The BSF Server is a SLEE service that handles the GBA bootstrapping procedures (3GPP TS 33.220).
It receives bootstrapping requests from UEs (Ub interface), and contacts the HSS to generate authentication information (Zh interface). If bootstrapping for the UE is successful, the BSF writes an entry to a database, with an expiry time. When the UE later attempts to access the NAF, the NAF reads this database entry as part of its authentication procedure.
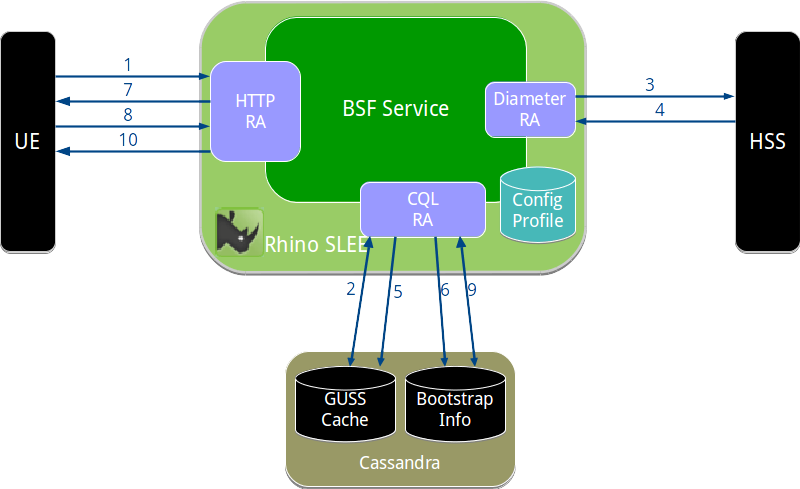
- BSF Server operation
- 1. UE sends bootstrapping request
- 2. BSF checks GUSS cache
- 3. BSF sends Zh request to HSS
- 4. HSS returns Zh response
- 5. BSF stores new GUSS
- 6. BSF stores authentication vector
- 7. BSF sends challenge
- 8. UE sends challenge response
- 9. BSF checks response, generates B-TID
- 10. BSF sends success response to UE
BSF Server operation
An overview of the bootstrapping process is shown below.
As in NAF Authentication Filter operation, we will describe the BSF by walking through a typical bootstrapping transaction.
1. UE sends bootstrapping request
A NAF has instructed the UE to initiate the bootstrapping process (see NAF filter rejects with challenge).
The UE derives its BSF server’s address, which will be bsf.home1.net for this example.
The address is derived from the subscriber’s private identity as per 3GPP TS 23.003 §16.2.
The UE sends an initial bootstrap request to its BSF.
This request contains an empty Authorization header containing the private identity and realm, but empty nonce and response parameters.
The empty parameters indicate to the BSF that this is a new bootstrapping request.
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: bsf.home1.net
User-Agent: Some-user-agent/1.0 3gpp-gba-tmpi
Authorization: Digest username="user@home1.net", realm="bsf.home1.net",
nonce="", uri="/", response=""|
|
UEs may also use a TMPI (temporary private identity) instead of their actual private identity.
This is supported, but not shown in this example.
TMPI to IMPI mappings are stored in the impi_by_tmpi Cassandra table.
|
The BSF service uses OpenCloud’s HTTP resource adaptor to receive HTTP requests and send responses.
2. BSF checks GUSS cache
The BSF needs to contact the HSS to request authentication information, but first it checks its GUSS cache to obtain the GBA User Security Settings for the subscriber.
If a cached GUSS entry is present, the BSF will send the GUSS timestamp to the HSS in the Zh request, to check if it is still up to date. If there is no GUSS entry, or it does not have a timestamp, the HSS will return its latest GUSS in the Zh response.
The BSF uses OpenCloud’s Cassandra-CQL resource adaptor to perform Cassandra queries.
3. BSF sends Zh request to HSS
The BSF sends a Zh request (see 3GPP TS 29.109 §4.2) using the Diameter Base resource adaptor. The Diameter Base RA can be configured to support many Diameter applications. In a Sentinel Authentication Gateway installation it is automatically configured to support the Zh Diameter application and AVPs.
Multimedia-Auth-Request (Command-Id 303, Application-Id 16777221 (Zh))
Session-Id: "12345@bsf.home1.net"
Vendor-Specific-Application-Id: (grouped)
Vendor-Id: 10415 (3GPP)
Auth-Application-Id: 16777221 (Zh)
Auth-Session-State: NO_STATE_MAINTAINED
Origin-Host: "bsf.home1.net"
Origin-Realm: "home1.net"
Destination-Realm: "home1.net"
Destination-Host: "hss.home1.net"
User-Name: "user@home1.net"
GUSS-Timestamp: <timestamp>4. HSS returns Zh response
The HSS generates a new authentication vector (AV) and sends this in the Zh response. If the GUSS has been updated since the GUSS timestamp sent in the Zh request, the new GUSS is included in the response.
The AV is made up of these values:
-
RAND— a randomly generated 16-byte value -
AUTN— the authentication token, contains a sequence number that the UE can verify -
CK— the confidentiality key -
IK— the integrity key -
XRES— the expected response from the UE.
Multimedia-Auth-Answer (Command-Id 303, Application-Id 16777221 (Zh))
Session-Id: "12345@bsf.home1.net"
Vendor-Specific-Application-Id: (grouped)
Vendor-Id: 10415 (3GPP)
Application-Id: 16777221 (Zh)
Auth-Session-State: NO_STATE_MAINTAINED
Origin-Host: "hss.home1.net"
Origin-Realm: "home1.net"
Result-Code: 2000
SIP-Auth-Data-Item: (grouped)
SIP-Authenticate: RAND || AUTN
Confidentiality-Key: CK
Integrity-Key: IK
SIP-Authorization: XRES
GBA-UserSecSettings: <guss id="user@home1.net">...</guss>5. BSF stores new GUSS
If the Zh response included a new GUSS document, this is stored in the BSF’s GUSS cache.
6. BSF stores authentication vector
The BSF stores the values RAND, AUTN, CK, IK and XRES in the auth_vector Cassandra table, with an expiry time (default 60s).
When the challenge response arrives, any BSF node in the cluster can process it using the stored authentication vector details.
7. BSF sends challenge
The BSF uses the HTTP RA to send the UE a challenge, using values from the authentication vector. This uses the Digest Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) scheme specified in RFC 3310.
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Server: sentinel-gaa-bsf/1.0.0 3gpp-gba-tmpi
Date: Thu, 08 Jan 2004 10:13:17 GMT
WWW-Authenticate: Digest realm="bsf.home1.net",
nonce=base64(RAND || AUTN),
algorithm=AKAv1-MD5,
qop="auth-int",
opaque="37a63ff9d543ca979f467b05632670d1"8. UE sends challenge response
The UE extracts the RAND and AUTN values from the nonce parameter.
Because the UE shares the secret K with the HSS, it can independently calculate CK, IK, and RES.
The UE sends a challenge response in its next HTTP GET request.
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: bsf.home1.net
User-Agent: Some-user-agent/1.0 3gpp-gba-tmpi
Authorization: Digest username="user@home1.net", realm="bsf.home1.net",
nonce=base64(RAND || AUTN), uri="/",
nc=00000001, cnonce="6e47229c626bb136c135"
response=(digest calculated using RES value)9. BSF checks response, generates B-TID
The BSF receives the challenge response over HTTP, and checks that the digest value in the response directive matches the value calculated by the BSF using XRES.
If the digest values match, this means the UE has successfully authenticated.
This value could have only been computed with knowledge of shared secret K, stored on the HSS and the UE’s tamper-proof SIM.
The BSF creates a Bootstrap Transaction Identifier (B-TID), which is used as the UE’s user name in subsequent NAF requests. The B-TID identifies a security association between the UE and the BSF. The lifetime of this security association is determined by the user’s GUSS, configured on the HSS.
The B-TID, RAND, CK and IK values are written to a record in the bootstrap_info Cassandra table.
The record is expired automatically according to the security association’s lifetime.
The NAF Authentication Filter will read this record when authenticating requests to the NAF; see NAF filter retrieves bootstrap information.
10. BSF sends success response to UE
Finally the BSF sends an HTTP 200 OK response to the UE. This response contains the bootstrapped security association info in XML form, as per 3GPP TS 24.109 Annex C.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: sentinel-gaa-bsf/1.0.0 3gpp-gba-tmpi
Authentication-Info: rspauth="eb52a0caba3df288aff385925c1d05f9"
nc=00000001, cnonce="6e47229c626bb136c135"
Content-Type: application/vnd.3gpp.bsf+xml
Content-Length: 123
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<BootstrappingInfo xmlns="uri:3gpp-gba">
<btid>CH8Bm4AA/38BADV/f4DBAQ==@bsf.home1.net</btid>
<lifetime>2016-02-14T13:20:00Z</lifetime>
</BootstrappingInfo>Now the UE has enough information to authenticate with a NAF; see UE sends challenge response using bootstrapped security association.
