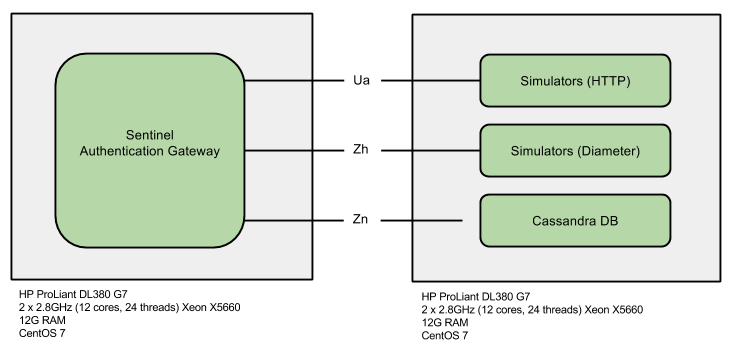
This book contains performance benchmarks using the Sentinel Authentication Gateway
Topics
Descriptions of each of the benchmark scenarios, and notes on the benchmark methodology used |
|
Details of the hardware, software, and configuration used for the benchmarks |
|
Summaries of the benchmarks and links to detailed metrics. |
Other documentation for the Sentinel Authentication Gateway can be found on the Sentinel Authentication Gateway product page.
Benchmark Scenarios
This page describes the scenarios and methodology used when running the benchmarks.
In all benchmarks, the OpenCloud Scenario Simulator performs the roles of UE and HSS.
BSF Scenarios
Successful bootstrapping scenario
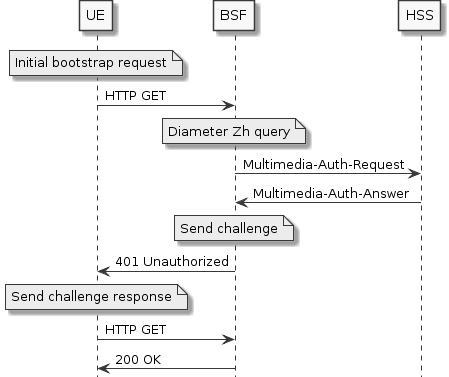
In this scenario, a UE completes a typical bootstrapping procedure with the BSF.
-
The UE sends an initial, unauthorized bootstrapping request to the BSF, containing the IMPI.
-
The BSF sends a Diameter Zh
Multimedia-Auth-Requestto the HSS. -
The HSS responds with a
Multimedia-Auth-Answer, containing an Authentication Vector and the user’s GUSS.-
The Authentication Vector and GUSS are written to the BSF’s Cassandra database.
-
-
The BSF sends a challenge to the UE in the HTTP 401 response.
-
The UE sends a new HTTP request to the BSF, containing the challenge response in the
Authorizationheader. -
The BSF validates the challenge response, and sends an HTTP 200 OK response to the UE containing the B-TID and lifetime of the security association, completing the bootstrapping procedure.
-
The BSF reads the Authentication Vector and GUSS from Cassandra, and inserts a new entry for the security association.
-
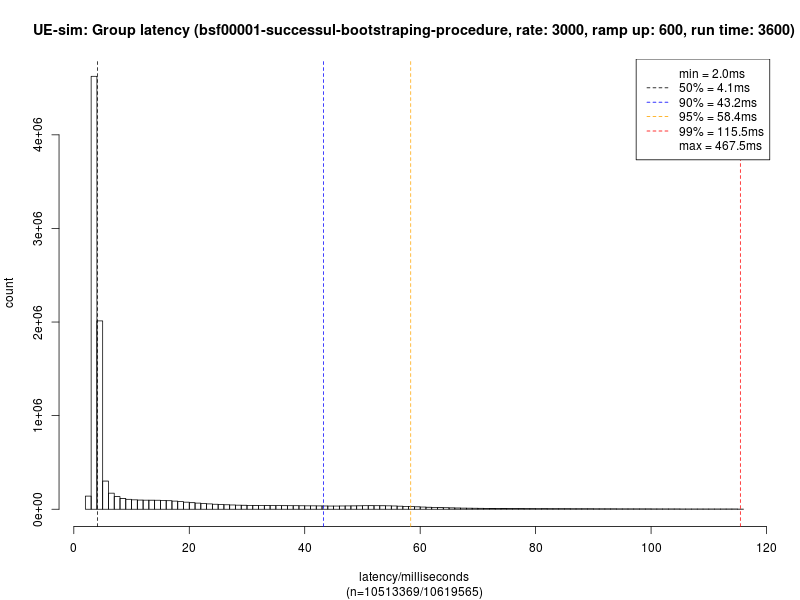
Response time is measured at the UE, from when the initial HTTP request is sent to the arrival of the 401 response from the BSF. This includes the time taken for the BSF to contact the HSS and its Cassandra database.
Test Setup
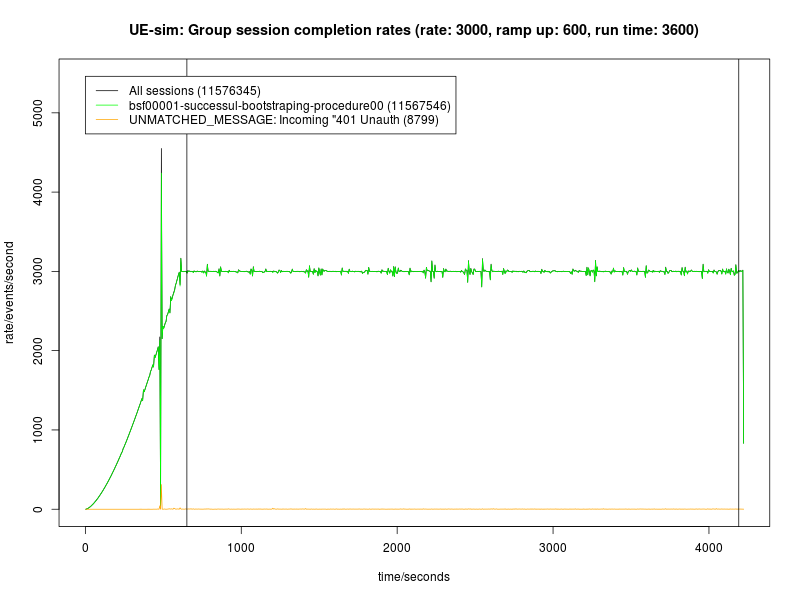
Each test run consists of a 10 minute ramp-up period where load is increased from zero to the target rate, then a 60 minute measurement period at peak load.
The ramp-up period is included as the Oracle JVM provides a Just In Time (JIT) compiler. The JIT compiler compiles Java bytecode to machine code, and recompiles code on the fly to take advantage of optimizations not otherwise possible. This dynamic compilation and optimization process takes some time to complete. During the early stages of JIT compilation/optimization, the node cannot process full load. JVM garbage collection does not reach full efficiency until several major garbage collection cycles have completed.
Only latency measurements during the measurement period are used; latency measurements during the ramp-up period are ignored.
Load is not stopped between ramp up and starting the test timer.
Hardware and Software
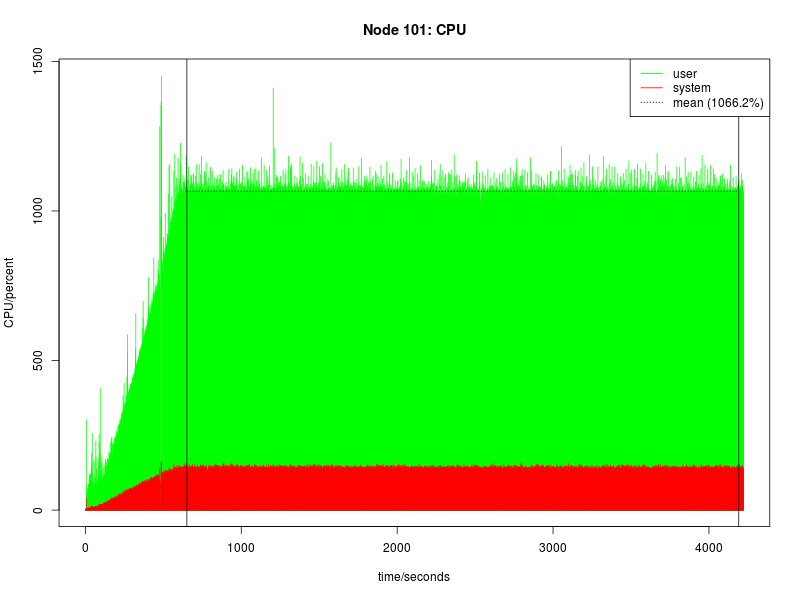
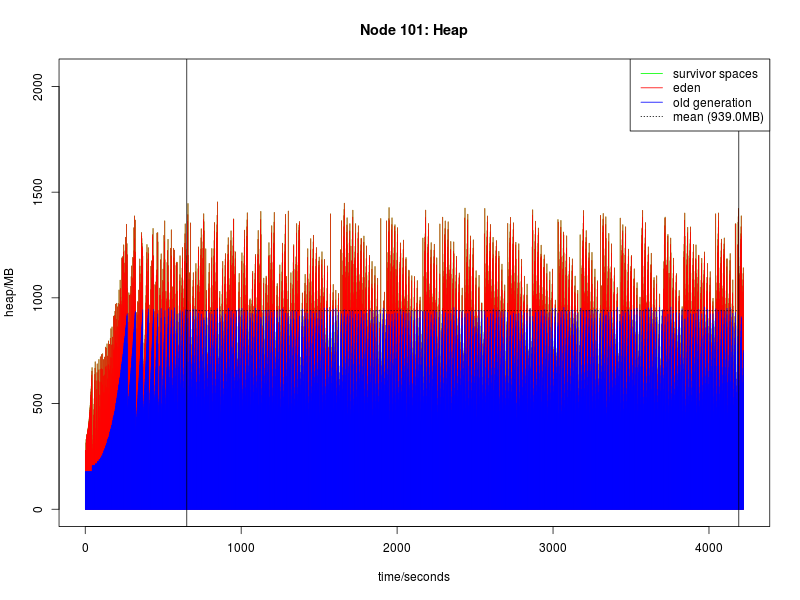
Benchmark Results
This page summarises the results for the Sentinel Authentication Gateway benchmarks. Detailed metrics follow the summary tables.
The benchmark scenarios has more information on how these configurations are defined.