This book contains performance benchmarks using the Sentinel IP Short Message Gateway.
Topics
Descriptions of each of the benchmark scenarios, and notes on the benchmark methodology used |
|
Details of the hardware, software, and configuration used for the benchmarks |
|
Summaries of the benchmarks and links to detailed metrics. |
Other documentation for the Sentinel IP Short Message Gateway can be found on the Sentinel IP Short Message Gateway product page.
Benchmark Scenarios
This page describes the scenarios and methodology used when running the benchmarks.
MO Submission
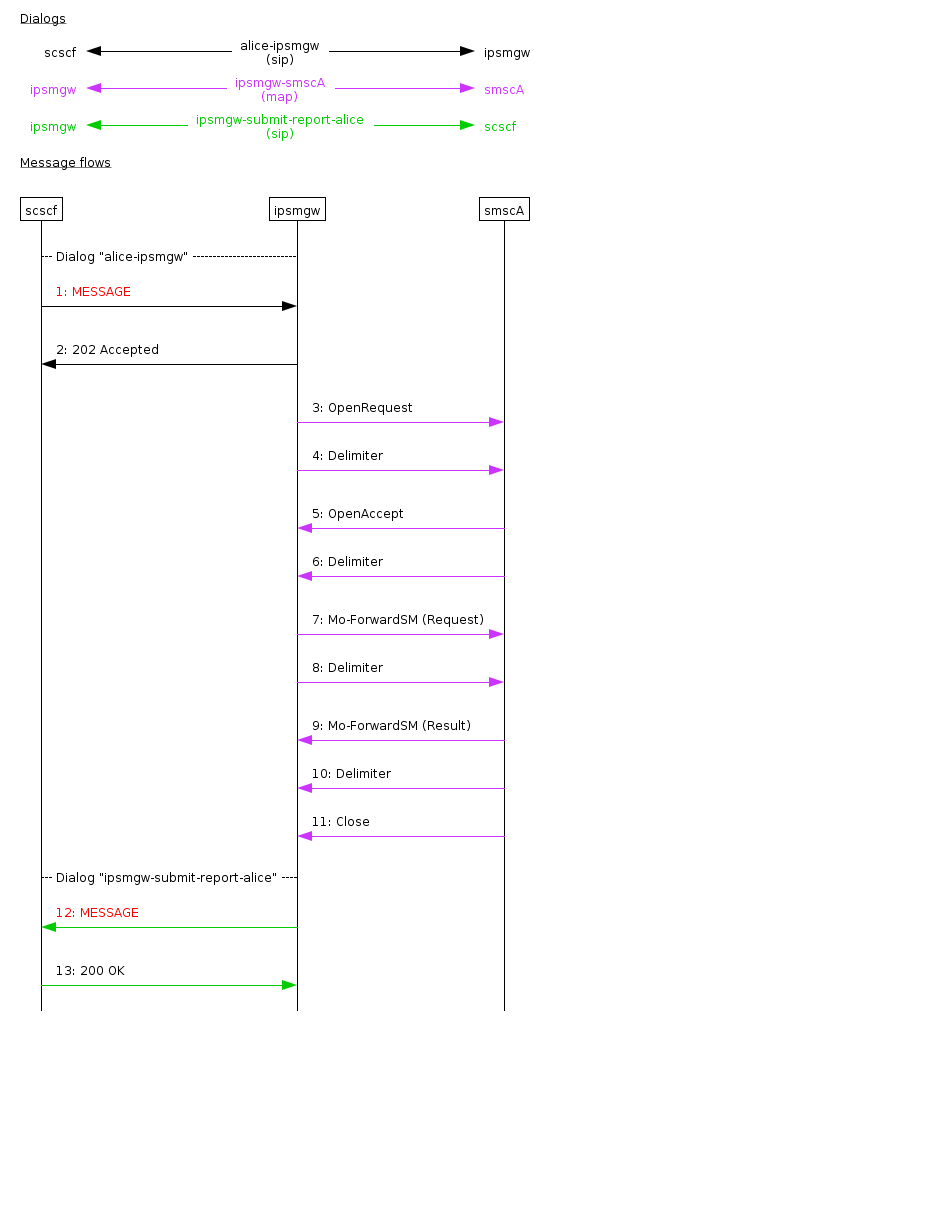
In this scenario, the SCSCF sends a SIP message containing a short message to the IP-SM-GW, which then sends an MO-ForwardSM request to the SMSC. The Opencloud Scenario Simulator performs the role of SMSC and SCSCF. For details of the message processing, see MO Submission Flows
-
The SCSCF sends a SIP Message containing a valid RP-Data payload to the IP-SM-GW.
-
The IP-SM-GW responds to the SCSCF with a 202 Accepted message.
-
The IP-SM-GW sends a TCAP OpenRequest to the SMSC.
-
The SMSC replies with an OpenAccept.
-
The IP-SM-GW sends an MO-ForwardSM request to the SMSC.
-
The SMSC replies with an MO-ForwardSM response, and closes the TCAP dialog.
-
The IP-SM-GW sends a SIP Message containing an RP-ACK to the SCSCF.
-
The SCSCF replies with a 200 OK.
CS Delivery
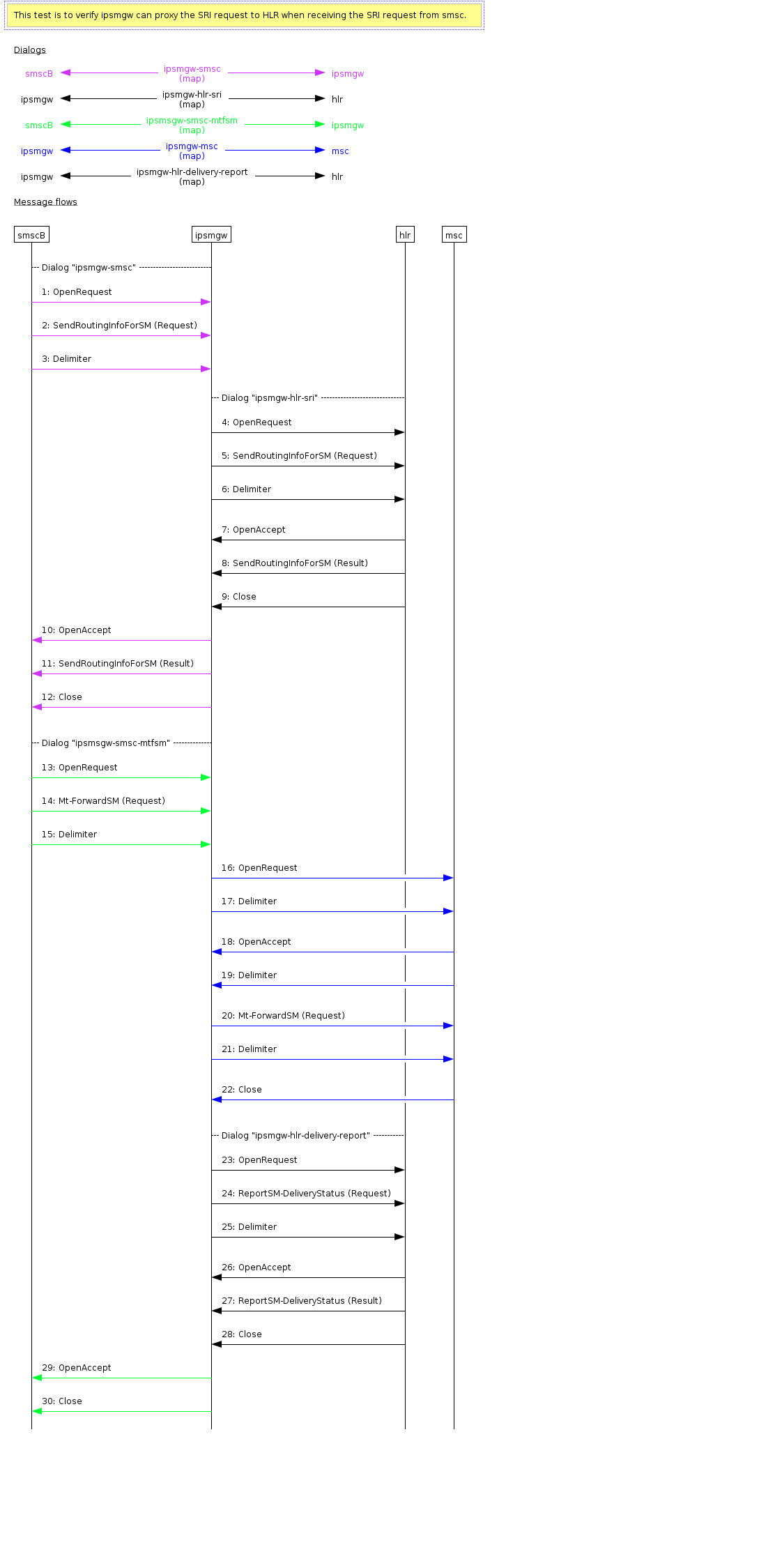
In this scenario, the SMSC delivers a MT SMS to the IP-SM-GW, which then sends the message over the CS network. The OpenCloud Scenario Simulator performs the role of SMSC, MSC, and HLR. For details of changes made to proxied messages and details of message processing, see MT Delivery Flows.
-
The SMSC sends an OpenRequest containing a SendRoutingInfoForSM request to the IP-SM-GW.
-
The IP-SM-GW proxies that message to the HLR.
-
The HLR replies with a SendRoutingInfoForSM response.
-
The IP-SM-GW proxies that response to the SMSC, and closes the dialog to the SMSC.
-
The SMSC sends an OpenRequest containing an MT-ForwardSM request to the IP-SM-GW.
-
The IP-SM-GW sends an empty OpenRequest to the MSC.
-
The MSC response with an OpenAccept
-
The IP-SM-GW sends the MT-Forward-SM request to the MSC on the established dialog
-
The MSC closes the dialog
-
The IP-SM-GW sends an OpenAccept to the SMSC, and closes the dialog.
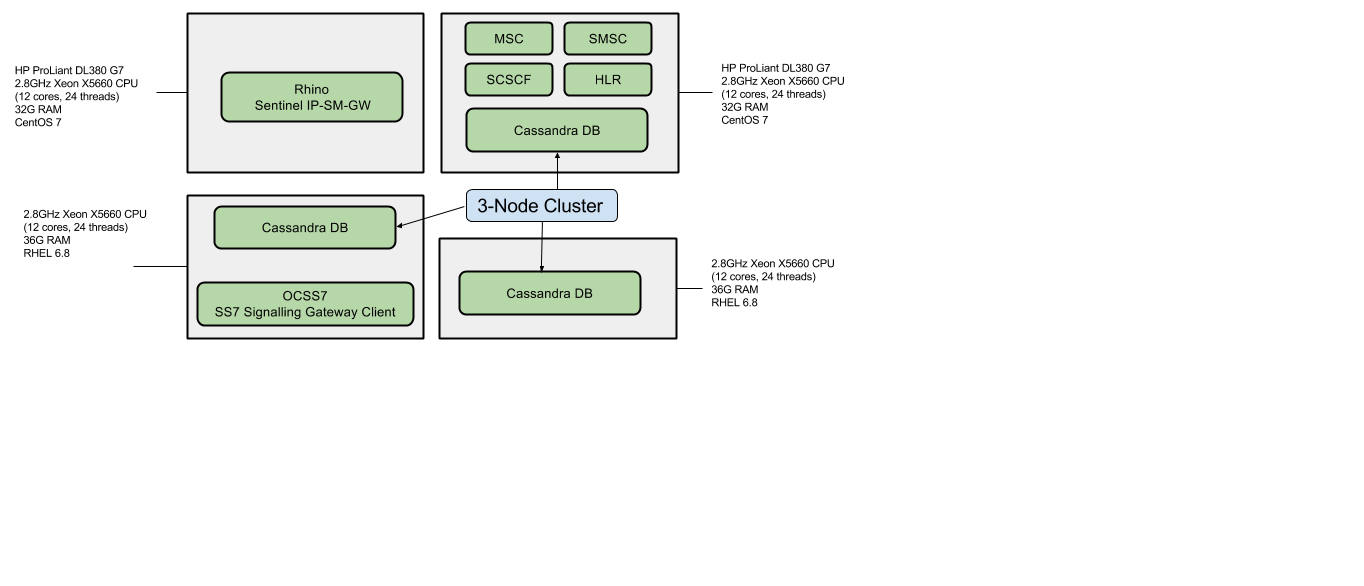
Hardware and Software
Benchmark Results
This page contains the results for the Sentinel IP-SM-GW benchmarks, with both summaries and detailed metrics.
Context for these results are provided by the benchmark scenarios description.
Benchmarks
|
1000 messages per second, evenly split across the MO-Submission and CS-Delivery call flows. |
||||||||||||||||
|
1300% across 12 cores
|
||||||||||||||||
|
2300MB average heap |
||||||||||||||||
|