOD service provisioned |
|
|
handles the transfer request and route it to the previous bound session |
|
|
intercepts the transfer INVITE routed by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature and connects the existing called led to the new calling leg and releases the previous calling leg |
|
|
enables a party involved in a communication to transfer their role in that communication to a third party |
|
|
adds the |
Call Barring Features
Call Barring Features.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
implements incoming communication barring and anonymous communication rejection |
|
|
implements outgoing communication barring |
|
|
are barring conditions determined by the operator that takes precedence over MMTelICB and MMTelOCB |
|
|
are 4 operator defined rules that are stored in the AS. The ODB data indicates which of them should be evaluated and, like all others ODB conditions, they take precedence over MMTelICB and MMTelOCB |
MMTelICB
The MMTelICB feature implements incoming communication barring and anonymous communication rejection . (The MMTelOCB feature implements outgoing communication barring.)
What is ICB?
3GPP defines Communication Barring in TS 24.611, including Incoming Communication Barring (ICB), Anonymous Communication Rejection as a special case of ICB, and Outgoing Communication Barring (OCB):
|
The incoming communication barring (ICB) is a service that rejects incoming communications that fulfil certain provisioned or configured conditions on behalf of the terminating user. The anonymous communication rejection (ACR) is a particular case of the ICB service, that allows barring of incoming communications from an anonymous originator on behalf of the terminating user. The incoming communication barring (ICB) service makes it possible for a user to have barring of certain categories of incoming communications according to a provisioned or user configured barring program and is valid for all incoming communications. A barring program is expressed as a set of rules in which the rules have a conditional part and an action part. Examples of conditions are whether the asserted originating public user identity matches a specific public user identity or whether the originating public user identity is restricted (anonymous). The action part could specify for a rule that contains a matching condition that the specific incoming communication is barred. The inhibition of incoming forwarded calls is a special case of the ICB and allows the served user to reject incoming communications from users or subscribers who have diverted the communication towards the served user. The communication history information will be used to trigger the service. The anonymous communication rejection (ACR) service allows the served user to reject incoming communications on which the asserted public user identity of the originating user is restricted. In case the asserted public user identity of the originating user is not provided then the communication is allowed by the ACR service. It is highlighted here because it is a regulatory service in many countries. |
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
SipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
Yes |
Yes, comes from the HSS |
Stateless |
POJO |
Prerequisite Features
-
DetermineCallType
-
SubscriberDetermination
-
MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status (used for Roaming, International and International-exHC detection)
| |
For announcements, SIPPlayAnnouncement is a dependent feature; but it is not a prerequisite. |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-communication-barring module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-cb-module opencloud#mmtel-communication-barring#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-communication-barring |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-communication-barring-library |
Contains code shared by both communication barring features. |
mmtel-icb-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-icb |
Contains the feature itself. |
Network Operator Data
This data is stored in a JSLEE Configuration Profile Table, called MMTelICBConfigProfileTable.
Operator data is scoped according to a Sentinel selection key. There is one profile in the ProfileTable for each network operator.
| Attribute Name | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
PlayAnnouncement |
Boolean |
false |
If true, ICB will request an announcement is played in the case that it bars the session setup. |
ACRAnnouncementID |
int |
0 |
The ID for the announcement to be played in the case of Anonymous Call Rejection. If set to zero there is no announcement. |
AnnouncementID |
int |
0 |
The ID for the announcement to be played in all other ICB cases. If set to zero there is no announcement. |
InternationalRulesActive |
Boolean |
false |
If false, ICB will ignore International and International-exHC rules. |
Session Input Variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
|
RoamingIndicator |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature. |
International |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature. |
InternationalExHC |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature. |
Session Output Variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ICBBarred |
Boolean |
Set to true if the ICB feature bars the call. It exists so that feature execution scripts can read the variable and take action |
ICBBarredWithAnnouncement |
Boolean |
Set to true if the ICB feature bars the call, and the feature is configured to request an announcement as part of barring |
AnnouncementID |
int |
The announcement ID to be used if an announcement is configured as part of barring |
EndSessionAfterAnnouncement |
int |
The status code used when ending the session — if barring has occurred and announcements are used. |
RanIcb |
Boolean |
Signals to other features that ICB ran on this session. |
Supported Barring Rule Conditions
Barring rule conditions that are evaluated include:
Anonymous
To comply with the requirements as set for simulation of the ACR service, the anonymous element only evaluates to true when the conditions as set out in subclause 4.5.2.6.2 for asserted originating public user identity apply.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for anonymous calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="anonymous">
<cp:conditions>
<anonymous/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Roaming
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable RoamingIndicator is true. This is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for roaming calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="roaming">
<cp:conditions>
<roaming/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Media
This condition evaluates to true when the value of this condition matches the media field in one of the "m=" lines in the SDP message body offered in an INVITE request.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for calls offering specific media:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no_video">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Combinations of media types may be expressed as multiple conditions within the same rule. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no_video_and_text">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
<media>text</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Identity
This condition evaluates to true if the identity of the other party in the communication matches that which is expressed in the condition. Identities within the condition can be expressed in different ways:
-
a single, fully expressed identity (e.g. sip:alice@example.com)
-
a whole domain (e.g. example.com)
-
a whole domain, but with exceptional identities or domains (e.g. example.com except for alice@example.com)
-
all identities (may also have exceptions)
-
any combination of the above
The following XML snippets show how to configure the user’s Subscriber data for each of the above cases.
This example, without any other rule, blocks any session from 'sip:alice@example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="bar-alice">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session from domain 'example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="bar-domain">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session from domain 'example.com' except if originated from 'sip:alice@example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domain-with-exception">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com">
<except id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session from domain 'example.com' except if originated from the subdomain 'callcentre.example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domain-except-callcentre">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com">
<except domain="callcentre.example.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>| |
Note the attribute of the 'except' element is now 'domain'. |
This example, without any other rule, blocks all sessions from any user.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-all">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many />
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session from all users registered in the domain 'example2.com', from the user 'sip:alice@example1.com' and from the user sip:bob@example1.com, except from 'sip:charlie@example2.com.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-some">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example1.com"/>
<one id="sip:bob@example1.com"/>
<many domain="example2.com">
<except id="sip:charlie@example2.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, always blocks some domains, always allow other domains and a set of sip URIs.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="always-allow-these-domains">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="emergency.org"></many>
<many domain="police.org"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>true</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
<cp:rule id="always-barr-these-domains">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="fakelotery.org"></many>
<many domain="dhueb!.org"></many>
<many domain="fakeprize.com"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
<cp:rule id="always-barr-these-identities">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:john@example.com"/>
<one id="sip:marc@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>| |
Depending on the value of the 'allow' element of the rule, the rule can essentially become a 'whitelist' or a 'blacklist'. |
International
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable International is true and 'InternationalRulesActive' is true. 'International' is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature. 'InternationalRulesActive' is configured in the ICB feature profile and defaults to false. This is because it is not possible to accurately determine whether the calling party is international in all circumstances.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for international calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="international">
<cp:conditions>
<international/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>International-exHC
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable InternationalExHC is true and 'InternationalRulesActive' is true. 'International' is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature. 'InternationalRulesActive' is configured in the ICB feature profile and defaults to false. This is because it is not possible to accurately determine whether the calling party is international in all circumstances.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for international-exHC calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="international-exHC">
<cp:conditions>
<international-exHC/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Unconditional
An empty conditions element is used to represent unconditional.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for all calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="anonymous">
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Communication Diverted
This condition evaluates to true when the incoming communication has been previously diverted.
Diverted communication can be recognised by the presence of the History header field, as specified in 3GPP TS 24.604
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for diverted calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="diverted">
<cp:conditions>
<communication-diverted/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Validity
This condition evaluates to true if the current time is within the times specified by the validity period Time is based on the Home Network time; that is, the time of the MMTel Server.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure ICB for a validity period:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="validity">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>2000-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>2099-12-31T23:59:59</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Rule Deactivated
This condition always evaluates to false. Generally used to disable a rule that has other conditions without removing the rule entirely.
The rule is re-enabled by removing this condition.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure a deactivated rule:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="deactivated">
<cp:conditions>
<rule-deactivated/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Barring Rule Actions
Barring rule actions are a string. There could be many actions defined, but the only one that makes any sense is the allow action.
The allow action has a Boolean attribute, with meaning as follows:
-
true— allow session setup to proceed -
false— deny session setup from proceeding.
Any other rule action (in other words, an action that is not set to allow) will result in us treating the action as the following:
-
allow rule action with value of true.
Statistics
MMTelICB statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelICBFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelICBFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelICBFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelICBFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelICBFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelICBFeatureCallBarred |
the feature bars a call (including when barring due to ACR) |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarredByOdb |
the feature bars a call by Operator Determined Barring rule |
MMTelICBFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature requests that an announcement be played to the calling party |
MMTelICBFeatureACRTriggered |
a call is barred by ACR |
MMTelICBFeatureOdbRulesEvaluatedTrue |
a rule was evaluated to be True |
Behaviour
If operator data is not present, the ICB feature:
-
Increments an error statistic.
-
Logs a message at the
Finelevel. -
Informs the Sentinel core that the feature is not configured appropriately (
Invalid Configuration). -
Exits.
If MMTelICBServiceData.Active is false, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
If the rules do not parse, then the feature:
-
instructs Sentinel core that the feature has failed due to configuration problems
-
finishes execution without modifying any state.
When the feature processes a set of rules:
| For each rule, if | then |
|---|---|
|
the rule matches. |
The actions from all matching rules are combined.
| If… | then the combined result for the rule set is: |
|---|---|
|
any matching rules had the action |
|
|
all matching rules had the action |
|
|
no rules matched |
|
| |
When a rule contains multiple conditions, they all must match for the whole rule to match. This is essentially a logical 'AND' between the conditions. To express a logical 'OR' of conditions, the conditions must be placed in different rules. |
If the combined result is allow=false, then the ICB feature sets the session output variable ICBBarred to true. Otherwise the ICB feature sets the session output variable ICBBarred to false and finishes without modifying any further state.
If network configuration has PlayAnnouncement set to true (MmtelICBConfig.PlayAnnouncement == true), and ICB has decided to bar the communication, then the ICB feature sets session output variable AnnouncementID to MmtelICBConfig.AnnouncementID.
Finally, if the communication is to be barred, ICB rejects the call with the appropriate SIP error response code:
If any matching rule contains the “anonymous” condition, use 433 Anonymity Disallowed. This is to provide ACR functionality. (See section 4.5.2.6.1.)
Otherwise use 603 Decline.
Roaming Determination
The ICB feature does not compute whether or not the served user is roaming; rather it relies on a session input variable (isRoaming). This is set by Sentinel’s DetermineIfRoaming feature.
Example feature execution script fragment:
run DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus run MMTelICB
Playing Announcements
The MMTelICB feature does not play announcements itself; rather it relies on setting of session output variables (AnnouncementID, ICBBarredWithAnnouncement, EndSessionAfterAnnouncement). These are set by the MMTelICB feature if an announcement is to be played. They are used by the out-of-the-box feature execution scripts such that if announcements are desired to be played prior to the barred call being terminated, it is played using the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature.
This is an example feature execution script, taken from a fragment of the out-of-the-box execution scripts.
run MMTelICB
if (session.ICBBarredWithAnnouncement) {
run SIPPlayAnnouncement
}
The SIPPlayAnnouncement feature checks session state for the AnnouncementID field, and if the value is non-zero will play an announcement. When the announcement is played using the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature, it is played to the calling party.
Finally, when the announcement is complete the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature ends the session with the appropriate SIP error response (provided by MMTelICB during its execution). The SIP error response code is set in the EndSessionAfterAnnouncement session output variable.
Background Information on Format of Barring Rules
Each rule is expressed as an XCAP cp-rule.
That is, it is an XML fragment:
<cp:rule id="rule66">
<cp:conditions>
condition1
condition2
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
In case that the allow element is not found, the feature assumes allow = false.
MMTelOCB
The MMTelOCB feature implements outgoing communication barring .
(The MMTelICB feature implements incoming communication barring and anonymous communication rejection.)
What is OCB?
3GPP defines communication barring in TS 24.611, including Incoming Communication Barring (ICB), Anonymous Communication Rejection as a special case of ICB, and Outgoing Communication Barring (OCB):
|
The Outgoing Communication Barring (OCB) is a service that rejects outgoing communications that fulfil certain provisioned or configured conditions on behalf of the originating user. The Outgoing Communication Barring (OCB) service makes it possible for a user to have barring of certain categories of outgoing communications according to a provisioned or user configured barring program and is valid for all outgoing communications. A barring program is expressed as a set of rules in which the rules have a conditional part and an action part. An example condition is whether the request uri matches a specific public user identity. The action part can specify for a rule that contains a matching condition that the specific outgoing communication it to be barred. The complete set of conditions and actions that apply to this service and their semantics is described in subclause 4.9.Incoming. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
OriginatingSipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
SipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Prerequisite features
-
DetermineCallType
-
MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status (used for Roaming, International and International-exHC detection)
| |
For announcements, SIPPlayAnnouncement is a dependent feature; but it is not a prerequisite. |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-communication-barring module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-cb-module opencloud#mmtel-communication-barring#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-communication-barring |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-communication-barring-library |
Contains code shared by both communication barring features. |
mmtel-ocb-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-ocb |
Contains the feature itself. |
Network operator data
This data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile table, called MMTelOCBConfigProfileTable.
Operator data is scoped according to a Sentinel selection key. There is one profile in the profile table for each network operator.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OCBPlayAnnouncement |
Boolean |
If true, MMTelOCB will request an announcement is played in the case that it bars the session setup. |
OCBAnnouncementID |
int |
The ID for the announcement to be played. If set to zero there is no announcement. |
Session input variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
|
RoamingIndicator |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature |
International |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature |
InternationalExHC |
Boolean |
Set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
OCBBarred |
Boolean |
Set to true if the OCB feature bars the call. It exists so that feature execution scripts can read the variable and take action. |
OCBBarredWithAnnouncement |
Boolean |
Set to true if the OCB feature bars the call, and the feature is configured to request an announcement as part of barring |
AnnouncementID |
int |
The value of the announcement ID to be played. Zero has a special meaning — that no announcement is to be played. |
EndSessionAfterAnnouncement |
int |
The status code used when ending the session — if barring has occurred and announcements are used. |
RanOcb |
Boolean |
Signals to other features that OCB ran on this session. |
Supported barring rule conditions
Roaming
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable RoamingIndicator is true. This is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data page to configure OCB for roaming calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="roaming">
<cp:conditions>
<roaming/>
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Media
This condition evaluates to true when the value of this condition matches the media field in one of the "m=" lines in the SDP message body offered in an INVITE request.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data Page to configure OCB for calls offering specific media:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no_video">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Combinations of media types may be expressed as multiple conditions within the same rule. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no_video_and_text">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
<media>text</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Identity
This condition evaluates to true if the identity of the other party in the communication matches that which is expressed in the condition. Identities within the condition can be expressed in different ways:
-
a single, fully expressed identity (e.g. sip:alice@example.com)
-
a whole domain (e.g. example.com)
-
a whole domain, but with exceptional identities or domains (e.g. example.com except for alice@example.com)
-
all identities (may also have exceptions)
-
any combination of the above
The following XML snippets show how to configure the user’s Subscriber data for each of the above cases.
This example, without any other rule, blocks any session torwards 'sip:alice@example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-alice">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session torwards any user in the 'example.com' domain.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domains">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session torwards all users in the 'example.com' domain, except for 'sip:alice@example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domains-with-exceptions">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com">
<except id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session torwards all users in the 'example.com' domain, except for users within the domain 'callcentre.example.com'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domain-except-callcentre">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com">
<except domain="callcentre.example.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>| |
Note the attribute of the 'except' element is now 'domain'. |
This example, without any other rule, blocks all sessions torwards any user.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-all">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many />
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, without any other rule, blocks any session torwards all users registered in the domain 'example2.com', for 'sip:alice@example1.com' and sip:bob@example1.com, except for 'sip:charlie@example2.com.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-some">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example1.com"/>
<one id="sip:bob@example1.com"/>
<many domain="example2.com">
<except id="sip:charlie@example2.com"/>
</many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>This example, always blocks some domains, always allow other domains and a set of sip URIs.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="always-allow-these-domains">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="emergency.org"></many>
<many domain="police.org"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>true</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
<cp:rule id="always-barr-these-domains">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="fakelotery.org"></many>
<many domain="dhueb!.org"></many>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
<cp:rule id="always-barr-these-identities">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:john@example.com"/>
<one id="sip:marc@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>| |
Depending on the value of the 'allow' element of the rule, the rule can essentially become a 'whitelist' or a 'blacklist'. |
International
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable International is true. This is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data page to configure OCB for international calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="international">
<cp:conditions>
<international/>
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>International-exHC
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable InternationalExHC is true. This is set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data page to configure OCB for international-exHC calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="international-exHC">
<cp:conditions>
<international-exHC/>
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>International when roaming
This condition evaluates to true if the session state variable International is true and RoamingIndicator is true. These are set by the MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status feature.
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data page to configure OCB for international when roaming calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="international">
<cp:conditions>
<roaming/>
<international/>
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Unconditional
Use this XML in the REM HSS Subscriber Data page to configure OCB for all calls:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="all-calls">
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Validity
This condition evaluates to true if the current time is within the times specified by the validity period.
Time is based on the Home Network time (that is, the time of the MMTel Server).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="all-calls">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>1970-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>1970-01-01T00:00:00</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Rule deactivated
This condition always evaluates to false. Used to disable a rule without removing the rule entirely. The rule is re-enabled by removing this condition.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy" xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="all-calls">
<cp:conditions>
<rule-deactivated/>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>1970-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>1970-01-01T00:00:00</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>Barring rule actions
Barring rule actions are a string. There could be many actions defined, but the only one that makes any sense is the allow action.
The allow action has a Boolean attribute, with meaning as follows:
-
true— allow session setup to proceed -
false— deny session setup from proceeding.
Any other rule action (that is, an action that is not set to allow) will result in us treating the action as the following:
-
allow rule action with value of
true.
Statistics
MMTelOCB statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelOCBFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelOCBFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelOCBFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelOCBFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelOCBFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarred |
the feature bars a call |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarredByOdb |
the feature bars a call by Operator Determined Barring rule |
MMTelOCBFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature requests that an announcement be played to the calling party |
MMTelOCBFeatureOdbRulesEvaluatedTrue |
a rule was evaluated to be True |
Behaviour
If operator data is not present, the OCB feature:
-
Increments an error statistic.
-
Logs a message at the
Finelevel. -
Informs the Sentinel core that the feature is not configured appropriately (
Invalid Configuration). -
Exits.
If MMTelOCBServiceData.Active is false, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
If the rules do not parse, then the feature:
-
instructs Sentinel Core that the feature has failed due to configuration problems
-
finishes execution without modifying any state.
When the feature processes a set of rules, it does each in turn:
| For each rule, if: | then |
|---|---|
|
the rule matches |
The actions from all matching rules are combined.
| If… | then the combined result for the rule set is: |
|---|---|
|
any matching rules had the action |
|
|
all matching rules had the action |
|
|
no rules matched |
|
| |
When a rule contains multiple conditions, they all must match for the whole rule to match. This is essentially a logical 'AND' between the conditions. To express a logical 'OR' of conditions, the conditions must be placed in different rules. |
If the combined result is allow=false, then the OCB feature sets the session output variable OCBBarred to true. Otherwise the OCB feature sets the session output variable OCBBarred to false and finishes without modifying any further state.
If THE network configuration has OCBPlayAnnouncement set to true, and OCB has decided to bar the communication, then the OCB feature sets the session output variable AnnouncementID to MmtelOCBConfig.OCBAnnouncementID.
Finally, if the communication is to be barred, OCB rejects the call with the appropriate SIP error response code: 603 Decline.
Roaming determination
The MMTelOCB feature does not compute whether or not the served user is roaming; rather it relies on a session input variable (RoamingIndicator). This is set by Sentinel’s DetermineIfRoaming feature.
Here is an example feature execution script fragment:
run DetermineIfRoaming run MMTelOCB
Playing announcements
The MMTelOCB feature does not play announcements itself; rather it relies on setting session output variables (AnnouncementID, OCBBarredWithAnnouncement, EndSessionAfterAnnouncement). These are set by the MMTelOCB feature if an announcement is to be played. They are used by the out-of-the-box feature execution scripts such that if announcements are desired to be played prior to the barred call being terminated, it is played using the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature.
This is an example feature execution script, taken from a fragment of the out-of-the-box execution scripts.
run MMTelOCB
if (session.OCBBarredWithAnnouncement) {
run SIPPlayAnnouncement
}
The SIPPlayAnnouncement feature checks session state for the AnnouncementID field, and if the value is non-zero will play an announcement. When the announcement is played using the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature, it is played to the calling party.
Finally, when the announcement is complete the SIPPlayAnnouncement feature ends the session with the appropriate SIP error response (provided by MMTelOCB during its execution). The SIP error response code is set in the EndSessionAfterAnnouncement session output variable.
Background information on format of barring rules
Each rule is expressed as an XCAP cp-rule — as an XML fragment:
<cp:rule id="rule66">
<cp:conditions>
condition1
condition2
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
In case that the allow element is not found, the feature assumes allow = false.
Operator Determined Barring
The Operator Determined Barring are barring conditions determined by the operator that takes precedence over MMTelICB and MMTelOCB .
What is ODB?
Operator determined barring is specified for IMS in the 3GPP specifications TS 24.315 and TS 22.041:
from TS 24.315
The network feature Operator Determined Barring (ODB) allows a network operator or service provider to regulate access to IMS subsystem services, by the barring of certain categories of incoming or outgoing communications, the barring of certain categories of roaming and the barring of certain categories of supplementary services configuration and invocation. |
ODB Data
The ODB data is stored as transparent data in the HSS. The SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS feature is responsible to retrieve the ODB data from the HSS. The SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS Configuration should contain the service indication as IMS-ODB-Information and the proper codec. The SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS queries the HSS and if the operator had configured any ODB rules for that subscriber then user data will be returned, parsed and then stored in a session state field MMTelODBServiceData. The MMTelICB and MMTelOCB will use the session state field MMTelODBServiceData to evaluate the ODB conditions before the subscriber defined conditions.
Enabling ODB
ODB can be enabled using the DisableQuery option in the SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS. The sdk installer provides an option for setting DisableQuery on IMS and DisableQuery on MMTel.
Enabling ODB
The HSS IMS-ODB-Information query can be enabled using the DisableQuery option in the SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS.
Bar all outgoing communications
Bar all of the outgoing communications, The OutgoingBarring tag is set to "0".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OutgoingBarring>0</OutgoingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar all outgoing international communications
Barring of all outgoing communications to international destinations. The OutgoingBarring tag is set to "1".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OutgoingBarring>1</OutgoingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar all outgoing communications when international ex-hplmnc
Barring of all outgoing communications to international destinations excluding home network. The OutgoingBarring tag is set to "2".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OutgoingBarring>2</OutgoingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar all outgoing communications when roaming
Barring of all outgoing communications roaming outside the home PLMN country. The OutgoingBarring tag is set to "3".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OutgoingBarring>3</OutgoingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar all incoming communications
Barring of all international communications, the IncomingBarring tag is set to "0".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<IncomingBarring>0</IncomingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar all incoming communications when roaming
Barring of all incoming communications roaming outside the home PLMN country. The IncomingBarring tag is set to "0".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<IncomingBarring>1</IncomingBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar Outgoing Premium-Rate Communication
The premium-rate barring options can be described as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
PremiumRateCommunicationsInformation |
Bar all outgoing communications where "premium-rate" for "information" is indicated. |
PremiumRateCommunicationsEntertainment |
Bar all outgoing communications where "premium-rate" for "entertainment" is indicated. |
PremiumRateCallsInformationWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry |
The same as 'PremiumRateCommunicationsInformation' but only for communications that are roaming outside of the Home PLMN Country. |
PremiumRateCallsEntertainmentWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry |
The same as 'PremiumRateCommunicationsEntertainment' but only for communications that are roaming outside of the Home PLMN Country. |
Example XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OutgoingPremiumRateBarring>
<PremiumRateCommunicationsInformation>
true
</PremiumRateCommunicationsInformation>
<PremiumRateCommunicationsEntertainment>
true
</PremiumRateCommunicationsEntertainment>
<PremiumRateCallsInformationWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry>
true
</PremiumRateCallsInformationWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry>
<PremiumRateCallsEntertainmentWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry>
true
</PremiumRateCallsEntertainmentWhenRoamingOutsideHplmnCountry>
</OutgoingPremiumRateBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Operator Specific Barring Rules
The Operator Specific Barring Types conditions specifies 4 types of user defined rules. The rules are stored in the VoLTE profiles and follow the same schema for Simservs RuleSet. The information on ODB data in the HSS just indicates which rule type should be evaluated.
The example below indicated that all 4 rules should be evaluated.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<OperatorSpecificBarring>
<Type1>true</Type1>
<Type2>true</Type2>
<Type3>true</Type3>
<Type4>true</Type4>
</OperatorSpecificBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar Invocation of communication transfer
This condition prevents the Explicit Call Transfer feature MMTelECT from running. The conditions are:
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
SimpleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring |
Prevents user-invoked call transfers from happening. Has three options:
|
InvocationOfChargeableCommunicationTransferBarring |
Prevents user-invoked call transfers when both calls are charged to the served user. Not Supported |
MultipleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring |
Prevents a user-invoked call transfer when there is an existing transferred call for the served user. |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<SimpleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring>
0
</SimpleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring>
<InvocationOfChargeableCommunicationTransferBarring>
true
</InvocationOfChargeableCommunicationTransferBarring>
<MultipleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring>
true
</MultipleInvocationOfCommunicationTransferBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar Management of Supplementary Services
This condition is evaluated during provisioning time when the subscriber tries to change its own supplementary services configuration via XCAP Interface. If the condition is set to true the XCAP servers will deny any change to subscriber change attempt.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<BarringOfSupplementaryServicesManagement>
true
</BarringOfSupplementaryServicesManagement>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Bar Registration of Diverted To Address
This condition is evaluated during provisioning time when the subscriber tries to change the target to address of the supplementary services via XCAP Interface. Currently the diverted to address is present at the Communication Diversion (CDIV) settings. It is the <target> sub-element of the <forward-to> element in a CDIV rule’s actions.
The bar condition can have the following values:
-
0 Barring of Registration of any communication diverted-to address
-
currently supported
-
-
1 Barring of Registration of any international communication diverted-to address
-
not supported yet
-
-
2 Barring of Registration of any international communication diverted-to address EXHPLMNC
-
not supported yet
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>IMS-ODB-Information</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<OdbForImsOrientedServices xmlns="odb.mmtel.sentinel.volte.opencloud.com">
<OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
<DivertedToAddressRegistrationBarring>
0
</DivertedToAddressRegistrationBarring>
</OdbForImsMultimediaTelephonyServices>
</OdbForImsOrientedServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Operator Specific Barring Types
The Operator Specific Barring Types are 4 operator defined rules that are stored in the AS. The ODB data indicates which of them should be evaluated and, like all others ODB conditions, they take precedence over MMTelICB and MMTelOCB .
What is Operator Specific Barring?
The 3GPP specifications TS 24.315 defines:
The Operator specific barring definition for type 1, type 2, type 3, and type 4 is locally configured in the AS providing the ODB service. For operator specific barring the criteria that can be used by the operator to define conditions that are used to determine whether the category applies may be based on any signalling information from the incoming request. Examples of such criteria are: 1) destination type e.g. international numbers or specific numbers; 2) media used in the communication, e.g. audio, video, or text. |
The scope definition of what kind of conditions can be present in those rules is not specified. The OpenCloud implementation of those rules follows the simservs RuleSet definition (TS 29.364 ) for MMTelICB Supported Barring Rule Conditions and MMTelOCB Supported barring rule conditions. This way the operator can define the same MMTel barring conditions supported by the MMTelOCB and MMTelICB features.
ODB-Specific Conditions
There are conditions that are unique to ODB. These are:
Incoming Communications
To make a rule match on any communications that are 'incoming', add the <incoming /> element to its set of conditions.
Example:
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-alice-incoming">
<cp:conditions>
<incoming />
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
Outgoing Communications
To make a rule match on any communications that are 'outgoing', add the <outgoing /> element to its set of conditions.
Example:
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-alice-outgoing">
<cp:conditions>
<outgoing />
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
How to provision the Operator Specific Barring rules
The operator can include the rules in the profile MMTelOdbOperatorSpecificTypesConfigProfileTable.
Attribute Name |
Type |
Default Value |
Description |
Type1 |
String |
null |
The ruleset to be evaluated when the ODB data OperatorSpecificBarring.Type1 is |
Type2 |
String |
null |
The ruleset to be evaluated when the ODB data OperatorSpecificBarring.Type2 is |
Type3 |
String |
null |
The ruleset to be evaluated when the ODB data OperatorSpecificBarring.Type3 is |
Type4 |
String |
null |
The ruleset to be evaluated when the ODB data OperatorSpecificBarring.Type4 is |
Examples
The sections below show XML data stored in the VoLTE profile MMTelOdbOperatorSpecificTypesConfigProfileTable. The values can be applied for type 1 to type 4. The fact that the <incoming\> and <outgoing\> are not present, means that those rules will be applied to both directions.
barr video
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no_video">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
barr identity
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-alice">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<one id="sip:alice@example.com"/>
</cp:identity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
barr specific domain for a 1 month period
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="barr-domain">
<cp:conditions>
<cp:identity>
<many domain="example.com"></many>
</cp:identity>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>2016-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>2016-01-31T23:59:59</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
Diameter MMTel Information
This feature records charging information about MMTel supplementary services invoked on a call.
The feature name is DiameterMMTelInfo, as it is based on 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 (vcb0).
Feature cheat-sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session state inputs and outputs
Inputs
| Name | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
Enum |
Used to set the Subscriber-Role AVP. |
RanOip |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that OIP was used on the call. |
RanOir |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that OIR was used on the call. |
RanTip |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that TIP was used on the call. |
RanTir |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that TIR was used on the call. |
RanIcb |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that ICB was used on the call. |
RanOcb |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that OCB was used on the call. |
RanCW |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that CW was used on the call. |
RanHOLD |
boolean |
If true, adds Supplementary-Service AVP indicating that HOLD was used on the call. |
LastDiversionType |
Enum |
Used to populate the CDIV Supplementary-Service AVP. |
DiversionCounter |
int |
Used to populate the CDIV Supplementary-Service AVP. |
Subscriber |
String |
Used to populate the Associated-Party-Address AVP in the CDIV Supplementary-Service AVP. |
Behaviour
The DiameterMMTelInfo feature populates the Diameter Ro MMTel-Information AVP with information about supplementary services used in the call. The feature stores an MMTel-Information AVP in session state, and updates it at various feature execution points when other supplementary services have run. The resulting MMTel-Information AVP is used by the VolteSipAvpCdr feature when writing a CDR. The MMTel-Information AVP is also sent in the final Credit-Control-Request to the OCS.
Flexible Alerting Features
Flexible Alerting Features
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
determines if and how the Flexible Alerting features will execute based on feature configuration and the HSS Subscriber Data. |
|
|
implements the Flexible Alerting service, by alerting the group members in parallel |
|
|
implements the Flexible Alerting service, by sequentially alerting the group members. |
MMTel Determine Flexible Alerting Mode
The MMTelDetermineFlexibleAlertingMode feature determines if and how the Flexible Alerting features will execute based on feature configuration and the HSS Subscriber Data. .
|
The Determine Flexible Alerting Mode feature runs before the Flexible Alerting features. It reads subscriber data and configuration profile tables to determine the flexible alerting mode and supplies this information to the MMTelParallelFA and MMTelSequentialFA features as a session state field. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating/Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
All |
Terminating |
Subscriber Check |
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-flexible-alerting module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-mmtel-flexible-alerting opencloud#mmtel-flexible-alerting#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode |
Group module for the Determine Flexible Alerting Mode feature. |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-profile |
The profile for this feature |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-library |
The common library for this module pack |
mmtel-parallel-fa |
The flexible alerting parallel feature. |
mmtel-sequential-fa |
The flexible alerting sequential feature. |
Network Operator Data
The data present in JSLEE profile table MMTelDetermineFAConfigProfileTable is used to configure the behaviour of the Flexible Alerting features: MMTelParallelFA and MMTelSequentialFA. This profile table is scoped by the sentinel key and the Pilot Number.
Here is an example of a profile entry:
'SomeOperatorName::::sip:callcentre@someoperator.com':
ModeIsParallel: true
ParallelMaxWaitTimeout: 5000
SequentialAnyResponseTimeout: 2000
SequentialFinalResponseTimeout: 5000
The default profile entry is not scoped by a Pilot Number:
'SomeOperatorName::::':
ModeIsParallel: true
ParallelMaxWaitTimeout: 5000
SequentialAnyResponseTimeout: 2000
SequentialFinalResponseTimeout: 5000
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ParallelMaxWaitTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelParallelFA waits for a final response before canceling the session for a pilot number. |
ModeIsParallel |
boolean |
Set the mode to parallel (true) or sequential (false). |
SequentialAnyResponseTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelSequentialFA waits for a any response from the INVITE before start alerting the next member. |
SequentialFinalResponseTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelSequentialFA waits for a final response from the INVITE before start alerting the next member. |
Session Input Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MMTelServiceData |
Complex |
Service data read from HSS |
Session Output Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
FlexibleAlertingMode |
Enum |
Determines whether the |
FlexibleAlertingGroupMode |
Enum |
Determines whether the |
Statistics
MMTelDetermineFAMode statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFAModeStarted |
each time the feature runs |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal error occurs while the feature is executing |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFAModeNoFA |
the feature fails to trigger Flexible Alerting under FA mode |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFANoProfile |
no valid profile is loaded for poilt subscriber |
MMTelDetermineFAModeFeatureFAValidPilotNumber |
subscriber data equals the requestUri header. |
Behaviour
When the feature starts, it tries to load the configuration profile for the pilot number present in the flexible alerting subscriber data. The table MMTelDetermineFAConfigProfileTable is expected to contain a profile with name scoped by the sentinel selection key and the Pilot Number, i.e, SomeOperatorName::::sip:callcentre@someoperator.com.
If there is no profile for the pilot number the feature try to get the configuration from the default profile: SomeOperatorName::::.
When there is no suitable profile the FlexibleAlertingMode is set to NONE and the FlexibleAlertingGroupMode is set to GROUP_NONE. It means that the neither MMTelParallelFA nor MMTelSequentialFA will run.
When there is a suitable profile, the feature checks if the flexible-alerting is active by checking the authorized field in the flexible-alerting Subscriber Data. If the service is not active, i.e authorized="false", neither MMTelParallelFA nor MMTelSequentialFA will run. The HSS schema for flexible alerting defines two sets of services that can contain the key authorized: operator-flexible-alerting and operator-flexible-alerting-group. The feature checks both to define if the service is authorized. The table below shows the logic:
operator-flexible-alerting authorized |
operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized |
service status |
true |
true |
active |
true |
null |
active |
null |
true |
active |
false |
any |
inactive |
any |
false |
inactive |
null |
null |
inactive |
When flexible alerting is active, the group type in the Subscriber Data (single-user or multiple-users) is written into the Session State variable FlexibleAlertingGroupMode. The FlexibleAlertingMode Session State field is set according to the value in the configuration profile (ModeIsParallel attribute).
Subscriber data examples
MULTIPLE_USERS
HSS Subscriber Data
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices
xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:friends@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>multiple-users</group-type>
<membership>permanent</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:charlie@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:daisy@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Profile configuration
ModeIsParallel: true ParallelMaxWaitTimeout: 20000 SequentialAnyResponseTimeout: 2000 SequentialFinalResponseTimeout: 5000
In the example above, the group sip:friends@home1.opencloud.co.nz has three active members. The FlexibleAlertingGroupMode is set to MULTIPLE_USERS , the FlexibleAlertingMode is set to PARALLEL, and the timeout is set to 20 seconds.
SINGLE_USER
HSS Subscriber Data
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices
xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>single-user</group-type>
<membership>permanent</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bob-mobile@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bob-desk@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Profile configuration
ModeIsParallel: false ParallelMaxWaitTimeout: 5000 SequentialAnyResponseTimeout: 2000 SequentialFinalResponseTimeout: 5000
In the example above, the group sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz has three active members. The FlexibleAlertingGroupMode is set to SINGLE_USER, the FlexibleAlertingMode is set to SEQUENTIAL and the timeout is for receiving any response from a member is set to 2 seconds and the timeout for receiving a final response from a member is 5 seconds.
MMTelParallelFA
The MMTelParallelFA feature implements the Flexible Alerting service, by alerting the group members in parallel
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
Sip_Access_Subscriber_Check, Sip_Access_Party_Request, Sip_Access_Party_Response, Sip_Access_Service_Timer, SipMidSession_Party_Request, Sip_Mid_Session_Party_Response, SipLegEnd |
Yes |
Yes |
Statefull |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-flexible-alerting module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-mmtel-flexible-alerting opencloud#mmtel-flexible-alerting#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode |
Group module for the Determine Flexible Alerting Mode feature. |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-profile |
The profile for this feature |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-library |
The common library for this module pack |
mmtel-parallel-fa |
The the flexible alerting parallel feature. |
mmtel-sequential-fa |
The the flexible alerting sequential feature. |
Statistics
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ProcessingRequest |
processing a request message. |
ProcessingResponse |
processing a response from the downstream forked legs. |
InviteRequestReceived |
the original INVITE is received. |
CancelRequestReceived |
a CANCEL message is received. |
ProvisionalResponseReceived |
a 1xx message is received. |
SuccessResponseReceived |
a 200 (OK) message is received. |
BusyErrorResponseReceived |
a 486 (Busy Here) message is received. |
NonBusyErrorResponseReceived |
a 4xx message is received that is not a 486 (Busy Here). |
GroupMemberAlerted |
an INVITE request is sent to a group member. |
LegReleased |
a dialog leg is released. |
UpstreamForkCreated |
the feature creates a new leg towards the calling party. It happens on the provisional responses. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
the feature is triggered on a response message. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
the feature is triggered on a request message. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
the feature is triggered on a timmer. |
TimeoutTimerCancelled |
the feature cancel the timer. |
TimeoutTimerSet |
the feature sets the timer. The timer is set before the INVITE is sent to the first group member. |
ExitedEarlyNoMembersToAlert |
there is just one member in the group and it is the pilot number. |
Received480 |
receives a 480 (Temporarily Unavailable) response from a member |
Received486 |
receives a 486 (Busy Here) response from a member |
Received408 |
receives a 408 (Timeout) response from a member |
Received404 |
receives a 404 (Not found) response from a member |
ReceivedSuccess |
receives a 200 (OK) response from a member |
RespondedUpstreamWith480 |
the feature sends a 480 (Temporarily Unavailable) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith486 |
the feature sends a 486 (Busy Here) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith408 |
the feature sends a 408 (Timeout) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith404 |
the feature sends a 404 (Not found) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWithSuccess |
the feature sends a 200 (OK) to the calling party. |
Interaction with other MMTel Services
CDIV Unconditional
If CDIV Unconditional is active for the Pilot Identity, CDIV Unconditional procedures will be applied and no FA group member will be alerted.
CDIV Busy
If CDIV Busy is active for the Pilot Identity, CDIV Busy procedures will be applied if the pilot number is considered busy. The definition of Busy for the pilot number depends on the group type: single-user or multiple-users. For single-user, when one member is busy the pilot number is busy, while for multiple-uses all group members have to be busy for the pilot number to be considered busy.
CDIV No Reply and CDIV Not Reachable
If the FA Pilot Number is considered in a state of No Reply or Not Reachable then the CDIV procedures for those MMTel services will be applied.
CDIV Not Logged-in
If the FA Pilot Identity has CDIV Not Registered active, the procedures for CDIV Not Registered will be applied.
MMTelOIP
OIP applied to any FA group member when OIP is active for the FA Pilot Identity.
MMTelTIP
If the FA Pilot Identity did not apply TIR, the termination identification is the FA Pilot Identity.
MMTelTIR
If the FA Pilot Identity has TIR activated, the termination identification is not presented.
MMTelICB
If the FA Pilot Identity has ICB activated, the procedures for ICB will be applied.
MMTelOCB
If any FA group member has OCB activated, the procedures for OCB will be applied for that member.
Network Operator Data
The data present in JSLEE profile table MMTelDetermineFAConfigProfileTable is used to configure the behaviour of the Parallel Flexible Alerting feature.
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ParallelMaxWaitTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelParallelFA feature waits before canceling the session for a pilot number. |
Session Input Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MMTelFAServiceData |
Complex |
Service data read from the HSS |
FlexibleAlertingGroupMode |
Enum |
Determines whether single user or multi-user Flexible Alerting is used. |
Session Output Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SuppressCdiv |
Boolean |
Indicates whether response should be ignored by the MMTel CDIV feature. |
ParallelFATimerID |
int |
Indicates the MMTelParallelFA timer identification. |
Behaviour
The MMTelParallelFA implements the Flexible Alerting in parallel. It reads the MMTelFAServiceData session variable for the group information and issues INVITE requests towards all members in parallel using SIP parallel forking.
The INVITE request URI will have two parameters added to it.
-
The first is the Cause Parameter with the value always set to
cause=302. -
The second is the MMTel Service Type Parameter with the value set to
mmtel-service-type=11for flexible alerting.
When a member answers the call with 200 (OK) the feature cancels all other sessions towards the other members and finishes the call setup procedures between the calling party and the member that answered.
It also controls the state of the FA Pilot Identity regarding busy, not reachable and no reply states. The determination of those states, depends on the members responses and on the FA group type: single-user or multiple-users. For further information regarding the state of a Pilot Identity see Flexible Alerting.
Parallel Flexible Alerting and MMTelCDIV interaction
The CDIV feature runs before the Flexible Alerting feature on INVITE path. This way, the CFNL and CFU conditions can be applied to the Pilot Number before alerting any FA-Group member.
On the Response path, the CDIV feature runs after the Flexible Alerting feature. CDIV applies the conditions CFB, CFNR, and CFNRc based on the final response that the MMTelParallelFA feature sends to the caller. To avoid the CDIV feature being triggered on any final FA-Group members response, the MMTelParallelFA feature suppresses the CDIV feature execution by setting the session state variable SuppressCdiv. MMTelParallelFA will allow the CDIV feature to execute only after the the state of the Pilot Number is defined by receiving all members final responses or by timing out.
CDIV and MMTelParallelFA are both triggered on each other timers. This guarantees that the MMTelParallelFA feature cancels the ongoing downstream dialogs and that the CDIV feature can execute the CFNR and CFNRc conditions properly.
When the CDIV timer fires first, the MMTelParallelFA feature cancels the downstream dialogs and sends a 408 (Timeout) response towards the caller party. When CDIV executes, it will identify the 408 response and do the proper re-targeting towards the diverted subscriber.
When the MMTelParallelFA timer fires first, the MMTelParallelFA feature stops the CDIV timer and cancels the downstream dialogs and sends a 408 (Timeout) response towards the caller party. When CDIV executes, it identifies the trigger is the MMTelParallelFA timer, identifies the 408 response and do the proper re-targeting towards the diverted subscriber.
In the case when no timer has been fired, CDIV feature uses the sip response sent from the MMTelParallelFA feature to evaluate and execute the proper MMTelCDIV conditions.
HSS Subscriber Data Examples
single user group type
In the first example the Subscriber Data configures a flexible alerting group with type single-user. The group has three active members and the flexible alerting service is authorized or active.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>single-user</group-type>
<membership>permanent</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bobmobile@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bobdesk@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
multiple-users group type
The following example shows a group of multiple-users type with four members. The flexible alerting service is authorized or active.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:office@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>multiple-users</group-type>
<membership>demand</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:desk1@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk2@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk3@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk4@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
MMTelSequentialFA
The MMTelSequentialFA feature implements the Flexible Alerting service, by sequentially alerting the group members.
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
Sip_Access_Subscriber_Check, Sip_Access_Party_Request, Sip_Access_Party_Response, Sip_Access_Service_Timer, SipMidSession_Party_Request, Sip_Mid_Session_Party_Response, SipLegEnd |
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
The source code for this feature is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-flexible-alerting module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-mmtel-flexible-alerting opencloud#mmtel-flexible-alerting#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode |
Group module for the Determine Flexible Alerting Mode feature. |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-profile |
The profile for this feature |
mmtel-determine-flexible-alerting-mode-library |
The common library for this module pack |
mmtel-parallel-fa |
The flexible alerting parallel feature. |
mmtel-sequential-fa |
The flexible alerting sequential feature. |
Statistics
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ProcessingRequest |
processing a request message. |
ProcessingResponse |
processing a response from a downstream forked leg. |
InviteRequestReceived |
the original invite is received. |
CancelRequestReceived |
a CANCEL message is received. |
ProvisionalResponseReceived |
a 1xx message is received. |
SuccessResponseReceived |
a 200 (OK) message is received. |
GroupMemberAlerted |
an INVITE message was sent to a group member. |
GroupMemberAddedToQueue |
a group member was queued for alerting. |
MemberLegReleased |
a dialog leg is released. |
RespondedUpstreamManually |
the feature created an upstream response. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
the feature is triggered on a response message. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
the feature is triggered on a request message. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
the feature is triggered on a timer event. |
TriggeredOnLegEndEvent |
the feature is triggered on a SIP leg end event. |
AnyResponseTimerSet |
the feature set a timer to wait for a response on a downstream leg. |
FinalResponseTimerSet |
the feature set a timer to wait for a final response on a downstream leg. |
AnyResponseTimerCancelled |
the timer waiting for a response on a downstream leg was cancelled. |
FinalResponseTimerCancelled |
the timer waiting for a final response on a downstream leg was cancelled. |
TimerFired |
the feature handled a timer event. |
ExitedEarlyNoMembersToAlert |
there is just one member in the group and it is the pilot number. |
Interaction with other MMTel Services
CDIV Unconditional
If CDIV Unconditional is active for the Pilot Identity, CDIV Unconditional procedures will be applied and no group member will be alerted.
CDIV Busy
If CDIV Busy is active for the Pilot Identity, CDIV Busy procedures will be applied if the pilot number is considered busy. The definition of Busy for the pilot number depends on the group type: single-user or multiple-users. For single-user, when one member is busy the pilot number is busy, while for multiple-uses all group members have to be busy for the pilot number to be considered busy.
CDIV No Reply and CDIV Not Reachable
If the FA Pilot Number is considered in a state of No Reply or Not Reachable then the CDIV procedures for those MMTel services will be applied.
CDIV Not Logged-in
If the FA Pilot Identity has CDIV Not Registered active, the procedures for CDIV Not Registered will be applied.
MMTelOIP
OIP applied to any FA group member when OIP is active for the FA Pilot Identity.
MMTelTIP
If the FA Pilot Identity did not apply TIR, the termination identification is the FA Pilot Identity.
MMTelTIR
If the FA Pilot Identity has TIR activated, the termination identification is not presented.
MMTelICB
If the FA Pilot Identity has ICB activated, the procedures for ICB will be applied.
MMTelOCB
If any FA group member has OCB activated, the procedures for OCB will be applied for that member.
Network Operator Data
The data present in the JSLEE profile table MMTelDetermineFAConfigProfileTable is used to configure the behaviour of the Sequential Flexible Alerting Feature.
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SequentialAnyResponseTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelSequentialFA feature waits for a response before cancelling the dialog with that group member. |
SequentialFinalResponseTimeout |
int |
Set the amount of time in milliseconds that the MMTelSequentialFA feature waits for a final response before cancelling the dialog with that group member. |
Session Input Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MMTelFAServiceData |
Complex |
Service data read from the HSS |
FlexibleAlertingGroupMode |
Enum |
Determines whether single user or multi-user Flexible Alerting is used. |
Session Output Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
SuppressCdiv |
Boolean |
Indicates whether response should be ignored by the MMTel CDIV feature. |
Behaviour
The MMTelSequentialFA implements Flexible Alerting sequentially. It reads the MMTelFAServiceData session variable to get the group information and will alert each active group member one at a time, using SIP sequential forking.
The INVITE request URI will have two parameters added to it.
-
The first is the Cause Parameter with the value always set to
cause=302. -
The second is the MMTel Service Type Parameter with the value set to
mmtel-service-type=11for flexible alerting.
If a member responds with a final response other than a 200 (OK) or a timer event occurs the feature will end the dialog for that member and alert the next member in the queue. When a member answers the call with a 200 (OK) the feature will finish the call setup procedure between the calling party and the member that answered.
The feature also controls the state of the FA Pilot Identity regarding the busy, not reachable and no reply states. The determination of those states depends on the responses of the members and the FA group type: single-user multiple-users. For further information regarding the state of a Pilot Identity see Flexible Alerting.
Sequential Flexible Alerting and MMTelCDIV interaction
The CDIV feature runs before the Flexible Alerting feature on INVITE path. This way, the CFNL and CFU conditions can be applied to the pilot number before alerting any group member.
On the Response path, the CDIV feature runs after the Flexible Alerting feature. CDIV applies the conditions CFB, CFNR, and CFNRc based on the final response that the MMTelSequentialFA feature sends to the caller. To avoid the CDIV feature being triggered on any final response from a group member, the MMTelSequentialFA feature suppresses the CDIV feature execution by setting the session state variable SuppressCdiv. MMTelSequentialFA will allow the CDIV feature to execute only after the state of the pilot number is defined by receiving all members final responses or by timing out.
HSS Subscriber Data Examples
single user group type
In the first example the Subscriber Data configures a flexible alerting group with type single-user. The group has three active members and the flexible alerting service is authorized or active.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>single-user</group-type>
<membership>permanent</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bobmobile@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:bobdesk@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
multiple-users group type
The following example shows a group of multiple-users type with four members. The flexible alerting service is authorized or active.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sh-Data>
<RepositoryData>
<ServiceIndication>MMTEL-Services</ServiceIndication>
<SequenceNumber>1</SequenceNumber>
<ServiceData>
<MMTelServices xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<complete-flexible-alerting>
<operator-flexible-alerting authorized="true"/>
<operator-flexible-alerting-group authorized="true">
<identity>sip:office@home1.opencloud.co.nz</identity>
<group-type>multiple-users</group-type>
<membership>demand</membership>
<members>
<member active="true">sip:desk1@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk2@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk3@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
<member active="true">sip:desk4@home1.opencloud.co.nz</member>
</members>
</operator-flexible-alerting-group>
</complete-flexible-alerting>
</MMTelServices>
</ServiceData>
</RepositoryData>
</Sh-Data>
Geo Local Normalization
The GeoLocalNormalization service adds the geo-local value to the Tel URI phone-context parameter for local numbers that should not be translated to international format.
The GeoLocalNormalization feature includes the geo-local value in case the served user is in roaming and request URI is not in international format or already contains the geo-local value. If geo-local value is added to the phone-context parameter the feature sets the session state GeoLocalNormalizationApplied to true. This value is used to suppress the SIP Normalization Feature, that is executed afterwards.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTEL |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Reads Session State |
SBB Feature |
Session input variables
The roaming indicator is set by the DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature.
Statistics
statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → GeoLocalNormalization
or with rhino-stats:
SLEE-Usage → [volte.sentinel.sip service name] → [volte.sentinel.sip SBB name] → .feature.GeoLocalNormalization
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
ContainsPhoneContext |
Incremented when the requestURI contains the phone-context |
ProcessingSipRequest |
Incremented when the incoming SIP request is an INVITE |
ProcessingSipURI |
Incremented when the requestURI is a SIP URI |
ProcessingTelURL |
Incremented when the requestURI is a TelURL |
Source
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-geo-local-normalization module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-geoloc-module opencloud#mmtel-geo-local-normalization#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new module, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new module.
Identity Presentation and Identity Restriction Features
Identity Presentation and Identity Restriction Features.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
implements the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) service |
|
|
implements the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) service |
|
|
implements the Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) service |
|
|
implements the Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) service |
MMTelOIP
The MMTelOIP feature implements the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) service .
What is OIP?
From 3GPP 24.607:
The Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) service provides the terminating user with the possibility of receiving identity information in order to identify the originating user. The OIP service provides the terminating user with the possibility of receiving trusted (i.e. network provided) identity information in order to identify the originating user. In addition to the trusted identity information, the identity information from the originating user can include identity information generated by the originating user and in general transparently transported by the network. In the particular case where the “no screening” special arrangement does not apply, the originating network shall verify the content of this user generated identity information. The terminating network cannot be responsible for the content of this user generated identity information. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
SipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-id-presentation-restriction module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-idpr-module opencloud#mmtel-id-presentation-restriction#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction-library |
Contains code shared by all ID presentation and restriction features. |
mmtel-oip-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-oip |
Contains the feature itself. |
Statistics
MMTelOIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → MMTelOIP
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded. |
ReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-standard ‘Privacy’ header is found in an incoming SIP message. |
FromHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘From’ header in an outgoing SIP request. |
ContactHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘Contact’ header in an outgoing SIP message. |
ReferredByHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘Referred-By’ header in an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedUserLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies user-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedHeaderLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies header-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedSessionLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies session-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedCustomHeaderAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds and evaluates custom header privacy rules for a message. |
OverrideCategoryTriggered |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature disregards requested privacy settings on an incoming SIP message (due to the subscriber having override category status). |
CriticalPrivacyCannotBeFulfilled |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature refuses an incoming request due to a |
Network Operator Data
This data is stored in a JSLEE Configuration Profile table called MMTelOIPConfigProfileTable. The operator data is scoped according to a Sentinel selection key. In the profile table, there is one profile for each network operator.
| Attribute Name | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Enum ( |
DO_NOT_ANONYMIZE |
When set to |
|
PrivacyHeaderRemovalPolicy |
Enum ( |
USE_3GPP |
This value is deprecated and no longer used by the feature. |
Override |
Enum ( |
OVERRIDE_NOT_ACTIVE |
This value is deprecated and has been replaced by subscriber level data, see MMTelOIPServiceData. |
boolean |
false |
Flag to allow History-Info header deletion. |
Additionally, the feature reads a second profile table that contains custom rules for removing additional headers under specified circumstances. See Custom Header Privacy Rules below.
Session input variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RanOip |
boolean |
Signals to other features that OIP ran on this session. |
Behaviour
If operator data is not present, the OIP feature:
-
Increments an error statistic.
-
Logs a message at the
Finelevel. -
Informs the Sentinel core that the feature is not configured appropriately (
Invalid Configuration). -
Exits.
Graceful handling of originating access
As OIP is a terminating feature. It will finish execution without modifying any state if it is invoked in an originating attempt.
OIP Override Category
The OIP override category overrides OIR’s requests for privacy, and provides as much identity information as is available to the terminating party.
It is extracted from the operator data in HSS or from HLR field ClipData.OverrideCategory field in ASN.1.
Critical Privacy Request
If the incoming request includes a Privacy header with the value critical, then the OIP feature will check to ensure that it can fulfill the privacy request. If another Privacy header value is present in the request that is not recognised by the OIP feature, it will assume that it can not fulfill the privacy request and refuse the incoming request with 500 Server Internal Error. If all of the Privacy header values are recognised by the feature, then the request will be handled as per normal behaviour.
Recognised privacy header values are: header, user, session, history, id, none, critical.
SIP Header Manipulation
The primary purpose of MMTelOIP is to remove and anonymize headers that the originating UE and the OIR service requested to be removed or anonymized.
MMTelOIP Active
SIP Header [1] |
Originating Subscriber’s Privacy Setting |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
User |
Header |
Session |
Id |
History |
None [2] |
|
Outgoing Requests to the Terminating Subscriber |
||||||
Call-Info |
Removed |
|||||
Contact |
Anonymized |
|||||
From |
Anonymized |
|||||
History-Info [3] |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
|||
In-Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Organization |
Removed |
|||||
Privacy |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Subject |
Removed |
|||||
User-Agent |
Removed |
|||||
Outgoing Responses to the Terminating Subscriber |
||||||
Call-Info |
Removed |
|||||
History-Info [3] |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
|||
Organization |
Removed |
|||||
Privacy |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Preserved |
Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Server |
Removed |
|||||
Warning |
Anonymized |
|||||
MMTelOIP Not Active
SIP Header [1] |
Originating Subscriber’s Privacy Setting |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
User |
Header |
Session |
Id |
History |
None [2] |
|
Outgoing Requests to the Terminating Subscriber |
||||||
Call-Info |
Removed |
|||||
Contact |
Anonymized |
|||||
From |
Anonymized |
Anonymized if the Network Operator Setting AnonymizeFromPolicy is set to |
||||
History-Info [3] |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
|||
In-Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Organization |
Removed |
|||||
Privacy |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Subject |
Removed |
|||||
User-Agent |
Removed |
|||||
Outgoing Responses to the Terminating Subscriber |
||||||
Call-Info |
Removed |
|||||
History-Info [3] |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
|||
Organization |
Removed |
|||||
Privacy |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Removed |
Reply-To |
Removed |
|||||
Server |
Removed |
|||||
Warning |
Anonymized |
|||||
Custom Header Privacy Rules
The MMTelOIP feature has support for configuring custom rules that instruct the feature to remove additional headers depending on the message type and the value of the Privacy header. These rules are defined in a profile table called MMTelCustomHeaderPrivacyRules. Alternatively, the rules can be controlled per network operator by prefixing the network operator name followed by an underscore to the profile table name (e.g. Metaswitch_MMTelCustomHeaderPrivacyRules). Each profile in the profile table represents a single rule for the feature to evaluate. The profile name is cosmetic, it can be any string. The profiles have the following fields:
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
HeaderName |
String |
The name of the header that should be removed when this rule is applied to a message. |
ApplicableMessageTypeAsString |
Enumeration |
One of three values based on what type of message this rule should be applied to. Value must be one of: |
ApplicablePrivacyHeaderValues |
String Array |
A list of |
| |
HeaderName matching is case-insensitive. Wildcards are not supported. |
Black Listed SIP Headers
The following SIP headers can not be removed by MMTelOIP custom header privacy rules:
-
From
-
Call-ID
-
Contact
-
Content-Length
-
CSeq
-
Max-Forwards
-
Record-Route
-
Request-URI
-
Route
-
To
-
Via
Rule Evaluation
Whenever the feature is processing a message, it will look for this profile table and check if there are any rules defined. If it finds rules, it will iterate through them and evaluate each one to determine if it should be applied to the message. For each rule, the evaluation process is as follows:
1. Check the Message Type
The ApplicableMessageType field indicates what type of SIP message the rule should be applied to: REQUEST indicates the rule should be applied to SIP requests. RESPONSE indicates the rule should be applied to SIP responses. BOTH indicates the rule should be applied to all SIP messages.
2. Check the Privacy Header
The feature will look at the value(s) of the Privacy header on the message and compare them to the ApplicablePrivacyHeaderValues for the rule. If any one value of the Privacy header matches any one value in the ApplicablePrivacyHeaderValues field, the rule applies.
3. Apply Rule
If the previous two checks both indicate the rule should be applied, the feature will strip all headers from the message that match the HeaderName field of the rule.
MMTelOIR
The MMTelOIR feature implements the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) service .
What is OIR?
From 3GPP 24.607:
The Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) service enables the originating user to prevent presentation of its identity information to the terminating user. When the OIR service is applicable and activated, the originating network provides the destination network with the indication that the originating user’s identity information is not allowed to be presented to the terminating user. In this case, no originating user’s identity information shall be included in the requests sent to the terminating user. The presentation restriction function shall not influence the forwarding of the originating user’s identity information within the network as part of the supplementary service procedures. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Originating |
SipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
Yes |
Yes |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-id-presentation-restriction module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-idpr-module opencloud#mmtel-id-presentation-restriction#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction-library |
Contains code shared by all ID presentation and restriction features. |
mmtel-oir-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-oir |
Contains the feature itself. |
Network operator data
OIR Network Operator Data is present in a JSLEE configuration profile table named MMTelOIRConfigProfileTable. The operator data is scoped according to a Sentinel selection key. There is one profile in the profile table for each network operator.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OIRMode (deprecated, present in
|
An enum with two values: Fully qualified type name is |
|
OIRPresentationRestrictionType |
An enum with two values: Fully qualified type name is |
Use of Use of |
OIRUserPolicy |
An enum with three values: Fully qualified type name is |
Session input variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Stored from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RanOir |
boolean |
Signals to other features that OIR ran on this session. |
Statistics
MMTelOIR statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Increments when… |
|---|---|
MMTelOIRFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelOIRFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelOIRFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelOIRFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelOIRFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelOIRFeatureMisconfigured |
a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded |
MMTelOIRFeatureReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
a non-standard |
MMTelOIRFeatureFromHeaderAnonymized |
the feature anonymizes the |
MMTelOIRFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
Behaviour
If operator data is not present, the OIR feature:
-
Increments an error statistic.
-
Logs a message at the
Finelevel. -
Informs the Sentinel core that the feature is not configured appropriately (
Invalid Configuration). -
Exits.
If MMTelOIRServiceData.Active is false, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
The rest of the behaviour section assumes that MMTelOIRServiceData.Active is true.
Temporary mode vs permanent mode
OIR behaves in temporary mode if the network configuration for MMTelOIRServiceData.Mode is set to TEMPORARY
It behaves in permanent mode if the network configuration for MMTelOIRServiceData.Mode is set to PERMANENT.
The UE signals its request for privacy through use of the Privacy header.
Adjustments to identity headers in temporary mode
When in temporary mode, the OIR feature will apply header manipulation related to privacy, based on:
-
whether or not the UE’s request has any
Privacyheader at all, -
whether or not the
Privacyheader indicates that privacy should be enabled or disabled (for this dialog), and -
the value of
MMTelOIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType.
| UE request | Value of MMTelOIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType | Privacy based header manipulation occurs |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
Yes |
|
|
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
No |
|
UE asks for privacy — |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
Yes |
|
No |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
No |
|
|
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
No |
|
UE asks for privacy — |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
Yes |
Adjustments to identity headers in permanent mode
When in permanent mode, the OIR feature will apply header manipulation related to privacy regardless of whether or not the UE’s request indicated that privacy is requested. Whether or not anything is modified is based on the value of the MMTelOIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType session state variable. The value of PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED means that the OIR feature will not modify header manipulation related to privacy.
| UE request indicates privacy shall apply | Value of MMTelOIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType | Privacy-based header manipulation occurs |
|---|---|---|
|
N/A (the UE is ignored) |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
Yes |
|
N/A (the UE is ignored) |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
No |
Headers read and modified in SIP INVITE
Information about headers that are modified under different conditions are documented on the following links:
A few of the options are in the table below. For more refer to the links above.
| MMTelOIRServiceData.Mode (operator data) | MMTelOIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType (subscriber) | OIRPresentationRestrictionType (network data) | OIRUserPolicy (network data) | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
NONE |
|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
ANONYMIZE_FROM |
|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
ADD_USER_PRIVACY |
|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
NONE |
|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
ANONYMIZE_FROM |
|
|
TEMPORARY |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
ONLY_IDENTITY |
ADD_USER_PRIVACY |
MMTel OIR Header Manipulation
OIRMode=TEMPORARY
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED
In this mode the network default is to not restrict the originating user identity. If the originating user wishes to override the "no restriction" default the UE of the originating user will add Privacy header set to the value "id", "header" or "user".
If the OIRDefaultBehaviourType is set to PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED and the request received contains Privacy header with value set to "id" or "header" (user is temporarily requesting privacy) the AS of originating user shall either (as a matter of operator policy):
-
Add Privacy value set to "user", or
-
change the From header value to remove the originating user identity.
In the example below, AS change the From header to anonymous values while preserving the privacy header value:
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>;tag=171828
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
30: Privacy: id
...1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=637364
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
31: Privacy: id
...OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED - OIRUserPolicy=NONE
No action is required at AS of originating user. Unrestricted privacy level is overridden by UE setting the Privacy header value to an appropriate value (other than none).
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED - OIRUserPolicy=ANONYMIZE_FROM
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
Privacy header value contains id or header or both values |
1. Set URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid 2. Set display name of the From header to "Anonymous" |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED - OIRUserPolicy=ADD_USER_PRIVACY
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
No action |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value set to header |
Unless already included add value user |
Privacy header value set to id |
Unless already included add value user |
Privacy header value set to id and header |
Unless already included add value user |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED
In this mode the network default is to restrict the originating user identity. The default is overridden by UE inserting Privacy header set to value "none" in a received request.
If request contains no Privacy header or the Privacy header is not set to the value of "none" then the AS of originating user shall insert Privacy header with value to "id" or "header" according to the Restriction Privacy Attribute.
In the example below the privacy option id is added (asserted identity restriction option):
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>;tag=171828
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
30: Privacy: user
...In the below example, the UE sets the privacy value of "none" in the received request indicates user’s preference to override the PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED default. In this case, headers P-Asserted-Identity and Privacy with value set to "none" will be forwarded by AS unchanged.
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>;tag=171828
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
30: Privacy: none
...OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=NONE
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Add Privacy header set to value id |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include id |
Add value id |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=ANONYMISE_FROM
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
1. Add Privacy header set to value id 2. Set URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid 3. Set display name of the From header to "Anonymous" |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include id |
1. Add value id 2. Set URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid 3. Set display name of the From header to "Anonymous" |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=ADD_USER_PRIVACY
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Add Privacy header set to value id and user |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include id |
1. Add value id 2. Add value user unless already included |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=NONE
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Add Privacy header set to value header |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include header |
Add value header |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=ANONYMIZE_FROM
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
1. Add Privacy header set to value header 2. Set URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid 3. Set display name of the From header to "Anonymous" |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include header |
1. Add value header 2. Set URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid 3. Set display name of the From header to "Anonymous" |
OIRMode=TEMPORARY - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=ADD_USER_PRIVACY
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Add Privacy header set to value header and user |
Privacy header value set to none |
No Action |
Privacy header value doesn’t include header |
1. Add value header 2. Add value user unless already included |
OIRMode=PERMANENT
In a simple scenario, the AS of the originating user must inspect the identity of the originating caller.
-
If Privacy header is not present AS must insert Privacy header set to header information
-
If Privacy header is present and does not include values "id" or "header" corresponding to subscription restriction option AS must insert the appropriate value.
-
If Privacy header is present and includes value "none" this value must be removed
The Privacy value of "id" is selected when "restrict asserted identity" restriction option is subscribed to. The Privacy value of "header" is selected when "restrict all private header information" restriction option is subscribed to.
Additionally, as an operator option From header can be anonymized or Privacy header value "user" added. The latter shall mandate AS of terminating user to anonymize all user configurable headers before forwarding the request to terminating P-CSCF. In case of internetworking, IBCF will be responsible for stripping identity headers and anonymizing other headers before forwarding the request into untrusted network.
Where From header is required to be anonymized the URI value shall be set to the value "sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid".
Typically, the originating UE would already have the Privacy header value set correctly, however, since UE is considered to be untrusted entity AS must apply these procedures.
Example of Privacy header received from S-CSCF without privacy being requested by UE:
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>;tag=171828
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
30: Privacy: none
...AS adjusts the value of Privacy header by removing "none" and adding "id" (restrict asserted identity option):
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>;tag=637364
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
31: Privacy: id
...Example of anonymization of the From header in the outgoing INVITE (operator option):
1: INVITE sip:userB_public1@home1.net;gr=2ad8950e-48a5-4a74-8d99-ad76cc7fc74c SIP/2.0
...
10: From: <sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=637364
18: Contact: <sip:userA_public1@home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:388s9-48js9-37749-3774-usuw8u38;comp=sigcomp>;+g.3gpp.icsi - ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel"
30: P-Asserted-Identity: "John Doe" <sip:userA_public1@home1.net>
31: Privacy: id
...OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=NONE
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Insert header "Privacy: id" |
Privacy header value set to none |
Replace value none with id |
Privacy header exists but doesn’t include value id |
Add value id |
OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=ANONYMIZE_FROM
-
Replace URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid
-
Set the From header display name to "Anonymous"
OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ONLY_IDENTITY - OIRUserPolicy=ADD_USER_PRIVACY
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Insert header "Privacy: id;user" |
Privacy header value set to none |
Replace value none with id;user |
Privacy header exists but doesn’t include value id or user |
Add value id or user to make sure both are included |
OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=NONE
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Insert header "Privacy: header" |
Privacy header value set to none |
Replace value none with header |
Privacy header exists but doesn’t include value header |
Add value header |
OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=ANONYMIZE_FROM
-
Replace URI of the From header to sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid
-
Set the From header display name to "Anonymous"
OIRMode=PERMANENT - OIRDefaultBehaviourType=PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED - OIRPresentationRestrictionType=ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION - OIRUserPolicy=ADD_USER_PRIVACY
AS of originating user shall set/adjust value of the Privacy header in the request received depending on precondition.
| Precondition | Action of AS originating user |
|---|---|
No Privacy header |
Insert header "Privacy: header;user" |
Privacy header value set to none |
Replace value none with header;user |
Privacy header exists but doesn’t include value header or user |
Add value header or user to make sure both are included |
MMTelTIP
The MMTelTIP feature implements the Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) service .
What is TIP?
From 3GPP TS 24.608:
The Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) service provides the originating party with the possibility of receiving identity information in order to identify the terminating party. The network shall deliver the Terminating Identity to the originating party on communication acceptance regardless of the terminal capability to handle the information. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
MMTEL |
Originating |
SipAccess_SubscriberCheck, and SipAccess_PartyResponse |
No |
Yes |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-id-presentation-restriction module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-idpr-module opencloud#mmtel-id-presentation-restriction#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction-library |
Contains code shared by all ID presentation and restriction features. |
mmtel-tip-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-tip |
Contains the feature itself. |
Session input variables
TIP requires the following session state input variables:
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
|
APartyFromHeaderAnonymized |
boolean |
Used to determine whether the "from-change" tag needs to be removed from outgoing responses. |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RanTip |
boolean |
Signals to other features that TIP ran on this session. |
Statistics
MMTelTIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelTIPFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelTIPFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelTIPFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelTIPFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelTIPFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelTIPFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature processes a SIP response |
MMTelTIPFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature processes a SIP request |
MMTelTIPFeatureOverrideCategoryTriggered |
the feature disregards requested privacy settings on an incoming SIP message (due to the subscriber having override category status) |
MMTelTIPFeatureFromChangeTagRemoved |
the feature removes the |
MMTelTIPFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
Behaviour
TIP may modify the INVITE traversing through from A to B, and may modify responses from B to A.
Header manipulation behaviour
| SIP Operation | TIPActive | Originating User TIP Override Category | Action(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
N/A |
|
|
Yes |
N/A |
|
Response from B party |
Yes/No |
Yes |
|
Response from B party |
No |
No |
|
Response from B party |
Yes |
No |
|
MMTelTIR
The MMTelTIR feature implements the Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) service .
What is TIR?
From 3GPP TS 24.608:
The Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) is a service offered to the terminating party which enables the terminating party to prevent presentation of the terminating identity information to originating party. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
SipAccess_SubscriberPreCreditCheck |
Yes |
Yes, loaded from HSS |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-id-presentation-restriction module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-idpr-module opencloud#mmtel-id-presentation-restriction#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction-library |
Contains code shared by all ID presentation and restriction features. |
mmtel-tir-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-tir |
Contains the feature itself. |
Network operator data
TIR’s Network Operator Data is held in a JSLEE configuration profile table named MMTelTIRConfigProfileTable. This data is scoped by sentinel selection key — each network operator has one entry in the table.
Attribute Name |
Type |
TIRMode (deprecated, present in
|
An enum with values Fully qualified class name is |
Session input variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Loaded from the HSS in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or from HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RanTir |
boolean |
Signals to other features that TIR ran on this session. |
Statistics
MMTelTIR statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
Statistic |
Incremented when… |
MMTelTIRFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelTIRFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelTIRFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelTIRFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelTIRFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelTIRFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature processes a SIP response |
MMTelTIRFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature processes a SIP request |
MMTelTIRFeatureFromChangeTagRemoved |
the feature removes the |
MMTelTIRFeatureReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
a non-standard |
MMTelTIRFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
Behaviour
If operator data is not present, the TIR feature:
-
Increments an error statistic.
-
Logs a message at the
Finelevel. -
Informs the Sentinel core that the feature is not configured appropriately (
Invalid Configuration). -
Exits.
Header manipulation
| MMTelTIRServiceData.Mode (Operator data) |
SIP Operation | MMTelTIRServiceData.Active (Subscriber data) |
MMTelTIRServiceData.DefaultBehaviourType (Subscriber data) |
Action(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TEMPORARY |
|
No |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
See row for Temporary, Active, Presentation Not Restricted |
|
TEMPORARY |
B-Party Responses |
No |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
See row for Temporary, Active, Presentation Not Restricted |
|
TEMPORARY |
|
No |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
See row for Temporary, Active, Presentation Restricted |
|
TEMPORARY |
B-Party Responses |
No |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
See row for Temporary, Active, Presentation Restricted |
|
TEMPORARY |
|
Yes |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
Forward |
|
TEMPORARY |
|
Yes |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
Forward |
|
TEMPORARY |
B-Party Responses |
Yes |
PRESENTATION_NOT_RESTRICTED |
Forward Response to A party |
|
TEMPORARY |
B-Party Responses |
Yes |
PRESENTATION_RESTRICTED |
If a response does not contain a If the response contains a If the response contains a |
|
PERMANENT |
INVITE |
Yes |
Behave as though
|
If INVITE contains an option-tag |
|
PERMANENT |
B-Party Responses |
Yes |
Behave as though
|
If a response does not contain a If the response contains a If the response contains a |
MMTel Conference
This feature lets users create multi-party sessions between two or more parties .
Feature cheat-sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateful |
SBB with multiple FSMs encoded into session state |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-conferencing module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-conf-module opencloud#mmtel-conferencing#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-conferencing |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-conf-library |
Contains common code for the conference modules. |
mmtel-conf-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the conferencing configuration profile table. |
mmtel-conf-view-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the profile table used to track information about a conference. |
mmtel-conf-event-schema-library |
Generates java code for the the conference event XML schema. |
mmtel-conf-msml-schema-library-dialogic |
Generates java code for the MSML XML schema. Required for interaction with Dialogic MRF. |
mmtel-conf-msml-schema-library-radisys |
Generates java code for the MSML XML schema. Required for interaction with Radisys MRF. |
mmtel-conf-mapper-library-dialogic |
Mapper library that uses mmtel-conf-msml-schema-library-dialogic to create conference MSML. |
mmtel-conf-mapper-library-radisys |
Mapper library that uses mmtel-conf-msml-schema-library-radisys to create conference MSML. |
mmtel-conf |
Contains the feature itself. |
Subscriber data
Not applicable; the feature is generally available unless disabled at the network level.
Network data
Data is stored in the MMTelCONFConfigProfileTable profile
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
MRFURI |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for the MRF |
none |
|
ICSCFURI |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for the I-SCSCF |
none |
Mandatory when the |
ConfFactoryPSI |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for conferencing service PSI |
none |
|
ConfMaxParticipants |
Integer { |
Maximum number of participants; |
3 |
|
ConfCascadingEnabled |
Boolean |
Allow other conference participants to cascade conferencing |
true |
Reserved. Current implementation ignores it. Cascading is not explicitly disabled. |
ConferenceViewRemovalDelay |
Long |
Delay after conference ends before ConferenceView profiles are removed |
none |
Delay to allow all outstanding subscriptions to conference to end |
IsVideoConferenceAllowed |
Boolean |
Policy setting that allows a video conference to be created or not |
False |
|
IsMrfRoutableViaIMS |
Boolean |
Policy setting that specifies if calls to the MRF should be routed via IMS |
False |
If set to true, then the ICSCFURI has to be set |
AddOrigParameter |
Boolean |
Indicates whether or not to add the orig URI parameter to the Route header for initiating calls to participants |
True |
|
RootOnSelector |
Boolean |
Decides whether the 'root' element will be a child of the 'selector' element, otherwise will be a child of 'videolayout' |
False |
|
Bandwidth |
Integer |
Bandwidth value to be used as an attribute of the 'root' element if not specified in INVITE SDP |
128 |
Required for integration with Radisys MRF |
MinimumPictureInterval |
Integer |
Mpi value to be used as an attribute of the 'root' element if not specified in INVITE SDP |
16 |
Required for integration with Radisys MRF |
MaximumPictureSize |
String |
Bpp value to be used as an attribute of the 'root' element if not specified in INVITE SDP |
none |
Required for integration with Radisys MRF |
Framesize |
Integer |
Framesize value to be used as an attribute of the 'root' element if not specified in INVITE SDP |
396 |
Required for integration with Radisys MRF |
ProfileLevelId |
String |
ProfileLevelId value to be used as an attribute of the 'root' element if not specified in INVITE SDP |
00800a |
Required for integration with Radisys MRF |
Description
Feature name |
|
|---|---|
Applicable contexts |
SIP service |
Prerequisite features |
This feature allows a user to create a multi-party session between two or more parties. The feature is initially triggered when a subscriber (conference moderator) makes a call to the conferencing factory URI that points towards a media server (MRFC/MRFP). Subsequently, the conference moderator joins one or more participants into the conference by creating a call leg between the media server and every participant. For every participant added to the conference the feature instructs the media server to join (or mix) media of the new participant with the conference session media. The feature enables n-way voice communication between all conference participants by mixing media from each participant session.
Conference moderator is a special role that allows adding and removing participants to and from a conference. Charging is correlated to the moderator session. Accordingly, all participants' sessions are terminated when the moderator disconnects.
The feature feeds conference state data into the MMTel Conference Subscription, which renders the state of a conference to arbitrary endpoints subscribed to the conference event package.
Specification compliance
-
IR.92 v9.0, section 2.3.3, Ad-Hoc Multi Party Conference of IR.92 IMS Profile for Voice and SMS
-
IR.94 v10.0, section 2.3.3, Ad-Hoc Multi Party Conference of IR.94 IMS Profile for Conversational Video Service
-
3GPP 24.605 Conferencing using the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem. Release 12.
-
RFC4579 Session Initiation Protocol Call Control — Conferencing for User Agents
-
RFC4575 A Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Event Package for Conference State
-
RFC3891 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) “Replaces” Header
-
RFC3892 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Referred-By Mechanism
Conferencing between three participants
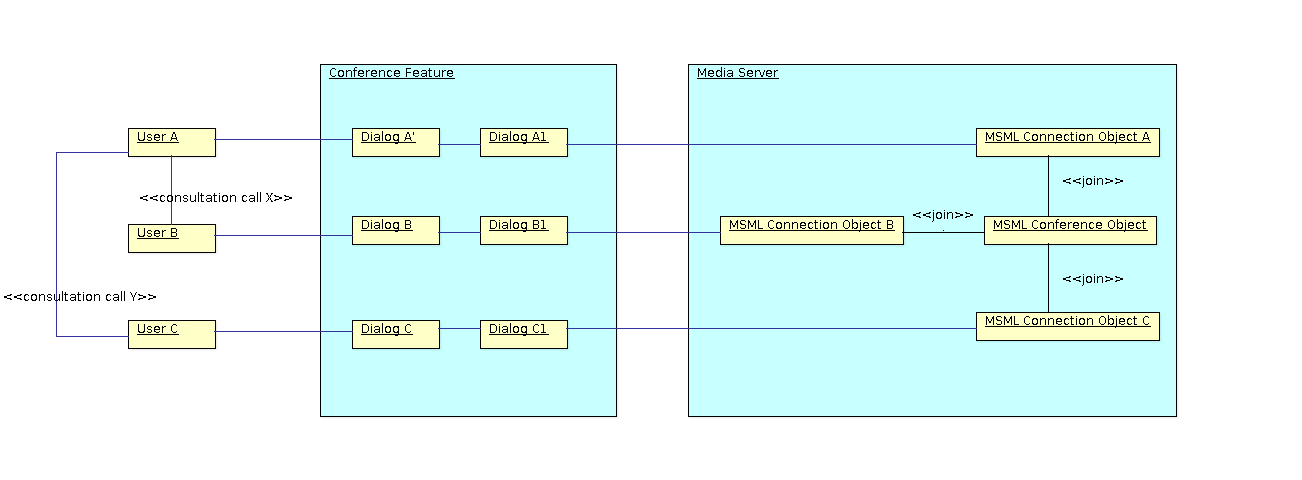
Conference setup begins when the conference moderator establishes a session with the media server using the conferencing feature. Although not strictly a precondition, the conference moderator would have established sessions with party B and C (dialogs x and y). These are established outside the scope of the conferencing feature. The moderator dials a destination that is translated into a conference factory URI by the feature, and routed to the media server.
Additionally, when the moderator sets up a connection to the media server, the feature allocates a conference focus URI. It is an opaque SIP URI that identifies the conference instance, and essentially the multi-party session. The conference focus URI is used as a SIP target by all participants including the moderator for all subsequent SIP messaging.
Having set up the initial connection, the conference moderator creates a conference object and begins adding participants to the conference. It is a multi-step process that involves setting up new sessions with the new participants and interaction with the media server, using the MSML protocol over SIP/INFO as the protocol transaction transport. See Interaction with Media Server for details.
Three-party conference setup overview
When the moderator establishes the session with the media server (control connection) the conferencing feature:
-
creates the MSML conferencing object and the first MSML connection for the moderator.
The moderator can then join a participant by creating a SIP REFER transaction on dialog A, where the REFER request has a Refer-to header with a URI header Replaces that references an existing call x between the moderator (user A) and prospective participant (user B).
The conferencing feature then:
-
acknowledges the
REFERrequest with a202response -
performs a charging authorization check
-
if charging authorization check is successful, creates and links two SIP sessions:
-
the conferencing server and the media server (dialog B1)
-
the new participant and the conferencing server (dialog B)
-
| |
After dialog B has been successfully created, the corresponding call x is terminated by the UA of the user B, as a part of processing of the INVITE request with the Replaces header copied from the corresponding REFER request. |
-
re-uses the MSML conferencing object, and joins the participant into the conference.
Once successful, the first two participants are joined into the conference. Adding subsequent participants is an identical process.
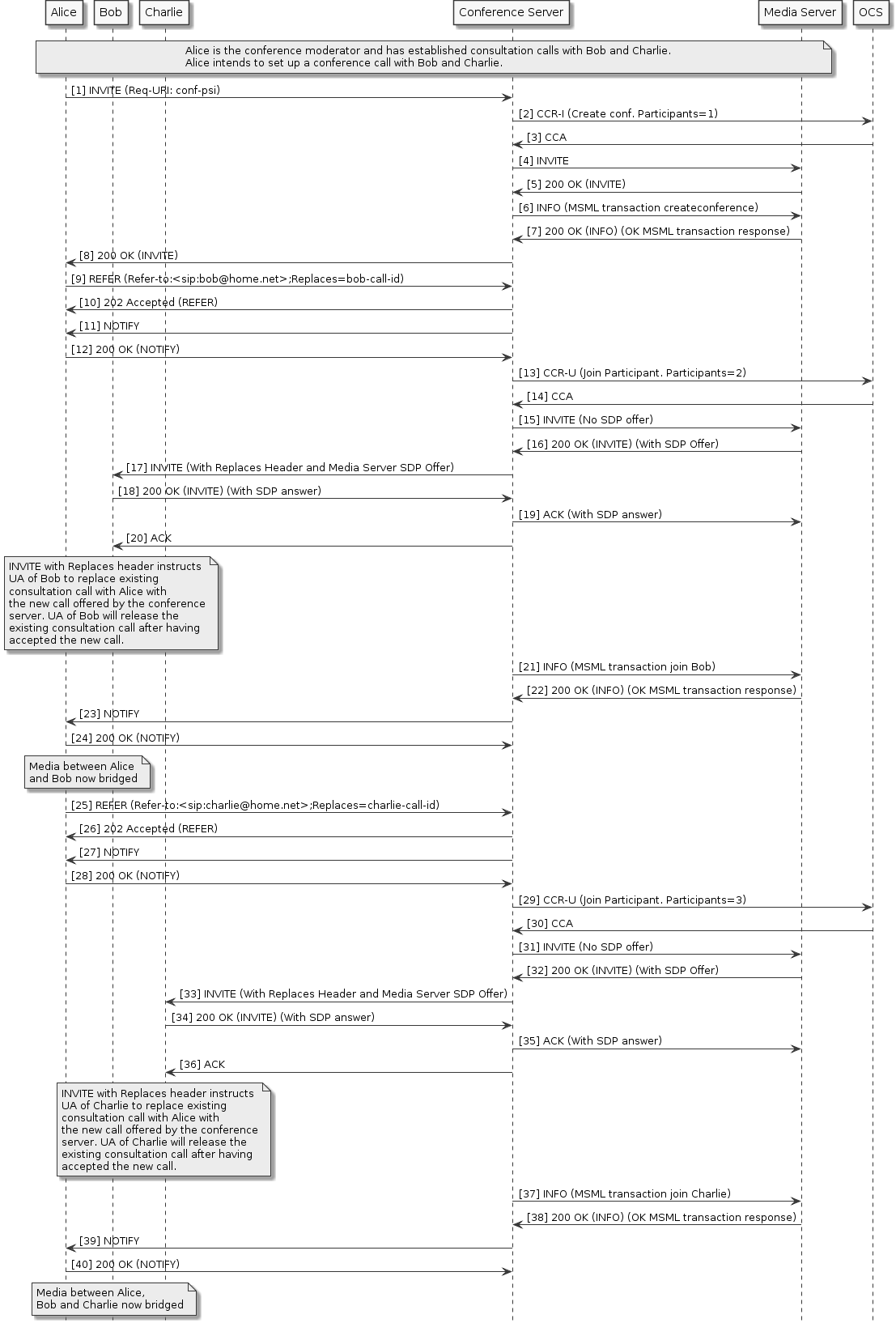
Routing SIP traffic towards Media Server (MRF) through the IMS
The MMTelCONF feature may directly contact a Media Server/Media Resource Function. This means that any INVITE from the feature is sent directly to the MRF. The Request URI of the outbound INVITE is set to the URI of the MRF.
This feature also supports routing INVITEs destined for the MRF through the IMS. In order to route through the IMS, the network configuration attribute IsMrfRoutableViaIMS must be set to true in the MMTelCONFConfigProfileTable
When this attribute is set to true and the initial INVITE from the conference moderator is received via the S-CSCF, the feature stores the Record-route SIP URI in the Session State attribute named SCSCFRouteAddress. In order to route the INVITE through the IMS, the feature retrieves the SIP URI (of the S-CSCF) from Session State, and places it as the topmost route header of the outbound INVITE.
The feature will also add a header parameter specified in configuration attribute RouteOrigUrlParameter to the Route header. For example, if parameter is set to value "orig" it will enable originating services to be run on outbound sessions from the conference server towards the conference participants.
Conference media
Every conference participant establishes signalling and media sessions with Media Server. Media Server performs mixing of media of all participants and enables all participants to hear each other (audio conference) and see each other (video conference).
Conference audio mixer
Loudest participants Optional MSML element <n-loudest> determines the number of participants from which audio is mixed based on their audio energy. MMTelCONF doesn’t define this element and relies on the default behaviour that causes Media Server to mix audio from all participants.
Audio sampling rate
Optional attribute samplerate determines the sample rate for the audio mixer. MMTelCONF doesn’t define this attribute leaving to the default 8000 kHz.
Active speaker notification
Active speaker notification enables active speaker to be notified with appropriate type of MSML event. MMTelCONF doesn’t define this attribute leaving to the default behaviour where notification is not supported.
DTMF and in-band tone clamping
When enabled Media Server blocks DTMF and in-band tones from being mixed. MMTelCONF doesn’t define this attribute leaving to the default where clamping is not performed.
Video layout
MMTelCONF implements a simple video layout where a single region over the root window displays the most active speaker. The same video output is offered to all conference participants.
Video resolution
Range of video resolutions are supported and configurable at a feature level. Media Server must support the values configured.
| Abbreviation | MSML schema v1.1 compliant | Value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CIF |
Yes |
352 × 288 |
Supported; Default |
|
QCIF |
Yes |
176 × 144 |
Supported |
|
4CIF |
Yes |
704 × 576 |
Not supported |
|
16CIF |
Yes |
1408 × 1152 |
Not supported |
|
SQCIF |
No |
128 × 96 |
Proprietary support only |
|
VGA |
No |
640 x 480 |
Proprietary support only |
|
QVGA |
No |
320 x 240 |
Proprietary support only |
|
HD720p |
No |
1280 x 720 |
Proprietary support only |
|
HD720p_4x3 |
No |
960 x 720 |
Proprietary support only |
Degrading from and upgrading to video media
Video conference is triggered when:
Video conferencing is administratively enabled (IsVideoConferenceAllowed=true), and Conference moderator makes a video media offer that is acceptable to Media Server If one of these preconditions is not met the conference shall have only audio media mixed irrespective if all or some participants have successfully negotiated video session with Media Server. This is because the feature will not instruct the Media Server to mix video media.
When the feature has determined a video conference session state field IsVideoConference will be set to true. The conference will remain marked as video conference regardless of whether some or all participants downgrade their media to audio only.
If a conference has been determined as a video conference any one participant including the moderator can downgrade/upgrade the media to/from video by sending re-INVITE with video media description IP port set to zero (downgrade) or non-zero (upgrade). Alternatively, conference participant can re-INVITE with video media description excluded or included achieving the same result.
Video only conference
Video only communication may occur on any one participant leg provided this is acceptable to both Media Server and the participant. Video only communication can occur when a participant or media server didn’t have matching audio codecs or have mismatching parameters.
Terminating conference
The conference is considered to be terminated when the conference moderator, either:
-
has disconnected, which will trigger the feature to remove all remaining participants
-
is the last participant remaining after all other participants have disconnected.
Removing participants
The conference moderator can eject any participant at will by creating a REFER transaction with a request that contains a Refer-to header with a URI parameter method=BYE and a URI referencing the participant to be ejected. This feature removes the participant by terminating both call legs for that participant.
Re-INVITE Based Three-party conference setup overview
There is an alternative flow when setting up a conference. Under this flow, participants receive a re-INVITE on the consulting call rather than an INVITE with Replaces. This means that releasing the consulting call between the moderator and the participant is now the responsibility of the AS, rather than the UE.
In order for the re-INVITE based flow to function:
-
SCC Conference Handling configuration must be toggled on (set the
EnableSCCConfHandlingattribute totrue) -
there is no originating iFC for the call from the moderator towards the Conference Factory PSI
-
originating and terminating SCC-AS must be implemented
-
the INVITE with Replaces sent by conferencing must trigger originating SCC processing
-
all sessions are subject to Session Tracking (this is automatically enabled when the
EnableSCCConfHandlingattribute is set totrue)
Once the requirements are met the originating SCC-AS can implement the re-INVITE based flow. For a reference to the features used to implement this in the SCC-AS please refer to Reuse of access transfer procedures for conferencing. Configuration and flows for this capability are described in the following portion.
SCC Conference Handling Configuration
SCC Conference handling configuration data is stored in the SCCConfHandlingConfigProfileTable profile table. Each profile is scoped according to a Sentinel Selection Key. By default there is one profile in the table. Each profile contains the following attributes.
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
EnableSCCConfHandling |
Boolean |
Enables SCC conf handling |
false |
|
ConfFactoryPSI |
String |
SIP or TEL URI for conferencing service PSI |
none |
Needs to match the value of |
Flows
The first flow shows standard treatment where the INVITE with Replaces is passed and translated all the way through to the participant.
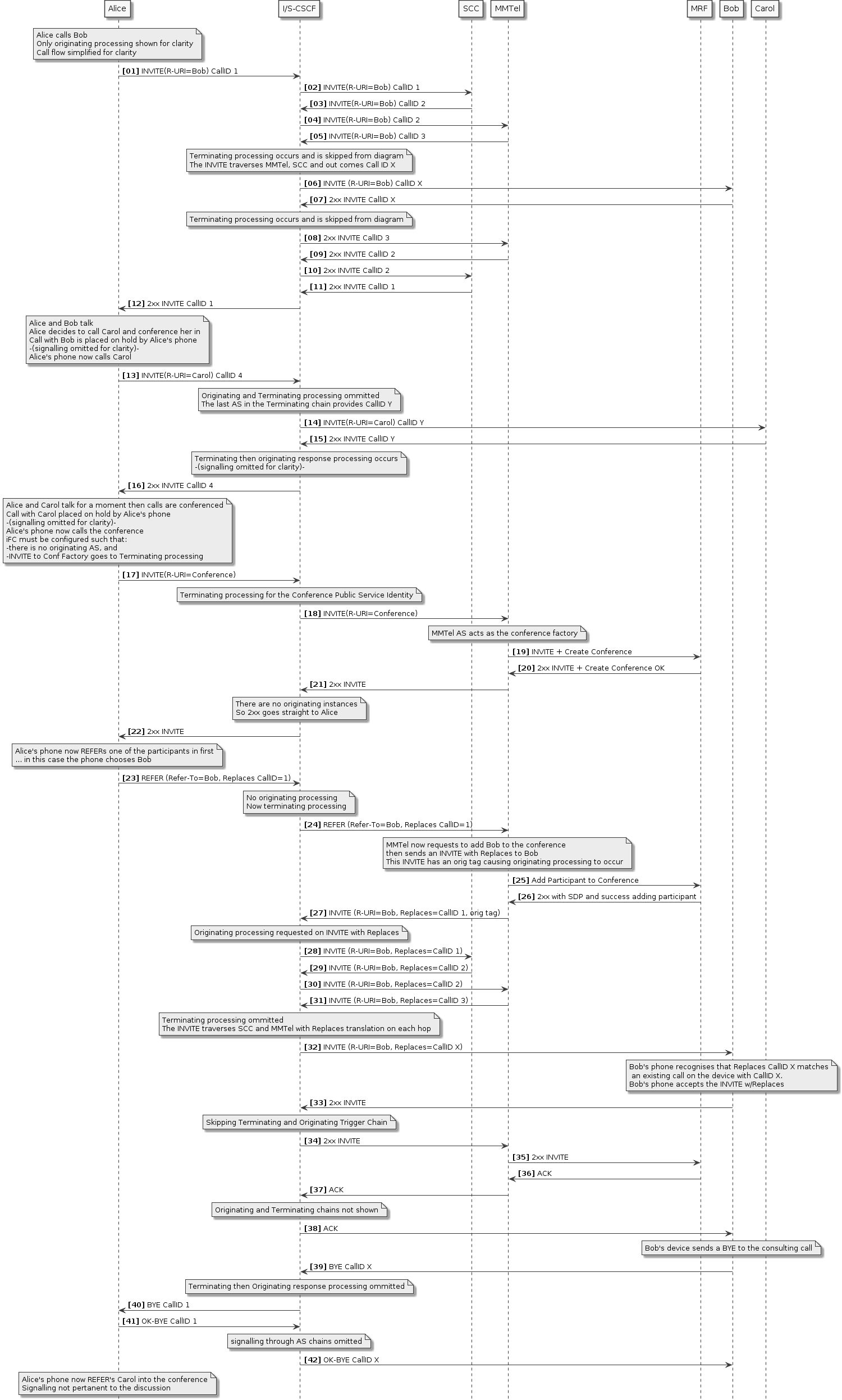
The second flow shows the re-INVITE based alternative enabled by the originating SCC where the INVITE with Replaces is converted to a re-INVITE on the participant’s consulting call.
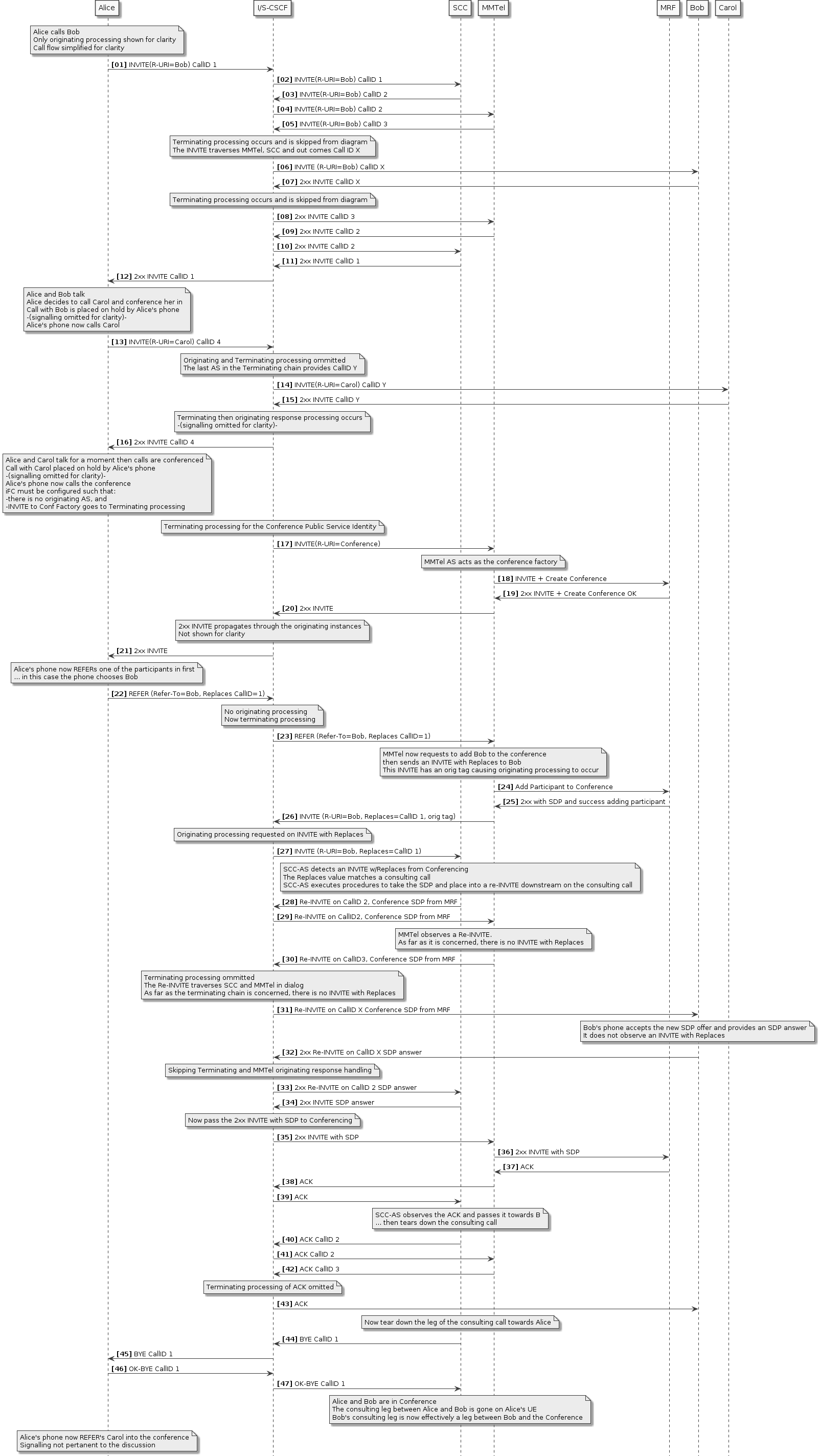
Interaction with MMTel Conference Subscription feature
MMTel Conference and MMTel Conference Subscription features share the data stored in the MMTelCONFView profiles associated with a given conference if there is at least one active subscription session for the associated conferenceID. The data is updated in the MMTel Conference feature when the conference is modified and is subsequently read by the MMTel Conference Subscription feature when it periodically polls for state changes. The ConferenceViewRemovalDelay in the MMTel Conference feature’s configuration provides a mechanism to allow all subscription sessions associated with MMTel Conference Subscription feature for the ended conference to complete before the MMTelCONFView profiles are removed.
Feature interaction
An initial INVITE with a Replaces header must be exempted from processing by a feature that performs call re-targeting, call barring, call rejection, or early session announcements.
Charging
Online charging uses a single OCS session for all legs of the conference:
-
The OCS Session begins when the conference creator sets up a call with the conference server (MT instance).
-
A credit check is performed before each participant is joined (event-based charging).
-
A credit check/reservation is performed on the MO instance of every participant leg.
-
The
icidvalue of theP-Charging-Vectorheader in the receivedINVITEfrom the conference creator is copied into theP-Charging-Vectorof everyINVITEsent towards a participant, as a way of charging correlation.
Inputs and outputs
Session state and leg manager data
Inputs
| Name | Type | Format | Description | Behaviour if null/invalid | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sentinel Selection Key |
com.opencloud.sentinel.common.SentinelSelectionKey |
selection key (for example, |
For selecting configuration data |
Feature not executed |
Session State Data |
Sentinel Script Execution Point |
enum com.opencloud.sentinel.feature.SipFeatureScriptExecutionPoint |
Determination of context of execution, such as credit check, early session, mid-dialog session |
No execution |
Session State Data |
|
Call Type |
enum com.opencloud.sentinel.common.CallType |
Determination of context of execution, such as |
NA |
Session State Data |
|
Call Leg |
com.opencloud.sentinel.multileg.Leg |
Determination of leg that receives an event |
Call terminated |
Leg Manager API |
Outputs
| Name | Type | Format | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ConferenceID |
String |
A 16-character alpha-numeric string prefixed with |
Generated by the feature when setting up moderator connection |
|
ConferenceFocusAddress |
String |
SIP URI |
URI derived from conference ID used to address the conference UA instance, such as |
Session State Data |
ControlPartLegName |
String |
Control leg name, participant side |
Session State Data |
|
ControlMRFLegName |
String |
Control leg name, Media server side |
Session State Data |
|
CurrentConnectionRequest |
|
Value object that represent request data and state of processing for joining a new participant; request that is being processed currently |
Session State Data |
|
ConnectionRequestQueue |
|
Pending requests to join new participants |
Session State Data |
|
JoiningParticipants |
|
Requests for which media bridging is in progress (MSML transaction is in progress) |
Session State Data |
|
JoinedParticipants |
|
Value objects that represent that participants that have been joined into conference including those already disconnected |
Session State Data |
|
VideoConferenceResolution |
|
Value to represent the video conference resolution used for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
Bandwidth |
Integer |
Bandwidth value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
MinimumPictureInterval |
Integer |
Mpi value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
MaximumPictureSize |
String |
Bpp value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
FrameSize |
Integer |
Framesize value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
ProfileLevelId |
String |
Profile-level-id value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
|
Codec |
String |
Codec value to use for control MRF session |
Session State Data |
Execution of this feature can also affect the conference view during execution if a participant is added or their status has changed.
Statistics
MMTelCONF statistics are tracked by the MMTelCONF SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → MMTelCONF SBB ID.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
FeatureInvocations |
the conference feature runs |
FeatureFsmCompletions |
the main conference FSM reaches its end state |
SentinelAborts |
Sentinel VoLTE instructs the conference feature to abort execution |
SipParseMinorFailure |
a non-fatal error occurs while attempting to read the information in a SIP message |
SipDataAccessFailure |
a problem occurs while trying to access a SIP leg or message |
SipParticipantSentByeOnActiveConnection |
a |
SipParticipantSentByeOnInactiveConnection |
a |
SipMRFSentByeOnActiveConnection |
a |
SipMRFSentByeOnInactiveConnection |
a |
ConferenceFeatureConfigurationFailure |
a problem occurs while trying to load the conference feature’s network-level configuration data |
ConferenceCoreError |
a fatal error occurs in the core conference feature FSM |
ConferenceConnectionError |
a fatal error occurs in the conference feature’s non-control connection management FSM |
ConferenceConnectionEstablished |
a non-control connection is successfully established between a conference participant and the MRF |
ConferenceConnectionMRFLegCreated |
a non-control leg to the MRF is successfully established |
ConferenceConnectionTerminated |
a fully established non-control conference connection is terminated |
ConferenceConnectionCreditCheckInitiated |
the conference feature triggers a credit check |
ConferenceConnectionParticipantSupportsVideo |
a participant has indicated that they support video in an SDP answer |
ConferenceControlConnectionError |
a fatal error occurs in the conference feature’s control connection management FSM |
ConferenceControlConnectionEstablished |
a control connection is successfully established between a conference moderator and the MRF. |
ConferenceControlConnectionTerminated |
a fully established conference control connection is terminated. |
ConferenceControlConnectionReceivedMalformedMessage |
a badly formed REFER request is received from the conference moderator. |
FromHeaderAnonymised |
the moderator has indicated they want privacy applied to the outgoing INVITE |
ConferenceMediaVideoSelected |
the moderator sets the conference up as a video session |
ConferenceMediaServerIsAccessedViaSCSCF |
the feature makes a call to the MRF via the S-CSCF |
Error scenarios
| Scenario | Handling |
|---|---|
Second initial request received towards conference PSI |
Report |
Non MT request received by conference PSI |
Report |
Mappers
This feature uses two different sets of mappers that conform to:
| Mapping | Mapper Execution Point |
|---|---|
MMTelCONFConfigWrapper.class → CreateConferenceMSML.class |
|
MMTelCONFConnectionRequestQueue.class → JoinConferenceMSML.class |
|
IncomingSipResponse.class → ResponseMSML.class |
Mapper Configuration
As mentioned in the previous section this feature uses two different sets of mappers. The set to configure depends on the media server in use with the feature. Configuring mappers can be done in the SentinelMapperSetEntryTable. The following yaml excerpts outline which profiles should be configured for each vendor.
Dialogic
SentinelMapperSetEntryTable:
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-CreateConference-Dialogic:
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-CreateConference-Dialogic
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-JoinConference-Dialogic:
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-JoinConference-Dialogic
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-Response-Dialogic:
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-Response-Dialogic
Radisys
SentinelMapperSetEntryTable:
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-CreateConference-Radisys:
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-CreateConference-Radisys
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-JoinConference-Radisys:
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-JoinConference-Radisys
${platform.operator.name}::sipcall:::MMTelConfMSML-Response-Radisys
MapperSetName: '${platform.operator.name}:'
SessionType: sipcall
PlanId: ''
MapperExecutionPoint: ''
MappingName: MMTelConfMSML-Response-Radisys
Feature responses
| Response | Reason |
|---|---|
endSession |
Max number of participants < 3 |
featureFailedToExecute |
Multiple initial requests or non MT initial request received towards conference PSI |
featureHasFinished |
Feature has finished |
Configuration profile naming
| Configuration Profile Table Name | Description | Profile Naming |
|---|---|---|
MMTelCONFConfigProfileTable |
See Network Data for a detailed description of parameters |
Example configuration for conference feature where localhost:5260 is the address of the MMTel TAS:
| ConfFactoryPSI | ConfMaxParticipants | ConfCascadingEnabled | ConferenceViewRemovalDelay |
|---|---|---|---|
sip:conf-factory@localhost:5260 |
3 |
false |
30000 |
Conference view
The current view of a conference is stored as a series of read-only profiles (one for each participant) within the MMTelCONFViewTable profile table.
| Profile Table Name | Description | Profile Naming |
|---|---|---|
MMTelCONFViewTable |
Stores the current state of a participant within a conference |
${CONFERENCE_ID}__${CONNECTION_ID}
|
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ConferenceEndpointStatus |
String |
Current status of a participant connected, disconnected or on-hold |
ConferenceID |
String |
Unique 16-character alpha-numeric string prefixed by |
ConnectionID |
String |
Unique identifier for a participant as the uniqueness of |
ParticipantID |
String |
URI identifying the participant |
ParticipantDisplayText |
String |
participant display text |
EndpointID |
String Unique |
identifier for the endpoint |
ConferenceEnded |
Boolean |
|
LastUpdateTime |
Long |
timestamp representing the last time the profile was updated |
Conference event package
A UE may attempt to subscribe to notifications for the conference event package. Subscriptions for the conference event package are handled by the MMTel Conference Subscription.
Interaction with Media Server
The conferencing feature facilitates connecting conference participants to the media server and instructs the media server to mix audio media from all participants to form an audio conference.
The feature controls mixing, using the MSML protocol over SIP in the context of an existing SIP dialog. For this purpose, this implementation uses the moderator SIP dialog established between the conferencing server and the media server, as long as the the lifeline of any conference instance is aligned with the lifeline of the moderator connection.
MSML transactions are carried by SIP INFO transactions and encoded as application/msml+xml content type. The result of the MSML transaction is returned in a SIP INFO 200 OK response.
This feature uses the MSML conference object and MSML connection object capabilities of MSML protocols.
Each MSML connection is linked or “joined” with an MSML conference object that creates a media bridge with other connections.
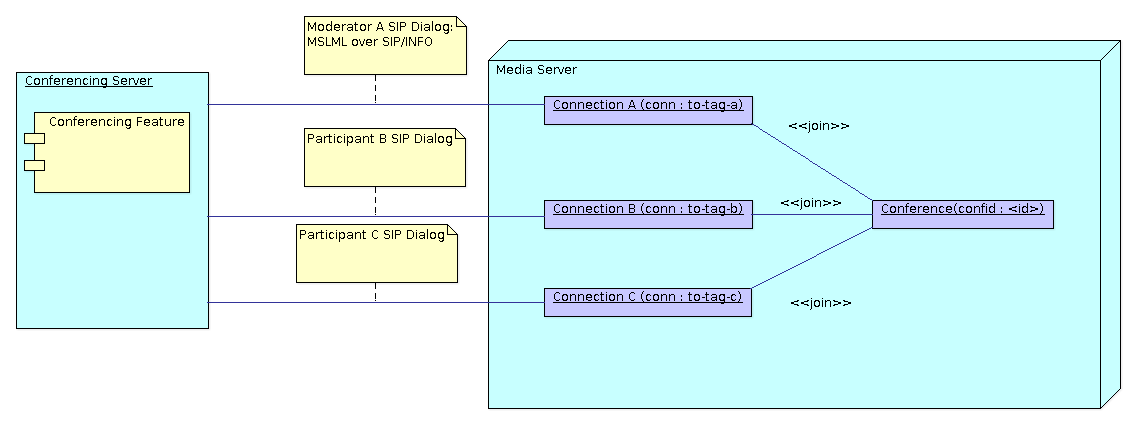
MSML conference object
A conference object is a media bridge that links media with MSML connections. By joining MSML connection objects with the MSML conference objects, media between all connections are mixed, achieving conference functionality. A conference object is identified by a conference ID, which is a randomly unique string prefixed with conf:.
The conferencing feature creates an MSML conference object using the <createconference> MSML command. This command has several parameters, such as mixer type, half or full-duplex, and termination policy. This implementation creates a full-duplex audio mixer without a conference termination policy.
Here an is an example of a <createconference> MSML request that creates a conference object:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<msml version="1.1">
<createconference name="conf:mmtel-conf-378237676" deletewhen="nocontrol" term="false"/>
</msml>
The media server returns with MSML response 200 indicating success:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<msml version="1.1">
<result response="200"/>
</msml>
The conference object created has parameters that specify:
-
Conference ID
mmtel-conf-378237676. -
The media server automatically removes the conference object when the moderator disconnects.
-
The media server doesn’t disconnect remaining participants when the conference object is deleted. (This task is left to the conferencing server.)
-
A full-duplex audio mixer will be used, with mixing active at all times, without notification of the active speakers.
MSML connection object
A session between each participant and the media server (using the conferencing feature) is referred to as an MSML connection and is identified by the SIP to-tag (prefixed by conn:) of the SIP session between the conferencing server and the media server. An MSML connection is joined into the conference by the MSML command <join>, which takes arguments of the connection ID of the connection to be joined and the conference ID of the conference object.
Forming a media conference
A conference is formed by creating a media bridge between the MSML conference object and each MSML connection. This is achieved by an MSML join transaction, as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<msml version="1.1">
<join id1="conn:e7826yde8" id2="conf:mmtel-conf-378237676"/>
<stream media="audio"/>
</join>
</msml>
MMTel Conference Subscription
This feature provides a means for UEs to subscribe to “conference” event package notifications for a conference .
Feature cheat-sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Both |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateful |
POJO with FSMs |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-conferencing module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-conf-module opencloud#mmtel-conferencing#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules relevant to this feature:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-conferencing |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-conf-library |
Contains common code for the conference modules. |
mmtel-conf-subscription-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-conf-view-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the profile table used to track information about a conference. |
mmtel-conf-event-schema-library |
Generates java code for the conference event XML schema. |
mmtel-conf-subscription |
Contains the feature itself. |
Subscriber data
Not applicable; the feature is generally available unless disabled at the network level.
Network data
Data is stored in the MMTelCONFSubscriptionConfigurationTable profile
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
DefaultSubscriptionExpirySecs |
Integer |
3600 |
Expires value is used if SUBSCRIBE doesn’t contain Expires header |
MinSubscriptionExpirySecs |
Integer |
5 |
SUBSCRIBE requests with a Expires value lower than this are are rejected |
PollingIntervalSecs |
Integer |
5 |
Frequency of polls for changes to conference view |
Statistics
MMTelCONFSubscription statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → MMTelCONFSubscription
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
SubscriptionStarted |
Counter |
Incremented when a subscription is successfully initiated. |
SubscriptionRefreshed |
Counter |
Incremented when an in-progress subscription is refreshed with a new |
SubscriptionEnded |
Counter |
Incremented when an in-progress subscription is ended with a |
SubscriptionRejected |
Counter |
Incremented when a |
NewSubscriptionRequestedInNewDialog |
Counter |
Incremented when a subscription is initiated by a |
NewSubscriptionRequestedInExistingDialog |
Counter |
Incremented when a subscription is initiated by a |
NotifySent |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature generates and sends a |
Behaviour
Name |
|
|---|---|
Applicable contexts |
SIP service |
Prerequisite features |
|
The MMTel Conference Subscription feature is to be used in conjunction with the MMTel Conference feature. It provides a means for UEs to subscribe to “conference” event package notifications for a conference managed by the MMTel Conference feature. Currently no distinction is made between conference and non conference participants.
Notifications are triggered by changes in the state of the conference for example when a participant joins or leaves. The feature is triggered initially on an incoming SUBSCRIBE and is subsequently triggered by a re-SUBSCRIBE attempt or on the expiry of the features polling timer. In the case where the feature is triggered by a incoming SUBSCRIBE message a NOTIFY will be sent detailing the complete state of the conference. In the case where the feature is triggered on the expiry of the polling timer a NOTIFY containing the current state of the conference will only be sent if the conference view has been modified since the last expiry of the timer. The feature may also be triggered by BYE requests and REFER requests that have a Refer-To method of BYE, this affects subscriptions that are created in the INVITE dialog for the conference and will trigger the same behaviour as a polling timer expiry.
Interaction with MMTel Conference feature
MMTel Conference and MMTel Conference Subscription features share the data stored in the MMTelCONFView profiles associated with a given conference if there is at least one active subscription session for the associated conferenceID. The data is updated in the MMTel Conference feature when the conference is modified and is subsequently read by the MMTel Conference Subscription feature when it periodically polls for state changes. The ConferenceViewRemovalDelay in the MMTel Conference feature’s configuration provides a mechanism to allow all subscription sessions associated with MMTel Conference Subscription feature for the ended conference to complete before the MMTelCONFView profiles are removed. There is a configurable delay in the MMTel Conference feature for how long the profiles should remain for after the conference ends. Generally the PollingIntervalSecs of MMTel Conference Subscription should be lower than this delay.
Conference view
The current view of a conference is stored as a series of read-only profiles (one for each participant) within the MMTelCONFViewTable. A conference is considered active and therefore a subscription successful if at least one profile exists with the requested ConferenceID and ConferenceEnded is false. Profiles from this table are used to create the body of outgoing NOTIFY messages.
| Configuration profile table name | Description | Profile naming |
|---|---|---|
MMTelCONFViewTable |
Stores the current state of a participant within a conference |
${CONFERENCE_ID}__${CONNECTION_ID} |
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ConferenceEndpointStatusInternal |
String Current |
status of a participant connected, disconnected or on-hold |
ConferenceID |
String Unique |
16 character alpha-numeric string prefixed by “mmtel-conf-” (common amongst all participants) |
ConnectionID |
String Unique |
identifier for a participant as the uniqueness of ParticipantID cannot be guaranteed |
ParticipantID |
String URI |
identifying the participant |
ParticipantDisplayText |
String |
participant display text |
EndpointID |
String Unique |
identifier for the endpoint |
ConferenceEnded |
Boolean |
|
LastUpdateTime |
Long |
timestamp representing the last time the profile was updated |
Conference event schema
Event Package for Conference State and the associated schema are used to convey the current state of the conference for subscribed resources. The feature will always render the complete state of the conference regardless of subscription state.
MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status
This feature determines if the SIP session is roaming and if it represents an international, or international ex HC call, based on the location of the calling party and the destination address . The results of this feature are applied by the VoLTE communication barring features (MMTelOCB and MMTelICB).
From the spec
Here’s what 3GPP 24.611 says:
|
international: This condition evaluates to true when the request URI of the outgoing SIP request:
international-exHC: This condition for international barring, excluding the home country, evaluates to true when the request URI of the outgoing SIP request:
|
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Both |
Any |
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Prerequisite features
Sentinel-SIP:
-
SIP Determine Network Operator
-
SND:Determine Call Type Feature
-
SIP Extract Network Info
-
SIP Normalization (recommended)
VoLTE:
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-diar-module opencloud#volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status-address-list |
Contains the profile specification for the feature address list profile table. |
volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status-feature |
Contains the feature itself. |
Behaviour
Get the address string to use in address analysis
The DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature analyses a digit string that corresponds to the destination (or called) party. Digit strings may be in a Tel URL, or the user part of a SIP URI.
If the number retrieved from the Tel URI or SIP URI user part contains a + sign, the + sign is removed to leave just the digits.
The DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature uses different properties of the initial INVITE request for originating and terminating treatment:
-
If the session is originating, then it checks the
request-uriandToaddress. -
If the session is terminating, then it checks the
P-Asserted-Identityaddress, theFromaddress, and theReferred-Byaddress.
Otherwise, the feature execution ends.
If a digit string is not found, then the feature will respond to the sentinel-core with featureCannotStart, and end.
Determine if address international and roaming status should be skipped
The DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature may decide to not handle the address if either:
-
The address is shorter than the configured
MinLengthdefined inDetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatusConfigProfileTable -
The address matches an entry in the
SkipDIRSAddressList
This allows for short codes and specific longer length numbers to avoid DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus. The SkipDIRSAddressList is a configurable address list scoped by the Sentinel selection key; it is only given to the component when used by the SIP normalization component.
Get the visited Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code
The visited MCC and MNCs are retrieved from session state field previously populated by the ExtractNetworkInfo feature. Those values will be used when determining the roaming and international statuses.
Get the visited-network-id for the served user
The feature check first if the session state IMSInformation contains a valid IMS Visited Network Identifier populated by Diameter Per Leg Info Feature.
If no value is present, it extracts the visited network id for the served user as follows:
-
If the session is originating, the
P-Visited-Network-Id headeris checked in the incoming request.-
If this header exists, then the visited network id is set from the header value.
-
-
If the session is terminating, the
OC-Term-P-Visited-Network-Idheader is checked in the incoming request.-
If this header exists, then the visited network id is set from the header value.
-
If the incoming request did not contain the visited network id, and if the served user is logged into the IMS, then Third Party Registration Data is consulted - to find the P-Visited-Network-Id at the time of IMS registration. Third Party Registration data is looked up with an access key of the default public identity for the served user. It is accessed via the Sh Cache.
If a visited network id cannot be determined, the feature checks the configuration in the DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatusConfigProfileTable to determine if the call should proceed or not. If EndCallIfNoVisitedNetwork is false, then the feature exits without modifying session state. If EndCallIfNoVisitedNetwork is true then the call is terminated.
Get the address prefix address list
An important part of this feature is an address list of prefixes for each MCC or each visited network. Each entry in the list states whether an address with this prefix, for a subscriber of the network operator, registered with a subscriber location network, represents a visited or home network.
For a session processed by VoLTE:
-
The session is scoped to the network operator by the SIP Determine Network Operator feature (this is the subscriber’s home).
-
The MCC or
visited-network-idis found as described above. -
There is an entry for each MCC or visited network in the
DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus_AddressListConfigurationTableprofile and an address list of prefixes for each MCC or visited network stored in theDetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus_AddressListEntryTableprofiles. Both are scoped to the Network operator.
If the profile field useMCCSpecificAddressListTables is false then the feature will attempt to use the default address list named DEFAULT. If the profile field useMCCSpecificAddressListTables is true the feature will attempt to use an address list named after the MCC. The feature will use a visited-network-id prefix address list if no MCC could be found or if no address list for the MCC could be found.
If no such address list is found, the feature will respond to the sentinel-core with featureFailedToExecute, and end.
Determine international and international-exHC status
The DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature does a longest-prefix search of the prefix address list with the address string (extracted in step #1).
If a match is found, then the address starts with a prefix of significance within the scope of the MCC or visited network. The feature can set the International session state field in two ways: * If an MCC has been determined for the served user and there is an MCC present in the prefix address list entry then 'International' is set to 'true' if the MCCs are different. * If either MCC could not be found then 'International' is set to not networkPrefixListEntry.isVisitedNetwork(). The internationalExHC session state field is set to International and not networkPrefixListEntry.isHomeNetwork().
If a prefix address list match is not found, then it must be an international call; so the feature sets the International session state field to true and the internationalExHC session state field to false.
Using MCC specific prefix address lists
The DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus feature uses a single prefix address list named DEFAULT unless useMCCSpecificAddressListTables is configured as true in the feature’s profile.
MCC specific prefix address list tables may be needed for more advanced scenarios where different MCCs are desired to not be treated as international.
Determine roaming status
The SIP Sentinel SipSentinelConfiguration profile (scoped on the Sentinel selection key) defines the home Mobile Country Code (MCC), the Mobile Network Codes (MNCs) and the home network ids for the network operator. The home network ids define the home network for the subscriber.
If the feature found a non empty MCC for the visited network, it compares that value with the home MCC present in SipSentinelConfiguration profile.
If they are different the feature sets the RoamingStatus to INTERNATIONAL and the RoamingIndicator session state field is set to true.
If they are equal and the visited MNC is present in the home MNCs, the feature sets the RoamingStatus to NOT_ROAMING and the RoamingIndicator session state field is set to false.
If they are equal and the visited MNC is not present in the home MNCs, the feature sets the RoamingStatus to NATIONAL and the RoamingIndicator session state field is set to false.
If no MCC is present then the feature do the roaming analysis based on the visited-network-id. If the visited-network-id is not a member of the set of home network ids, the RoamingIndicator session state field is set to true.
If they are no visited MNC and no visited network was found, the feature sets the RoamingStatus to UNKNOWN.
Session state inputs and outputs
Inputs
| Name | Type | Format | Description | Behaviour if null/invalid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SentinelSelectionKey |
com.opencloud. sentinel.common.SentinelSelectionKey |
selection key (for example, |
For selecting configuration data |
Report featureCannotStart, featureHasFinished if the network operator field is not set. |
|
CallType |
com.opencloud.sentinel.common.CallType |
One of: |
Session type of this call |
Report |
|
IMSDefaultPublicID |
java.lang.String |
tel URL or SIP URI |
the |
Increment statistic |
|
ImsInformation. ImsVisitedNetworkIdentifier |
java.lang.String |
recommended format is |
the visited network id extracted from the Invite request or from the registration data by the Diameter Leg Info feature |
try to extract from the triggered request |
|
PaniMccsMncs |
List<MccMnc> |
MCC and MNC as String |
a list of MCC and MNC extracted from P-Access-Network-Info header from the request or from the registration data by the Diameter Leg Info feature |
try to extract from the session state PvniMccMnc |
|
PvniMccMnc |
com.opencloud.sentinel.common.MccMnc |
MCC and MNC as String |
a list of MCC and MNC extracted from P-Visited-Network-Id header from the request or from the registration data by the Diameter Leg Info feature |
use the |
Outputs
| Name | Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
International |
boolean |
true or false |
the international condition as defined by 3GPP 24.611 |
InternationalExHC |
boolean |
true or false |
the international-exHC condition as defined by 3GPP 24.611 |
RoamingIndicator |
boolean |
true or false |
true, if the subscriber is roaming |
RoamingStatus |
enum |
|
|
Error scenarios
These scenarios trigger the following reports.
| Scenario | Report |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
No Called Party Leg available from the |
|
Cannot determine a digit String to analyse in originating case |
|
Cannot determine a digit String to analyse in terminating case |
|
There is no prefix address list for a |
|
No registration data found for |
|
Registration data fetched for |
|
Statistics
DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus"
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
VisitedNetworkHeaderFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the requestURI identity is in RegistrationRecords list of public identities. |
AccessNetworkMccFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the mobile-Country-Code is found in the P-Access-Network-Info header. |
DeterminedInternationalUsingAccessNetworkMcc |
Counter |
Incremented when the MCC prefix address list is used to determine whether the call is international. |
DeterminedInternationalUsingVisitedNetworkId |
Counter |
Incremented when the visited-network-id prefix address list is used to determine whether the call is international. |
CouldNotGetPVisitedNetworkID |
Counter |
Incremented when no visited network ID information could be found. |
HomeNetworkIdSetForNetworkOperatorIsEmpty |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sentinel SIP configuration for the network operator has an empty |
InternationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is roaming in a foreign country. |
NationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is roaming in their home country. |
NotRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is on their home network. |
UnknownRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine the served user’s roaming status. |
AddressNotMinimumLength |
Counter |
Incremented when destination address is less than the configured minimum length. |
AddressOnBlackList |
Counter |
Incremented when destination address matches an entry in the |
MMTel Subscriber Data Representation
The MMTel Subscriber Data Representation is a logical representation of supplementary service data as a group of POJO objects. It allows MMTel services/features to execute independently of any concrete schema for the supplementary service data. Therefore it can be loaded from the HSS or the HLR using the MMTel-Services XML schema or 3GPP MAP ASN.1 schema. For mapping details see SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS and SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR.
Motivation
The subscriber data schemas used by an HSS and HLR are very different. While HSS supports complex types in XML format (through the Sh interface), the HLR schema format is ASN.1 with different semantics (through the MAP interface). One example of a simple concept is the 'active' flags. The HSS and Sh protocol provide an XML document that indicates if the service is active or not as an option boolean flag (active=true or false, or not present). While the HLR and MAP protocol represents the data as a state vector which includes the service status indication with three values (Active and Operative, Not Active and Active and Quiescent).
The objective of this representation is to decouple the concrete representation of Subscriber Data to an extensible internal representation that supports different schemas.
Description
The internal representation works by:
-
defining one subscriber data containing class for each MMTel feature, and defining a suitable session state field for an instance of that class
-
retrieving the supplementary service data from the suitable network element (HSS via Sh pull, or HLR via AnytimeSubscriptionInterrogation)
-
invoking a schema specific adapter class based on the response i.e. the simServes adaptor or the ASN.1 adaptor
-
for each MMTel feature, the adaptor writes an instance of the subscriber data containing class into the appropriate session state field
The adapter has the function of converting the concrete schema into the logical representation, and storing it into session state. After the adaptor has written the session state fields, the MMTel features are invoked and read their data from session state fields.
ServiceData Types
Each of these types has a corresponding Java class.
MMTelTIPServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
Override |
Indicates if the feature can take precedence over the TIR feature |
MMTelTIRServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
DefaultBehaviour |
Indicates if the the user data presentation is restricted or not |
Mode |
Indicates if it is permanent or temporary |
MMTelOIPServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
Override |
Indicates if the feature can take precedence over the OIR feature |
MMTelOIRServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
DefaultBehaviour |
Indicates if the user data presentation is restricted or not |
Mode |
Indicates if it is permanent or temporary |
MMTelCDIVServiceData
These properties are from the <communication-diversion> element.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
NoReplyTimeout |
The time waiting for the response to trigger the noReply rule |
Ruleset |
This is a Java implementation of IETF’s common policy Ruleset as used by 3GPPs CDIV specification. A ruleset is a collection of Rules |
Rule.ID |
Unique identification for the rule |
Rule.conditions |
The conditions |
Rule.forwardActions |
The actions to forward the session. It includes the destination address and the notification and privacy rules for the caller and called parties |
These properties are from the <operator-communication-diversion> element.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
OperatorTotalNumberOfDiversionsForEachCommunication |
The maximum number of times a communication may be diverted. |
OperatorCommunicationForwardingOnNoReplyTimer |
The time waiting for the response to trigger the noReply rule |
OperatorRuleset |
This is a Java implementation of IETF’s common policy Ruleset as used by 3GPPs CDIV specification. A ruleset is a collection of Rules |
| |
The schema for the Operator part of the Communication Diversion (CDIV) services has been extended to support an optional ruleset. This feature is supported by some HSS vendors. |
MMTelCWServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
MMTelOCBServiceData
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
Ruleset |
Contains the subscriber’s barring rules. Read from the HSS and configurable via XCAP or read from HLR. It is a Java-parsed representation of a Common Policy Ruleset. |
Rule.ID |
Unique identification for the rule |
Rule.conditions |
The conditions |
Rule.allow |
Allow or not allow the session to be forwarded |
MMTelICBServiceData
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Active |
Indicates if the feature is active |
Ruleset |
Contains the subscriber’s barring rules. Read from the HSS and configurable via XCAP or read from HLR. It is a Java-parsed representation of a Common Policy Ruleset. |
Rule.ID |
Unique identification for the rule |
Rule.conditions |
The conditions |
Rule.allow |
Allow or not allow the session towards the served user |
MMTelFAServiceData
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Authorized |
Indicates if the feature is active |
Identity |
The |
Group |
The group type for the Flexible Alerting |
Membership |
The membership type: |
Members |
List of member attached to the |
Members.Active |
If the member can be alerted |
Members.Uri |
The member URI identity |
MMTelCDIV
The Communications Diversion (CDIV) service enables a ‘diverting user’ to divert communications addressed to the ‘diverting user’ to another destination .
The service description of CDIV’s services CFU, CFB, CFNR, and CD is based on the PSTN/ISDN supplementary services; whereas CFNL is a CDIV service based on requirements for IP-based networks; and CFNRc is based on requirements for mobile networks.
The services are:
-
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU)
-
Communication Forwarding on Busy user (CFB)
-
Communication Forwarding on no Reply (CFNR)
-
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc)
-
Communication Deflection (CD)
-
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in (CFNL).
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes — CDIV rules are stored in the HSS |
Stateless w/FSM in Session State |
POJO but with much stateful behaviour implemented by storing an FSM instance into Session state |
Implications on Charging for Forwarded calls |
Prerequisite Features
-
DetermineCallType
-
MMTelTIR (only when MMTelTIR is in use)
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-communication-diversion module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-cdiv-module opencloud#mmtel-communication-diversion#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-communication-diversion |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-cdiv-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-cdiv |
Contains the feature itself. |
Specification References
-
3GPP TS 24.604 Rel 11: http://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Specs/html-info/24604.htm
-
GSMA IR.92 (a subset of 24.604) This feature targets the IR.92 subset.
-
RFC 4244 (“The History-Info header RFC”): http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4244
-
RFC 4458 (“SIP Voicemail URI” — target and cause in request URI) RFC: http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4458
GSMA IR.92 Reference Information
This is taken from IR.92 v9.0:
2.3.8 Communication Diversion
The UE and IMS core network must support the SIP procedures in 3GPP TS 24.604 for Communication Diversion (CDIV). For CDIV service activation, deactivation, and interrogation (XCAP operations), the UE and IMS core network must support the XML rules for Call Forwarding Unconditional and the conditions, actions and elements listed in Table 2.2. The UE and IMS core network shall support the XML rules as described in 3GPP TS 24.604 section 4.9.1. The UE must support the History-Info header for identification of diverting parties at the terminating side and of diverted-to parties at the originating side. At the terminating side, a History-Info entry shall be used for the identification of the diverting party only if another History-Info entry exists that has assigned the next index in sequence AND includes a cause value. At the originating side only History-Info entries including a cause value shall be used for presentation of the diverted-to party. Note: Support of subscription options and other conditions and actions are out of scope of the document. |
It then shows the following table (reformatted)
| Type | Parameter |
|---|---|
Rule Condition |
Busy |
Rule Condition |
media (supported media types: audio, audio AND video) |
Rule Condition |
no-answer |
Rule Condition |
not-registered |
Rule Condition |
not-reachable(Note) |
Rule Condition |
rule-deactivated |
Rule Action |
target |
Element |
NoReplyTimer |
Note: The GSM version of Communication Forwarding on Not Reachable (CFNRc) implies diversion when the user is not registered in the CS core or cannot be reached. To mimic this behaviour, it is recommended that an UE activates both the CFNRc (CDIV using condition not-reachable) and the Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in (CFNL) (CDIV using condition not-registered) to the same target. |
Scope
In Scope
The following are in scope:
-
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU)
-
Communication Forwarding on Busy user (CFB)
-
Support for User Determined User Busy (UDUB)
-
Communication Forwarding on No Reply (CFNR)
-
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc)
-
Communication Deflection (CD)
-
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in (CFNL)
-
Checking of the diversion limits
-
Communication Diversion Notification (CDIVN) — 181 responses
Out of Scope
The following are out of scope:
-
There is no support for “Ringing continues” in the no reply timeout case (option for CFNR).
-
There is no support for Network Determined User Busy (NDUB).
-
Deliver to last diverted user is not implemented as an approach when Max Diversions has been exceeded. This is because we consider it a bad practice.
Network Operator Data
Network (or Operator) data may come from two sources:
-
Provisioned data in the VoLTE platform stored in a profile table named
MMTelCDIVConfigProfileTable. -
Received from the HSS in the
<operator-communication-diversion>section of the CDIV network data fetched from the HSS.
Properties received from the HSS in the <operator-communication-diversion> section of an MMTel-Services XML document take precedence over data in the MMTelCDIVConfigProfileTable.
Platform Network Operator Data
Network configuration is stored in a JSLEE profile table named MMTelCDIVConfigProfileTable.
Individual configurations are entries in this table. The data is scoped on Sentinel Selection Key.
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
int |
|
Maximum number of diversion hops that may occur, see the Diversion Limit section. |
|
Enum ( |
|
Determines the action to be taken when the |
|
String, must be a valid SIP or Tel URI |
|
The fixed destination to deliver to when |
|
String, comma separated list of SIP and/or TEL URIs |
|
List of destination URI’s that are known to not re-target calls, diversions to these URIs are permitted even when |
|
String |
|
A default URI for use when re-targeting sip requests in the event that there are re-targeting rules and no target URI. |
|
Boolean |
|
A boolean flag indicating whether to apply the procedure for default re-targeting. |
|
boolean |
|
Determines if an announcement will be played when diversion occurs. |
|
int |
|
The announcement ID of the announcement that should be played when diversion occurs. |
|
int |
|
The announcement ID of the announcement that should be played when diversion to a known voice mail server occurs. If the call should not be allowed to reach the voice mail server if the announcement fails, the announcement must be configured with |
|
String[] |
|
The list of known voice mail server URIs. When a call is diverted to one of these URIs, an announcement may be played if configured. |
|
int |
|
The maximum time (in seconds) to wait for a reply before triggering CFNR. |
|
boolean |
|
Determines whether to add an |
|
boolean |
|
Determines whether CDIV’s behaviour should be suppressed when a call is on a CS network, see the CDIV Suppression section. |
|
int[] |
|
Can be used to trigger the CDIV not-reachable condition (CFNRc) with SIP response status codes not included in the CFNRc specification. This list may not include status codes that have other purposes in CDIV (i.e. 1xx, 2xx, 404, 408, 486, 487). |
|
boolean |
|
A flag that when set to true, will allow the CDIV not-reachable condition to trigger when the call is in the alerting state (usually this condition only triggers in the pre-alerting state). |
HSS Network Operator Data
There are three elements of <operator-communication-diversion> received from the HSS that the CDIV feature may apply.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
This property, if present, take precedence over the |
|
This property, if present, take precedence over the |
|
The CDIV feature supports an extension to the standard that allows an operator ruleset to be defined. Operator rules are evaluated before other rules. |
The other child elements of <operator-communication-diversion> are not read by the CDIV feature.
| |
The schema for the Operator part of the Communication Diversion (CDIV) services has been extended to support an optional ruleset. |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS or HLR in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS or SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR |
Session Output Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
DiversionCounter |
int |
The number of re-targeting attempts caused by the feature in one Session, whether immediate or due to a response |
HiLastReceivedIndex |
String |
The index for the history-info received in the initial |
HistoryInfoHeaders |
String [] |
The latest history-info headers sent or received |
LastDiversionType |
DiversionType (an enum) |
One of: |
EarlyMediaAnnouncementQueue |
List<Integer> |
Updated announcement queue with diversion announcement id if any |
Statistics
MMTelCDIV statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelCDIVFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelCDIVFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelCDIVFeatureMisconfigured |
the feature configuration could not be loaded |
MMTelCDIVFeatureProcessingSipResponse |
the feature is triggered on a SIP response |
MMTelCDIVFeatureProcessingSipRequest |
the feature is triggered on a SIP request |
MMTelCDIVFeatureLegManagerError |
a problem occurs while trying to access data from the SIP leg manager |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorProcessingSipRequest |
a problem occurs while trying to read or modify to a SIP request |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorProcessingSipResponse |
a problem occurs while trying to read or modify to a SIP response |
MMTelCDIVFeatureDiversionLoopDetected |
diversion is aborted due to a diversion loop being detected |
MMTelCDIVFeatureDiversionLimitExceeded |
diversion is aborted due to the diversion limit being hit |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCancelledInviteRequest |
the CDIV feature cancels an |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorCancellingInviteRequest |
a problem occurs while attempting to cancel an |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTerminatedByResponse |
CDIV is aborted by sending an error response on the originating leg |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTerminatedByRetargeting |
CDIV is aborted by attempting to divert to a fixed final destination |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorTerminatingByRetargeting |
diversion fails while trying to terminate by re-targeting |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerSet |
the feature sets a timer for CFNR |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerCancelled |
the feature cancels a timer for CFNR |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerFired |
the feature is triggered by a CFNR timer expiring |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorSettingTimer |
a problem occurs while trying to set a CFNR timer |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerSuppressedByResponseFromCSDomain |
timer is suppressed when parallel fork is done and the CS domain answers first |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDIVSuppressedByResponseFromCSDomain |
CDIV service is suppressed when parallel fork is done and the CS domain answers first |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCallerNotifiedOfDiversion |
the feature notify the caller the session is being diverted |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedToNotifyCallerOfDiversion |
the feature fails to notify the caller the session is being diverted |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFUSucceeded |
unconditional call forwarding is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFUFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute unconditional call forwarding |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNLSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user not being logged into IMS is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNLFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user not being logged into IMS |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user not replying is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user not replying |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFBSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user being busy is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFBFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user being busy |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRcSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user being unreachable is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRcFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user being unreachable |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDImmediateSucceeded |
call forwarding due to immediate call deflection is successful. |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDImmediateFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to immediate call deflection |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDAlertingSucceeded |
call forwarding due to call deflection during alerting is successful |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDAlertingFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to call deflection during alerting |
MMTelCDIVFeatureToHeaderChanged |
'To' header is set to diverted party or served user |
Behaviour
Condition Evaluation
Triggered conditions and non-triggered conditions are part of CDIV rule and condition evaluation.
-
Triggered conditions include:
-
Communication Forwarding on Busy user (CFB)
-
Communication Forwarding on No Reply (CFNR)
-
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc)
-
Communication Deflection (CD)
-
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in (CFNL)
-
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU)
-
| |
Triggered conditions are mutually exclusive, therefore if more than one is in a rule the rule will evaluate to false. |
-
Non-triggered conditions include:
-
Media Type
-
Validity.
-
| |
Non-triggered conditions can evaluate to true in any type of diversion.Triggered conditions can only evaluate to true at particular points of session processing. |
| Triggered condition name | Applicable point in session | XML condition element value from HSS |
|---|---|---|
|
Communication Forwarding on Busy user (CFB) |
|
|
|
Communication Forwarding on No Reply (CFNR) |
A 180 Ringing response followed by a |
|
|
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc) |
|
|
|
Communication Deflection (CD) |
|
Not configurable through XCAP |
|
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in (CFNL) |
Receipt of |
|
|
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU) |
Receipt of |
|
Media
Media is evaluated as part of condition evaluation. Therefore CFB can cause a re-targeting to different destinations if there are several diversion rules with busy and media conditions.
Media-only conditions can be used to immediately re-target INVITE requests matching media conditions.
An example where all sessions that contain both audio and video are diverted is as follows:
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
<media>audio</media>
</cp:conditions>
Each <media> element value is searched against all media descriptions in the INVITE request SDP. If all media conditions match, then the conditions block evaluates to true.
Validity
Validity provides the ability to filter a condition based on date comparisons. For example:
<cp:conditions>
<busy/>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>2015-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>2015-01-31T23:59:59</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
This conditions block will evaluate to true if the condition is evaluated during January 2015.
Request URI for a Re-targeted INVITE
The request URI is set to the SIP URI or tel URI where the communication is being diverted to.
This comes from the <target> sub-element of the <forward-to> element in a CDIV rule’s actions:
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
It may or may not have a target parameter, and always has a cause parameter and MMTel service type parameter.
Target Parameter
The request URI has a target parameter if and only if the re-targeting is due to a response, such as in the following cases:
-
busy
-
no-answer
-
deflection
-
not-reachable.
The target parameter is set to the request URI for the received initial INVITE, including all parameters. Any parameters of the original request URI are in escaped format. This is to ensure that the SIP message has valid syntax.
Conversely, if communication forwarding is due to Unconditional, or Not Logged In, then there is no target parameter in the request URI.
Cause Parameter
There is always a cause parameter for every re-targeted INVITE.
The cause-param parameter of the request URI is simple cause= appended with a “cause value”.
| Cause | Cause Value | Determination Rule |
|---|---|---|
Communication Forwarding on Busy |
486 |
|
Communication Forwarding on No Reply |
408 |
|
Communication Forwarding Unconditional |
302 |
|
Communication Deflection (immediate response) |
480 |
Immediate deflection: |
Communication Forwarding not logged in |
404 |
|
Communication Deflection during alerting |
487 |
deflection: 302 received after 180-RINGING is received |
Communication Forwarding Subscriber not Reachable |
503 |
|
MMTel Service Type Parameter
There is always a MMTel service type for every re-targeted INVITE.
The mmtel-service-type parameter of the request URI is simple mmtel-service-type=6 for CDIV.
181 Responses
A 181 notification is sent to the calling party in a CDIV scenario if the <notify-caller> element is set to true or if the element is missing from the condition. For example:
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
| |
A 181 notification will not be sent if the <notify-caller> element is set to false. |
Reveal Served User Identity to Caller
There is an optional flag that triggers TIR on 181 responses to the calling party.
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
<reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller>true</reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
Reveal Served User Identity to Diverted-To Party
There is an optional flag - reveal-identity-to-target - that determines whether the identity of the diverting party is revealed to the diverted-to party or not.
<cp:conditions/>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
<reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller>true</reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller>
<reveal-identity-to-target>false</reveal-identity-to-target>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
-
If reveal-identity-to-target is set to true, then the To header is the SIP identity of the diverting party.
-
If reveal-identity-to-target is set to false, then the To header is modified to the SIP identity of the diverted-to party.
-
If reveal-identity-to-target is omitted, the default is true
CDIV, OIR and Served User Identity
The OIR Feature also determines if the identity of the diverting party is revealed to the diverted-to party or not
-
If OIR is inactive for the diverting party, then the To header is the SIP identity of the diverting party.
-
If OIR is active for the diverting party, then the To header is modified to the SIP identity of the diverted-to party.
One Re-targeted INVITE
The MMTelCDIV feature will only ever re-target once. This is because MMTelCDIV is designed to execute on a public network. Private network derivations of this feature do not need to follow this rule.
As the feature re-targets once, it will insert one history-info element into one INVITE to represent a re-targeting.
The only case the feature inserts more than one element into history-info is in the case where no history-info or an empty history-info was received in the initial INVITE.
CDIV Suppression
There is a case where the CDIV feature needs to be suppressed even though it may be active. This is needed on an MT call, when the SCC-AS diverts a call to a CS network as the MSC will have its own CDIV services. This means that, when the call is diverted to CS, the MMTel-AS does not divert any calls, and cancels any remaining no-reply timers. If the SCC-AS utilizes parallel-routing (i.e. forwards call to both PS and CS domain), the MMTel-AS will respond in the same way.
CDIV suppression is achieved by analysing the provisional responses for the given call. These responses contain the OC-Terminating-Domain custom header, which indicates what network the call is diverted to. Because the no-reply timers are typically set upon provisional responses (i.e. 18X responses), it is here that CDIV suppression is engaged/disengaged.
The presence of CDIV suppression is configurable. Setting the SuppressForCSTerminatingDomain attribute of the MmtelCDIVConfigProfile profile to false will disable the aforementioned CDIV suppression. Its default value is true, which leaves CDIV suppression enabled.
CDIV Default Target URI
The CDIV feature can optionally use a default URI for re-targeting requests. The default URI is stored in the DefaultTargetURI field as a String. This default URI is applied when there is a re-targeting rule and no URI to forward to. The default re-targeting URI can be enabled using the DefaultTargetEnabled boolean variable.
CDIV No Reply Timer
When CDIV sees a 180 Ringing response, it will check to see if there are any rules relevant to Communication Forwarding on No Reply (CFNR). If there is at least one relevant rule, CDIV sets a CDIV No Reply Timer. The duration of the timer is:
-
the
<communication-forwarding-on-no-reply-timer>value in the<operator-communication-diversion>section of the MMTel-Services XML data, if present -
… or the Network Operator Data
NoReplyTimeoutfield
Diversion Limit
The CDIV feature enforces a limit on the maximum number of times a call may be diverted, this limit is:
-
the
<total-number-of-diversions-for-each-communication>value in the<operator-communication-diversion>section of the MMTel-Services XML data, if present -
… or the
MaxDiversionCountfield in the feature’s network operator data.
Before a call is diverted, this limit is checked against the number of diversions that have already occurred to ensure the new diversion can go ahead.
When the diversion limit is exceeded there are a number of things that can happen based on these Network Operator Data fields: NoRetargetURI, MaxDiversionAction, and MaxDiversionFixedDestination.
First, the feature will check the value of the next target URI against the list of URI’s in the NoRetargetURI field. This field contains a comma separated list of known URI’s that will never themselves trigger additional re-targeting. If the next target URI is present in this list, the feature considers it "safe" to allow the diversion to take place and the diversion limit will not be immediately enforced.
In the event that the next target URI is not in the NoRetargetURI list, the feature will execute its max diversion behaviour. There are two possible outcomes, based on the value of the MaxDiversionAction field.
-
If the field is set to
REJECT, then the feature will reject the INVITE request with a 486 response in the event that the last re-target was triggered by CFB (Call Forward Busy), or a 480 response in all other cases. -
If the field is set to
DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION, then the feature will attempt to re-target the call to the URI given in theMaxDiversionFixedDestinationfield.
If the MaxDiversionAction field is set to DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION, but the MaxDiversionFixedDestination field does not contain a valid URI, then the feature will reject the INVITE as if MaxDiversionAction field had been set to REJECT.
Choosing the CDIV Rule to Apply
The <communication-diversion> and <operator-communication-diversion> sections of the MMTel-Services XML document can contain diversion rules. A rule may be relevant for a diversion scenario (e.g CFB) and it may be applicable to a particular communication session (i.e its condition evaluates to true).
The CDIV feature:
-
finds all rules that are appropriate for a diversion scenario (e.g CFU)
-
evaluates the operator rules first
-
If no operator rule was applied, then evaluate subscriber rules
Consider the following example, where there are two rules relevant for CFU.
<complete-communication-diversion>
<communication-diversion active="true">
<!-- ... -->
<cp:ruleset>
<cp:rule id="Audio">
<cp:conditions>
<media>audio</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:bob@audio.somewhere.com</target>
<notify-caller>false</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
</communication-diversion>
<operator-communication-diversion authorized="true">
<!-- ... -->
<cp:ruleset>
<cp:rule id="Video">
<cp:conditions>
<media>video</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:bob@video.somewhere.com</target>
<notify-caller>false</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
</operator-communication-diversion>
</complete-communication-diversion>The subscriber rule will cause audio calls to be forwarded to sip:bob@audio.somewhere.com. The operator rule will cause video calls to be forwarded to sip:bob@video.somewhere.com.
case #1 Alice makes a Video call to bob.
-
Search operator rules and evaluate rule 'Video', which matches, so forward the call.
---alice---[Video]--->bob----->(rule id="Video")---->bob@video.somewhere.com
case #2 Alice makes an Audio call to bob.
-
Search operator rules and evaluate rule 'Video', which does not match
-
Search subscriber rules and evaluate rule 'Audio`, which matches, so forward the call.
---alice---[Audio]--->bob--+-->(rule id="Video") X
|
+-->(rule id="Audio")---->bob@audio.somewhere.com
Example CDIV Rules
For clarity, here are some example CDIV rules.
They can be pasted directly into the Transparent Data editor in REM.
CDIV Unconditional
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="unconditional">
<cp:conditions>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>false</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
CDIV Busy
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="busy">
<cp:conditions>
<busy/>
<media>video</media>
<media>audio</media>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
CDIV Not Reachable
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="not-reachable">
<cp:conditions>
<not-reachable/>
<cp:validity>
<cp:from>2015-01-01T00:00:00</cp:from>
<cp:until>2015-01-31T23:59:59</cp:until>
</cp:validity>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
CDIV No Reply
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="no-answer">
<cp:conditions>
<no-answer/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
CDIV Not Registered
<cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
<cp:rule id="not-registered">
<cp:conditions>
<not-registered/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<forward-to>
<target>sip:6505550201@example.com</target>
<notify-caller>true</notify-caller>
</forward-to>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
MMTelCW
The Communication Waiting (CW) service lets a UE be informed that no resources are available for an incoming communication . The user then has the choice of accepting, rejecting, or ignoring the incoming communication (as per basic communication procedures).
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTEL |
Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes, Active flag stored in the HSS |
Stateless w/FSM in session state |
POJO but with much stateful behaviour implemented by storing an FSM instance into session state |
Raises session state flags to enable interaction with announcement playing (or other notification) features |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-communication-waiting module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-cw-module opencloud#mmtel-communication-waiting#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-communication-waiting |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-cw-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-cw |
Contains the feature itself. |
Description
When a call arrives towards the destination user and the user is already involved in a call, the user is alerted and has a choice of either accepting, ignoring, or rejecting the communication. For example: the destination user is already on a call; notification for a new call is delivered; and the user can decide to put the existing call on hold or reject the new call.
A notification may be offered to the destination user if the network or UE has determined the Approaching Busy condition. Approaching Busy can be in the forms of:
-
Approaching Network Determined User Busy (A-NDUB) — the network (including the MMTEL AS) determines that the user is Approaching Busy, or
-
Approaching User Determined User Busy (A-UDUB) — the user equipment determines that the user is Approaching Busy.
This feature targets the IR.92 scope for Communication Waiting. Therefore, support for A-UDUB is included, and A-NDUB is not.
The calling user may be offered an in-band (audio) announcement, subject to network configuration.
Communication Waiting is a terminating feature.
User Determined User Busy (UDUB)
Communication arrived at the UE, and the UE has determined the Approaching User Busy condition, for any reason. For example, the user is on a call, and maximum number of waiting communications has been reached. The UE shall reject communication with an appropriate SIP response.
Approaching User Determined User Busy (A-UDUB)
Communication arrived at the UE, and the UE has determined Approaching User Busy condition, for any reason. For example, the user is on a call, and maximum number of waiting communications has not been reached. The UE shall reject communication with an appropriate SIP response.
Network data
Network operator data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile with a profile table name of: MMTelCWConfigProfileTable.
| Variable Name | Type | Constraint | Default | Default Value Interpretation | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CWTimerCW |
Integer |
0, 30..120 |
0 |
Timer doesn’t apply |
Time in seconds for Communication Waiting timer |
CWAnnouncementID |
Integer |
0 |
CW calling user not notified |
ID for an announcement to be played if Calling User Notifications are enabled |
|
CWCallingUserNotification |
Boolean |
False |
Do not notify the calling User |
Session input variables
| Field | Type | Default | Interpretation | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Complex |
MMTelCWServiceData.false |
True |
If feature should make any changes to signalling |
|
CWCallingUserNotification |
Boolean |
false |
True |
If calling user to receive announcement |
Session output variables
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
AnnouncementID |
Int |
The ID of the announcement to be played, or zero if no announcement if the feature did not request an announcement |
CWAnnouncement |
Boolean |
If true, the MMTelCW feature has indicated that an announcement should be played. The AnnouncementID field will also be set if this flag is set. Otherwise no announcement should be played |
RanCW |
Boolean |
Signals to other features that CW ran on this session. |
If the calling user should be notified of an Approaching UDUB condition, the Communication Waiting feature sets the CWAnnouncement session state flag indicating that an announcement should be played. It also sets the AnnouncementID field, indicating that an announcement should be played.
Statistics
MMTelCW statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelCWFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelCWFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelCWFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelCWFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelCWFeatureMisconfigured |
a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerError |
there is an error while trying to set a timer |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerCancelled |
a timer is cancelled by the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerSet |
a timer is set by the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP response |
MMTelCWFeatureProcessingTimerEvent |
the feature is invoked on a timer firing |
MMTelCWFeatureOutgoingMessageContentChanged |
the feature changes the contents of an outgoing SIP message |
MMTelCWFeatureReattemptedCallSetup |
the feature requests that call set up be reattempted |
MMTelCWFeatureTriggered180AUDUBResponse |
the feature requests a 180 response be sent back to the original caller, indicating call waiting service |
MMTelCWFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature triggers an announcement to be played |
MMTelCWFeatureCancelledInviteRequest |
the feature cancels an outgoing |
MMTelCWFeatureFinalResponseChangedTo486 |
the feature changes a SIP response status code to |
MMTelCWFeatureFinalResponseChangedTo480 |
the feature changes a SIP response status code to |
Feature interactions
When handling responses, CDIV No Answer and CDIV Busy must run after CW. CW may return a 480 (no answer condition) or 486 response (busy).
Behaviour
User equipment can signal an Approaching User Determined User Busy (A-UDUB) by placing certain headers in responses passed back.
The MMTelCW feature looks for these inside responses:
-
In the case of a
180-RINGINGresponse to an initialINVITE, the response contains anAlert-Infoheader with the header’s value set to<urn:alert:service:call-waiting>if the UE wishes to communication A-UDUB. -
In the case of a
486-BUSYresponse to an initialINVITE, the response contains a370warning header with the value set toinsufficient bandwidthif the UE wishes to communicate A-UDUB.
As a simplification, consider Communication Waiting where there is no Announcement to the A-party. In this case, there are two main “modes of operation” for Communication Waiting:
-
a pure routing B2BUA that largely passes requests+responses between SIP dialogs
-
a routing B2BUA that initiates new transactions, sometimes acting like a UAC.
The differences in behaviour are best explained with a few key flows. In these flows we simplify the IMS signalling by showing three nodes, UE-A, the MMTEL-AS (AS), and UE-B.
180 Ringing Response handling
486 Busy Response handling
486 response — due to A-UDUB
The 486 response indicates UDUB. The feature sends a 180-RINGING upstream indicating approaching-UDUB.
The AS then sends a new INVITE to UE-B. This new INVITE includes:
-
a MIME body according to the
<communication-waiting-indication>element contained in the<ims-cw>root element -
a content-type of
application/vnd.3gpp.cw+xml.
An example is:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ims-cw xmlns="urn:3gpp:ns:cw:1.0">
<communication-waiting-indication/>
</ims-cw>
The feature also starts a CW timer.
The following flow illustrates the signalling. In this example, the new INVITE is rejected.
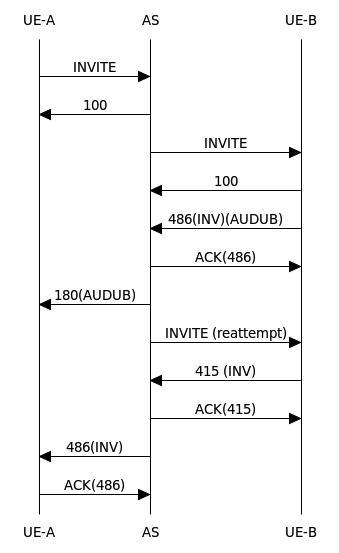
Notifying the CallingParty of AUDUB via an in-band announcement
According to session output variables, the feature will set two session state fields to indicate that an announcement should be played.
The corresponding feature execution script can be written two ways:
run MMTelCW run SIPPlayAnnouncement
This works because of a subtlety in SipPlayAnnouncement, it checks if the AnnouncementID field is not equal to zero.
However, the following is clearer and recommended:
run MMTelCW
if (CWAnnouncement) {
run SIPPlayAnnouncement
}
MMTelECT
The Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) service enables a party involved in a communication to transfer their role in that communication to a third party .
For a general overview of the service see Explicit Communication Transfer.
Consultative ECT using the 3pcc procedure does not support reusing the existing leg between the AS and the transfer-target, instead a new leg is created to link to the transferee.
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Originating and/or Terminating |
|
Yes |
Yes — Transferor authorization is stored in the HSS |
Stateful |
POJO |
Implications on Charging for transferred communications |
Cassandra storage
The ECT feature utilises the Cassandra database to store session information for transfers
Data Schema
The Cassandra table for ECT exists in a keyspace named opencloud_mmtel_ect
-
For a production environment, the keyspace can be created such that it is replicated. A sample command for creating this keyspace is:
CREATE KEYSPACE opencloud_mmtel_ect WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy' ,'replication_factor' : 3 };-
For testing purposes, replication may not be necessary. A sample CQL command for creating such a keyspace is:
CREATE KEYSPACE opencloud_mmtel_ect WITH REPLICATION={'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 1};Once the keyspace is created, the required table can be created. The following CQL statements provides the structure of the required table.
USE opencloud_mmtel_ect;
CREATE TABLE ExplicitCommunicationTransfer (
ect_id text, // The generated ECT identifier
target_uri text, // URI of the transfer target
transferor_p_asserted_id text, // P-Asserted-Identity of transferor
transfer_timeout int, // Value of REFER request's Expired header
PRIMARY KEY (ect_id)
);Session Input Variables
| Variable Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Complex |
Read from the HSS in SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS |
|
TransfereeLegName |
String |
The |
TransferorLegName |
String |
The |
ReferNotAllowedByTransferee |
boolean |
True if the Transferee is not allowed to send a REFER request. |
EctSessionId |
String |
The unique ID of the ECT session. |
TransferorIdentity |
String |
The ID of the Transferor as found in the |
TransfereeCallID |
String |
The |
TransfereeFromTag |
String |
The |
TransfereeToTag |
String |
The |
ExpiresTime |
int |
The time indicated in the |
TransferTargetUri |
String |
The URI found in the |
TransfereeUri |
String |
The URI found in the |
TransferorReferSequenceNumber |
long |
The sequence number found in the |
ReleasedTransferorLeg |
boolean |
True if the Transferor’s |
NoSubscriptionForRefer |
boolean |
True if the REFER request contains the |
NoAnswerTimerId |
TimerID |
The ID of the Timer used to guard against unanswered requests. |
Session Output Variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
TransfereeLegName |
String |
The |
TransferorLegName |
String |
The |
TransferorReferSequenceNumber |
long |
The sequence number found in the |
TransfereeUri |
String |
The URI found in the |
NoSubscriptionForRefer |
boolean |
True if the REFER request contains the |
TransfereeCallID |
String |
The |
TransfereeFromTag |
String |
The |
TransfereeToTag |
String |
The |
TransferorIdentity |
String |
The ID of the Transferor as found in the |
ExpiresTime |
int |
The time indicated in the |
TransferTargetUri |
String |
The URI found in the |
EctSessionId |
String |
The unique ID of the ECT session. |
ReleasedTransferorLeg |
boolean |
True if the Transferor’s |
NoAnswerTimerId |
TimerID |
The ID of the Timer used to guard against unanswered requests. |
RanEct |
boolean |
True if the ECT feature was invoked. |
ThirdPartyCallInitialisationRequested |
boolean |
True if Third-Party Call Control (3PCC) was invoked. |
ECTOngoing |
boolean |
True if an ECT operation is still ongoing. |
Behaviour
The ECT feature acts on INVITE, REFER, and NOTIFY requests and their responses. It also acts on service timers.
REFER Path
The feature creates an identifier for the transfer session by concatenating the prefix configured in Network Operator Data along with the from-tag, call-id, and to-tag of the REFER request. It then extracts the URI of the transfer-target from the Refer-To header, the P-Asserted-Identity and the value of the Expires header field. This information is stored in the database against the generated ID to be used when the transferee sends an INVITE request to the generated URI.
The feature then manipulates the outgoing REFER request by replacing the Refer-To header address with the generated URI and sets the Referred-By header to the P-Asserted-Identity in the request.
If ID privacy was requested the feature then adds a Privacy header with priv-value 'user'.
INVITE Path
The feature checks if the Request URI of the INVITE request could have been generated by the REFER handling behaviour of the ECT feature and if so attempts to query the database for the ECT session information. If no record can be found in the database table matching the Request URI the request is forwarded to the recipient without modification. If a record is found, the feature replaces the Request-URI of the downstream INVITE request with the URI of the transfer target.
If the retrieved Request-URI contains a 'Replaces' parameter the feature adds a 'Replaces' header with the same value to the INVITE request. If the Request-URI contains a Require header field parameter with a 'Replaces' token the feature adds a Require header field parameter with a 'Replaces' token to the INVITE request. If the downstream INVITE message does not contain a Referred-By header containing the transferor’s P-Asserted-Identity then the feature adds one.
NOTIFY Path
If the feature is triggered by a NOTIFY, and that NOTIFY is for a SIP 400 (Bad Request), the feature will invoke the 3PCC procedures. Otherwise, the NOTIFY is not acted upon.
Third Party Call Control
Scenarios
Under certain conditions where the standard signalling flow is impossible the feature invokes the Third Party Call Control (3pcc) procedures. These conditions are described in the following tables.
Terminating party sends a REFER request
| Content of the Allow header in the initial INVITE request | Actions of the feature on the REFER request | Actions of the feature on the initial INVITE request |
|---|---|---|
|
INVITE request with an Allow header with no REFER token |
Invoke the 3pcc procedures directly |
Add a REFER token to the allow header |
|
INVITE request with an Allow header including a REFER token |
Forward the REFER request and if a 403 (Forbidden) or 501 (Not Implemented) response is received invoke the 3pcc procedure |
No actions |
|
INVITE request without an Allow header |
Forward the REFER request and if a 403 (Forbidden) or 501 (Not Implemented) response is received invoke the 3pcc procedure |
No actions |
Originating party sends a REFER request
| Content of the Allow header in the 200 (OK) response to the initial INVITE request | Actions of the feature on the REFER request | Actions of the feature on the 200 (OK) response to the initial INVITE request |
|---|---|---|
|
200 (OK) response with an Allow header with no REFER token |
Invoke the 3pcc procedures directly |
Add a REFER token to the allow header |
|
200 (OK) response with an Allow header including a REFER token |
Forward the REFER request and if a 403 (Forbidden) or 501 (Not Implemented) response is received invoke the 3pcc procedure |
No actions |
|
200 (OK) response without an Allow header |
Forward the REFER request and if a 403 (Forbidden) or 501 (Not Implemented) response is received invoke the 3pcc procedure |
No actions |
Procedure
If the 3pcc procedures were triggered by a REFER request or a 403 (Forbidden) or 501 (Not Implemented) response the feature intercepts the message before it is forwarded to the recipient and instead responds to the REFER request by sending a 202 (Accepted). It then creates and sends a hold reINVITE request according to the procedures specified in 3GPP TS 24.610 subclause 4.5.2.1.
If however the 3pcc procedures were triggered by a NOTIFY request with a 420 (Bad Extension) status line the feature responds to the NOTIFY request with a 200 (OK) message and removes the message from the outgoing queue before sending the hold request.
Upon receipt of a success response to the hold request the feature then creates a new INVITE request to the transfer-target, and places this on the outgoing message queue of a new leg. The feature then creates a re-INVITE request to the transferee. If the Refer-To URI in the REFER request contained an Expires header, the feature starts a service timer set to its value. It then creates the re-INVITE request with same Call-ID, from-tag and to-tag as the existing dialogue between the transferee and the transferor, but replaces the address field of the From header with the address of the transfer-target. The feature then places the re-INVITE request on the outgoing message queue of the leg to the transferee and unlinks this leg from the leg to the transferor. MMTelECT then handles the call setup and SDP negotiation between the transferee and transfer-target.
MMTelECT continues to monitor the legs to the transferee and the transfer-target. When the INVITE to the transfer-target is acknowledged with a 200 (OK) response the feature sends a NOTIFY request with a 100 (trying) status line on the original leg to the transferor and when the re-INVITE to the transferee is acknowledged with a 200 (OK) the feature sends a NOTIFY request with a 200 (OK) status line towards the transferor and releases the leg.
If the Expires Service Timer fires before the transfer-target responds the feature sends a CANCEL and closes the partial dialogue to the transfer-target, then sends a NOTIFY request to the transferor with Subscription-State terminated and relinks the transferor and transferee legs resuming their original dialogue.
If the transfer-target responds to the INVITE request with a failure status code, the feature sends a NOTIFY request to the transferor with the Subcription-State header set to terminated and resumes the original dialogue between the transferor and transferee.
The transferor can request to not receive NOTIFY messages regarding the transfer progress by including a Refer-Sub header with value 'false' in the REFER request. The transferor can also release its leg at any time during the transfer attempt, in which case the feature will release the leg to the transferee and end the call in the event of a transfer failure.
Response Timer
The platform operator can configure a response timer for the feature which will trigger if the feature did not receive a response to a previously sent request within the configured period.
Scenarios where the response timer may be triggered:
-
The transferee did not respond to a REFER request — Respond to the REFER request with a 603 (Decline) and send a REFER request with a cancel URI parameter in the Refer-To address
-
The transfer-target did not respond to the INVITE request when executing 3pcc procedures — Release the newly-created leg to the transfer-target and attempt to resume the dialogue between the transferor and transferee. If the transferor has left the call release the leg to the transferee.
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-explicit-communication-transfer module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-ect-module opencloud#mmtel-explicit-communication-transfer#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-explicit-communication-transfer |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-ect-feature |
The feature itself. |
mmtel-ect-profile |
The profile for this feature. |
Statistics
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ReferReceivedFromServedUser |
a REFER request has been received from the served user |
ReferDeclined |
the feature has sent responded to a REFER request with 603 (Decline) |
ReferSuccessful |
the transferee has responded to a processed REFER request with a 202 Accepted) |
ReferProcessedAndForwarded |
a REFER request has been received from the transferor, appropriately modified and sent to the transferee |
EctInviteReceived |
an INVITE request has been received from the transferor as a result of a previous REFER request |
EctInviteProcessedAndForwarded |
an ECT INVITE request has been received by the transferee, appropriately modified and sent to the transfer-target |
ThirdPartyCallControlProceduresInvoked |
the Third Party Call Control (3pcc) transfer procedures have been invoked |
ThirdPartyCallControlProceduresFailed |
the Third Party Call Control (3pcc) transfer procedures did not result in a successful dialogue between the transferee and transfer-target |
OriginalCallResumed |
the original dialogue between the transferee and the transferor has been resumed if the 3pcc procedures failed |
CassandraInsertSucceeded |
ECT session information has been successfully inserted into the Cassandra DB |
CassandraInsertFailed |
an error occurred attempting to insert ECT session information into the Cassandra DB |
CassandraQuerySucceeded |
ECT session information has been successfully retrieved from the Cassandra DB |
CassandraQueryFailed |
an error occurred attempting to retrieve ECT session information from the Cassandra DB |
DeletedCassandraRow |
REFER request was cancelled by user, and so the Cassandra ECT record was deleted. |
StoppedHandlingAndAllowedB2BUA |
an INVITE request with a Request URI matching the ECT URI pattern was received and forwarded without modification |
TransferSuccessful |
a 200 (OK) was received from the transfer-target as a result of the ECT procedures |
ErrorOccurredDuringExecution |
an error occurred attempting to execute the feature |
NoAnswerTimerFired |
The feature timed-out waiting for an answer from a sent request. |
Scope
Network Operator Data
Network configuration is stored in the JSLEE profile table named MMTelECTConfigProfileTable.
The data is scoped on Sentinel Selection Key. The fields present in the JSLEE profile table are used to configure the behaviour of the Explicit Communication Transfer feature.
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
integer |
|
Determines how long ECT session information should remain in the Cassandra DB before being cleared. |
|
boolean |
|
Determines if a transferor is authorized for ECT if no provisioning information is available. |
|
String |
|
The address of the Interrogating-CSCF. |
|
boolean |
|
Determines if an |
|
boolean |
|
Determines if an |
|
String |
|
Determines the prefix appended to generated URIs to identify them as relating to ECT session identifiers. |
|
integer |
|
Milliseconds to wait for a response to a request sent by this feature. |
MMTelHold
The Communication Hold supplementary service lets a user suspend reception of the media stream(s) of an established IP multimedia session, and resume the media stream(s) at a later time .
3GPP specification
3GPP define a specification for the Communication Hold supplementary service running in the IMS, in 24.610.
CommunicationHold feature
OpenCloud’s CommunicationHold feature implements the capability of holding and resuming a session, according to the 3GPP spec.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTEL |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
FSM state |
POJO with FSM encoded into Session State |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-communication-hold module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-hold-module opencloud#mmtel-communication-hold#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-communication-hold |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
mmtel-hold-profile |
Contains the profile specification for the feature configuration profile table. |
mmtel-hold |
Contains the feature itself. |
In scope
-
Hold/resume an established session
-
Adjusting bandwidth of responses to the Holding
INVITEtransaction -
Interaction with
MidCallPlayAnnouncement
Network operator data
Network operator data indicates:
-
whether or not bandwidth should be adjusted
-
what we should set each bandwidth attribute to
-
whether or not an announcement should be played to the held party.
Network operator data is in a JSLEE configuration profile table: MMTelHoldConfigProfileTable.
This data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
Each configuration has its own profile in this profile table.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
CHoldAdjustBandwidth |
Boolean |
Indicates whether or not (true/false) Communication Hold should lower or increase the bandwidth of responses during sessions being Held and Resumed. |
CHoldB_AS |
int |
The value of this attribute corresponds to the value for the |
CHoldB_RR |
int |
The value of this attribute corresponds to the value for the |
CHoldB_RS |
int |
The value of this attribute corresponds to the value for the |
CHoldPlayAnnouncement |
Boolean |
Indicates whether or not (true/false) Communication Hold requests an Announcement to be played when a session is held. |
CHoldAnnouncementID |
int |
The announcement ID to be used when an announcement is requested |
Defaults for network operator data
| Attribute name | Default Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
CHoldAdjustBandwidth |
false |
Hold does not adjust bandwidth |
CHoldB_AS |
0 (zero) |
If |
CHoldB_RR |
800 |
If |
CHoldB_RS |
800 |
If |
CHoldPlayAnnouncement |
false |
Hold does not request an announcement is played |
CHoldAnnouncementID |
0 (zero) |
The |
Session output variables
| Attribute Name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RequestingLegCSeq |
string |
|
RespondingLegCSeq |
string |
|
AnnouncementID |
int |
|
MidCallAnnouncementPlayedParty |
An enum with two fields: |
|
RanHOLD |
Boolean |
Signals to other features that HOLD ran on this session. |
Statistics
MMTelHOLD statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelHoldFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelHoldFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelHoldFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelHoldFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelHoldFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelHoldFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP request |
MMTelHoldFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP response |
MMTelHoldFeatureSipDataAccessError |
an error occurs while trying to access a SIP leg or message |
MMTelHoldFeatureSipMessageSDPUpdated |
the feature changes the SDP content in a SIP message |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedHoldRequest |
the feature determines that an incoming message is a hold request |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedResumeRequest |
the feature determines that an incoming message is a resume request |
MMTelHoldFeatureSessionBandwidthAdjusted |
any bandwidth information is adjusted in an SDP body |
MMTelHoldFeatureMediaStreamBandwidthAdjusted |
bandwidth information is adjusted on a SDP media stream description |
MMTelHoldFeatureMissingDataWarningTriggered |
an operation on SDP data fails due to the data being unavailable |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedMalformedMessage |
the feature determines that an incoming message is mal formed |
MMTelHoldFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature determines triggers the play announcement |
Terminology
The UE invoking Hold/Resume is referred to as the invoking party.
The AS of this UE is referred to as the AS of the invoking party.
The UE that is being held/resumed is referred to as the receiving party.
The AS of this UE is referred to as the AS of the receiving party.
The invoking party makes an SDP offer. The receiving party responds with a SDP answer or rejects the offer with an error response. For each party, the SDP offer and corresponding answer from the other party need to be stored by the AS. The AS (B2BUA) refers to these as :
-
In the B2BUA instance of the invoking party:
-
local SDP offer from the invoking party
-
remote SDP answer from the receiving party
-
-
In the B2BUA instance of the receiving party:
-
remote SDP offer from the invoking party
-
local SDP answer from the receiving party.
-
THe SDP offer and answer are accompanied by sdp-session-id and sdp-session-version. Specifications mandate these parameters to change when the SDP changes.
Behaviour
General behaviour for the MMTEL AS for the invoking UE:
-
detecting if a Hold or Resume transaction is taking place:
-
The session-id or session-version of the SDP offer for the local or remote party has changed and follows the
HOLDrequest rules:
(sendrecv→sendonly,recvonly→inactive) -
The session-id or session-version of the SDP answer for the local or remote party has changed and follows the
HOLDrequest rules:
(sendrecv→recvonly,sendonly→inactive)
-
-
adjusting SDP bandwidth parameters in an offer and answer to reflect increased or reduced bandwidth demand.
How these simple goals are achieved is the subject of the rest of the behaviour description.
B2BUA instances and invoking UE
When the call is first set up, the AS of each party stores local and remote SDP offers and answers. That is, the AS of calling party that makes the SDP offer stores the current set of local SDP offers and remote SDP answers (see Behaviour).
When the originating party is the invoking party (that is, the originating party performs HOLD) then the originating B2BUA instance is active and the terminating B2BUA instance is passive for this request and its associated response.
When the terminating party is the invoking party (that is, the terminating party performs HOLD) then the terminating B2BUA instance is active and the originating B2BUA instance is passive for this request and its associated response.
Request processing
If the request is not a Re-INVITE, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
The feature determines if it is active or passive for a particular request.
If it is passive, it forwards the request upstream.
If it is active, it classifies the following:
-
Session Refreshor not.-
If
Session Refresh, the feature finishes execution. -
Otherwise, it classifies if the
Re-INVITEshould be anOpor aNo-op.-
If
No-Op, it forwards the request. -
Otherwise, if
Op, it sets the session state fieldHoldResumeResponseIsOptoTRUE; then forwards the request.
-
-
Distinguishing hold requests from session refreshes
The AS of the invoking user stores the SDP session ID and version of the last successful offer or answer received from the invoking user. If a Re-INVITE received from the invoking user has both parameters unchanged, the Re-INVITE is a session audit (that is, session timer refresh). If either the session ID or version has changed, the SDP of the request must be inspected.
If the SDP session ID and session version are the same, then the Re-INVITE request represents a session refresh.
In case of a session refresh, both the originating and terminating B2BUA instance are passive.
Behaviour if the request is a session refresh
The feature does not alter any state, and finishes execution.
Hold request Op or No-op in the context of no announcements
Hold requests may be treated as an Op (short for Operation) or a No-op (short for No-Operation).
-
If a request is classified as a
No-oprequest, then the request is passed through as is, and its associated response is passed through as is. -
If a request is classified as an
Oprequest, then the response’s bandwidth may be adjusted before being passed to the invoking UE.
-
If the B2BUA instance is
passivefor a given request, then the request is always classified as aNo-Op. -
If the B2BUA instance is
activefor a given request, then the request will be classified as either aNo-Opor anOp.
If all of the streams within a request are treated as Stream No-Op, then the request is treated as a No-op request.
The following table shows how each stream within a request is treated as a No-Op or as an Op.
Most |normal case tables are taken from actions at the invoking UE 4.5.2.1
| UE intention | Current Stream State | Requested State for Stream | Stream Op or Stream No-Op | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hold a media stream |
|
UE1 sends offer |
|
normal case for Hold where the session was fully active in both directions |
|
Hold a media stream |
|
UE2 sends offer |
|
normal case where your UE got put on hold and you want to put the other on hold |
|
Resume a media stream |
|
UE1 sends offer |
|
normal case where both UEs had held each other, and one UE wants to resume |
|
Resume a media stream |
|
UE2 offers sendrecv, UE1 response with |
|
normal case where stream is held by one UE, and it wants to be resumed |
|
Hold all media streams using session-level direction attribute in SDP |
media streams are |
UE1 sends SDP where session-level direction attribute is set (with new session version) with offer of |
|
normal case where all streams are to be held, and some are |
|
Hold all media streams using media-level direction attribute in SDP |
at least one of the sessions media streams are in |
UE1 sends SDP with N direction attributes set to |
|
normal case where all streams are to be held, and some are single SDP offer can be sent combining this row and the next row |
|
Hold all media streams using media-level direction attribute in SDP |
at least one of the sessions media streams are in |
invoking UE sends SDP with M direction attributes (1 per media stream that is set to |
|
normal case where all streams are to be held, and some are in single SDP offer can be send combining this row and the previous row |
|
Resume all media streams using session-level direction attribute in SDP |
media streams are in |
invoking UE sends SDP offer where session-level direction attribute is |
|
normal resume-all case where media was inactive |
|
Resume all media streams using session-level direction attribute in SDP |
media streams are in |
invoking UE sends SDP where session-level direction attribute is |
|
normal resume-all case where session was held in one direction only, and the held UE wants to resume |
|
Resume all, using Media level SDP |
several possible states, one for each media stream; also similar to Hold all where there are different streams in different states |
similar to the hold all cases, except the offer is to resume; that is, the media attributes are set to |
|
|
Response processing
If the response is not a response to a Re-INVITE, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
When processing a response, the feature detects if it is active or passive for the response.
-
Read the session state field
HoldResumeResponseIsOp. -
If
TRUE, process the response in active manner-
If the response is a final response (a 2xx or 4xx. response) set the session state field
HoldResumeResponseIsOptoFALSE.
-
-
If
FALSE, process the response in passive manner.
Passive processing of response
When processing the response (SDP answer) in a passive manner, the feature forwards the response without modifying it.
Active processing of response
If the Network Data’s AdjustBandwidth attribute is set to False, the feature then finishes execution without modifying any state.
Otherwise the following steps are then performed:
-
walks through each media stream in the answer, that is
held -
checks to see if the media stream is marked as
recvonly, and if so (as a network option) performs the following on eachheldmedia stream:-
lowers the bandwidth of the invoking UE (the UE that sent the SDP offer) to a small value, by setting the
b=AS:parameter (for example, settingb=AS:0).
-
The b=RR: and b=RS: parameters are set to values large enough to enable continuation of the RTCP flow; for example, b=RR:800 and b=RS:800.
The values to be used for b=AS:, b=RR:, and b=RS: parameters are found in the network configuration’s B-AS, B-RR, and B-RS attributes respectively.
The adjusted response is then forwarded onwards.
Background on SIP Sentinel and SDP negotiation
Sentinel stores the current set of SDP offers and answers along with the sdp-session-id and sdp-session-version for the offers and answers (this is accessible through the Leg API). When a SIP dialog is set up (whether early or confirmed) the set of (local|remote)(offer, sdp-session-id, sdp-session-version) and (local|remote)(answer, sdp-session-id, sdp-session-version) are recorded.
When SDP is updated by means of n UPDATE or Re-INVITE transaction, the session-id and session-version will change. If the session-id and session-version remain unchanged ,this indicates the media is unchanged (this is typically a session refresh).
While a transaction is in progress, the current SDP offer and answer is available in the “latest” SDP pair.
Upon successful SIP transaction completion, the latest SDP offer and answer are copied into the “committed” set.
Upon transaction failure, the committed set is not modified.
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation
The MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation feature handles the finalisation of charging when a call is answered over WiFi.
What is MMTel WiFi Charging Finalisation?
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation interacts with the T-ADS features in the Sentinel VoLTE SCC AS. It looks for a header that those features attach to responses to the initial INVITE in order to determine if a call has been answered over a WiFi network. If that is the case, it finalises charging.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTEL |
Originating and Terminating |
SipAccess_PartyResponse |
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-wifi-charging-finalisation module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-wcf-module opencloud#mmtel-wifi-charging-finalisation#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes a single module:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
mmtel-wifi-charging-finalisation |
Contains all of the code for this feature. |
Session Input Variables
| Attribute | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
CallType (enum) |
Set by the DetermineCallType feature |
ChargeMode |
ChargeMode (enum) |
Set by the DetermineChargeMode feature |
Session Output Variables
| Attribute | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MonitorCallOnly |
boolean |
The feature will set this to |
TerminatingDomain |
String |
The feature will set this to the value of OC-Terminating-Domain header of any 200 response to the original INVITE |
Statistics
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → [volte.sentinel.sip service name] → [volte.sentinel.sip SBB name] → feature.MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation
Statistic |
Increments when… |
Started |
The feature is started. |
OCTerminatingDomainHeaderStripped |
An OC-Terminating-Domain header is found on an outgoing message and removed. |
ChargingInstanceFinalised |
A non-finalised reservation charging instance is found and finalised. |
Received2xxForOriginalInvite |
A SIP 2xx response for the initial INVITE is received by the feature. |
TerminatingDomainIsWifi |
The feature determines that terminating access is over WiFi. |
FailedToStart |
Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
A non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
A fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
The feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
Behaviour
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation has simple behaviour and always executes in the same way.
Basic Checks
After being triggered the feature undertakes some basic checks to ensure it should be running, they are:
-
Ensure that a Call Type has been set in session state (i.e. the DetermineCallType feature has run)
-
Ensure that a Charge Mode has been set in session state (i.e. the DetermineChargeMode feature has run)
-
Ensure that the feature was triggered on an incoming SIP response message.
If any of these conditions is not met, the feature immediately terminates execution an raises an error. If they are both met, the feature will continue as described below.
Classifying the Session Status and Response
Once confirming that it is running under the correct conditions, the feature checks the session state and the incoming response to determine if a decision about charging should be made. The requirements for making a decision are:
-
The Call Type is
MobileTerminating -
The Charge Mode is
RO(Online charging) -
The response has a
200 OKstatus. -
The response has been sent in reply to the initial
INVITEfor the call.
If these requirements are all met, the feature will check the response to determine if charging should be finalised. If any are not met, the feature will skip to checking if it needs to strip the OC-Terminating-Domain from the outgoing response.
Handling Charging Status
If the feature has confirmed that the incoming response is a 200 OK for the initial INVITE, it will look for the OC-Terminating-Domain header on the response. If the header is present and has the value PS=WLAN (which indicates the call has been routed to the terminating user over a WiFi network) the feature will finalise charging for the terminating leg of the call.
If it is present, the value of the OC-Terminating-Domain header (regardless of it is) will be stored in the TerminatingDomain session output variable.
If the header is not present or has a value not equal to PS=WLAN, charging for the call will not be affected.
Finalising Charging
If the feature has determined that it is necessary to finalise charging, it will carry out the following procedure:
-
Set the session output variable called
MonitorCallOnlytotrue. -
Find all charging instances associated with the session.
-
For each charging instance it finds it will:
-
Determine if it is a reservation charging instance.
-
Check that the instance has not already been finalised.
-
If both of those conditions are true, the feature will instruct the instance to undertake charging finalisation.
-
Stripping the OC-Terminating-Domain Header
Under certain conditions, the feature will strip the OC-Terminating-Domain header from any outgoing messages before finishing execution. These conditions are met when either one of the following is true:
-
The Call Type is
MobileOriginating -
The Call Type is
MobileTerminating, and the Charge Mode isRO(online) orDEFAULT(which is treated as online)
If the conditions are met, the feature will strip the header by accessing the outgoing message queue for the leg linked to the leg the response was received on. For every message found in the queue, the feature will check if the header is present and if so, remove it.
If the response was received on a leg that is not linked to another leg, or neither of the above conditions were met, the feature will not attempt to strip the header.
Session Transfer to Own Device
Session Transfer to Own Device features. For an overview see Session Transfer to Own Device on Sentinel VoLTE Architecture.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
checks if the subscriber has the STOD service provisioned |
|
|
adds the subscribers IMPU to the set of external session tracking keys |
|
|
connects the IMPU acquired from the subscriber registration to the existing ACI for the session transfer |
|
|
handles the transfer request and route it to the previous bound session |
|
|
intercepts the transfer INVITE routed by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature and connects the existing called led to the new calling leg and releases the previous calling leg |
|
|
Reads STOD tracking information out of a database and sets it into the session state for processing by External Session Tracking features. |
Source Code
This feature’s source code is available in the Sentinel VoLTE SDK in the mmtel-session-transfer module pack. It can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK with that module pack, for example:
> create-module new-session-transfer-module opencloud#mmtel-session-transfer#volte/2.7.0;2.7.0.0
This command will prompt you for information needed to create the new modules, once completed the original source for the feature can be found in the new modules.
The module-pack includes the following modules:
| Module Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
mmtel-session-transfer |
Group module for the feature that includes all of the modules listed below. |
|
mmtel-stod-enabled |
checks if the subscriber has the STOD service provisioned |
|
mmtel-stod-enable-session-tracking |
adds the subscribers IMPU to the set of external session tracking keys |
|
mmtel-bind-aci |
connects the IMPU acquired from the subscriber registration to the existing ACI for the session transfer |
|
mmtel-stod-trigger-anchor |
handles the transfer request and route it to the previous bound session |
|
mmtel-stod-process-handover |
intercepts the transfer INVITE routed by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature and connects the existing called led to the new calling leg and releases the previous calling leg |
|
mmtel-session-transfer-event-handler |
The internal event used by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature. |
|
mmtel-stod-determine-target-session |
Reads STOD tracking information out of a database and sets it into the session state for processing by External Session Tracking features. |
MMTelStodBind
The MMTelStodBind feature connects the IMPU acquired from the subscriber registration to the existing ACI for the session transfer .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Both |
|
Yes |
Yes - subscriber data is from the HSS |
Stateless |
SBB Feature |
Implications on Charging for Forwarded calls |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecords |
Complex |
Registration Records contain the public IMPU |
Subscriber |
String |
The subscriber Id |
CallType |
Complex |
The sip call type |
StodIsEnabledForUser |
boolean |
Is the STOD enabled ? |
Statistics
Name |
Incremented when… |
BoundAciToImpu |
the ACI is bound to an this is incremented. |
UsedLinkedAciForBinding |
the triggering ACI is not used for binding, i.e the call is not MobileTerminating then the linked ACI is used. |
UsedTriggeringAciForBinding |
the call is a MobileTerminating call the Triggering ACI is used for binding. |
Behaviour
The feature connects the IMPU acquired from the subscriber registration to the existing ACI for the session transfer. The subscriber has to be provisioned for the service, otherwise the feature won’t bind the session. The feature will only bind the session if the 200 OK from the INVITE is received.
Source
For source code information see MMTel Session Transfer Source Code
MMTelStodDetermineTargetSession
The STODDetermineTargetSession feature Reads STOD tracking information out of a database and sets it into the session state for processing by External Session Tracking features. .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stod |
Originating |
|
Yes |
Yes - subscriber data is from the HSS |
Statefull |
SBB Feature |
Requires other features in STOD to work |
Service Description
The STODDetermineTargetSession feature uses the session tracking information stored in an CQL database to set a session state field. The session state field is used in other features to get the ACI of the session that was tracked.
Prerequisites
-
The subscriber has to have the STOD service enabled (see MMTelStodEnabled)
-
The special number has to be configured in the AS (see DetermineVoltePlanId)
-
See the MMTelStodEnableSessionTracking for the Session Tracking
-
Session tracking information must have been written to the database by other STOD features.
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
Complex |
The calltype |
RequestIsForMmtelTransfer |
boolean |
Get request is for MMtel transfer |
MMTelDetermineTransferableSetQueryTime |
long |
The query time |
MMTelIsNewCassandraSession |
boolean |
Is the session a new Cassandra session |
SessionTrackingCassandraSessionACI |
Complex |
get the ACI for session tracking |
ASURI |
String |
Insert the application server Uri into the session state |
Session Output Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MMTelDetermineTransferableSetQueryTime |
long |
Set the time for the initial invocation |
MMTelIsNewCassandraSession |
boolean |
Is it a new Cassandra session |
MMTelSessionToTransfer |
Complex |
Insert the session tracking information into the Session State |
MMTelAccessTransferIsLocal |
boolean |
Set whether the access transfer is local |
Statistics
Name |
Incremented when… |
StodDetTargetSessionInvoked |
The feature has started |
StodCassandraTimeout |
The query result event has been received however the result is an error and the error is a time-out |
StodCassandraError |
The query result event has been received however the result is an error |
StodSampleCassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
The query result event has been received however the result is an error |
StodCassandraSuccess |
The query result event has been received with a non error result |
StodSampleCassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
The query result event has been received with a non error result |
StodCassandraQueried |
The Cassandra query has been sent |
StodCassandraNoDataFound |
The results of the Cassandra query showed that there was no session in the database for session transfer |
StodFoundTrackedSession |
The session to transfer has been found in a database |
StodSavedSessionToTransfer |
The session to transfer returned non null and has been set into a session state variable |
Behaviour
When the feature is invoked, We determine whether the invocation was for a transfer attempt or the response to a transfer attempt. In the event that the trigger was a transfer attempt then there is an asynchronous query to the Cassandra database for the tracked session information. Otherwise if the trigger was for the result of a Cassandra query we process it and exit. If an existing session is found for the served user, the target session is set to that dialog. If not the feature answers with a Sip Response 404 Not Found.
Source
For source code information see MMTel Session Transfer Source Code.
MMTelStodEnableSessionTracking
The MMTelStodEnableSessionTracking feature adds the subscribers IMPU to the set of external session tracking keys .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Both |
|
Yes |
Yes - subscriber data is from the HSS |
Stateless |
POJO Feature |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
Subscriber |
String |
The subscriber Id |
StodIsEnabledForUser |
boolean |
Session Transfer to Own Device is enabled for the subscriber |
Session Output Variables
| Session State Variable Name | Type | Contents |
|---|---|---|
External Session Tracking Keys |
Set<String> |
The set of external session tracking keys |
External Session Tracking Active |
boolean |
Whether or not this session will be externally tracked |
Statistics
| Name | Incremented when |
|---|---|
StodEnableSessionTracking |
STOD session tracking is enabled for this session |
StodSessionTrackingDisabled |
STOD session tracking is disabled for this session |
FoundTrackingKey |
A tracking key has been created for this session and added to the set |
Behavior
The StodEnableSessionTracking feature checks to make sure that STOD session tracking has been enabled for the Served-User in the triggering message. In the event that the trigger is on a 200 (OK) response for an incoming INVITE request the feature will create a tracking key. The tracking key is taken from an IMPU in session state and the Tracking Key Prefix IMPU. The tracking key is then added to the External Session Tracking Keys. When there is no subscriber in session state or in the registration records there will be no IMPU in which case there will be no session tracking.
MMTelStodEnabled
The MMTelStodEnabled feature checks if the subscriber has the STOD service provisioned .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Both |
|
Yes |
Yes - subscriber data is from the HSS |
Stateless |
SBB Feature |
Session Input Variables
Session State variable name |
Type |
Comments |
RegistrationRecords |
Complex |
List of registration records containing public id |
Subscriber |
String |
subscriber id |
Configuration
The configuration is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile with a profile table name of: MMTelStodEnabledConfigProfileTable. The profile is scoped by the Sentinel selection key and by the subscriber uri. Example : Opencloud:::::alice@opencloud.com.
| Variable Name | Type | Constraint | Default | Default Value Interpretation | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
StodEnabled |
Boolean |
False |
Indicates the subscriber is not allowed to use the STOD service |
Session Output Variables
Session State variable name |
Type |
Comments |
StodIsEnabledForUser |
boolean |
Set to |
Statistics
| Name | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
StodIsEnabled |
the Stod is enabled for a subscriber |
StodIsNotEnabled |
the Stod is not enabled for a subscriber |
Behaviour
The feature checks if the subscriber has the STOD service provisioned.
The feature acts on INVITE request and the IMPU is retrieved from registration data and matched with profile configuration.
If the profile exists and the StodEnabled boolean variable is true, the feature sets the StodIsEnabledForUser session state field.
Source
For source code information see MMTel Session Transfer Source Code
MMTelStodProcessHandover
The MMTelStodProcessHandover feature intercepts the transfer INVITE routed by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature and connects the existing called led to the new calling leg and releases the previous calling leg .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MMTel |
Both |
|
No |
Stateful |
SBB Feature |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
enum |
MobileOriginating or MobileTerminating |
Statistics
Name |
Incremented when… |
SentRemoteUpdate |
a re-INVITE is sent to the called party. |
RemoteUpdateSuccess |
re-INVITE was accepted (200 OK). |
RemoteUpdateError |
re-INVITE was not accepted. |
CallAnsweredWith200 |
the (200 OK) from the re-INVITE is sent to the new access leg |
ReleasedOldAccessLeg |
the previous calling leg is released |
LinkedNewAccessLegToRemoteLeg |
the transfer INVITE leg is linked to the existing called party leg |
TerminatedSession |
the session finishes |
AccessTransferComplete |
the session transfer was done successfully |
HandoverRequestReceived |
a session transfer INVITE is received |
StodEnableSessionTracking |
tries to mark the new transfered session to be tracked |
FoundTrackingKey |
the tracking key is set |
StodSessionTrackingDisabled |
when failed to set the new transfered session to be tracked |
Behaviour
The feature intercepts the transfer INVITE routed by the MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature and connects the existing called led to the new calling leg and releases the previous calling leg.
The feature also does the SDP remote update by sending the transfer INVITE as a reINVITE on the existing called leg and guarantees the SDP integrity and correctness on all involved dialogs.
Source
For source code information see MMTel Session Transfer Source Code
MMTelStodTriggerAnchor
The MMTelStodTriggerAnchor feature handles the transfer request and route it to the previous bound session .
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stod |
Originating |
|
Yes |
Yes - subscriber data is from the HSS |
Stateless |
SBB Feature |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecords |
Complex |
Registration Records contain the public IMPU |
Subscriber |
String |
The subscriber Id |
StodIsEnabledForUser |
boolean |
Is the STOD enabled ? |
Statistics
Name |
Incremented when… |
FiredIncomingRequestEvent |
the transfer INVITE is sent to the session to be transfered. |
Behaviour
The feature handles the transfer request and route it to the previous bound session.
The feature retrieves the existing session based on the IMPU from the registration records and fire an internal event, routing the transfer request to the previous bound existing session.
Source
For source code information see MMTel Session Transfer Source Code
SCC Features
These features are SCC specific.
| Group | What it provides |
|---|---|
|
The feature classifies INVITE requests for various SCC functions |
|
|
These features implement SCC-AS support for Single Radio VCC |
|
|
These features implement support for service centralization via the SCP as described in GSMA IR.64 |
|
|
These features implement the routing strategy for the terminating trigger |
SCCDetermineSessionType
toc: :sortorder: 1
What is SCC Determine Session Type?
This feature classifies incoming INVITE and MESSAGE requests to determine if they are invoking SCC services.
An INVITE request may be classified as:
-
a Reorigination
INVITErequest -
an Access Transfer Request
-
Which will be further classified by the type of Access Transfer
-
-
a standard
INVITErequest
A MESSAGE request may be classified as:
-
an OpenCloud internal Access Transfer directive
-
not of interest to the SCC AS
Once classified, it rejects those that the implementation is known not to handle, by sending a 403 Forbidden error response. If an incoming request appears to be invoking an SCC service but is missing critical information, it will be rejected with a 400 Bad Request error response.
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Classifies an incoming Request, sets a session state field |
Related Features
This feature is part of a group of features that implement SCC-AS behaviour. This feature is a prerequisite for SCCSendRequestToAnchor and for DetermineVoltePlanId (on an SCC-AS only).
Network Operator Data
VoLTE Shared Config
Configuration from the JSLEE profile table VoLTESharedConfigProfileTable is used to define the per node URI The following values are used:
-
SCCASURI - When running as an SCC AS this value is used for the ASURI in Session State
Conferencing
Conferencing handover detection relies on configuration data that is retrieved from the SCCConfHandlingConfigProfileTable JSLEE profile table.
The following values are used:
-
EnableSCCConfHandling - Used to determine whether conferencing handover is enabled
-
ConfFactoryPSI - Used to determine if the request is from the conference factory
Reorigination
Reorigination detection relies on configuration data that is retrieved from the JSLEE profile table named SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationConfigProfileTable.
The following values are used:
-
UsePrefix - Used to determine if a network prefix is used to detect reorigination
-
NetworkPrefix - The prefix that should be used to detect reorigination
Access Transfer
Access Transfer detection relies on the platform having three values configured:
-
the Access Transfer Update - Session Transfer Identifier (ATU-STI)
-
the Session Transfer Number - Single Radio (STN-SR)
-
the SCC AS’s own URI
The ATU-STI and STN-SR are configured in a JSLEE profile table RegistrarConfigurationTable, and the SCC AS URI is configured in a second JSLEE profile table VoLTESharedConfigProfileTable.
Notes on Config Profiles
The profile tables used by this feature are RegistrarConfigurationTable, VoLTESharedConfigProfileTable, SCCCamelToIMSReoriginationConfigProfileTable, and SCCConfHandlingConfigProfileTable.
The Profile Name within the tables is scoped according to the Sentinel Selection Key.
An example profile name is "OpenCloud:::::". This means:
The platform name is "OpenCloud". There is no Network Operator, Session Type, Plan Id, or Subscription ID scoping. The values may also be configured through the Sentinel REM screen:
-
Sentinel ▶ Feature Configuration ▶ SCC Determine Session Type (SIP)
-
Sentinel ▶ Feature Configuration ▶ SCC Camel To IMS Reorigination (SIP)
-
Sentinel ▶ Feature Configuration ▶ VoLTE Shared Config Profile (SIP)
Session Output Variables
| Session State Variable Name | Java Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
SCCSessionType |
A Java enum with type name |
AccessTransfer, Reorigination, Standard |
AccessTransferType |
A Java enum with type name |
eSRVCC_Anchored, eSRVCC_Not_Anchored, Additional_Session_Transfer, SRVCC, Internal_Directive, Bad_Request_STNSR, Bad_Request_ATUSTI, Bad_Request_SCCURI, None |
ASURI |
String |
A SIP URI |
Statistics
SCCDetermineSessionType statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → [volte.sentinel.sip service name] → [volte.sentinel.sip SBB name] → feature.SCCDetermineSessionType
Statistic |
Increments when… |
Started |
The feature is started. |
FailedToStart |
Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
A non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
A fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
The feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
SelectedStandardScc |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedReorigination |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedESRVCCAnchored |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedESRVCCNotAnchored |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedSRVCC |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedAdditionalSessionTransfer |
The feature determines that the incoming |
SelectedInternalAccessTransferDirective |
The feature determines that the incoming |
InvokedProxyAndDoNotRecordRouteForRequest |
The feature determines that the incoming |
ReceivedBadRequestToSTNSR |
The feature receives a malformed request for rel-8 access transfer. |
ReceivedBadRequestToATUSTI |
The feature receives a malformed request for rel-10 access transfer. |
ReceivedBadRequestToSCCURI |
The feature receives a malformed request for an additional session transfer. |
Behaviour
The feature begins by checking that it was triggered by an initial SIP INVITE or MESSAGE request.
-
If the trigger is not an initial SIP request at all, the feature will raise an unsupported trigger event error and complete processing.
-
If the trigger is an initial SIP request but is not an
INVITEorMESSAGE, then no further action is required and the feature will complete processing. -
If the trigger is an initial
INVITEorMESSAGErequest, the feature will move on to load its configuration
If any configuration data is missing, then the feature will raise an invalid configuration error and complete processing.
Once configuration is loaded, the feature will analyse the incoming request to determine what type of session the request is for. It populates the SCCSessionType and AccessTransferType session state fields based on what it determines.
For an INVITE request the feature will check if it is one of:
-
A "Reorigination" request
-
A "Rel-8 Access Transfer (SRVCC)" request
-
A "Rel-10 Access Transfer (eSRVCC)" request
-
An "Additional Session Transfer" request
If none of the above is true, then the INVITE will be treated as a "Standard SCC Session".
For a MESSAGE request the feature will check if it is an "Internal Access Transfer Directive", if it is not then the request will be treated as a "Proxy and Do Not Record Route" case.
The following sections detail the conditions and feature behaviour for each possible session type.
Reorigination
Reorigination is determined by looking at the Request-URI of the incoming INVITE. If it is a tel: URI that begins with the configured reorigination prefix number, then the request is considered a reorigination request and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoReorigination. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoNone. -
increment the
SelectedReoriginationstatistic.
Rel-8 Access Transfer (SRVCC)
Rel-8 Access Transfer is determined by looking at the Request-URI of the incoming INVITE. If it begins with the configured STN-SR prefix number, then the request is considered a rel-8 access transfer request. In 3GPP specifications this is known as a "SIP INVITE request due to STN-SR".
The feature will then do an additional check for the presence of a P-Asserted-Identity header on the INVITE request. If the header is present, then the request is considered to be a rel-8 access transfer request and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoSRVCC. -
increment the
SelectedSRVCCstatistic.
If the P-Asserted-Identity header is absent, then the request is malformed and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoBad_Request_STNSR. -
increment the
ReceivedBadRequestToSTNSRstatistic. -
terminate the session by replying to the
INVITEwith a400 Bad Requestresponse.
Rel-10 Access Transfer (eSRVCC)
Rel-10 Access Transfer is determined by looking at the Request-URI of the incoming INVITE. If it matches the configured value for the ATU-STI, then the request is considered to be a rel-10 access transfer request. In 3GPP specifications this is known as a "SIP INVITE request due to ATU-STI for PS to CS SRVCC".
The feature will then do an additional check for the presence of a Target-Dialog or Replaces header on the INVITE request. If one of those headers is present, then the request is considered to be a rel-10 access transfer request for the case where media is anchored in the ATCF and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoeSRVCC_Anchored. -
increment the
SelectedESRVCCAnchoredstatistic.
If both the Target-Dialog and Replaces headers are absent, the feature will move on to check for the presence of a P-Asserted-Identity header. If that header is present, then the request is considered to be a rel-10 access transfer request for the case where media is not anchored in the ATCF, and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoeSRVCC_Not_Anchored. -
increment the
SelectedESRVCCNotAnchoredstatistic.
If both the P-Asserted-Identity is also absent, then the request is malformed and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoBad_Request_ATUSTI. -
increment the
ReceivedBadRequestToATUSTIstatistic. -
terminate the session by replying to the
INVITEwith a400 Bad Requestresponse.
Additional Session Transfer
Additional session transfer is determined by looking at the Request-URI of the incoming INVITE. If it matches the configured value for the URI of the SCC-AS, then the request is considered to be for an additional session transfer.
The feature will then do an additional check for the presence of a Target-Dialog header on the INVITE request. If the header is present, then the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoAdditional_Session_Transfer. -
increment the
SelectedAdditionalSessionTransferstatistic. -
terminate the session by replying to the
INVITEwith a403 Forbiddenresponse, as this type of access transfer is not supported by the SCC-AS.
If the Target-Dialog header is absent, then the request is malformed and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoBad_Request_SCCURI. -
increment the
ReceivedBadRequestToSCCURIstatistic. -
terminate the session by replying to the
INVITEwith a400 Bad Requestresponse.
Standard SCC Session
If an INVITE meets none of the above conditions, then the request is considered to be for a standard SCC session and the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoStandard. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoNone. -
increment the
SelectedStandardSccstatistic.
Internal Access Transfer Directive
An Internal Access Transfer Directive is a MESSAGE request sent from a remote SCC AS node that is handling an access transfer request. Such a request is sent when the remote node determines that the node receiving the request is responsible for handling a session associated with the access transfer that it is processing. The request instructs the receiving node on what to do with that associated session.
To be considered an Internal Access Transfer Directive, a MESSAGE request must meet two conditions:
-
The
Request-URImust match the URI of the receiving SCC AS. -
The request must include an OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header.
If those conditions are met, then the feature will do the following:
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoAccessTransfer. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoInternal_Directive. -
increment the
SelectedInternalAccessTransferDirectivestatistic.
Proxy And Do Not Record Route
If an incoming MESSAGE request is not an Internal Access Transfer Directive, then the SCC AS does not need to handle it. The feature will do the following
-
set the
SCCSessionTypetoStandard. -
set the
AccessTransferTypetoNone. -
increment the
InvokedProxyAndDoNotRecordRouteForRequeststatistic. -
Instruct Sentinel to proxy the message without recording itself on the route.
Packet Switched to Circuit Switched Access Transfer Features
An architecture view of SCC-AS capabilities is available in the Service Continuity and Access Transfer section of the architecture document.
Feature listing
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
prepares a signalling anchor such that it is ready to receive and process an access transfer request for the current session |
|
|
receives an Access Transfer |
|
|
implements the procedures for SCC-AS transferring of a single active session. It executes inside a signalling anchor instance |
|
|
determines the transferable set for access transfer |
|
|
sends SIP MESSAGE requests to instruct superfluous session removal |
|
|
terminates a superfluous session as part of access transfer procedures |
|
|
enables Session Tracking for the current session if the UE is SR-VCC capable and has a C-MSISDN |
|
|
implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of a terminating call in the alerting phase using PS to CS SRVCC |
|
|
implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of an originating call in the alerting or pre-alerting phases using PS to CS SRVCC |
Relationship between the features
A high level relationship between the features is illustrated through a series of diagrams.
Access transfer of a single established session
Call flow diagrams for this case are shown on Call flows for Session transfer of an active session.
The following diagram shows the main features used for transfer of a single active session. It assumes all signalling involves a single cluster member for the purposes of simplicity.
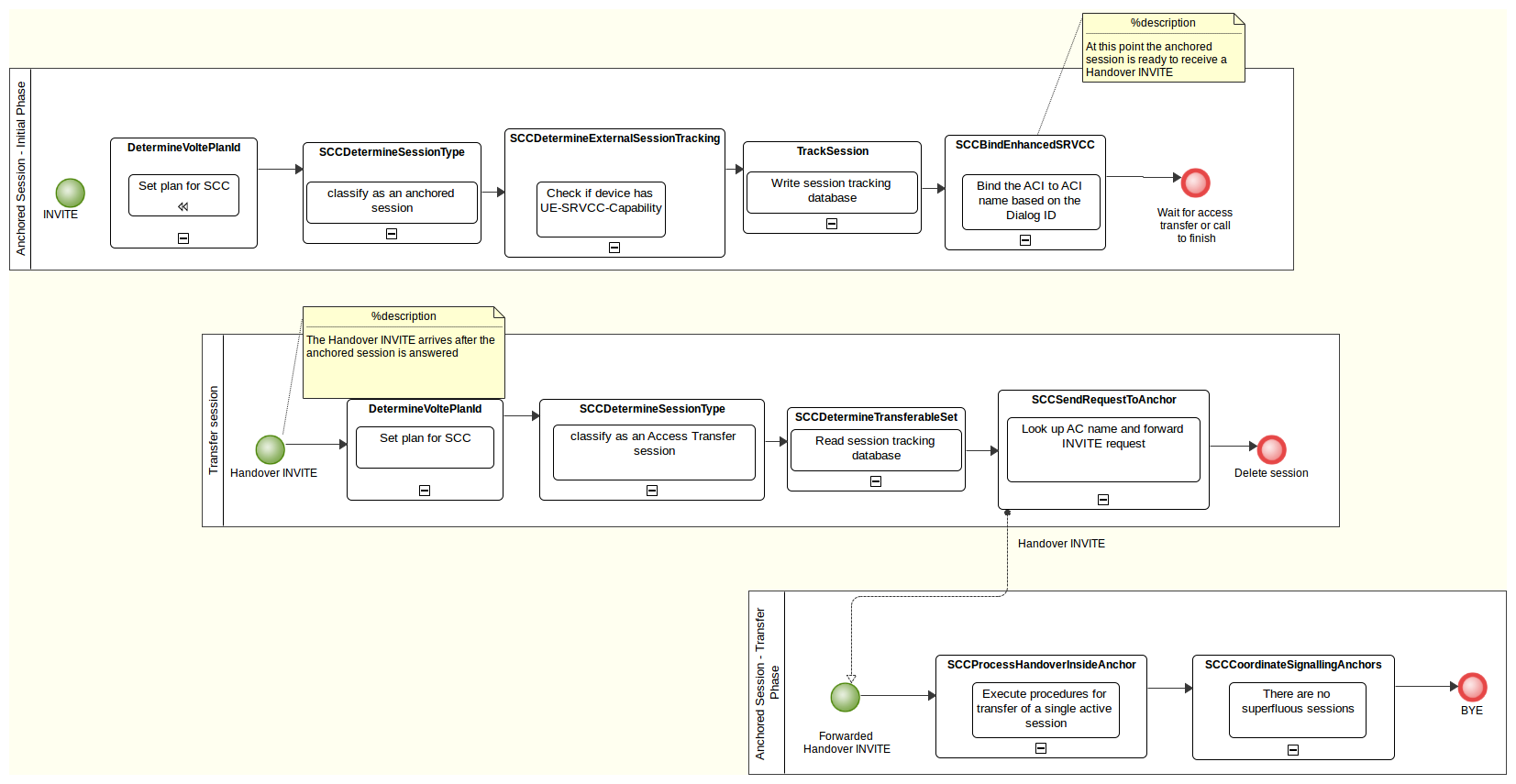
There are two sessions shown:
-
the "Anchored session" - the session to be transferred and
-
the "Transfer session" - the session initiated by the Handover INVITE
The Anchored session is shown twice in the diagram to represent its two phases, the initial phase and the transfer phase. At the top of the diagram, the Anchored session in its initial phase is first executed until SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC feature has finished. The diagram shows that the DetermineVoltePlanId, SCCDetermineSessionType, SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking, TrackSession, and SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC features are executed sequentially. At this point the call is answered.
In the middle of the diagram the Transfer session is shown. Some time after the Anchored session is answered, a Handover INVITE arrives at the SCC-AS. This then executes the DetermineVoltePlanId, SCCDetermineSessionType, SCCDetermineTransferableSet, and SCCSendRequestToAnchor features in sequence. The SCCSendRequestToAnchor feature internally passes the Handover INVITE to the existing Anchored session. The Transfer session is then deleted without performing any further signalling.
Finally at the bottom of the diagram, the Anchored session is shown for the transfer phase. It executes the SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor feature to perform access transfer for the established session, and then the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors feature once access transfer has completed. In this case there are no superfluous sessions and so it finishes execution without modifying any state.
Access transfer of an originating session in the alerting or pre-alerting state
Call flow diagrams for this case are shown on Call flows for Session transfer of an outgoing call in the alerting phases.
The following diagram shows the main features used for transfer of an outgoing call in the alerting phase. It assumes all signalling involves a single cluster member for the purposes of simplicity.
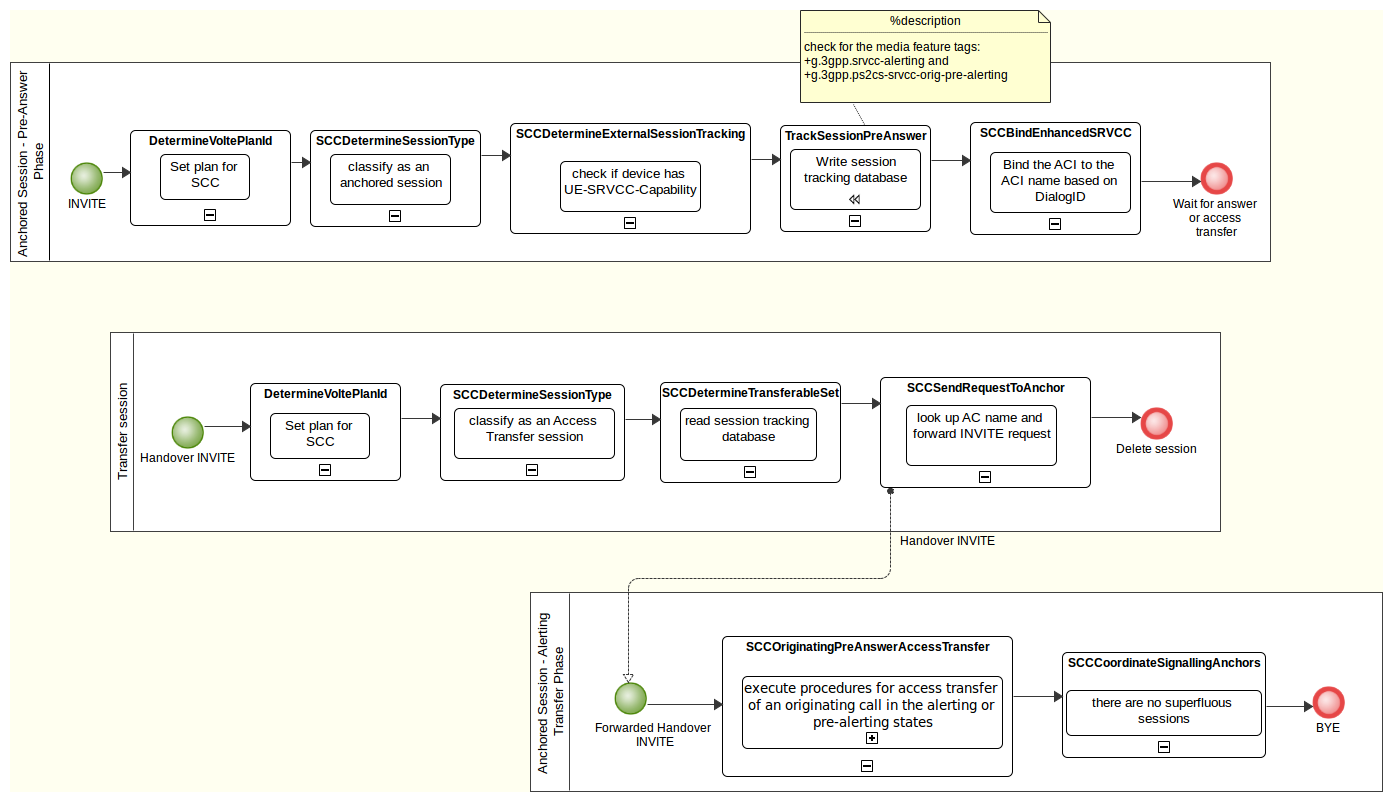
There are two sessions shown:
-
the "Anchored session" - the session to be transfered (in the alerting phase), and
-
the "Transfer session" - the session initiated by the Handover INVITE
The Anchored session is shown twice in the diagram to represent its two phases, the initial phase and the transfer phase. The initial phase in starts on receipt of an initial INVITE request and has finished when the call is in the alerting state. The sequence of the features executed in the initial phase are DetermineVoltePlanId, SCCDetermineSessionType, SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking, TrackSessionPreAnswer and SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC. At this point the call is in the alerting phase.
In the middle of the diagram the Transfer session is shown. Some time after the Anchored session is alerting, a Handover INVITE arrives at the SCC-AS. This executes the DetermineVoltePlanId, SCCDetermineSessionType, SCCDetermineTransferableSet, and SCCSendRequestToAnchor features in sequence. The SCCSendRequestToAnchor feature internally passes the Handover INVITE to the existing Anchored session. The Transfer session is then deleted without performing any further signalling.
The last stage of the diagram shows the Anchored session during the transfer phase. It executes the SCCOriginatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer feature to perform access transfer for the originating alerting session. Once the transfer is complete (a 2xx to the Handover INVITE has been sent to the MSC and an ACK to that 2xx received) the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors feature executes. In this case there are no superfluous sessions and so it finishes execution without modifying any state.
Access transfer of a single established session and removal of a held session
A call flow for a similar case is shown in the Administration guide on the Complex co-ordination example.
The following diagram simplifies the case to simply having two established sessions, one in the held state (i.e call on hold), and another in the active state (i.e. call in speech).
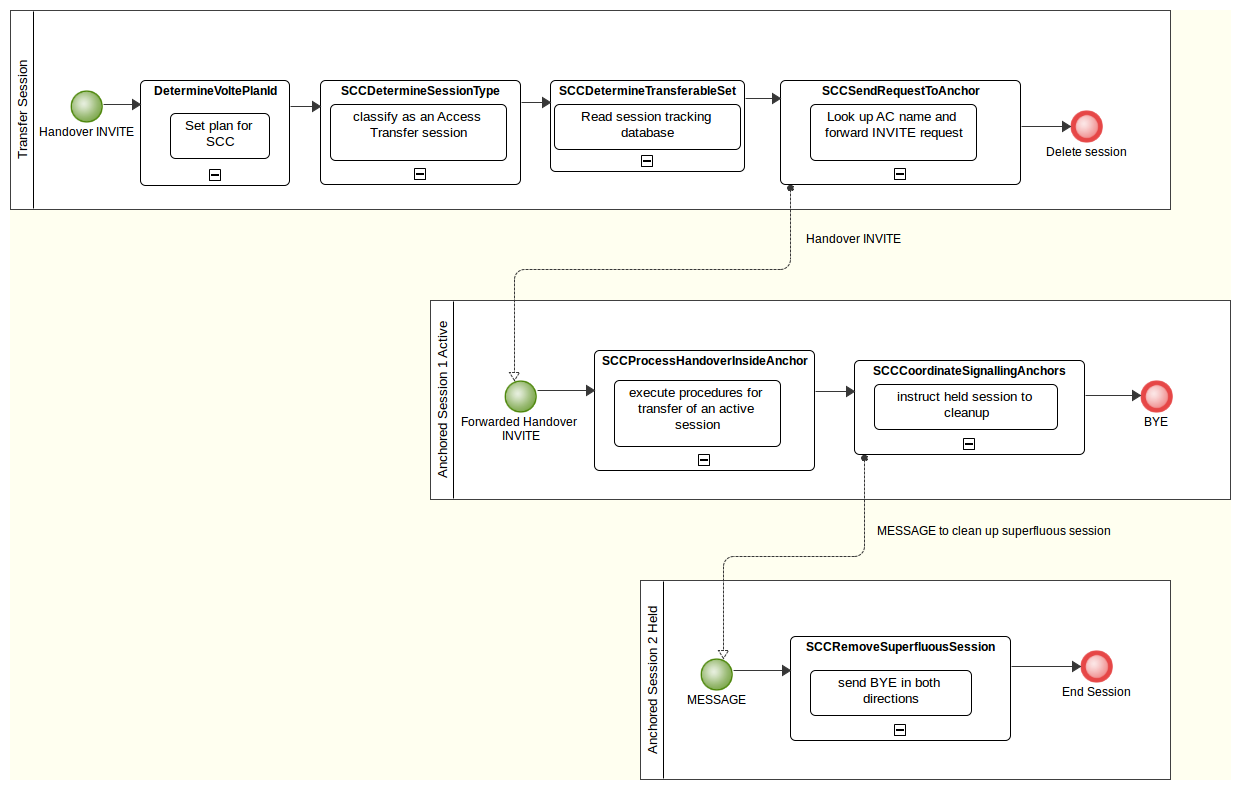
There are three sessions shown:
-
the active session,
-
the held session, and
-
the transfer session
In time, prior to the diagram there are two established sessions, one active and one held.
The top of the diagram shows the receipt of a Handover INVITE. The transfer session executes these features in order DetermineVoltePlanId, SCCDetermineSessionType, SCCDetermineTransferableSet, SCCSendRequestToAnchor. In this example the transferable set indicates that there is one session to transfer (the active session), and one superfluous session (the held session).
The Handover INVITE is provided to the active session. This causes execution of SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor. Once the handover has completed, the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors feature executes. As the transferable set contains a superfluous session, SCCCoordinatingSignallingAnchors informs the held session to clean up. This is achieved through the use of a SIP MESSAGE request containing an OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header with value remove-superfluous. The active session continues to exist until the call is terminated.
The MESSAGE request is received inside the held session. The SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession feature executes checking the OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header value. As the session is established, it terminates the session through sending a BYE request on both the access leg and remote leg.
Reuse of Access Transfer procedures for conferencing
The SCC-AS is able to be configured to convert an INVITE w/Replaces from the Conference Factory to a re-INVITE on the consulting call. It follows similar procedures to Access transfer of a single established session with the following key differences:
-
The "Anchored Session" is the consulting call between the conference moderator and the participant, that will be in the held state.
-
The "Transfer Session" is the INVITE w/Replaces sent towards the participant from the conference factory.
-
No sessions are classified as superfluous or additional sessions.
For how this affects the call flow see Re-INVITE Based Three-party conference setup overview
SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC
This feature prepares a signalling anchor such that it is ready to receive and process an access transfer request for the current session .
The preparation takes place during session establishment. The notification is in the form of a SIP request. It includes the ID of the SIP dialog for the access leg to be transferred.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Binds a name in |
Related features
3GPP Rel 10 Packet Switched to Circuit Switched support is implemented as a grouping of features and Sentinel capabilities.
Related features are:
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
Enum |
Used to determine whether originating or terminating instance behaviour should be invoked. |
EnhancedSRVCCBound |
boolean |
Indicates whether an activity context name has already been bound for this session. |
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Management interface for controlling Feature-Caps header values on outgoing messages. |
Statistics
SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → [volte.sentinel.sip service name] → [volte.sentinel.sip SBB name] → feature.SCCBindEnhancedSRVCC
| Statistic | Increments when… |
|---|---|
Started |
The feature is started. |
FailedToStart |
Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
A non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
A fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
BoundACName |
The feature binds and activity context name using the full dialog-ID. |
BoundPartialACName |
The feature binds and activity context name using the partial dialog-ID. |
UnboundACName |
The feature unbinds a full dialog-ID activity context name. |
UnboundPartialACName |
The feature unbinds a partial dialog-ID activity context name. |
Behaviour
This feature binds an activity context name for the access dialog.
Activity Context Name Binding
The feature binds the access dialog (access leg in 3GPP terminology) to a normalised name in the Activity Context Naming Facility.
The binding takes place once a non-100 provisional or a success response is received for the initial INVITE.
The feature does not attempt to bind more than once per session.
Once the name is bound successfully, the feature sets the session output variable enhancedSRVCCBound to true.
The access dialog is as follows:
-
for an originating B2BUA instance, the access dialog is the dialog from the A party
-
for a terminating B2BUA instance, the access dialog is the dialog towards the B party.
Therefore when acting as an originating anchor, the feature obtains the full SIP Dialog ID from the response in SessionState.latestCallingPartyResponse.
When acting as a terminating anchor, the feature obtains the full SIP Dialog ID from the response in SessionState.latestCalledPartyResponse.
Procedure for normalising the name to use
The normalised name string is comprised of four parts:
-
the CallID header in string form (for example,
me03a0s09a2sdfgjk1491777) -
the remote tag parameter value (for example,
774321) -
the local tag parameter value (for example,
64727891) -
a string to help with readability (for example,
esrindicating “enhanced SRVCC”).
| |
For the originating SCC B2BUA instance, the local tag is the For the terminating SCC B2BUA instance, the local tag is the |
These are then normalised into a single string form as follows:
-
CallID value followed by a semi-colon, then
-
r=followed by the value of the remote tag parameter, followed by a semi-colon, then -
l=followed by the value of the local tag parameter, followed by a semi-colon, then -
esr;
So, given the following:
-
CallID of
me03a0s09a2sdfgjk1491777 -
remote tag parameter value of
774321 -
local tag parameter value of
64727891
We generate the following normalised string:
me03a0s09a2sdfgjk1491777;r=774321;l=64727891;esr;
The rationale for choosing a format like this is so that an administrator can look at the string, and see:
-
esrmeans it is enhanced SRVCC as opposed to SRVCC (because our BindSRVCC feature usessrnotesr) -
randlare easy short hand forremoteandlocal.
SCCSendRequestToAnchor
This feature receives an Access Transfer INVITE or MESSAGE request and forwards the request to the appropriate Signalling Anchor instance .
For an architectural view of co-ordinating signalling anchors refer to Shared ATU-STI.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
None |
Stateless |
Feature SBB |
Looks up an AC Name and fires an event |
Prerequisite features
SCCDetermineSessionType must run before this feature.
Network operator data
Network operator data for SCCSendRequestToAnchor is stored in a profile table named SCCSendRequestToAnchorConfigProfileTable.
The data is scoped according to a Sentinel selection key.
The following attributes are network operator specific.
Session input and output variables
Statistics
SCCSendRequestToAnchor statistics are tracked by the scc-send-request-to-anchor-sbb SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → scc-send-request-to-anchor-sbb
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=scc-send-request-to-anchor,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0]"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Invoked |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
Error |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TerminatedSessionWith480 |
Incremented when the feature rejects an access transfer request with a 480 response |
SentInviteRequest |
Incremented when the feature sends an access transfer INVITE to the signalling anchor instance |
SentMessageRequest |
Incremented when the feature sends an access transfer MESSAGE to the signalling anchor instance |
InviteSessionMismatched |
Incremented when the dialog-ID from the access transfer request does not match the session to transfer in session state |
Behaviour
On starting, the feature will check the method of the triggering SIP Request and read the session input attribute AccessTransferType.
If the request method is INVITE, and the AccessTransferType has the value eSRVCC_Anchored, eSRVCC_Not_Anchored or SRVCC the feature will execute the behaviour described in Handling of Access Transfer Request.
If the request method is MESSAGE, and the AccessTransferType has the value Internal_Directive the feature will execute the behaviour described in Handling of Access Transfer Request.
Otherwise the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
Handling of Access Transfer Request
The feature will examine certain headers in the incoming request to determine a Activity Context Name that can be used to find the session that the request is targeted at. Which headers that are considered depend on the method of the request.
-
For
INVITErequests, the feature will check theTarget-Dialogheader first, if one is not found theReplacesheader will also be checked. -
For
MESSAGErequests, only theTarget-Dialogheader is considered.
If no appropriate header is present, the feature rejects the incoming request with a 480 Temporarily Unavailable error response and complete execution.
The feature will use the header to create a normalised lookup string as described in Creation of Activity Context Naming lookup string. This string is used to look up an Activity Context from the Activity Context Naming Facility.
If the naming lookup indicates that there was no Activity Context bound to the name the feature will reject the incoming request with a 480 Temporarily Unavailable error response and complete execution.
If the naming lookup returns an Activity Context the feature:
-
fires the
INVITEorMESSAGErequest event on the returned activity context;-
the OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header will be added to the request (if not already present), to pass instructions to the receiving SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor feature.
-
-
removes the AC name binding (unbinds the
ACNamethat was just looked up); -
instructs the Sentinel core that this Sentinel instance shall finish; and in doing so, shall not modify any SIP signaling on the dialog.
Creation of Activity Context Naming lookup string
The feature creates a normalised string from the Target-Dialog or Replaces header using four values:
-
the
Call-IDvalue -
the
remote-tagparameter value (orfrom-taginReplaces) -
the
local-tagparameter value (orto-taginReplaces) -
and a string to help with readability (the value
esrshort form for “Enhanced SRVCC”).
It then takes these four values and constructs a lookup key as follows:
-
Call-IDvalue, followed by a semi-colon -
r=followed by the value of the remote-tag parameter, and a semi-colon -
l=followed by the value of the local-tag parameter, and a semi-colon -
esr;
If the AttemptWithReversedTags configuration option is set to true the values for l= and 'r=' will be swapped.
The following example shows a Target-Dialog header and the normalised form:
-
header is
Target-Dialog: me03a0s09a2sdfgjkl491777; remote-tag=774321; local-tag=64727891 -
normalised form is
me03a0s09a2sdfgjkl491777;r=774321;l=64727891;esr; -
normalised form with reversed tags is
me03a0s09a2sdfgjkl491777;r=64727891;l=774321;esr;
SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor
This feature implements the procedures for SCC-AS transferring of a single active session. It executes inside a signalling anchor instance .
It is executed once the SCC-AS has determined that there is an active session, and has provided the INVITE to the signalling anchor. It is responsible for processing incoming access transfer handover INVITE requests i.e. INVITE due to STN-SR or INVITE due to ATU-STI. It performs a remote update if necessary, and closes the old Access Leg (source access leg).
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SIP Mid-Session Party Request/Response |
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
String |
Used to determine if access transfer is being performed for the called party or the calling party. |
CurrentRemoteLegName |
String |
Used to find the remote leg. |
CurrentLocalLegName |
String |
Used to find the old access leg. |
Session output variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
NewAccessLegName |
String |
The name of the new access leg. |
OldAccessLegName |
String |
The name of the old access leg. |
CurrentCalledLegName |
String |
The name of the current called leg, updated when access transfer is performed for the called party. |
CurrentCallingLegName |
String |
The name of the current calling leg, updated when access transfer is performed for the calling party. |
CurrentLocalLegName |
String |
The name of the current local leg, updated when access transfer occurs. |
Statistics
SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RemoteUpdateRequired |
Incremented when the feature determines that a remote update is required. |
RemoteUpdateNotRequired |
Incremented when the feature determines that a remote update is not required. |
SentRemoteUpdate |
Incremented when a remote update is sent to the remote party. |
RemoteUpdateSuccess |
Incremented when a success response is received for the remote update request. |
RemoteUpdateError |
Incremented when a failure response is received for the remote update request. |
CallAnsweredWith200 |
Incremented when a success response is sent for the handover INVITE on the new access leg. |
ReleasedOldAccessLeg |
Incremented when the old access leg is released. |
LinkedNewAccessLegToRemoteLeg |
Incremented when the new access leg is linked to the remote leg. |
TerminatedSession |
Incremented when the session is terminated due to an error during access transfer. |
AccessTransferComplete |
Incremented when the access transfer process is complete, after the ACK is received on the new access leg. |
Behaviour
An INVITE due to ATU-STI, or an INVITE due to STN-SR that arrive at the SCC-AS are referred to as a "Handover INVITE" in this page. This feature implements the transfer of a single active session as per section 12.3.5 of 3GPP TS 24.237. It includes support for anchored and non-anchored media at the ATGW. The removal of superfluous sessions is implemented by the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors and SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession features.
Remote and Access Legs
An Originating SCC signalling anchor has two legs, prior to access transfer. One from the A party (the Access Leg), and one towards the B party (the Remote Leg). I.e. the INVITE received by the SCC-AS from the S-CSCF is on the Access Leg. The INVITE sent towards the S-CSCF is on the Remote Leg.
A Terminating SCC signalling anchor has two legs, prior to access transfer. One from the A party (the Remote Leg), and one towards the B party (the Access Leg). I.e. the INVITE received by the SCC-AS from the S-CSCF is on the Remote Leg. The INVITE sent towards the S-CSCF is on the Access Leg.
The SCC-AS acts as a routing B2BUA between the Access and Remote legs.
In 3GPP TS 24.237, the phrases source access leg and target access leg are used. This document refers to the old access leg and new access leg respectively.
Detecting Handover INVITE
The feature is initially triggered on any mid-session INVITE request. In order to determine if the request is a handover INVITE, the feature looks for the OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header, set by the SCCSendRequestToAnchor feature.
If this header is not present, the feature ignores the request and finishes without interfering with the call flow.
If the header is present, the feature will begin Initial Handover Procedures, and then continue according to the selected access transfer type.
Initial Handover Procedures
Upon detecting a handover INVITE, the feature begins the access transfer process. It starts by importing the SIP leg that the handover INVITE was received on into the current call session as the "new access" leg. The feature then examines the SDP in the handover request to see if it is in line with the currently negotiated SDP for the session. If the SDP is different, then the feature will undertake Access Transfer Procedures for Non-Anchored Media to renegotiate the SDP with the remote party; if the SDP matches the currently negotiated SDP then Access Transfer Procedures for Anchored Media will be undertaken. Regardless of whether SDP needs to be renegotiated, the feature will unlink the old access SIP leg from the leg towards the remote party.
Access Transfer Procedures for Non-Anchored Media
If the SDP needs to be renegotiated with the remote party, the feature will generate a Re-INVITE request for the remote party based on the original handover request (with the OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header removed). The feature will send this Re-INVITE and then end processing until triggered by a response (or a new request). The feature’s next action will depend on what triggers it:
| Trigger | Behaviour |
|---|---|
Error response from remote leg |
Access transfer will be aborted, the old access leg will be re-linked to the remote leg, and the error response will be forwarded on the new access leg. |
BYE request from remote leg |
All legs will be terminated. A 200 OK to the BYE will be sent on the remote leg. A 480 Temporarily Unavailable in response to the access transfer INVITE will be sent on the new access leg. A BYE request will be sent on the old access leg. |
New INVITE request from the old access leg |
Reject the INVITE with a 491 response, continue waiting for Re-INVITE response |
BYE request from old access leg |
Reply with 200 OK, continue waiting for Re-INVITE response |
Success response from remote leg |
Forward the response on the new access leg and link the new access leg to the remote leg, await ACK |
After receiving a 200 OK response from the remote leg, the feature will await the ACK for the 200 from the new access leg. Upon receiving the ACK, the feature will terminate the old access leg (sending a BYE).
The signalling anchor (Sentinel instance) hosting the SCC features is now acting as a B2BUA between the new access leg (from the ATCF) and the remote leg (through the S-CSCF).
The feature is then complete.
Access Transfer Procedures for Anchored Media
In the event that no change in the SDP needs to be negotiated with the remote party, the feature will immediately answer the handover INVITE with a 200 OK response, and await the ACK from the new access leg. Upon receiving the ACK from the new access leg, the feature will link that leg to the remote leg. The ACK will not be forwarded.
If a BYE is received from the old access leg while waiting for the ACK, the BYE will be accepted with a 200 OK, terminating the old access leg. If no BYE is received then the feature will automatically terminate the old access leg (sending a BYE) upon receiving the ACK from the new access leg.
Once the ACK has been received the transfer is complete.
The signalling anchor (Sentinel instance) hosting the SCC features is now acting as a B2BUA between the new access leg (from the ATCF) and the remote leg (through the S-CSCF).
A call flow for this procedure is shown SCC Access Transfer Media Anchored Flow.
Call flows for Session transfer of an active session
The following flows described in 3GPP TS 24.237 and illustrate the signalling for transfer of a single active session.
SCCDetermineTransferableSet
This feature determines the transferable set for access transfer .
The transferable set is a phrase from 3GPP 24.237, and includes sessions that will be transferred during an access transfer, and those that are considered superfluous.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SCCAccessTransfer_SipAccess_SessionStart |
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AccessTransferType |
AccessTransferType (Enum) |
This feature will only run when this field is set to |
ASURI |
String |
The SIP URI of the current node |
Session output variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MostRecentlyActive |
TrackedSession (POJO) |
Contains all the information in TrackedDialogKeys about the most recently active session |
SuperfluousSessions |
Set<TrackedSession> |
A set of all of the other sessions found from querying the TrackedDialogKeys table |
AccessTransferIsLocal |
boolean |
True if the MostRecentlyActive’s ASURI field is the same as the current nodes ASURI |
Statistics
SCCDetermineTransferableSet statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCDetermineTransferableSet
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCDetermineTransferableSet"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
CassandraQueried |
Incremented when the feature sends a query to Cassandra |
CassandraError |
Incremented when a TrackedDialogKeys lookup fails with a Cassandra error |
CassandraSuccess |
Incremented when a TrackedDialogKeys lookup returns successfully from Cassandra |
CassandraTimeout |
Incremented when a TrackedDialogKeys lookup fails with a Cassandra timeout |
CassandraNoDataFound |
Incremented when no matching tracked dialog keys entries were found in Cassandra |
FoundTrackedSession |
Incremented when the feature successfully passes a row of the Cassandra result as a TrackedSession |
SavedSessionToTransfer |
Incremented when the feature saves the most recently active TrackedSession to session state |
SavedSuperfluousSessions |
Incremented when the feature saves all of the remaining TrackedSession’s to session state |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeSuccess |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a success response arriving from Cassandra |
CassandraAsyncQueryTimeFailure |
Samples the elapsed time between starting a query and a failure response arriving from Cassandra |
Behaviour
This feature uses the P-Asserted-Identity header from the handover INVITE as a CMSISDN to lookup the TrackedDialogKeys table in Cassandra saved by the External Session Tracking Features. The resulting data is then parsed into TrackedSession objects, one per result row.
The TrackedSession with the most recent LastActiveTime is stored in Session State as the MostRecentlyActiveSession. All other TrackedSessions are stored in the SuperfluousSessions set. The feature sets the AccessTransferIsLocal flag in Session State if the MostRecentlyActiveSession has an ASURI value the same as the current node’s ASURI.
SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors
This feature sends SIP MESSAGE requests to instruct superfluous session removal .
For an architectural view of co-ordinating signalling anchors refer to Shared ATU-STI.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SCC |
Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Network Operator Data
Network configuration is stored in a JSLEE profile table named SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchorsConfigProfileTable.
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
int |
|
Time in milliseconds to wait between receiving the access transfer ACK and sending out SIP MESSAGEs to remove superfluous sessions. |
Session input variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ASURI |
String |
The URI of this SCC node loaded by SCCDetermineSessionType |
AccessTransferACKed |
boolean |
Set by SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor to indicate that the Access Transfer INVITE has been ACK’d. |
SuperfluousSessions |
Set<TrackedSession> |
The set of TrackedSessions that will be removed. A SIP MESSAGE is sent for each entry. Set by SCCDetermineTransferableSet. |
Statistics
SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
TimerStarted |
Incremented when the feature starts the timer |
TimerFired |
Incremented when the feature receives the timer event |
TimerCanceled |
Incremented when the feature cancels the timer |
SentSuperfluousSessionMessage |
Incremented when the feature sends a SIP MESSAGE request to a remote node to remove a superfluous session |
SentSuperfluousSessionMessageInternally |
Incremented when the feature sends a SIP MESSAGE event internally to remove a superfluous session |
Behaviour
The feature is first triggered when an Access Transfer is completed by receiving an ACK for the handover INVITE. When the ACK is received, the SCCProcessHandoverInsideAnchor feature sets the session state flag AccessTransferACKed. When that flag is TRUE, this feature will arm a timer with the value in CoordinateSessionsDelay.
Then when either the timer fires, or the session is ending the feature will construct a SIP MESSAGE for each TrackedSession in SuperfluousSessions. These MESSAGEs are sent to trigger SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession on the node in control of those sessions.
The MESSAGE will have the following headers set:
| Header Name | Header Value |
|---|---|
|
The |
|
The |
|
The |
|
The |
|
|
|
The |
SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession
This feature terminates a superfluous session as part of access transfer procedures .
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
SipTransaction_Request |
None |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Statistics
SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
TriggeredOnSipRequest |
Incremented when the feature is triggered by a SIP |
TriggeredOnAccessTransferRequest |
Incremented when the feature is triggered by an internal |
SentMessageResponse |
Incremented when a response to the triggering |
SessionTerminated |
Incremented when the session is terminated |
Behaviour
Background
This feature is one part of the SCC Access Transfer system. It is triggered on an existing INVITE session by a SIP MESSAGE request, which directed into the session by the SCCSendRequestToAnchor feature.
Feature Execution
When invoked, the feature will perform a check to ensure that it was triggered by an incoming SIP request; if not, the feature will complete execution raising an unsupported trigger error. If the trigger is an incoming SIP request, additional checks will be made to determine if the request is both a MESSAGE request, and has an OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure header with the value Remove-Superfluous. If either of those checks fail, the feature will ignore the request and complete execution normally.
If the trigger is confirmed to be an incoming SIP MESSAGE request with the appropriate header, the feature will do two things before completing execution:
-
Immediately send a SIP
200 OKresponse for theMESSAGErequest. -
Terminate the session using the appropriate procedure based on the call state:
-
For sessions still being established, a
404 Not Foundresponse for the initialINVITEwill be sent upstream and aCANCELrequest will be sent downstream. -
For established sessions, a
BYEwill be sent in both directions.
-
If 200 OK response for the MESSAGE request fails to send for any reason, the feature will raise an error, but will still attempt to end the session.
SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking
This feature enables Session Tracking for the current session if the UE is SR-VCC capable and has a C-MSISDN .
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Both Originating and Terminating |
|
Yes |
None |
Stateless |
POJO |
Consults third party registration state |
Session input and output variables
Session input variables
| Session state variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecord |
Object |
This contains all of the registration information for the served user. |
CMSISDN |
String |
A string set to a non-null value if there is a C-MSISDN provisioned for the user, and if the user is logged in; |
ExternalSessionTrackingKeys |
Set<String> |
The tracking keys to use for the current sessions. |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Used to check for session plans that do not require session tracking. |
Session output variables
| Session state variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
ExternalSessionTrackingKeys |
Set<String> |
The tracking keys to use for the current session. The feature adds to this set. |
ExternalSessionTrackingActive |
boolean |
Set to true if the UE has a C-MSISDN and UE-SRVCC capability. |
AccessLegUESRVCCSupport |
Enumeration |
Set to one of NONE, DEFAULT, ALERTING, PRE-ALERTING. |
Statistics
SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCDetermineExternalSessionTracking"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
FoundTrackingKey |
Incremented when the Served User has an IMS registration with UE-SRVCC-Capability and a C-MSISDN |
ExternalSessionTrackingDisabled |
Incremented when the Served User does not have an IMS registration with UE-SRVCC-Capability and a C-MSISDN |
PartialDialogExternalSessionTrackingEnabled |
Incremented when the Served User supports UE-SRVCC-Capability and has the |
Behaviour
The feature scans all Third Party Registration information for the Served User’s IMS Public Identity. If any registration indicates that the device has support for UE-SRVCC-Capability, and it has an assigned C-MSISDN, then:
-
Session Tracking is enabled via setting the
ExternalSessionTrackingActiveflag in session state toTRUE, -
the value of the C-MSISDN is added to the
ExternalSessionTrackingKeysset in session state, and -
the
AccessUESRVCCSupportsession state field is set toDEFAULT -
the feature increments the
FoundTrackingKeystatistic and finishes execution
Otherwise the feature sets the ExternalSessionTrackingActive flag to FALSE, increments the ExternalSessionTrackingDisabled statistic and finishes execution.
| |
When running a T-ADS only session plan, this feature immediately determines that session tracking is not required and skips the registration data check. |
SCCTerminatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer
This feature implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of a terminating call in the alerting phase using PS to CS SRVCC .
This page refers to SIP INVITE due to STN-SR or SIP INVITE due to ATU-STI as a "Handover INVITE".
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Points in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Feature FSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SCC |
Terminating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Yes |
Statistics
SCCTerminatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCTerminatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCTerminatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
AccessTransferSuccessful |
Incremented when the ACK to the 2xx-INVITE due to ATU-STI or STN-SR is received by the feature |
AccessTransferAborted |
Incremented when the access transfer procedures are aborted before the transfer is complete |
SentPost405Update183 |
Incremented when a 183 is sent to the MSC after a 405-UPDATE is received |
SentRemoteReInvite |
Incremented when a remote reINVITE occurs |
SentRemoteUpdate |
Incremented when a remote UPDATE occurs |
SentPostUpdate183 |
Incremented when a 183 is sent to the MSC following an UPDATE-200 to the originating party |
SentInfoOnNewAccessLeg |
Incremented when an INFO is sent to the MSC as part of an Access Transfer |
SentForked183Response |
Incremented when a forked 183 response follows an UPDATE-200 with different SDP sent and received |
SentImmediate183 |
Incremented when an access transfer does not trigger an UPDATE to the originating party and a 183 is immediately sent to the MSC |
Behaviour
This feature implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of a terminating call in the alerting phase using PS to CS SRVCC. It includes support for media anchored in the ATGW and media non-anchored.
The behaviour is best described by reading section 12.3.4.2 in 3GPP TS 24.237. The feature implements the full text. A call flow diagram showing the media anchored case is in the Example call flow section of this page.
Removal of superfluous sessions is implemented through the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors and SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession features.
The following sections define additional behaviour to cover specification gaps.
UEs with an Allow header that does not include UPDATE
TS 24.237 specification doesn’t explicitly describe procedures at the SCC-AS for the case where a UE has specified an Allows header without including an UPDATE as the value. This feature implements behaviour as though it has received a 405-UPDATE when it receives the handover INVITE if:
-
the speech media component of the session to transfer is not equal to that in the Handover INVITE, and
-
the session to transfer has an Allows header without including UPDATE
That is, it creates a new early dialog towards the MSC using a 183 response. The 183 response includes signalling elements described in subclause 6A.4.3A. It includes an SDP answer:
-
with c-line set to the unspecified address (0.0.0.0) if IPv4 or to a domain name within the ".invalid" DNS top-level domain in case of IPv6 as described in IETF RFC 6157; and
-
including media of media types received in SDP offer of the SIP INVITE request due to STN-SR, which are also offered in the SIP INVITE request from the served user; and
SCCOriginatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer
This feature implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of an originating call in the alerting or pre-alerting phases using PS to CS SRVCC .
This page refers to SIP INVITE due to STN-SR or SIP INVITE due to ATU-STI as a "Handover INVITE".
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Points in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Feature FSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SCC |
Originating |
|
No |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
Yes |
Statistics
SCCOriginatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCOriginatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.SCCOriginatingPreAnswerSessionTransfer"
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
AccessTransferSuccessful |
Counter |
Incremented when the ACK to the 2xx-INVITE due to ATU-STI or STN-SR is received by the feature |
AccessTransferAborted |
Counter |
Incremented when access transfer procedures are aborted before the transfer is complete |
SentRemoteUpdateUsingUpdate |
Counter |
Incremented when a remote update occurs using the UPDATE method (prior to 2xx-INVITE on the remote leg) |
SentRemoteUpdateUsingPrack |
Counter |
Incremented when a remote update should occur prior to session establishment, but the remote UE does not support the UPDATE method |
SentRemoteUpdateUsingInvite |
Counter |
Incremented when a remote update occurs using the INVITE (reINVITE) method. Post 2xx-INVITE on the remote leg. |
MaskedInviteEvent |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature masks delivery of further INVITE events on the new access leg. |
UnmaskedInviteEvent |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature unmasks delivery of further INVITE events on the new access leg. |
Behaviour
This feature implements SCC-AS procedures for access transfer of an originating call in the alerting or pre-alerting phases using PS to CS SRVCC. It includes support for media anchored in the ATGW and media non-anchored, forks of the remote leg, and various race conditions between processing the Handover INVITE and the remote leg answering the call.
The behaviour is best described by reading section 12.3.4.3 in 3GPP TS 24.237. The feature implements the full text. Several call flows showing different success cases are shown in the Example call flows section of this page.
Removal of superfluous sessions is implemented through the SCCCoordinateSignallingAnchors and SCCRemoveSuperfluousSession features.
The following sections define additional behaviour to cover specification gaps.
UEs with an Allow header that does not include UPDATE
TS 24.237 specification doesn’t explicitly describe procedures at the SCC-AS for the case where a UE has specified an Allows header without including an UPDATE as the value. This feature implements behaviour as though it has received a 405-UPDATE when it receives the handover INVITE if:
-
the speech media component of the session to transfer is not equal to that in the Handover INVITE, and
-
the session to transfer has an Allows header without including UPDATE
That is, it creates a new early dialog towards the MSC using a 183 response. The 183 response includes signalling elements described in subclause 6A.4.3A. It includes an SDP answer:
-
with c-line set to the unspecified address (0.0.0.0) if IPv4 or to a domain name within the ".invalid" DNS top-level domain in case of IPv6 as described in IETF RFC 6157; and
-
including media of media types received in SDP offer of the SIP INVITE request due to STN-SR, which are also offered in the SIP INVITE request from the served user; and
It then waits for the 2xx-INVITE from the remote leg and does not forward that on to the MSC. It initiates a re-INVITE to provide the new SDP offer to the remote UE, waits for the 2xx response and forwards it to the MSC.
Error responses other than 405-UPDATE
The specification does not describe behaviour for error responses other than 405-UPDATE. If a necessary SIP procedure fails due to an error response, the feature terminates:
-
the old access leg
-
the new access leg
-
the remote leg
Receipt of non reliable provisional responses from the remote UE
The specification does not cover the remote UE sending non-reliable provisional responses. The feature deals with this case by:
-
making all provisional responses that it sends to the MSC be reliable,
-
when it receives a PRACK from the MSC, it waits for 2xx-INVITE from the remote leg (and does not forward it onwards to the MSC. It then sends a re-INVITE with SDP from the Handover INVITE. When it receives a 2xx to the re-INVITE it forwards that onwards to the MSC.
Call flows for session transfer of an outgoing call in the alerting phases
Session Transfer for an outgoing call in the alerting phase
Please refer to 3GPP TS 24.237 appendix A.17.3. It is a single "successful case" for a originating alerting access transfer where media is not anchored in the ATGW.
Session Transfer for an outgoing call in the alerting phase with forks
Please refer to 3GPP TS 24.237 appendix A.17.6. It is a single "successful case" for a originating alerting access transfer where media is not anchored in the ATGW. Additionally the SC UE has received several forked responses prior to access transfer.
Service Centralisation Features
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
specifies information shared by the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN and SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP features |
|
|
receives a CAP trigger, stores re-origination information, and is able to forward the call such that it is routed into the IMS |
|
|
triggered from the I-CSCF and retrieves re-origination information; optionally it can retrieve the subscriber’s assigned S-CSCF either from a HSS or from a profile from network configuration, then acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the subscriber’s assigned S-CSCF |
ReOriginationSharedInformation
This feature specifies information shared by the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN and SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP features .
Both the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN and SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP features use:
-
shared network operation configuration, and
-
a shared Correlation RA entity for re-origination information.
Network operator configuration
Network configuration data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile table named SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationConfigProfileTable.
| Attribute name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
UsePrefix |
boolean |
|
NetworkPrefix |
string |
|
RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber |
An enum. See RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber |
Used by the IN feature when forwarding the call. For allowed values, see RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber |
Nature |
An enum. See Nature |
Used by the IN feature when forwarding the call. For allowed values see Nature. |
NumberingPlan |
An enum. See NumberingPlan |
Used by the IN feature when forwarding the call. For allowed values see NumberingPlan |
OriginHost |
string |
The value to use for the OriginHost AVP when communicating to the HSS. Used by the SIP feature* |
OriginRealm |
string |
The value to use for the OriginRealm AVP when communicating with the HSS. Used by the SIP feature* when retrieving the S-CSCF name for the subscriber |
DestinationHost |
string |
The value to use for the DestinationHost AVP when communicating with the HSS. Used by the SIP feature* when retrieving the S-CSCF name for the subscriber |
DestinationRealm |
string |
The value to use for the DestinationRealm AVP when communicating with the HSS. Used by the SIP feature* when retrieving the S-CSCF name for the subscriber |
SkipHSSLookup |
boolean |
This decides whether the SIP feature will do a query to the HSS for the S-CSCF address or not |
DirectRoutingURI |
string |
The value to use for the address to add to the route header that will be added to the INVITE after it has been re-originated. |
* Not currently used by the feature. Uses default Sh-Cache settings.
RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber
This value is part of the CAP and ETSI INAP CalledPartyNumber.
The allowed values are:
-
ALLOWED -
NOT_ALLOWED
The values are as if the type were specified in ASN.1 as follows:
RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber ::= ENUMERATED {
ALLOWED (0),
NOT_ALLOWED (1)
}
For more information, please see OpenCloud’s CGIN.
Nature
This value is part of the CAP and ETSI INAP CalledPartyNumber. The allowed values are:
-
SUBSCRIBER -
UNKNOWN -
NATIONAL -
INTERNATIONAL -
NETWORK_SPECIFIC -
NETWORK_ROUTING_NATIONAL -
NETWORK_ROUTING_NETWORK_SPECIFIC -
NETWORK_ROUTING_WITH_CALLED_DIRECTORY
The values are as if the type were specified in ASN.1 as follows:
Nature ::= ENUMERATED {
... ,
SUBSCRIBER (1),
UNKNOWN (2),
NATIONAL (3),
INTERNATIONAL (4),
NETWORK_SPECIFIC (5),
NETWORK_ROUTING_NATIONAL (6),
NETWORK_ROUTING_NETWORK_SPECIFIC (7),
NETWORK_ROUTING_WITH_CALLED_DIRECTORY (8),
...
}
For more information, please see OpenCloud’s CGIN.
NumberingPlan
This value is part of the CAP and ETSI INAP CalledPartyNumber.
The allowed values are:
-
SPARE_0 -
ISDN -
SPARE_2 -
DATA -
TELEX -
NATIONAL_5 -
NATIONAL_6 -
SPARE_7
The values are as if the type were specified in ASN.1 as follows:
NumberingPlan ::= ENUMERATED {
SPARE_0 (0),
ISDN (1),
SPARE_2 (2),
DATA (3),
TELEX (4),
NATIONAL_5 (5),
NATIONAL_6 (6),
SPARE_7 (7)
}
For more information, please see OpenCloud’s CGIN.
Visited Network ID Address List
Both the IN and SIP Reorigination features make use of an address list for mapping a given VLR address to a Visited Network ID. This is used as a fallback if the InitialDP does not contain suitable location information.
The SIP feature uses this address list in order to populate headers on the outgoing INVITE message. The IN feature uses the address list purely as an early failure measure. It checks that there exists a matching Visited Network ID for the VLR address; this prevents network resources from being wasted establishing a SIP dialog that will ultimately fail at the SIP Reorigination feature anyway.
| |
Currently, we require that the VLR address’s nature is International and its numbering plan is ISDN. |
There are two profile tables associated with this address list:
-
<PlatformOperatorName>_SCCReorigination_AddressListConfigurationTable
-
<PlatformOperatorName>_SCCReorigination_AddressListEntryTable
The configuration table is a standard address list configuration table, see Address List Configuration Profile for more information. The list entry table is an extended version of the standard address list entry table (details here: Address List Entry Profile) with one additional field, a String called VisitedNetworkId. Profiles in this table must use a standard format for their names, made up of three fields: the Sentinel Selection Key, a fixed String VisitedNetworks, and the VLR address prefix to be matched when searching for a Visited Network ID. The name should be formatted like this:
-
<SelectionKey>:VisitedNetworks:<AddressPrefix>
Here’s an example:
-
OpenCloud:OpenCloud::::VisitedNetworks:6421
See the respective behaviour sections of the IN and SIP Reorigination feature pages for details on how each feature uses the address list.
For an overview of how address lists work in general, see: Address Lists.
| |
We recommend that the visited network is formatted according to GSMA IR.65 section 6.2.1. I.e. is of the format epc.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org |
Use of the Correlation RA
Both the IN feature and SIP feature share (and communicate) correlation information through the Correlation RA. The resource adaptor entity is specified using the resource-adaptor-entity-link name of sentinel-correlation-reorigination.
The re-origination addresses allocated by the Correlation RA must route through to the IMS, and allow the I-CSCF to trigger the SCC-AS. Typically this is done by configuring a range of numbers that correspond to one or more IMS public service identifiers.
Re-origination basic flow
In the following diagram:
-
Sentinel VoLTE acts as the SCC-AS.
-
The “IN feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature.
-
The “SIP feature” is the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP feature.
-
The User-Data-Request and Answer will not occur if the SkipHSSLookup flag is set to true and instead the value in the DirectRoutingURI will be used.
This flow diagram shows a configuration where the SkipHSSLookup flag is set to false, so that the SCC-AS looks up the HSS and acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the S-CSCF after B number restoration.
As a variation to the above diagram, the follow shows the effect of configuring:
-
SkipHSSLookup flag set to true
-
DirectRoutingURI set to the I-CSCF
For further information related to headers set in the outgoing SIP INVITE, please refer to SIP headers in the outgoing INVITE.
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN
This feature receives a CAP trigger, stores re-origination information, and is able to forward the call such that it is routed into the IMS .
It enables processing circuit-switched originating calls in the SCC-AS.
The related feature is SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP; these features are part of service centralization in the IMS. For this feature’s fit into the overall flow, please see the Re-origination basic flow diagram.
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This feature is IN only, it does not exist in a SIP B2BUA |
Mobile Originating and Mobile Terminating only |
Session_PreInitialCreditCheck |
Yes. See Correlation RA |
No |
Stateless |
1 POJO for IN behaviour |
Network operator data
Network configuration data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile table named SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationConfigProfileTable.
The IN feature shares network operator configuration with the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP feature.
This data is scoped by Sentinel selection key. In other words, each network operator will have one entry in this table.
For more information, see the shared configuration between the IN and SIP feature.
Use of Correlation resource adaptor
For information about use of the Correlation RA, please see the shared Correlation RA.
Session input and output variables
Statistics
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.ss7 SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.ss7 service → volte.sentinel.ss7 SBB → feature → SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature starts. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature failed to start due to an error. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature raised a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature failed due to a major error. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature timed out during execution. |
CallReOriginated |
Counter |
Incremented when the call is successfully re-originated. |
CallReleased |
Counter |
Incremented when reorigination fails and the call is released. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature has not been correctly configured. |
IdpVlrNumberPresent |
Counter |
Incremented when the VLR number is found in the incoming InitialDP. |
IdpVlrNumberNotPresent |
Counter |
Incremented when the VLR number is not found in the incoming InitialDP. |
VisitedNetworkIdNotFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine the Visited Network ID. |
VisitedNetworkIdFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is able to determine the Visited Network ID based on the VLR address. |
PoolAllocationFailed |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to acquire a correlation ID from the correlation RA. |
PoolAllocationSucceeded |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature acquires a correlation ID from the correlation RA. |
OriginatingIMRNAttempt |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature executes reorigination for an originating call leg. |
TerminatingIMRNAttempt |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature executes reorigination for a terminating call leg. |
Behaviour
The feature is triggered with an Initial DP. If the call type is not Mobile Originating or Mobile Terminating, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
The feature checks if the Initial DP is a CAMEL initial DP. If not, it finishes executing without modifying any state.
It then checks network configuration, and if not present it informs Sentinel that it failed to execute, with an invalid configuration cause. It then finishes execution.
Once configuration is loaded, it attempts to re-originate the call (that is, forward the call into the IMS). This works as per the re-origination section.
Re-originating the call
The IDP is checked for the presence of the CalledPartyBCDNumber. If not present, the call is treated as per the Failure to re-originate section.
Following that, the feature uses the Visited Network ID Address List to check that there is a known Visited Network ID for the VLR address present in the IDP location information. If there is a matching ID, the feature will continue processing as normal. If there is no matching ID the feature will terminate the call as per the Failure to re-originate section. The purpose of this is to avoid wasting resources establishing the SIP side of the call, only to have it fail when the SIP reorigination feature is unable to find a matching Visited Network ID.
The feature then consults the Correlation resource adaptor entity in order to allocate a re-origination address. This is an address that is used for routing the call onwards. The Correlation resource adaptor entity stores both the correlation number allocation, and the key fields of the CAP Initial DP argument. These are used later, in the SIP feature.
The feature then builds a destination routing address, using the address returned by the Correlation RA, and the network configuration for the address’s Nature, RoutingToInternalNetworkNumber, and NumberingPlan fields. The network configuration for a prefix is used if the network configuration indicates a prefix is required. This address is called the “IP Multimedia Routing Number”, or IMRN for short.
It then creates a new Connect operation, using the IMRN in the Destination Routing Address field, and requests sending of the Connect and a close of the TCAP dialog.
| If | Then |
|---|---|
|
there are any problems with any of:
|
the call is treated according to Failure to re-originate and a |
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP
This feature is triggered from the I-CSCF and retrieves re-origination information; optionally it can retrieve the subscriber’s assigned S-CSCF either from a HSS or from a profile from network configuration, then acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the subscriber’s assigned S-CSCF .
It is one of two features that enable circuit switched originating calls to be processed in the SCC-AS. The related feature is SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN. These features are part of service centralization in the IMS.
| |
For this feature’s fit into the overall flow, please see the Re-origination basic flow diagram. |
Feature cheat sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC signalling anchor B2BUA |
From SIP triggering perspective, neither. Mobile Originating and Mobile Terminating determined from saved CAMEL IDP |
SipAccess_SessionAccept |
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
Triggered by the I-CSCF |
Network operator data
Network configuration data is stored in a JSLEE configuration profile table named: SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationConfigProfileTable.
The SIP feature shares network operator configuration with the SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN feature.
This data is scoped by Sentinel selection key. In other words, each network operator will have one entry in this table.
For more information, please see shared configuration between the IN and SIP feature.
Use of Correlation resource adaptor
For information about use of the Correlation RA, please see the shared Correlation RA..
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Reoriginated |
Boolean |
Set to |
Statistics
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
Complete |
The feature ran to completion |
MultipleHistoryInfoHeadersFound |
Multiple history-info headers found on the INVITE |
NoHistoryInfoHeaderFound |
no history-info header found on the INVITE |
OneHistoryInfoHeaderFoundAndRemoved |
One history-info header found on the INVITE and removed |
HSSLookupFailed |
HSS lookup failed |
HSSLookupSuccess |
HSS lookup succeeded |
HSSLookupSkipped |
HSS lookup was skipped due to SkipHSSLookup feature configuration flag |
CorrelationRaQueried |
Correlation RA was queried for the call information |
CorrelationRaQuerySuccess |
The Correlation RA query succeeded |
CorrelationRaQueryFailure |
The Correlation RA query failed |
IdpVlrNumberPresent |
The VLR number is present in the initial IDP |
IdpVlrNumberNotPresent |
The VLR number is not present in the initial IDP |
VisitedNetworkIdFound |
The feature could set the Visited Network Id based on the Location information or on the VLR address |
VisitedNetworkIdNotFound |
The feature could set the Visited Network Id |
IdpCalledPartyNumberPresent |
The initial IDP has a called party number or called party BCD number |
IdpCalledPartyNumberNotPresent |
The initial IDP does not have a called party number or called party BCD number |
SCSCFAddressNotFound |
The SCSCF could not be found in configuration, or retrieved from the HSS |
Started |
The feature starts |
FailedToStart |
The feature failed to start due to an error |
IssuedWarning |
The feature raised a warning |
FailedDuringExecution |
The feature failed due to a major error |
TimedOut |
The feature timed out during execution |
Behaviour
The feature is triggered on receipt of a SIP INVITE from the I-CSCF.
It checks for network operator data. If not present, the feature informs Sentinel that it failed to execute due to invalid configuration.
It looks at the received INVITE Request URI, and checks that it represents a phone number.
If the network configuration indicates a prefix is in use, it checks that the request URI’s digits start with that prefix. If not, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state. In other words, this is treated as an INVITE that is not for this feature.
The feature then attempts to retrieve the correlation data that was stored by the IN feature. This data is looked up using the request URI’s digits as the key for the correlation data.
If correlation data is not found, the feature finishes execution without modifying any state.
If correlation data is found, the feature tries to extract the Mobile Country Code and the Mobile Network Code from the Cell Global Id or Location Area Id present in the Location Information section of the Initial IDP. If a MCC and MNC is found, a Visited Network Id is created in the format epc.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org, according to IR65 section 6.2.1.
In the case of originating Initial DP arguments, if a MCC and MNC is found, and the Initial DP includes a Cell Global ID with a Location Area Code, the P-Access-Network-Info header is set to the form 3GPP-GERAN;cgi=3gpp=<mcc><mnc><location area code><cellId>.
If MCC or MNC is not present, the feature uses the Visited Network ID Address List to find the Visited Network ID for the VLR address in the data. If a matching Visited Network ID is found, it is included in a header in the outgoing SIP request. If no matching ID is found then reorigination will be aborted. In practice this should never happen, as the IN reorigination feature performs this check as well and will terminate reorigination before any SIP signalling occurs if no Visited Network ID is found.
Next, the feature then retrieves the S-CSCF name for the calling party from either of two places based on the SkipHSSLookup flag:
| Flag Value | Effect |
|---|---|
|
Use the value in DirectRoutingURI from network configuration. |
|
Do a lookup from the HSS through the Sh Cache RA. |
The feature then adjusts or sets various headers in the outgoing INVITE.
Finally, the SIP Sentinel instance hosting this feature acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the S-CSCF.
SIP headers in the outgoing INVITE
The feature sets or adjusts the following headers in the outgoing INVITE:
| Header Name | Change |
|---|---|
|
Set to a tel URI with the digits being the original IDP’s called party number digit string (non-BCD encoded). |
|
Set to the original IDP’s called party number digit string (non-BCD encoded). |
|
If only one such header exists on the |
|
If it is not present in the |
|
Set to |
|
A new route to the S-CSCF for the served user is added, if the feature was invoked on an originating trigger an |
|
In case of originating Initial DP argument containing suitable location information, the feature sets this header in the form of |
|
If the feature was invoked on an originating trigger, this is set to the Visited Network ID found in the corresponding to MCC and MNC or from Address List based on the VLR address. |
|
If the feature was invoked on an terminating trigger, this is set to the Visited Network ID found in the corresponding to MCC and MNC or from Address List based on the VLR address. |
|
Set to the VLR address from the correlation data as a VLR Number address in a string. |
|
If such header exists in the |
| |
The OC-Term-P-Visited-Network and OC-VLR-Number are proprietary headers created by OpenCloud. |
Formatting of the OC-VLR-Number header
The OC-VLR-Number header value is built by:
-
retrieving the VLR address in the original InitialDP
-
converting the SCCP address into an ascii string, formatted according to SS7’s AddressStringParser
-
setting resulting the string into the SIP header value
The resulting complete header will be OC-VLR-Number: address=651232343,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN
Terminating Access Domain Selection Features
For an overview of Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS) see Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS).
T-ADS features implement the routing strategy for a terminating call. It provides support for route signaling towards PS and CS domains, in a sequential, parallel or exclusive manner.
Sequential routing attempts to route towards a single preferred domain, and "falls back" to the non-preferred domain upon receipt of certain responses.
Parallel routing routes towards the PS and CS domains simultaneously. It decides the "chosen" domain based on responses that it receives.
The conditions for routing to PS and CS are checked by the SCCTADSDataLookup feature.
| Feature | What it does |
|---|---|
|
T-ADS Data Lookup gathers information from the received SIP signalling, and optionally queries the HSS, in order to determine available PS and CS routes that can be used to deliver the call to the served user. |
|
|
It takes the T-ADS preferred routing decision from SCCTADSDataLookup, and uses it to attempt routing. |
|
|
The T-ADS Parallel Routing feature parallel-forks the incoming message to both CS and PS legs, and forwards the response from the leg that successfully responds first |
|
|
Retrieves the Correlation MSISDN (C-MSISDN) from the HSS by using the "Sh-Pull" operation |
|
|
Retrieves the Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) from the HLR by using MAP "Send Routing Information" operation |
FetchMSRN
FetchMSRN retrieves the MSRN (Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number) and the VLR number from the HLR.
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
SBB |
Session input variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
The list of registration records for the subscriber, used to find the subscriber’s identity for the HLR lookup. |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Used to retrieve configuration data for the feature. |
Subscriber |
String |
Used to obtain the subscriber’s identity if it could not be determined from the registration data. |
Session output variables
| Variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
MSRN |
String |
The MSRN of the served user, if the feature could retrieve it. |
HasMSRN |
boolean |
Boolean indicating whether the MSRN session state field has been populated. |
CallReferenceNumber |
byte[] |
The Call Reference Number used in the SRI request to the HLR. |
VLRNumber |
AddressString |
The VLR number for the served user, if the feature could retrieve it. |
Network Operator Data
The FetchMSRN feature depends on network operator data in two configuration profile tables. One is for feature specific configuration, the other is for general HLR connection configuration.
Feature Configuration
Feature specific configuration is set in a profile table called: SCCFetchMSRNConfigProfileTable. Profiles are scoped on Sentinel Selection Key.
SCCFetchMSRNConfigProfileTable
| Attribute | Type | Default Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
SuppressTcsi |
boolean |
true |
If enabled the feature will set the |
ForceSipUserEqualsPhone |
boolean |
false |
If true, when attempting to extract a number from a SIP URI, the feature will extract a number even if the URI does not have the |
HLR Connection Configuration
The FetchMSRN feature uses the common HLR configuration profile table. See this page for details: HLR CGIN MAP Configuration.
Statistics
FetchMSRN statistics are tracked by the FetchMSRN SBB and can be found using the parameter set SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=scc-fetch-msrn-feature,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0]
Or in REM under the following parameter sets:
SLEE-Usage → Services → volte.sentinel.sip service → scc-fetch-msrn-feature SBB
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is invoked. |
Failed |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error has occurred. |
RequestSent |
Counter |
Incremented when a request is sent to the HLR. |
RequestFailed |
Counter |
Incremented when a MSRN is not received from the HLR. |
RequestReceivedAbsentSubscriber |
Counter |
Incremented if the HLR indicates that the requested subscriber is not CS attached. |
RetrievedVLRNumber |
Counter |
Incremented if a VLR number is included in the result from the HLR. |
RetrievedMSRN |
Counter |
Incremented when an MSRN is received from the HLR. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between sending the request to the HLR and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
The feature issues a query to the HLR for the MSRN using the MAP operation Send Routing Info. The MAP Application Context used is locationInfoRetrievalContext_v3_ac.
When building the request to the HLR, the feature retrieves the "digits" portion of the IMS default public ID of the Served user from the first entry in the RegistrationRecords session state field. If this field does not contain digits, the "digits" portion of the subscriber ID is used.
Note that the feature does not use the entire ID, only the digits portion. Specifically, the feature will use the numbers in a Tel URI, or the user part of a SIP URI that has the 'user=phone' parameter if ForceSipUserEqualsPhone is false, or the user part of a SIP URI without the 'user=phone' parameter if ForceSipUserEqualsPhone is true.
Also while building the HLR request the feature will generate a Call Reference Number. This is then put into a header on the outgoing INVITE called OC-IM-CallReferenceNumber.
If the feature configuration option SuppressTcsi is enabled, then the Suppress_T_CSI flag will be set in the CamelInfo on the request. This will prevent the VLR number from being included in the response.
The HLR may return either a failure response, or a SendRoutingInfo-Res response containing the MSRN in the field ExtendedRoutingInfo.
If the feature is invoked, it increments the Started counter.
If any fatal error during the feature execution occurs, it increments the Failed counter.
If the feature is able to find an MSRN in the returned set, it increments the RequestSuccessful counter, and modifies the output session state variables. If there is a VLR number in the returned set, this will also be output to a session state variable.
If the returned set is empty, the feature increments the RequestFailed counter, and does not modify any output session state variables.
If the HLR returns a failure response, the feature increments the RequestFailed counter, and does not modify any output session state variables.
SCCTADSDataLookup
T-ADS Data Lookup gathers information from the received SIP signalling, and optionally queries the HSS, in order to determine available PS and CS routes that can be used to deliver the call to the served user.
All valid routes to PS and CS domains are written into session state. This information is then read by the appropriate T-ADS Routing feature, either SCCTADSRouting (for sequential routing) or SCCTADSParallelRouting (for parallel routing).
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Terminating |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
SBB |
Session Input Variables
| Session state variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
CallType (Enum) |
The call-type for the incoming call (e.g. MobileTerminating). |
RoutingMode |
TADSRoutingMode (Enum) |
Determines whether CS and/or PS routing is enabled and the preferred attempt order. |
IsLoggedIn |
boolean |
Set to true when the served user is currently logged in to the IMS. |
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
This contains all of the current registration information for the served user. |
CMSISDN |
String |
A string set to a non-null value if there is a C-MSISDN provisioned for the user, and if the user is logged in; |
MSRN |
String |
A string set to a non-null value if there is a MSRN provisioned for the user, and if the user is logged in; |
Subscriber |
String |
The subscriber’s identity. |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Used to acquire configuration information. |
Session Output Variables
| Session state variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
BlindPSRouting |
boolean |
Indicates whether blind PS routing is permitted. |
RoutingMode |
TADSRoutingMode (Enum) |
The routing strategy to be used by the T-ADS routing features. |
TADSSipInstanceRoutingPossible |
boolean |
Indicates whether T-ADS sip.instance routing is possible for the served user. |
TADSCircuitRoutes |
Queue<String> |
Contains all valid CS domain routes (CSRNs) that the feature has calculated |
TADSPacketRoutes |
Queue<RouteAndTerminatingDomain> |
Contains all valid PS domain routes that the feature has found along with the network type for each route. |
Network Operator Data
T-ADS Data Lookup has network operator data in a JSLEE profile table named SCCTADSDataLookUpConfigProfileTable and also SCCTADSNetworkTypeConfigProfileTable. The data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
SCCTADSDataLookUpConfigProfileTable
| Attribute | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
CSRNPrefix |
String |
The prefix is prepended to the beginning of a C-MSISDN or MSRN to create a CSRN. |
ForceSipUserEqualsPhone |
boolean |
If true, when attempting to extract a CS routable number from a SIP URI, the feature will proceed even if the URI does not have the |
VoiceOverPSSupportRequired |
boolean |
If true, the HSS must be queried for voice over PS support as part of the decision to attempt to route via PS. |
RequestUserIdentityType |
TADSRequestIdentities (Enum) |
Specifies which identities will be used for the voice over PS support request to the HSS. |
EnableSipInstanceRouting |
boolean |
Determines whether the feature should attempt to use +sip.instance routing to calculate PS routes. |
EndSessionWhenNoValidRouteFound |
boolean |
Will cause the feature to refuse an incoming |
EnableCSRoutingFromRequestUri |
boolean |
When enabled, if there is no CMSISDN or MSRN available, the feature will attempt to derive a CSRN from the Request-URI of the incoming INVITE request. |
SCCTADSNetworkTypeConfigProfileTable
| Attributes | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
NetworkType |
String |
Either the RAT value or the Network Access Type value. |
TerminatingDomain |
String |
The value used to populate the OC-Terminating-Domain Header when processing a response from a network of this type |
Description |
String |
A text field for a description. |
The SCCTADSNetworkTypeConfigProfileTable has multiple profiles, each one being either a RAT value or Network Access Type that will be checked to determine if a call can proceed on the PS network.
Each profile includes a TerminatingDomain value that T-ADS Data Lookup uses this value to populate the PSTerminatingDomainHeaderValue session state variable. The T-ADS Routing features use this to send information about the terminating access domain to upstream network nodes as described here.
The system comes with some default profiles pre-configured as follows, Where ${platform.operator.name} will be substituted with the value used on installation.
| Profile Name | Network Type | TerminatingDomain | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
${platform.operator.name}:::::1004
|
1004 |
PS=EUTRAN |
RAT value 1004 = E-UTRAN from TS 29.212 section 5.3.31 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::3GPP-E-UTRAN
|
3GPP-E-UTRAN |
PS=EUTRAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::3GPP-E-UTRAN-FDD
|
3GPP-E-UTRAN-FDD |
PS=EUTRAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::3GPP-E-UTRAN-TDD
|
3GPP-E-UTRAN-TDD |
PS=EUTRAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
Additionally if WLAN is chosen as part of the installation for allowed access types, the following entries will also be present in the profile table.
| Profile Name | Network Type | TerminatingDomain | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
${platform.operator.name}:::::0
|
0 |
PS=WLAN |
RAT value 0 = WLAN from TS 29.212 section 5.3.31 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::3GPP-WLAN
|
3GPP-WLAN |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::IEEE-802.11
|
IEEE-802.11 |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::IEEE-802.11A
|
IEEE-802.11A |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::IEEE-802.11B
|
IEEE-802.11B |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::IEEE-802.11G
|
IEEE-802.11G |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
${platform.operator.name}:::::IEEE-802.11N
|
IEEE-802.11N |
PS=WLAN |
P-Access-Network-Info value from TS 24.229 section 7.2A.4 |
Statistics
SCCTADSDataLookUp statistics are tracked by the SCCTADSDataLookUp SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SCCTADSDataLookUp SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
QueriedShCache |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sh Cache is queried. |
ShCacheDataReceived |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sh Cache returns data from the query. |
FoundValidCSRoute |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds a valid route to the CS domain. |
FoundValidPSRoute |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds a valid route to the PS domain. |
MsrnAndCmsisdnBothSet |
Counter |
Incremented when both CMSISDN and MSRN are set in session state. |
CannotSetCSRN |
Counter |
Incremented when the CSRN cannot be calculated. |
BlindPSRoutingRequested |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature has set the BlindPSRouting Session State field. |
NoForkDispositionOverrodeRoutingMode |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature does not fork due to disposition header. |
TriggeredEndSession |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature rejects an |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between requesting data from the Sh-Cache RA and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Behaviour
Determining Routing Strategy
On receiving an INVITE request, the feature will analyse several headers in the request to determine how terminating domain selection should proceed. The main value checked is the oc-tads-routing parameter on the top-most Route header URI; in addition the feature also looks for the oc-blindpsrouting parameter on the same header, and certain values in the Request-Disposition header.
OC-TADS-Routing Parameter
oc-tads-routing is a custom parameter for the Route header. It determines the routing strategy used by T-ADS for domain selection. The following table shows the possible values of the parameter and resulting behavior:
| Parameter Value | Behaviour |
|---|---|
|
|
SCCTADSRouting feature will be invoked to attempt connection over PS first, sequentially forking to CS if that fails. |
|
|
SCCTADSRouting feature will be invoked to attempt connection over CS first, sequentially forking to PS if that fails. |
|
|
SCCTADSRouting feature will be invoked to attempt connection over PS only. |
|
|
SCCTADSRouting feature will be invoked to attempt connection over CS only. |
|
|
SCCTADSParallelRouting feature will be invoked to attempt connection over CS and PS simultaneously. |
OC-Blindpsrouting Parameter
oc-blindpsrouting is another custom parameter for the route header. If this parameter is present on the top-most Route header URI, T-ADS will allow blind PS routing (i.e. no attempt will be made to verify that termination in the PS domain is supported/allowed).
Request-Disposition header
The Request-Disposition header is specified by RFC-3841. The header contains a comma separated list of values. There are many possible values that can be contained within this header, but TADS Data Lookup is only interested in two:
| Value | Behaviour |
|---|---|
|
|
This will cause T-ADS to override the |
|
|
If this value is present in the header, the |
Determining CS Routes
The feature will always try to calculate a CSRN for use if CS routing is needed.
-
First it will try to calculate a CSRN based on the
CsrnPrefix+root. Therootwill be either C-MSISDN or MSRN, depending on which is present. If both are set, a statistic will be incremented and the MSRN will be used in preference. -
If this fails, and the
EnableCSRoutingFromRequestUriconfiguration parameter is enabled (the default), it will then attempt to calculate the CSRN by prepending the CSRN prefix to the 'digits' in theRequest-URI.
| If the Request-URI is… | Then |
|---|---|
|
a tel URI |
any |
|
a SIP URI with parameter |
any |
|
a SIP URI without parameter |
the feature checks if the user part of the
|
If a CSRN is successfully calculated, it will be added to the TADSCircuitRoutes queue in session state.
If all of these fail, then no CS route will be set and the T-ADS routing features will not attempt to route to CS.
Some examples where the feature cannot compute a CSRN include when the user is not logged in, and:
-
the
Request-URIis not a Digits URI (that is, not a tel URI, or not a SIP URI withuser=phone);
andForceSipUserEqualsPhoneis false -
the
Request-URIis a SIP URI withoutuser=phone;
andForceSipUserEqualsPhoneistrue, but the user part does not “look like” a phone number.
Retrieving the CMSISDN or MSRN
The FetchCMSISDN and FetchMSRN features query the HSS and HLR respectively. The CMSISDN or MSRN form part of the Circuit Switched Routing Number (CSRN). If the CMSISDN is in the third-party registration data store, then the FetchCMSISDN feature is not executed during INVITE processing.
Determining PS Routes
The T-ADS Data Lookup feature has two ways of determining PS routes. Which one it uses depends on whether +sip.instance routing is enabled in the feature configuration. If +sip.instance routing is disabled, the feature will attempt to use the subscriber’s identity from Sentinel session state as a destination route. If +sip.instance routing is enabled, the feature will analyse all active registrations for the served user, searching for pub-gruus to use as destination routes. Regardless of how a route is determined, the feature will perform additional analysis to discover if the route is actually usable for PS routing.
If the subscriber is not logged in to the IMS according to the IsLoggedIn session state field, the T-ADS Data Lookup feature will not select any PS routes under any circumstances.
Determining Possible Route When +sip.instance Routing is Disabled
When +sip.instance routing is not in use, the feature will attempt to use the current subscriber identity from Sentinel session state. This identity is determined by the SIP Subscriber Determination Feature. The subscriber identity will be checked using the procedures outlined below, and if it is found to be a valid PS route it will be added to the TADSPacketRoutes queue in session state.
Determining Possible Routes When +sip.instance Routing is Enabled
When using +sip.instance routing, the feature will search for PS routes in the served user’s registration data. The Contact headers associated with every active registration for the served user will be checked for a pub-gruu parameter. The value of each pub-gruu parameter that is found will be checked using the procedures outlined below, and if it is found to be a valid PS route it will be added to the TADSPacketRoutes queue in session state. If no valid +sip.instance routes are found, the feature will attempt to find a PS route with the procedure used when +sip.instance routing is disabled.
Note that +sip.instance routing cannot be used with T-ADS parallel routing.
Determining Validity of a PS Route
Regardless of which of the above methods were used to find the possible PS route(s), each route will be checked to ensure it is valid to attempt to route to it over the PS domain.
There are three approaches the feature can use to validate the route:
-
Checking the registration data associated with the route
-
Querying the HSS for T-ADS information
-
No additional validation beyond checking the subscriber is logged into the IMS
Which method is used is based on the VoiceOverPSSupportRequired feature configuration option, and the oc-blindpsrouting Route header parameter:
| VoiceOverPSSupportRequired | oc-blindpsrouting Route Parameter | Validation method |
|---|---|---|
False |
Absent |
Registration Data |
False |
Present |
No Additional Validation |
True |
Absent |
HSS Query |
True |
Present |
No Additional Validation |
Once a route is found to be valid, it will be added to the TADSPacketRoutes queue in session state.
Validation by Registration Data
When validating a route by registration data, the feature will retrieve the registration record associated with the route:
-
For routes determined with +sip.instance routing, this will be the registration that contained the
pub-gruuthat is being validated. -
For routes determined without +sip.instance routing, every active registration will be checked (only one needs to pass validation).
The feature will check the P-Access-Network-Info header information in the registration data to decide if PS can be supported. If the access-type values in any of the P-Access-Network-Info headers can be found in the SCCTADSNetworkTypeConfigProfileTable then the feature will consider the route valid.
Validation by HSS Query
If the feature needs to validate routes using the HSS it will form a query to the Sh-Cache RA. This query uses Data Reference 26 T-ADS Information. The access key is determined by the value of the RequestUserIdentityType feature configuration value:
| RequestUserIdentityType | Access Key Public ID | Access Key Private ID |
|---|---|---|
IMPU |
SessionState → |
None |
MSISDN |
SessionState → |
None |
IMPU_IMPI |
SessionState → |
Registration → |
MSISDN_IMPI |
SessionState → |
Registration → |
Which registration is used to get the private ID will depend on how the PS routes were determined:
-
For routes determined with +sip.instance routing, this will be the registration that contained the
pub-gruuthat is being validated. -
For routes determined without +sip.instance routing, every active registration will be checked (only one needs to pass validation).
This means when an IMPI is required in the query, multiple queries may be needed.
The response to each query will be analysed:
-
If the HSS response indicates that voice over PS is not supported, then the associated route(s) will be considered invalid.
-
If the HSS response indicates that voice over PS is supported and the RAT type in the same response is present in the
SCCTADSNetworkTypeConfigProfileTable, then the associated route(s) will be considered valid.
If No Valid Routes Are Found
If the feature is unable to determine any valid PS or CS routes for the given routing strategy, then its behaviour will be determined by the EndSessionWhenNoValidRouteFound configuration parameter. If the parameter is set to false (the default), then T-ADS will allow the incoming INVITE to be forwarded as-is. If the parameter is set to true, the feature will generate a 503 response to the incoming INVITE request, terminating the call.
SCCTADSRouting
T-ADS Routing executes after T-ADS data lookup feature and performs sequential forked routing.
It takes the T-ADS preferred routing decision from SCCTADSDataLookup, and uses it to attempt routing.
It makes the necessary adjustments for PS or CS routing to the outgoing INVITE as required.
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Terminating only |
|
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
The feature itself is stateless, but an FSM is encoded into session state |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
CallType (Enum) |
The call-type for the incoming call (e.g. MobileTerminating). |
RoutingMode |
TADSRoutingMode (Enum) |
Determines whether CS and/or PS routing is enabled and the preferred attempt order. |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Used to acquire configuration information. |
TADSCircuitRoutes |
Queue<String> |
Contains all valid CS domain routes (CSRNs). |
TADSPacketRoutes |
Queue<RouteAndTerminatingDomain> |
Contains all valid PS domain routes along with the network type for each route. |
TADSSipInstanceRoutingPossible |
boolean |
Indicates whether T-ADS +sip.instance routing is possible for the served user. |
BlindPSRouting |
boolean |
True if Blind PS Routing behaviour is to be used. |
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Management interface for controlling Feature-Caps header values on outgoing messages. |
RegistrationRecords |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
List of registered devices for the served user, determines the maximum number of downstream forks to wait for when routing on the preferred domain. |
Session Output Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
TerminatingDomain |
String |
Records the current value being used for the OC-Terminating-Domain Header |
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Management interface for controlling Feature-Caps header values on outgoing messages. |
Network Operator Data
T-ADS Routing has network operator data in a JSLEE profile table named SCCTADSRoutingConfigProfileTable. The data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
| Attributes | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
TimerTADS |
int |
The time in milliseconds that the feature will wait for an acceptable response when routing to the preferred leg. This value is required to be between 500 and 5000 ms. |
BlindRoutingCSFallbackResponseCodes |
int[] |
The list of SIP error response codes that will be checked if Blind PS Routing is used |
RouteCSDirectlyThroughICSCF |
boolean |
When true, T-ADS will route requests to the CS domain directly via the I-CSCF (bypassing the S-CSCF) |
T-ADS Routing also draws additional network operator data from SIP service configuration in a J-SLEE profile table named SipSentinelConfigurationTable. The data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
| Attributes | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
IcscfUri |
String |
The |
Statistics
SCCTADSRouting statistics are tracked by the SCCTADSRouting SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SCCTADSRouting SBB ID.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
RouteToPreferredPS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a preferred leg when PS is preferred. |
RouteToPreferredCS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a preferred leg when CS is preferred. |
RouteToFallbackPS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a fallback leg when PS is preferred. |
RouteToFallbackCS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a fallback leg when CS is preferred. |
ErrorResponseMatched |
Incremented when the PS call error response code matches a value in |
Error18xMatched |
Incremented when the PS call 18x response matches the SDP requirements outlined in 18x Response. |
Received18xResponse |
Incremented when the feature receives a 18x response to the initial |
Received488Response |
Incremented when the feature receives a 488 message from the PS call. |
ReceivedBlindPSRoutingResponse |
Incremented when the feature receives a error message from the PS call that is contained in |
TerminatingDomainHeaderSet |
Incremented when the feature adds a terminating domain header to an upstream response |
TADSTimerFired |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer for a response on a routing attempt is exceeded |
Behaviour
The following behaviour is described below:
Sequential routing strategies
The default routing strategy in VoLTE is to try to route to PS domain first and fallback to CS domain. This behaviour can be changed by the value of the parameter oc-tads-routing in the Route Header Parameters.
Based on the value of the RoutingMode session state field (calculated from the content of oc-tads-routing parameter), one of the following sequential routing modes is selected:
PS Domain only
RoutingMode = PS-ONLY
The feature tries to route towards the PS domain with no fall back to the CS domain. 100-TRYING responses and QoS negotiation are not shown in the flow. 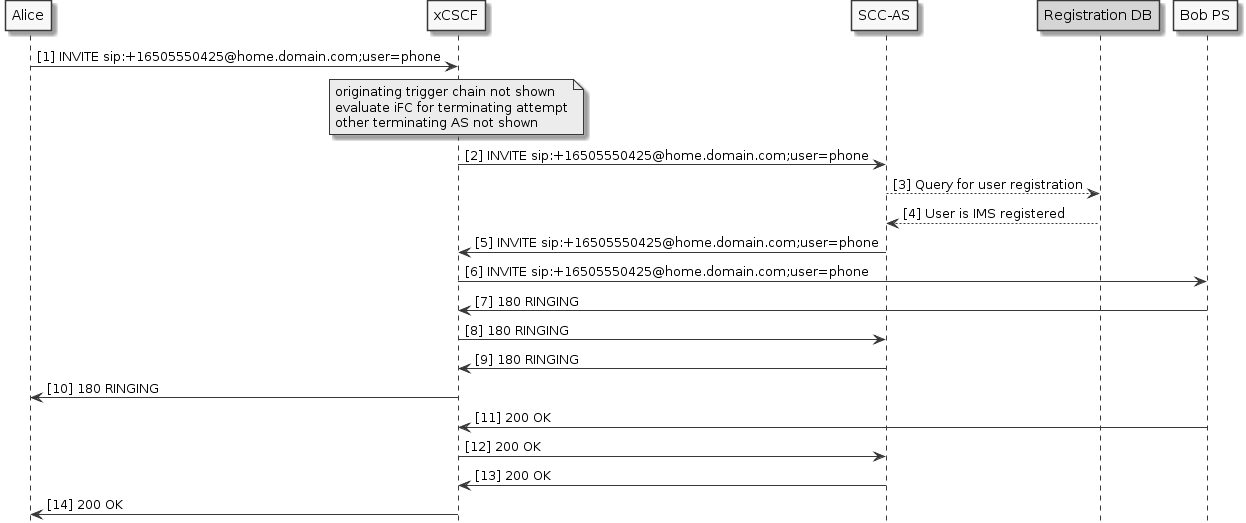
CS Domain only
RoutingMode = CS-ONLY
The feature tries to route towards the CS domain with no fall back to PS domain. 100-TRYING responses and QoS negotiation are not shown in the flow. 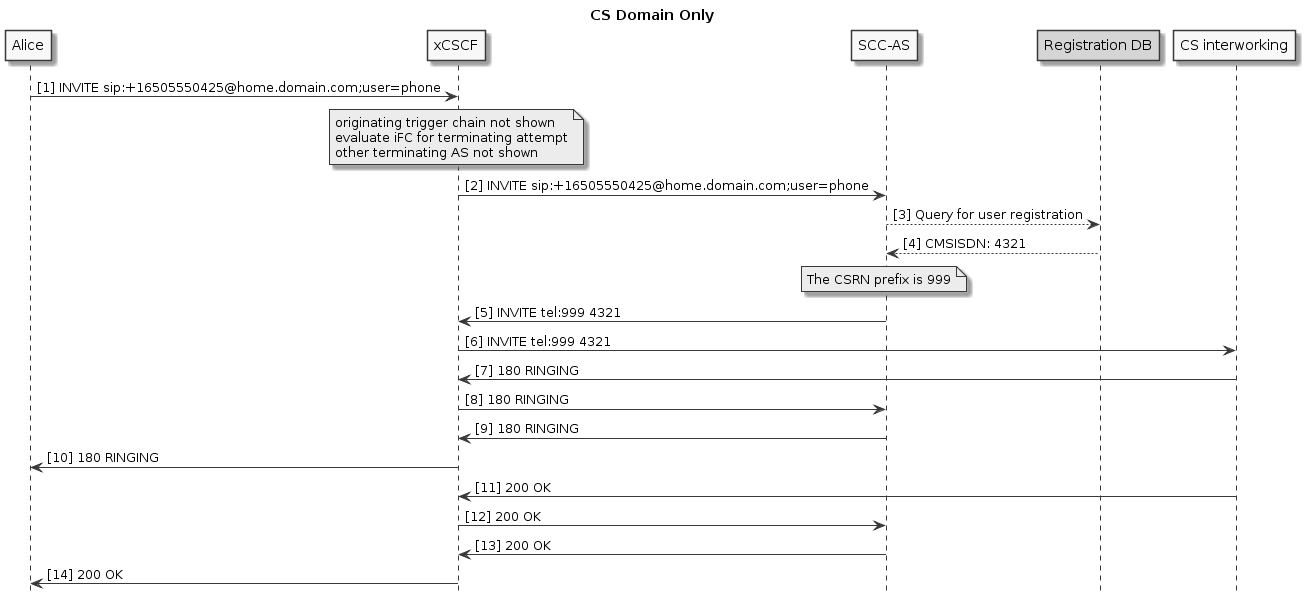
PS network first with fallback to CS network
RoutingMode = PS-CS
The feature tries the PS domain first and drops to CS if the PS conditions don’t match. This allows the setting of Package Switch network as a preferred domain but also allows the usage of a Circuit Switch network if the user is available. This is the default mode. 100-TRYING responses and QoS negotiation are not shown in the flow. 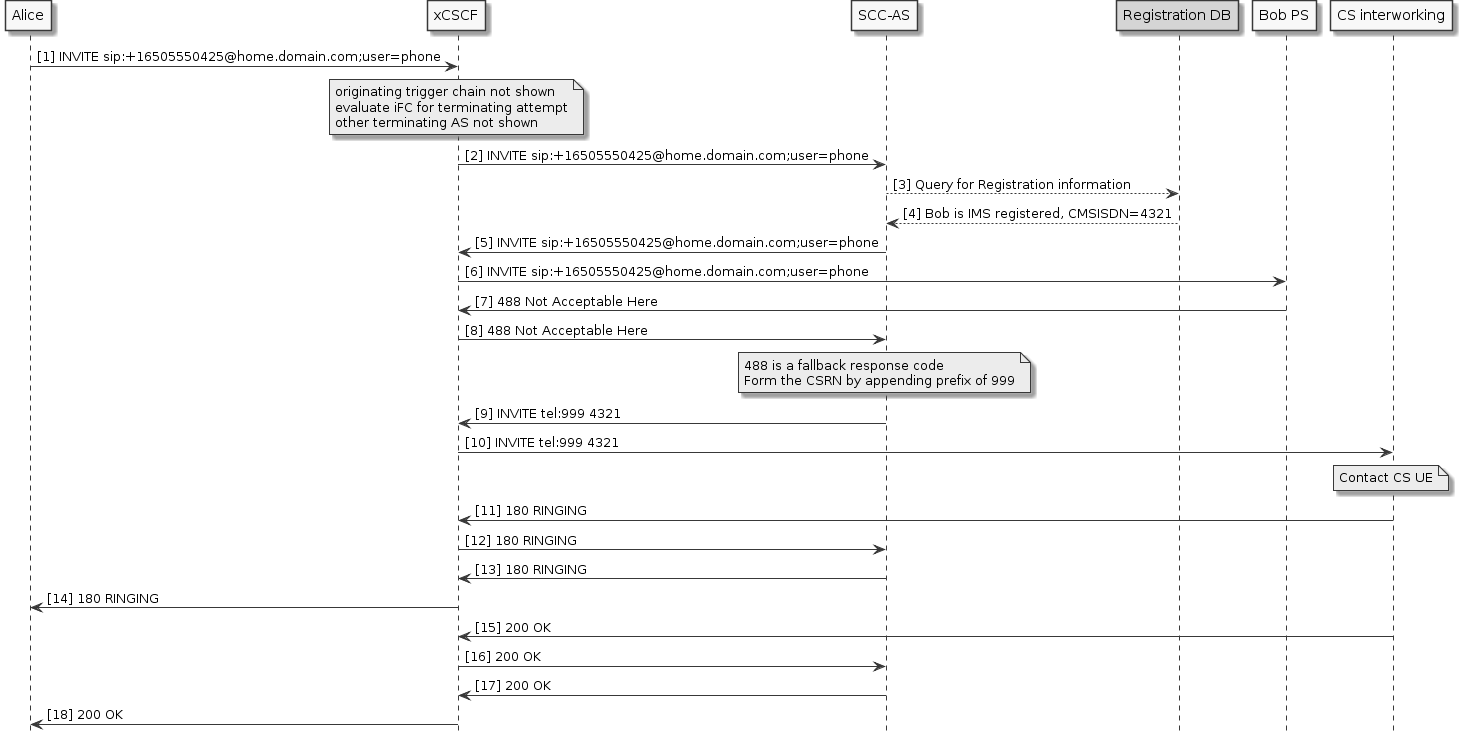
CS network first with fallback to PS network
RoutingMode = CS-PS
The feature tries the CS domain first and drops to PS if the CS conditions don’t match. This allows the setting of Circuit Switch network as a preferred domain but also allows the usage of a Package Switch network if the user is logged in. 100-TRYING responses and QoS negotiation are not shown in the flow. 
Selected Domain is CS
If T-ADS chooses to deliver on the CS domain, the T-ADS Routing feature will iterate through the CSRNs queued in the TADSCircuitRoutes session state field.
Going one at a time, for each CSRN the feature will:
-
Create an
INVITEto the called party using the CSRN as theRequest-URIand also as theToheader. -
If
RouteCSDirectlyThroughICSCFis enabled in feature configuration, theRouteheader will be modified to direct the request to the configuredIcscfUri. -
Add a
Request-Dispositionheader indicatingno-fork. -
Send the
INVITEand await a response. -
Handle responses according to behaviour outlined below.
The feature will iterate to the next CSRN if the call fails but meets the conditions for fallback. If all possible CSRNs are exhausted and the routing strategy is CS-PS, the feature will fall-back to PS routing.
Note that the response handling for 488 and 18x Responses is the same when the PS domain is selected and the same fallback rules are applied.
Selected Domain is PS
If T-ADS chooses to deliver on the PS domain, the T-ADS Routing feature will iterate through the URIs queued in the TADSPacketRoutes session state field.
Going one at a time, for each URI the feature will:
-
Create an
INVITEto the called party using the URI as theRequest-URIand also as theToheader. -
If
TADSSipInstanceRoutingPossibleistruein session state, add aRequest-Dispositionheader indicatingno-fork. -
Send the
INVITEand await a response. -
Handle responses according to behaviour outlined below.
The feature will iterate to the next URI if the call fails but meets the conditions for fall-back. If all possible URIs are exhausted and the routing strategy is PS-CS, the feature will fall-back to CS routing.
Response handling
The responses are handled the same way for PS and CS domains.
Max Wait Timer
Upon forwarding the INVITE request towards the preferred access network, the T-ADS routing feature arms a timer with the value from TimerTADS configuration. If this timer expires before a response to the INVITE request is received, the INVITE will be cancelled and the feature will fall-back to the next available route. The timer will be cancelled if a response is received before it expires, though it may be replaced with a new timer under the conditions outlined in the 18x Response section.
488 Response
After forwarding the INVITE, if the T-ADS Routing feature receives a 488 ("Not Acceptable Here") response from the UE that:
-
does not include any SDP body; OR
-
includes an SDP body:
-
without a media description (
m=) indicatingaudio; -
with a media description (
m=) only indicatingaudiowith the<proto>subfield set toPSTNand with a connection data line (c=) with<nettype>set toPSTN
-
The feature will not forward the response, and it will fall-back to the next available route.
A 488 response that does not meet the above conditions will be forwarded to the calling party.
18x Response
If the T-ADS Routing feature receives a 18x response it will evaluate it to determine if it is acceptable. If the 18x response contains an SDP answer with a media description (m=) set to audio and port portion set to 0, then it is not acceptable. In all other cases the 18x will be considered acceptable.
If the 18x is acceptable the call will proceed on the leg it was received on and T-ADS will complete execution.
If the 18x is not acceptable the feature will arm a timer using the TimerTADS feature configuration value as the duration. The feature will then wait until:
-
a acceptable
18xresponse arrives, in which case the timer will be cancelled and the call will proceed, OR -
a non-
18xresponse arrives, which will be handled as described in its respective response handling section, OR -
the timer expires, OR
-
the number of forked responses is equal to the number of simultaneously registered devices for the served user.
If either of the last two conditions are met, the T-ADS Routing feature will send a CANCEL for the outbound INVITE, and fall-back to the next available route.
Blind PS Routing Response Handling
If the BlindPSRouting flag has been set, then the feature will additionally consider SIP response error codes that are contained in the configured BlindRoutingCSFallbackResponseCodes. These error responses are inspected for the same condition as the 488 Response.
OC-Terminating-Domain header addition
The OC-Terminating-Domain header is added to responses heading upstream (usually for charging purposes). The feature adds this header to all responses for the original INVITE that are forwarded upstream.
For more details see OC-Terminating-Domain Header
SCCTADSParallelRouting
T-ADS Parallel Routing executes after the T-ADS data lookup feature if the session field RoutingMode is set to PARALLEL.
The T-ADS Parallel Routing feature parallel-forks the incoming message to both CS and PS legs, and forwards the response from the leg that successfully responds first
Feature Cheat Sheet
| B2BUA Instance | Originating / Terminating | Point(s) in Session Plan | Network Operator Data | Subscriber Data | Stateful or Stateless | POJO Feature or SBB Feature | Other notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SCC |
Terminating only |
SIP Access Session Pre-Credit Check |
Yes |
No |
Stateless |
POJO |
The feature itself is stateless, but an FSM is encoded into session state |
Session Input Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
CallType |
CallType (Enum) |
The call-type for the incoming call (e.g. MobileTerminating). |
SentinelSelectionKey |
SentinelSelectionKey |
Used to acquire configuration information. |
TADSCircuitRoutes |
Queue<String> |
Used to retrieve a CSRN for CS routing. |
TADSPacketRoutes |
Queue<RouteAndTerminatingDomain> |
Used to determine if PS routing is possible. |
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Management interface for controlling Feature-Caps header values on outgoing messages. |
Session Output Variables
| Session State variable name | Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
TerminatingDomain |
String |
Records the current value being used for the OC-Terminating-Domain Header |
FeatureCapsManager |
FeatureCapsManager |
Management interface for controlling Feature-Caps header values on outgoing messages. |
Network Operator Data
T-ADS Routing has network operator data in a J-SLEE profile table named SccTADSParallelRoutingConfigProfileTable. The data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
| Attributes | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
ParallelTimerMaxWait |
int |
The time in milliseconds that the feature will wait for a final response on the CS fork before abandoning it. |
RouteCSDirectlyThroughICSCF |
boolean |
When true, T-ADS will route requests to the CS domain directly via the I-CSCF (bypassing the S-CSCF) |
T-ADS Parallel Routing also draws additional network operator data from SIP service configuration in a J-SLEE profile table named SipSentinelConfigurationTable. The data is scoped by Sentinel selection key.
| Attributes | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
IcscfUri |
String |
The |
Statistics
SCCTADSParallelRouting statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID → feature.SCCTADSParallelRouting
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on a SIP Request. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on a SIP Response. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on the timer firing. |
CSRNNotFound |
Incremented when the CS fork cannot be established because no CSRN can be found. |
MaxWaitTimerSet |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer is started. |
MaxWaitTimerCancelled |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer is cancelled. |
UpstreamForkCreated |
Incremented when an upstream forked leg is created for forward a provisional or success response from the CS leg. |
ReceivedProvisionalResponse |
Incremented when a provisional 18x response is received. |
ReceivedFinalResponse |
Incremented when a final response is received for the initial INVITE. |
RouteToCSAttempted |
Incremented when an INVITE is routed down the CS forked leg. |
RouteToPSAttempted |
Incremented when an INVITE is routed down the PS forked leg. |
RouteToCSFailed |
Incremented when the CS leg is torn down without being answered. |
RouteToPSFailed |
Incremented when the PS leg is torn down without being answered. |
AnsweredOnCS |
Incremented when a success response is received on the CS leg. |
AnsweredOnPS |
Incremented when a success response is received on the PS leg. |
Behaviour
The following behaviour is described below:
Initial Forking
This feature will initiate an INVITE towards the PS domain if the session state field IsPSRouting is TRUE. It will also initiate an INVITE towards the CS domain if the session state field CSRN is populated.
If both of these conditions are true, then the two INVITEs form a parallel fork.
The outgoing INVITE for the CS leg is generated from the original incoming INVITE received from the calling party. The Request-URI and To headers are changed to a Tel URI generated from the CSRN. If configured in network operator data, the Route header will be modified to route the request directly to the I-CSCF.
If both INVITEs are sent, the feature starts a timer. This timer will be set to expire after a length of time determined by the ParallelTimerMaxWait setting in the feature configuration profile. If this timer expires before a final response is received from either leg, the CS fork will be canceled.
In the event that both the PS and CS legs cannot be created, then the feature instructs Sentinel VoLTE to end the INVITE session by responding to the calling party with a final SIP error response with status code 480 (Temporarily Unavailable).
If only one of the legs is attempted then the TADS Parallel Routing feature did not create a parallel fork. In this case T-ADS acts as a routing B2BUA adding the OC-Terminating-Domain header as per the OC-Terminating-Domain header addition section.
| |
T-ADS parallel routing is not compatible with +sip.instance routing. If +sip.instance routing is enabled, a sequential T-ADS routing strategy must be used. |
On Receiving a Provisional Response
Provisional responses are always forwarded upstream.
In addition, the feature will add an OC-Terminating-Domain header to the forwarded response.
On Receiving a Final Error Response
When a final error response is received on one of the forked legs the exact behavior of the feature depends on the state of the other forked leg.
If the other forked leg is still active, then the leg the final error was received on will be released. In this case the feature will prevent the error response from being forwarded to the calling party.
If the other forked leg has been aborted or was never created, then the error response will be forwarded upstream, effectively ending the call.
If the error is forwarded upstream, the OC-Terminating-Domain header will be added to the response.
On Receiving a Final Success Response
In the case of a parallel fork, the first 2xx success response processed by this feature will be forwarded and the call will be established over that Dialog. The remaining forked leg is terminated as per SIP procedures.
The OC-Terminating-Domain header will be included on the response.
In the event that both the CS and PS legs answer at the same time, they are processed in an order. The first response to be processed by the feature "wins".
On Receiving a CANCEL Request
If the calling party sends a CANCEL for the original INVITE, the TADS Parallel Routing feature will immediately terminate all remaining legs according to standard SIP protocol.
OC-Terminating-Domain Header addition
The OC-Terminating-Domain header is added to responses heading upstream (usually for charging purposes). The feature adds this header to all responses for the original INVITE that are forwarded upstream.
For more details see OC-Terminating-Domain Header
Illustrative scenarios
To better illustrate the feature, consider the following scenarios.
Third Party Registration features
The General Registrar Features provide general Third Party Registrar support in Sentinel. They are installed out-of-the box in a Sentinel VoLTE installation. The following features support the ESRVCC registration process within VOLTE.
| Feature | What it provides |
|---|---|
|
Fetches the Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) from the HLR to be included in registration data. |
|
|
Fetches the Correlation MSISDN (CMSISDN) from the HSS to be included in registration data and ESRVCC Registration. |
|
|
Implements the ESRVCC registration process (outlined in the Finite State Machine below). |
|
|
Handles ESRVCC re-registration procedures. |
|
|
Invalidates the Sh Cache’s Supplementary Service Data entry for the de-registering user. |
|
|
Warms the Sh Cache for the registering user’s Supplementary Service Data. |
ESRVCCRegistration
This feature implements the initial registration procedures for ESRVCC.
ESRVCC registration process
ATCF is involved in registration
-
The Feature-Caps header of the first-party REGISTER request includes a number of ATCF-related parameters:
-
+g.3gpp.atcf -
+g.3gpp.atcf-mgmt -
+g.3gpp.atcf-path
-
-
The ESRVCC registration feature:
-
queries the HSS to obtain the STN-SR and the C-MSISDN (correlation MSISDN)
-
compares the STN-SR returned by the HSS with the STN-SR that was in the first-party REGISTER request
-
If they are different, the HSS is updated with the STN-SR from the first-party REGISTER request
-
-
updates the ATCF, passing it the SCC AS’s own ATU-STI and the C-MSISDN, by sending the ATCF a SIP MESSAGE message.
-
The address of the ATCF is taken from the
+g.3gpp.atcf-mgmtparameter in the Feature-Caps header of the first-party REGISTER request. -
The body of the SIP MESSAGE has a content type application/vnd.3gpp.SRVCC-info+xml and contains an XML document such as:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <SRVCC-infos> <SRVCC-info ATCF-Path-URI="<sip:termsdgfdfwe@localhost:5560>"> <ATU-STI>sip:sccas1.home1.net:5060</ATU-STI> <C-MSISDN>tel:+16505550425</C-MSISDN> </SRVCC-info> </SRVCC-infos>
-
-
| |
If any of these steps fail (for example, the ATCF update times out, or the HSS returns a failed Answer) the ESRVCC registration feature responds to the registrar core with rejectRegisterRequest(). |
Related features
-
ESRVCCReregistration handles the re-registration procedures for ESRVCC.
Session state
Before …
SentinelSelectionKey |
A selection key with the platform operator, network operator and session type set to ESRVCCRegistration (such as |
|---|---|
EncapsulatedRegisterRequest |
The first-party REGISTER request that was in the body of the third-party REGISTER request received by the registrar. The ESRVCC feature processes the Feature-Caps header from the REGISTER request. |
Mappers
This feature uses mappers that conform to:
| Mapping | Mapper Execution Point |
|---|---|
SentinelRegistrarSessionState.class → OutgoingSipRequest.class |
RegistrarMappingPoint.UpdateATCF |
Statistics
Stats interface |
ESRVCCRegistrationStats |
|---|---|
Parameter set to monitor |
|
| Parameter | … incremented if … |
|---|---|
FailedToCreateShSession |
The registrar could not create an Sh activity with the Diameter Sh resource adaptor |
HssRequestTimedOut |
A request made to the HSS times out |
MapperErrorSendingUDR |
The mapper that creates a UserDataRequest fails |
NetworkErrorSendingUDR |
There is a network error sending a UserDataRequest to the HSS |
CouldNotExtractUserDataFromUDA |
There is a problem parsing the UserData in a UserDataAnswer |
CouldNotExtractCMsisdnFromShData |
There is a problem getting the correlation MSISDN from the UserData in the UserDataAnswer |
HssSentErrorUDA |
The HSS responded to a UserDataRequest with an error response |
MapperErrorSendingPUR |
The mapper that creates a ProfileUpdateRequest fails |
NetworkErrorSendingPUR |
There is a network error sending a ProfileUpdateRequest to the HSS |
HssSentErrorPUA |
The HSS responded to a ProfileUpdateRequest with an error response |
MapperErrorUpdatingATCF |
The mapper that creates a SIP MESSAGE message, to pass to the ATCF, fails |
NetworkErrorUpdatingATCF |
There is a network error sending a SIP MESSAGE message to the ATCF |
ATCFRespondsWithSipError |
The ATCF responds to a SIP MESSAGE message with an error response |
ATCFResponseTimesOut |
There is no response to the SIP MESSAGE message sent to the ATCF |
RegisterMissingFeatureCAPSHeader |
The REGISTER message is missing a Feature-Caps header |
RegisterFeatureCAPSHeaderMissingAtcfMgmt |
The Feature-Caps header does not contain a |
Error scenarios
The ESRVCC feature increments statistics and responds to the registrar core with rejectReqisterRequest() if:
-
the REGISTER request is missing essential headers or header parameters
-
there is a problem sending a UserDataRequest to the HSS, such as a mapper error creating the message, or a network error sending the message
-
there is a problem sending a ProfileUpdateRequest to the HSS, such as a mapper error creating the message, or a network error sending the message
-
there is a problem sending a SIP MESSAGE message to the ATCF, such as a mapper error creating the message, or a network error sending the message.
Configuration
This feature has a configuration profile which determines the user identities used when querying the HSS. The default profile table is named CacheESRVCCRegistrationConfigProfileTable and profiles are named with a Sentinel Selection Key e.g. opencloud::::. The feature has a Sentinel Feature Configuration page in REM.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
UserIdentityTypeStringForStnSrRequest |
An enum with value |
Determines whether the user’s IMS Public ID or C-MSISDN will be used for their identity when requesting the STN-SR from the HSS. |
IncludePrivateIdInStnSrRequest |
boolean |
Determines whether the user’s IMS Private ID will be included in the request for the STN-SR. |
There are also fields relevant to this feature in the RegistrarConfigurationTable table:
AtcfUpdateTimeout |
The time (ms) the ESRVCC registration feature should wait for a response from the ATCF. |
|---|
ESRVCCReregistration
This feature implements the re-registration procedures for ESRVCC.
Related Features
-
ESRVCCRegistration handles the initial registration procedures for ESRVCC.
Session Input Variables
| Variable name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
PreviousRegistrationData |
List<RegistrationRecord> |
The list of active registration records for the current subscriber and call ID. |
Session Output Variables
| Variable name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
CurrentATUSTI |
String |
ATU-STI to be stored in the third-party registrar database. |
AtcfMgmtUri |
String |
ATCF Management URI to be stored in the third-party registrar database. |
AtcfPathUri |
String |
ATCF Path URI to be stored in the third-party registrar database. |
StnSr |
String |
STN-SR to be stored in the third-party registrar database. |
Statistics
| Name | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
Started |
The feature is invoked (initial invocation only, not subsequent event triggers). |
FailedDuringExecution |
The feature fails during execution due to an internal |
IssuedWarning |
The feature issues a warning message. |
ATCFUpdateRequestSent |
A |
ATCFUpdateFailed |
The |
ATCFUpdateSucceeded |
The |
Configuration
The ESRVCCReregistration feature does not have its own configuration, however it does depend on the Registrar Configuration Table to determine the currently configured value for the ATU-STI, and the length of time to wait for a response from the ATCF (AtcfUpdateTimeout).
Behaviour
The primary function of this feature is to ensure the ATCF will trigger the correct SCC-AS during ESRVCC access transfer. This is may be necessary if re-registrations are sent to an SCC-AS node with a different ATU-STI than the initial (or previous) registration’s ATU-STI.
REGISTER trigger
The feature is triggered when the registration session type is determined to be ESRVCCRegistration and the registration action type is determined to be re_register.
The feature first checks the previous registration data provided by the FetchPreviousRegistrationData feature, searching for a registration record that includes all required ESRVCC registration information. If a record is found, the feature will load the ESRVCC specific data from the record and compare the ATU-STI value in that data to the currently configured ATU-STI for the SCC AS. If no previous ESRVCC registration data can be found, or only partial information can be found, the feature terminates with a FeatureError, and no other action is taken.
If the currently configured ATU-STI matches the one in the previous registration record, the feature will have nothing left to do and will terminate normally. If there is a mismatch, the feature will begin the procedure for updating the ATU-STI in the ATCF to match the currently configured value.
The feature starts the update procedure by attempting to generate a SIP MESSAGE request towards the ATCF Management URI. The request will have an XML body containing the updated ATU-STI, the ATCF Path URI and the subscriber’s C-MSISDN:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SRVCC-infos>
<SRVCC-info ATCF-Path-URI="<sip:atcf@atcf.example.net:5560>">
<ATU-STI>sip:scc-as.example.net:5060</ATU-STI>
<C-MSISDN>tel:+16505550425</C-MSISDN>
</SRVCC-info>
</SRVCC-infos>
| |
the ATCF Path URI, the C-MSISDN and the ATCF Management URI will all be taken from the initial REGISTER request for the subscriber NOT the current re-REGISTER request (though in practice these values should be identical). |
Once the MESSAGE request is ready the feature will trigger the request to be sent, and attach to the Activity Context Interface (ACI) for the resulting SIP session. The feature will then terminate and await a response.
Response Event Triggers
Any one of three events can trigger the feature at this point: a SIP success response, and SIP error response, or a SIP timeout.
| |
In all of these cases, when triggered the feature will check that the triggering ACI matches the ACI that was created when the MESSAGE request was sent. If there is a mismatch, the feature will log a warning and return to waiting for the correct trigger. |
SIP Success Response
If the ATCF replies to the MESSAGE request with a SIP 200 OK response, then the update was successful and the feature will update the session data to reflect the new ATU-STI.
SIP Error Response
If the ATCF replies to the MESSAGE request with any SIP error response, the feature will consider the update procedure to have failed and will execute error handling procedures.
SIP Timeout
If the ATCF does not reply to the MESSAGE request within the configured time frame, the feature will consider the update procedure to have failed and will execute error handling procedures.
| |
A timeout will be triggered after a period of time determined by the AtcfUpdateTimeout field on the Registrar Configuration Table; by default this is much faster than a standard SIP timeout. |
Error Handling
If the ATCF update procedure fails at any point (be it from an internal FeatureError, a SIP error response, or a SIP timeout) the feature will rewrite the ATU-STI stored in session data to match the ATU-STI of the previous registration. This ensures the third party registrar database contains an accurate representation of the ATU-STI currently in use for the registration in the ATCF.
FetchCMSISDN
This feature fetches the Correlation MSISDN from the HSS, using an "Sh-Pull". It can be invoked during Third Party Registration and INVITE session processing.
Description
This feature fetches the Correlation MSISDN from the HSS. It can be invoked during Third Party Registration and INVITE session processing.
The feature issues a query to the HSS for the Correlation MSISDN. When building the request to the HSS, it uses a User Data Request with Sh Data Reference 17 - MSISDN or MSISDN + ExtendedMSISDN. The query access key is the default Public Identity, or the default Public Identity plus the IMS Private Identity. The access chosen is based on the feature configuration attribute "UDRIncludedIdentities".
The HSS may return either a failure response, or an Sh document.
If the feature is configured to look for the Correlation MSISDN in MSISDN, it uses the first MSISDN in the returned set at Sh-Data/PublicIdentifiers/MSISDN in the Sh UDA response.
If the feature is configured to look for the Correlation MSISDN in Extended-MSISDNs, it uses the first MSISDN in the returned Extended MSISDNs set at Sh-Data/PublicIdentifiers/Extension/Extension/Extension/ExtendedMSISDN in the Sh UDA response.
If the feature is able to find an MSISDN in the returned set, it increments the SuccessfullyRetrievedCMSISDN counter, and modifies the output session state variables.
If the returned set is empty, the feature increments the FailedToRetrieveCMSISDN counter, and does not modify any output session state variables.
If the HSS returns a failure response, the feature increments the ShCacheError counter, and does not modify any output session state variables.
Statistics
There are two sets of statistics, one as the feature is invoked during Registration, and another during INVITE processing.
Both sets of statistics share the same interface. They are located in different SLEE services.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
FailedToRetrieveCMSISDN |
Counter |
Incremented when the HSS query returns a document that does not contain the CMSISDN in the expected location. |
SuccessfullyRetrievedCMSISDN |
Counter |
Incremented when the HSS query returns a document that does contain a CMSISDN in the expected location. |
ShCacheError |
Counter |
Incremented when the HSS query returns a non-success response code. |
InvalidConfig |
Counter |
Incremented when unsupported CMSISDN source is configured. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between requesting data from the Sh-Cache RA and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
Statistics as part of Registration
| |
Some of the listed statistics are not available for registration processing. |
These statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found using the parameter set SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=sentinel.registrar,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=sentinel.registrar,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.FetchCMSISDN
Or in REM under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → sentinel.registrar service → sentinel.registrar SBB → feature → FetchCMSISDN
Statistics as part of INVITE processing
These statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found using the parameter set SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.FetchCMSISDN
Or in REM under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → FetchCMSISDN
Configuration
The configuration is scoped according to the Sentinel Selection key, and is stored in the FetchCMSISDNFeatureConfigProfileTable profile.
There are two configuration attributes, as follows:
| Attribute name | Type | Valid values |
|---|---|---|
CMSISDNSource |
String |
"MSISDN", or "EXTENDED_MSISDN" |
UDRIncludedIdentities |
String |
"IMPU" , or "IMPU_AND_IMPI" |
Note: If the CMSISDN source is set to "EXTENDED_MSISDN" then the UDRIncludedIdentities must be set to "IMPU_AND_IMPI".
Invalidate MMTel Subscriber Data Cache on De-registration
Description
The purpose of the feature is to invalidate the Sh Cache’s Supplementary Service Data entry for the de-registering user. This feature is intended for use upon De-Registration.
It is related to the Load MMTel Subscriber Data Cache On Registration feature.
Session state
Before …
SentinelSelectionKey |
A selection key with the platform operator, network operator, session type, and plan-id set. The plan-id must be set to |
|---|---|
CallId |
The call-id associate with the activation session |
PrivateId |
The private-id of the UE |
Load MMTel Subscriber Data Cache on Registration
Description
The purpose of this feature is to "warm" the Sh Cache for the Registering User’s MMTel Supplementary Service Data. It issues an Sh-Pull using the served users default public identity. This ensures that the Sh Cache is seeded after the registration request is processed.
This feature is intended for use upon Initial Registration.
It is related to the Invalidate MMTel Subscriber Data Cache on De-registration feature.
Session state
Before …
SentinelSelectionKey |
A selection key with the platform operator, network operator, session type, and plan-id set. The plan-id must be set to |
|---|---|
CallId |
The call-id associate with the activation session |
PrivateId |
The private-id of the UE |
CAMEL features
The CAMEL Features are used to provide a basis for the SCP functionality in the SCC-AS. These are applicable to CAP triggers. These features are installed out-of-the-box.
General features
The Sentinel product General Features are essentially utility features that are installed out-of-the-box.
The Sentinel VoLTE product does not use the Subscriber Data Lookup and Subscriber Validity features as the General VoLTE Features are used instead. These features may be used when customising Sentinel VoLTE.
Mappers
VOLTE uses mappers as it processes third-party REGISTER requests.
The General Registrar Mappers provide general Third Party Registrar support in Sentinel. They are installed out-of-the box in a Sentinel VoLTE installation. The following mappers support the ESRVCC registration process within VOLTE.
| |
For an overview of what mappers are and how they work, please see Mappers in the Sentinel documentation. |
Mapper execution points
The Registrar searches for mappers at the following mapper execution points:
| Mapper Execution Point | Role of mappers at this point |
|---|---|
UpdateATCF |
Building a SIP MESSAGE message to the ATCF. |
| |
See the enum com.opencloud.sentinel.mapper.RegistrarMappingPoint in the sentinel-sip-registrar-common module. |
Mapping of GSMA IR.92 to Sentinel VoLTE Features
| Supplementary Service | Sentinel VoLTE support | Sentinel VoLTE feature |
|---|---|---|
Originating Identification Presentation 3GPP TS 24.607 |
Yes |
|
Terminating Identification Presentation 3GPP TS 24.608 |
Yes |
|
Originating Identification Restriction 3GPP TS 24.607 |
Yes |
|
Terminating Identification Restriction 3GPP TS 24.608 |
Yes |
|
Communication Forwarding Unconditional 3GPP TS 24.604 |
Yes |
|
Communication Forwarding on not Logged in 3GPP TS 24.604 |
Yes |
|
Communication Forwarding on Busy 3GPP TS 24.604 |
Yes |
|
Communication Forwarding on not Reachable 3GPP TS 24.604 |
Yes |
|
Communication Forwarding on No Reply 3GPP TS 24.604 |
Yes |
|
Barring of All Incoming Calls 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Barring of All Outgoing Calls 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Barring of Outgoing International Calls 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Barring of Outgoing International Calls — ex Home Country 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Barring of Outgoing International Calls — When Roaming 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Barring of Incoming Calls - When Roaming 3GPP TS 24.611 |
Yes |
|
Communication Hold 3GPP TS 24.610 |
Yes |
|
Message Waiting Indication 3GPP TS 24.606 |
N/A |
No MMTelAS requirements |
Communication Waiting 3GPP TS 24.615 |
Yes |
|
Ad-Hoc Multi Party Conference 3GPP TS 24.605 |
Yes |
Provisioning
You provision Sentinel VoLTE using the Sentinel VoLTE Element Manager, which provides a web interface and machine API.
| |
The Sentinel VoLTE Element Manager is an extension of the Rhino Element Manager (REM). See Installing the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning Module to install the Sentinel VoLTE provisioning module in REM. For general information on using Rhino Element Manager, see the Rhino Element Manager User Guide. |
To provision Sentinel VoLTE, see the procedures to:
Provisioning Web Interface
The provisioning web interface appears as an extension inside the Rhino Element Manager (REM) web application.
| |
Using Rhino Element Manager For general information on using REM, see the Rhino Element Manager User Guide. To use the Sentinel provisioning web interface and machine API you will, at minimum, need to configure a Rhino instance in REM. |
To access the Sentinel VoLTE provisioning interface in REM:
1 |
Open a browser, and enter the URL of the REM server where the Sentinel REM extension has been installed (for example, http://localhost:8080/rem). |
|---|---|
2 |
Enter your REM login credentials (the default account credentials are |
3 |
Select Manage a Rhino Element. |
4 |
Connect to the Rhino instance where Sentinel VoLTE is installed. |
5 |
Select one of the options from the Sentinel menu.
|
For documentation on each of the VoLTE Sentinel panels, please see the following links:
| Menu item(s) | Link |
|---|---|
Session Plans |
Managing Session Plans (Sentinel) |
Feature Execution Scripts |
Managing Feature Execution Scripts (Sentinel) |
HSS Subscriber Data |
REM HSS Transparent Data Editor (VoLTE) |
Feature Configuration |
Configuring Features, Services, Sentinel Core, and Promotions (Sentinel) |
Mappers |
Managing Mappers (Sentinel) |
Plans |
|
Correlation |
|
XCAP and XCAP - Simservs |
XCAP Server (VoLTE) |
HSS Configuration |
Sentinel VoLTE and Data
Sentinel VoLTE has several uses of data, and different types of data.
Types of data
The data Sentinel VoLTE uses can broadly be described as fitting one of the following three classifications:
-
Platform data — typically indicating configuration data for the platform and its services
-
Network operator data — enabling different network operators to be hosted on a single platform
-
Subscriber data — stored as transparent user data in the HSS.
-
Data Stored by the Third Party Registrar in HSS — stored as transparent data in the HSS.
Platform Data
Platform data includes, but is not limited to:
-
Sentinel services and feature code
-
Sentinel services configuration and feature configuration
-
Protocol stacks and resource adaptors, and associated configuration
-
Rhino Service Interaction Server and its configuration
-
Rhino TAS configuration.
Service configuration
Sentinel service configuration is stored in JSLEE configuration profiles. It includes multiple configuration areas, notably:
-
Sentinel’s core configuration
-
Sentinel’s mediation-layer configuration (configuration for online charging)
-
Sentinel’s SIP Sentinel configuration.
Network Operator Data
With network operator data, you can enable multiple network operators on top of a single Sentinel platform installation.
Sentinel VoLTE features define configuration properties that you scope by Sentinel selection key.
This means that different network operators can have different settings for the same feature. For example, Operator 1 might play an announcement when a session is held, whereas Operator 2 may not. — as specified in the MMTelHold feature’s network configuration.
Key aspects of Sentinel VoLTE are also multi-tenanted. For example, each network operator may have different:
-
OCS addresses configured
-
HSS destination realms and hosts
-
Sh Cache instances
-
Field mappings for Sh transparent data
-
and so on.
Sentinel VoLTE stores network operator data per-component, in JSLEE configuration profiles. Please see each component’s documentation for details on network operator and selection key based configuration.
| |
This document refers to the data as ‘Network Operator’ data, as this is its most common scoping — but the Sentinel selection key concept is flexible: a feature’s configuration data can be scoped in other ways. For details, please see Sentinel’s selection key documentation. |
Subscriber Data
In Sentinel VoLTE, subscriber data is stored either as transparent user data in the HSS or in the HLR.
When using HSS, it is accessed through:
-
the XCAP Server
-
the REST Provisioning API
-
and various screens in REM.
When using HLR, it is accessed through:
Session processing uses the Sh Cache RA via the SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS feature or CGIN RA via SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR.
For more information, see Sh Cache RA configuration and Supplementary Service Data Access.
Data Stored by the Third Party Registrar in HSS
Overview
The default option for Registrar Data Storage uses Transparent Data in the HSS through the Diameter Sh interface. Documents stored in the HSS conform to an OpenCloud defined XML schema. During the Sentinel VoLTE installation the user is asked to choose between using an HSS or a Cassandra Database as the data repository technology.
For further information related to use of Cassandra for registration data please refer to Registrar Cassandra Subscriber Data Store Config.
How it works
The HSS storage system creates, updates and removes documents from the HSS as appropriate based on SIP User Agent registration life cycle, catering for cases such as simultaneous registration of shared IMS public identities. Documents are created/updated/removed using an access of an IMS Public Identity and Service Indication of opencloud-3rd-party-registrar.
During INVITE processing, the IMSIDLookup feature uses the Served User’s IMS Public Identity and Service Indication of opencloud-3rd-party-registrar as the Diameter Sh Access Key.
It then populates Session State according to documents found in HSS storage. Both the HSS storage system, and the IMSIDLookup use the Sh Cache RA to interface to the HSS.
Data Schema
The schema used by OpenCloud for Third Party Registration is shown below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://opencloud.com/sentinel/registrar/xml"
xmlns:ss="http://opencloud.com/sentinel/registrar/xml"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
version="1.0"
>
<xs:element name="publicId">
<!-- Use an anonymous type so xjc will add an XmlRootElement to the generated PublicId class. -->
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0" name="registration" type="ss:RegistrationData"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0" name="reverseMapping" type="ss:ReverseMapping"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute default="false" name="default" type="xs:boolean" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="EsrvccData">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="cmsisdn" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="gruu" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="tempGruu" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="stnSr" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="isUeSrvccCapable" default="false" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:element name="currentAtuSti" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="atcfMgmtUri" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="atcfPathUri" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ReverseMapping">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" name="validityTime" type="ss:ValidityTime"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="callId" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="defaultPublicId" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="RegistrationData">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="privateId" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" name="publicIds" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" name="contact" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="validityTime" type="ss:ValidityTime"/>
<xs:element name="visitedNetworkId" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" name="pAccessNetworkInfo" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" name="esrvcc" type="ss:EsrvccData"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="callId" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ValidityTime">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="created" type="xs:dateTime"/>
<xs:element name="expires" type="xs:duration"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>Configuration
The Diameter Sh interface is configured during the VoLTE installation.
Statistics
The statistics are updated during the processing of the feature.
| Parameter | … incremented if … |
|---|---|
failedToAddRegistrationData |
Could not add a registration. |
failedToAddReverseMappings |
Could not decode the registration data. |
failedToRemoveRegistrationData |
Could not remove the registration data. |
failedToRemoveReverseMappings |
Could not remove the decoder for the registration data. |
noDataToRemoveForDefaultPubicIdAndCallId |
No registration found under the specified callid. |
noDataToRemoveForDefaultPublicId |
No registration foung undet the specified public id. |
noMappingToRemoveForPubicIdAndCallId |
Could not find any mapping associated to the specified callid. |
noMappingToRemoveForPublicId |
Could not find any mapping associated to the specified public id. |
For Third Party Registration, the statistics are tracked by the sentinel.registrar SBB and can be found using the parameter set SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=registrar.subscribers.hsscache,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0]
REM HSS Transparent Data Editor
The REM HSS Transparent Data Editor lets you use a web browser to view and edit HSS transparent user data.
How it works
The web interface communicates with a web application hosted by Rhino Element Manager, which communicates with the HSS through Diameter Sh. Administrators can use it to:
-
view provisioned data
-
configure important settings
-
add new data to the HSS
-
remove data from the HSS.
Prerequisites
Before using the editor, you need to configure:
-
an appropriate HSS configuration for the network operator
-
required settings for MMTel services. *
For more information on Operator Determined Barring see Operator Determined Barring.
Using the Data Editor
To use the Data Editor:
1 |
From REM’s monitoring screen, select Sentinel ▶ HSS Subscriber Data. 
It may take a few seconds before the screen appears on first load. It should look like this: 
|
|---|---|
2 |
Follow the procedures to load or view, edit, or remove transparent data for an IMS public identity. |
Load or view transparent data for an IMS public identity
| |
The HSS that the Editor queries depends on which network you’ve chosen. These instructions assume that, before loading data, you have configured the HSS address for the network operator. |
To load or view data:
1 |
Type the IMS public identity into the IMS User Identity field, and click the Load button. 
HSS Subscriber Data displays. 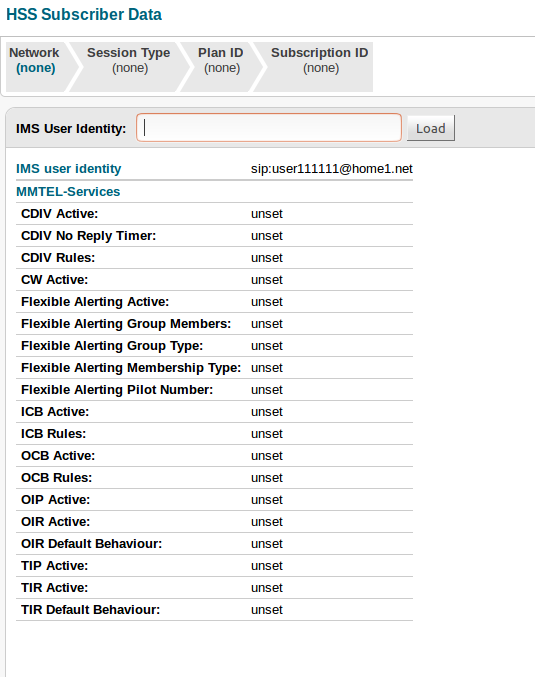
|
|---|
| |
Loading errors
If there’s an error — for example, because the HSS is unavailable, the network operator is not configured properly, or the data cannot be parsed — a red-coloured error message will display in the panel, and red text in the log below. In the following example, a new Sentinel network operator called ‘SteveInc’ has not been configured properly. 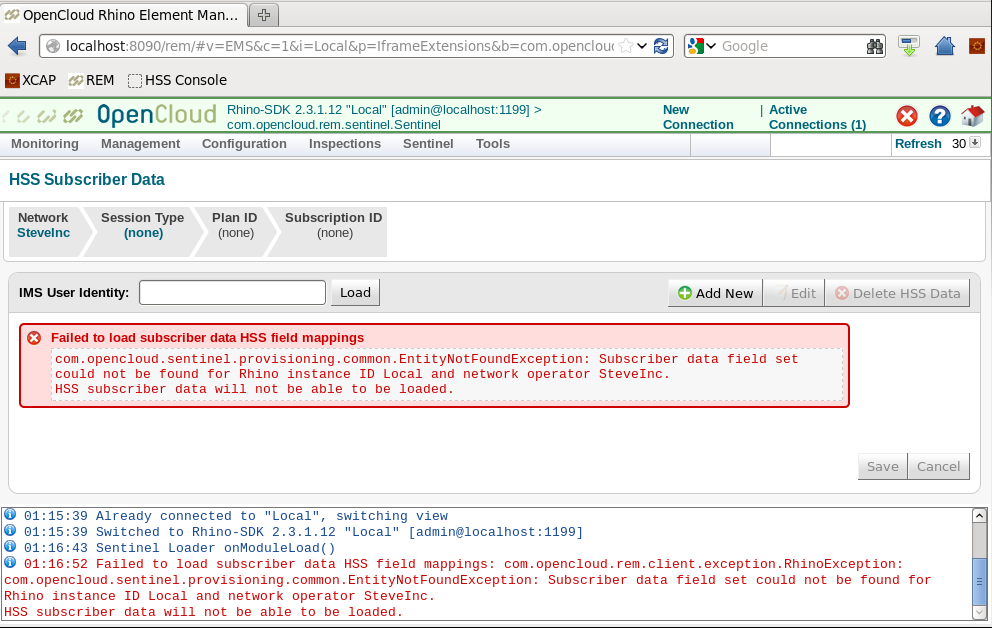
|
Edit transparent data for an IMS public identity
To edit data that you’ve loaded in the Editor:
1 |
Click the Edit button. Fields become editable. 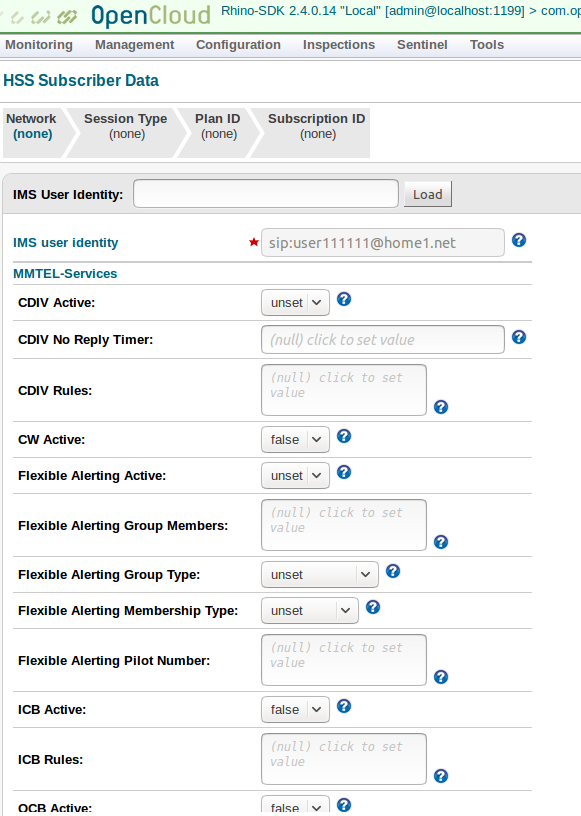
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Make your changes, depending on the field type.
|
|||||||||||||||
3 |
Click the Save button at the lower right. If entered data is validated and saved successfully to the HSS, a green message displays in the panel and REM log. 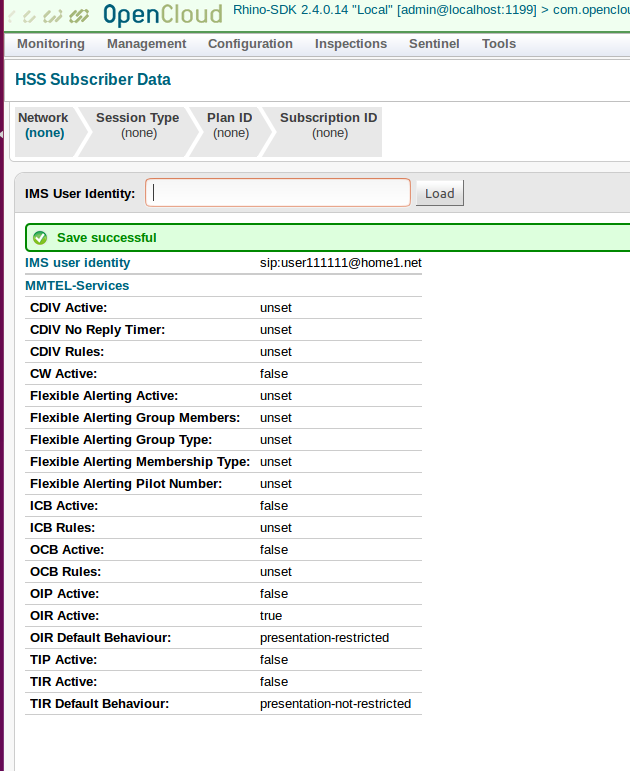
If saving fails, a red message displays in the panel and log. In the following example, the XML is not well-formed (in the 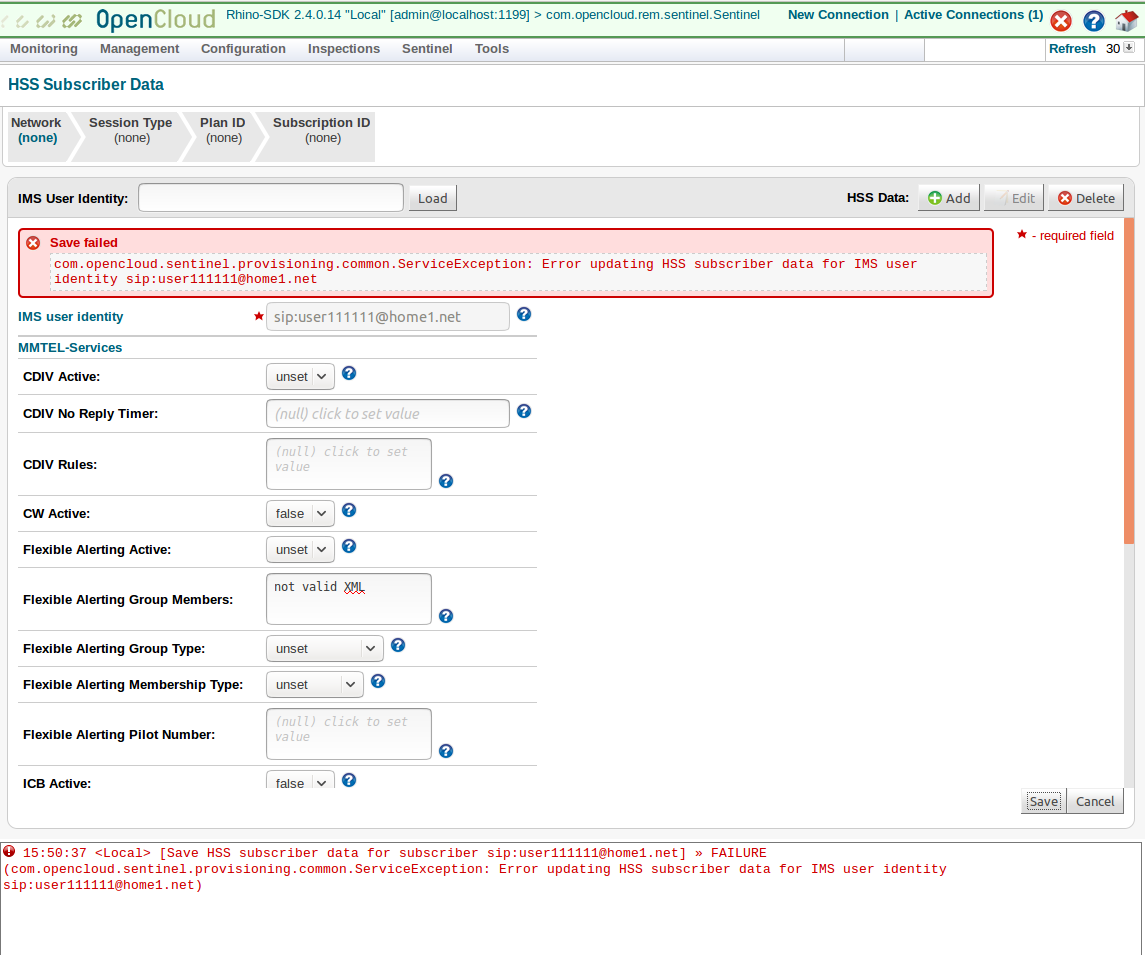
|
Remove transparent data for an IMS public identity
To remove data that you’ve loaded in the Editor:
1 |
Click the Delete button ( The editor prompts you to confirm the deletion. 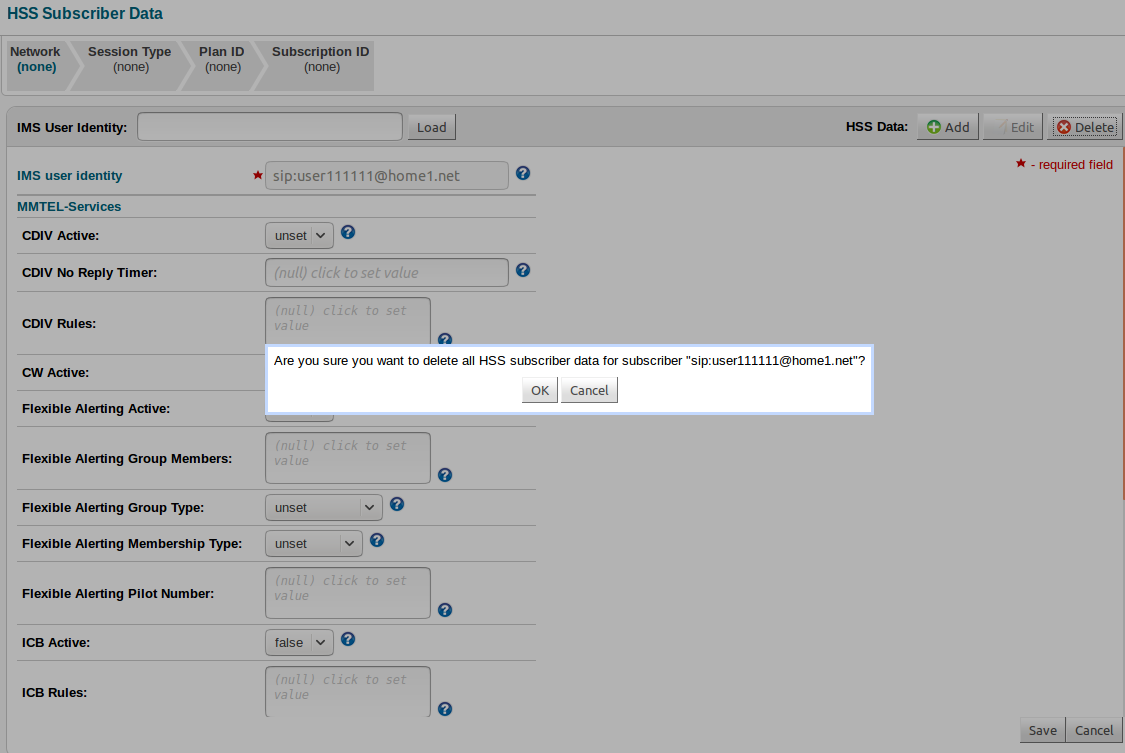
|
|---|---|
2 |
Click OK. The panel becomes blank, and a green message displays in the REM log below. |
Required configuration for MMTel
To edit HSS transparent user data so it can use OpenCloud’s out-of-the-box IR.92 features, follow the manual configuration steps below.
| |
The volte-sentinel-mappings-config tool will carry out these steps for you. See Populate XCAP server settings and MMTel service data. |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Once the data’s loaded, select the Provisioning Field Mappings tab.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
Each network operator installed in Sentinel can have their own configuration. To select the defaults for the platform, select (none) under the Network section of the screen. Otherwise, to configure a particular operator, select it. Below are examples with and without fields configured for the currently selected network operator. 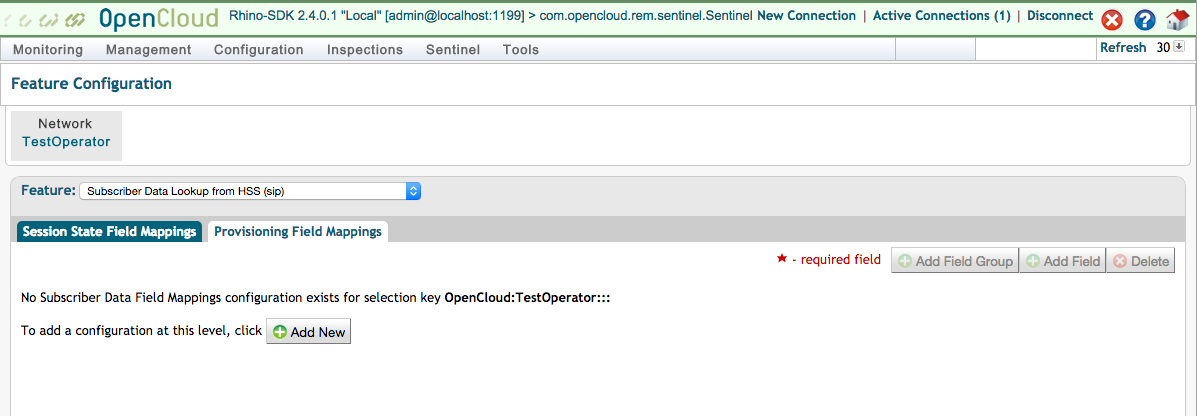
image::{here}field-mappings.png[]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Click the Add Field Group button. A prompt displays to enter details. 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Fill in the following values — either by typing, or by selecting the text box and pressing the down arrow on your keyboard to select these default values:
And select OK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Once the field group for MMTEL-Services has been added, select it; and click the Add Field button to add the following fields:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Click Save. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Once you have finished adding, editing, and/or removing fields — for the changes to take effect — disconnect from REM, and then log in again |
Active flags information
The active flags (OIRActive, CDIVActive, and ICBActive) are specified as optional Boolean attributes in the XCAP and MMTEL XML schemas.
In an XML document, this means they can have three possible values:
-
does not exist (that is, attribute is not declared)
-
exists with the value
true -
exists with the value
false.
In the transparent data editor user interface, these are reflected by these three values: Unset, True, or False,
For short, we refer to them as the ‘active’ attributes.
The XCAP and MMTEL specifications assign special meaning to these ‘active’ attributes when their attribute does not exist (that is, when they have the value ‘unset’ in the REM user interface):
-
The session processing (that is, the feature) should act as though the value is
true. -
The XCAP requests from the user equipment are subject to special rules:
-
A request is not allowed to
-
create the ‘active’ attribute (if a request does this, the XCAP server returns an HTTP error response)
-
toggle the ‘active’ attribute for the feature via the XCAP interface (if a request does this the XCAP server returns an HTTP error response).
-
-
A request is allowed to configure other portions of that service’s data.
For example, if Communication Diversion has no ‘active’ attribute, a request can configure communication diversion rules.
-
In summary, the means that the user equipment cannot disable the feature. If the operator wants the user equipment to be able to enable or disable the feature, then the ‘active’ attribute should exist (and therefore be either true or false).
Required configuration for Operator Determined Barring
To edit HSS transparent user data so it can use OpenCloud’s out-of-the-box IR.92 features:
1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Once the data’s loaded, select the Provisioning Field Mappings tab.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
Each network operator installed in Sentinel can have their own configuration. To select the defaults for the platform, select (none) under the Network section of the screen. Otherwise, to configure a particular operator, select it. Below are examples with and without fields configured for the currently selected network operator. 
image::{here}field-mappings.png[]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Click the Add Field Group button. A prompt displays to enter details. 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Fill in the following values — either by typing, or by selecting the text box and pressing the down arrow on your keyboard to select these default values:
And select OK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Once the field group for IMS-ODB-Information has been added, select it; and click the Add Field button to add the following fields:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Click Save. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Once you have finished adding, editing, and/or removing fields — for the changes to take effect — disconnect from REM, and then log in again |
Configuring Diameter Sh for the XCAP Server and REM
This section describes configuration of the Diameter Sh stack instance(s) inside the Rhino EM Web Application.
| |
Architecture reference
For background on the architecture related to the instructions below, please read the XCAP Support page. |
Diameter Sh stack configuration
As seen in XCAP Support, the Diameter Sh stack is used by the XCAP Server and Rhino EM’s Web User interface.
Instances of the Diameter Sh stack are configured through two ‘locations’:
| |
Both ‘locations’ are required to configure an instance. |
Configuring an Sh stack instance with REM
To configure an Sh stack with the REM:
1 |
Navigate to Sentinel ▶ HSS Configuration. 
The Diameter Instance Configuration page displays. 
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
The Diameter instance name field identifies each instance of the Diameter Sh stack. Select an Sh stack instance, and specify entries in the other fields to configure key parameters.
|
| |
Use a unique Sh stack instance per cluster
Selecting the name of the Diameter Sh stack instance in this panel links it with the Rhino cluster that your REM session is logged into. This means that when an administrator uses the HSS Transparent Data Editor, since they’ve logged into a Rhino cluster, the associated Diameter Sh stack instance in REM will be selected. Also, when processing an XCAP request, the XCAP Server will find the Rhino cluster to use, as it queries this for some settings. The Diameter Sh stack instance is then selected by the Rhino cluster’s linked Diameter Sh stack instance. In the case where REM is connected to only one Rhino cluster, there only needs to be one Diameter Sh stack instance. *We strongly recommend that you configure each Rhino cluster to use a unique Diameter Sh stack instance!_ |
Configuring an Sh stack instance with a file
When REM starts, it reads a configuration file. This file is formatted according to a Rhino Profile Export format.
| |
Although REM uses this file format for a profile export; but this information is not stored in JSLEE profiles. The file itself is read and parsed as REM initialises. |
The file name is VolteHssDiameterConfig.xml, in the rem_home directory. (With the Tomcat HTTP Servlet container, this directory is a subdirectory of the Tomcat home directory.)
Diameter Sh stack instance name and attributes
In the configuration file, each Diameter Sh stack instance is declared using a <profile> element. The <profile> element must have a name (the name of the Diameter Sh Stack instance) and an action attribute. The action attribute should be set to create. For example:
<profile name="xcapserver" action="create">
In this case, the Diameter Sh stack instance is named xcapserver. This name is the core link between the XML configuration file and the REM configuration screen.
The following attributes are also required:
| Attribute name | What it specifies |
|---|---|
productVendorId |
used for the Vendor-Id AVP of the CER and CEA messages |
applicationVendorId |
Vendor ID; must be |
host |
host to use in all Origin-Host AVPs; must be resolvable |
applicationId |
Diameter Application ID |
realm |
realm to use in all Origin-Realm AVPs |
peerTable |
a diameter peer table XML encoded as Character Data See the Diameter documentation |
realmTable |
a diameter realm table XML encoded as Character Data See the Diameter documentation |
product |
product name to use in Product-Name AVPs generated by the stack |
version |
version number to use in all Firmware-Revision AVPs generated by the stack; must be a positive integer |
Example configuration file
This example shows a single Diameter Sh stack instance, with the name xcapserver.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE exported-profile-data PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Exported Profile Data Collection 1.1//EN" "http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/exported_profile_data_1_1.dtd">
<exported-profile-data table="VolteHssDiameterConfiguration">
<attributes>
<attribute-desc name="productVendorId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="applicationVendorId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="host" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="applicationId" type="long" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="realm" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="peerTable" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="realmTable" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="product" type="java.lang.String" serialised="false"/>
<attribute-desc name="version" type="int" serialised="false"/>
</attributes>
<profile name="xcapserver" action="create">
<attribute-value name="productVendorId">19808</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="applicationVendorId">0</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="host">xcapserver</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="applicationId">0</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="realm">example</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="peerTable">
<![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE peer-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Peer Table Configuration 1.1.0//EN"
"http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-peer-table-1.1.0.dtd">
<peer-table>
<default-options>
<option>
<option-name>TCP_NODELAY</option-name>
<option-type>java.lang.Boolean</option-type>
<option-value>true</option-value>
</option>
</default-options>
<peer connectAtStartup="true">
<uri>aaa://hss:3888;transport=tcp</uri>
<address>127.0.0.1</address>
<option>
<option-name>TCP_NODELAY</option-name>
<option-type>java.lang.Boolean</option-type>
<option-value>false</option-value>
</option>
</peer>
</peer-table>]]>
</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="realmTable">
<![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE realm-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Realm Table Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-realm-table-1.0.dtd">
<realm-table>
<realm>
<realm-name>example</realm-name>
<application-route>
<application>
<application-id>4</application-id>
<vendor-id>0</vendor-id> <!-- optional, default is zero -->
</application>
<action>LOCAL</action>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>hss</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</application-route>
</realm>
<default-route>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>hss</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</default-route>
</realm-table>]]>
</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="product">OpenCloud Diameter</attribute-value>
<attribute-value name="version">1</attribute-value>
</profile>
</exported-profile-data>Configuring the Sentinel network operator’s destination HSS
Now that we have a test operator, the HSS configuration can be added for this operator:
1 |
In REM, navigate to Sentinel ▶ HSS Configuration. 
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Select the Diameter Destinations tab. 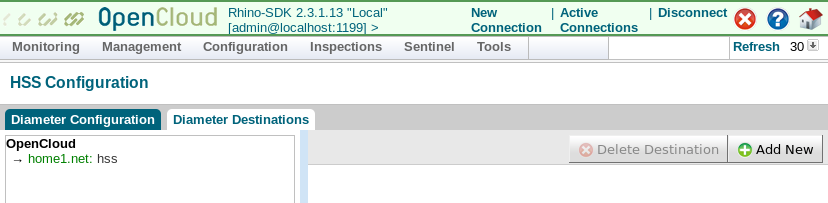
The screen above shows a network operator named |
||
3 |
Click the + Add New button. |
||
4 |
Enter these parameters:
|
||
5 |
Click the Save button. Once saved, the panel will display a green-coloured success message, and the REM log will have a green-coloured log message. 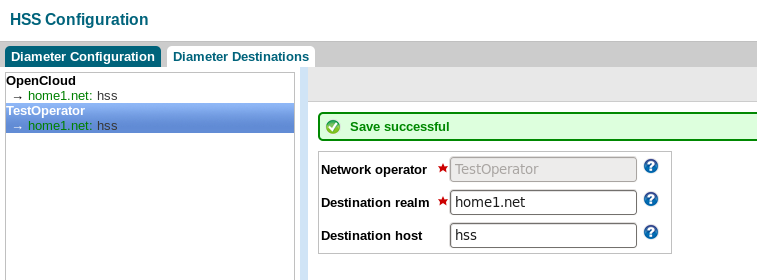
|
Adding a Network Operator to Sentinel VoLTE
Configuration for Sentinel and Sentinel features is scoped by a Sentinel selection key.
Brief background on Sentinel configuration and the Sentinel selection key
When Sentinel is installed, it is installed with a single platform operator, and a single default network operator. This means that the most specific data is looked for first; and when that data is not found, the next most specific data is looked for; and when that is not found the next most specific data is looked for (and so on). In other words, Sentinel configuration lookup falls back multiple times, until it stops at the platform configuration.
Part of the Sentinel selection key is dedicated to the network operator — thereby enabling multiple network operators on one platform.
Viewing the network operators in a Sentinel install
Network operators can be viewed in Sentinel’s core configuration:
1 |
From the REM dashboard, select Sentinel ▶ Sentinel Core Configuration. 
The configuration displays. For example, the following Sentinel Core Configuration screen shows a configuration where the Platform operator and Default network operator names are both 
|
|---|
Adding a network operator
To add a new network operator:
1 |
Click the Network operators text box. |
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Type in the operator name. |
||
3 |
Click Save. When the configuration is saved, a green success message appears in the panel and REM log. The example below shows 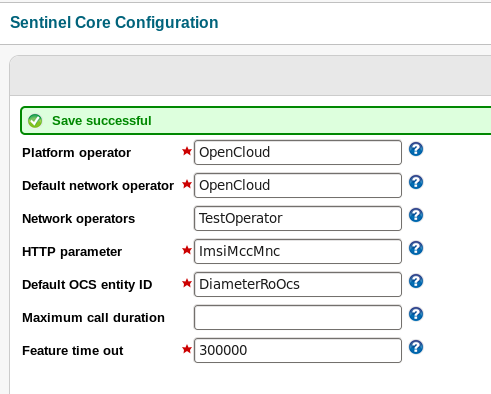
|
Other topics to configure
Now that a network operator has been added to Sentinel VoLTE, other areas need to be configured: Diameter Sh for REM and the XCAP server.
Session Processing
Session processing includes topics related to how the Sentinel VoLTE product executes various different call flows.
-
Selection of MMTel and SCC functionality — how the different AS functions are able to be selected through URI parameters
-
Selection of charging mode — how online/offline charging is selected through URI parameters
-
Initial Filter Criteria — example Initial Filter Criteria for use with Sentinel VoLTE
-
Session Processing and the Use of HSS — how Sentinel VoLTE makes use of the HSS
-
Service Compositions — selection of services that execute on each SIP session
-
Sentinel VoLTE Session Plans — selection of features that execute inside a SIP session
-
Custom Headers — OpenCloud defined headers that influence session processing behaviour
Out of the box, the Sentinel VoLTE product can:
-
function as an SCC-AS, or an MMTel-AS for a given trigger
-
function as a combined SCC+MMTel-AS off a single trigger, thereby optimising performance.
-
perform offline charging only
-
perform online charging, through either acting as a Charging Trigger Function using Diameter Ro, or CAP (using the IM-SSF)
These different configurations are all available on a per-trigger basis, rather than being a "hard configuration mode".
Online charging via the CAP interface is delivered through the use of OpenCloud’s IM-SSF, and is an optionally installed component.
Selection of MMTel and SCC functionality through the Application Server URI
Different modes of operation (e.g. MMTel functionality, or SCC functionality) are determined through parameters added to the Application Server URI during initial filter criteria (iFC) configuration.
When the Sentinel VoLTE application server receives an initial SIP request (for example, an initial INVITE or third-party register request) parameters are present on the topmost route header. There are certain parameters that can be added to alter the behaviour of Sentinel VoLTE. That is to say, the iFC and application server configuration in the HSS may include URI parameters that select different sets of behaviour from the Sentinel VoLTE product.
Session plans are available that enable execution of MMTel and SCC feature sets in different combinations. These are selected through the use of the oc-mode parameter.
The specific URI parameters are discussed in the Custom Headers section.
| |
For a high-level view of the architecture, see Instance Architecture for Sentinel VoLTE. For a detailed description of the format of the oc-mode parameter, see the DetermineVoltePlanId feature page. |
Selection of charging mode
The system charging mode can be set to:
-
offline only, meaning the system only writes CDRs
-
online charging via Diameter Ro, meaning that the system acts as a charging trigger function towards the OCS as well as writing CDRs
-
online charging via CAMEL, meaning it includes an IM-SSF component that triggers a prepaid service control point via the CAP protocol.
The charging mode is selected through the oc-charge-mode parameter. This is an Application Server URI parameter.
| |
For detailed descriptions of the oc-charge-mode parameter, see the DetermineChargeMode and Service Compositions pages. |
Initial Filter Criteria
Initial Filter Criteria (iFC) is the mechanism used by the IMS to invoke Application Servers. It applies to SIP initial requests.
Sentinel VoLTE defines various Route Header Parameters such that the iFC can select specific behaviour from the Sentinel VoLTE applications.
For example, SCC or MMTel functionality, or influencing the T-ADS routing mode are selected through the use of Route Header Parameters.
Requirements for Sentinel VoLTE iFC
The iFC requirements can be met through various different iFC configurations. The purpose of this section is to cover the requirements.
INVITE related
Registered and Un-Registered Service Point Triggers
Both the MMTel and SCC require INVITE processing for originating, terminating, and the registered and un-registered cases. There are not any particular headers that are able to be used to "narrow" which INVITEs the SCC or MMTel receive such that they are triggered in certain cases only (unlike e.g. a voice-mail service that is only triggered on terminating INVITEs to a PSI).
| Session Case | Consumers of case |
|---|---|
Originating Registered |
SCC Originating Signalling Anchor for access transfer, MMTel Originating Features |
Originating Un-Registered |
MMTel Originating Features in case of and unregistered originating party. This is typical when using IMS centralised services without I2. I.e. a non IMS-registered user making an outgoing Circuit Switched call that is routed into the IMS for service control. |
Terminating Registered |
SCC Terminating Signalling Anchor for access transfer, SCC T-ADS, MMTel Terminating Features |
Terminating Un-Registered |
SCC T-ADS, MMTel Terminating features (e.g CDIV Not Logged In) |
INVITE trigger chaining
VoLTE calls can be processed sequentially by both the MMTel-AS and SCC-AS with INVITE iFC chaining. iFCs are chained together by associating the same Trigger Point (group of one or more SPTs) with multiple AS in a specific order.
The SCC-AS must be the first SIP-AS in the originating iFC trigger chain and last in the terminating iFC trigger chain. I.e it "wraps" the other SIP-AS nodes, and is the "closest" AS to the served UE. Therefore it directly observes the true SIP Dialog Identifier used between the IMS core and the served UE.
Third Party Registration Service Point Triggers
SCC-AS requires third party registration, as both eSRVCC and T-ADS functionality need access to (for example) the IMS private identity. MMTel-AS also requires third party registration so that it can access the default IMS public identity.
Typically the SCC-AS and MMTel-AS are co-located on the same TAS. In this case, there must be only one Third Party Registration request sent to the TAS. The TAS then performs appropriate logic for the MMTel and SCC functions based on the single request. Multiple distinct Third Party Registration requests should only be sent to the SCC-AS and MMTel-AS when the functions are not co-located on the same TAS.
| Registration Case | Consumers of case | Needs first party registration content |
|---|---|---|
Initial Registration |
SCC for eSRVCC registration and T-ADS. MMTel for default public identity. |
Both first-party request and response |
Re-registration |
SCC for eSRVCC re-registration and T-ADS (e.g. P-Access-Network-Info). MMTel to refresh its registration data. |
Both first-party request and response |
De-registration |
SCC and MMTel to clean up registration state database |
Both first-party request and response |
| |
Depending on your HSS, the configuration for including first-party request and response messages could be on the iFC or the associated AS. |
MMTel Conferencing Service Point Triggers
MMTel Conferencing requires that the Conference Focus has a URI termed the Conference Factory Public Service Identity, or Conference Factory PSI for short.
Both Invites and Subscriptions to the Conference Factory PSI are implemented at the Conference Focus within the MMTel-AS.
Therefore the iFC for Conferencing needs to ensure that SIP SUBSCRIBE and INVITE sessions where the Request URI host part matches the host part of the Conference Factory PSI trigger the MMTel-AS.
Trigger examples
Due to the nature of the iFC XML, and that Method and SessionCase elements are part of a choice (meaning one or the other can be specified inside an SPT) sometimes logical OR is used for different SPT elements inside a Trigger, and sometimes logical AND is used.
SCC-AS INVITE Trigger
The following XML fragment shows the use a single Trigger element to capture the various INVITE cases for the SCC-AS.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- this is a snippet of an iFC showing only the Trigger elements necessary for SCC-AS INVITE processing -->
<!-- An example of INVITE trigger point for SCC-AS -->
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are AND'd together -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- logically the statement is INVITE AND (ORIGINATING_REGISTERED OR TERMINATING_REGISTERED OR TERMINATING_UNREGISTERED) -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>INVITE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>0</SessionCase><!-- ORIGINATING_REGISTERED -->
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>1</SessionCase><!-- TERMINATING_REGISTERED -->
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>2</SessionCase><!-- TERMINATING_UNREGISTERED -->
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>SCC-AS Third Party Register Trigger
The following XML fragment shows the use of a Trigger element that includes all three cases of Third Party registration.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- this is a snippet of an iFC showing only the Trigger element necessary for Third Party Registration -->
<!-- Initial Register OR Re-register OR de-register -->
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- there is only a single SPT so ConditionTypeCNF is not important yet it is a mandatory element so it is here as 1-->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- Register, re-register and de-register -->
<SPT>
<Group>4</Group>
<Method>REGISTER</Method>
</SPT>
<Extension>
<RegistrationType>0</RegistrationType> <!-- INITIAL_REGISTRATION -->
<RegistrationType>1</RegistrationType> <!-- RE_REGISTRATION -->
<RegistrationType>2</RegistrationType> <!-- DE_REGISTRATION -->
</Extension>
</TriggerPoint>MMTel-AS INVITE Trigger
The following XML fragment shows the use of a single Trigger element to invoke the MMTel-AS for all INVITE sessions except those going to voicemail.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- this is a snippet of an iFC showing only the Trigger elements necessary for MMTel-AS INVITE processing -->
<!-- An example of INVITE trigger point for MMTel-AS excluding voicemail All MMTel services will be served on the same AS here -->
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are OR'd togethered -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- MMTel needs INVITEs for all SessionCases Voicemail is often not implemented on the same MMTel-AS platform Therefore exclude the voicemail AS, assuming it has a URI of voicemail.example.com Logically this is INVITE AND NOT (RequestURI equals voicemail.example.com) -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>INVITE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated> <!-- Use ConditionNegated to exclude the RequestURI -->
<Group>2</Group>
<RequestURI>voicemail.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>MMTel-AS SUBSCRIBE Trigger
The following XML fragment shows the use of a Trigger element to invoke the MMTel-AS for subscriptions to the Conference Factory PSI.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- this is a snippet of an iFC showing only the Trigger for subscriptions to the Conf Factory PSI -->
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are OR'd togethered -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- Logically this is SUBSCRIBE AND (RequestURI host part equals conf.example.com) -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>SUBSCRIBE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<RequestURI>conf.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>Recommendations for Application Server element
An iFC document joins an Application Server and zero or more Trigger Point elements. Each Trigger Point element includes one or more Service Trigger Points (SPTs). These are discussed above.
This section discusses recommendations for the Application Server section.
Use a TCP transport
The default SIP transport mechanism for AS communication is UDP. TCP can be specified by appending ;transport=tcp to the configured AS URI.
AS functional separation
One Sentinel VoLTE TAS instance can handle both SCC-AS and MMTel-AS roles. However it is possible to logically separate the roles onto their own instance or node. This can be useful for non-functional reasons such as sizing, or functional reasons such as debugging.
This is achieved with the oc-mode parameter as part of the AS URI. The mmtel oc-mode handles MMTel and Conferencing. Conferencing traffic can be diverted to its own node via iFC association.
For example, to split MMTel, SCC and MMTel-Conferencing traffic on such that they are on distinct ports 5060, 5070 and 5080.
| Role | AS URI | Associated TP / iFC |
|---|---|---|
MMTel |
sip:<volte-tas-address>:5060;transport=tcp;oc-mode=mmtel |
MMTel iFCs |
SCC |
sip:<volte-tas-address>:5070;transport=tcp;oc-mode=scc |
SCC iFCs |
MMTel-Conferencing |
sip:<volte-tas-address>:5080;transport=tcp;oc-mode=mmtel |
Conf iFC |
For each configured AS it is possible to assign further specific functions through the use of Route Header Parameters
iFC examples
These examples provide a full initial filter criteria including TriggerPoint and ApplicationServer elements.
SCC-AS INVITE
The SCC-AS is invoked in three INVITE cases
-
originating
-
terminating registered
-
terminating un-registered
These can be shown in a single iFC for the INVITE case
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<InitialFilterCriteria>
<Priority>2</Priority>
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are AND'd together -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- logically the statement is INVITE AND (ORIGINATING_REGISTERED OR TERMINATING_REGISTERED OR TERMINATING_UNREGISTERED) AND NOT (Recv-Info Header equals 'g.3gpp.ussd') -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>INVITE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>0</SessionCase><!-- ORIGINATING_REGISTERED -->
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>1</SessionCase><!-- TERMINATING_REGISTERED -->
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<SessionCase>2</SessionCase><!-- TERMINATING_UNREGISTERED -->
</SPT>
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated>
<Group>2</Group>
<SIPHeader>
<Header>Recv-Info</Header>
<Content>g.3gpp.ussd</Content>
</SIPHeader>
<Extension/>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>
<ApplicationServer>
<ServerName>sip:scc-as.domain.name:5060;transport=tcp;oc-mode=scc</ServerName>
<DefaultHandling>1</DefaultHandling>
<Extension>
<IncludeRegisterRequest/>
<IncludeRegisterResponse/>
</Extension>
</ApplicationServer>
</InitialFilterCriteria>MMTel-AS INVITE
An example showing the iFC for an MMTel-AS for INVITE requests is below.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<InitialFilterCriteria>
<Priority>2</Priority>
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are AND'd together -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- MMTel needs INVITEs for all SessionCases Voicemail is often not implemented on the same MMTel-AS platform Therefore exclude the voicemail AS, assuming it has a URI of voicemail.example.com Logically this is INVITE AND NOT (RequestURI equals voicemail.example.com) AND NOT (Recv-Info Header equals 'g.3gpp.ussd') -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>INVITE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated> <!-- Use ConditionNegated to exclude the RequestURI -->
<Group>2</Group>
<RequestURI>voicemail.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated>
<Group>3</Group>
<SIPHeader>
<Header>Recv-Info</Header>
<Content>g.3gpp.ussd</Content>
</SIPHeader>
<Extension/>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>
<ApplicationServer>
<ServerName>sip:mmtel-as.domain.name:5060;transport=tcp;oc-mode=mmtel</ServerName>
<DefaultHandling>1</DefaultHandling>
<Extension>
<IncludeRegisterRequest/>
<IncludeRegisterResponse/>
</Extension>
</ApplicationServer>
</InitialFilterCriteria>Note: if the MMTel-AS will run the MMTel-Conferencing feature (ie. not the discrete conferencing example) then the iFC needs to also include SUBSCRIBE requests where the RequestURI matches the host name part of the conference factory PSI.
MMTel-AS SUBSCRIBE
If the MMTel-AS is running the MMTel-Conferencing feature, rather than a discrete MMTel-Conferencing AS node, then the MMTel-AS needs to receive SUBSCRIBE requests for the Conference Factory PSI.
An example is shown
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<InitialFilterCriteria>
<Priority>2</Priority>
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- ConditionTypeCNF 0 means logical AND of SPT elements in the same group ConditionTypeCNF 1 means logical OR of SPT elements the same group See TS 29.228 for Conjunctive Normal Form vs Disjunctive Normal Form SPT elements in different groups are OR'd togethered -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- Logically this is SUBSCRIBE AND (RequestURI host part equals conf.example.com) -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>SUBSCRIBE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<RequestURI>conf.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>
<ApplicationServer>
<ServerName>sip:mmtel-as.domain.name:5060;transport=tcp;oc-mode=mmtel</ServerName>
<DefaultHandling>1</DefaultHandling>
<Extension>
<IncludeRegisterRequest/>
<IncludeRegisterResponse/>
</Extension>
</ApplicationServer>
</InitialFilterCriteria>Third Party Registration example
The following example adds triggers for REGISTER request, for:
-
initial registration
-
re-registration
-
de-registration
When sending the third-party register request, both the first party register request and response are included.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- sip registration IFC -->
<InitialFilterCriteria>
<Priority>1</Priority>
<!-- Initial Register OR Re-register OR de-register -->
<TriggerPoint>
<!-- there are three SPTs, and we want OR, so ConditionTypeCNF 1 -->
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<!-- Register -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>REGISTER</Method>
<Extension>
<RegistrationType>0</RegistrationType> <!-- INITIAL_REGISTRATION -->
</Extension>
</SPT>
<!-- re-register -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>REGISTER</Method>
<Extension>
<RegistrationType>1</RegistrationType> <!-- RE_REGISTRATION -->
</Extension>
</SPT>
<!-- de-register -->
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>REGISTER</Method>
<Extension>
<RegistrationType>2</RegistrationType> <!-- DE_REGISTRATION -->
</Extension>
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>
<ApplicationServer>
<ServerName>sip:third-party-registrar:5060;transport=tcp</ServerName>
<DefaultHandling>0</DefaultHandling>
<Extension>
<IncludeRegisterRequest/>
<IncludeRegisterResponse/>
</Extension>
</ApplicationServer>
</InitialFilterCriteria>Discrete Conferencing Example
Sentinel VoLTE implements many MMTel Services, including MMTel Conferencing. It may be useful to configure the Conference as a different set of VMs than the rest of MMTel, for example for sizing reasons.
If so, this iFC for conferencing can be defined.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!-- Conferencing IFC MMTel Conferencing requires SUBSCRIBE and INVITE requests to the Conference Factory PSI -->
<InitialFilterCriteria>
<Priority>2</Priority>
<!-- Logically (INVITE OR SUBSCRIBE) AND (RequestURI host part equals conf.example.com) AND Terminating Unregistered -->
<TriggerPoint>
<ConditionTypeCNF>1</ConditionTypeCNF>
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>INVITE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>0</Group>
<Method>SUBSCRIBE</Method>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>1</Group>
<RequestURI>conf.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>
<SPT>
<Group>2</Group>
<SessionCase>2</SessionCase> <!-- Terminating Unregistered -->
</SPT>
</TriggerPoint>
<ApplicationServer>
<ServerName>sip:conf-as.example.com:5060;transport=tcp;oc-mode=mmtel</ServerName>
<DefaultHandling>0</DefaultHandling>
</ApplicationServer>
</InitialFilterCriteria>Note: if MMTel-Conferencing is provided on a different node, then the Conference Factory PSI should be excluded from the MMTel-AS Trigger.
Excluding services
There are cases where there are services that are not implemented on a particular SIP-AS. If there are no other distinguishing characteristics of the INVITE (such as for MMTel) then any Public Service Identifiers for services that are not implemented on the MMTel-AS should be excluded. If there are distinguishing characteristics, such as a unique SIP header, these can be used for exclusion.
-
Example - Voicemail AS
Add a negated condition specifying a Service Point Trigger where the URI is the host-part of the PSI for the VoiceMail service. An example is shown below.
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated>
<Group>3</Group>
<RequestURI>voicemail.example.com</RequestURI>
</SPT>-
Example - USSI AS
Sentinel VoLTE does not implement the role of a USSI Application Server. As USSD over IMS requests are signalled using SIP INVITE, and MMTel and SCC AS are signalled using INVITE, a negated condition is added to the iFC for Sentinel VoLTE. USSI INVITE requests contain a Recv-Info header with the value g.3gpp.ussd.
An example is shown below.
<SPT>
<ConditionNegated>1</ConditionNegated>
<Group>4</Group>
<SIPHeader>
<Header>Recv-Info</Header>
<Content>g.3gpp.ussd</Content>
</SIPHeader>
<Extension/>
</SPT>Note: each excluded service should be in a Group that is independent of the other groups. This is because SPTs in different groups are AND’ed together.
Session Processing and the Use of HSS
XML schemas in use
| Standard Name | 3GPP TS | 3GPP Release version | Specific document version |
|---|---|---|---|
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Configuration Access Protocol (XCAP) over the Ut interface for Manipulating Supplementary Services |
3GPP TS 24.623 |
Release 11 |
11.1.0 |
Flexible Alerting (FA) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem |
3GPP TS 24.239 |
Release 11 |
11.0.0 |
Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) and Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem |
3GPP TS 24.607 |
Release 11 |
11.2.0 |
Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) and Terminating Identification Restriction (TIR) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem |
3GPP TS 24.608 |
Release 11 |
11.2.0 |
Communication Diversion (CDIV) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem |
3GPP TS 24.604 |
Release 11 |
11.5.0 |
Anonymous Communication Rejection (ACR) and Communication Barring (CB) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem |
3GPP TS 24.611 |
Release 11 |
11.2.0 |
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IMS Operator Determined Barring |
3GPP TS 24.315 |
Release 12 |
12.1.0 |
Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS); LTE; Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) using IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network (CN) subsystem; Protocol specification |
3GPP TS 24.629 |
Release 12 |
12.7.0 |
| |
There is no user data in the schema for the following features defined in the standards at the time of writing:
|
Data references used by MMTEL
-
Data Reference of RepositoryData (0)
-
Service indications of:
-
“MMTEL-Services”
-
“opencloud-3rd-party-registrar”
-
Service Compositions
Sentinel VoLTE is a set of JSLEE services.
| |
For background, see Sentinel VoLTE Architecture. |
A SIS service composition sends SIP signaling to the correct service. Sentinel VoLTE comes with three compositions pre-configured for different requirements:
-
The default composition just invokes the VoLTE service:
Standard VoLTE composition -
The other two compositions support CAP-based charging. This functionality is enabled by configuring the iFC to send an additional parameter in the AS URI called
oc-charge-modeand setting its value tocap. The following diagrams illustrate the originating and terminating cases:Mobile OriginatingMobile Terminating
Listing the service compositions
You can list the services compositions by accessing the sis-console, normally under the volte installation path sis/admin and use the commands listcompositions and dumpcomposition. See the example below. The output may change for different releases.
[Rhino@localhost (#0)] listcompositions sip-sis-ra
CompositionID[name=SentinelVolteAndRegistrarOriginatingComposition,vendor=OpenCloud,version={majorversion}]
CompositionID[name=SentinelVolteAndRegistrarTerminatingComposition,vendor=OpenCloud,version={majorversion}]
[Rhino@localhost (#5)] dumpcomposition sip-sis-ra name=SentinelVolteAndRegistrarOriginatingComposition,vendor=OpenCloud,version={majorversion}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?><composition xmlns="http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition" xmlns:in="http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition/IN" xmlns:sip="http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition/SIP" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition/SIP sip-sis-composition-1.6.xsd http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition/IN in-sis-composition-1.6.xsd http://www.opencloud.com/SIS/Composition sis-composition-1.6.xsd">
<composition-name>SentinelVolteAndRegistrarOriginatingComposition</composition-name>
<composition-vendor>OpenCloud</composition-vendor>
<composition-version>{majorversion}</composition-version>
<script>
<if>
<equal>
<value value="${method}"/>
<value value="REGISTER"/>
</equal>
<then>
<!-- Invoke Registrar -->
<invoke on-timeout="ignore-service-and-continue" service="sentinel.registrar"/>
</then>
<else>
<if>
<equal a="${oc-mode}" b="mmtel-scc"/>
<then>
<!-- Invoke SCC -->
<invoke on-timeout="ignore-service-and-continue" service="volte.sentinel.sip">
<service-input-interceptor>
<delete variable="${oc-mode}"/>
<assign toVariable="${oc-mode}" value="scc"/>
</service-input-interceptor>
</invoke>
<!-- Invoke MMTel -->
<invoke on-timeout="ignore-service-and-continue" service="volte.sentinel.sip">
<service-input-interceptor>
<delete variable="${oc-mode}"/>
<assign toVariable="${oc-mode}" value="mmtel"/>
</service-input-interceptor>
</invoke>
</then>
<else>
<!-- Invoke VoLTE -->
<invoke on-timeout="ignore-service-and-continue" service="volte.sentinel.sip"/>
</else>
</if>
</else>
</if>
<delete variable="${oc-mode}"/>
</script>
<debug-level>0</debug-level>
<audit>false</audit>
</composition>
Creating and modifying service compositions
Service compositions are part of the OpenCloud Service Interaction SLEE (SIS). For more information on how to create and modify service compositions refer to SIS Documentation.
Sentinel VoLTE Session Plans
Sentinel VoLTE Session Plans define the system’s behaviour, and enable customisation.
Sentinel VoLTE Session Plans
For out of the box Session Plans and their Feature Execution Scripts, please see Built-In session plans.
Modifying the system through Session Plans
Sentinel VoLTE provides an implementation of core VoLTE standards as features. These features may be enhanced, replaced or even by-passed.
In order to add new features, replace features, or customise existing features it makes sense to read Sentinel Session Plans and Feature Execution Scripts. These “wire together” multiple features to form services that MMTel AS and SCC AS provide.
Both session plans and feature execution scripts are scoped via a Sentinel Selection Key. This provides flexibility, in allowing different combinations of features on a single platform. For example, you might want to scope features by network operator, or have sets of features associated with a different plans.
Sentinel successively falls back to a broader scoping of the selection key, to load the feature execution script for processing a session. Ultimately the least specific portion of the selection key, the platform operator, is used to load a feature execution script.
Feature execution scripts can change on-the-fly. For example, when an administrator changes a feature execution script, it can be used in processing subsequent sessions without a restart.
Different session plans for different types of sessions
Sentinel supports session plans for various different types of services:
-
SIP INVITE-based session processing — see Session Plans for the SIP Service
-
SS7 CAMEL-triggered session plan — see Session Plans for the SS7 Service
-
Third-party Registration session plans — described in 3rd Party Registration Session Plans
Built-in Session Plans
SIP INVITE session plans
Some session plans can be executed on an INVITE.
| |
Details on how they are selected can be found in the documentation for the DetermineVoltePlanId feature. |
The session plans are:
Plan ID |
Executed by |
mmtel-orig |
MMTel AS serving the originating user |
mmtel-term |
MMTel AS serving the terminating user |
mmtel-conf |
MMTel AS providing conferencing (MMTelCONF) functionality |
scc-orig |
SCC AS serving the originating user |
scc-term |
SCC AS serving the terminating user |
scc-term-anchor |
SCC AS serving the terminating user but only executing access transfer functions |
scc-term-tads |
SCC AS serving the terminating user but only executing T-ADS functions |
scc-access-transfer |
SCC AS on receiving an access transfer request |
scc-reorigination |
SCC AS on receiving a reorigination request |
SIP REGISTER session plans
The Registrar uses the session type and plan ID portion of the selection key in order to simplify the feature execution scripts that run for different types of third-party registration.
The main two features that do this are:
-
DetermineRegistrationSessionType — sets the session type to one of
eSRVCCRegistrationorRegular3rdPartyRegistration -
DetermineRegistrationActionType — sets the plan ID to one of
register,re-register, orde-register.
| Session type | Plan ID | Executed by |
|---|---|---|
Regular3rdPartyRegistration |
register |
MMTel AS with third-party registrar |
Regular3rdPartyRegistration |
re-register |
MMTel AS with third-party registrar |
Regular3rdPartyRegistration |
de-register |
MMTel AS with third-party registrar |
eSRVCCRegistration |
register |
SCC AS with third-party registrar |
eSRVCCRegistration |
re-register |
SCC AS with third-party registrar |
eSRVCCRegistration |
de-register |
SCC AS with third-party registrar |
Registration session plans for register and re-register distinguish the features that they execute. The register session plans are intended to execution upon Initial Registration into the IMS, whereas re-register corresponds to registration refreshes. Examples of features that should run on Initial Registration but not registration refresh are FetchCMSISDN, or ESRVCCRegistration
IN session plan
Sentinel VoLTE uses minimal feature execution scripts for IN call processing — they exist purely for the purpose of IMS service centralization. This will result in the call being connected to an IP Multimedia Routing Number (IMRN) and the TCAP dialog being closed; no online charging request will be made as part of InitialDP processing.
These feature execution scripts run in the SS7 sessions initiated via the CAMEL IDP session plan. For more information refer to Service Centralisation Features.
Viewing session plans
The list of execution points and their associated feature scripts can be viewed through REM by selecting the Management→Profiles menu, then selecting the ${PLATFORM_OPERATOR_NAME}_FeatureExecutionScriptTable table. Here the variable ${PLATFORM_OPERATOR_NAME} is replaced by the Platform Operator Name chosen at installation time. So if the Platform Operator Name was set to "Rocket" the table name would be "Rocket_FeatureExecutionScriptTable".
To view the same information from the rhino console, view the list of execution scripts by running listprofiles ${PLATFORM_OPERATOR_NAME}_FeatureExecutionScriptTable. To view an individual script use listprofileattributes ${PLATFORM_OPERATOR_NAME}_FeatureExecutionScriptTable ${SCRIPT_NAME}.
To view the Feature Execution Script name that is invoked for a particular Plan ID’s execution point, use listprofileattributes ${PLATFORM_OPERATOR_NAME}_FeatureExecutionPointTable ${EXECUTION_POINT}.
For more information related to Feature Execution Points, Feature Execution Scripts and Plan IDs refer to Session Plans
Custom Headers
Sentinel VoLTE supports specific custom headers and header parameters to indicate or propagate certain conditions between nodes in the network.
OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure Header
The OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure Header header is a custom SIP header used by Sentinel VoLTE SCC-AS to coordinate access transfer procedures across multiple nodes. This header is inserted into handover INVITE requests and special internal MESSAGE requests when they are forwarded between Sentinel VoLTE SCC-AS nodes. It is also inserted into handover INVITE requests when they are forwarded into an existing session on the same node. The header indicates to the receiving session which access transfer procedures it should execute.
Header Format
The header name is OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure and its value is a simple string with no special formatting. The header does not have any special parameters. Possible values are described below.
Example:
OC-Access-Transfer-Procedure: Remove-SuperfluousHeader Values
Value |
Associated Access Transfer Procedure |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently active (not held), established (INVITE-200-ACK received), and with media anchored in the ATGW. |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently active (not held), established (INVITE-200-ACK received), and with media not anchored in the ATGW. |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently pre-alerting (INVITE-180 not yet received), and with media anchored in the ATGW. |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently pre-alerting (INVITE-180 not yet received), and with media not anchored in the ATGW. |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently alerting (INVITE-180 received, INVITE-2xx not yet received), and with media anchored in the ATGW. |
|
Enhanced SRVCC for sessions that are currently alerting (INVITE-180 received, INVITE-2xx not yet received), and with media not anchored in the ATGW. |
|
SRVCC for sessions that are currently active (not held) and established (INVITE-200-ACK received). |
|
End a session that has been deemed superfluous and will not be transferred. |
Header Usage
The header is used extensively by the Packet Switched to Circuit Switched Access Transfer Features. See the individual feature pages for specifics on where it is set and used.
It is also used by the SCCDetermineSessionType feature.
A call flow diagram showing its use is available on the Shared ATU-STI page.
OC-IM-CallReferenceNumber Header
The OC-IM-CallReferenceNumber header is a custom SIP header used by Sentinel VoLTE SCC-AS to send the Call Reference Number to the IM-SSF to use in future messages.
Header Format
The header name is OC-IM-CallReferenceNumber and its value is a string representing the 8 bytes of the call reference number in Hexadecimal format. The header does not have any special parameters.
Example:
OC-IM-CallReferenceNumber: 006500655F68D12BHeader Usage
The header is set by the FetchMSRN Feature.
OC-Terminating-Domain Header
The OC-Terminating-Domain header is a custom SIP header used by Sentinel VoLTE SCC-AS to communicate information about the terminating domain to upstream nodes in a network. This header is inserted into responses that go "upstream" (towards the calling party). This is typically used for charging purposes, as by definition the SCC-AS is the final AS in the iFC trigger chain for terminating triggers, and does not perform charging. Therefore any other SIP AS invoked in the terminating trigger chain was invoked prior to the SCC-AS. The SCCTADSRouting and SCCTADSParallelRouting features both add this header to all provisional and success responses for an initial INVITE that are forwarded upstream from a terminating instance. The header will never appear on a final error response.
Header Format
The header name is OC-Terminating-Domain and its value is a simple string with no special formatting. The header does not have any special parameters. Possible values are described below.
Example:
OC-Terminating-Domain: PS=EUTRANHeader Values
The value of the header will depend on which domain the response originated in:
-
Responses from the CS domain will always have the header value set to
CS -
Responses from the PS domain will always have the header value set to the match the String stored in the
PSTerminatingDomainHeaderValuein session state
The value stored in PSTerminatingDomainHeaderValue is determined by the TADS Data Lookup feature.
Default Values
Out of the box, Sentinel VoLTE supports the following values for the OC-Terminating-Domain header:
| Value | Access Domain | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
CS |
CS |
The response was received from a leg that routed towards the Circuit Switched network. |
PS |
PS |
The response was received from a leg that was routed towards the Packet Switched network. This value is used when more specific information about the Packet Switched network is not available |
PS=EUTRAN |
PS |
Indicates terminating access is over E-UTRAN (LTE) radio network |
PS=WLAN |
PS |
Indicates terminating access is over WLAN |
Route Header Parameters
Custom Route Header Parameters
| Parameter Name | Parameter Values | Description | used by |
|---|---|---|---|
oc-charge-mode |
|
This is a custom parameter on the URI of the top-most route header. It is expected that this will be added by the S-CSCF based on iFCs. For more information see Session Processing. |
DetermineChargeMode feature |
oc-mode |
|
Indicates the selection of SCC or MMTel behaviour for an INVITE session. The values For more information see Session Processing. |
DetermineVoltePlanId feature |
oc-blindpsrouting |
N/A |
If present, indicates T-ADS should blindly attempt to route towards PS (only applicable if oc-mode is |
SCCTADSDataLookup feature |
oc-tads-routing |
|
If set to parallel, indicates TADS should run the SCCTADSParallelRouting feature, if the parameter is not present or set to any other value SCCTADSRouting will run (only applicable if oc-mode is |
SCCTADSDataLookup feature |
Charging Information
Charging Information describes the format and content of CDR files, and the information present in Diameter Ro.
Topics
-
CDR Formats — describes the formats used for CDRs
-
Charging Content AVPs — describes the populated AVPs for both online and offline charging
-
Ro Interface AVPs — describes the population of AVPs on the Ro interface
-
Working with CDRs — describes tooling to extract the content of CDRs
-
Interim CDRs — describes Interim CDRs for offline charging
-
Sizing AVP CDRs — describes sizing requirements when using AVP CDRs
CDR Formats
Sentinel supports two CDR formats "out of the box". These are the AVP CDR format, and the legacy format.
Note that Sentinel can be configured to use a user provided CDR format, or even no CDRs.
AVP CDRs
An AVP CDR is an OpenCloud defined CDR that contains AVPs. This type of CDR is consistent with the approaches used in Diameter Ro and Diameter Rf interfaces. An AVP CDR contains AVPs that are standardised (e.g. 3GPP and IETF), or non-standardised (e.g. product specific or project specific).
AVP CDRs can almost be considered an "on-disk" form of the content contained in the Rf interface.
AVP CDRs are used by default in the Sentinel SIP service. The Sentinel SIP service can be configured to use the legacy format.
Legacy CDRs
A legacy CDR is an OpenCloud defined CDR that is used in the Sentinel product set prior to (and during) the introduction of AVP CDRs. The product continues support for this format so that customers who use this format do not need migrate.
Legacy CDRs remain in use by the Sentinel SS7 and Sentinel Diameter services.
Topics
-
AVP CDR Format — describes the formats used for AVP CDRs
-
Legacy CDR Format — describes the format used for Legacy CDRs
AVP CDR Format
AVP CDRs have logical content, and an on-disk format.
Logical content
Each CDR inside a CDR file has logical content. We use a BNF syntax to describe this logical content.
CDR ::=
[ Subscription-Id ]
[ IMS-Information ]
[ User-Equipment-Info ]
*[ Multiple-Services-Credit-Control ]
[ OC-Call-Type ]
[ OC-Service-Type ]
[ OC-Charging-Result ]
*[ OC-OCS-Session-Id ]
[ OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause ]
[ OC-Sentinel-Error ]
*[ OC-Charging-Instance ]
[ OC-Event-Id ]
[ OC-Call-Id ]
[ OC-End-Session-Cause ]
[ OC-Session-Start-Time ]
[ OC-Session-Established-Time ]
[ OC-Session-End-Time ]
[ User-Name ]
[ OC-Selection-Key ]
[ OC-Play-Announcement-Id ]
[ OC-Terminating-Domain ]
*[ AVP ]
Logically this means that an individual CDR has optional content. It may have zero or one Subscription-Id AVP, zero or one IMS-Information AVP, and so-on. It may have zero or more OC-Play-Announcement-Id AVPs, and zero or more OC-OCS-Session-Id AVPs, and so-on.
A CDR inside the CDR file is not an AVP. It is a protobuf record, and as such may contain additional "root" AVPs. So, for example an application may use the format, but add a LCS-Information AVP, or custom AVP.
You could consider each CDR to be roughly equivalent to the Service-Information AVP, yet more flexible/extensible regarding its content. This is because the Service-Information AVP is essentially closed for extension by non-3GPP groups.
To view the population of AVPs in use, refer to Charging Content AVPs
On disk format
AVP CDRs are written using Google protocol buffers (protobuf).
An AVP CDR file has a protobuf schema. This schema allows any AVP to be written to a CDR.
package com.opencloud.cdrformat;
// AVP based CDR
message AvpCdr {
repeated AVP avps = 1;
message AVP {
required bytes avpData = 1; // The Diameter binary encoded AVP data
required string interfaceName = 2; // The interface which the AVP is being written out as, e.g "Rf", "Ro"
required string specRevision = 3; // E.g. "vcb0"
optional string avpName = 4;
}
}
Legacy CDR Format
The Legacy CDR format has an on-disk format defined using Google Protocol Buffers (aka protobuf).
There is a common "types definition" schema file that is used by multiple Sentinel Services for their CDRs. These types are called "base types". Each Sentinel Service then defines its own CDRs using these types and defining its own types.
Base types
The base types are used in CDRs for Sentinel SS7, Sentinel Diameter Mediation, and for legacy format support in Sentinel SIP (as non-default).
package com.opencloud.sentinel.cdr;
message CdrSessionCounters {
repeated CdrSessionCounterAccess counters = 1;
}
message CdrSessionCounterAccess {
required string subscriberId = 1;
required string bucketName = 2;
optional int64 cumulativeRequestedUnits = 3;
optional int64 cumulativeGrantedUnits = 4;
optional int64 cumulativeSentUsedUnits = 5;
optional int64 cumulativeCommittedUsedUnits = 6;
optional int64 cumulativeRequestedRefundUnits = 7;
optional int64 cumulativeGrantedRefundUnits = 8;
repeated CdrSessionSubCounterAccess subCounters = 9;
}
message CdrSessionSubCounterAccess {
required string subCounterId = 1;
optional int64 cumulativeRequestedUnits = 3;
optional int64 cumulativeGrantedUnits = 4;
optional int64 cumulativeSentUsedUnits = 5;
optional int64 cumulativeCommittedUsedUnits = 6;
optional int64 cumulativeRequestedRefundUnits = 7;
optional int64 cumulativeGrantedRefundUnits = 8;
repeated CdrSessionSubCounterAccess subCounters = 9;
}
message Time {
required int64 milliseconds_since_epoch = 1;
required sint32 zoneoffset_minutes = 2;
}
enum SentinelError {
None = 1;
OcsTimeout = 2;
OcsCommunicationFailure = 3;
SentinelOverload = 4;
ProtocolError = 5;
InternalError = 6;
MappingError = 7;
OtherError = 8;
}
Sentinel SIP Service
By default the Sentinel SIP Service uses the AVP CDR Format.
Sentinel SIP can be configured to use the legacy format. This format is defined as follows:
package com.opencloud.sentinel.cdr;
import "com/opencloud/sentinel/cdr/base-cdr-types.proto";
// SIP CDR
message SipCdr {
optional string subscriber = 1;
optional Time sessionInitiated = 2;
optional Time sessionEstablished = 3;
optional Time sessionEnded = 4;
optional CallType callType = 5;
optional string callingPartyAddress = 6;
optional string calledPartyAddress = 7;
optional string callId = 8;
optional sint32 chargingResult = 9 [default = -1];
optional int64 cumulativeReported = 10;
repeated int32 ocsLatencySamples = 12 [packed=true];
repeated int32 announcementIDs = 13;
optional SipServiceType serviceType = 14 [default = Unknown];
optional SentinelError sentinelError = 15 [default = None];
optional int32 endSessionCause = 16;
optional int32 ocsSessionTerminationCause = 17;
optional string sentinelSelectionKey = 18;
repeated string ocsSessionIDs = 19;
repeated CDRChargingInstance chargingInstances = 21;
optional string eventId = 22;
extensions 50 to max;
enum CallType {
MOC = 1;
MOC_3RDPTY = 2;
MTC = 3;
MFC = 4;
EMERGENCY_CALL = 9;
}
enum SipServiceType {
Unknown = 1;
SipCall = 2;
Subscription = 3;
Message = 5;
}
message CDRChargingInstance {
required string name = 1;
repeated CDRSessionCounter sessionCounter = 2;
}
message CDRSessionCounter {
required SessionCounterAddress address = 1;
optional int64 reportedUsed = 2;
optional int64 pendingRequested = 3;
optional int64 cumulativeSentUsed = 4;
optional int64 cumulativeCommittedUsed = 5;
optional int64 cumulativeRequested = 6;
optional int64 cumulativeGranted = 7;
optional int64 cumulativeRequestedRefund = 8;
optional int64 cumulativeGrantedRefund = 9;
optional Time startTime = 10;
optional Time endTime = 11;
optional int64 cumulativeSuspendedDuration = 12;
extensions 50 to max;
message SessionCounterAddress {
repeated AddressEntry entry = 1;
message AddressEntry {
required string key = 1;
required string value = 2;
}
}
}
}
Charging Content AVPs
The population of AVPs for Sentinel VoLTE is described on this page. A definition of the AVPs used for the Sentinel VoLTE product is provided on Sentinel VoLTE AVP definitions.
Detecting Online Charging
The OC-Charging-Result AVP in a CDR indicates whether online (Diameter Ro) charging was used for a session. This may be used to determine if further action is needed when processing CDRs offline.
-
An
OC-Charging-Resultvalue of-1means that online charging was not used for the session. -
Otherwise the value is set to the Diameter
Result-CodeAVP value.
Populated AVPs in the Multiple-Services-Credit-Control AVP
The Multiple-Services-Credit-Control AVP is of type grouped, and is defined in RFC 4006. Section 7.1.4 of 3GPP TS 32.299 defines it with additional 3GPP specific parameters and states some IETF parameters are not used in the 3GPP.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Requested-Service-Unit |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
No |
Used in the CCR. The CDR represents this information in the OC-Session-Counter AVP |
Used-Service-Unit |
IETF RFC 4006 and 3GPP TS 32.299 |
No |
Yes |
No |
Used in the CCR according to Populated AVPs in the Used-Service-Unit AVP. The CDR represents this information in the OC-Session-Counter AVP |
Service-Identifier |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel uses the Rating-Group AVP in preference to the Service-Identifier |
Rating-Group |
IETF RFC 4006 and 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.1.10 |
No |
Yes |
No |
This AVP is set according to Session Counters and the |
Reporting-Reason |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.175 |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
Trigger |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.235 |
No |
No |
No |
|
PS-Furnish-Charging-Information |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.157 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Refund-Information |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.171 |
No |
No |
No |
|
AF-Correlation-Information |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.11 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Envelope |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.59 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Envelope-Reporting |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.61 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Time-Quota-Mechanism |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.228 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Service-Specific-Info |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.195 |
No |
No |
No |
|
QoS-Information |
3GPP TS 29.212 |
No |
No |
No |
The BNF grammar for this AVP in 32.299 v12.11.0 is as follows:
<Multiple-Services-Credit-Control> ::= < AVP Header: 456 >
[ Granted-Service-Unit ] // not used in CCR
[ Requested-Service-Unit ]
* [ Used-Service-Unit ]
[ Tariff-Change-Usage ] // not used in 3GPP
* [ Service-Identifier ]
[ Rating-Group ]
* [ G-S-U-Pool-Reference ] // not used in CCR
[ Validity-Time ] // not used in CCR
[ Result-Code ] // not used in CCR
[ Final-Unit-Indication ] // not used in CCR
[ Time-Quota-Threshold ] // not used in CCR
[ Volume-Quota-Threshold ] // not used in CCR
[ Unit-Quota-Threshold ] // not used in CCR
[ Quota-Holding-Time ] // not used in CCR
[ Quota-Consumption-Time ] // not used in CCR
* [ Reporting-Reason ]
[ Trigger ]
[ PS-Furnish-Charging-Information ]
[ Refund-Information ]
* [ AF-Correlation-Information]
* [ Envelope ]
[ Envelope-Reporting ]
[ Time-Quota-Mechanism ]
* [ Service-Specific-Info ]
[ QoS-Information ]
* [ AVP ] // not used in 3GPP
Populated AVPs in the Used-Service-Unit AVP
The Used-Service-Unit AVP is defined in IETF RFC 4006, and then its BNF is modified slightly in 3GPP TS 32.299 section 7.1.9.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Reporting-Reason |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.175 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Tariff-Change-Usage |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
No |
|
CC-Time |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
No |
Used by default as the unit type for SIP Sessions |
CC-Money |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No typically |
No |
Not used out-of-the-box for Sentinel SIP |
CC-Total-Octets |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Not typically |
No |
Not used out-of-the-box for Sentinel SIP |
CC-Input-Octets |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Not typically |
No |
Not used out-of-the-box for Sentinel SIP |
CC-Output-Octets |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Not typically |
No |
Not used out-of-the-box for Sentinel SIP |
The 3GPP definition (in v12.11.0) is
<Used-Service-Unit> ::= < AVP Header: 446 >
[ Reporting-Reason ]
[ Tariff-Change-Usage ]
[ CC-Time ]
[ CC-Money ] // not used in 3GPP
[ CC-Total-Octets ]
[ CC-Input-Octets ]
[ CC-Output-Octets ]
[ CC-Service-Specific-Units ]
*[ Event-Charging-TimeStamp ]
*[ AVP ] // not used in 3GPP
Populated AVPs in the Service-Information AVP
The Service-Information AVP is defined in 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0. It is a grouped AVP. This table lists the AVPs grouped within Service-Information and how the product populates them.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SMS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.211 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
The Sentinel IP-SM-GW product populates this AVP |
MMTel-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.111 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Subscription-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 states that it should be set on the Rf interface, not the Ro interface (see section 7.2.149) |
AoC-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.15 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement the advice of charge service out-of-the-box |
PS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.158 |
No |
No |
No |
PS-Information AVP contains EPC layer information and as such is not populated by a SIP-AS. |
IMS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.77 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
See the IMS-Information table for further details |
MMS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.110 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement any MMS node roles out-of-the-box |
LCS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.89 |
No |
No |
No |
|
PoC-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.144 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement the PoC service out-of-the-box |
MBMS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.99 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement the MBMS service out-of-the-box |
SMS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.211 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement the SMS service out-of-the-box |
VCS-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.242A |
No |
No |
No |
|
MMTel-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.111 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
ProSe-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.154I |
No |
No |
No |
|
Service-Generic-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.191 |
No |
No |
No |
|
IM-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.69 |
No |
No |
No |
Sentinel does not implement IM services out-of-the-box |
DCD-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.50 |
No |
No |
No |
The BNF for the AVP is defined in section 7.2.149. It is as follows:
Service-Information :: = < AVP Header: 873>
* [ Subscription-Id ]
[ AoC-Information ]
[ PS-Information ]
[ IMS-Information ]
[ MMS-Information ]
[ LCS-Information ]
[ PoC-Information ]
[ MBMS-Information ]
[ SMS-Information ]
[ VCS-Information ]
[ MMTel-Information ]
[ ProSe-Information ]
[ Service-Generic-Information ]
[ IM-Information ]
[ DCD-Information ]
Populated AVPs in the MMTel-Information AVP
The MMTel-Information AVP is a grouped AVP. It is defined in 3GPP TS 32.299 v 12.11.0 section 7.2.111.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Supplementary-Service |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.219 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
There is one for each supplementary service used in a Session |
It has the following BNF grammar:
MMTel-Information :: = < AVP Header: 2030> * [ Supplementary-Service ]
Populated AVPs in the Supplementary Service AVP
The Supplementary-Service AVP is a grouped AVP. It is defined in 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.219.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MMTel-SService-Type |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.111A |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Each supplementary service sets this enumeration to itself |
Service-Mode |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.193 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel CDIV and MMTel ICB/OCB features. If these features are not invoked, it will not be present. |
Number-Of-Diversions |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.115 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel CDIV. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
Associated-Party-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.25 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel CDIV. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
Service-ID |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.190 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel Conferencing. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
Change-Time |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.38 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel Conferencing. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
Number-Of-Participants |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.117 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel Conferencing. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
Participant-Action-Type |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.133 |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
Yes see comments |
This is populated according to invocation of MMTel Conferencing. If this feature is not invoked, it will not be present. |
CUG-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.48 |
No |
No |
No |
|
AoC-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.15 |
No |
No |
No |
Supplementary-Service: = < AVP Header: 2048>
[ MMTel-SService-Type ]
[ Service-Mode ]
[ Number-Of-Diversions ]
[ Associated-Party-Address ]
[ Service-ID ]
[ Change-Time ]
[ Number-Of-Participants ]
[ Participant-Action-Type ]
[ CUG-Information ]
[ AoC-Information ]
Populated AVPs in the IMS-Information AVP
The IMS-Information AVP is defined in 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0. It is a grouped AVP. This table lists the AVPs grouped within IMS-Information and how the product populates them.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Event-Type |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.65 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Role-Of-Node |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.177 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Sessions with sescase of |
Node-Functionality |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.113 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Set to value |
User-Session-Id |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.242 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Set to the Call-Id for the initial request |
Outgoing-Session-Id |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.128A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Session-Priority |
29.229 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Set to value |
Calling-Party-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.33 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Called-Party-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.32 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Called-Asserted-Identity |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.31 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Number-Portability-Routing-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.120 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Carrier-Select-Routing-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.34 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Alternate-Charged-Party-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.12 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Requested-Party-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.176 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
This field is only included if different from the |
Associated-URI |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.26 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Application-Server-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.24 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Inter-Operator-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.80 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Transit-IOI-List |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.233B |
No |
No |
No |
|
IMS-Charging-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.75 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
SDP-Session-Description |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.184 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
SDP-Media-Component |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.180 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Served-Party-IP-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.187 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Server-Capabilities |
29.229 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Trunk-Group-ID |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.237 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Bearer-Service |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.30 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Service-Id |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.190 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Service-Specific-Info |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.195 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Message-Body |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.103 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Cause-Code |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.35 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Reason-Header |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.164A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Access-Network-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.1 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
The first value in the SIP P-Access-Network-Info header is included as the value for this AVP |
Early-Media-Description |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.58 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
The most recent Early Media offer/answer is included |
IMS-Communication-Service-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.76 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
IMS-Application-Reference-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.74A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Online-Charging-Flag |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.122 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Real-Time-Tariff-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.164 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Account-Expiration |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.2 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Initial-IMS-Charging-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.79A |
No |
No |
No |
|
NNI-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.112A |
No |
No |
No |
|
From-Address |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.67A |
No |
No |
No |
|
IMS-Emergency-Indicator |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.76A |
No |
No |
No |
|
IMS-Visited-Network-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.77A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Access-Transfer-Information |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.1A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Related-IMS-Charging-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.171B |
No |
No |
No |
|
Related-IMS-Charging-Identifier-Node |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.171C |
No |
No |
No |
|
Route-Header-Received |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.177A |
No |
No |
No |
|
Route-Header-Transmitted |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.177B |
No |
No |
No |
|
Instance-Id |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.70A |
No |
No |
No |
|
TAD-Identifier |
32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.2.219A |
No |
No |
No |
The BNF syntax for the IMS-Information AVP according to 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 is as follows
IMS-Information :: = < AVP Header: 876>
[ Event-Type ]
[ Role-Of-Node ]
{ Node-Functionality }
[ User-Session-Id ]
[ Outgoing-Session-Id ]
[ Session-Priority ]
* [ Calling-Party-Address ]
[ Called-Party-Address ]
* [ Called-Asserted-Identity ]
[ Number-Portability-Routing-Information ]
[ Carrier-Select-Routing-Information ]
[ Alternate-Charged-Party-Address ]
* [ Requested-Party-Address ]
* [ Associated-URI ]
[ Time-Stamps ]
* [ Application-Server-Information ]
* [ Inter-Operator-Identifier ]
* [ Transit-IOI-List ]
[ IMS-Charging-Identifier ]
* [ SDP-Session-Description ]
* [ SDP-Media-Component ]
[ Served-Party-IP-Address ]
[ Server-Capabilities ]
[ Trunk-Group-ID ]
[ Bearer-Service ]
[ Service-Id ]
* [ Service-Specific-Info ]
* [ Message-Body ]
[ Cause-Code ]
* [ Reason-Header ]
* [ Access-Network-Information ]
* [ Early-Media-Description ]
[ IMS-Communication-Service-Identifier ]
[ IMS-Application-Reference-Identifier ]
[ Online-Charging-Flag ]
[ Real-Time-Tariff-Information ]
[ Account-Expiration ]
[ Initial-IMS-Charging-Identifier ]
* [ NNI-Information ]
[ From-Address ]
[ IMS-Emergency-Indicator ]
[ IMS-Visited-Network-Identifier ]
* [ Access-Transfer-Information ]
[ Related-IMS-Charging-Identifier ]
[ Related-IMS-Charging-Identifier-Node ]
[ Route-Header-Received ]
[ Route-Header-Transmitted ]
[ Instance-Id ]
[TAD-Identifier]
Populated OpenCloud AVPs
The population of OpenCloud AVPs is described here. The definition of OpenCloud AVPs is provided in Sentinel AVP definitions.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
n/a |
|
OC-Play-Announcement-Id |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
n/a |
|
OC-Call-Type |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Role-Of-Node AVP has similar meaning on the Ro interface |
|
OC-Service-Type |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
n/a |
|
OC-Charging-Result |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-OCS-Session-Id |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
This is the session ID in Ro |
|
OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Sentinel-Error |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Charging-Instance |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Event-Id |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Call-Id |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
The Ro Session Id optional part includes the SIP Call ID |
|
OC-End-Session-Cause |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Start-Time |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-End-Time |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Session-Start-Time |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Session-Established-Time |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Included if an INVITE session is answered |
|
OC-Session-End-Time |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Session-Counter |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-Interim-CDR-Trigger |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
||
OC-AGE-OF-INFORMATION |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||
OC-MCC-MNC |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||
OC-ACCESS-NETWORK-MCC-MNC |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||
OC-VISITED-NETWORK-MCC-MNC |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||
OC-IMSI-MCC-MNC |
Optional |
Optional |
Optional |
It is included if the call flow performs a SRI request or SRI-for-SM request |
|
OC-Terminating-Domain |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
n/a |
|
OC-IMSSF-Call-Reference-Number |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
n/a |
|
OC-Conf-Type |
No |
Yes |
No |
n/a |
Sentinel AVP definitions
The following AVPs are OpenCloud defined AVPs used that are used in the Sentinel VoLTE product. All OpenCloud defined AVPs have a diameter vendor ID of 19808.
AVPs defined in the Sentinel VoLTE product
The Sentinel VoLTE product extends Sentinel Express and adds the following AVP.
OC-Terminating-Domain
The OC-Terminating-Domain AVP (AVP code 1005) is of type UTF8String and contains the value of the OC-Terminating-Domain Header SIP header.
AVPs defined in Sentinel Express
The following AVPs are defined in the Sentinel Express product, and are used in the Sentinel VoLTE product.
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key
The OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key AVP (AVP code 1001) is of type UTF8String and contains the Sentinel Selection Key for the session.
OC-Play-Announcement-Id
The OC-Play-Announcement-Id AVP (AVP code 1002) is of type Integer32 and contains the ID of an announcement used during the session.
OC-Call-Type
The OC-Call-Type AVP (AVP code 1003) is of type Enumerated and specifies the type of trigger for the session.
It can be one of the following:
-
MOC= 1, the trigger was Originating -
MOC_3RDPTY= 2, the trigger was a non-SIP third party call setup request (e.g. via HTTP) -
MTC= 3, the trigger was Terminating -
MFC= 4, the trigger was Forwarding -
EMERGENCY_CALL= 9, the trigger was classified as emergency
OC-Service-Type
The OC-Service-Type AVP (AVP code 1004) is of type Enumerated and specifies the initiating message for the session.
It can be one of the following:
-
UNKNOWN= 1, the initiating reason is unknown -
SipCall= 2, the session was initiated due to receipt of SIP INVITE -
Subscription= 3, the session was initiated due to receipt of SIP SUBSCRIBE -
Message= 5, the session was initiated due to receipt of SIP MESSAGE
OC-Charging-Result
The OC-Charging-Result AVP (AVP code 1006) is of type Integer32. It contains the value of the Diameter CCA result-code AVP. In case there was no Ro session, it will have the value of -1.
OC-OCS-Session-Id
The OC-OCS-Session-Id AVP (AVP code 1008) is of type UTF8String. It indicates a Session Id used to communicate with the OCS during the session.
OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause
The OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause AVP (AVP code 1009) is of type Integer32. It communicates the reason that the OCS (or mediation layer) terminated the Ro session. It can be one of the following:
-
NORMAL_SESSION_COMPLETION= 0, the session terminated normally. -
ERROR_CCA= 1, the session was terminated due to a CCA error response. -
CREDIT_LIMIT_REACHED= 2, the session was terminated due to Credit-Limit-Reached. -
OCS_ABORT= 3, the session was terminated due to an ASR received from the OCS. -
TCC_EXPIRED= 4, the session was terminated due to the Sentinel Tcc timer expiring. -
CREDIT_CONTROL_FAILURE= 5, the session was terminated due to a failure generating CCR. -
CLIENT_ABORT= 6, the session terminated due to a client request, typically as a result of an abnormal event.
OC-Sentinel-Error
The OC-Sentinel-Error AVP (AVP code 1010) is of type Enumerated.
It can be one of the following:
-
None= 1 -
OcsTimeout= 2 -
OcsCommunicationFailure= 3 -
SentinelOverload= 4 -
ProtocolError= 5 -
InternalError= 6 -
MappingError= 7 -
OtherError= 8
If there is a Credit Control Answer, and it has an Experimental Result Code, and that has an OpenCloud vendor ID, then this AVP is filled.
OC-Charging-Instance
The OC-Charging-Instance AVP (AVP code 1011) is of type Grouped. An OC-Charging-Instance AVP represents an online charging instance used during the session.
OC-Charging-Instance ::= < AVP Header: 1011 >
[ OC-Charging-Instance-Name ]
*[ OC-Session-Counter ]
OC-Charging-Instance-Name
The OC-Charging-Instance-Name AVP (AVP code 1012) is of type UTF8String. It represents the name of an OC-Charging-Instance.
OC-Session-Counter
The OC-Session-Counter AVP (AVP code 1013) is of type Grouped. It represents a Session Counter used during the session.
OC-Session-Counter ::= < AVP Header: 1013 >
*[ OC-Session-Counter-Address ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Granted ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Requested ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used ]
[ OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration ]
[ OC-Reported-Used ]
[ OC-End-Time ]
[ OC-Pending-Requested ]
[ OC-Start-Time ]
OC-Session-Counter-Address
The OC-Session-Counter-Address AVP (AVP code 1014) is of type Grouped. It represents a Session Counter address field, as documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Session-Counter-Address ::= < AVP Header: 1014 >
[ OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key ]
[ OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value ]
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key
The OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key AVP (AVP code 1015) is of type UTF8String.
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value
The OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value AVP (AVP code 1016) is of type UTF8String.
OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used
The OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used AVP (AVP code 1017) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulativeCommittedUsed unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Granted
The OC-Cumulative-Granted AVP (AVP code 1018) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulativeGranted unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund
The OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund AVP (AVP code 1019) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulatedGrantedRefund unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Requested
The OC-Cumulative-Request AVP (AVP code 1020) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulatedRequested unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund
The OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund AVP (AVP code 1021) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulativeRequestedRefund unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used
The OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used AVP (AVP code 1022) is of type Integer64. It contains the cumulative used units sent to the OCS for the Session Counter.
It contains the value of the cumulativeSentUsed unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration
The OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration AVP (AVP code 1023) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the cumulativeSuspendedDuration field documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Reported-Used
The OC-Reported-Used AVP (AVP code 1024) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the reportedUsed field documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Pending-Requested
The OC-Pending-Requested AVP (AVP code 1025) is of type Integer64.
It contains the value of the pendingRequested unit counter documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Start-Time
The OC-Start-Time AVP (AVP code 1026) is of type Time.
It contains the value of the startTime field documented in Session counter structure.
OC-End-Time
The OC-End-Time AVP (AVP code 1027) is of type Time.
It contains the value of the endTime field documented in Session counter structure.
OC-Event-Id
The OC-Event-Id AVP (AVP code 1028) is of type UTF8String.
If the initial request for the Session was a SIP SUBSCRIBE or SIP NOTIFY request, this is set to the value of the Event: header in the initial request.
If the initial request for the Session was a SIP REFER request, this is set to the CSeq of the REFER request.
OC-Call-Id
The OC-Call-Id AVP (AVP code 1029) is of type UTF8String. This is set to the Call-ID of the initial SIP request for the Session.
OC-End-Session-Cause
The OC-End-Session-Cause AVP (AVP code 1036) is of type Integer32. This is set to indicate the reason a service or feature ended the session.
If the LegManager.endSession instruction is called with a cause value, the AVP value is set to the cause value.
Otherwise, if the session state field endSessionCause is set, the AVP value is set to the session state value.
OC-Interim-CDR-Trigger
The OC-Interim-CDR-Trigger AVP (AVP code 1037) is a repeated AVP of type Grouped and appears only in interim CDRs. Each occurrence indicates a reason for writing an Interim CDR and the leg for which the reason applies.
OC-Interim-CDR-Trigger ::= < AVP Header: 1037 >
[ OC-Interim-CDR-Reason ]
[ OC-Interim-CDR-Leg ]
OC-Session-Start-Time
The OC-Session-Start-Time AVP (AVP code 1040) is of type Time.
It contains the time that the session’s Initial Request was processed.
OC-Session-Established-Time
The OC-Session-Established-Time AVP (AVP code 1041) is of type Time.
It contains the time that the session was answered, that is the ACK to the 2xx-INVITE was processed.
OC-Session-End-Time
The OC-Session-End-Time AVP (AVP code 1042) is of type Time.
It contains the time that the session was ended.
OC-Age-Of-Information
The OC-Age-Of-Information AVP (AVP code 1060) is of type Integer64. The time in milliseconds of the source information. The value depends on which of the grouped AVP’s contains the OC-Age-Of-Information.
OC-MCC-MNC
The OC-MCC-MNC AVP (AVP code 1061) is of type UTF8String. The length is 5 or 6 digits depending on the value of MNC, that can be 2 or 3. It is encoded as UTF8String characters representing the IMSI MCC-MNC numerical values. In accordance with 3GPP TS 29.060 24 (for GGSN), 3GPP TS 29.274 81 (for P-GW) and 3GPP TS 23.003 40, the MCC is 3 digits and the MNC is either 2 or 3 digits. There are no padding characters between the MCC and MNC.
OC-Access-Network-MCC-MNC
The OC-Access-Network-MCC-MNC (AVP code 1062) indicates the home network MCC-MNC, in case the access network can be identified. The information is extracted from the P-Access-Network-Info header.In the event that the P-Access-Network-Header header is not present the information can be extracted from registration records. It is a grouped AVP formed by:
-
OC-MCC-MNC
-
OC-Age-Of-Information
The OC-Age-Of-Information is the registration time.
OC-Visited-Network-MCC-MNC
The OC-Visited-Network-MCC-MNC (AVP code 1063) indicates the visited network MCC-MNC, in case the visited network can be identified. This information is extracted from the P-Visited-Network-Id header. In the event that the P-Visited-Network-Id header is not present the information can be extracted from registration records. It is a grouped AVP formed by:
-
OC-MCC-MNC
-
OC-Age-Of-Information
The OC-Age-Of-Information is the registration time.
OC-IMSI-MCC-MNC
The OC-IMSI-MCC-MNC (AVP code 1064) is extracted from the IMSI and indicates the network related to the subscriber’s IMSI. It is a grouped AVP formed by:
-
OC-MCC-MNC
-
OC-Age-Of-Information
The OC-Age-Of-Information is:
-
registration time
-
SRI response time in case it is extracted from the SRI response.
Interim CDRs
The purpose, lifecycle, and features related to Interim CDRs are described on this page.
Overview
Interim CDRs are a CDR format used for recording CDRs at multiple points during the lifetime of a session. This format has several benefits over the once-per-session CDRs written by the session-based CDR features:
-
Improved failure characteristics. Interim CDRs are recording more frequently during a session, so any system failures will result in less records being lost.
-
Interop with offline charging systems. This format is designed to reflect the message content requirements for interaction with offline charging systems via the Rf interface.
-
More accurate. This format records changes in specific AVPs (e.g. SIP SDP AVPs) during the lifecycle of a session allowing changes in media state to be more accurately tracked.
Interim CDR content
Interim CDRs are written as a collection of AVPs conforming to the definitions listed in Sentinel AVP definitions. In addition to the standard AVPs, Interim CDRs contain additional AVPs to facilitate interpretation and correlation of their content.
These additions are summarized in the following table:
| AVP | Description | Specification |
|---|---|---|
Accounting-Record-Type |
Lifecycle enum indicating when the record was written. See below table. |
RFC 6733 |
Accounting-Record-Number |
Unique-per-session number starting at 0 indicating how many records have been written for this session. |
RFC 6733 |
OC-Interim-CDR-Reason |
Contains the leg the Interim CDR relates to, and the reason it was written. |
The Accounting-Record-Type AVP can have the following enumerated values:
| Accounting-Record-Type | When written… |
|---|---|
START_RECORD |
When a session is established (answered). |
INTERIM_RECORD |
Mid-session, either in response to SDP changes or based on timer events (both configurable). |
STOP_RECORD |
When a session finishes. |
EVENT_RECORD |
When the last Interim CDR written is also the first one written, e.g. for recording of one-off SMS events. |
Interim CDR Correlation
If the IMS Charging Identifier (ICID) is present during network interactions it will be included in all Interim CDRs produced for a session.
When Running List CDRs, ICIDs present in a CDR file can be listed with --list-icids, or filtered with a specific ICID using --filter-by-icid.
Related features
For configuring when Interim CDRs are written, refer to the VoLTE Interim Cdr feature documentation.
Other features can inform the VoLTE Interim Cdr feature of important session state changes by writing values to the control fields defined by the SipInterimCdrSessionState session state interface.
The features which affect the behaviour of the VoLTE Interim Cdr features are:
| Feature | Behaviour |
|---|---|
Determines which leg to charge then records it to the |
|
Detects when SDPs have changed and sets the |
|
Sets the |
|
Unsets the |
Controlling when Interim CDRs are written
The Interim CDR feature writes CDRs at specific points during a session. There are several mechanisms to control when interim CDRs are written including feature configuration and session state control fields, as described in the feature documentation.
Example call flow
Below is an annotated call flow indicating where Interim CDRs are written during a typical SIP Mobile Originating session.
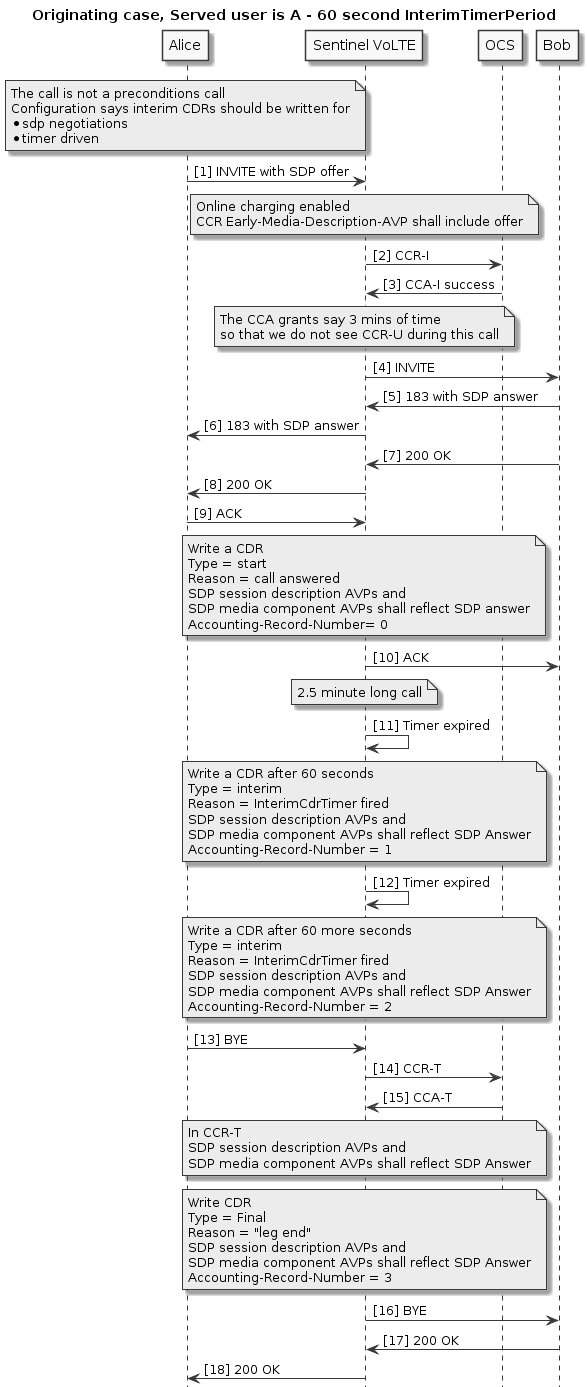
Extending CDR content
To customise the content included in Interim CDRs, refer to Customising CDRs from the SDK documentation.
Rf Interface AVPs
The AVPs used by Sentinel VoLTE in the Accounting request are described.
Sentinel VoLTE SIP Service population of Accounting Request
The Accounting Request message is defined according to IETF RFC 6733, and the diameter Rf interface is defined in 3GPP TS 32.299. Sentinel products use the definition in 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 for ACR.
This table indicates the top-level AVPs inside an ACR request and how the Sentinel SIP service populates them.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in ACR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Service-Context-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 and refined by 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.1.12 |
Yes |
Yes |
For MMTel the value is set to |
User-Name |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
Set in Sentinel VoLTE to the IMS Private Identifier for the served user if the served user is IMS registered. |
Session-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
The Session-Id optional part is set to the Call-ID of the initial request for the Session |
Origin-Host |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
Yes |
Resource Adaptor entity configuration defines the value to be used for this AVP |
Origin-Realm |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
Yes |
Resource Adaptor entity configuration defines the value to be used for this AVP |
Destination-Realm |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
Yes |
This is set in Sentinel configuration, when selecting a CDF to use for the Session |
Accounting-Record-Type |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Accounting-Record-Number |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Acct-Application-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
Yes |
Set to the value |
Vendor-Specific-Application-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
## in volte documentation |
User-Name |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
This contains the Private Id from registration data |
Destination-Host |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Accounting-Sub-Session-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Acct-Session-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Acct-Multi-Session-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Acct-Interim-Interval |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Accounting-Realtime-Required |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Origin-State-Id |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Event-Timestamp |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
Yes |
|
Proxy-Info |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
|
Route-Record |
IETF RFC 6733 |
No |
No |
## in volte documentation |
Service-Context-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Service-Information |
3GPP TS 32.299 |
No |
Yes |
The BNF for the ACR message according to 32.299 v12.11.0 section 6.2.2 is
<ACR> ::= < Diameter Header: 271, REQ, PXY >
< Session-Id >
{ Origin-Host }
{ Origin-Realm }
{ Destination-Realm }
{ Accounting-Record-Type }
{ Accounting-Record-Number }
[ Acct-Application-Id ]
[ Vendor-Specific-Application-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ User-Name ]
[ Destination-Host ]
[ Accounting-Sub-Session-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Acct-Session-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Acct-Multi-Session-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Acct-Interim-Interval ]
[ Accounting-Realtime-Required ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Origin-State-Id ]
[ Event-Timestamp ]
* [ Proxy-Info ]
* [ Route-Record ]
[ Service-Context-Id ]
[ Service-Information ]
* [ AVP ]
Ro Interface AVPs
The AVPs used by Sentinel VoLTE in the credit control request are described.
Sentinel VoLTE SIP Service population of Credit Control Request
The Credit Control Request message is defined according to IETF RFC 4006, and some AVPs are removed and not used according to 3GPP TS 32.299. Sentinel products use the definition in 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 for CCR.
This table indicates the top-level AVPs inside a CCR request and how the Sentinel SIP service populates them.
| AVP Name | Specification reference | Included in CDR | Included in CCR | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Service-Context-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 and refined by 3GPP TS 32.299 v12.11.0 section 7.1.12 |
Yes |
Yes |
For MMTel the value is set to |
User-Name |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
Set in Sentinel VoLTE to the IMS Private Identifier for the served user if the served user is IMS registered. |
Session-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
The Session-Id optional part is set to the Call-ID of the initial request for the Session |
Origin-Host |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
Resource Adaptor entity configuration defines the value to be used for this AVP |
Origin-Realm |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
Resource Adaptor entity configuration defines the value to be used for this AVP |
Destination-Realm |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
This is set in Sentinel configuration, when selecting an OCS to use for the Session |
Auth-Application-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
Set to the value |
Service-Context-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
CC-Request-Type |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
|
CC-Request-Number |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
|
Destination-Host |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
Origin-State-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
Event-Timestamp |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
|
Subscription-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
Set to the Served User, either as a SIP URI or Tel URI. This is populated via the SIP Subscriber Determination Feature. |
Termination-Cause |
IETF RFC 3588 |
No |
No |
|
Requested-Action |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
|
AoC-Request-Type |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
Multiple-Services-Indicator |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
Yes |
Set to |
Multiple-Services-Credit-Control |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
In the case of AVP CDRs, if Ro charging is used then MSCC AVPs from the most recent CCA are written to the CDR. In the case of Ro charging the CCR’s MSCC AVP includes Populated AVPs in the Multiple-Services-Credit-Control AVP |
CC-Correlation-Id |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
User-Equipment-Info |
IETF RFC 4006 |
Yes |
Yes |
The IMEI is used rather than the IMEISV, and the User-Equipment-Type AVP is set to IMEISV. |
Proxy-Info |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
Route-Record |
IETF RFC 4006 |
No |
No |
|
Service-Information |
3GPP TS 32.299 |
No |
Yes |
Refer to Populated AVPs in the Service-Information AVP ## in volte documentation |
User-Name |
IETF RFC 6733 |
Yes |
Yes |
This contains the Private Id from registration data |
The BNF for the CCR message according to 32.299 v12.11.0 section 6.4.2 is
<CCR> ::= < Diameter Header: 272, REQ, PXY >
< Session-Id >
{ Origin-Host }
{ Origin-Realm }
{ Destination-Realm }
{ Auth-Application-Id }
{ Service-Context-Id }
{ CC-Request-Type }
{ CC-Request-Number }
[ Destination-Host ]
[ User-Name ]
[ CC-Sub-Session-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Acct-Multi-Session-Id ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Origin-State-Id ]
[ Event-Timestamp ]
*[ Subscription-Id ]
[ Service-Identifier ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Termination-Cause ]
[ Requested-Service-Unit ] // not used in 3GPP
[ Requested-Action ]
*[ Used-Service-Unit ] // not used in 3GPP
[ AoC-Request-Type ]
[ Multiple-Services-Indicator ]
*[ Multiple-Services-Credit-Control ]
*[ Service-Parameter-Info ] // not used in 3GPP
[ CC-Correlation-Id ]
[ User-Equipment-Info ]
*[ Proxy-Info ]
*[ Route-Record ]
[ Service-Information ]
*[ AVP ]
Sizing AVP CDRs
This section documents the storage requirements for AVP CDRs.
Binary CDR log structure
Each CDR log file can be broken down into the following parts:
-
Protobuf overhead - a small amount of type information about contained records.
-
A header section - a small amount of data written by the CDR RA including version, host, and timestamp information.
-
Zero or more AVP CDRs - these records will vary in individual size, and usually form the majority of a CDR log.
-
A footer - this is empty for Sentinel products.
Sizing analysis
The combined size of the header, footer, and protobuf overhead is normally trivial (<1KB) compared to the size of each finished CDR log file.
Individual CDR records will vary in size based on dynamic content such as hostnames, Sentinel selection key names, SDP content, and other similarly variable character data. As such, it is not possible to provide exact sizing for a given system without examining the CDR logs written while under a test load, but some approximations can be made.
A basic CDR record containing the information normally written by Sentinel will be on the order of 2000-3000 bytes. With this in mind, the following sections provide rough estimates regarding how much storage would be required for specific scenarios.
If Sentinel is configured to write Session CDRs (i.e. not writing Interim CDRs), then each session will write a single CDR on the order of 2000-3000 bytes.
This section documents the storage requirements for the AVP CDRs written by the CDR RA when Sentinel VoLTE Public is configured to output Interim CDRs.
B2BUA CDR Sizing
This scenario involves writing CDRs for a single leg of a two party call.
Assuming a Start and End CDR are always written for the call, and assuming an average CDR size of 2500 bytes, each call will require a minimum of 5000 bytes. In addition, the Interim CDR feature can be configured to write CDRs periodically as a call progresses, or in response to SDP changes. Each of these events will produce additional records.
Taking these additional timer driven and SDP driven records into account, a rough approximation of the CDR storage requirements can be made with a formula such as:
2500 * Sessions Per Second * (2 + (Average SDP Driven CDRs Per Session) + (Average Timer Driven Interim CDRs Per Session))
It isn’t possible to use average call length when calculating storage requirements for timer driven CDRs as the number of timer driven CDRs written per call is sensitive to actual rather than average call length.
With the guideline above, we can perform approximations based on an example scenario:
-
No SDP changes outside of initial call setup.
-
95% of calls last under the default Interim CDR timer threshold (5 minutes by default).
-
5% of calls last for 59 minutes and trigger numerous timer driven Interim CDRs during that period. With a 5 minute interim CDR timer, this will mean 11 timer driven interim CDRs.
-
The overall system is running at 100 session per second.
Using the above, we can assume that the average number of interim timer CDRs per call is 0.05 * 11, or 0.55 per session. This results in an estimated storage requirement per second of:
2500 * 100 * (2 + 0 + 0.55) = 637500 bytes / second
or 2189MB / hour
Additional considerations for MMTel B2BUAs
MMTel is invoked for originating and terminating triggers, and therefore for each call one originating session and one terminating session.
Therefore MMTel typically uses 2x the storage requirements of a single B2BUA.
It is often the case that terminating calls are not charged unless the served user is roaming; therefore the default configuration for MMTel suppresses writing of SDP CDRs for terminating calls if the served user is not roaming. This is supported through use of the SuppressSdpCdr feature.
MMTel Conference CDR sizing
A conference call involves a long lived moderator leg, and one or more short lived consultation legs used to bring an additional users into the conference. A three-party conference call flow is available for reference.
The moderator’s conference leg will write 2 CDRs (start and end) plus additional SDP and timer driven CDRs. The short-lived consultation legs will usually only write 2 CDRs as they are just used to bring additional participants into the conference.
This means that for a three party conference, there will be a minimum of 6 CDRs written, plus any SDP and timer driven CDRs for the moderator leg.
A rough approximation of the CDR storage requirements can be made with a formula such as:
2500 * Conferences Per Second * ((2 + Average SDP driven CDRs Per Moderator Leg + Average Timer Driven Interim CDRs Per Moderator Leg) + (2 * Average number of participants))
Using the guideline above, if we assume the following scenario:
-
No SDP changes outside of initial call setup.
-
Each conference has 5 participants.
-
Each conference lasts 59 minutes (triggering 11 timer-driven Interim CDRs).
-
System is running at 5 conferences per second.
Then we can assume that the CDR storage requirements will be:
2500 * 5 * ((2 + 0 + 11) + (2 * 5)) = 287500 bytes / second
or 987MB / hour
Working with CDRs
| |
Sentinel writes binary CDRs using the CDR RA. Refer to CDR Resource Adaptor section of this guide for more information about Sentinel and the CDR RA. |
List CDRs
The Sentinel SDK contains a List CDRs tool, which can be used to print Sentinel’s binary CDRs files to a human readable format.
The CDR files contain binary encoded Diameter AVPs files in addition to a header and footer. The List CDRs tool decodes the binary CDR file and all the Diameter AVPs which is contains, printing them to the console.
It also supports printing the older 'legacy' CDR format which is not based on AVPs, as used by Sentinel version 2.4.x and earlier.
How to use it in a nutshell:
-
Install the SDK normally using the SDK installer script, which will automatically install list-cdrs at
sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs -
Run
sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs/list-cdrs.sh CDRFILE1 [CDRFILE2]…
This guide covers the installation options and customisation options available for List CDRs.
Protobuf
Protobuf 2.3.0 is required to build and extend CDR modules included with the SDK. This guide covers installing Protobuf for use with the SDK. If using the product "out of the box", Protobuf is not required.
Topics
-
Installing List CDRs — describes how to install the List CDRs tool
-
Obtaining CDRs — describes how to obtain CDRs used as input to the List CDRs tool
-
Running List CDRs — describes how to run the List CDRs tool
-
Extension AVPs — describes how to configure extension AVPs in the List CDRs tool
-
Installing Protobuf — describes how to install Protobuf
Installing List CDRs
Installing the List CDRs tools using the SDK installer
If you install the SDK using the sentinel-volte-sdk/build/bin/installer script, then the installer will automatically install the list-cdrs tool at /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/list-cdrs/.
$ ./build/bin/installer [...] Creating deployment module deploy-volte ... done. [...] Configuration changes written. [...] Installing List CDRs tool ... done. [...]
Installing List CDRs from the SDK using Ant
To install the List CDRs tool using the Ant script instead, use the install-list-cdrs Ant build target under the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools directory:
$ cd /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
$ ant install-list-cdrs
Buildfile: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/build.xml
init-build-extensions:
[...]
install-list-cdrs:
[echo]
[echo] Retrieving List CDRs...
[ivy:resolve] downloading https://repo.opencloud.come/artifactory/opencloud-internal-snapshots/opencloud/sentinel-core/2.7.0/sentinel-list-cdrs/2.7.0.0/sentinel-list-cdrs-package-2.7.0.0.zip ...
[ivy:resolve] ..... (8971kB)
[ivy:resolve] .. (0kB)
[ivy:resolve] [SUCCESSFUL ] opencloud#sentinel-list-cdrs#sentinel-core/2.7.0;2.7.0.0!sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip (1143ms)
[echo]
[echo] List CDRs retrieved.
[echo]
[echo] Installing List CDRs ...
[echo]
[unzip] Expanding: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip into /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
[echo]
[echo]
[echo] List CDRs installed.
[echo] To print CDR files, use the script at list-cdrs/list-cdrs.sh
[echo] Usage: list-cdrs CDRFILE [CDRFILE]...
[echo]
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 14 seconds
| |
See Setting up Ant in the Sentinel VoLTE Public SDK guide. |
Installing List CDRs Standalone
The above two approaches are automated ways of installing the List CDRs package (sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip) into a particular location: sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs/.
Both the above methods place a List CDRs installer archive at sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip.
This sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip archive can be moved to and unzipped into another location outside of the SDK and used as a standalone tool.
To install the List CDRs package as a standalone tool, simply unzip the sentinel-list-cdrs-package.zip archive to your chosen destination directory.
The mechanisms for invoking and configuration the List CDRs tools are the same as when running the tool inside the SDK. Simply substitute /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs with /your/chosen/directory/list-cdrs.
Uninstalling List CDRs
If you want to uninstall the List CDRs tool, use the uninstall-list-cdrs Ant target under the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools directory:
$ cd /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
$ ant uninstall-list-cdrs
Buildfile: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/build.xml
uninstall-list-cdrs:
[echo] Uninstalling (deleting) the list-cdrs install from: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs/
[delete] Deleting directory /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 0 seconds
Alternatively, just delete the list-cdrs directory:
$ rm -rf sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs/
Obtaining CDRs
Obtaining CDR files
The List CDRs tool is designed to read completed binary CDR files generated by Sentinel.
Sentinel uses the CDR RA to write CDR files in a binary format. It typically writes these CDR files to the cdr directory inside the Rhino installation, and writes these binary CDR files using names such as cdr_101_1468259745367.log.
The List CDRs tool can read these completed binary CDR files either in their raw binary format (e.g. cdr_101_1468259745367.log), or in gzip compressed format (e.g. cdr_101_1468259745367.log.gz).
| |
Before a CDR file is completed, Sentinel may write a partial CDR file to disk, e.g. cdr_101_cdr-stream_28929467492591509.tmp. When a partially written CDR is ready to be rolled over, the CDR RA converts it to a completed binary CDR file, e.g. cdr_101_1468259745367.log. The List CDRs tool cannot read partially written CDR files. It can only read complete CDR files. |
Running List CDRs
To invoke the List CDRs tool, run the list-cdrs.sh script under the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs directory. Pass one or more file paths as arguments, each being a path to a completed binary CDR file generated by Sentinel.
| |
If the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools parent directory does not contain a list-cdrs directory, then the List CDRs tool needs to be installed. The Installing List CDRs page describes how to install the List CDRs tool. |
Calling the script with no arguments shows the expected syntax:
$ ./tools/list-cdrs/list-cdrs.sh
Usage: list-cdrs.sh [--no-header] [--no-footer] [--no-protocol] [--ignore-error]
[--output-file OUTPUTFILE] [--size-limit BYTES]
[--cdr-filter FIELD=REGEX] CDRFILE [CDRFILE]...
--no-header - Disable printing of CDR headers.
--no-footer - Disable printing of CDR footers.
--no-protocol - Disable printing of protocol and spec revisions
in top level AVPs, e.g. "(Ro,vcb0)".
--ignore-error - Continue processing CDRs files when encountering
recoverable errors.
--list-icids - List all unique IMS Charging Identifiers in the given CDR file(s),
in order of first appearance.
--filter-by-icid ICID - Print CDR message body only when CDR contains the given IMS Charging Identifier.
ICID can be listed by "--list-icids" option.
--output-file OUTPUTFILE - Append CDR output to OUTPUTFILE rather than to the console.
--size-limit BYTES - CDR record size limit. Minimum and default value is
67108864 (64MB). Increase if encountering
"Protocol message was too large" exception.
--cdr-filter FIELD=REGEX - Print CDR message body only when the given FIELD
matches the given regular expression. FIELD can be
a field name, an AVP name, or an AVP path like
"/IMS-Information/User-Session-Id".
CDRFILE - A completed binary CDR file as produced by Sentinel. Both the new
AVP based format (Sentinel 2.5 and later) and the older
format (Sentinel 2.4 and earlier) are supported. CDR files
can optionally be in gzip format, using a '.gz' suffix.
Partially written CDR files (ending in ".tmp") are not supported.
An example invocation, showing how to print a CDR file:
$ ./tools/list-cdrs/list-cdrs.sh /path/to/cdr_101_1467865845057.log
2016-07-07T16:30:36.554+1200 Header {
ra_name=CDR Generation,
ra_vendor=OpenCloud,
ra_version=2.3,
ra_release=2.3.0.0-M1,
ra_build=20160706024526,
ra_revision=cdr-ra/2.3.0@d55f6a1,
description=CDR session,
rhino_node=101,
ra_entity=cdr,
hostname=mortadella
}
2016-07-07T16:30:36.600+1200 AvpCdr {
avps=[
Subscription-Id(Ro,vcb0)[
Subscription-Id-Type[2],
Subscription-Id-Data[tel:34600000002]
],
IMS-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Role-Of-Node[ORIGINATING_ROLE(0)],
Node-Functionality[AS(6)],
User-Session-Id[08tE5q0fRdQRrus7F4FWqg],
Session-Priority[PRIORITY_2(2)],
Calling-Party-Address[tel:34600000002],
Called-Party-Address[tel:34600000001],
Time-Stamps[
SIP-Request-Timestamp[1467865834000],
SIP-Response-Timestamp[1467865834000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 1000 1000 IN IP4 127.0.0.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0],
Cause-Code[0],
Early-Media-Description[
SDP-TimeStamps[
SDP-Offer-Timestamp[1467865834000],
SDP-Answer-Timestamp[1467865834000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 1000 1000 IN IP4 127.0.0.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0]
]
],
Service-Context-Id(Ro,vcb0)[12.32274@3gpp.org],
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key(Ext,Ext)[DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:sipcall:mmtel-orig:],
OC-Call-Type(Ext,Ext)[MOC(1)],
OC-Service-Type(Ext,Ext)[SipCall(2)],
OC-Charging-Result(Ext,Ext)[2001],
OC-OCS-Session-Id(Ext,Ext)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;0;08tE5q0fRdQRrus7F4FWqg],
Session-Id(Ro,vcb0)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;0;08tE5q0fRdQRrus7F4FWqg],
OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause(Ext,Ext)[0],
OC-Sentinel-Error(Ext,Ext)[None(1)],
OC-Charging-Instance(Ext,Ext)[
OC-Charging-Instance-Name[scur_charging_instance],
OC-Session-Counter[
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Subscriber-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[tel:34600000002]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Service-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[1]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Cc-Unit-Type],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[Cc-Time]
],
OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used[1000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted[60000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Requested[60000],
OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used[1000],
OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration[0],
OC-Reported-Used[0],
OC-Pending-Requested[0],
OC-Start-Time[1467865834000],
OC-End-Time[1467865836000]
]
],
OC-Call-Id(Ext,Ext)[08tE5q0fRdQRrus7F4FWqg],
MMTel-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Supplementary-Service[
Service-Type[2]
],
Subscriber-Role[ORIGINATING(0)]
]
]
}
2016-07-07T16:30:38.937+1200 AvpCdr {
avps=[
Subscription-Id(Ro,vcb0)[
Subscription-Id-Type[2],
Subscription-Id-Data[tel:34600000002]
],
IMS-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Role-Of-Node[ORIGINATING_ROLE(0)],
Node-Functionality[AS(6)],
User-Session-Id[cXD7xzRmA1w4iWBzT9XMdQ],
Session-Priority[PRIORITY_2(2)],
Calling-Party-Address[tel:34600000002],
Called-Party-Address[tel:34600000003],
Time-Stamps[
SIP-Request-Timestamp[1467865837000],
SIP-Response-Timestamp[1467865837000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 1000 1000 IN IP4 127.0.0.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0],
Cause-Code[0],
Early-Media-Description[
SDP-TimeStamps[
SDP-Offer-Timestamp[1467865837000],
SDP-Answer-Timestamp[1467865837000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 1000 1000 IN IP4 127.0.0.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0]
]
],
Service-Context-Id(Ro,vcb0)[12.32274@3gpp.org],
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key(Ext,Ext)[DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:sipcall:mmtel-orig:],
OC-Call-Type(Ext,Ext)[MOC(1)],
OC-Service-Type(Ext,Ext)[SipCall(2)],
OC-Charging-Result(Ext,Ext)[2001],
OC-OCS-Session-Id(Ext,Ext)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;2;cXD7xzRmA1w4iWBzT9XMdQ],
Session-Id(Ro,vcb0)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;2;cXD7xzRmA1w4iWBzT9XMdQ],
OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause(Ext,Ext)[0],
OC-Sentinel-Error(Ext,Ext)[None(1)],
OC-Charging-Instance(Ext,Ext)[
OC-Charging-Instance-Name[scur_charging_instance],
OC-Session-Counter[
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Subscriber-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[tel:34600000002]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Service-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[1]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Cc-Unit-Type],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[Cc-Time]
],
OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used[1000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted[60000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Requested[60000],
OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used[1000],
OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration[0],
OC-Reported-Used[0],
OC-Pending-Requested[0],
OC-Start-Time[1467865837000],
OC-End-Time[1467865838000]
]
],
OC-Call-Id(Ext,Ext)[cXD7xzRmA1w4iWBzT9XMdQ],
MMTel-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Supplementary-Service[
Service-Type[2]
],
Subscriber-Role[ORIGINATING(0)]
]
]
}
2016-07-07T16:30:43.991+1200 AvpCdr {
avps=[
Subscription-Id(Ro,vcb0)[
Subscription-Id-Type[2],
Subscription-Id-Data[tel:34600000002]
],
IMS-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Role-Of-Node[TERMINATING_ROLE(1)],
Node-Functionality[AS(6)],
User-Session-Id[AhzD75RR1S7WP1_BN88Ajg],
Session-Priority[PRIORITY_2(2)],
Calling-Party-Address[tel:34600000002],
Called-Party-Address[sip:conf-factory@localhost:5280],
Requested-Party-Address[sip:conf-factory@localhost:5060],
Time-Stamps[
SIP-Request-Timestamp[1467865835000],
SIP-Response-Timestamp[1467865835000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 2000 1000 IN IP4 10.4.1.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0],
Cause-Code[0],
Early-Media-Description[
SDP-TimeStamps[
SDP-Offer-Timestamp[1467865838000],
SDP-Answer-Timestamp[1467865838000]
],
SDP-Session-Description[v=0],
SDP-Session-Description[o=- 2000 1000 IN IP4 10.4.1.1],
SDP-Session-Description[s=test-session],
SDP-Session-Description[t=0 0]
]
],
Service-Context-Id(Ro,vcb0)[12.32274@3gpp.org],
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key(Ext,Ext)[DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:DefinitelyNotOpenCloud:sipcall:mmtel-conf:],
OC-Call-Type(Ext,Ext)[MTC(3)],
OC-Service-Type(Ext,Ext)[SipCall(2)],
OC-Charging-Result(Ext,Ext)[2001],
OC-OCS-Session-Id(Ext,Ext)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;1;daJvi_dNie_W_v-fzDOflg],
Session-Id(Ro,vcb0)[diameterclient;diameterro-0;1529370976;1;daJvi_dNie_W_v-fzDOflg],
OC-OCS-Session-Termination-Cause(Ext,Ext)[0],
OC-Sentinel-Error(Ext,Ext)[None(1)],
OC-Charging-Instance(Ext,Ext)[
OC-Charging-Instance-Name[scur_charging_instance],
OC-Session-Counter[
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Subscriber-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[tel:34600000002]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Service-Id],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[3]
],
OC-Session-Counter-Address[
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Key[Cc-Unit-Type],
OC-Session-Counter-Address-Value[Cc-Time]
],
OC-Cumulative-Committed-Used[8000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted[63000],
OC-Cumulative-Granted-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Requested[180000],
OC-Cumulative-Requested-Refund[0],
OC-Cumulative-Sent-Used[8000],
OC-Cumulative-Suspended-Duration[0],
OC-Reported-Used[0],
OC-Pending-Requested[0],
OC-Start-Time[1467865835000],
OC-End-Time[1467865843000]
]
],
OC-Call-Id(Ext,Ext)[daJvi_dNie_W_v-fzDOflg],
MMTel-Information(Ro,vcb0)[
Supplementary-Service[
Service-Type[10],
Associated-Party-Address[tel:34600000002],
Service-Id[mmtelconf101MpAdqRMBdip0aIpqObY1hQ],
Change-Time[1467865843000]
],
Subscriber-Role[TERMINATING(1)]
]
]
}
2016-07-07T16:30:45.057+1200 Footer {}
Logging output
The List CDRs tool writes its main output to the console, but it can be configured to write some extra debugging to a log file.
It uses the log4j logging library, and its log4j configuration file is located at sentinel-volte-sdk/list-cdrs/log4j.properties.
By default, it will log to sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/list-cdrs/logs/list-cdrs.log. It logs very little when using the default configuration — the log file will typically be empty unless configured for debug logging.
To enable debug logging, change the log level on the last line of the log4j.properties file to DEBUG:
log4j.logger.sentinel.cdr=DEBUG
Extension AVPs
Built-in AVPs and extension AVPs
The binary CDR format contains Diameter AVPs encoded in binary form, and the List CDRs tool decodes these binary AVPs before printing them in a human readable format.
The tool has built-in knowledge of AVPs which are defined in Diameter protocols such as Rf and Ro.
It can also be customized with knowledge of user defined extension AVPs, by providing definitions of those AVPs in YAML files.
The List CDRs tool looks in the list-cdrs/extension-avps directory for YAML based files which define these extension AVPs.
A default installation of the List CDRs tool contains a DiameterExtension-AVP.yaml file inside this directory, which defines OpenCloud’s extension AVPs. This means that by default, the List CDRs tool recognizes all the AVPs in the CDR files produced by Sentinel.
Known AVPs vs Undefined AVPs
When encountering an AVP which it does not recognize, the List CDRs tool treats it as an Undefined AVP. Because the tool can’t see which type of AVP it is (e.g. UTF8String or Integer32), it prints the raw binary content of the AVP in hexadecimal format.
This is how the List CDRs tool will print an extension AVP that it doesn’t recognize:
Undefined-AVP[code=1029,vendor=19808,hex=64 61 4a 76 69 5f 64 4e 69 65 5f 57 5f 76 2d 66 7a 44 4f 66 6c 67,ascii=daJvi_dNie_W_v-fzDOflg],
This is how the List CDRs tool prints that same extension AVP, when that AVP is configured as an extension AVP (see below):
OC-Call-Id[daJvi_dNie_W_v-fzDOflg],
Built-in extension AVPs
This is an excerpt from the default extension AVP configuration file at
list-cdrs/extension-avps/DiameterExtension-AVP.yaml, showing the first two extension AVPs:
$ cat extension-avps/DiameterExtension-AVP.yaml
!profiles
DiameterExtension-AVP:
id:
name: 'Diameter Extension AVP'
vendor: 'OpenCloud'
version: '2.7'
imports: null
profiles:
? ''
: AvpCode: 0
AvpName: null
AvpType: null
MandatoryRule: 1
ProtectedRule: 1
VendorId: 0
OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key:
AvpCode: 1001
AvpName: OC-Sentinel-Selection-Key
AvpType: UTF8String
MandatoryRule: 0
ProtectedRule: 0
VendorId: 19808
OC-Play-Announcement-Id:
AvpCode: 1002
AvpName: OC-Play-Announcement-Id
AvpType: Integer32
MandatoryRule: 0
ProtectedRule: 0
VendorId: 19808
[...]
Customisation of extension AVPs
To configure your own custom AVP, add a new file with the same opening structure as extension-avps/DiameterExtension-AVP.yaml, but with your own extensions.
| |
Be sure to use your own Vendor ID, which we’ll assume to be 19404 below for the sake of example. |
An example configuration file:
$ cat extension-avps/ACME-DiameterExtension-AVP.yaml
!profiles
DiameterExtension-AVP:
id:
name: 'Diameter Extension AVP'
vendor: 'OpenCloud'
version: '2.7'
imports: null
profiles:
? ''
: AvpCode: 0
AvpName: null
AvpType: null
MandatoryRule: 1
ProtectedRule: 1
VendorId: 0
ACME-My-First-Custom-Code:
AvpCode: 1000
AvpName: ACME-My-First-Custom-Code
AvpType: UTF8String
MandatoryRule: 0
ProtectedRule: 0
VendorId: 19404
ACME-My-Second-Custom-Code:
AvpCode: 1000
AvpName: ACME-My-Second-Custom-Code
AvpType: UTF8String
MandatoryRule: 0
ProtectedRule: 0
VendorId: 19404
[...]
After you have created such a file you will also have to add the AVP names to the Charging profile in the DiameterExtensions profile table, which lives in the file extension-avps/DiameterExtensions.yaml. The profile consists of an array that lists all of the desired AVPs in the format <profile table name>/<profile name>. So for the two AVPs from the example above you would have to add these two lines to the Charging profile:
- DiameterExtension-AVP/ACME-My-First-Custom-Code - DiameterExtension-AVP/ACME-My-Second-Custom-Code
Note that the profile to use for the supported extension AVP list is configured with the ExtensionAvpSet property of the Diameter RA. See Configuring Extension AVPs for the full documentation of these profile tables.
The required fields for each AVP:
- AvpCode
-
The code of the AVP. If using your own vendor code, then this AVP code is within your own namespace.
- AvpName
-
The name of the AVP.
- AvpType
-
The type of the AVP. See the available AVP types below.
- MandatoryRule
-
The "M" bit or Mandatory bit.
1if set,0if not set. Indicates whether support of the AVP is mandatory on the receiving end. - ProtectedRule
-
The "P" bit, indicating the need for encryption.
1if set,0if not set. - VendorId
-
The Vendor ID of the company which has defined this AVP.
- The available AVP types
-
-
OctetString -
Integer32 -
Integer64 -
Unsigned32 -
Unsigned64 -
Float32 -
Float64 -
Grouped -
Address -
Time -
UTF8String -
DiameterIdentity -
DiameterURI -
Enumerated -
IPFilterRule -
QoSFilterRule -
Undefined
-
Installing Protobuf
Protobuf 2.3.0 is required to build and extend CDR modules included with the SDK. The SDK infrastructure makes this version available for download from an Ant target.
| |
Protobuf 2.3.0 can be downloaded as a standalone package here. To complete installation, follow the instructions in the included README.txt. |
Installing Protobuf from the SDK using Ant
To install Protobuf use the install-protobuf Ant build target under the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools directory:
$ cd /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
$ ant install-protobuf
init-build-extensions:
[...]
init-tools-common:
install-protobuf:
[echo]
[echo] Retrieving Protobuf...
[mkdir] Created dir: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target
[get] Getting: https://s3-ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/ocaws-downloads/third-party/google/protobuf/protobuf-2.3.0.tar.gz
[get] To: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/protobuf-2.3.0.tar.gz
[get] ....................................................
[get] ....................................................
[get] ....................................................
[get] ....................................................
[get] .....
[echo]
[echo] Protobuf retrieved.
[echo]
[echo] Unpacking Protobuf...
[echo]
[gunzip] Expanding: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/protobuf-2.3.0.tar.gz to /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/protobuf-2.3.0.tar
[untar] Expanding: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/target/protobuf-2.3.0.tar into /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
[echo]
[echo]
[echo] Protobuf unpacked.
[echo] Requires further install steps, please read protobuf-2.3.0/README.txt for further details.
[echo]
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 6 seconds
| |
See Setting up Ant in the Sentinel VoLTE Public SDK guide. |
To complete installation, follow the instructions in sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/protobuf-2.3.0/README.txt.
Uninstalling Protobuf
If you want to uninstall the version of Protobuf installed by the SDK, use the uninstall-protobuf Ant target under the sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/ directory:
$ cd /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools
$ ant install-protobuf
init-build-extensions:
[...]
init-tools-common:
uninstall-protobuf:
[echo] Uninstalling (deleting) the protobuf install from: /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/protobuf-2.3.0/
[delete] Deleting directory /home/testuser/sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/protobuf-2.3.0
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 2 seconds
Alternatively, just delete the protobuf-2.3.0 directory:
$ rm -rf sentinel-volte-sdk/tools/protobuf-2.3.0/
XCAP Server
The XCAP Server is a software component that runs inside a web application called Rhino Element Manager (or REM for short).
It uses OpenCloud’s Diameter Sh stack to communicate with the HSS.
| |
For information on this piece of the Sentinel VoLTE product architecture, please see XCAP Support. |
Diameter Sh configuration
The Diameter Sh stack must be configured before running the XCAP server functioning. See Configuring Diameter Sh for the XCAP server and REM.
HTTP configuration
The XCAP Server runs inside an HTTP servlet container. To configure it, please see that container’s documentation.
XCAP simservs configuration
The XCAP simservs configuration defines how an XML simservs document (typically coming from a UE) is mapped into an MMTel services document (stored in transparent data in the HSS).
A tool is available that will populate XCAP server settings with MMTel service data mappings The rest of this section describes how to manually configure those same settings.
This configuration is defined using XPath:
1 |
Select Sentinel ▶ XCAP — Simservs. The resulting panel differs depending on whether a configuration has already been entered for the selected network operator.
|
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 |
For an existing configuration, to enter sufficient XCAP Simservs mappings for IR.92:
A popup prompts you to enter details. 
|
||||||||||||||||||
3 |
With the mapping group created, add mappings:
A prompt displays to enter the mapping. 
Enter these defaults:
|
XCAP simservs extensions mappings
The XCAP server also supports simservs extensions mappings. This allows arbitrary elements of any transparent user data XML document from the HSS to be mapped to an element in the simservs document under the extensions parent element.
Examples:
| Simservs Path | HSS Document Path |
|---|---|
extensions/operator-flexible-alerting |
complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting |
extensions/operator-flexible-alerting-group |
complete-flexible-alerting/operator-flexible-alerting-group |
In these examples, select parts of operator data from the MMTel services document are being exposed to the UE for viewing and updating via XCAP as part of the Simservs document. Each can be specifically accessed via the simservs XCAP URL with the node selector specified as per the simservs path in the mapping.
Rules for creating extensions mappings
-
An extension simservs path must start with
extensions/. -
The element name after
extensions/can be any alphanumeric string. Special characters are not allowed. -
The element name must be singular. e.g.
extensions/path1is ok, butextensions/path1/path2is not. -
The HSS document path has to match an actual location in the HSS data.
-
Only simple element names can be used for the HSS Document Path. i.e. no positional or attribute selectors.
| |
Extensions mappings have to be created in the MMTEL-Services Mapping Group, alongside the standard MMTel mappings. |
XCAP host mappings
The XCAP server may be configured to function on behalf of multiple network operators, by using host mappings. Host mappings take the ‘host’ part of an HTTP URI (in other words, XCAP query URI) and treat it as a key.
This key then identifies the:
-
Rhino cluster in REM to communicate with
-
the Sentinel network operator to use for XCAP queries.
The Sentinel network operator determines various key AVPs that are required when communicating via the diameter Sh interface.
| |
For more information see: |
To navigate and view XCAP host mappings:
1 |
In REM, select Sentinel ▶ XCAP. 
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
To view a mapping in more detail, select it in the panel at left. The example shows a single host mapping, for 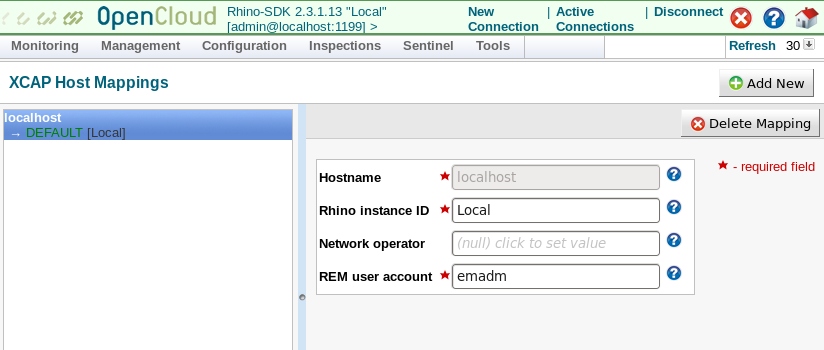
|
XCAP authentication
In the absence of an Authentication Proxy (AP), the XCAP server can be configured to authenticate requests itself using OpenCloud Sentinel AGW. Sentinel AGW provides an implementation of 3GPP GAA (Generic Authentication Architecture) procedures.
For more information, and instructions on configuring the XCAP Server with Sentinel AGW, see the Sentinel AGW Guide.
Example XCAP query
The following XCAP query requests subscriber configuration data for incoming-communication-barring.
The subscriber in question is identified by the IMS public identity sip:user222222@home1.net.
http://localhost:8090/rem/sentinel/xcap/simservs.ngn.etsi.org/users/sip:user222222@home1.net/simservs/~~/incoming-communication-barring
In this example query, the host part of the URI is localhost. The XCAP server will look for a configuration keyed on the host value (localhost).
Sentinel VoLTE Manual Upgrade Procedure
This page describes how to manually upgrade a Sentinel VoLTE 2.7.0.x install to a newer version of 2.7.0.x. This procedure includes saving the configuration from your running system, installing a new version, and then applying the configuration from the old install to the new install. Generally you can just use the sentinel-volte-sdk installer to install a new version. However if you have bespoke post-install configuration in your current Sentinel VoLTE install that you want to retain, you can follow these instructions.
| |
This manual procedure is no longer the recommended way to upgrade VoLTE in production. Use the semi-automated VoLTE upgrade procedure instead. However, this manual procedure still applies when using the Rhino SDK. |
| |
This page does not cover upgrading between major releases, e.g. 2.6.x to 2.7.0.x. |
| |
This upgrade procedure should not be used in conjunction with changes to your installer choices, e.g. changing from HSS to HLR. A fresh install is required if you wish to change your network components. |
| |
It may be necessary to increase the Rhino Management Tools default memory settings in order to successfully export and import profiles. See Rhino Management Tools Memory Considerations for more details. |
-
Rhino Production — Use these instructions if you are using a Rhino Production Cluster.
-
Rhino SDK — Use these instructions if you are using the Rhino SDK.
Rhino Production
Manual Upgrade of a Sentinel VoLTE 2.7.0 install in a Rhino Production Cluster
| |
This manual procedure is no longer the recommended way to upgrade VoLTE in production. Use the semi-automated VoLTE upgrade procedure instead. |
| |
This document assumes a 2 node cluster, with each node on a separate server. Modify the steps accordingly if you have more nodes. |
Upgrade Steps
1 |
From the Rhino client bin directory |
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
Run a Rhino full export |
||
3 |
On the node101 server, stop Rhino |
||
4 |
On the node102 server, stop Rhino |
||
5 |
Stop REM from the init-d directory (if you followed these post install Instructions otherwise you can stop Catalina. |
||
6 |
Backup your Apache Tomcat install to a new location |
||
7 |
If you have configured REM redundancy, repeat steps 5 and 6 on each node where you have Apache Tomcat REM installed |
||
8 |
On the node101 server, backup the node101 directory to a new location |
||
9 |
On the node101 server, recreate node101 (say yes to initializing the db) |
||
10 |
Copy any configuration settings that you changed during your initial install from your old node101 directory to your new node101 directory. e.g. jvm settings, paths, ports etc. |
||
11 |
Start node101 |
||
12 |
On the node102 server, backup the node102 directory to a new location |
||
13 |
On the node102 server, recreate node102 (say yes to initializing the db) |
||
14 |
Copy any configuration settings that you changed during your initial install from your old node102 directory to your new node102 directory. e.g. jvm settings, paths, ports etc. |
||
15 |
Start node102 |
||
16 |
Install your license into Rhino |
||
17 |
Install the new Sentinel VoLTE version and REM extension as per these instructions:
|
||
18 |
Import the exported profiles into Rhino |
||
19 |
Restart Rhino nodes and REM |
Rhino SDK
Manual Upgrade of a Sentinel VoLTE 2.7.0 install in a Rhino SDK
Upgrade Steps
1 |
From the Rhino SDK client bin directory |
|---|---|
2 |
Run a Rhino full export. For more information see Rhino Administration Guide - Export and Import. |
3 |
Stop Rhino |
4 |
Stop REM from the init-d directory (if you followed these post install Instructions otherwise you can stop catalina. |
5 |
From the Rhino install directory move the Rhino SDK directory to a new location |
6 |
From the Rhino install directory unzip the Rhino SDK install zip |
7 |
Install the new Sentinel VoLTE version and REM extension as per these instructions:
|
8 |
Start Rhino |
9 |
From the Rhino client bin directory |
10 |
Copy the backup directory (export) created as part of the export step (step 2) to the new Rhino SDK install |
11 |
Import the exported profiles into the Rhino SDK environment. For more information see Rhino Administration Guide - Export and Import. |
12 |
Restart Rhino and REM |
DNS Redundancy
This page provides notes and guidance regarding DNS redundancy for a Sentinel VoLTE TAS cluster.
Background SIP Routing mechanism
The AS URI defined within a subscriber’s iFC is targeted by the S-CSCF using DNS procedures defined by RFC 3263 which can be summarised as follows:
-
Determine a transport protocol (NAPTR query)
-
Find a server port on a hostname (SRV query)
-
Find an IP Address (A-Record query)
Step 2 is relevant here. The structure of a SRV record is:
_Service._Proto.Name TTL Class SRV Priority Weight Port TargetRFC 2782 provides more detail.
The information element of particular interest is the "Priority". Multiple results are sorted in priority order and when communication toward one fails the next is chosen. RFCs 2782 and 3263 provide details.
Additionally, the response received to an SRV query can be determined by the source IP Address using DNS "views" functionality which enables co-ordinated preference routing between IMS sites.
DNS names for each node
| Node name | DNS Name | Rhino node ID | Savanna Cluster ID |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VoLTE-1 |
node1.site1.domain.com |
101 |
1 |
|
VoLTE-2 |
node2.site1.domain.com |
102 |
1 |
|
VoLTE-3 |
node3.site1.domain.com |
103 |
1 |
|
VoLTE-4 |
node4.site1.domain.com |
104 |
1 |
How DNS SRV is configured
At least 4 different SRV lookups, because there are 4 nodes (for load sharing purposes).
At minimum for a 4 node cluster in a site, you need
SRV Query 1:
_sip._tcp.volte1.domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 2:
_sip._tcp.volte2.domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 3:
_sip._tcp.volte3.domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 4:
_sip._tcp.volte4.domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060It is desirable to have more SRV queries than you have nodes. This is so that you can have a big pool and the ability to add new nodes into the site without changing the URIs configured in iFCs.
AS URI and iFC configuration/provisioning
There are at least four AS URIs, as there are four nodes.
At minimum you need these AS URIs:
sip:volte1.domain.com;transport=tcp
sip:volte2.domain.com;transport=tcp
sip:volte3.domain.com;transport=tcp
sip:volte4.domain.com;transport=tcpThere are therefore four different AS’s configured in the HSS. Each one has one of these URIs.
25% of subscribers use an iFC that has volte1 as the URI, 25% have volte2, and so-on.
This subscriber → iFC mapping is done during provisioning.
Over provisioning for later flexibility
It makes sense to over provision the number of AS URIs and number of SRV records. This is so that there is flexibility to change the SRV DNS lookups without changing the provision of subscriber → iFC provisioned in the HSS.
I.e. have AS URIs of volte[1-100].domain.com;transport=tcp
Then have SRV queries set up like this, assuming 4 nodes in a site. Later on if you need 6 nodes in a site you have more groups of SRV queries.
SRV Query 1 to include over provisioning:
_sip._tcp.volte[001-025].domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 2 becomes:
_sip._tcp.volte[026-050].domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 3 becomes:
_sip._tcp.volte[051-075].domain.comSRV response:
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060SRV Query 4 becomes:
_sip._tcp.volte[076-100].domain.com
SRV response:_sip._tcp.node4.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 0 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node1.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 10 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node2.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 20 0 5060
_sip._tcp.node3.site1.domain.com 3600 IN SRV 30 0 5060DNS failover configuration
The SIS product within the VoLTE TAS handles the configuration of the DNS failover method. Refer to this page in the SIS documentation for details.
Feature Source
Source code is available for all of Sentinel VoLTE’s MMTel features and most of its general features. Source for some of the "base" Sentinel features is also provided. The code can be viewed by using the create-module command in the SDK to create a new module from the module pack that contains the feature. For more information on creating a feature, refer to Creating a Feature.
Features with Source Available
The following tables list the features that have source code available through the SDK, and the name of module packs that contain their source.
General VoLTE Features
| Feature | Module Pack |
|---|---|
volte-hlr-subscriber-data-lookup |
|
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup-2 |
|
volte-hss-subscriber-data-lookup |
|
volte-imsid-lookup |
|
volte-imsid-lookup-cassandra |
|
volte-avp-cdr-feature |
|
volte-interim-cdr |
MMTel Features
| Feature | Module Pack |
|---|---|
mmtel-conferencing |
|
mmtel-conferencing |
|
volte-determine-international-and-roaming-status |
|
mmtel-communication-diversion |
|
mmtel-communication-waiting |
|
mmtel-explicit-communication-transfer |
|
mmtel-communication-hold |
|
mmtel-communication-barring |
|
mmtel-communication-barring |
|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
|
mmtel-id-presentation-restriction |
|
mmtel-flexible-alerting |
|
mmtel-wifi-charging-finalisation |
|
mmtel-session-transfer |
|
mmtel-geo-local-normalization |
Base Sentinel Features
| Feature | Module Pack |
|---|---|
sentinel-core-do-not-monitor-session-feature |
|
OCS Round Robin |
sentinel-core-ocs-round-robin-feature |
sentinel-core-platform-operator-is-network-operator-feature |
|
sentinel-core-session-tracing-feature |
|
sentinel-core-subscriber-data-lookup-feature |
|
sentinel-sip-determine-network-operator-feature |
|
sentinel-sip-avp-cdr-feature and sentinel-sip-avp-cdr-util |
|
sentinel-sip-interim-cdr |
Resource Adaptors
In Rhino, a Resource Adaptor (RA) provides the interface between the application (Sentinel VoLTE) and the network. Sentinel VoLTE makes use of a number of Resource Adaptors, for purposes ranging from database connections to network integration.
OpenCloud Resource Adaptors used by Sentinel VoLTE
Sentinel VoLTE configures the following Resource Adaptor Entities out of the box.
| Resource Adaptor Entity | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
cassandra-cql-ra |
communication with the Cassandra Database |
|
cassandra-third-party-reg |
communication with the Cassandra Database for Third Party Registrar |
|
cassandra-external-session-tracking |
communication with the Cassandra Database for External Session Tracking |
|
cdr |
writing of call detail records (or 3GPP Charging Data Records) |
|
cginmapra |
querying the HLR (optional, depending on installation choices) |
|
dbquery-0 |
communication with an SQL Database |
|
diameter-sentinel-internal |
internal Ro communication between protocol handling front-ends and the internal mediation subsystem |
|
diameterro-0 |
communication with Online Charging Systems |
|
http |
enabling queries to external systems (such as RESTful queries), or enabling |
|
reorigination-correlation-ra |
|
|
sentinel-management |
management of Sentinel subsystems |
|
sh-cache-ra |
communication with the HSS |
|
sip-sis-ra |
SIP interface for the TAS |
|
sipra |
utility mechanisms for the SIP protocol |
|
uid |
allocation of globally unique IDs |
| |
All these RAs can be viewed and configured using the Sentinel Element Manager. Future releases of Sentinel will have resource adaptors to support other protocols, such as Diameter CCA. Customers can also add their own resource adaptors, using the Sentinel VoLTE Public SDK. |
CDR Resource Adaptor
CDR resource adaptor entities
The Sentinel installer creates a CDR resource adaptor entity called cdr. This resource adaptor entity is used by all Sentinel services.
CDR resource adaptor configuration
| |
Refer to the CDR RA Documentation for more information about the CDR RA. |
The cdr resource adaptor entity is configured to use the cdr-stream profile of the CdrStreamConfiguration profile table by default.
The output behaviour of the CDR resource adaptor can be customised by modifying this profile in accordance with the CDR RA Documentation.
Sentinel configuration requirements
The cdr RA entity must be configured with CdrFileType=Binary.
For more information about CDRs in the Sentinel platform, refer to:
-
Working with CDRs section of this administration guide to learn about the content of Sentinel CDRs.
-
Customising CDRs in the Extending Sentinel with the SDK guide to learn how to customise the format of the CDRs that Sentinel creates, as well as customising the data included in the CDRs.
Correlation Resource Adaptor
Correlation RA Overview
What is the Correlation RA?
The Correlation RA provides a mechanism to correlate two otherwise independent sessions. The correlation data is replicated across the Rhino cluster. All nodes in the cluster have access to read/write correlation data.
This is used in the SCC-AS as part of IMS Service Centralisation via CAMEL triggers.
Below are procedures for [configuration], [monitoring], and [using].
Configuring a Correlation RA entity
A Correlation RA entity configuration consists of:
The following diagram shows the Reorigination Correlation RA entity.

| |
The Correlation resource adaptor supports live re-configuration, so the administrator may update the configuration properties of a Correlation resource adaptor entity that has already been created. |
Correlation RA configuration properties
The Correlation RA configuration properties are:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
String |
The SLEE profile table with an RA configuration profile for this RA entity. |
|
String |
The SLEE profile in the ConfigProfileTable with configuration for this RA entity. |
|
String |
The SLEE profile table with correlation ID pool definitions for this Correlation RA entity. |
For example, the Reorigination Correlation RA entity has the following configuration:
[Rhino@localhost (#9)] listraentityconfigproperties reorigination-correlation-ra Configuration properties for resource adaptor entity reorigination-correlation-ra: ConfigProfile (java.lang.String): ReoriginationCorrelationConfigProfile ConfigProfileTable (java.lang.String): CorrelationConfigTable CorrelationIdPoolTable (java.lang.String): ReoriginationCorrelationIdPools
Correlation RA entity configuration profile
The Correlation RA configuration profile has the following attributes:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Int |
The maximum time (measured in ms) the Correlation RA will spend trying to allocate a correlation ID. |
|
Int |
The maximum time (measured in ms) that an active correlation ID is considered to be still valid. |
|
Int |
How many threads the Correlation RA entity should use. |
For example, the Reorigination Correlation RA entity has the following configuration:
[Rhino@localhost (#8)] listprofileattributes CorrelationConfigTable ReoriginationCorrelationConfigProfile CorrelationIDExpiryTimerPeriod=55000 NumberOfThreadPool=5 RequestTimeout=5000
Correlation RA entity ID pools configuration
Each Correlation RA entity has one or more correlation ID pools.
-
a default ID pool (optional)
-
a set of named ID pools. Each named ID pool is identified by a set of prefixes for choosing/selecting the ID pool. From the Correlation RA standpoint, the prefixes can be any address string. The client to the RA provides an address that the RA uses via a longestPrefix match address list search to select the pool to use.
Each correlation ID pool is defined in a SLEE profile in an ID pools profile table. There is one correlation ID pools table per Correlation RA entity.
| |
The correlation resource adaptor entity will raise an alarm if there are no correlation ID pools configured, or if there are configuration errors with the correlation ID pools. |
|
An array of address prefixes that corresponds to this pool. The default pool has an empty addressPrefixes array. |
|
An array of node IDs for which this pool has correlation IDs. |
|
If true, configure this ID pool with a pre-configured set of correlation IDs, else derive the correlation IDs. |
|
The preconfigured set of correlation IDs per node (delimited with ‘:’). |
|
The minimum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to maxCorrelationIDInCluster |
|
The maximum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to (10^18-1) |
|
The number of digits the correlation ID should have. Minimum of number of digits in maxCorrelationIDInCluster to 18 maximum. |
|
The number of correlation IDs that can be used for each node in the cluster. |
There are two possible configuration options for correlation ID pools.
A prescribed set of IDs for each node
Defines the prescribed correlation IDs for each node in the following way:
-
NodeIds[0]—PreconfiguredCorrelationIdSet[0]which is a ‘:’ separated string containing all the correlation IDs forNodeIds[0] -
NodeIds[1]—PreconfiguredCorrelationIdSet[1]which is a ‘:’ separated string containing all the correlation IDs forNodeIds[1] -
etc.
A range of correlation IDs (min, max) for each node
Defines the range of values used in each node in conjunction with the NodeIds attribute in the following way:
-
The node whose identifier is
NodeIds[i]has a range of values ofCorrelationIDRangePerNode[i] -
Each cluster has a range of CorrelationIDs defined by:
[MinCorrelationIDInCluster, MaxCorrelationIDInCluster]
These values are allocated to the different cluster nodes in the following way:
-
NodeIds[0]—[MinCorrelationIDInCluster … MinCorrelationIDInCluster + CorrelationIDRangePerNode[0]] -
NodeIds[1]—[MinCorrelationIDInCluster + CorrelationIDRangePerNode[0] + 1 … MinCorrelationIDInCluster + +CorrelationIDRangePerNode[0] + 1 + CorrelationIDRangePerNode[1]] -
etc.
The maximum number of correlation IDs defined in the range is 1,000,000.
Provisioning Interfaces
The Correlation RA configuration and ID pools are provisioned using the Sentinel REST API or web interface.
Monitoring Correlation RA entity statistics
Each Correlation RA entity collects the following statistics that may be monitored via the Rhino statistics client.
Counters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Count of correlation IDs which have been requested via |
|
Count of correlation queries which returned immediately (synchronous delivery) as the local RA had the data available. |
|
Count of correlation queries which did not return immediately (asynchronous delivery) as the local RA did not have the data available. |
|
Count of correlation queries which required delivering data to another correlation RA instance. |
|
Count of correlation queries which could not be remotely delivered as the destination RA for a correlation ID was unknown. |
| |
The count correlationGets should equal the sum of localGets + remoteGets. |
These statistics can use used to create threshold-based alarms.
Using the Correlation RA
A feature uses the Correlation RA by invoking methods on the provider interface.
-
To store data for correlation, a feature calls either the
getNewCorrelationID(byte[] correlationData)or thegetNewCorrelationID(String associatedAddress, byte[] correlationData)method on theCorrelationProvider. These methods will store the correlation data locally, and return an identifier String (the correlation ID) which can later be used to access the data from elsewhere. This operation will flag the returned ID as ‘in use’ until it is freed (on query) or expires (on timeout). -
To query the correlation data (for example, from another session) a feature calls the
getCorrelationData(String correlationId)method on theCorrelationProvider. This returns aCorrelationResultwhich will either contain the requested data (if it is available locally), or a flag indicating that the data is not available locally. -
If the data is available locally then it can be immediately access via the [synchronous] API call CorrelationResult.getCorrelationData()
-
If the data is only available for asynchronous delivery,
CorrelationResult.isAvailableAsynchronously()will be true, andCorrelationResult.getCorrelationData()will return null. See the following section for how to handle [asynchronous] result delivery.
CorrelationProvider interface:
public interface CorrelationProvider {
/**
* Creates an activity used for async requests.
*
* @return
* @throws StartActivityException
*/
public CorrelationActivity createActivity() throws StartActivityException;
/**
* This returns immediately and will return a CorrelationResult. This will either contain the correlation data if this is available on
* this node or else will contain a flag that says this is only available on another node. In the later case you should then call an
* async request to get the data.
*
* @param correlationId the Correlation ID
* @return the CorrelationResult
* @throws UnknownCorrelationIdException if the correlation id is not known in this pool
* @throws NoDataFoundException if there is no data found for the correlation id specified
* @throws CorrelationIDExpiredException if the correlation id has expired
*/
public CorrelationResult getCorrelationData(String correlationId) throws UnknownCorrelationIdException, NoDataFoundException, CorrelationIDExpiredException;
/**
* This will return the CorrelationResult. This method will block and only return when the CorrelationResult is available. If the data is only
* available on a remote node this may take some time to return. This should only be used if synchronous behavior is required.
*
* @param correlationId
* @return
* @throws CorrelationRequestException
*/
public CorrelationResult getCorrelationDataSynchronously(String correlationId) throws CorrelationRequestException;
/**
* Request a new Correlation ID from the default pool
*
* @param correlationData data to be correlated
* @return a new Correlation ID with a correlation name that is not being used in any other session
* @throws NoAvailableEntries if there is any problem accessing data
*/
public String getNewCorrelationID(byte[] correlationData) throws NoAvailableEntriesException;
/**
* Request a new Correlation ID String from a correlation id pool associated with an address.
*
* @param associatedAddress an address that the correlation RA will use to select a pool from which to return a correlation id
* @param correlationData data to be correlated
* @return a new Correlation ID String with a correlation name that is not being used in any other session
* @throws NoAvailableEntries if there is any problem accessing data
*/
public String getNewCorrelationID(String associatedAddress, byte[] correlationData) throws NoAvailableEntriesException;
/**
* Determine if an id is a correlation id we know about
* @param possibleCorrelationId an id we wish to check to see if it is a correlation id
* @return true iff this id is a correlation id we know about
*/
public boolean isValidCorrelationId(String possibleCorrelationId);
}
CorrelationResult interface:
public interface CorrelationResult {
/**
* Contains correlation data associated with the requested correlation ID or null if the
* data is only available asynchronously.
*
* @return
*/
public byte[] getCorrelationData();
/**
* String containing requested correlation ID.
*
* @return the String containing the Correlation ID
*/
public String getCorrelationId();
/**
* If the correlation data is not available locally but is available via an asynchronous call.
*
* An asynchronous call can be made by creating a CorrelationActivity with the provider and then making
* the asynchronous call on the CorrelationActivity.
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isAvailableAsynchronously();
}
CorrelationActivity interface:
public interface CorrelationActivity {
/**
* Request the correlation data associated with the specified Correlation ID.
*
* The result will be fired as a {@link CorrelationResultEvent}
* event on this activity. Failed queries will be fired as a {@link CorrelationFailureEvent}.
*
* @param correlationId The Correlation ID
*/
public void requestCorrelationData(String correlationId);
}
Handling synchronous results
Synchronous queries occur when the RA which is queried is also storing the queried information. In these circumstances, the data is included in the returned CorrelationResult from a query. The following example demonstrates how to handle synchronous return results:
private void syncRequest(byte [] correlationData) {
//
// Store some data against a new correlation ID.
//
String correlationId;
try {
correlationId = corrProvider.getNewCorrelationID(correlationData);
} catch (NoAvailableEntriesException e) {
// ... handle exception ...
return;
}
// ... do work until correlation data is required again.
// In practice, the following will usually be done in another transaction which only knows the correlation ID.
// It is done inline here for the sake of simplicity.
//
// Query the saved correlation data.
//
try {
CorrelationResult result = corrProvider.getCorrelationData(correlationId);
byte [] corrData = result.getCorrelationData();
if (corrData != null) {
// Do something with data
} else {
if (result.isAvailableAsynchronously()) {
// ... Here we could optionally proceed with an asynchronous correlation data query. See following example.
}
}
} catch (UnknownCorrelationIdException e) {
// ... handle exception ...
return;
} catch (NoDataFoundException e) {
// ... handle exception ...
return;
} catch (CorrelationIDExpiredException e) {
// ... handle exception ...
return;
}
}
Handling asynchronous results
Asynchronous result handling is required when the correlated data for the requested ID is only available from a non-local Correlation RA (that is, on a different Rhino node). After the correlation data is requested, the result is returned in a CorrelationEvent which is delivered to the service. This CorrelationEvents must be explicitly handled with a SLEE event handler.
Requesting correlation data asynchronously is done as follows:
-
Create a new correlation activity using
CorrelationProvider.createActivity() -
Get an
ActivityContextInterfaceobject for the activity. -
Attach the SBB local object to the ACI.
-
Send the request using the
requestCorrelationData(String)method on the activity. -
Handle the result in an event handler for the
com.opencloud.slee.resources.correlation.CorrelationResultEventevent. -
Handle failures in an event handler for the
com.opencloud.slee.resources.correlation.CorrelationFailureEventevent.
The follow example demonstrates the handling an asynchronous correlation query:
private void asyncRequest(String correlationId) {
try {
CorrelationActivity corrActivity = corrProvider.createActivity();
ActivityContextInterface corrAci = corrACIFactory.getActivityContextInterface(corrActivity);
corrAci.attach(getSbbLocalObject());
corrActivity.requestCorrelationData(correlationId);
}
catch (StartActivityException e) {
// ... handle exception ...
}
}
public void onCorrelationResult(CorrelationResultEvent result, ActivityContextInterface aci) {
aci.detach(getSbbLocalObject());
byte [] corrData = result.getCorrelationData()
// ... do something with the data ...
}
public void onCorrelationFailure(CorrelationFailureEvent failure, ActivityContextInterface aci) {
aci.detach(getSbbLocalObject());
// ... handle failure ...
}
Javadoc API
Javadoc for the Correlation RA is available here: Sentinel Correlation RA API 1.0.
Diameter Resource Adaptor
Diameter resource adaptors
There are currently 2 Diameter Ro Resource Adaptor Entities in Sentinel VoLTE:
-
diameterro-0— for OCS connections -
diameter-sentinel-internal— used as a message factory by mappers in Sentinel’s Diameter mediation layer.
diameterro-0 and diameter-sentinel-internal are used by all Sentinel services.
Session timeouts
The default Sentinel configuration has a 10 minute timeout for diameterro-1 (client) and 13 minute timeout for diameterro-0 (OCS). This configuration ensures that if there are events dropped due to overload, the ActivityEndEvents fired on the RA entities will cause the client side to end first. The 3 minute gap is set to allow time for all the ActivityEndEvents on the client side to be delivered before any are fired on the OCS side due.
Diameter version configuration
The Diameter version spoken on the network to either the OCS or the Diameter client can be configured by setting two properties in the relevant resource adaptor. To change the version used in the OCS dialog, diameterro-0 should be reconfigured. Likewise, to change the version used on the client dialog (Sentinel Diameter only), diameterro-1 should be reconfigured. The Diameter version used by diameter-sentinel-internal should not be reconfigured, as it is tied to the internal implementation of Sentinel.
When reconfiguring the Diameter version of either of the external resource adaptors, two fields must be set - Slee3GPPVersion and 3GPPVersion. Slee3GPPVersion should always be set to Vcb0. This is the version of Diameter used by Sentinel internally. 3GPPVersion can be set to the desired protocol version to be used over the network, ranging from V820 to Vcb0.
Alternatively, the Diameter version spoken to the OCS can be set during installation.
OCS load balancing
Load balancing of OCS connections can be achieved using the diameterro-0 resource adaptor entity, by configuring multiple hosts within a realm and addressing messages to the realm only (not the host).
Example configuration for OCS load balancing
This example shows the diameterro-0 resource adaptor entity configured to load balance across two OCS nodes.
-
The resource adaptor entity config properties show that it is configured using a profile in the
DiameterConfigtable. -
The config profile shows that the known OCS nodes are named
diameterserveranddiameterserver1. -
The routing priority metric for both nodes is set to 1 to indicate equal priority, meaning that load balancing will be applied.
-
The
DiameterMediationOcsConfigurationTableconfiguration profile at platform scope does not specify a host, so all outbound Diameter messages will not have the destination host set, but only the realm. This means the resource adaptor entity will round robin among all the hosts configured for the specified realm (in this caseopencloud). However this behaviour can be overridden on a per-session basis by setting theOCSIdfield in session state using, for example,SubscriberDataLookupor a custom feature added with the SDK.
The following rhino-console session shows the complete configuration:
[Rhino@localhost (#0)] listraentityconfigproperties diameterro-0
Configuration properties for resource adaptor entity diameterro-0:
3GPPVersion (java.lang.String): Vcb0
BaseMessageApplicationID (java.lang.Integer): 0
CertificateKeyStore (java.lang.String):
CertificateKeyStorePassword (java.lang.String):
CipherSuites (java.lang.String):
ConfigurationProfile (java.lang.String): DiameterConfig/DiameterRoOcsProfile
ConfigurationProfilePollTime (java.lang.Integer): 0
ConnectTimeout (java.lang.Long): 30000
ExtendedTransportConfiguration (java.lang.String):
ExtensionAvpSet (java.lang.String): DiameterExtensions/Charging
ExtensionAvpSetPollTime (java.lang.Integer): 0
ExtensionMessages (java.lang.Boolean): true
FireToServiceID (java.lang.String):
ForceReconnectAfterDPR (java.lang.Boolean): true
IOClientWorkers (java.lang.Integer): 0
IOServerWorkers (java.lang.Integer): 0
Quirks (java.lang.String):
ReconnectDelay (java.lang.Long): 5000
RequestTimeout (java.lang.Long): 2000
SSLSessionTimeout (java.lang.Integer): 0
ServiceContextId (java.lang.String): session@opencloud.com
SessionTimeout (java.lang.Long): 780000
SupportedVendorIds (java.lang.String):
ThreadPoolSize (java.lang.Integer): 0
TrustKeyStore (java.lang.String):
TrustKeyStorePassword (java.lang.String):
WatchdogTimeout (java.lang.Long): 30000
WorkQueueSize (java.lang.Integer): 0
slee-vendor:com.opencloud.rhino_max_activities (java.lang.Integer): 0
slee-vendor:com.opencloud.rhino_replicate_activities (java.lang.String): none
[Rhino@localhost (#1)] listprofileattributes DiameterConfig DiameterRoOcsProfile
Action=LOCAL
AllowUnknownPeers=true
ApplicationId=0
ApplicationVendorId=0
EnableMultiNodeConfig=false
Host=diameterclient
ListenAddress={null}
NodeIDs={null}
PeerAddress=127.0.0.1
PeerConnectAtStartup=true
PeerHost=diameterserver
PeerPort=3868
PeerTable=<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!DOCTYPE peer-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Peer Table Configuration 1.0.1//EN" "http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-peer-table-1.0.1.dtd">
<peer-table allowUnknownPeers="true">
<!-- If allowUnknownPeers is true, then any peer may connect to this node.
If allowUnknownPeers is not true, peers connecting to this node as clients must be defined in the Peer Table.-->
<peer connectAtStartup="true">
<hostname>diameterserver</hostname> <!-- Will accept connections from this peer -->
<port>3868</port>
<address>127.0.0.1</address>
<tls>false</tls>
<tcp-no-delay>true</tcp-no-delay>
</peer>
</peer-table>
PeerUri={null}
PerNodeHosts={null}
PerNodeListenAddresses={null}
PerNodePorts={null}
PerNodeSecondaryAddresses={null}
Port=3869
Product=OpenCloud Diameter
ProductVendorId=19808
Realm=opencloud
RealmTable=<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE realm-table PUBLIC "-//Open Cloud Ltd.//DTD Diameter Realm Table Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://www.opencloud.com/dtd/diameter-realm-table-1.0.dtd">
<realm-table>
<realm>
<realm-name>opencloud</realm-name>
<application-route>
<application>
<application-id>4</application-id> <!-- 4=CCA -->
<vendor-id>0</vendor-id> <!-- optional, default is zero -->
</application>
<action>LOCAL</action>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>diameterserver</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</application-route>
</realm>
<default-route>
<peer-ref>
<hostname>diameterserver</hostname>
<metric>1</metric>
</peer-ref>
</default-route>
</realm-table>
SecondaryAddresses={null}
Transports=tcp
UseTLS=false
ValidDN={null}
Version=1
[Rhino@localhost (#2)] listprofileattributes DiameterMediationOcsConfigurationTable UNSET::::
DestinationHost={null}
DestinationRealm=opencloud
TimeoutDuration=2000
HLR CGIN MAP Configuration
Sentinel VoLTE uses the CGIN RA for all of its interactions with an HLR over the MAP protocol.
MAP usage
Within Sentinel VoLTE, the main users of MAP and the HLR are:
-
FetchMSRN features --- Used to retrieve a subscriber’s MSRN from the HLR via a Send Routing Info request.
-
SubscriberDataLookupFromHLR --- Used to retrieve supplementary service data used for applying MMTel services from the HLR via a Any Time Subscription Interrogation request.
Configuration
Configuration for HLR communication is done via the HLRConfigProfileTable. This profile has the following fields:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
HLRSccpAddress |
String encoding an SCCP Address |
SCCP Address of the HLR, used when establishing the MAP dialog. Treated as a template when |
SentinelSCCPAddress |
String encoding an SCCP Address |
SCCP Address of Sentinel, used when establishing the MAP dialog. |
SentinelSCCPMscEndpointAddress |
String encoding an SCCP Address |
SCCP Address of Sentinel when Sentinel is acting as an MSC, used when establishing the MAP dialog. Will default to the value of SentinelSccpAddress if unset. Typically used to set a different originating SSN when sending a SendRoutingInformation message to the HLR. |
SentinelAddressString |
String encoding an Address String |
Address of Sentinel included in MAP requests. |
HLRInvokeTimeout |
Long representing milliseconds |
The timeout for waiting the HLR response. Used in the TCAP layer for the invoke timeout. |
CallReferenceNumberSystemConstant |
int between 0 and 65535 |
A constant value used during the construction of the Call Reference Number |
UseMsisdnAsHlrAddress |
Boolean |
Controls whether to address the outbound HLR leg using a GT address formed by adding the subscriber MSISDN digits to the |
SCCP Address Format
The configuration profile includes two SCCP addresses encoded in strings. Broadly speaking SCCP addresses come in two forms:
-
Point-Code Subsystem Number (PC-SSN)
-
Global Title Number (GT)
The string encoded format for an SCCP address takes the form of a comma separated series of key/value pairs. The exact set of valid keys varies between the two forms of SCCP address, and are outlined below.
Shared Key/Value Pairs
These keys are required in all SCCP Addresses.
| Key | Description | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
|
SCCP Address Type |
|
|
Routing Indicator |
|
PC-SSN Specific Key/Value Pairs
These keys are required only in Point-Code Subsystem Number SCCP Addresses.
| Key | Description | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Point Code |
Multiple formats (see below) |
|
Subsystem Number |
a number in the range 0-255 |
Point Code Formats Point codes can take the form of:
-
A single decimal value in the range 0-16777215, which supports all addressing formats up to 24-bits long expressed as a single number.
-
A '/' separated triple:
-
If
type=C7has been specified, an x/y/z triple is taken to mean the 3/8/3 bit fields of the zone/area/signal point address format. -
If
type=A7ortype=CH7, an x/y/z triple is taken to mean the 8/8/8 bit fields of the member/cluster/network address format.
-
Examples of a valid Point-Code SCCP Address
-
type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=4012,ssn=123 -
type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=1/245/7,ssn=123
GT Specific Key/Value Pairs
These keys are used only in Global Title SCCP Addresses. Of these keys, it is only mandatory to include digits in the encoded string.
| Key | Description | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Address digits |
Any digits string |
|
Address nature |
|
|
Address numbering plan |
|
|
Translation type |
a number in the range 0-255 |
|
National Indicator |
|
|
Global Tile Indicator |
This value is automatically determined any may be omitted. |
Examples of a valid GT SCCP Address
-
type=C7,ri=gt,digits=34607012345,nature=international,national=true -
type=C7,ri=gt,digits=654444444,nature=international,numbering=isdn,tt=0,national=true
Address String Format
The configuration profile also includes an Address String encoded into a string. The string format is very similar to the GT SCCP Address format, however there are fewer keys and the key names are slightly different for equivalent value types.
Address String Key/Value Pairs
| Key | Description | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Address digits |
Any digits string |
|
Address nature |
|
|
Address numbering plan |
|
Example of a valid Address String
-
address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN
SIP SIS Resource Adaptor
SIP SIS resource adaptor entity (sip-sis-ra)
| |
Refer to the SIS documentation for more information about the SIP SIS resource adaptor. |
The sip-sis-ra is used for initiating and third-party SIP dialogs for both the Sentinel SIP Service and the Sentinel Subscription Service.
| Link name | Default Bound RA entity |
|---|---|
|
|
Sentinel and SIS
The sip-sis-ra interacts directly with the SIS, which is configured with compositions for the Sentinel SIP Service. The Sentinel SIP Service is triggered by all events from the SIP SIS RA entity. This behaviour is configurable. See the SIS documentation for more information about compositions and triggers.
Configuring SIS
Use the sis-console or SIS REM Module to modify the default SIS and sip-sis-ra configuration properties; see the SIS administration guide and SIS REM Module user guide for more details on managing the SIS instance.
System Statistics
This page provides a summary of the statistics defined for Sentinel VoLTE features.
General Features
DetermineChargeMode
DetermineChargeMode statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineChargeMode
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineChargeMode"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
MonitorOnly |
Incremented when the feature has set the MonitorCallOnly Session State field to true |
NonMonitorOnly |
Incremented when the feature has set the MonitorCallOnly Session State field to false |
Error |
Incremented when the feature was unable to determine the charge mode |
DetermineInitialLegNames
DetermineInitialLegNames statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureStarted |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureFailedToStart |
Incremented when sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureIssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureTimedOut |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureCallingLegNameSet |
Incremented when calling leg name is found |
DetermineInitialLegNamesFeatureCalledLegNameSet |
Incremented when called leg name is found |
DetermineVoltePlanId
DetermineVoltePlanId statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineVoltePlanId
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineVoltePlanId"
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
NoPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature fails to select an appropriate plan ID |
MmtelOriginatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-orig” |
MmtelTerminatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-term” |
MmtelConferencingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “mmtel-conf” |
SccOriginatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-orig” |
SccTerminatingPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term” |
SccTerminatingTadsOnlyPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term-tads” |
SccTerminatingAnchorOnlyPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-term-anchor” |
SccReoriginationPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-reorigination” |
SccAccessTransferPlanSelected |
Incremented when the feature selects the plan ID as “scc-access-transfer” |
ConferenceConfigurationNotFound |
Incremented when the feature is unable to find a valid conference PSI from configuration profiles |
IMSIDLookup
IMSIDLookup statistics are tracked by the IMSIDLookup SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ IMSIDLookup SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Invoked |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature runs. |
FeatureError |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution. |
NoSubscriberSpecified |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine which subscriber to retrieve IDs for. |
IMSIDRetrieveSuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when IDs are successfully retrieved and decoded. |
IMSIDRetrieveFail |
Counter |
Incremented when ID retrieval or decoding fails. |
CacheQueried |
Counter |
Incremented when a query is made to the Sh-Cache. |
CacheIndicatedQuerySuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when a success response is received from the Sh-Cache. |
CacheIndicatedQueryFailure |
Counter |
Incremented when a failure response is received from the Sh-Cache. |
SubscriberNotRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber is not present in the Sh-Cache or has no valid registration. |
RegistrationOutOfSync |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber information is not consistent between the network and the Sh-Cache. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between requesting data from the Sh-Cache RA and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
IMSIDLookupFromCassandra
IMSIDLookupFromCassandra statistics are tracked by the IMSIDLookupFromCassandra feature and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage ▶ volte.sentinel.sip service ID ▶ volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID ▶ IMSIDLookupFromCassandra.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature runs. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
NoSubscriberSpecified |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine which subscriber to retrieve IDs for. |
IMSIDRetrieveSuccess |
Counter |
Incremented when IDs are successfully retrieved and decoded. |
IMSIDRetrieveFail |
Counter |
Incremented when ID retrieval or decoding fails. |
CassandraQueried |
Counter |
Incremented when a query is made to Cassandra. |
MultipleDevicesRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when multiple registered devices have been detected. |
SubscriberNotRegistered |
Counter |
Incremented when could not find an active subscriber. |
RegistrationOutOfSync |
Counter |
Incremented when the searched subscriber information is not consistent between the network and the database. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between querying the Cassandra database and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
SubscriberDataLookupFromHSS
SubscriberDataLookupFromHss statistics are tracked by the SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2 SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SubscriberDataLookupFromHss2 SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Invoked |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs. |
Failed |
Counter |
Incremented if a fatal error occurs while the feature is running. |
SubscriberDataRetrieved |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature receives subscriber data from the HSS or Sh-Cache. |
SessionStatePopulated |
Counter |
Incremented after the feature successfully processes the data it received, and loads it into session state fields. |
AdaptorClassError |
Counter |
Incremented when Adaptor class is not of type SimservsSessionAdaptor or the feature fails to retrieve adaptor class. |
CodecClassError |
Counter |
Incremented when Codec class is not of type ServiceDataCodec or the feature fails to retrieve codec class. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when absent configuration data prevents the feature from running. |
SessionStateNotFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the session state field the feature requires for operation is missing. |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between sending the request to the HSS and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
MMTel Features
MMTel Conference
MMTelCONF statistics are tracked by the MMTelCONF SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → MMTelCONF SBB ID.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
FeatureInvocations |
the conference feature runs |
FeatureFsmCompletions |
the main conference FSM reaches its end state |
SentinelAborts |
Sentinel VoLTE instructs the conference feature to abort execution |
SipParseMinorFailure |
a non-fatal error occurs while attempting to read the information in a SIP message |
SipDataAccessFailure |
a problem occurs while trying to access a SIP leg or message |
SipParticipantSentByeOnActiveConnection |
a |
SipParticipantSentByeOnInactiveConnection |
a |
SipMRFSentByeOnActiveConnection |
a |
SipMRFSentByeOnInactiveConnection |
a |
ConferenceFeatureConfigurationFailure |
a problem occurs while trying to load the conference feature’s network-level configuration data |
ConferenceCoreError |
a fatal error occurs in the core conference feature FSM |
ConferenceConnectionError |
a fatal error occurs in the conference feature’s non-control connection management FSM |
ConferenceConnectionEstablished |
a non-control connection is successfully established between a conference participant and the MRF |
ConferenceConnectionMRFLegCreated |
a non-control leg to the MRF is successfully established |
ConferenceConnectionTerminated |
a fully established non-control conference connection is terminated |
ConferenceConnectionCreditCheckInitiated |
the conference feature triggers a credit check |
ConferenceConnectionParticipantSupportsVideo |
a participant has indicated that they support video in an SDP answer |
ConferenceControlConnectionError |
a fatal error occurs in the conference feature’s control connection management FSM |
ConferenceControlConnectionEstablished |
a control connection is successfully established between a conference moderator and the MRF. |
ConferenceControlConnectionTerminated |
a fully established conference control connection is terminated. |
ConferenceControlConnectionReceivedMalformedMessage |
a badly formed REFER request is received from the conference moderator. |
FromHeaderAnonymised |
the moderator has indicated they want privacy applied to the outgoing INVITE |
ConferenceMediaVideoSelected |
the moderator sets the conference up as a video session |
ConferenceMediaServerIsAccessedViaSCSCF |
the feature makes a call to the MRF via the S-CSCF |
MMTel Determine International and Roaming Status
DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set in REM:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus
or with rhino-stats:
"SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].SbbID[name=volte.sentinel.sip,vendor=OpenCloud,version=2.7.0].feature.DetermineInternationalAndRoamingStatus"
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented each time the feature runs |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs before feature execution |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-fatal error occurs during feature execution |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error occurs during feature execution |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when feature execution does not complete within a reasonable time frame |
VisitedNetworkHeaderFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the requestURI identity is in RegistrationRecords list of public identities. |
AccessNetworkMccFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the mobile-Country-Code is found in the P-Access-Network-Info header. |
DeterminedInternationalUsingAccessNetworkMcc |
Counter |
Incremented when the MCC prefix address list is used to determine whether the call is international. |
DeterminedInternationalUsingVisitedNetworkId |
Counter |
Incremented when the visited-network-id prefix address list is used to determine whether the call is international. |
CouldNotGetPVisitedNetworkID |
Counter |
Incremented when no visited network ID information could be found. |
HomeNetworkIdSetForNetworkOperatorIsEmpty |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sentinel SIP configuration for the network operator has an empty |
InternationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is roaming in a foreign country. |
NationalRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is roaming in their home country. |
NotRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature determines that the served user is on their home network. |
UnknownRoaming |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine the served user’s roaming status. |
AddressNotMinimumLength |
Counter |
Incremented when destination address is less than the configured minimum length. |
AddressOnBlackList |
Counter |
Incremented when destination address matches an entry in the |
MMTelCDIV
MMTelCDIV statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelCDIVFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelCDIVFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelCDIVFeatureMisconfigured |
the feature configuration could not be loaded |
MMTelCDIVFeatureProcessingSipResponse |
the feature is triggered on a SIP response |
MMTelCDIVFeatureProcessingSipRequest |
the feature is triggered on a SIP request |
MMTelCDIVFeatureLegManagerError |
a problem occurs while trying to access data from the SIP leg manager |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorProcessingSipRequest |
a problem occurs while trying to read or modify to a SIP request |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorProcessingSipResponse |
a problem occurs while trying to read or modify to a SIP response |
MMTelCDIVFeatureDiversionLoopDetected |
diversion is aborted due to a diversion loop being detected |
MMTelCDIVFeatureDiversionLimitExceeded |
diversion is aborted due to the diversion limit being hit |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCancelledInviteRequest |
the CDIV feature cancels an |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorCancellingInviteRequest |
a problem occurs while attempting to cancel an |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTerminatedByResponse |
CDIV is aborted by sending an error response on the originating leg |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTerminatedByRetargeting |
CDIV is aborted by attempting to divert to a fixed final destination |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorTerminatingByRetargeting |
diversion fails while trying to terminate by re-targeting |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerSet |
the feature sets a timer for CFNR |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerCancelled |
the feature cancels a timer for CFNR |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerFired |
the feature is triggered by a CFNR timer expiring |
MMTelCDIVFeatureErrorSettingTimer |
a problem occurs while trying to set a CFNR timer |
MMTelCDIVFeatureTimerSuppressedByResponseFromCSDomain |
timer is suppressed when parallel fork is done and the CS domain answers first |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDIVSuppressedByResponseFromCSDomain |
CDIV service is suppressed when parallel fork is done and the CS domain answers first |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCallerNotifiedOfDiversion |
the feature notify the caller the session is being diverted |
MMTelCDIVFeatureFailedToNotifyCallerOfDiversion |
the feature fails to notify the caller the session is being diverted |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFUSucceeded |
unconditional call forwarding is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFUFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute unconditional call forwarding |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNLSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user not being logged into IMS is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNLFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user not being logged into IMS |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user not replying is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user not replying |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFBSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user being busy is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFBFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user being busy |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRcSucceeded |
call forwarding due to the target user being unreachable is successfully executed |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCFNRcFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to the target user being unreachable |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDImmediateSucceeded |
call forwarding due to immediate call deflection is successful. |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDImmediateFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to immediate call deflection |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDAlertingSucceeded |
call forwarding due to call deflection during alerting is successful |
MMTelCDIVFeatureCDAlertingFailed |
a fatal problem occurs while trying to execute call forwarding due to call deflection during alerting |
MMTelCDIVFeatureToHeaderChanged |
'To' header is set to diverted party or served user |
MMTelCW
MMTelCW statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelCWFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelCWFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelCWFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelCWFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelCWFeatureMisconfigured |
a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerError |
there is an error while trying to set a timer |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerCancelled |
a timer is cancelled by the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureTimerSet |
a timer is set by the feature |
MMTelCWFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP response |
MMTelCWFeatureProcessingTimerEvent |
the feature is invoked on a timer firing |
MMTelCWFeatureOutgoingMessageContentChanged |
the feature changes the contents of an outgoing SIP message |
MMTelCWFeatureReattemptedCallSetup |
the feature requests that call set up be reattempted |
MMTelCWFeatureTriggered180AUDUBResponse |
the feature requests a 180 response be sent back to the original caller, indicating call waiting service |
MMTelCWFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature triggers an announcement to be played |
MMTelCWFeatureCancelledInviteRequest |
the feature cancels an outgoing |
MMTelCWFeatureFinalResponseChangedTo486 |
the feature changes a SIP response status code to |
MMTelCWFeatureFinalResponseChangedTo480 |
the feature changes a SIP response status code to |
MMTelHold
MMTelHOLD statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelHoldFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelHoldFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelHoldFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelHoldFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelHoldFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelHoldFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP request |
MMTelHoldFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature is invoked on receiving a SIP response |
MMTelHoldFeatureSipDataAccessError |
an error occurs while trying to access a SIP leg or message |
MMTelHoldFeatureSipMessageSDPUpdated |
the feature changes the SDP content in a SIP message |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedHoldRequest |
the feature determines that an incoming message is a hold request |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedResumeRequest |
the feature determines that an incoming message is a resume request |
MMTelHoldFeatureSessionBandwidthAdjusted |
any bandwidth information is adjusted in an SDP body |
MMTelHoldFeatureMediaStreamBandwidthAdjusted |
bandwidth information is adjusted on a SDP media stream description |
MMTelHoldFeatureMissingDataWarningTriggered |
an operation on SDP data fails due to the data being unavailable |
MMTelHoldFeatureReceivedMalformedMessage |
the feature determines that an incoming message is mal formed |
MMTelHoldFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature determines triggers the play announcement |
MMTelICB
MMTelICB statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelICBFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelICBFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelICBFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelICBFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelICBFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelICBFeatureCallBarred |
the feature bars a call (including when barring due to ACR) |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarredByOdb |
the feature bars a call by Operator Determined Barring rule |
MMTelICBFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature requests that an announcement be played to the calling party |
MMTelICBFeatureACRTriggered |
a call is barred by ACR |
MMTelICBFeatureOdbRulesEvaluatedTrue |
a rule was evaluated to be True |
MMTelOCB
MMTelOCB statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelOCBFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelOCBFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelOCBFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelOCBFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelOCBFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarred |
the feature bars a call |
MMTelOCBFeatureCallBarredByOdb |
the feature bars a call by Operator Determined Barring rule |
MMTelOCBFeaturePlayAnnouncementTriggered |
the feature requests that an announcement be played to the calling party |
MMTelOCBFeatureOdbRulesEvaluatedTrue |
a rule was evaluated to be True |
MMTelOIP
MMTelOIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → MMTelOIP
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded. |
ReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
Counter |
Incremented when a non-standard ‘Privacy’ header is found in an incoming SIP message. |
FromHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘From’ header in an outgoing SIP request. |
ContactHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘Contact’ header in an outgoing SIP message. |
ReferredByHeaderAnonymized |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature anonymizes the ‘Referred-By’ header in an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedUserLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies user-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedHeaderLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies header-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedSessionLevelAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature applies session-level privacy to an outgoing SIP message. |
PerformedCustomHeaderAnonymization |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds and evaluates custom header privacy rules for a message. |
OverrideCategoryTriggered |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature disregards requested privacy settings on an incoming SIP message (due to the subscriber having override category status). |
CriticalPrivacyCannotBeFulfilled |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature refuses an incoming request due to a |
MMTelOIR
MMTelOIR statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Increments when… |
|---|---|
MMTelOIRFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelOIRFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelOIRFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelOIRFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelOIRFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelOIRFeatureMisconfigured |
a fatal error if the feature configuration can not be loaded |
MMTelOIRFeatureReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
a non-standard |
MMTelOIRFeatureFromHeaderAnonymized |
the feature anonymizes the |
MMTelOIRFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
MMTelTIP
MMTelTIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
MMTelTIPFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelTIPFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelTIPFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelTIPFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelTIPFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelTIPFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature processes a SIP response |
MMTelTIPFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature processes a SIP request |
MMTelTIPFeatureOverrideCategoryTriggered |
the feature disregards requested privacy settings on an incoming SIP message (due to the subscriber having override category status) |
MMTelTIPFeatureFromChangeTagRemoved |
the feature removes the |
MMTelTIPFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
MMTelTIR
MMTelTIR statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB.
Statistic |
Incremented when… |
MMTelTIRFeatureStarted |
the feature runs |
MMTelTIRFeatureFailedToStart |
sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature |
MMTelTIRFeatureIssuedWarning |
a non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning |
MMTelTIRFeatureFailedDuringExecution |
a fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly |
MMTelTIRFeatureTimedOut |
the feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution |
MMTelTIRFeatureProcessingResponse |
the feature processes a SIP response |
MMTelTIRFeatureProcessingRequest |
the feature processes a SIP request |
MMTelTIRFeatureFromChangeTagRemoved |
the feature removes the |
MMTelTIRFeatureReceivedMalformedPrivacyHeader |
a non-standard |
MMTelTIRFeaturePrivacyHeaderChanged |
the feature changes the contents of the |
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation
MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → [volte.sentinel.sip service name] → [volte.sentinel.sip SBB name] → feature.MMTelWifiChargingFinalisation
Statistic |
Increments when… |
Started |
The feature is started. |
OCTerminatingDomainHeaderStripped |
An OC-Terminating-Domain header is found on an outgoing message and removed. |
ChargingInstanceFinalised |
A non-finalised reservation charging instance is found and finalised. |
Received2xxForOriginalInvite |
A SIP 2xx response for the initial INVITE is received by the feature. |
TerminatingDomainIsWifi |
The feature determines that terminating access is over WiFi. |
FailedToStart |
Sentinel VoLTE encounters an error while attempting to start the feature. |
IssuedWarning |
A non-fatal problem is encountered and the feature and issues a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
A fatal problem is encountered and the feature cannot execute correctly. |
TimedOut |
The feature takes too long to complete and Sentinel VoLTE aborts execution. |
MMTelParallelFA
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ProcessingRequest |
processing a request message. |
ProcessingResponse |
processing a response from the downstream forked legs. |
InviteRequestReceived |
the original INVITE is received. |
CancelRequestReceived |
a CANCEL message is received. |
ProvisionalResponseReceived |
a 1xx message is received. |
SuccessResponseReceived |
a 200 (OK) message is received. |
BusyErrorResponseReceived |
a 486 (Busy Here) message is received. |
NonBusyErrorResponseReceived |
a 4xx message is received that is not a 486 (Busy Here). |
GroupMemberAlerted |
an INVITE request is sent to a group member. |
LegReleased |
a dialog leg is released. |
UpstreamForkCreated |
the feature creates a new leg towards the calling party. It happens on the provisional responses. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
the feature is triggered on a response message. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
the feature is triggered on a request message. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
the feature is triggered on a timmer. |
TimeoutTimerCancelled |
the feature cancel the timer. |
TimeoutTimerSet |
the feature sets the timer. The timer is set before the INVITE is sent to the first group member. |
ExitedEarlyNoMembersToAlert |
there is just one member in the group and it is the pilot number. |
Received480 |
receives a 480 (Temporarily Unavailable) response from a member |
Received486 |
receives a 486 (Busy Here) response from a member |
Received408 |
receives a 408 (Timeout) response from a member |
Received404 |
receives a 404 (Not found) response from a member |
ReceivedSuccess |
receives a 200 (OK) response from a member |
RespondedUpstreamWith480 |
the feature sends a 480 (Temporarily Unavailable) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith486 |
the feature sends a 486 (Busy Here) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith408 |
the feature sends a 408 (Timeout) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWith404 |
the feature sends a 404 (Not found) to the calling party. |
RespondedUpstreamWithSuccess |
the feature sends a 200 (OK) to the calling party. |
MMTelSequentialFA
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ProcessingRequest |
processing a request message. |
ProcessingResponse |
processing a response from a downstream forked leg. |
InviteRequestReceived |
the original invite is received. |
CancelRequestReceived |
a CANCEL message is received. |
ProvisionalResponseReceived |
a 1xx message is received. |
SuccessResponseReceived |
a 200 (OK) message is received. |
GroupMemberAlerted |
an INVITE message was sent to a group member. |
GroupMemberAddedToQueue |
a group member was queued for alerting. |
MemberLegReleased |
a dialog leg is released. |
RespondedUpstreamManually |
the feature created an upstream response. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
the feature is triggered on a response message. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
the feature is triggered on a request message. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
the feature is triggered on a timer event. |
TriggeredOnLegEndEvent |
the feature is triggered on a SIP leg end event. |
AnyResponseTimerSet |
the feature set a timer to wait for a response on a downstream leg. |
FinalResponseTimerSet |
the feature set a timer to wait for a final response on a downstream leg. |
AnyResponseTimerCancelled |
the timer waiting for a response on a downstream leg was cancelled. |
FinalResponseTimerCancelled |
the timer waiting for a final response on a downstream leg was cancelled. |
TimerFired |
the feature handled a timer event. |
ExitedEarlyNoMembersToAlert |
there is just one member in the group and it is the pilot number. |
MMTelECT
| Name | Increments when … |
|---|---|
ReferReceivedFromServedUser |
a REFER request has been received from the served user |
ReferDeclined |
the feature has sent responded to a REFER request with 603 (Decline) |
ReferSuccessful |
the transferee has responded to a processed REFER request with a 202 Accepted) |
ReferProcessedAndForwarded |
a REFER request has been received from the transferor, appropriately modified and sent to the transferee |
EctInviteReceived |
an INVITE request has been received from the transferor as a result of a previous REFER request |
EctInviteProcessedAndForwarded |
an ECT INVITE request has been received by the transferee, appropriately modified and sent to the transfer-target |
ThirdPartyCallControlProceduresInvoked |
the Third Party Call Control (3pcc) transfer procedures have been invoked |
ThirdPartyCallControlProceduresFailed |
the Third Party Call Control (3pcc) transfer procedures did not result in a successful dialogue between the transferee and transfer-target |
OriginalCallResumed |
the original dialogue between the transferee and the transferor has been resumed if the 3pcc procedures failed |
CassandraInsertSucceeded |
ECT session information has been successfully inserted into the Cassandra DB |
CassandraInsertFailed |
an error occurred attempting to insert ECT session information into the Cassandra DB |
CassandraQuerySucceeded |
ECT session information has been successfully retrieved from the Cassandra DB |
CassandraQueryFailed |
an error occurred attempting to retrieve ECT session information from the Cassandra DB |
DeletedCassandraRow |
REFER request was cancelled by user, and so the Cassandra ECT record was deleted. |
StoppedHandlingAndAllowedB2BUA |
an INVITE request with a Request URI matching the ECT URI pattern was received and forwarded without modification |
TransferSuccessful |
a 200 (OK) was received from the transfer-target as a result of the ECT procedures |
ErrorOccurredDuringExecution |
an error occurred attempting to execute the feature |
NoAnswerTimerFired |
The feature timed-out waiting for an answer from a sent request. |
MMTel Session Transfer features
MMTelStodBind
Name |
Incremented when… |
BoundAciToImpu |
the ACI is bound to an this is incremented. |
UsedLinkedAciForBinding |
the triggering ACI is not used for binding, i.e the call is not MobileTerminating then the linked ACI is used. |
UsedTriggeringAciForBinding |
the call is a MobileTerminating call the Triggering ACI is used for binding. |
MMTelStodEnabled
| Name | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
StodIsEnabled |
the Stod is enabled for a subscriber |
StodIsNotEnabled |
the Stod is not enabled for a subscriber |
MMTelStodProcessHandover
Name |
Incremented when… |
SentRemoteUpdate |
a re-INVITE is sent to the called party. |
RemoteUpdateSuccess |
re-INVITE was accepted (200 OK). |
RemoteUpdateError |
re-INVITE was not accepted. |
CallAnsweredWith200 |
the (200 OK) from the re-INVITE is sent to the new access leg |
ReleasedOldAccessLeg |
the previous calling leg is released |
LinkedNewAccessLegToRemoteLeg |
the transfer INVITE leg is linked to the existing called party leg |
TerminatedSession |
the session finishes |
AccessTransferComplete |
the session transfer was done successfully |
HandoverRequestReceived |
a session transfer INVITE is received |
StodEnableSessionTracking |
tries to mark the new transfered session to be tracked |
FoundTrackingKey |
the tracking key is set |
StodSessionTrackingDisabled |
when failed to set the new transfered session to be tracked |
SCC Features
Service Centralisation Features
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.ss7 SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.ss7 service → volte.sentinel.ss7 SBB → feature → SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationIN
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature starts. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature failed to start due to an error. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature raised a warning. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature failed due to a major error. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature timed out during execution. |
CallReOriginated |
Counter |
Incremented when the call is successfully re-originated. |
CallReleased |
Counter |
Incremented when reorigination fails and the call is released. |
Misconfigured |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature has not been correctly configured. |
IdpVlrNumberPresent |
Counter |
Incremented when the VLR number is found in the incoming InitialDP. |
IdpVlrNumberNotPresent |
Counter |
Incremented when the VLR number is not found in the incoming InitialDP. |
VisitedNetworkIdNotFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is unable to determine the Visited Network ID. |
VisitedNetworkIdFound |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is able to determine the Visited Network ID based on the VLR address. |
PoolAllocationFailed |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to acquire a correlation ID from the correlation RA. |
PoolAllocationSucceeded |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature acquires a correlation ID from the correlation RA. |
OriginatingIMRNAttempt |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature executes reorigination for an originating call leg. |
TerminatingIMRNAttempt |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature executes reorigination for a terminating call leg. |
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP
SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service → volte.sentinel.sip SBB → feature → SCCCamelToIMSReOriginationSIP
| Statistic | Incremented when… |
|---|---|
Complete |
The feature ran to completion |
MultipleHistoryInfoHeadersFound |
Multiple history-info headers found on the INVITE |
NoHistoryInfoHeaderFound |
no history-info header found on the INVITE |
OneHistoryInfoHeaderFoundAndRemoved |
One history-info header found on the INVITE and removed |
HSSLookupFailed |
HSS lookup failed |
HSSLookupSuccess |
HSS lookup succeeded |
HSSLookupSkipped |
HSS lookup was skipped due to SkipHSSLookup feature configuration flag |
CorrelationRaQueried |
Correlation RA was queried for the call information |
CorrelationRaQuerySuccess |
The Correlation RA query succeeded |
CorrelationRaQueryFailure |
The Correlation RA query failed |
IdpVlrNumberPresent |
The VLR number is present in the initial IDP |
IdpVlrNumberNotPresent |
The VLR number is not present in the initial IDP |
VisitedNetworkIdFound |
The feature could set the Visited Network Id based on the Location information or on the VLR address |
VisitedNetworkIdNotFound |
The feature could set the Visited Network Id |
IdpCalledPartyNumberPresent |
The initial IDP has a called party number or called party BCD number |
IdpCalledPartyNumberNotPresent |
The initial IDP does not have a called party number or called party BCD number |
SCSCFAddressNotFound |
The SCSCF could not be found in configuration, or retrieved from the HSS |
Started |
The feature starts |
FailedToStart |
The feature failed to start due to an error |
IssuedWarning |
The feature raised a warning |
FailedDuringExecution |
The feature failed due to a major error |
TimedOut |
The feature timed out during execution |
Terminating Access Domain Selection Features
SCCTADSDataLookup
SCCTADSDataLookUp statistics are tracked by the SCCTADSDataLookUp SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SCCTADSDataLookUp SBB ID.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Started |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
QueriedShCache |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sh Cache is queried. |
ShCacheDataReceived |
Counter |
Incremented when the Sh Cache returns data from the query. |
FoundValidCSRoute |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds a valid route to the CS domain. |
FoundValidPSRoute |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature finds a valid route to the PS domain. |
MsrnAndCmsisdnBothSet |
Counter |
Incremented when both CMSISDN and MSRN are set in session state. |
CannotSetCSRN |
Counter |
Incremented when the CSRN cannot be calculated. |
BlindPSRoutingRequested |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature has set the BlindPSRouting Session State field. |
NoForkDispositionOverrodeRoutingMode |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature does not fork due to disposition header. |
TriggeredEndSession |
Counter |
Incremented when the feature rejects an |
ResponseLatency |
Sampled |
Records elapsed time between requesting data from the Sh-Cache RA and getting a response (in milliseconds). |
SCCTADSParallelRouting
SCCTADSParallelRouting statistics are tracked by the volte.sentinel.sip SBB and can be found under the following parameter set:
SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → volte.sentinel.sip SBB ID → feature.SCCTADSParallelRouting
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
TriggeredOnRequest |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on a SIP Request. |
TriggeredOnResponse |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on a SIP Response. |
TriggeredOnTimer |
Incremented when the feature is triggered on the timer firing. |
CSRNNotFound |
Incremented when the CS fork cannot be established because no CSRN can be found. |
MaxWaitTimerSet |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer is started. |
MaxWaitTimerCancelled |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer is cancelled. |
UpstreamForkCreated |
Incremented when an upstream forked leg is created for forward a provisional or success response from the CS leg. |
ReceivedProvisionalResponse |
Incremented when a provisional 18x response is received. |
ReceivedFinalResponse |
Incremented when a final response is received for the initial INVITE. |
RouteToCSAttempted |
Incremented when an INVITE is routed down the CS forked leg. |
RouteToPSAttempted |
Incremented when an INVITE is routed down the PS forked leg. |
RouteToCSFailed |
Incremented when the CS leg is torn down without being answered. |
RouteToPSFailed |
Incremented when the PS leg is torn down without being answered. |
AnsweredOnCS |
Incremented when a success response is received on the CS leg. |
AnsweredOnPS |
Incremented when a success response is received on the PS leg. |
SCCTADSRouting
SCCTADSRouting statistics are tracked by the SCCTADSRouting SBB and can be found under the following parameter set: SLEE-Usage → volte.sentinel.sip service ID → SCCTADSRouting SBB ID.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
Started |
Incremented when the feature is triggered. |
FailedToStart |
Incremented when the feature fails to start. |
FailedDuringExecution |
Incremented when the feature fails while executing. |
IssuedWarning |
Incremented when the feature issues a warning. |
TimedOut |
Incremented when the feature times out during execution. |
RouteToPreferredPS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a preferred leg when PS is preferred. |
RouteToPreferredCS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a preferred leg when CS is preferred. |
RouteToFallbackPS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a fallback leg when PS is preferred. |
RouteToFallbackCS |
Incremented when the feature successfully to routes to a fallback leg when CS is preferred. |
ErrorResponseMatched |
Incremented when the PS call error response code matches a value in |
Error18xMatched |
Incremented when the PS call 18x response matches the SDP requirements outlined in 18x Response. |
Received18xResponse |
Incremented when the feature receives a 18x response to the initial |
Received488Response |
Incremented when the feature receives a 488 message from the PS call. |
ReceivedBlindPSRoutingResponse |
Incremented when the feature receives a error message from the PS call that is contained in |
TerminatingDomainHeaderSet |
Incremented when the feature adds a terminating domain header to an upstream response |
TADSTimerFired |
Incremented when the Max Wait Timer for a response on a routing attempt is exceeded |
License Requirements
This page gives information about license requirements for running Sentinel VoLTE.
Required License Functions
All services and resource adaptors require the following license function:
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino |
No |
Capacity |
This following sections list the additional license functions required by certain components of Sentinel VoLTE. Some of the components listed below modify the Rhino license function to be only necessary for Activation instead of Capacity.
| |
Not all of the components listed below will be present in all Sentinel VoLTE deployments. |
Services
Sentinel VoLTE SIP Service
Component Name: volte.sentinel.sip
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino |
No |
Activation |
Sentinel |
No |
Activation |
Sentinel-VoLTE |
No |
Capacity |
Sentinel VoLTE SS7 Service
Component Name: volte.sentinel.ss7
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino |
No |
Activation |
Sentinel |
No |
Activation |
Sentinel-VoLTE |
No |
Capacity |
Resource Adaptors
SIS-SIP/EasySIP RA
Component Name: SIS-SIP/EasySIP RA
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino-SIS |
No |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-SIP |
No |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-SIP-External-Service |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-SIP-Local-Service |
Yes |
Capacity |
SIS-IN Unified RA
Component Name: SIS-IN Unified
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino-SIS |
No |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN |
No |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-External-Service |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-Local-Service |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-Protocol-CAP |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-Protocol-ETSI-INAP-CS1 |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-SMS |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-SPS |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-TPS |
Yes |
Capacity |
Rhino-SIS-IN-IN-Voice |
Yes |
Capacity |
CGIN Unified RA
Component Name: CGIN Unified RA
| License Function | Optional | Required For |
|---|---|---|
Rhino-CGIN |
No |
Activation |
Rhino-CGIN-Base |
No |
Activation |