This document is the Configuration and Management guide for Rhino VoLTE TAS 4.1.
- Notices
- Where to start
- Declarative configuration
- RVT system configuration
- RVT service centralization and continuity configuration
- RVT MMTel configuration
- Announcements
- Announcements on call failure
- PSAP callback
- Dial plan enforcement (DPE)
- MMTel privacy settings
- Conference (CONF)
- Call barring
- Communication Waiting (CW)
- Communication Hold (HOLD)
- Communications Diversion (CDIV)
- Voicemail forwarding
- Companion device
- Vertical service codes (VSC)
- International Call Management
- Location based dialing (LBD)
- Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT)
- Flexible Alerting (FA)
- Session transfer to own device
- RVT XCAP
- RVT Authentication Gateway
- RVT IP Short Message Gateway (IP-SM-GW)
- RVT USSD over IM CN subsystem (USSI)
- RVT declarative configuration reference
- Example configuration and schemas
Notices
Copyright © 2014-2021 Metaswitch Networks. All rights reserved
This manual is issued on a controlled basis to a specific person on the understanding that no part of the Metaswitch Networks product code or documentation (including this manual) will be copied or distributed without prior agreement in writing from Metaswitch Networks.
Metaswitch Networks reserves the right to, without notice, modify or revise all or part of this document and/or change product features or specifications and shall not be responsible for any loss, cost, or damage, including consequential damage, caused by reliance on these materials.
Metaswitch and the Metaswitch logo are trademarks of Metaswitch Networks. Other brands and products referenced herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Where to start
Welcome to the Configuration and Management guide for the Rhino VoLTE TAS, Metaswitch’s carrier-class VoLTE Telephony Application Server (VoLTE TAS) product.
This page will guide you through the process of getting a freshly installed Rhino VoLTE TAS up and running in your network. If this is your first time setting up a Rhino VoLTE TAS, we recommend following the steps laid out below in order.
.1. Familiarize yourself with how configuration works in the Rhino VoLTE TAS
Before getting into configuring the system, you should make sure you are familiar with how configuration in the Rhino VoLTE TAS works, and how to modify the configuration files. Read through Declarative configuration to learn about this.
While using this guide, if you come across a particular field or section in the configuration and you want to find more detailed information about it, click the link on its name in the text. This takes you to its entry in the RVT declarative configuration reference included in this guide.
.2. Set up the Rhino VoLTE TAS platform
The first step is to configure the identity of the platform and the identity of the virtual machines (VM) and VM pools for each node type, and in some cases set up user access and integration between nodes of the system.
Read through The platform for details.
.3. Set up integration with other network systems
The next step is to get the Rhino VoLTE TAS talking to other nodes in the network. Instructions for doing this for each relevant node are in Integration with other systems. Exactly which systems that need to be configured will be specific to your network and requirements.
.4. Set up charging
The next thing to do is set up the charging systems you want to use. There are several different systems for doing charging, including online and offline charging systems. This is also the place where Call Data Record (CDR) generation is configured. Exactly which systems you choose to use will depend on your particular network. See Charging for a description of each system and how to configure it.
.5. Set up home network information
Next, you need to get the Rhino VoLTE TAS up to speed with the details of your network.
This means configuring:
-
how phone numbers should be normalized
-
country codes
-
handling of international and roaming calls
-
reserved URIs and phone numbers.
See Home networks and roaming for instructions.
.6. Set up SCC services
By this point the Rhino VoLTE TAS should be ready to process a basic LTE call. The next step is to get the service centralization and continuity (SCC) services up and running. They are responsible for providing interoperability between the GSM/CDMA and LTE networks.
There are three services that you may need to configure:
-
T-ADS, which selects whether a called subscriber will receive the call over the GSM/CDMA or the LTE (or a Wi-Fi) network.
-
Access transfer, which keeps calls up and running when a subscriber leaves LTE coverage.
-
Reorigination, which allows a subscriber to access and use their VoLTE services while outside of LTE coverage.
.7. Set up MMTel services
The final step for configuring call processing is to get the MultiMedia Telephony (MMTel) services set up. These services provide a variety of ways for operators and subscribers to control calls. Some of the services provided are defined by the 3GPP; others are unique to the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
Not all networks will use all of the available services. So look through the following list and go to the linked page for each service required in your network.
The available MMTel services are:
-
Announcements, which plays announcements to subscribers. Details of all possible announcements that can be played to subscribers must be configured here. Other services count on this configuration to nominate announcements to be played at various times.
-
Call failure announcements, which selects which announcements to play under various call failure conditions.
-
PSAP callback, which provides special handling for return calls from emergency services to a subscriber.
-
Dial plan enforcement, which checks the number dialed by a subscriber to ensure it is valid for the network before permitting a call.
-
Privacy, which controls whether or not each subscriber in a call can see the other’s identity. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Originating Identity Restriction (OIR), Originating Identity Presentation (OIP), Terminating Identity Restriction (TIR), and Terminating Identity Presentation (TIP) services.
-
Conferencing, which enables calls with more than two participants. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Conference (CONF) service.
-
Call barring, which blocks incoming and/or outgoing calls for a subscriber according to set rules. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Outgoing Call Barring (OCB), Incoming Call Barring (ICB), and Anonymous Call Rejection (ACR) services. It provides support for both subscriber and operator defined barring rules.
-
Communication waiting, which notifies a subscriber when they have an incoming call while they are already on another call, and gives them a chance to answer it. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Communication Waiting (CW) service.
-
Communication hold, which manages announcements and media stream bandwidth when a call is put on hold. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Communication Hold (HOLD) service.
-
Communications diversion, which forwards calls to new destinations according to rules set by or for a called subscriber. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Communications Diversion (CDIV) service.
-
Voicemail forwarding, which forwards an incoming call to a subscriber’s nominated voicemail server.
-
Companion device, which provides features supporting LTE connected devices besides a subscriber’s main phone (e.g. smart watches).
-
Vertical service codes, which enables the creation of phone numbers and number prefixes/suffixes that invoke services in the network.
-
Location based dialing, which allows for phone numbers that direct to different places depending on a subscriber’s location.
-
Explicit communication transfer, which allows a subscriber to transfer a call to someone else. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) service.
-
Flexible alerting, which allows a single phone number to be used for multiple people or devices. It covers the functionality for the 3GPP defined Flexible Alerting (FA) service.
-
Session transfer to own device, which allows a subscriber to transfer a call from their current device to a different one without creating a new call.
.8. Set up XCAP
XCAP is an interface used to manage subscriber specific configuration. The Rhino VoLTE TAS incorporates an XCAP server which can be used by both the operator and subscriber to manage subscriber specific configuration data in the HSS. See RVT XCAP for details of how to set this up.
You will also need to set up the authentication gateway so that XCAP requests can be verified. See RVT Authentication Gateway for details.
.9. Set up the IP-SM-GW
Depending on your particular installation, the Rhino VoLTE TAS may include an IP-SM-GW (Internet Protocol Short Message Gateway). The purpose of the IP-SM-GW is to allow SMS messages to cross between GSM and LTE networks. See RVT IP Short Message Gateway (IP-SM-GW) for information about configuring the IP-SM-GW.
Declarative configuration
This section describes how to configure the Rhino VoLTE TAS - that is, the processes of making and applying configuration changes.
It is not intended as a full checklist of the steps to take during an upgrade or full installation - for example, business level change-control processes are not discussed.
The configuration process is based on modifying configuration files, which are validated and sent to a central configuration data store (CDS) using the rvtconfig tool. The nodes in the Rhino VoLTE TAS will poll the CDS, and will pull down and apply any changes.

Initial setup
The initial configuration process starts with the example YAML files distributed alongside the Rhino VoLTE TAS, as described in Example configuration YAML files.
| |
Metaswitch strongly recommends that the configuration files are stored in a version control system (VCS). A VCS allows version control, rollback, traceability, and reliable storage of the system’s configuration. |
If a VCS is not a viable option for you, it is still required and your responsibility every time a change is needed to take backups of the configuration before making any changes. In this case, the recommended approach is to store the full set of configuration files in a reliable cloud storage system (e.g. OneDrive) and to keep the backups in different folders named with a progressive number and a timestamp of the backup date (e.g. v1-20210310T1301).
The rest of the guide is written assuming a VCS is being used to manage the configuration files.
Initially, add the full set of example YAMLs into your VCS as a baseline, alongside the solution definition files (SDFs) described in the RVT VM install guides. You should store all files (including the SDFs for all nodes) in a single directory yamls with no subdirectories.
Making changes
The first step to changing the system configuration is to edit the configuration files, making the desired changes (as described in this guide). You can do this on any machine using a text editor (one with YAML support is recommended). After you have made the changes, they should be recorded to the VCS.
Validating the changes
On the SIMPL VM, as the admin user, change to the directory /home/admin/. Check out (or copy) your yamls directory to this location, as /home/admin/yamls/.
| |
If network access allows, it is recommended to retrieve the files directly from the VCS into this directory, rather than copying them. Having a direct VCS connection means that changes made at this point in the process are more likely to be committed back into the VCS, a critical part of maintaining the match between live and stored configuration. |
At this point, use the rvtconfig tool to validate the configuration used for all relevant nodes.
| |
For more information on the rvtconfig tool, see rvtconfig reference. |
The relevant nodes depend on which configuration files have been changed. To determine the mapping between configuration files and nodes, consult Example configuration YAML files in the install guide for:
The rvtconfig tool is delivered as part of the VM image CSAR file, and unpacked into /home/admin/.local/share/csar/<csar name>/<version>/resources/rvtconfig.
| |
It is important that the rvtconfig binary used to validate a node’s configuration is from a matching release. That is, if the change is being made to a mag node which is at version x.y.z-p1, the rvtconfig binary must be from a version x.y.z CSAR. |
For example, assume a change has been made to the home-network-config.yaml file in a CDMA network. This would require reconfiguration of the smo, mmt-cdma and mag nodes, with all nodes at version 4.0.0. To validate this change, use the following commands from the /home/admin/ directory.
./.local/share/csar/mmt-cdma/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig validate -t mmt-cdma -i ./yamls
./.local/share/csar/smo/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig validate -t smo -i ./yamls
./.local/share/csar/mag/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig validate -t mag -i ./yamlsIf any of the nodes fail validation, update the files to fix the errors as reported, and record the changes in your VCS.
Uploading the changes
Once the file is validated, record the local changes in your VCS.
Next, use the rvtconfig upload-config command to upload the changes to the CDS. As described in Uploading configuration to CDS with upload-config, the upload-config command requires a number of command line arguments.
The full syntax to use for this use case is:
rvtconfig upload-config -c <cds-ip-addresses> -t <node type> -i <config-path> --vm-version <vm_version>
where:
-
<cds-ip-addresses>is the signaling IP address of a TSN node -
<deployment-id>can be found in the relevant SDF -
<node type>is the node being configured, as described above -
<config-path>is the path of the directory containing the YAML and SDFs -
<vm_version>is the version string of the node being configured
As with validation, the rvtconfig executable must match the version of software being configured. Take the example of a change to the home-network-config.yaml as above, on a CDMA network with nodes at version 4.0.0, a deployment ID of prod, and a CDS at IP 192.0.0.1. In this environment the configuration could be uploaded with the following commands (from /home/admin/:
./.local/share/csar/mmt-cdma/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig upload-config -c 192.0.0.1 -t mmt-cdma -i ./yamls --vm-version 4.0.0
./.local/share/csar/smo/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig upload-config -c 192.0.0.1 -t smo -i ./yamls --version--vm-version 4.0.0
./.local/share/csar/mag/4.0.0/resources/rvtconfig upload-config -c 192.0.0.1 -t mag -i ./yamls --vm-version 4.0.0rvtconfig reference
Overview
To apply an update to the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s declarative configuration, the rvtconfig tool is used. rvtconfig applies configuration to the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s configuration data store (CDS). The CDS distributes this configuration to the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s VMs. The rvtconfig tool is provided on the VMs that the RVT runs on and the SIMPL VM.
For further information on configuring the RVT’s virtual machines, refer to the RVT VM Install Guide (CDMA) and the RVT VM Install Guide (GSM).
rvtconfig tool
Configuration YAML files can be validated and uploaded to the CDS using the rvtconfig tool. The rvtconfig tool can be run either on the SIMPL VM or any RVT VM.
On the SIMPL VM, you can find the command in the resources subdirectory of any RVT (tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo) CSAR, after it has been extracted using csar unpack.
/home/admin/.local/share/csar/<csar name>/<version>/resources/rvtconfig
On any RVT VM, the rvtconfig tool is in the PATH for the sentinel user and can be run directly by running:
rvtconfig <command>
The available rvtconfig commands are:
-
rvtconfig validatevalidates the configuration, even before booting any VMs by using the SIMPL VM. -
rvtconfig upload-configvalidates, encrypts, and uploads the configuration to the CDS. -
rvtconfig delete-deploymentdeletes a deployment from the CDS.
Only use this when advised to do so by a Customer Care Representative. -
rvtconfig delete-node-type-versiondeletes state and configuration for a specified version of a given node type from the CDS.
This should only be used when there are no VMs of that version deployed. -
rvtconfig delete-node-type-all-versionsdeletes state and configuration for all versions of a given node type from the CDS.
Only use this after deleting all VMs for a given node type. -
rvtconfig delete-node-type-retain-versiondeletes state and configuration for a given node type from the CDS, except for the specified version. -
rvtconfig list-configdisplays a summary of the configurations stored in the CDS. -
rvtconfig dump-configdumps the current configuration from the CDS. -
rvtconfig print-leader-seedprints the current leader seed as stored in the CDS. -
rvtconfig generate-private-keygenerates a new private key for use in the SDF. -
rvtconfig enter-maintenance-windowdisables VMs' scheduled tasks for a period of time. -
rvtconfig leave-maintenance-windowre-enables VMs' scheduled tasks. -
rvtconfig calculate-maintenance-windowcalculates the required length of a maintenance window for rolling upgrades. -
rvtconfig maintenance-window-statusdisplays a message indicating whether there is an maintenance window period reserved or not. -
rvtconfig export-log-historyexports the quiesce log history from the CDS. -
rvtconfig initconf-logretrievesinitconf.logfile from the specified remote RVT node. -
rvtconfig describe-versionsprints the current values of the versions of the VM found in the config and in the SDF. -
rvtconfig compare-configcompares currently uploaded config with a given set of configuration. -
rvtconfig backup-cdscreates a backup of the CDS database intarformat and retrieves it. -
rvtconfig restore-cdsuses CDS database backup taken withbackup-cdsto restore the CDS database to a previous state. -
rvtconfig set-desired-running-statesetsDesiredRunningStateto stopped/started in MDM.-
If
--state Startedor no--stateis specified, all initconf processes of non-TSN VMs will pause their configuration loops. -
If
--state Stoppedis specified, all initconf processes of non-TSN VMs will resume their configuration loops.
-
-
rvtconfig cassandra-upgradeperforms a cassandra upgrade operation from {cassandra-version-three} to {cassandra-version-four}. This command can only be used after a Major TSN upgrade has been successfully executed to TSN 4.1 and the cassandra version running is {cassandra-version-three}. This operation must be done one TSN node at a time and no parallelization is allowed. -
rvtconfig cassandra-statusprints the cassandra database status of all the specified CDS IP addresses. -
rvtconfig cassandra-upgrade-sstablesupgradessstablesstatus once all TSN 4.1 nodes have been upgraded to Cassandra version {cassandra-version-four} withrvtconfig cassandra-upgrade
Common arguments
Commands that read or modify CDS state take a --cds-address parameter (which is also aliased as --cds-addresses, --cassandra-contact-point, --cassandra-contact-points, or simply -c). For this parameter, specify the management address(es) of at least one machine hosting the CDS database. Separate multiple addresses with a space, for example --cds-address 1.2.3.4 1.2.3.5.
The upload-config and export-audit-history commands read UNRESOLVABLE BXREF: sdf-secrets[secrets] from QSG. If you have not yet uploaded secrets to QSG, you can specify a --secrets-file <file> argument, passing in the path to your secrets file (the YAML file which you pass to csar secrets add). QSG is only available on the SIMPL VM; if running rvtconfig on a platform other than the SIMPL VM, for example on the VM itself, then you must pass the --secrets-file argument.
Commands that read or modify CDS state may also require additional parameters if the CDS endpoints are configured to use authentication and/or SSL encryption as per UNRESOLVABLE BXREF: cassandra-security[Cassandra security configuration]. If the CDS endpoints are configured to use authentication, you must pass the --cds-username argument with your configured password and either the --cds-password or --cds-password-secret-name argument with the configured password or its ID in the secrets file. If the CDS endpoints are configured to use SSL encryption, you must pass the --ssl flag and also pass either the --ssl-ca-certificate or --ssl-ca-certificate-secret-name argument containing a file with the SSL signing certificate, or its ID in the secrets file.
The various delete-node-type commands, and the report-group-status command, require an SSH private key to access the VMs. You can specify this key as either a path to the private key file with the --ssh-key argument, or as a secret ID with the --ssh-key-secret-id argument. If you are running rvtconfig on the SIMPL VM, the recommended approach is to use the secret ID of the SIMPL VM-specific private key that you specified in the SDF (see UNRESOLVABLE BXREF: solution-service-group#simpl-vm-ssh-private-key[SIMPL VM SSH private key] ). Otherwise, use the SSH private key file itself (copying it to the machine on which you are running rvtconfig, and deleting it once you have finished, if necessary).
For more information, run rvtconfig --help. You can also view help about a particular command using, for example, rvtconfig upload-config --help.
rvtconfig limitations
The following limitations apply when running rvtconfig on the SIMPL VM:
-
All files and directories mentioned in parameter values and the secrets file must reside within the root (
/) filesystem of the SIMPL VM. A good way to ensure this is the case is to store files only in directories under/home/admin. -
rvtconfigassumes files specified without paths are located in the current directory. If multiple directories are involved, it is recommended to use absolute paths everywhere. (Relative paths can be used, but may not use..to navigate out of the current directory.)
Verifying and uploading configuration
-
Create a directory to hold the configuration YAML files.
mkdir yamls -
Ensure the directory contains the following:
-
configuration YAML files
-
the Solution Definition File (SDF)
-
Rhino license for nodes running Rhino.
-
| |
Do not create any subdirectories. Ensure the file names match the example YAML files. |
Verifying configuration with validate
To validate configuration, run the command:
rvtconfig validate -t <node type> -i ~/yamls
where <node type> is the node type you want to verify, which can be tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo. If there are any errors, fix them, move the fixed files to the yamls directory, and then re-run the above rvtconfig validate command on the yamls directory.
Once the files pass validation, store the YAML files in the CDS using the rvtconfig upload-config command.
| |
If using the SIMPL VM, the |
Uploading configuration to the CDS with upload-config
To upload the YAML files to the CDS, run the command:
rvtconfig upload-config [--secrets-file <file>] -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -t <node type> -i ~/yamls
[(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version] | --vm-version <vm_version>)] [--reload-resource-adaptors]
| |
The |
If you would like to specify a version, you can use:
-
--vm-versionto specify the exact version of the VM to target (as configuration can differ across a VM upgrade). -
--vm-version-sourceto automatically derive the VM version from the given source. Failure to determine the version will result in an error.-
Use
this-rvtconfigwhen running thervtconfigtool included in the CSAR for the target VM, to extract the version information packaged intorvtconfig. -
Use
this-vmif running thervtconfigtool directly on the VM being configured, to extract the version information from the VM. -
Option
sdf-versionextracts the version value written in the SDF for the given node.
-
If the version is not specified, then the version in the SDF will be compared to the this-rvtconfig or this-vm version (whichever is appropriate given how the rvtconfig command is run). If they match, this value will be used. Otherwise, the command will fail.
| |
Whatever way you enter the version, the value obtained must match the version in the SDF. Otherwise, the upload will fail. |
Any YAML configuration values which are specified as secrets are marked as such in the YAML files' comments. These values will be encrypted using the generated private-key created by rvtconfig generate-private-key and prior to uploading the SDF. In other words, the secrets should be entered in plain text in the SDF, and the upload-config command takes care of encrypting them. Currently this applies to the following:
-
Rhino users' passwords
-
REM users' passwords
-
SSH keys for accessing the VM
-
the SNMPv3 authentication key and privacy key
| |
Use the |
If the CDS is not yet available, this will retry every 30 seconds for up to 15 minutes. As a large Cassandra cluster can take up to one hour to form, this means the command could time out if run before the cluster is fully formed. If the command still fails after several attempts over an hour, troubleshoot Cassandra on the machines hosting the CDS database.
This command first compares the configuration files currently uploaded for the target version with those in the input directory. It summarizes which files are different, how many lines differ, and if there are any configuration changes that are unsupported (for example, changing the VMs' IP addresses). If there are any unsupported configuration changes, the config will not be uploaded. Follow the instructions in the error message(s) to revert unsupported changes in the configuration, then try again.
If the changes are valid, but any files are different, rvtconfig will prompt the user to confirm the differences are as expected before continuing with the upload. If the upload is canceled, and --output-dir is specified, then full details of any files with differences will be put into the given output directory, which rvtconfig creates if it doesn’t already exist.
Changes to secrets and non-YAML files cannot be detected due to encryption; they will not appear in the summary or detailed output. Any such changes will still be uploaded.
You can disable this pre-upload check on config differences using the --skip-diff flag (also aliased as -f).
| |
Restarting resource adaptors
Specify the The If you apply configuration changes that don’t include changes to any fields marked as needing an RA restart, then you do not need to specify the If you apply configuration changes that include changes to such fields, and do not specify the |
Comparing existing configuration in the CDS with compare-config
Compare the configuration in an input directory with the currently uploaded configuration in the CDS using the command:
rvtconfig compare-config -c <cds-mgmt-addresses> -t <node type> -i ~/yamls --output-dir <output-directory>
[--deployment-id <deployment ID>] [--site-id <site ID>] [(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version] | --vm-version <vm_version>)]
This will compare the currently uploaded configuration in the CDS with the configuration in the local input directory.
The deployment ID, site ID, and version of configuration to look up in CDS will be automatically taken from the SDF. These can be overridden by using the --deployment-id, --site-id, and one of the --vm-version-source or --vm-version parameters respectively. For example, you can specify --vm-version <downlevel version> to check what has changed just before running an upgrade, where the version in the input SDF will be the uplevel version.
The files that have differences will be displayed, along with the number of different lines, and any errors or warnings about the changes themselves. Any errors will need to be corrected before you can run rvtconfig upload-config.
The command puts the full contents of each version of these files into the output directory, along with separate files showing the differences found. The command ignores non-YAML files and any secrets in YAML files. The files in this output directory use the suffix .local for a redacted version of the input file, .live for a redacted version of the live file, and .diff for a file showing the differences between the two.
| |
The contents of the files in the output directory are reordered and no longer have comments; these won’t match the formatting of the original input files, but contain the same information. |
Deleting configuration from the CDS with delete-deployment
Delete all deployment configuration from the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig delete-deployment -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> [--delete-audit-history]
| |
Only use this when advised to do so by a Customer Care Representative. |
| |
Only use this after deleting all VMs of the deployment within the specified site. Functionality of all nodes of this type and version within the given site will be lost. These nodes will have to be deployed again to restore functionality. |
Deleting state and configuration for a specific node type and version from the CDS with delete-node-type-version
Delete all state and configuration for a given node type and version from the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig delete-node-type-version -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --site-id <site-id> --node-type <node type>
(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version -i ~/yamls] | --vm-version <vm_version>) (--ssh-key SSH_KEY | --ssh-key-secret-id SSH_KEY_SECRET_ID) [-y]
| |
The argument -i ~/yamls is only needed if sdf-version is used. |
| |
Only use this after deleting all VMs of this node type and version within the specified site. Functionality of all nodes of this type and version within the given site will be lost. These nodes will have to be deployed again to restore functionality. |
Deleting all state and configuration for a specific node type from the CDS with delete-node-type-all-versions
Delete all state and configuration for a given node type from the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig delete-node-type-all-versions -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --site-id <site-id>
--node-type <node type> (--ssh-key SSH_KEY | --ssh-key-secret-id SSH_KEY_SECRET_ID) [--delete-certificates] [-y]
| |
Only use this after deleting all VMs of this node type within the specified site. Functionality of all nodes of this type within the given site will be lost. These nodes will have to be deployed again to restore functionality. |
| |
The --delete-certificates option should only be used when advised by a Customer Care Representative. |
Deleting historical state and configuration for a given node type from the CDS with delete-node-type-retain-version
Remove all state and configuration relating to a versions of the node type other than the specified version from CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig delete-node-type-retain-version -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --site-id <site-id> --node-type <node-type>
(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version -i ~/yamls] | --vm-version <vm_version>) (--ssh-key SSH_KEY | --ssh-key-secret-id SSH_KEY_SECRET_ID) [-y]
| |
The argument -i ~/yamls is only needed if sdf-version is used. |
| |
The version specified in this command must be the only running VM version for this node type. i.e. do not use during an upgrade or rollback when multiple versions of the same node type may be running. All state and configuration relating to other versions will be deleted from CDS. |
Removing unused Rhino-generated keyspaces
Following an upgrade or rollback, you may wish to clean up keyspaces in the Cassandra ramdisk database from version(s) that are no longer in use. This conserves memory and disk space.
To clean up unused keyspaces, use the following command:
rvtconfig remove-unused-keyspaces -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> -g <group-id> [-y]
| |
Group ID syntax: RVT-<node type>.<site ID>Example: RVT-tsn.DC1Here, <node type> can be tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo. |
Confirm that the active VM versions that the command identifies are correct. rvtconfig removes keyspaces relating to all other versions from Cassandra.
Listing configurations available in the CDS with list-config
List all currently available configurations in the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig list-config -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id>
This command will print a short summary of the configurations uploaded, the VM version they are uploaded for, and which VMs are commissioned in that version.
Retrieving configuration from the CDS with dump-config
Retrieve the VM group configuration from the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig dump-config -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --group-id <group-id>
(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version -i ~/yamls -t <node type>] | --vm-version <vm_version>)
[--output-dir <output-dir>]
| |
Group ID syntax: RVT-<node type>.<site ID>Example: RVT-tsn.DC1Here, <node type> can be tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo. |
If the optional --output-dir <directory> argument is specified, then the configuration will be dumped as individual files in the given directory. The directory can be expressed as either an absolute or relative path. It will be created if it doesn’t exist.
If the --output-dir argument is omitted, then the configuration is printed to the terminal.
| |
The arguments -i ~/yamls and -t <node type> are only needed if sdf-version is used. |
Displaying the current leader seed with print-leader-seed
Display the current leader seed by running the command:
rvtconfig print-leader-seed -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --group-id <group-id>
(--vm-version-source [this-vm | this-rvtconfig | sdf-version -i ~/yamls -t <node type>] | --vm-version <vm_version>)
| |
Group ID syntax: RVT-<node type>.<site ID>Example: RVT-tsn.DC1Here, <node type> can be tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo. |
The command will display the current leader seed for the specified deployment, group, and VM version. A leader seed may not always exist, in which case the output will include No leader seed found. Conditions where a leader seed may not exist include:
-
No deployment exists with the specified deployment, group, and VM version.
-
A deployment exists, but initconf has not yet initialized.
-
A deployment exists, but the previous leader seed has quiesced and a new leader seed has not yet been selected.
| |
The arguments -i ~/yamls and -t <node type> are only needed if sdf-version is used. |
Generating a secrets-private-key for Encrypting Secrets with generate-private-key
Some configuration, for example Rhino or REM users' passwords, are configured in plaintext, but stored encrypted in CDS for security. rvtconfig automatically performs this encryption using a secrets private key which you configure in the SDF. This key must be a Fernet key, in Base64 format. Use the following rvtconfig command to generate a suitable secrets private key:
rvtconfig generate-private-key
Add the generated secrets private key to your secrets input file when UNRESOLVABLE BXREF: sdf-secrets#adding-secrets[adding secrets to QSG].
Maintenance window support
The rvtconfig enter-maintenance-window and rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window commands allow you to pause and resume UNRESOLVABLE BXREF: scheduled-tasks[scheduled tasks] (Rhino restarts, SBB/activity cleanup, and Cassandra repair) on the VMs for a period of time. This is useful to avoid the scheduled tasks interfering with maintenance window activities, such as patching a VM or making substantial configuration changes.
To start a maintenance window, use
rvtconfig enter-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id> [--hours <hours>]
-
The <site-id> is in the form
DC1toDC32. It can be found in the SDF. -
The number of hours defaults to 6 if not specified, and must be between 1 and 24 hours.
Once started, the maintenance window can be extended by running the same command again (but not shortened). rvtconfig will display the end time of the maintenance window in the command output. Until this time, all scheduled tasks on all VMs in the specified site will not be run.
| |
Any scheduled tasks which are in progress at the time the maintenance window is started will continue until they are finished. If the maintenance window is starting around the time of a scheduled task as configured in the YAML files, it is advisable to manually check that the task is complete before starting maintenance (or run the |
When the maintenance window is complete, use the following command:
rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>
Scheduled tasks will now resume as per their configured schedules.
To check whether or not a maintenance window is currently active, use the following command:
rvtconfig maintenance-window-status -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>
Calculating the required length of a maintenance window with calculate-maintenance-window
The rvtconfig calculate-maintenance-window commands allows you to estimate how long an upgrade or rollback is expected to take, so that an adequate maintenance window can be scheduled.
To calculate the recommended maintenance window duration, use
rvtconfig calculate-maintenance-window -i ~/yamls -t <node type> -s <site-id> [--index-range <index range>]
-
The <site-id> is in the form
DC1toDC32. It can be found in the SDF. -
If
--index-rangeis not specified, a maintenance window for upgrading all VMs will be calculated. If only some VMs are to be upgraded, specify the--index-rangeargument exactly as it will be specified for thecsar updatecommand to be used to upgrade the subset of VMs. For example, if only nodes with indices 0, 3, 4 and 5 are to be upgraded, the argument is--index-range 0,3-5.
Retrieving VM logs with export-log-history
During upgrade, when a downlevel VM is removed, it uploads Initconf, Rhino and SGC logs to the CDS. The log files are stored as encrypted data in the CDS.
| |
Only the portions of the logs written during quiesce are stored. |
Retrieve the VM logs for a deployment from the CDS by running the command:
rvtconfig export-log-history -c <tsn-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> --zip-destination-dir <directory>
--secrets-private-key-id <secrets-private-key-id>
| |
The --secrets-private-key-id must match the ID used in the SDF (secrets-private-key-id). |
| |
The Initconf, Rhino and SGC logs are exported in unencrypted zip files. The zip file names will consist of VM hostname, version, and type of log. |
Viewing the values associated with the special sdf-version, this-vm, and this-rvtconfig versions with describe-versions
Some commands, upload-config for example, can be used with the special version values sdf-version, this-vm, and this-rvtconfig.
-
Calling
sdf-versionextracts the version from the value given in the SDF for a given node. -
The
this-vmoption takes the version of the VM the command is being run from. This can only be used when the commands are run on a node VM. -
Using
this-rvtconfigextracts the version from the rvtconfig found in the directory the command is being run from. This can only be used on a SIMPL VM.
To view the real version strings associated with each of these special values:
rvtconfig describe-versions [-i ~/yamls]
Optional argument -i ~/yamls is required for the sdf-version value to be given. If it is called, the sdf-version will be found for each node type in the SDF. If a node type is expected but not printed this may be because the config yaml files for that node are invalid or not present in the ~/yamls directory.
If a special version value cannot be found, for example if this-vm is run on a SIMPL VM or the optional argument is not called, the describe-versions command will print N/A for that special version.
Reporting group status, to help guide VM recovery
This command reports the status of each node in the given group, providing information to help inform which approach to take when recovering VMs.
It connects to each of the VMs in the group via SSH, as well as querying the CDS service. It then prints a detailed summary of status information for each VM, as well as a high level summary of the status of the group.
It does not log its output to a file. When using this command to aid in recovery operations, it’s good practice to redirect its output to a file locally on disk, which can then be used as part of any root cause analysis efforts afterwards.
On the SIMPL VM, run the command as follows, under the resources dir of the unpacked CSAR:
./rvtconfig report-group-status -c <cds-mgmt-addresses> -d <deployment-id> \
--g <group-id> --ssh-key-secret-id <simpl-private-key-id>| |
Group ID syntax: RVT-<node type>.<site ID>Example: RVT-tsn.DC1Here, <node type> can be tsn, shcm, mag, mmt-gsm, mmt-cdma or smo. |
Gathering diagnostics and initconf log files
It is possible to obtain diagnostic files from RVT nodes with the command rvtconfig gather-diags. These diagnostic files include system files and solution configuration files, are packaged as a tar.gz file and deposited in the given output directory. Depending on the node type there will be different kinds of solution configuration files. These files can be crucial to troubleshoot problems on the VMs.
./rvtconfig gather-diags --sdf <SDF File> -t <node type> --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> --ssh-username sentinel --output-dir <output-directory>
If you need to quickly check the initconf.log file from a certain VM or VMs, it is possible to do it with the command rvtconfig initconf-log. This command executes a tail on the initconf.log file of the specified VM or VMs and dumps it to the standard output.
rvtconfig initconf-log --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> --ssh-username sentinel --ip-addresses <Space separated VM IP address list> --tail <num lines>
Operate the TSN Cassandra Database
From RVT 4.1-3-1.0.0, the TSN nodes can be deployed with Cassandra version {cassandra-version-three} or {cassandra-version-four}. Both Cassandra versions are installed in the VM Image, but only one is active. The commands rvtconfig cassandra-upgrade and rvtconfig cassandra-upgrade-sstables allow you to perform a Cassandra upgrade from {cassandra-version-three} to {cassandra-version-four} on a running TSN VM 4.1-3-1.0.0 or higher. These two commands must only be run if the target TSNs are running Cassandra {cassandra-version-three}.
To upgrade a single TSN node from {cassandra-version-three} to {cassandra-version-four} you can run ./rvtconfig cassandra-upgrade --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> --ip-addresses <TSN Address> for every TSN VM, one by one, and not in parallel.
Once all TSN nodes have been upgraded to {cassandra-version-four}, we must perform a sstables upgrade operation with the following command ./rvtconfig cassandra-upgrade-sstables --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> --ip-addresses <TSN Addresses>
Additionally the command rvtconfig cassandra-status prints the cassandra database status for the specified CDS IP addresses. Here is a couple of examples:
-
./rvtconfig cassandra-status --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> --ip-addresses <TSN Address 1> <TSN Address 2> …
CDS Backup and Restore operations.
From RVT 4.1-3-1.0.0, the TSNs' CDS database can be backed up and restored. This provides a faster recovery procedure in case TSN upgrades go wrong.
To backup the CDS of a running TSN cluster, run ./rvtconfig backup-cds --sdf /home/admin/uplevel-config/sdf-rvt.yaml --site-id <site ID> --output-dir <backup-cds-bundle-dir> --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> -c <CDS address> <CDS auth args>
To restore the CDS of a running TSN cluster, run ./rvtconfig restore-cds --sdf /home/admin/uplevel-config/sdf-rvt.yaml --site-id <site ID> --snapshot-file <backup-cds-bundle-dir>/tsn_cassandra_backup.tar --ssh-key-secret-id <SSH key secret ID> -c <CDS Address> <CDS auth args>
| |
Only use restore-cds when advised to do so by a Customer Care Representative. |
Control initconf configuration loop in non-TSN nodes.
During maintenance windows which involve upgrading TSN nodes, the command rvtconfig set-desired-running-state allows you stop/start the configuration tasks performed by the initconf that read from the CDS database in all non-TSN VMs. This operation does not stop the non-TSN VMs or the initconf process within it. But it instructs the initconf to pause or resume, the configuration tasks, while operating normally under traffic.
To pause initconf configuration tasks of all non-TSN VMs, run ./rvtconfig set-desired-running-state --sdf /home/admin/uplevel-config/sdf-rvt.yaml --site-id <site ID> --state Stopped.
To resume initconf configuration tasks of all non-TSN VMs, run ./rvtconfig set-desired-running-state --sdf /home/admin/uplevel-config/sdf-rvt.yaml --site-id <site ID> --state Started.
RVT system configuration
This section describes how to set up the Rhino VoLTE TAS system.
The platform
Set the platform operator name
Within common-config.yaml, in the common section, set your platform operator name:
platform-operator-name: MetaswitchConfigure session replication
Session replication allows established calls to continue if the node that previously processed the call becomes unavailable.
Within either sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config, in the sentinel-volte section, set session-replication-enabled
session-replication-enabled: trueIf enabling on a system where session replication was previously disabled, please contact Metaswitch support.
Review the SIP session settings
Within either sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config, in the session-refresh section, check that these values are appropriate and change if necessary.
# Configuration for the Session Refresh feature.
session-refresh:
# The interval of the periodic timer (in seconds).
timer-interval-seconds: 30
# Period of no activity for leg tp refresh (in seconds).
refresh-period-seconds: 570
# Whether the session should be refreshed using UPDATE requests,
# as long as the endpoint allows UPDATE requests.
refresh-with-update-if-allowed: true
# Maximum allowed duration of a call (in seconds).
max-call-duration-seconds: 86400Configuring integration within the system
For each node type deployed, you need to configure the names of the cluster and individual virtual machines using data from the node type’s site definition files (SDF) which were created as part of the VM Install process. In some cases you also need to configure user access and node specific integration parameters.
Parameters
This table cross references the node types and which parameters need configuring.
Parameter |
Applicable node types |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MAG |
MMT GSM |
MMT CDMA |
SHCM |
TSN |
SMO |
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||
✔ |
||||||
Per node parameters |
||||||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||
✔ |
✔ |
|||||
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||
✔ |
||||||
✔ |
||||||
✔ |
||||||
deployment-id and site-id
deployment-id and site-id must be set to match the parameters of the same name in the SDFs created as part of the VM Installation process.
cassandra-contact-points
Leave the cassandra-contact-points blank unless directed otherwise by Metaswitch support.
additional-rhino-jvm-options
Leave the additional-rhino-jvm-options blank unless directed otherwise by Metaswitch support.
rhino-auth and rem-auth
Some node types have lists of rhino-auth and/or rem-auth authentication data. These are used to access rhino and rem respectively. See the appropriate reference for details.
Per node parameters
These parameters are in a list called virtual-machines, with one entry per VM.
vm-id
The vm-id values under virtual-machines must be the same as the name values under instances in the SDF.
rhino-node-id
For nodes supporting a Rhino cluster, specify the node-id for the Rhino rhino-node-id on each VM.
scheduled-rhino-restarts
For nodes that run Rhino, you can optionally specify that Rhino should be automatically restarted on a regular schedule. This can be useful if you observe resource leaks (memory, file handles, activities, and so on) in Rhino which require a restart to clean up the leftover resources.
The available options for scheduled restarts are daily, weekly, or monthly schedules. The following shows example configuration for each:
# a daily schedule
scheduled-rhino-restarts:
time-of-day: "02:00"
# or, a weekly schedule
scheduled-rhino-restarts:
time-of-day: "02:00"
day-of-week: "Wednesday"
# or, a monthly schedule
scheduled-rhino-restarts:
time-of-day: "02:00"
day-of-month: 9| |
|
To disable automatic Rhino restarts, omit the scheduled-rhino-restarts section from the configuration. By default, restarts are disabled.
per-node-diameter-rf and per-node-diameter-ro
To set the origin-host value for Diameter Rf per-node-diameter-rf and Diameter Ro per-node-diameter-ro protocols, see Charging.
diameter-zh-origin-host
To set the origin-host value for Diameter Zh protocol diameter-zh-origin-host, see Diameter Zh interface.
diameter-sh-origin-host
To set the origin-host value for Diameter diameter-sh-origin-host Sh protocol, see Diameter Sh interface.
Integration with other systems
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires integration with several other services in an IMS network to utilize its full capability. This section discusses the several configuration options to integrate Rhino VoLTE TAS operations with other parts of the network. You will usually find the information required in your network design/topology document.
- I-CSCF integration
- ATCF integration
- SS7 integration
- HSS integration
- HLR integration
- Diagnostics systems integration
- Media server integration
- IP-SM-GW specific integration
What it does
Integration of the Rhino VoLTE TAS to your network involves editing interface specific addresses and values for the relevant Rhino VoLTE TAS YAML configurations that are being used. For example, a VoLTE network with GSM networking support will require configuration changes to the sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml file. If there is an interface that is left unused by the network, it can be disabled by deleting or commenting out the specific interface’s section.
Further information on how to specify and edit configuration YAML files is specified in the guide on how to use the declarative configuration system. In addition, there are further options available beyond system integration, such as tuning message timeouts, in the configuration reference guide.
| |
The example configurations in this section use valid, but placeholder, values that will not work with your network. You will need to replace the values according to your network setup. |
I-CSCF integration
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires access to the I-CSCF (Interrogating Call Session Control Function) to integrate into the IMS network.
Setting up the I-CSCF interface
The configuration for the I-CSCF to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the icscf-config.yaml file.
In the icscf section, configure the i-cscf-uri value. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating the Rhino VoLTE TAS with the network’s I-CSCF.
icscf:
# The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function.
# For MMT, the Conf and ECT features will automatically add an "lr" parameter to it.
# The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the I-CSCF.
i-cscf-uri: sip:icscf@icscfhost.example:5060ATCF integration
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires integration with the ATCF (Access Transfer Control Function) in the IMS network for SCC AS functionality.
Setting up the ATCF interface
The configuration for the ATCF to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml file.
In the service-continuity section, configure the stn-sr values. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating the Rhino VoLTE TAS with the network’s ATCF.
sentinel-volte:
scc:
# Service continuity configuration.
service-continuity:
# STN-SR.
stn-sr: "6421999999"SS7 integration
To communicate with the SS7 protocols in a network, you need to set up the SS7 signaling gateway client (SGC).
Integration with the Rhino VoLTE TAS and IN interfaces requires an SCCP address assigned to it.
Setting up the SS7 SGC
The SS7 SGC in the Rhino VoLTE TAS provides support for communicating with the SS7 protocols in a network. The configuration for it is located in the sgc-config.yaml file.
If the SGC is being reconfigured after its initial configuration has been applied, you need to follow the steps in Reconfiguring the SGC before applying the new configuration.
M3UA interface configuration
The SGC uses the M3UA (MTP Level 3 User Adaptation Layer) interface for handling networking between the Rhino VoLTE TAS and the network’s SS7 signaling.
General configuration
This configuration determines what the SGC’s attributes are for SS7 signaling. This will be what systems outside of the Rhino VoLTE TAS require to direct SS7 signaling towards the SGC.
What you need
The following must be defined in the configuration:
-
❏ The
local-portM3UA endpoint used for SS7 signaling. -
❏ The
sccp-variantused by the SGC. EitherITUorANSI. -
❏ The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s local
point-code.
The following may be defined in the configuration:
-
❏ The value for the
nationalindicator to use for SCMG (SCCP management) messages.-
This would override the defaults of
INTERNATIONALfor ITU-T SCCP, andNATIONALfor ANSI SCCP.
-
-
❏ The value for the M3UA
network-indicatorfield.-
This would override the default of
INTERNATIONAL
-
Example configuration
The example configuration given in the snippet below sets the SGC in the Rhino VoLTE TAS to:
-
Have the SGC’s local endpoint port at 2905
-
Use the ITU variant for SCCP addresses
-
Have a local point code of
5 -
The default national indicator for ITU-T SCCP messages is used — which is
INTERNATIONAL -
The default network-indicator field is used, which is
INTERNATIONAL.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
local-port: 2905
sccp-variant: ITU
point-code: "5"| |
The supported format of the point code depends on the sccp-variant. Contact Metaswitch support for further details if you would like to use these other forms. |
If sccp-variant is… |
format of point-code is… |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
simple numeric, quoted |
|
Remote peer configuration
For details on how to configure remote peers in the Rhino VoLTE TAS, see SGC M3UA remote peer addresses.
Global title translation configuration
For details on how to configure global title translation in the Rhino VoLTE TAS, see SGC M3UA global title translation.
SGC properties
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports further configuration of the SGC via the sgc-properties field. This field offers additional configuration of the SGC beyond the given declarative configuration.
For further configuration of the SGC, contact Metaswitch support for more details.
deployment-config:sgc:
sgc-properties:Hazelcast
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports using Hazelcast for communication in the cluster of subsystems in the SS7 SGC stack. The declarative configuration in the hazelcast section allows for:
-
the number of backup instances in the cluster to be defined.
| |
Unless specified by Metaswitch support, the backup-count must be left unspecified. If incorrectly set, the cluster can experience data loss. The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s VMs will default to a valid and working backup-count. |
-
an optional password for the Hazelcast subsystem.
| |
The password will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the site definition file (SDF). |
deployment-config:sgc:
hazelcast:
backup-count:
password:For further configuration of using Hazelcast in the SGC, contact Metaswitch support for more details.
sgcenv
The declarative configuration supports configuring the port for which the internal sgc CLI in the SMO nodes is binded to. This is set in the jmx-port field.
deployment-config:sgc:
sgcenv:
jmx-port: 55555Setting up for IN interfaces
The configuration for the IN signaling to the Rhino VoLTE TAS is in the sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml file.
In the service-centralisation section, configure the inbound-ss7-address value. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating the Rhino VoLTE TAS with the SS7 network.
sentinel-volte:
# Service Centralisation configuration.
service-centralisation:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
inbound-ss7-address: type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=123456| |
If the inbound-ss7-address contains a pc= parameter, that parameter’s value must be the same as the point-code value in sgc-config.yaml. See General configuration. |
The SS7 point code needs to be used consistently in other places.
-
In
sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yamlorsentinel-volte-cdma-config.yamlfile, if theinbound-ss7-addressvalue contains apc=parameter, that parameter’s value must be the same as thepoint-codevalue insgc-config.yaml. -
In
sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yamlfile, if theoriginating-addressvalue contains apc=parameter, that parameter’s value must be the same as thepoint-codevalue insgc-config.yaml. For more details, see step 3 of IP-SM-GW Initial configuration.
| |
Do not quote the point code in SCCP addresses, e.g. use pc=5, not pc="5". Quoting is only required when the point code is a standalone field value in a YAML configuration file. |
There are also requirements for assigning SSNs correctly. Contact Metaswitch support for details.
SGC M3UA remote peer addresses
The Rhino VoLTE TAS SGC requires the configuration of the networking details of its remote peers. These remote peers host application servers (AS) that interact with the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s SS7 signaling.
What you need
-
❏ The remote peer addresses that act as the signal transfer points (STP) in the network.
-
❏ The AS(s) accessible via these remote peer addresses.
-
❏ The AS destination point code(s) (DPC).
-
❏ The subsystem number(s) (SSN) to monitor for each of the DPCs.
Remote peer configuration
The remote M3UA peer application servers in the network are designated in the peers section. Multiple remote peers to the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s SGC can be defined here.
What you need
For each remote M3UA AS peer, define the following:
-
❏ A unique
idfor each remote peer. -
❏ The set of IPv4 addresses that belong to the server peer. This is defined in
remote-ips. -
❏ Whether a specific SMO node or any SMO node in the Rhino VoLTE TAS should communicate with the peer’s set of IP addresses. This is defined in
node-index. -
❏ At least one AS ID defined in
as-idwhich is related to the remote peer. This is defined inapplication-servers.
Optional configuration may include:
-
❏ The
portfor the remote peer. -
❏ Whether the SGC takes an active role in M3UA state maintenance or not with the peer. This is set in the
state-maintenance-rolefield. -
❏ Whether the SGC connects to the remote peer (client mode) or waits for a connection from the remote peer (server mode). This is set in the
conn-typefield. -
❏ Whether the SGC is an IP server Process (IPSP) for the peer or not. This is set in the
is-ipspfield. -
❏ Whether to define the
asp-idto use in ASP-UP/DOWN messages. -
❏ For a specified AS
as-id, whether to send Destination State Audit (DAUD) when the Application Server Process (ASP) goes active in this AS. This is set in thedaud-on-asp-acfield.
Example configuration
In the following example snippet, two remote peers are configured.
They are both configured to:
-
the same port number of 2906
-
have no restriction on what SMO node in the Rhino VoLTE TAS they can communicate with
-
correspond to the same AS identifier that is defined in the
application-serversexample -
each have their own distinct sets of IP addresses.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
peers:
- id: 'STP-1'
remote-ips:
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.14.144.71
- 10.14.144.134
port: 2906
application-servers:
- as-id: 'NN-AS'
- id: 'STP-2'
remote-ips:
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.14.144.81
- 10.14.144.144
port: 2906
application-servers:
- as-id: 'NN-AS'Defined application servers
The SGC interacts with known application server(s) for routing SS7 signaling. These ASs are accessible on the remote peer addresses configured in peers. The declarative configuration defines these ASs in the application-servers list.
What you need
For each M3UA AS hosted on these remote peers, define the following:
-
❏ A unique
idfor each AS that the SGC interacts with. This value is only used by the declarative configuration and is not exposed externally. -
❏ A
default-priorityfor any routes for the AS. -
❏ The list of
dpc-idsthat may be accessible from the AS. This includes for each DPC:
Optional configuration may include:
-
❏ Whether the AS would assume an active or passive
traffic-maintenance-role. -
❏ Whether the AS has a
routing-context. -
❏ Whether to not allow the AS to be become active until there is at least one connected TCAP for each specified SSN. This is accessed in the
precond-ssnsfield.
Defined DPCs
The SGC interacts with known DPCs for routing SS7 signaling through application servers. Multiple DPCs can be defined in the dpcs section.
What you need
For each designated DPC in the network interacting with the SGC, we must define:
Optional configuration may include the DPC’s:
Example configuration
In the following example snippet, the SGC is configured to communicate with a remote DPC used by the AS.
SGC has the remote DPC configured to have:
-
an configuration specific identifier of the configured DPC 'alias-2-233-3' to connect to the AS configuration
-
an actual DPC code of
5963 -
a DPC MUSS of 252
-
a DPC MSS of 245.
| |
For ITU variant, specify point codes as quoted integers, e.g. For ANSI variant, specify point codes in |
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
dpcs:
- id: 'alias-2-233-3'
dpc: "5963"
muss: 252
mss: 245Concerned point code notifications
The defined Concerned Point Codes (CPCs) are specified DPCs that are notified if a local SSN status changes. Multiple CPCs can be defined in the cpcs section.
Example configuration
In the following example snippet, the SGC is configured to communicate with a remote CPC.
SGC has the remote CPC configured to have:
-
an actual DPC code of
5963 -
the SGC is to monitor the SSNs 8 and 146 for that DPC.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
cpcs:
- dpc: "5963"
ssns:
- 8
- 146Setting up SGC M3UA remote peer addresses
I want to …
Connect any sized SGC cluster to a dual-homed dual-node STP cluster
There are two peer STP nodes to configure for the remote-peers.
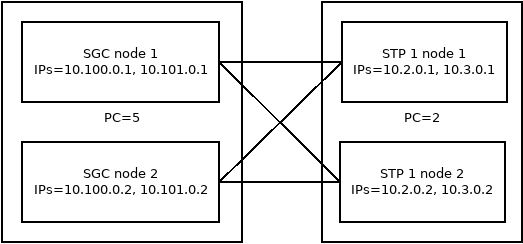
-
Add the set of IP addresses for each STP node to the
ipslist. -
Ensure that any SGC instance can connect to the STP cluster by setting for each remote peer their
node-indexto-1. -
Add the declarative configuration’s internal unique identifer of the STP AS to both remote peers'
application-servers.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
peers:
- id: 'to-STP-1-node-1'
remote-ips:
# All SGCs have connections to this member of the STP pair.
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.2.0.1
- 10.3.0.1
application-servers:
# This STP is a member of AS 'STP-1'
- as-id: 'STP-1'
- id: 'to-STP-1-node-2'
remote-ips:
# All SGCs have connections to this member of the STP pair.
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.2.0.2
- 10.3.0.2
application-servers:
# This STP is a member of AS 'STP-1'
- as-id: 'STP-1'For configuring the STP cluster’s DPC, add:
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
dpcs:
- id: "DPC-2"
dpc: "2"There is one AS operating on the STP cluster to configure for.
-
Add an AS instance with the same
idas used in both remote peers'application-servers.
For the AS’s route configuration, add:
-
The
default-priorityfor routing messages. -
The declarative configuration’s identifier for the STP’s DPC in the AS’s
dpc-idslist.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
peers:
application-servers:
- id: 'STP-1'
routes:
default-priority: 5
dpc-ids:
# The STP's own DPC.
- id: 'DPC-2'Connect an SGC cluster to two separate STPs that are connected to a remote peer used in load balancing mode
There are two peer STP nodes to configure for the remote-peers.
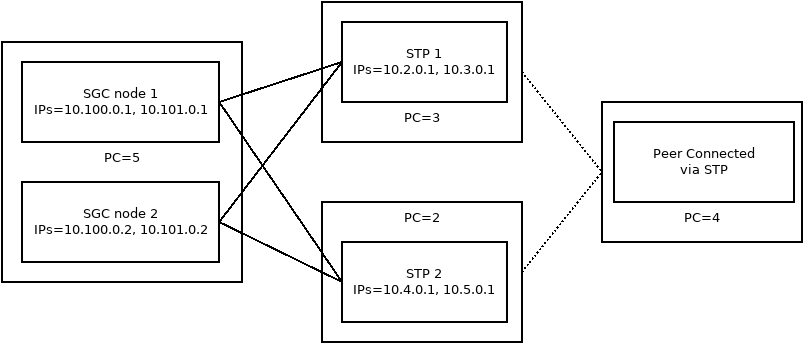
-
Add the set of IP addresses for each STP node to the
ipslist. -
Ensure that any SGC instance can connect to the STP cluster by setting for each remote peer their
node-indexto-1. -
Add the declarative configuration’s internal unique identifer each STP’s AS to their respective remote peer configuration
application-serversfield.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
peers:
- id: 'to-STP1'
remote-ips:
# All SGCs have connections to this STP.
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.2.0.1
- 10.3.0.1
application-servers:
# This STP is a member of AS 'STP-1'
- as-id: 'STP-1'
- id: 'to-STP-1-node-2'
remote-ips:
# All SGCs have connections to this STP.
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.4.0.1
- 10.5.0.1
application-servers:
# This STP is a member of AS 'STP-2'
- as-id: 'STP-2'For configuring each STP’s DPC, add:
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
dpcs:
- id: 'DPC-2'
dpc: '2'
- id: 'DPC-3'
dpc: '3'
- id: 'DPC-4'
dpc: '4'There are two application servers operating on the STP cluster to configure for.
-
Add an AS instance
idcorresponding to each remote peer’sapplication-servers.
For each AS’s route configuration, add:
-
The
default-priorityfor routing messages. -
The declarative configuration’s identifier for each STP’s DPC in the AS’s
dpc-idslist.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
remote:
application-servers:
- id: 'STP-1'
routes:
default-priority: 5
dpc-ids:
# The STP's own DPC.
- id: 'DPC-3'
# Add further DPC IDs here if the SGC should send DAUD for them (accessed via this STP).
- id: 'DPC-4'
- id: 'STP-2'
routes:
default-priority: 5
dpc-ids:
# The STP's own DPC.
- id: 'DPC-2'
# Add further DPC IDs here if the SGC should send DAUD for them (accessed via this STP).
- id: 'DPC-4'SGC M3UA global title translation
The SGC translates global titles (GTs) in incoming and outgoing SCCP messages. The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports creating specialized rules for translating these inbound and outbound messages.
Inbound GT translation
The SGC determines how GT translation occurs for inbound SCCP messages. Multiple incoming called addresses can be configured for the SGC.
For where the incoming called address for an SCCP message is a GT, it is:
-
matched against the configuration to determine whether it should be processed, and
-
may then determine which SSN should receive it.
Configuration
The configuration for the inbound GT translation matching rules are in the inbound section.
For matching inbound called addresses, you may configure:
-
❏ A unique
idfor the address for the configuration. This value is only used by the declarative configuration and is not exposed externally. -
❏ The called party address information to match on the inbound SCCP message digits. This is defined in the
addrinfofield. -
❏ For matching the incoming address, whether to allow the address information to match on the prefix or have to match the entire address. This is set in the
is-prefixfield. -
❏ The SCCP message’s nature of address (
natofaddr) code required for a match. The code is defined in the RFC 3868 Global Title Section. -
❏ The SCCP message’s numbering plan code (
numplan) required for a match. The code is defined in the RFC 3868 Global Title Section. -
❏ The SCCP message’s translation type code (
trtype) required for a match. The code is defined in the RFC 3868 Global Title Section. -
❏ The local
ssnto route matched messages towards.
Setting up inbound GT translation
I want to …
Send all inbound SCCP CdPA which have addressed digits=123456, in an international number format, in an ISDN numbering plan, and an unknown translation type to SSN 146
In the global-title, inbound section, add the inbound matching rule with a unique identifier.
Ensure that the following are set for the inbound rule:
-
id. -
addrinfois set to digits123456. -
is-prefixis set to false as we are only accepting an exact match. -
natofaddrcorresponds to Nature of Address for international numbers. -
numplancorresponds to the numbering plan code for the ISDN numbering plan. -
trtypecorresponds- to the unknown translation type. -
ssn.
deployment-config:sgc:
m3ua:
global-title:
inbound:
- id: 'to-sentinel-volte-gsm'
addrinfo: '123456'
is-prefix: false
natofaddr: 4
numplan: 1
trtype: 0
ssn: 146Send inbound SCCP CdPA addressed to digits prefixed with 123456 to SSN 146
In the global-title, inbound section, add the inbound matching rule with a unique identifier.
global-title:
inbound:
- id: 'inbound-rule-example'
addrinfo: '123456'
is-prefix: true
ssn: 146Send two different inbound SCCP CdPA addressed messages to different local SSNs
In the global-title, inbound section, add each inbound matching rule with their own unique identifiers.
In this case we have two inbound translation rules. For all inbound SCCP CdPA addressed to:
-
digits=1234567890, the message is sent to the local SSN 8.
inbound:
# All inbound SCCP CdPA addressed to digits=1234567890 will be sent to local SSN 8
- id: 'SSN_6'
addrinfo: '1234567890'
is-prefix: false
ssn: 8-
digits=2143658709, the message is sent to the local SSN 146.
inbound:
# All inbound SCCP CdPA addressed to digits=2143658709 will be sent to local SSN 146
- id: 'B'
addrinfo: '2143658709'
is-prefix: false
ssn: 146Outbound GT translation
The SGC determines how GT translation occurs for outbound SCCP messages. Multiple outgoing called addresses can be configured for the SGC.
When the outgoing SCCP called party address (SCCP CdPA) is set to ri=GT, global title translation function is invoked. The function uses the SCCP called party address to determine which destination point code (DPC) the M3UA layer should route the message to.
The parameters of the SCCP message are compared against the matcher rules defined in the configuration. If a match occurs, the message will be routed towards the DPC defined in one of the translation rules associated with that matcher.
Optionally after outbound GT translation, the GT rewriter rule(s) may modify the parameters of the SCCP called party address.
Configuration
There are three different types of rules defined for outbound GT translation.
These are:
-
The matching rule, which decides what SCCP addresses are to be translated. This invokes specified translation rules.
-
The translation rule, which decides the DPC to route and routing priority. This invokes specified rewriter rules.
-
The rewriter rule, which decides what is replaced and transformed in the SCCP address.
The configuration for the outbound GT translation matching rules are in the outbound section.
The scope of these rules overlap for parts of the SCCP message and interact with each other. The following table demonstrates how each configurable rule may interact with each other and the SCCP message.
| Scope of Rule on SCCP message | Matching Rule matchers |
Translation Rule translations |
Rewrite/Replace Rule rewriters |
|---|---|---|---|
Rule ID |
Matching rule |
Configuration specific translation rule |
Configuration specific rewrite rule |
Address Information |
Match to specific |
Replace with |
|
Treat digits to match as a prefix |
|||
GT Encoding |
Replace |
||
GTI Global Title Indicator |
Replace |
||
Nature of Address (code defined in RFC 3868) |
Match |
Replace |
|
Numbering Plan (code defined in RFC 3868) |
Match |
Replace |
|
Translation Type (code defined in RFC 3868) |
Match |
Replace |
|
SSN |
|||
Route on SSN, GT, or no change |
Replace |
||
Message DPC |
Add |
||
Local Routing |
|
||
Relative Rule Priority |
Rule |
||
Rules to Invoke |
Invoke |
Invoke |
To configure outbound GT translation, you must:
-
❏ Configure the matching rules to activate the translation rules on the outbound GTs.
-
❏ Configure the translation rule(s).
In addition, to rewrite the outbound GT after translation, you must:
-
❏ Ensure that the translation rule(s) activates the appropriate rewrite rule(s).
-
❏ Configure the rewrite rule(s).
| |
The declarative configuration supports several different matching, translation, and rewriter rules. This allows for different numbers to be routed to different DPCs and have their SSN rewritten. |
Setting up outbound GT translation
I want to …
Route all outbound SCCP messages to a specific DPC
In the global-title, outbound section:
-
Add an outbound matcher rule that matches with any outgoing message.
-
Add
is-prefix=trueto allow any dialled digits to be matched. -
Add to the matcher rule’s list of
translationsthe unique identifier for the translation rule to invoke it.
-
global-title:
outbound:
matchers:
rules:
- id: '1'
is-prefix: true
translations:
- 'all'-
Add a translation rule that is invoked by the matcher rule to the intended DPC.
| |
The priority for a translation rule is relative to other translation rules defined in the declarative configuration. |
global-title:
outbound:
translations:
- id: 'all'
dpc: "5963"
priority: 5Route all SCCP CdPA with digits starting with 44123456 to primary and backup DPCs
In the global-title, outbound section:
-
Add an outbound matcher rule that matches with any outgoing message.
-
The
addrinfois set to the digit string44123456. -
The
is-prefixis set true so SCCP addressed digits starting with44123456are accepted. -
The invoked
translationsrules list has the identifier for the primary DPC'to_4'and the secondary DPC'to_100'added.
-
outbound:
matchers:
rules:
# All outbound SCCP CdPA with ri=GT and digits starting with 44123456 will be sent to DPC 4 (primary) and DPC 100 (backup)
- id: 'to_44123456*'
addrinfo: '44123456'
is-prefix: true
translations:
- 'to_4'
- 'to_100'-
Add a translation rule that is invoked by the matcher rule to route to the primary DPC.
outbound:
translations:
- id: 'to_4'
dpc: '4'
priority: 10-
Add a translation rule that is invoked by the matcher rule to route to the backup DPC.
outbound:
translations:
- id: 'to_100'
dpc: '100'
priority: 5Route all SCCP CdPA with digits starting with 44666 to a primary DPCs and set their SSN to 146
In the global-title, outbound section:
-
Add an outbound matcher rule that matches with any outgoing message.
-
The
addrinfois set to the digit string44666. -
The
is-prefixis set true so SCCP addressed digits starting with44666are accepted. -
The invoked
translationsrules list has the identifier for the translation rule'rewrite'which will invoke the rewrite rule.
-
outbound:
matchers:
rules:
# All outbound SCCP CdPA with ri=GT and digits starting with 44666 will be sent to DPC 4 and have the SSN rewritten to 146
- id: 'to_44666*'
addrinfo: '44666'
is-prefix: true
translations:
- 'rewrite'-
Add a translation rule that is invoked by the matcher rule that will route to the primary DPC and invoke a rewrite rule.
-
The
idis set to match the translation rule invoked by the matcher rule. -
The
dpcis filled with the primary DPC in the network. -
The
rewriter-idis set to invoke therewrite_44666_to_have_ssnrewrite rule.
-
outbound:
translations:
- id: 'rewrite'
dpc: '4'
rewriter-id: 'rewrite_44666_to_have_ssn'-
Add a rewrite rule that is invoked by the translation rule that will make the messages route on SSN 146.
outbound:
rewriters:
- id: 'rewrite_44666_to_have_ssn'
route-on: SSN
ssn: 146By default, only translate outbound SCCP messages that have a telex numbering plan, and an unknown nature of address and translation type
These given number codes correspond to a telex numbering plan, and an unknown nature of address and translation type as per RFC 3868 Section 3.10.2.3.
outbound:
matchers:
# All addresses we care about are natofaddr=0, numplan=4 and trtype=0 so we can save some typing
defaults:
natofaddr: 0
numplan: 4
trtype: 0Reconfiguring the SGC
This section applies in the case where the Rhino VoLTE TAS SGC has previously received its initial configuration and now requires reconfiguration.
| |
If only the SGC’s SNMP subsystem requires reconfiguration it is recommended to follow the procedure at Reconfiguring the SGC’s SNMP Subsystem as that process does not cause a full SGC outage. |
Reconfiguration of the SGC requires a SMO or an SGC VM with version 4.0.0-9-1.0.0 or newer. Reconfiguration of the SGC component in older VMs is not supported.
| |
Reconfiguring the SGC will cause a full SS7 outage in live deployments. |
There are two stages to reconfiguring the SGC:
Even if you have reconfigured the SGC before it is essential that you follow both of these steps.
Reviewing the SGC configuration
This section applies in the case where the Rhino VoLTE TAS SGC received its initial configuration on a VM version less than or equal to 4.0.0-22-1.0.0 or was most recently reconfigured following the SGC reconfiguration procedure on a VM with version less than or equal to 4.0.0-22-1.0.0.
If the VM is part of a new deployment with VM version greater than or equal to 4.0.0-23-1.0.0 this section does not apply.
Overview
Previous VM releases have contained defects that resulted in some SGC configuration parameter values being applied incorrectly. Multiple subsequent VM releases have contained fixes for these defects and configuration is now correctly applied.
VMs retain their pre-existing SGC configuration during upgrade. This means that VMs that were initially configured using a release with the configuration defects, that were then upgraded, still retain the defective configuration. This ensures that upgrades don’t fail due to changes in how configuration is interpreted.
However, this MOP takes the SGC back to an unconfigured state, and then applies the new configuration. This means that there is a possibility that configuration parameters subject to the defect may be applied differently (correctly) compared with previously (incorrectly), resulting in the SGC behaving differently.
In some cases the difference in behavior can mean a loss of service.
Generally, this is only likely to be a problem when both:
-
The configuration YAML contains an error that sets an integer field to
0that should have been omitted or set tonull. -
The VM configuration defect treats
0as being absent ornull, when it should be treating it as an actual0.
The two together result in the VM exhibiting the behavior of a null or absent value.
Once the VM configuration defect is rectified and the VM reconfigured, the 0 will be treated as a 0.
To avoid this, follow these instructions to review the configuration.
Reviewing the configuration
It is strongly recommended that the existing configuration is reviewed and thoroughly tested prior to executing this MOP on the live site.
Steps to carry out:
-
Examine
m3uaconfiguration for any integer parameter values that are currently set to0. Determine if and how this parameter is affected by configuration defects by consulting the table below.-
If you wish to implement the correct behavior then no further action is required. Do not carry out the operation in the
action to retain incorrect behaviorcolumn. -
If you wish to retain the previous incorrect behavior, apply the action documented in the
action to retain incorrect behaviorcolumn. -
If the parameter is not documented in this table, check that it is an integer value, and that
0is a permitted value. Only integer values are affected. Contact support for further advice.
-
-
precond-ssnswere not applied prior to version4.0.0-18-1.0.0, regardless of their value. To retain that behavior, delete allprecond-ssnselements. To obtain the corrected behavior leave them configured as-is.
The configuration parameters that don’t correctly honor a value of 0 are:
| Fixed in | Parameter name | Incorrect behavior | Correct behavior | Action to retain incorrect behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
rewriter does not set |
rewriter sets |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
rewriter does not set |
rewriter sets |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
rewriter does not set |
rewriter sets |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
rewriter does not set |
rewriter sets |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
rewriter does not set |
rewriter sets |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
matcher may match on configured defaults if |
matcher will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
matcher may match on configured defaults if |
matcher will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
matcher may match on configured defaults if |
matcher will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
Initconf did not converge. |
Initconf will converge, and the priority will be set to |
N/A |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
inbound rule will match any |
inbound rule will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
inbound rule will match any |
inbound rule will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
inbound rule will match any |
inbound rule will only match a |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 |
|
ASP management messages will be sent without an |
ASP management messages will be sent with the |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 and 4.0.0-23-1.0.0 |
|
the |
the |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
4.0.0-10-1.0.0 and 4.0.0-23-1.0.0 |
|
the |
The route will be configured with a priority of |
Remove the parameter and its value. |
Applying the new SGC configuration
This section applies in the case where the Rhino VoLTE TAS SGC has previously received its initial configuration and now requires reconfiguration.
Reconfiguration of the SGC requires a SMO or an SGC VM with version 4.0.0-9-1.0.0 or newer. Reconfiguration of the SGC component in older VMs is not supported.
| |
Reconfiguring the SGC will cause a full SS7 outage in live deployments. |
| |
You must carry out the process documented here exactly as documented. It should not be skipped or modified. |
What you need
-
❏ The
sgctoolutility (available on the SGC or SMO VM). -
❏ The IP address of one of the deployment’s TSN nodes (
<cds_address>). -
❏ The deployment ID (
<deployment_id>). -
❏ The group ID (
<group_id>).
Process overview
Here is the high-level view of the required steps:
-
Review the configuration.
-
Stop the OCSS7 SGCs.
-
Verify that the OCSS7 SGCs are stopped.
-
Delete the OCSS7 SGCs.
-
Clear OCSS7 SGC-related state from the TSN nodes (CDS).
-
Apply the new configuration.
Process detail
1. Review the configuration
| |
Do not skip this step. Applying the configuration without reviewing it may result in loss of service. |
Previous releases of the Rhino VoLTE TAS VM contained defects that resulted in the configuration being incorrectly applied. These defects have since been corrected. The reconfiguration process removes all previous configuration, including the incorrectly applied configuration, and replaces it with correctly applied configuration. This may result in changes in behavior, which in some cases could result in loss of service if the configuration was affected by this defect and is not adjusted appropriately.
See reviewing the SGC configuration for full details.
2. Stop the OCSS7 SGCs
You need to stop every SGC in the cluster. On each SGC or SMO node, issue the following command:
$ sudo systemctl stop ocss7
| |
The following message may be safely ignored:
|
3. Verify that the OCSS7 SGCs are stopped
-
Check the systemctl status of the
ocss7service. On each SGC or SMO node issue the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status ocss7
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 systemd[1]: Stopping Start the OCSS7 SGC...
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: Stopping processes:
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: SGC:2027
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: DAEMON:2017
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: Initiating graceful shutdown for [2027] ...
Dec 22 15:45:28 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: Sleeping for max 32 sec waiting for graceful shutdown to complete.
Dec 22 15:45:39 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: Graceful shutdown successful
Dec 22 15:45:39 tst-sgc-1 ocss7[5029]: Shutdown complete (graceful)
Dec 22 15:45:39 tst-sgc-1 systemd[1]: Stopped Start the OCSS7 SGC.-
Check the OCSS7 SGC’s view of its own status. On each SGC or SMO node issue the following command:
$ ~/ocss7/<deployment_id>/<instance_id>/current/bin/sgc status
SGC is down4. Delete the OCSS7 SGCs
On each SGC or SMO node, remove the OCSS7 SGC installation:
$ rm -rf /home/sentinel/ocss7/<deployment_id>/| |
Do not delete |
5. Clear OCSS7 SGC-related state from the TSN nodes (CDS)
Remove OCSS7 SGC configuration data that was persisted to the Cassandra Data Store (CDS). This only needs to be carried out once per SGC or SMO cluster.
-
Run the
sgctoolfrom one SGC or SMO VM:
$ /opt/tasvmruntime-py/bin/sgctool clear-config --cds-address <cds_address> --deployment-id <deployment_id> --group-id <group_id>
The CDS SGC state has been cleared| |
The |
6. Apply the new configuration
You may now apply the new configuration using rvtconfig, as documented in Declarative configuration.
Reconfiguring the SGC’s SNMP Subsystem
This section applies in the case where the Rhino VoLTE TAS SGC has previously received its initial configuration and only the SNMP subsystem requires reconfiguration.
| |
If other SGC configuration has changed it is necessary to follow the Reconfiguring the SGC procedure. |
| |
Reconfiguring the SNMP subsystem will cause an SNMP outage in live deployments. This includes other SNMP services, such as Rhino and Initconf. Full SNMP service will resume once the procedure is complete. |
There are three situations where the SGC’s SNMP subsystem may require reconfiguring:
SNMP reconfiguration without upgrade or rollback
This process should be followed when the SGC SNMP subsystem requires reconfiguration. It consists of two phases:
-
Removal of existing SNMP configuration.
-
Application of desired SNMP configuration.
For each affected node type (SGC or SMO) the steps to follow are:
-
Complete Preparation for SGC SNMP reconfiguration.
-
Modify the
snmp-config.yamlto the desired final state and upload the modified configuration usingrvtconfig.
Upgrading when SNMPv3 is enabled
| |
This process is only required when both:
|
The process consists of two phases:
-
Preparation and removal of the existing SNMP configuration.
-
Performing the upgrade.
For each affected node type (SGC or SMO) the steps to follow are:
-
Complete Preparation for SGC SNMP reconfiguration.
-
Continue with the upgrade procedure, ensuring that the uplevel SNMP configuration reflects the desired final state. No additional steps are required; SNMP will automatically be configured and enabled as the nodes are upgraded.
Rolling back when SNMPv3 is enabled
| |
This process is only required when both:
|
The process consists of two phases:
-
Preparation and removal of the existing SNMP configuration.
-
Performing the rollback.
For each affected node type (SGC or SMO) the steps to follow are:
-
Then, continue with the rollback procedure, ensuring that the downlevel SNMP configuration reflects the desired final state. No additional steps are required; SNMP will automatically be configured and enabled as the nodes are rolled back.
Preparation for SGC SNMP reconfiguration
This step is common to all SGC SNMP reconfiguration processes and must only be followed when directed by those processes. This step removes the existing SNMP configuration from the SGC in preparation for a new configuration.
| |
Reconfiguring the SNMP subsystem will cause a full SNMP outage in live deployments for the affected node type. This includes other services that provide SNMP agents and notifications, such as Rhino and Initconf. |
For the node type being prepared, the steps to follow are:
-
Ensure that you have a backup copy of the active cluster’s original
snmp-config.yamlconfiguration file. -
Modify the active cluster’s
snmp-config.yamlto disable all SNMP:deployment-config:snmp: v1-enabled: false v2c-enabled: false v3-enabled: false -
Upload the modified configuration using
rvtconfigand wait for Initconf to converge. -
Remove the SGC’s existing SNMP configuration.
Remove the SGC’s existing SNMP configuration
| |
Perform this process once, on one VM of the type being reconfigured. The process affects the whole SGC cluster. |
| |
When performed as part of a rollback operation this process may be performed on any uplevel or downlevel cluster member where Initconf has successfully converged (i.e. "gone Green"). |
Automatic
The sgc_snmp_cleaner tool is included on newer VMs by default at /opt/tasvmruntime-py/bin/sgc_snmp_cleaner. If not present on your VM, request it from your support representative and follow the installation instructions provided with it.
It must be executed on an active VM in the cluster to be reconfigured
[sentinel@tst-smo-1 ~]$ /opt/tasvmruntime-py/bin/sgc_snmp_cleaner --deployment-id tstChecking the output
The script will report on the SNMP nodes, SNMP targets and USM users that it finds and removes. Successful completion will indicate:
SNMP configuration successfully clearedUnsuccessful completion may indicate one of the following:
-
USM user configuration still exists: -
Target address configuration still exists: -
SNMP node configuration still exists:
Example successful output from the script for a single node test cluster:
[sentinel@tst-smo-1 ~]$ PYTHONPATH=/opt/tasvmruntime-py/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ python3 sgc_snmp_cleaner.py --deployment-id tst
Found SNMP node: tst-smo-1_v2c
- Removed SNMP node: tst-smo-1_v2c
Found SNMP node: tst-smo-1_v3
- Removed SNMP node: tst-smo-1_v3
Found SNMP target: 172.30.102.143#162#v3#UdpIpv4#trap#v3user
- Removed SNMP target: 172.30.102.143#162#v3#UdpIpv4#trap#v3user
Found SNMP target: 172.30.102.143#162#v2c#UdpIpv4#trap#tst
- Removed SNMP target: 172.30.102.143#162#v2c#UdpIpv4#trap#tst
Found USM user: snmp_user
- Removed USM user: snmp_user
SNMP configuration successfully clearedIn the event that execution is unsuccessful follow the manual procedure.
Manual
-
Log into one VM of the type being reconfigured.
-
Start the SGC CLI:
/home/sentinel/ocss7/<deployment_id>/<deployment_id>-<node_id>/current/cli/sgc-cli.sh -
Then, view the configured SNMP nodes by executing the SGC CLI command
display-snmp-node.172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> display-snmp-node: Found 3 object(s): +--------------+----------+--------+--------+---------------+---------------+---------------+----------+--------------+---------------+--------+ |oname |dependenci|enabled |active |node |transport-type |host |port |snmp-version |community |extended| | |es | | | | | | | | |-traps | +--------------+----------+--------+--------+---------------+---------------+---------------+----------+--------------+---------------+--------+ |tst-smo-1_v3 |0 |true |true |tst-smo-1 |UDP |172.30.102.140 |11103 |v3 |tst |true | +--------------+----------+--------+--------+---------------+---------------+---------------+----------+--------------+---------------+--------+ |tst-smo-2_v3 |0 |true |true |tst-smo-2 |UDP |172.30.102.141 |11103 |v3 |tst |true | +--------------+----------+--------+--------+---------------+---------------+---------------+----------+--------------+---------------+--------+ |tst-smo-3_v3 |0 |true |true |tst-smo-3 |UDP |172.30.102.142 |11103 |v3 |tst |true | +--------------+----------+--------+--------+---------------+---------------+---------------+----------+--------------+---------------+--------+For each line in the returned table, execute the following two SGC CLI commands to disable and remove those nodes:
-
disable-snmp-node: oname=<oname> -
remove-snmp-node: oname=<oname>For instance:
172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> disable-snmp-node: oname=tst-smo-1_v3 OK snmp-node disabled. 172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> remove-snmp-node: oname=tst-smo-1_v3 OK snmp-node removed.
-
-
Similarly, view the configured SNMP notification targets by executing the SGC CLI command
display-target-address. For each line in the returned table, executeremove-target-address: oname=<oname>. -
Finally, view the configured SNMP USM users by executing the SGC CLI command
display-usm-user. For each line in the returned table, executeremove-usm-user: oname=<oname>. -
Check that no SNMP configuration remains by executing the following commands and verifying that there are no lines in the returned tables.
-
display-snmp-node -
display-target-address -
display-usm-userFor instance:
172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> display-snmp-node Found 0 objects. 172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> display-target-address: Found 0 objects. 172.30.102.140:55555 tst-smo-1> display-usm-user: Found 0 objects.
-
In the event that manual cleanup is unsuccessful please contact your support representative.
HSS integration
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires access to the HSS to acquire provisioned subscriber data for configuring network wide or subscriber specific functionality and options.
Diameter Sh interface
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires integration with the HSS using the Diameter Sh interface to be able to acquire provisioned subscriber data.
What you need
-
❏ The origin realm to use when sending Diameter Sh messages.
-
❏ The destination realm for where sent Diameter Sh messages go. This will be the HSS’s realm.
-
❏ The HSS destination peers' destination-hostname, port, and protocol-transport type.
-
❏ A sample user identity to be used for performing a health check on the interface.
-
❏ A unique origin host domain name for each VM in the pool to use when sending Diameter Sh messages.
Setting up the Diameter Sh interface
The configuration for the HSS to Rhino VoLTE TAS Diameter Sh interface is in the shcm-service-config.yaml file.
In the shcm-service section, configure the diameter-sh section. The example configuration given here indicates the format of the required configuration.
# Service configuration for the Sh Cache Microservice
shcm-service:
##
## Diameter Sh Configuration
##
diameter-sh:
# The origin realm to use when sending messages.
origin-realm: opencloud.com
# The value to use as the destination realm.
destination-realm: opencloud
# The HSS destination peers.
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: hss.opencloud.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
# The user identity that is put in the diameter message to the HSS when a health check is performed
health-check-user-identity: sip:shcm-health-check@example.com-
The
protocol-transportvariable is an enum. The valid values for this field are described in the reference guide’s section on Diameter Shprotocol transport type. -
The
metricvariable is an integer that determines which peer to route to. -
The
health-check-user-identityis a user identity that should also be configured in the HSS. This will allow health checks to query the HSS and confirm functionality without affecting non-test subscribers.
The configuration for the Diameter Sh origin host values is in the shcm-vmpool-config.yaml file.
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "ShCM group"
deployment-config:shcm-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vApp parameter
site-id: DC1
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-shcm-1
diameter-sh-origin-host: shcm1.shcm.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
rhino-node-id: 101
- vm-id: example-shcm-2
diameter-sh-origin-host: shcm2.shcm.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
rhino-node-id: 102-
For each virtual machine, set the
diameter-sh-origin-hostto a unique value.
Diameter Zh interface
The Diameter Zh interface allows IMS devices to authenticate with the network without any user interaction required.
What you need
-
❏ The origin realm to use when sending Diameter Zh messages.
-
❏ The destination realm for where sent Diameter Zh messages go. This will be the HSS’s realm.
-
❏ The HSS destination peers' destination-hostname, port, and protocol-transport type.
-
❏ A unique origin host domain name for each VM in the pool to use when sending Diameter Sh messages.
Setting up the Diameter Zh interface
The configuration for the HSS to Rhino VoLTE TAS Diameter Zh interface is in the bsf-config.yaml file.
In the bsf section, configure the zh-diameter section. The example configuration given here indicates the format of the required configuration.
bsf:
zh-diameter:
origin-realm: opencloud.com
destination-realm: opencloud.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: hss.opencloud.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1-
The
protocol-transportvariable is an enum. The valid values for this field are described in the reference guide’s section on Diameter Zhprotocol transport type. -
The
metricvariable is an integer that determines which peer to route to.
The configuration for the Diameter Zh origin host values is in the mag-vmpool-config.yaml file.
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "MAG cluster"
# there are some pieces of software on this VM type that require clustering and
# knowing each other's IP addresses, for example Rhino
deployment-config:mag-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
xcap-domains:
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc123.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.org
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc124.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.org
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
# Define one or more REM users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# each REM user maps to a Rhino user, when REM logs into Rhino
rem-auth:
- username: remreadonly
real-name: REM read only user
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-mag-1
rhino-node-id: 101
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag1.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mag-2
rhino-node-id: 102
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag2.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mag-3
rhino-node-id: 103
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag3.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
rem-debug-logging-enabled: false-
For each virtual machine, set the
diameter-zh-origin-hostto a unique value.
HLR integration
Integration with an HLR allows the Rhino VoLTE TAS to gather subscriber data for circuit switched (CS) domain calls.
What you need
For GSM or CDMA networks:
-
❏ The SCCP address of the HLR in the network.
-
❏ A unique SCCP address for the Rhino VoLTE TAS in the network.
For GSM networks:
-
❏ An MLC SCCP address for the Rhino VoLTE TAS for outgoing MAP requests to the HLR.
-
❏ If a separate address for the MSC is required, an MSC SCCP address for the Rhino VoLTE TAS for outgoing MAP requests to the HLR.
-
❏ Whether to use the configured destination
hlr-addressas the exact HLR address when establishing a MAP dialog, or to replace the digits in the address with the subscriber MSISDN.
For CDMA networks:
-
❏ The Market ID and Switch Number to be set on the MSCID of outgoing requests to the HLR.
Setting up the HLR interface
The Rhino VoLTE TAS to HLR interface configuration is in three files:
-
hlr-config.yamldetails the destination configuration of messages sent to the HLR Rhino VoLTE TAS. -
sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yamldetails the origin configuration of GSM compatible messages sent from the Rhino VoLTE TAS. -
sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yamldetails the origin configuration of CDMA compatible messages sent from the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
The GSM and CDMA YAML files share an overlap of configuration scope.
Destination configuration
The destination configuration specifies the HLR SCCP address for where messages are sent from the Rhino VoLTE TAS to the HLR.
In the hlr section, configure the hlr-address value. The example configuration given here indicates the required SCCP address format.
hlr:
hlr-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=6"Origin configuration
The origin configuration specifies details of the Rhino VoLTE TAS that are communicated to the HLR.
In the hlr-connectivity-origin section, configure the originating-address value. The example configuration given here indicates the format of the required configuration for either CDMA or GSM with:
-
The SCCP originating address of the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
-
The timeout value for opening a dialog with the HLR.
sentinel-volte:
# Origin configuration for this application when connecting to the HLR.
# The actual HLR SCCP address (destination) is in the hlr-configuration.yaml file
hlr-connectivity-origin:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
originating-address: type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=7,ssn=146
# The timeout value for opening the MAP dialog with the HLR (in milliseconds).
map-invoke-timeout-milliseconds: 5000GSM network configuration
There is a GSM specific configuration required for networking with an HLR for the GSM network.
In the hlr-connectivity-origin section, configure the mlc-address value. The example configuration given here indicates what is needed for integrating with an HLR used in a GSM network with:
-
The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s MLC originating address.
-
The destination HLR address has the digits replaced with the Subscriber MSISDN rather than the exact destination address as configured in
hlr-address. -
A dedicated MSC originating address that is different to the MLC address.
sentinel-volte:
hlr-connectivity-origin:
# GSM specific configuration.
gsm:
# The address of the MLC (Sentinel).
mlc-address: address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN
# Indicates if 'hlr-config/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR address, or have
# its digits replaced with the MSISDN of the subscriber.
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: true
# Originating SCCP address when acting as an MSC, used when
# establishing the MAP dialog. Will default to the value of
# 'originating-address' when not present. Typically used to set a
# different originating SSN when sending a SendRoutingInformation
# message to the HLR.
msc-originating-address: address=654444444,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDNCDMA network configuration
There is a CDMA specific configuration required for networking with an HLR for the CDMA network.
In the hlr-connectivity-origin section, configure the market-id and switch-number values. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating with an HLR used in a CDMA network. This example designates for the MSCID set on outgoing CDMA requests to the HLR using:
-
The market ID value.
-
The switch number value.
sentinel-volte:
hlr-connectivity-origin:
# CDMA specific configuration.
cdma:
# The market ID value to be used in the MSCID set on outgoing CDMA requests to the HLR
market-id: 1
# The switch number value to be used in the MSCID set on outgoing CDMA requests to the HLR
switch-number: 1Diagnostics systems integration
SAS integration
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports Metaswitch’s SAS (Service Assurance Service) integration.
What you need
-
❏ To chose whether or not to activate SAS tracing.
-
❏ The IP addresses or DNS hostnames of SAS servers to connect the Rhino VoLTE TAS to.
Setting up the SAS interface
The configuration for the SAS to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the sas-config.yaml file.
In the sas section, configure the servers list. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating the Rhino VoLTE TAS with SAS servers in a network.
sas:
# Whether SAS is enabled ('true') or disabled ('false')
enabled: true
# Parameters for connecting to SAS
sas-connection:
# List of SAS servers. Either IP addresess or DNS hostnames.
# Needs to be specified in a non-MDM deployment.
servers:
- 10.10.10.10
- 10.10.10.11
- sas.example.comSNMP integration
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports integration with SNMP based systems.
What you need
-
❏ The version of SNMP to be used.
-
❏ If using SNMP v2c, the SNMP community value.
-
❏ The SNMP agent details such as location and contact address.
-
❏ If using SNMP notifications, each notification target’s host, port, and specifc SNMP version.
Setting up the SNMP interface
The configuration for the SNMP to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the snmp-config.yaml file.
In the snmp section, configure the targets list. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating the Rhino VoLTE TAS with SNMP services in the network.
snmp:
# Enable SNMP v1 (not recommended)
v1-enabled: false
# Enable SNMP v2c
v2c-enabled: true
# Enable SNMP v3
v3-enabled: false
# SNMP Community. Required for SNMP v2c
community: clearwater
# SNMP agent details
agent-details:
location: Unknown location
contact: support.contact@invalid.com
# SNMP Notifications
notifications:
# Enable SNMP Notifications
enabled: true
# SNMP notification targets. Normally this is the address of your MVS
targets:
- version: v2c
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 162Media server integration
Announcement server integration
To play announcement media to a user, the Rhino VoLTE TAS requires the URI of the announcement media server.
Setting up the announcement server interface
The configuration for the announcement server to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml file.
In the announcement section, configure the announcements-media-server-uri value, as shown in the example.
sentinel-volte:
mmtel:
announcement:
# Media server URI, used when playing announcements
# This is distinct from mrf-uri for Conferencing
announcements-media-server-uri: sip:annc-audio@localhost:5260;lr;transport=tcpConferencing media server integration
To utilize conferencing functionality in the Rhino VoLTE TAS, a media server that specializes in handling conferencing needs to be specified.
Setting up the conferencing media server interface
The configuration for the conferencing media server server to Rhino VoLTE TAS interface is in the sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml file.
In the conferencing section, configure the conference-mrf-uri value, as shown in the example.
sentinel-volte:
mmtel:
# Configuration for conferencing.
conferencing:
# The URI of the Media Resource Function used for Conferencing.
# This is distinct from the media-server-uri used for Announcements
# The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the MRF.
conference-mrf-uri: sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060IP-SM-GW specific integration
MSC integration
There is a MAP interface between the IP Short Message Gateway (IP-SM-GW) in the Rhino VoLTE TAS and the MSC.
What you need
-
❏ A template default SMSC address for MAP messaging.
-
❏ A unique SCCP address for the Rhino VoLTE TAS in the network.
-
❏ An international address for the Rhino VoLTE TAS in the network.
Setting up the MSC interface
The Rhino VoLTE TAS to MSC interface configuration is in the sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml file.
In the map-messaging section, configure the template-smsc-address, originating-address and ipsmgw-as-msc-address values. The example configuration given here indicates input for what is needed for integrating with the MSC for SMS.
sentinel-ipsmgw:
# MAP messaging configuration
map-messaging:
# Template SMSC address. The digits are replaced by those of the received SMSC address.
template-smsc-address: "type=C7,ri=gt,digits=0,ssn=8,national=false,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,gti=4,tt=0"
# IPSMGW SCCP address.
originating-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=147"
# IPSMGW international address.
ipsmgw-as-msc-address: "address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN"Charging
What it does
The charging service communicates with a number of possible systems to charge subscribers for making and receiving calls. The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports three different charging methods:
-
offline charging using Diameter Rf to send reports to a Charging Data Function (CDF)
-
online charging using Diameter Ro protocol to communicate with an Online Charging Server (OCS)
-
online charging using SIP to CAP translation to communicate with a charging Service Control Point (SCP) in a GSM network.
Online and offline charging can be used simultaneously. It is also possible to use both types of supported online charging at the same time. The Rhino VoLTE TAS does not support CDMA based charging systems, so for those networks only Diameter based charging is available.
Additionally, the Rhino VoLTE TAS writes Charging Data Records (CDRs) for every call. These contain metadata about the call suitable to use for charging purposes.
Diameter Rf offline charging
What it does
When Diameter Rf charging is in use, the Rhino VoLTE TAS communicates with a CDF to deliver interim CDRs using Accounting Request (ACR) messages. If the communication with the CDF fails, ACR messages are held locally until it is restored.
Interim CDRs must be enabled to use Diameter Rf offline charging.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to Diameter Rf offline charging in the sentinel-volte/charging/rf-charging section.
What you need
-
❏ The release version of Diameter Rf to use with the offline charging system.
-
❏ The origin realm to use when sending Diameter Rf messages. This is the TAS’s realm.
-
❏ The destination realm to use when sending Diameter Rf messages. This is the offline charging system’s realm.
-
❏ The CDF peers' hostnames, ports, and transport protocols.
Setting up Diameter Rf based offline charging
I want to…
Use Diameter Rf offline charging
In the charging section, add an rf-charging section with:
rf-charging:
diameter-rf:
diameter-rf-release: Vcb0
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: sctp
metric: 1-
The
diameter-rf-releaseto use. -
The Diameter
origin-realmfor the Rhino VoLTE TAS. -
The Diameter
destination-realmfor the offline charging system. -
A Diameter
destination-peerslist that correspond to CDF servers. There must be at least one entry, and for each entry the following values must be set:-
the
destination-hostnamefor the CDF -
the
portfor the CDF -
the
protocol-transportto use with the CDF. -
the
metricto use for this CDF peer.
-
You must ensure that all per-node-diameter-rf sections in the MMT cluster configuration are present and not commented out. The sections are located:
-
for GSM deployments, in
mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml -
for CDMA deployments, in
mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
per-node-diameter-rf:
diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgDisable Diameter Rf offline charging
In the charging section, remove or comment out the entire rf-charging section:
# rf-charging:
# diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-release: Vcb0
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: sctp
# metric: 1You must comment out any per-node-diameter-rf sections in the MMT cluster configuration, which are located:
-
for GSM deployments, in
mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml -
for CDMA deployments, in
mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgDiameter Ro online charging
What it does
When Diameter Ro charging is in use, the Rhino VoLTE TAS communicates with one or more online charging systems (OCS) in real time to authorize credit for calls. While a call is in progress, Diameter Ro messages are exchanged with the OCS whenever more credit is required, or when there are significant changes in the call that could impact the cost (e.g. video is enabled). If at any point the OCS refuses to grant credit, the call is ended.
While the method for enabling Diameter Ro charging differs between GSM and CDMA based deployments, there is no functional difference in charging behavior as the GSM and CDMA parts of the network are not involved.
Diameter Ro charging announcements
When using Diameter Ro online charging, the Rhino VoLTE TAS supports playing announcements when:
-
the subscriber attempts to make a call when they are running low on credit
-
the subscriber attempts to make a call without having any credit
-
the subscriber begins to run low on credit during a call
-
the subscriber runs out of credit during the call
-
the OCS instructs the TAS to do so.
Low credit announcements are played when the OCS’s response to a credit check includes a low balance indicator. After playing a low credit announcement, the Rhino VoLTE TAS waits for a time before doing another credit check. The time period is set in the charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds field.
Out of credit announcements are played when the OCS sends an "Out of Credit" response to a credit check. The call is terminated after playing an out of credit announcement.
The OCS instructs announcements to be played by including announcement information in its response to a credit check. These announcements will take precedence over the low and out of credit announcements configured in the Rhino VoLTE TAS. If the announcement information came in a "Out of Credit" response, the call will end after the announcement has been played.
When configuring the charging service to play an announcement, you only provide the ID of the announcement that should be played. This ID must correspond to an announcement that has been configured in the announcement service. See Announcements for instruction about how to do this.
Multiple OCS Support
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports communicating with multiple different Diameter Ro online charging systems. Each OCS must have its own Diameter realm, and those realms must be configured as destination realms in the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s Diameter Ro configuration.
The particular OCS to use for a given call is determined from the ecf parameter of the P-Charging-Function-Addresses header on the initial SIP request for the call. The value of the ecf parameter that identifies a particular OCS is its realm name by default, but can be configured to be any arbitrary value by specifying a charging-function-address when configuring the destination realm for an OCS.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to Diameter Ro online charging in the sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging section.
What you need
-
❏ The release version of Diameter Ro to use with the online charging system.
-
❏ The origin realm to use when sending Diameter Ro messages. This is the TAS’s realm.
-
❏ The destination realm to use when sending Diameter Ro messages. This is the online charging system’s realm.
-
❏ The OCS peers' hostnames, ports, and transport protocols.
For low balance announcements:
-
❏ The ID of the low balance announcement to play in call setup.
-
❏ The ID of the low balance announcement to play in an active call.
-
❏ The time to wait after playing an announcement before doing another credit check.
For out of credit announcements:
-
❏ The ID of the out of credit announcement to play in call setup.
-
❏ The ID of the out of credit announcement to play in an active call.
For multiple OCS support:
-
❏ The destination realm of each OCS.
-
❏ A list of which peers are associated with which realms.
-
❏ (Optional) An identifier for each OCS that will be used to select it with a P-Charging-Function-Addresses header.
Setting up Diameter Ro online charging
I want to…
Use Diameter Ro online charging on a GSM based deployment
-
In the
chargingsection, set thegsm-online-charging-typetoroorcap-rofor mixed CAMEL/Ro deployments:
gsm-online-charging-type: ro-
In the
chargingsection, configure thero-chargingsection. See Configure Diameter Ro online charging. -
In
mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml, you must ensure that allper-node-diameter-rosections in the MMT cluster configuration are present and not commented out.
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgDisable Diameter Ro charging on a GSM based deployment
-
In the
chargingsection, set thegsm-online-charging-typetodisabled:
gsm-online-charging-type: disabled-
Remove or comment out the
ro-chargingsection:
# ro-charging:
# diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: aaa
# metric: 1
# continue-session-on-ocs-failure: false
#
# charging-announcements:
# low-credit-announcements:
# call-setup-announcement-id: 100
# mid-call-announcement-id: 100
# charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds: 30000
# out-of-credit-announcements:
# call-setup-announcement-id: 101
# mid-call-announcement-id: 102-
In
mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml, you must comment out allper-node-diameter-rosections in the MMT cluster configuration.
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
# per-node-diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgUse Diameter Ro online charging on a CDMA based deployment
-
In the
chargingsection, setcdma-online-charging-enabledtotrue:
cdma-online-charging-enabled: true-
In the
chargingsection, configure thero-chargingsection. See Configure Diameter Ro online charging. -
In
mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml, you must ensure that all per-node-diameter-ro sections in the MMT cluster configuration are present and not commented out.
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgDisable Diameter Ro charging on a CDMA based deployment
-
In the
chargingsection, setcdma-online-charging-enabledtofalse:
cdma-online-charging-enabled: false-
Remove or comment out the entire
ro-chargingsection:
# ro-charging:
# diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: aaa
# metric: 1
# continue-session-on-ocs-failure: false
#
# charging-announcements:
# low-credit-announcements:
# call-setup-announcement-id: 100
# mid-call-announcement-id: 100
# charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds: 30000
# out-of-credit-announcements:
# call-setup-announcement-id: 101
# mid-call-announcement-id: 102-
In
mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml, you must comment out allper-node-diameter-rosections in the MMT cluster configuration.
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
# per-node-diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgConfigure Diameter Ro online charging
In the charging section, ensure that the ro-charging section is present and not commented out:
ro-charging:
diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1-
The
diameter-ro-releaseof Diameter Ro to use. -
The Diameter
origin-realmfor the Rhino VoLTE TAS. -
The Diameter
destination-realmfor the online charging system. -
A Diameter
destination-peerslist that correspond to OCS servers. There must be at least one entry, and for each entry the following values must be set:-
the
destination-hostnamefor the OCS server -
the
portfor the OCS server -
the
protocol-transportto use with the OCS server. -
the
metricto use with this OCS server peer.
-
Play an announcement to subscribers when they run low on credit
| |
Ensure the announcement IDs you want to use have been set up in the announcement service. See Announcements. |
In charging, ro-charging, ensure that the charging-announcements section is present.:
charging-announcements:
low-credit-announcements:
call-setup-announcement-id: 100
mid-call-announcement-id: 100
charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds: 30000-
Add a
low-credit-announcementssection.-
Set the
call-setup-announcement-idof the announcement to play when a subscriber is low on credit at the beginning of a call. -
Set the
mid-call-announcement-idof the announcement to play when a subscriber becomes low on credit during a call. -
Set the
charging-reauth-delay-millisecondstime to wait (in milliseconds) before doing another credit check after playing a low balance announcement.
-
Related section: Diameter Ro charging announcements
Play an announcement to subscribers when they run out of credit
| |
Ensure the announcement IDs you want to use have been set up in the announcement service. See Announcements. |
In charging, ro-charging, ensure that the charging-announcements section is present:
charging-announcements:
out-of-credit-announcements:
call-setup-announcement-id: 101
mid-call-announcement-id: 102-
Add an
out-of-credit-announcementssection.-
Set the
call-setup-announcement-idof the announcement to play when a subscriber tries to make a call without having enough credit. -
Set the
mid-call-announcement-idof the announcement to play when a subscriber runs out of credit during a call.
-
Related section: Diameter Ro charging announcements
Configure multiple destination realms
In charging, ro-charging:
diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-realms:
- destination-realm: ocs1.metaswitch.com
peers:
- peer1.metaswitch.com
- destination-realm: ocs2.metaswitch.com
peers:
- peer2.metaswitch.com
- peer3.metaswitch.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer1.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
- destination-hostname: peer2.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
- destination-hostname: peer3.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 2-
Under
diameter-ro, add adestination-realmslist.-
If there is already a
destination-realmlisted underro-charging, remove it.
-
-
For each realm you want to add, create a new entry in the
destination-realmslist with:-
a
destination-realmgiving the realm name. -
a
peerslist giving the destination-hostnames of peers associated with the realm.
-
-
Ensure all the peers referenced by the realms are configured in the
destination-peerslist.
Set an identifier for an OCS for selecting it with a P-Charging-Function-Addresses header
In charging, ro-charging, diameter-ro:
destination-realms:
- destination-realm: ocs1.metaswitch.com
charging-function-address: ocs_1
peers:
- peer1.metaswitch.com
- destination-realm: ocs2.metaswitch.com
peers:
- peer2.metaswitch.com
- peer3.metaswitch.com-
Find the destination realm for the OCS you want to add an identifier for in the
destination-realmslist. -
Add a
charging-function-addressto the list entry with the identifier to use for the OCS.
Mixed Diameter Ro and CAP online charging
What it does
Operators may have a mixed Diameter Ro and CAP online charging environment. This is typically seen when an Operator is migrating off their SCP. To support this deployment the cap-ro gsm-online-charging-type is used, which instructs the installer to deploy both CAP and Diameter Ro configurations.
-
For more details on what CAP online charging does refer to what CAP online charging does
-
For more details on what Ro online charging does refer to what Ro online chargines does
Charging Mode Selection
When a call triggers RVT the online charging mode (either Diameter Ro or CAP) is determined by inspecting the top-most route header for the oc-charge-mode uri parameter which is set to either ro, cap, or offline. If ro is set then Diameter Ro is used for charging, if cap is set then CAP online charging is used.
| |
Check the Sentinel VoLTE Administration Guide for more details on the oc-charge-mode. |
For more details on the Diameter Ro and CAP online charging check these links.
Configuration
When using the mixed environment set the gsm-online-charging-type to cap-ro. Both Diameter Ro and CAP online charging configuration needs to be present.
What you need for CAP Online Charging
-
❏ The SCCP address of the GSM charging SCP.
-
❏ The TDP(s) to use when retrieving IM-CSI data from the HLR.
-
❏ Whether or not to send location information to the SCP.
If sending location information to the SCP:
-
❏ The format to sent the information in (see Location information).
-
❏ A default value to send when a subscriber’s location cannot be determined.
What you need for Diameter Ro Charging
-
❏ The release version of Diameter Ro to use with the online charging system.
-
❏ The origin realm to use when sending Diameter Ro messages. This is the TAS’s realm.
-
❏ The destination realm to use when sending Diameter Ro messages. This is the online charging system’s realm.
-
❏ The OCS peers' hostnames, ports, and transport protocols.
For low balance announcements:
-
❏ The ID of the low balance announcement to play in call setup.
-
❏ The ID of the low balance announcement to play in an active call.
-
❏ The time to wait after playing an announcement before doing another credit check.
For out of credit announcements:
-
❏ The ID of the out of credit announcement to play in call setup.
-
❏ The ID of the out of credit announcement to play in an active call.
I want to…
Use both Diameter Ro and CAP online charging on a GSM based deployment
-
In the
chargingsection, set thegsm-online-charging-typetocap-rofor mixed Diameter Ro/CAP deployments:
gsm-online-charging-type: cap-roAlso in the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
scf-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=156"-
Ensure there is a
cap-chargingsection. -
Ensure there is an
imssfsection. -
Set the
scf-addressto the SCCP address of the SCP that the Rhino VoLTE TAS should communicate with. -
Configure the
ro-chargingsection. See Configure Diameter Ro online charging. -
In
mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml, you must ensure that allper-node-diameter-rosections in the MMT cluster configuration are present and not commented out.
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgCAP online charging
What it does
When CAP online charging is in use, the Rhino VoLTE TAS functions as an IM-SSF (IP Multimedia Service Switching Function) and communicates with an SCP in a GSM network. At various points in the SIP signalling for the call the Rhino VoLTE TAS will translate the SIP to the equivalent CAP signalling towards the SCP, to give it the opportunity to intervene in call processing. Through this the SCP can provide a charging service. The exact details of how and when the Rhino VoLTE TAS will signal the SCP is determined by subscriber specific IM-CSI data in the HLR.
CAP online charging requires that integration with an SCP is set up. To do this, the SCCP (Signalling Connection Control Part) address of the SCP must be set in the scf-address field.
| |
CAMEL Application Part (CAP) is a GSM protocol, so naturally can only be used with GSM networks. |
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports CAP phase 2 and phase 3 triggers.
IM-CSI
The IM-CSI (IP multimedia CAMEL subscription information) is subscriber data retrieved from the HLR that is used to determine when and how to do SIP to CAP translation. There are different versions of the IM-CSI for the originating and terminating legs of the call; they are the O-IM-CSI and the VT-IM-CSI respectively. The Rhino VoLTE TAS can be configured to retrieve either the O-IM-CSI or the VT-IM-CSI independently of whether it is acting as an originating or terminating TAS.
The IM-CSI that is fetched on:
-
an originating TAS instance is determined by the
originating-tdpfield. -
the terminating TAS instance is determined by the
terminating-tdpfield.
Both fields can take the same values, which are numbers that correspond to CAP TDPs (trigger detection points).
The following values are valid for these fields.
| TDP number | TDP name | IM-CSI retrieved |
|---|---|---|
2 |
Collected_Info |
O-IM-CSI |
3 |
Analysed_Info |
O-IM-CSI |
12 |
Terminating_Attempt_Authorised |
VT-IM-CSI |
Location information
Information about a subscriber’s current country and access network can be sent to the SCP in the form of a charging GT (global title).
The format of the charging GT is configured in the format field, and it is made up from any combination of: fixed digits, the mobile country code (MCC), the mobile network code (MNC), and/or the two letter ISO country code. The value of the field should match any fixed digits to be included in the charging GT, with {mcc}, {mnc}, and/or {iso} tags inserted where those values should be substituted in. For example, 12345{mcc}{mnc} results in a charging GT that always starts with 12345 and has the current MCC and MNC for the subscriber appended on the end.
The unknown-location field can be used to set a default charging GT, which is used when a subscriber’s location cannot be determined.
When a subscriber receives a call, the CAP charging service is always invoked. This can be changed so that the service is only used for terminating calls when the charging GT data indicates that the subscriber is roaming in a foreign country.
Configuration
| |
CAP based charging is only available on GSM networks. |
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml shows example configuration relevant to CAP charging in the sentinel-volte/charging section.
What you need
-
❏ The SCCP address of the GSM charging SCP.
-
❏ The TDP(s) to use when retrieving IM-CSI data from the HLR.
-
❏ Whether or not to send location information to the SCP.
If sending location information to the SCP:
-
❏ The format to sent the information in (see Location information).
-
❏ A default value to send when a subscriber’s location cannot be determined.
Setting up CAP based online charging
I want to…
Enable CAP charging
In the charging section, set the gsm-online-charging-type to either cap or cap-ro for mixed CAMEL/Ro deployments:
gsm-online-charging-type: capAlso in the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
scf-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=156"-
Ensure there is a
cap-chargingsection. -
Ensure there is an
imssfsection. -
Set the
scf-addressto the SCCP address of the SCP that the Rhino VoLTE TAS should communicate with.
Disable CAP charging
In the charging section, set the gsm-online-charging-type to disabled:
gsm-online-charging-type: disabledComment out the entire cap-charging section:
# cap-charging:
# imssf:
# imcsi-fetching:
# originating-tdp: 2
# terminating-tdp: 12
# charging-gt:
# format: "6422142{iso}"
# unknown-location: "64221429090"
# only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming: false
# scf-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=156"Change the SCP that the CAP charging service communicates with
In the imssf section, set the scf-address to the SCCP address of the new SCP:
scf-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=156"Generate and send a charging GT containing location information for a subscriber to the SCP
In the imssf section:
charging-gt:
format: "6422142{iso}"
unknown-location: "64221429090"-
Add a
charging-gtsection. Inside it add:-
a
formatfield specifying how the location information should be delivered. It can be made up from fixed digits and any of these tags:{mcc},{mnc}, and/or{iso}; which will substitute in the MCC, MNC, and ISO two letter country code respectively. -
a
unknown-locationfield indicating what to send to the SCP if location information cannot be obtained.
-
Related section: Location information
Disable sending of the charging GT to the SCP
In the imssf section, comment out the entire charging-gt section:
# charging-gt:
# format: "6422142{iso}"
# unknown-location: "64221429090"Related section: Location information
Only invoke the CAP charging service for terminating subscribers when they are roaming in a foreign country
In the charging-gt section, set the only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming to true:
only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming: trueRelated section: Location information
Always invoke the CAP charging service for terminating subscribers regardless of their location
In the charging-gt section, set the only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming to false:
only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming: falseRelated section: Location information
Use O-IM-CSI data from the HLR on originating calls
In the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
imcsi-fetching:
originating-tdp: 2-
Ensure that a
cap-chargingsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imssfsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imcsi-fetchingsection is present.-
Set the
originating-tdpto2or3.
-
Related section: IM-CSI
Use VT-IM-CSI data from the HLR on originating calls
In the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
imcsi-fetching:
originating-tdp: 12-
Ensure that a
cap-chargingsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imssfsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imcsi-fetchingsection is present.-
Set the
originating-tdpto12.
-
Related section: IM-CSI
Use O-IM-CSI data from the HLR on terminating calls
In the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
imcsi-fetching:
terminating-tdp: 2-
Ensure that a
cap-chargingsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imssfsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imcsi-fetchingsection is present.-
Set the
terminating-tdpto2or3.
-
Related section: IM-CSI
Use VT-IM-CSI data from the HLR on terminating calls
In the charging section:
cap-charging:
imssf:
imcsi-fetching:
terminating-tdp: 12-
Ensure that a
cap-chargingsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imssfsection is present. -
Ensure that a
imcsi-fetchingsection is present.-
Set the
terminating-tdpto12.
-
Related section: IM-CSI
Disable retrieval of IM-CSI data from the HLR
In the imssf section, remove or comment out the entire imcsi-fetching section:
imssf:
# imcsi-fetching:
# originating-tdp: 2
# terminating-tdp: 12To disable retrieval for only:
-
originating calls, remove the
originating-tdp. -
terminating calls, remove the
terminating-tdp.
Related section: IM-CSI
Charging Data Records
What it does
Charging Data Records (CDRs) can be generated by the Rhino VoLTE TAS to record information about each call it processes. There are two types of CDRs: Interim CDRs and Session CDRs.
Interim CDRs
Interim CDRs are generated while a call is in progress, with multiple CDRs being generated during a single call. The Rhino VoLTE TAS can write the CDRs to the file system, send them to a CDF using Diameter Rf offline charging, or both.
There are two ways to control when interim CDRs should be generated:
-
You can change the maximum time to wait between creating each CDR.
-
You can instruct that a new CDR is created whenever the SDP for a call is modified.
In addition, one interim CDR is always generated when the call is answered and another when the call ends.
If you want to use Diameter Rf offline charging, interim CDR generation must be enabled.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to CDRs in the sentinel-volte/charging/cdr section.
What you need
-
❏ Whether to generate a session CDR at the end of each call.
-
❏ Whether to generate interim CDRs during a call.
When you are using interim CDRs:
-
❏ Whether an interim CDR should be created any time the SDP in a call changes.
-
❏ The maximum period to wait between creating interim CDRs.
-
❏ Whether the Rhino VoLTE TAS should write copies of each interim CDR to the file system.
Setting up CDRs
I want to…
Enable session CDR generation
In the charging, cdr section, set session-cdrs-enabled to true:
session-cdrs-enabled: trueRelated section: Session CDRs
Disable session CDR generation
In the charging, cdr section, set session-cdrs-enabled to false:
session-cdrs-enabled: falseRelated section: Session CDRs
Enable interim CDR generation
In the charging, cdr section, add an interim-cdrs section:
interim-cdrs:
write-cdrs-in-filesystem: true
write-cdr-on-sdp-change: true
interim-cdrs-period-seconds: 300Related section: Interim CDRs
Disable interim CDR generation
In the charging, cdr section, remove or comment out the entire interim-cdrs section:
# interim-cdrs:
# write-cdrs-in-filesystem: true
# write-cdr-on-sdp-change: true
# interim-cdrs-period-seconds: 300Related section: Interim CDRs
Generate an interim CDR whenever the SDP for a call changes
In the interim-cdrs section, set write-cdr-on-sdp-change to true:
write-cdr-on-sdp-change: trueRelated section: Interim CDRs
Prevent generation of interim CDRs when the SDP for a call changes
In the interim-cdrs section, set write-cdr-on-sdp-change to false:
write-cdr-on-sdp-change: falseRelated section: Interim CDRs
Change the maximum time to wait between generating interim CDRs
In the interim-cdrs section, set interim-cdrs-period-seconds to the desired maximum wait time in seconds:
interim-cdrs-period-seconds: 350Related section: Interim CDRs
Write copies of interim CDRs to the file system
In the interim-cdrs section, set write-cdrs-in-filesystem to true:
write-cdrs-in-filesystem: trueRelated section: Interim CDRs
Stop writing copies of interim CDRs to the file system
In the interim-cdrs section, set write-cdrs-in-filesystem to false:
write-cdrs-in-filesystem: falseRelated section: Interim CDRs
Home networks and roaming
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires configuration of its home network details in order to handle number normalization and roaming properly. This section describes how to set the home network information for the Rhino VoLTE TAS. Furthermore, there are details on how to handle behavior concerning home network configuration, such as number normalization and roaming determination.
Setting the address handling and home network information for the Rhino VoLTE TAS requires editing of specific YAML configuration files.
For further information on how to edit YAML configuration files, see Declarative configuration.
Home network dialing
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires information about the home network to correctly run number analysis.
How it works
The home network dialing configuration is composed of:
-
The home network’s domain name.
-
The country code dialing code, which is the home network’s code for dialing from external international networks.
-
The country’s ISO country code, which specifies the home network’s country in the two letter ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 format.
-
The home PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) IDs, which defines the operator’s home network codes in a country.
Using the home network dialing configuration, the Rhino VoLTE TAS runs number analysis to support:
-
designating multiple home PLMN IDs in the home network
-
normalization of international, national, unknown, or subscriber NADI format addresses into either national or international formats
-
determining a call’s roaming status.
Number normalization requires additional configuration to operate. More details on this configuration is in Number normalization.
Roaming determination has additional configurability available. More details of this configuration is in Roaming and international status determination.
Configuration
-
The Example for home-network-config.yaml file shows example configuration for the home network’s codes and PLMN IDs in the
home-networksection. -
The Example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml file shows example configuration for the PLMN ID used for correlation by the IP-SMGW, in the
correlation-ra-plmnidsection.
What you need
-
❏ The home network’s home domain.
-
❏ The home network’s country dialing code.
-
❏ The home network’s two letter ISO country code.
-
❏ The home network’s PLMN ID(s).
Setting up home network dialing
I want to …
Set my home network domain name
In the home-network section, set home-domain to your home network’s home domain:
home-domain: example.comSet my country dialing code for my network
In the home-network section, set home-network-country-dialing-code to your home network’s country dialing code:
home-network-country-dialing-code: "64"Set the ISO country code for my network
In the home-network section, set home-network-iso-country-code to your home network’s ISO country code:
home-network-iso-country-code: NZSet the PLMN IDs for my network
-
In the
home-networksection, sethome-plmn-idsto your home network’s home PLMN IDs:
home-plmn-ids:
- mcc: "001"
mncs:
- "01"
- "001"-
If the IP-SM-GW is in use, in the
sentinel-ipsmgwsection, setcorrelation-ra-plmnidto the home network’s primary PLMN ID:
correlation-ra-plmnid:
mcc: "001"
mnc: "01"Number normalization
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports number normalization to either the international format or the national format. The Rhino VoLTE TAS invokes the normalization process for number comparison, normalizing numbers on outgoing requests, checking if numbers are normalizable.
How it works
The Rhino VoLTE TAS may normalize numbers into the international format or the national format. The original number may be in one of the following formats:
-
International
-
National
-
Subscriber NADI format
-
an unknown format
When normalizing numbers to the international format:
-
If the original number is in the national format, the
home-network-country-dialing-codewill be prepended to the address. -
If the original number is in the subscriber format, the
home-network-country-dialing-codeandnetwork-dialing-codewill be prepended to the address. -
If the original number format is unknown, it is detected against the
international-prefixand thenational-prefix. If neither prefix matches, the number is unchanged.
When normalizing numbers to the national format:
-
If the original number is in the international format, the length of the
home-network-country-dialing-codewill be removed from the start of the address. -
If the original number is in the subscriber format,
network-dialing-codewill be prepended to the address. -
If the original number format is unknown, it is detected against the
international-prefixand thenational-prefix. If neither prefix matches, the number is unchanged.
Interactions with other services
Number normalization in used by several features of the Rhino VoLTE TAS for number comparison, checking if numbers are normalizable, or determining the status of a call. Since normalization is widespread in the Rhino VoLTE TAS, this section discusses only a selection of features that interact with number normalization.
MMTel services
MMTel services use the normalization to make URIs comparable and for call retarget destination.
For call barring services (ICB and OCB), normalization occurs for both an originating/terminating URI and the provisioned URI it is compared against.
For Communications Diversion (CDIV), normalization is used to check if a forwarding destination is valid by running a comparison. In addition, the forwarded target is set in the specified normalized format.
XCAP service
The XCAP service uses the configured normalization process to normalize numbers in MMTel CDIV rule targets and ICB/OCB conditions.
Short codes and vertical service codes
Request URIs may include short codes or vertical service codes. For an international format number prefixed by the home country code, the Rhino VoLTE TAS will normalize the number to remove the country code prefix before acting on the code. Normalization will not occur if the dialed string’s length is less than the configured min-normalizable-length value.
Configuration
The example number-analysis-config.yaml file shows example configuration for the home network’s number normalization rules in the normalization section.
The normalize-to variable is an enum. The valid values for this field are described in the reference guide’s section on normalize-to.
What you need
-
❏ The home network’s country dialing code.
-
❏ A minimum normalizable length for dialed numbers.
-
❏ The national prefix number (escape code) for dialed national numbers.
-
❏ The international prefix number (escape code) of dialed international numbers.
-
❏ The network’s dialing code — this will act as the MNC for normalizing from the subscriber NADI format.
-
❏ Whether to normalize numbers to an international or national format in the home network.
Setting up number normalization
I want to …
Set up the home network settings for normalization
The normalization process in the Rhino VoLTE TAS requires details about the home network for it to work properly. These apply for normalizing for both national and international formats.
To configure the home network specific settings for number normalization:
-
Ensure that the home networking country dialing code is set in the home network configuration section - see I want to set my country dialing code for my network.
-
In the
normalizationsection:
network-dialing-code: "6"
international-prefix: "00"
national-prefix: "0"
min-normalizable-length: "0"-
Set
network-dialing-codeto the home network’s dialing code. -
Set
international-prefixto the home network’s international call prefix (escape code). -
Set
national-prefixto the home network’s national call prefix (escape code). -
Set
min-normalizable-lengthto the home network’s minimum normalizable length used to prevent short dialed strings from being normalized.
Normalize numbers to the international format
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to normalize numbers into the international format, in the normalization section, set normalize-to to international:
normalize-to: internationalNormalize numbers to the national format
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to normalize numbers into the national format, in the normalization section, set normalize-to to national:
normalize-to: nationalRoaming and international status determination
The Rhino VoLTE TAS requires configuration of how it determines whether addresses are international and/or roaming on the home network.
How it works
The Rhino VoLTE TAS determines if a session is roaming and if it represents an international call based on:
-
the location of the calling party, and
-
the destination address.
Determining international status
The Rhino VoLTE TAS uses the home network configuration to determine the international status of a subscriber.
If the checked address is not in an international format and non-international-format-number-is-national is set to true, the Rhino VoLTE TAS determines the number is not an international or international-exHC number.
Otherwise, the Rhino VoLTE TAS analyzes the call alongside the home network information to determine international status.
The Rhino VoLTE TAS determines the call’s international status according to the definitions given by 3GPP 24.611:
|
international: This condition evaluates to true when the request URI of the outgoing SIP request:
international-exHC: This condition for international barring, excluding the home country, evaluates to true when the request URI of the outgoing SIP request:
|
Determining roaming status
The Rhino VoLTE TAS determines roaming status of a subscriber by checking the following:
-
Firstly, the
home-plmn-idsMCCs and MNCs are checked with the subscriber address’s respective MCC and MNC.-
If a home network MCC and MNC (PLMN ID) match with the address’s MCC and MNC respectively, the call is
NOT-ROAMING. -
If a home network MCC and address’s MCC match, but there is no MNC match, the call is
NATIONALroaming. -
If a home network MCC does not match with the address’s MCC, the call is
INTERNATIONALroaming.
-
-
If the address has no MCC present, the ISO country code of the party is compared with the network’s configured
home-network-iso-country-code.-
If the ISO country codes match, the call is
NOT-ROAMING, otherwise, it isINTERNATIONALroaming.
-
-
If there is no ISO country code present, the Visited Network ID of the party is compared with the network’s configured
home-domain.-
If the network IDs match, the call is
NOT-ROAMING, otherwise it isINTERNATIONALroaming.
-
-
Finally, if the call’s visited MCC nor visited network are not present, the roaming status is
UNKNOWN.
Using the visited network ID
The Rhino VoLTE TAS determines the visited network ID on an incoming request with the following techniques:
-
Firstly, if the Rhino VoLTE TAS has already loaded on the visited network ID for the session, it uses that.
-
Otherwise, the Rhino VoLTE TAS uses the
P-Visited-Network-Idheader for originating sessions orOC-Term-P-Visited-Network-Idfor terminating sessions on the incoming request. -
Finally, the Rhino VoLTE TAS will query for the third party registration data stored in subscriber data.
Interactions with other services
Call Barring
The Rhino VoLTE TAS uses the roaming and international status for MMTel communication barring features. For further information on barring feature configuration, see Call barring.
Configuration
Roaming determination depends on number normalization and home network dialing configurations.
It is possible to configure a list of addresses that will have roaming determination skipped. Contact Metaswitch support for more information on how to configure roaming determination skip lists.
-
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration for roaming determination logic in the Rhino VoLTE TAS in the
international-and-roamingsection. -
For a GSM network, there is an additional option to query the HLR for determining a number’s roaming status. The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml shows example configuration in the
mmtelsection.
What you need
-
❏ Whether to treat non-international numbers as national numbers.
-
❏ Whether to end a call if there is no visited network information on the incoming call request.
-
❏ The minimum length of the destination address required to set international and roaming status.
-
❏ For a GSM network, whether to use the HLR to determine roaming.
Setting up roaming and international status
I want to …
Treat any non-international format number as a national number
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to treat any non-international format number as a national number for roaming, in the international-and-roaming section, set non-international-format-number-is-national to true:
non-international-format-number-is-national: trueEnd a call if no visited network can be determined
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to end an incoming call if the P-Visited-Network-Id cannot be determined, in the international-and-roaming section, set end-call-if-no-visited-network to true:
end-call-if-no-visited-network: trueNot determine roaming and international status for dialed digits below a certain length
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to not determine roaming or international status for short dialed digit strings (such as any length below 7 for example), in the international-and-roaming section, set min-length to 7:
min-length: 7Use the HLR for determining roaming with the GSM network
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to query the HLR for determining roaming using GSM network information, in the mmtel section, set determine-roaming-from-hlr to true:
determine-roaming-from-hlr: trueNon-provisionable URIs
There will be URIs in the network that should not be provisioned for a subscriber.
How it works
The non-provisionable URIs specified in the Rhino VoLTE TAS are used for denying a call forward. If a non-provisionable URI matches a target URI (after normalization), any call forwarding rules related to this are ignored. For further information on call forwarding, see Communications Diversion (CDIV).
In addition, any XCAP request to create a forwarding rule which contains a non-provisonable URI is rejected.
Configuration
The non-provisionable-uris field designates what the Rhino VoLTE TAS will not provision, as shown in the example number-analysis-config.yaml file.
Setting up non-provisionable URIs configuration
I want to …
Specify a series of URIs that the Rhino VoLTE TAS will reject call forwarding rules for
To set the Rhino VoLTE TAS to disable provisioning for certain URIs, in the number-analysis section, set non-provisionable-uris with a list of non-provisionable URIs.
non-provisionable-uris:
- "tel:111"
- "sip:111@example.com"Managing the subscriber data
The Rhino VoLTE TAS uses subscriber data to specify the behavior of services for provisioned subscribers.
Subscriber data document schemas
Subscriber data document schemas supported by the Rhino VoLTE TAS:
MMTel supplementary services schema
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports all of GSMA IR.92 MMTel supplementary services except for Message Waiting Indication 3GPP TS 24.606.
The details of the MMTel-Services Schema are detailed in 3GPP 29.364 Section 7.2.
Supported services
The supported services in the MMTel Services schema for the Rhino VoLTE TAS are detailed in the following table.
| Service | XPath |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IMS-ODB-Information schema
The IMS-ODB-Information document allows for Operator Determined Barring rules to be defined in the network.
The IMS-ODB-Information Schema is detailed in 3GPP 29.364 Section 10.2.
Metaswitch-TAS-Services schema
The Rhino VoLTE TAS uses a non-standard user document to support additional functionality beyond the MMTel supplementary services. This user document has the service indicator Metaswitch-TAS-Services.
This page details the schema for the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document.
Document overview
The Metaswitch-TAS-Services document stores non-standard subscriber service data for certain Rhino VoLTE TAS functionality.
The services that use this non-standard user document are described in:
Schema structure
The schema for the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document is defined in several xsd files.
There are two types of files that define the schema. These files establish the components such as elements and types that are either:
-
shared across the schema
-
specific for each service that is configured in the document
General schema files
The Metaswitch-TAS-Services document defines elements and types that are shared across the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s services that require non-standard subscriber data. These are defined in the following files:
-
metaswitch-tas-services.xsd -
basic-settings.xsd -
additional-attributes.xsd
metaswitch-tas-services.xsd
The metaswitch-tas-services.xsd file serves as the basis of the schema definition. It includes within its definition the xsd files for the basic-settings.xsd and each of the service specific schema definitions.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy"
xmlns:ocp="urn:oma:xml:xdm:common-policy"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<!-- the standardised schemas are in another namespace, so use xs:import -->
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../XCAP.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-common-data.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../originating-identity-presentation.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../terminating-identity-presentation.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../communication-diversion.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../communication-waiting.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../communication-barring.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-originating-identity-presentation.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-terminating-identity-presentation.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-malicious-communication-identification.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-communication-diversion.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-communication-waiting.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-communication-hold.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-communication-barring.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-completion-of-communication.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-message-waiting-indication.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-conference.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-advice-of-charge.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-explicit-communication-transfer.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-customized-alerting-tone.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-flexible-alerting.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../flexible-alerting.xsd" />
<!-- tas-types is the same namespace, so use xs:include -->
<xs:include schemaLocation="basic-settings.xsd" />
<xs:include schemaLocation="location-based-dialling.xsd" />
<xs:include schemaLocation="forward-to-voicemail.xsd" />
<xs:include schemaLocation="companion-device.xsd" />
<xs:element name="metaswitch-services" type="mt:metaswitch-services-type"/>
<xs:complexType name="metaswitch-services-type">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="complete-basic-settings" type="mt:completeBasicSettingsType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="complete-location-based-dialling" type="mt:completeLocationBasedDiallingType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="complete-forward-to-voicemail" type="mt:completeForwardToVoicemailType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="complete-companion-device" type="mt:completeCompanionDeviceType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" processContents="lax" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>basic-settings.xsd
The basic-settings.xsd file includes the non-standard additional-attributes.xsd file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<!-- the standardised schemas are in another namespace, so use xs:import -->
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../XCAP.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-common-data.xsd" />
<xs:include schemaLocation="additional-attributes.xsd" />
<xs:complexType name="completeBasicSettingsType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="basic-settings" type="mt:basicSettingsType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="operator-basic-settings" type="mt:operatorBasicSettingsType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="basicSettingsType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="operatorBasicSettingsType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:operatorServiceConfigType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>additional-attributes.xsd
The additional-attributes.xsd file defines a key-value pair type to store additional attributes.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="additional-attributes">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="attribute" type="mt:keyValuePairType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="keyValuePairType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="key" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="value" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>Service specific schema files
companion-device.xsd
See Companion device subscriber data for more information on managing the subscriber data for the companion device service.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<!-- the standardised schemas are in another namespace, so use xs:import -->
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../XCAP.xsd"/>
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
schemaLocation="../operator-common-data.xsd"/>
<xs:include schemaLocation="additional-attributes.xsd"/>
<xs:complexType name="completeCompanionDeviceType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="companion-device" type="mt:companionDeviceType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="operator-companion-device" type="mt:operatorCompanionDeviceType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="companionDeviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="operatorCompanionDeviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:operatorServiceConfigType">
<xs:sequence>
<!-- The shared identity of the subscriber, this maybe a SIP or TEL URI, or both -->
<xs:element name="shared-identity-sip" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:element name="shared-identity-tel" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<!-- Whether or not to hide/block undisclosed numbers -->
<xs:element name="hide-companion-identity" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="devices" type="mt:devicesType"/>
<!-- Add additional-attributes to keep consistent with other metaswitch xml schema types -->
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="devicesType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="device" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" type="mt:deviceType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="deviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="model" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="radio-access" type="mt:radioAccessType"/>
<xs:element name="impi" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="imsi" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="imei" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="radioAccessType">
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="PS" type="mt:networkTypePS"/>
<xs:element name="CS" type="mt:networkTypeCS"/>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkTypePS">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="mt:networkType"/>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkTypeCS">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="mt:networkType">
<xs:attribute name="msisdn" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>location-based-dialling.xsd
See Location based dialing subscriber data for more information on managing the subscriber data for the location based dialing service.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<!-- the standardised schemas are in another namespace, so use xs:import -->
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../XCAP.xsd"/>
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
schemaLocation="../operator-common-data.xsd"/>
<xs:include schemaLocation="additional-attributes.xsd"/>
<xs:complexType name="completeCompanionDeviceType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="companion-device" type="mt:companionDeviceType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="operator-companion-device" type="mt:operatorCompanionDeviceType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="companionDeviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="operatorCompanionDeviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:operatorServiceConfigType">
<xs:sequence>
<!-- The shared identity of the subscriber, this maybe a SIP or TEL URI, or both -->
<xs:element name="shared-identity-sip" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:element name="shared-identity-tel" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<!-- Whether or not to hide/block undisclosed numbers -->
<xs:element name="hide-companion-identity" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="devices" type="mt:devicesType"/>
<!-- Add additional-attributes to keep consistent with other metaswitch xml schema types -->
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="devicesType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="device" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" type="mt:deviceType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="deviceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="model" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="radio-access" type="mt:radioAccessType"/>
<xs:element name="impi" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="imsi" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="imei" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="radioAccessType">
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="PS" type="mt:networkTypePS"/>
<xs:element name="CS" type="mt:networkTypeCS"/>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkTypePS">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="mt:networkType"/>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="networkTypeCS">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="mt:networkType">
<xs:attribute name="msisdn" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>forward-to-voicemail.xsd
See Forward to voicemail subscriber data for more information on managing the subscriber data for the forward to voicemail service.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:ss="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:mt="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
targetNamespace="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<!-- the standardised schemas are in another namespace, so use xs:import -->
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../XCAP.xsd" />
<xs:import namespace="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap" schemaLocation="../operator-common-data.xsd" />
<xs:include schemaLocation="additional-attributes.xsd" />
<xs:complexType name="completeForwardToVoicemailType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="forward-to-voicemail" type="mt:forwardToVoicemailType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="operator-forward-to-voicemail" type="mt:operatorForwardToVoicemailType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="forwardToVoicemailType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:simservType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="voicemail-server" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="operatorForwardToVoicemailType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ss:operatorServiceConfigType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="allow-subscriber-update" type="xs:boolean" default="false"/>
<xs:element ref="mt:additional-attributes" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:any namespace="##any" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>Companion device subscriber data
The companion device service uses data configured in the subscriber’s Metaswitch-TAS-Services document. To see what operator-wide service configuration is available for the companion device service, check Companion device.
Example document
This example subscriber data document specifies that:
-
The companion device service is active for the subscriber and authorized by the operator.
-
The shared identities of all companion devices declared is
sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz -
A PS-only companion device is configured for the subscriber.
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-basic-settings>
<basic-settings active="true"/>
<operator-basic-settings authorized="true"/>
</complete-basic-settings>
<complete-companion-device>
<companion-device active="true"/>
<operator-companion-device authorized="true">
<shared-identity-sip>sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</shared-identity-sip>
<devices>
<device active="true">
<model>companion-device-1</model>
<impi/>
<imsi/>
<imei/>
<radio-access>
<PS/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>
</operator-companion-device>
</complete-companion-device>
</metaswitch-services>Setting up the companion device service
I want to …
Authorize and activate the companion device service for the subscriber
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/operator-companion-device, set the authorized attribute to true:
<operator-companion-device authorized="true">In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/companion-device, set the active attribute to true:
<companion-device active="true"/>Set the shared SIP identity for the subscriber’s companion devices
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/operator-companion-device/shared-identity-sip, set the shared-identity-sip element to the SIP identity for the subscriber’s companion devices:
<shared-identity-sip>sip:bob@home1.opencloud.co.nz</shared-identity-sip>Add a PS domain only companion device
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/operator-companion-device/devices, add the following device type element to it:
<devices>
<device active="true">
<model>companion-device-1</model>
<impi/>
<imsi/>
<imei/>
<radio-access>
<PS/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>Add a PS and CS domain capable companion device
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/operator-companion-device/devices, add the following device type element to it:
<devices>
<device active="true">
<model>companion-device-1</model>
<impi/>
<imsi/>
<imei/>
<radio-access>
<PS/>
<CS msisdn="641234567"/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>Add a PS and CS domain capable companion device with a defined IMPI, IMSI, and IMEI
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-companion-device/operator-companion-device/devices, add the following device type element to it:
<devices>
<device active="true">
<model>companion-device-1</model>
<impi>234150999999999@ims.mnc015.mcc234.3gppnetwork.org</impi>
<imsi>234150999999999</imsi>
<imei>90420156-025763-0</imei>
<radio-access>
<PS/>
<CS msisdn="1234567"/>
</radio-access>
</device>
</devices>Schema
The schema definition dedicated to the companion device service is stored in the companion-device.xsd.
Location based dialing subscriber data
The location based dialing service uses data configured in the subscriber’s Metaswitch-TAS-Services document. To see what operator-wide service configuration is available for the location based dialing service, check Location based dialing (LBD).
Example document
This example subscriber data document specifies that:
-
The location based dialing service is active for the subscriber and authorized by the operator.
-
The location based dialing configured group ID for the subscriber is
PremiumGroup. This configured group ID may affect the destination address the subscriber is redirected to by the location based dialing service.
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-basic-settings>
<basic-settings active="true"/>
<operator-basic-settings authorized="true"/>
</complete-basic-settings>
<complete-location-based-dialling>
<location-based-dialling active="true"/>
<operator-location-based-dialling authorized="true">
<group-id>PremiumGroup</group-id>
</operator-location-based-dialling>
</complete-location-based-dialling>
</metaswitch-services>Setting up the location based dialing service
I want to …
Authorize and activate the location based dialing service for the subscriber
In the element at /metaswitch-services/location-based-diallingl/operator-location-based-dialling set the authorized attribute to true:
<operator-location-based-dialling authorized="true">In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-location-based-dialling/location-based-dialling set the active attribute to true:
<location-based-dialling active="true"/>Set the subscriber’s group ID used to decide location based dialing behavior
The configured group ID may affect the destination address the subscriber is redirected to by the location based dialing service. Contact Metaswitch support for more information on configuring the location based dialing service.
In the element at /metaswitch-services/location-based-diallingl/operator-location-based-dialling/group-id set the element content to the group ID configured for the location based dialing service:
<group-id>PremiumGroup</group-id>Schema
The schema definition dedicated to the location based dialing service is stored in the location-based-dialling.xsd.
Forward to voicemail subscriber data
The forward to voicemail service uses data configured in the subscriber’s Metaswitch-TAS-Services document. To see what operator-wide service configuration is available for the forward to voicemail service, check Voicemail forwarding.
Configuring the voicemail server URI
All subscribers using the Voicemail Forwarding service need to be configured with a voicemail server URI in the metaswitch-services section of their subscriber profile. This would normally be the single entry from the list of known voicemail servers.
Rhino VoLTE TAS has configuration to allow a subscriber to change their voicemail server URI. This is controlled by setting Allow Subscriber Update to true or false in the metaswitch-services section of their subscriber profile. The default deployment does not support subscribers being allowed to change their voicemail server URI. This is because there are policing and network routing issues related to user supplied URIs, especially Internet and email style URIs without user=phone.
Example document
This example subscriber data document specifies that:
-
The forward to voicemail service is active for the subscriber and authorized by the operator.
-
The voicemail server for which calls to the subscriber are forwarded to is
sip:vms@home1.opencloud.co.nz -
The subscriber is permitted to update and set their own voicemail server URI to forward calls to.
<metaswitch-services xmlns="http://metaswitch.com/XMLSchema/tas">
<complete-basic-settings>
<basic-settings active="true"/>
<operator-basic-settings authorized="true"/>
</complete-basic-settings>
<complete-forward-to-voicemail>
<forward-to-voicemail active="true">
<voicemail-server>sip:vms@home1.opencloud.co.nz</voicemail-server>
</forward-to-voicemail>
<operator-forward-to-voicemail authorized="true">
<allow-subscriber-update>true</allow-subscriber-update>
</operator-forward-to-voicemail>
</complete-forward-to-voicemail>
</metaswitch-services>Setting up the forward to voicemail service
I want to …
Authorize and activate the companion device service for the subscriber
In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-forward-to-voicemail/operator-forward-to-voicemail, set the authorized attribute to true:
<operator-forward-to-voicemail authorized="true">In the element at /metaswitch-services/complete-forward-to-voicemail/forward-to-voicemail, set the active attribute to true:
<forward-to-voicemail active="true">Schema
The schema definition dedicated to the forward to voicemail device service is stored in the forward-to-voicemail.xsd.
Accessing subscriber data
This page discusses the different parts of the Rhino VoLTE TAS that may access subscriber data stored in the network’s HSS and/or HLR.
Data stored on the HSS
The HSS stores the subscribers' service and subscription data used by the Rhino VoLTE TAS for IMS networking.
For running services that are dependent on the subscriber’s configuration profile, the Rhino VoLTE TAS accesses the HSS through the Diameter Sh interface.
What accesses the subscriber data
The Rhino VoLTE TAS retrieves a subscriber’s data via the internal Sh Cache Microservice (ShCM) node. Configuration of the Sh interface and ShCM is detailed in HSS integration.
Through the ShCM node, the following Rhino VoLTE TAS nodes access the HSS subscriber data:
-
The MMT node for data used by services on the MMTel TAS and SCC-AS.
-
The SMO node for data used by services on the IP-SM-GW.
-
The MAG node for features that manage subscriber data such as the XCAP server, REST API, or an internal web user interface. Provisioning subscriber data describes these features in further detail.
A UE may use the XCAP protocol to manage service specific data through the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
Data stored on the HLR
Service data used by the Rhino VoLTE TAS for GSM or CDMA networking is stored on the HLR. The Rhino VoLTE TAS uses the MAP protocol to access the HLR.
Access to service data in the HLR is necessary for many services to operate using GSM and CDMA networking.
Configuration of the MAP interface is detailed in HLR integration.
Provisioning subscriber data
IMS-defined subscriber data
The subscriber’s IMS subscription in the HSS needs to be provisioned to utilize IMS subscription data. This is not something that the Rhino VoLTE TAS can do. This must be performed by the operator using the tools or APIs provided by the HSS vendor.
Service-specific subscriber data
Service-specific subscriber data determines a subscriber’s service profile, services enabled for the subscribers, and calls they are allowed to make.
The following tools are available for managing service specific subscriber data.
Subscriber access via XCAP
The Rhino VoLTE TAS allows a UE to configure subscriber service data via the XCAP protocol on the Ut interface. This includes support for bootstrap authentication and NAF XCAP interactions on the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s MAG nodes. For detailed information on configuring the interfaces that use XCAP, see RVT XCAP.
Rhino TAS REST API framework
The Rhino TAS REST API allows for managing per-subscriber service data configurations. This supports the operations to Create, Read, Modify and Delete a subscriber’s service data.
For further information, see the Sentinel VoLTE Provisioning REST API documentation.
Using the alternate Cassandra schema
This section describes the procedures for changing the schema that Sentinel Registrar components of MMT and SMO nodes use.
The default schema for storing third-party registration data in the TSN may have high disk usage. This disk usage is a consequence of decisions about table schema used by Registrar components and data handling in the Cassandra database engine. Under some circumstances disk usage may become unpredicatable.
To reduce overall disk space usage and to improve predictablility an alternative Cassandra schema is provided. The instructions here allow you to change the MMT and SMO nodes to use the alternative schema.
Both the MMT and SMO nodes store third-party registration data on the TSN node. Separate instructions are provided for the MMT and SMO nodetypes. Parts of the proceedure require a maintenance window. Each nodetype may be done in a separate maintenance window.
Change the schema for MMT nodes
The default schema uses the first-party REGISTER callID field as a part of the primary key. RFC 3261 Section 10.2 states that User Equipment (UE) should use the same callID for the duration of the time it is registered. As the specification allows UE to use different CALLID values for the same registration, this requires proper handling.
As the callID is a part of the primary key, one row is used per unique callID, which may result in multiple rows representing the same logical registration. In cases where a significant proportion of UE on the network do not reuse their callID significantly more disk space is required to hold registration records. This contributes to the disk space for registration records being unpredictable under some circumstances.
The alternate schema uses the IMS private identity (hereafter deviceID) in place of callID in the schema. Per 3gpp 24.229 specification this must be set on all REGISTER attempts. As the deviceID does not change from registration attempt to registration attempt, the size of the database is more predictable.
See Data Schema for details of the Registrar schemas.
The following sections provide instructions for switching to the alternate schema on the MMT node. The required tables already exist on the TSN. You will change MMT configuration to use the alternate tables.
Impacts
During the change of the schema, the system may be affected as follows:
-
There will be an increase in the number of HSS queries. This is because the third-party registrations serve as a cache, and in their absence, devices can only be verified through queries to the HSS. After the procedure is complete, the number of HSS queries should gradually return to the pre-maintenance window level.

The speed at which the number of HSS queries returns to normal depends on the registration validity period. It can be very quick or fairly slow. It is anticipated to be very quick on average. -
When you run the
TRUNCATEcommand, disk usage will not drop immediately. Disk usage will only drop after thenodetool clearsnapshotcommand is run. This is because theTRUNCATEcommand moves the data to a snapshot instead of deleting. The snapshot is only removed when thenodetool clearsnapshotcommand is run.
| |
If you encounter any impacts that are not listed, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Pre-maintenance window steps for changing the Cassandra schema
Before entering the maintenance window you need to take some steps to get prepared. Performing these beforehand ensures that changing the Cassandra schema is a smooth exercise. Some steps can be done well in advance. Other steps need to bedone immediately before entering the maintenance window, as they are a final check to ensure everything is ready for the change.
Pre-maintenance window steps that can be done in advance
Verify the deployed MMT version
Make sure that the MMT VMs have already been upgraded to at least the maintenance version of RVT 4.1-1-1.0.0. The configuration changes that are being made will only work if the MMT is at least this version.
Create file with commands to run
There are commands that will need to be run in preparation for and during the Cassandra schema change. These commands requires specific arguments that need to be prepared beforehand. Creating a file of commands ready to be copy/pasted and run beforehand ensures smooth running of the steps. Placeholder values are of the form <…>. <a|b> means a choice of either a or b. For example, mmt-<gsm|cdma> means mmt-gsm or mmt-cdma.
The file of commands can be stored anywhere that is convenient.
Many of the commands are rvtconfig commands. Further information can be found in the rvtconfig reference.
Determine the following arguments:
-
tsn-mgmt-address- The management IP address of at least one TSN node. The TSN management IP addresses can be found in theTSNsection of the SDF. If multiple addresses are used, they should be formatted as-c <address1> <address2>…. -
deployment-id- This can be found in the SDF under the keydeployment-id. -
site-id- The site-id of the site you are changing config for. This can be found in the SDF assite-id. -
group-id- EitherRVT-mmt-gsm.<site-id>orRVT-mmt-cdma.<site-id>depending on whether the MMTs are of the GSM or CDMA variant. If you are unsure, this can be determined from thervtconfig-pathbelow. -
sdf-path- The path to the SDF file on your SIMPL VM. -
rvtconfig-path- The path to the rvtconfig on your SIMPL VM. This is expected to be something like:/home/admin/.local/share/csar/mmt-gsm/<version>/resources
If Cassandra authentication is enabled, then two additional arguments will be required for every rvtconfig command.
-
cds-username- Username to authenticate with Cassandra. You can find it in the SDF undercassandra-username. -
cds-password-secret-name- Password identifier to authenticate with Cassandra. You can find it in the SDF undercassandra-password-id.
They are added in the format --cds-username <cds-username> --cds-password-secret-name <cds-password-secret-name> as the last two arguments to every rvtconfig command.
Create a text file containing all the subsequent commands with substitutions completed.
Take a backup of the current configuration
In case you need to roll back later, prepare a copy of the current configuration. Otherwise, you may have to recreate your configuration files manually.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path> $ rvtconfig dump-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> --group-id <group-id> --vm-version-source this-rvtconfig --output-dir ~/yamls-rollback
--output-diris the output directory for thervtconfig dump-configcommand. Any easily accessible directory can be chosen and the command will create the directory if it does not exist. The recommendation is to maintain~/yamls-rollback, as this value is referenced in the rollback procedure. In the event that a different folder is used, substitute that value for~/yamls-rollbackin the rollback procedure.
Create the new configuration file
The new configuration needs to be written for upload. The configuration points to change are located in the mmt-<gsm|cdma>-overrides.yaml file in ~/yamls. Create the file if it does not exist.
MMT configuration change
| |
Contact Metaswitch technical support for assistance with writing the new configuration. |
| |
Yaml uses semantic whitespace. The resulting file must be valid yaml that rvtconfig can accept. |
If mmt-<gsm|cdma>-overrides.yaml does not exist, create it with the following content:
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''
profile-tables:
- name: RegistrarConfigurationTable
profiles:
- name: 'Metaswitch::::'
present: true
attributes:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'If mmt-<gsm|cdma>-overrides.yaml exists and does not contain the string RegistrarConfigurationTable, insert the following contents immediately below the line profile-tables::
- name: RegistrarConfigurationTable
profiles:
- name: 'Metaswitch::::'
present: true
attributes:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'If mmt-<gsm|cdma>-overrides.yaml exists and contains the string RegistrarConfigurationTable, insert the following into the attributes key of RegistrarConfigurationTable:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'Pre-maintenance window steps to be done immediately prior to entering the maintenance window
| |
Before performing these steps, ensure that you have: |
-
A file with all the commands that need to be run for changing the Cassandra schema. The commands will have all the required arguments substituted.
-
Two sets of
.yamlconfiguration files - the new configuration (~/yamls), the current config (~/yamls-rollback). -
Verified that the deployment consists of the right version of the VMs.
Compare live configuration on MMTs with configuration on SIMPL
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Verify that the directory
/tmp/checkdiffdoes not exist. If the directory does exist, remove it. -
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig compare-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t mmt-<gsm|cdma> -i ~/yamls-rollback --output-dir /tmp/checkdiff --vm-version-source this-rvtconfig| |
--output-dir is the output directory for the rvtconfig compare-config command. The command will create the directory if it does not exist and will return an error if the directory does exist. |
-
Verify that the command completes with:
No differences found in yaml files.
Uploading this configuration will have no effect unless secrets, certificates or licenses have changed, or --reload-resource-adaptors is specified.If the output returned does not include "No differences found in yaml files.", contact Metaswitch technical support.
Perform health checks on MMTs in the deployment
The deployment needs to be in a healthy state. To verify that the deployment is healthy, run the following tests.
Enter the maintenance window
If all the healthchecks above pass, start a maintenance window and then run through the steps for changing the Cassandra schema. To enter a maintenance window:
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig enter-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>Procedure
This section describes the steps for changing the primary key for MMT nodes. These steps are expected to take 30 minutes to complete.
| |
Before beginning these steps, ensure that the placeholder values in commands listed here have been substituted with the required values. Placeholder values are of the form <…>. |
Truncate the registrations and assocuris tables on Cassandra
The existing registrations and assocuris tables take up some space on disk. Truncate these tables to ensure free disk space is over 50%. Truncation must be run on one TSN node.
-
Use SSH to access the TSN as the primary user (
sentinel). -
Start the Cassandra CLI by running the command:
$ cqlsh-
Truncate the tables by running the command:
TRUNCATE opencloud_thirdparty_reg.REGISTRATIONDATA;
TRUNCATE opencloud_thirdparty_reg.ASSOCURIS;-
Verify that there are no messages printed to the console after running the TRUNCATE command.
-
Exit the Cassandra CLI by running:
$ exit| |
If the TRUNCATE command fails, run the next command (nodetool clearsnapshot), before attempting to run the TRUNCATE command and the nodetool command again. |
Clear snapshots on all TSN nodes
-
SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) into each of the TSNs sequentially and run the command:
$ nodetool clearsnapshot opencloud_thirdparty_reg --allVerify that the truncation has been successful
-
Run the command:
$ df -h-
Verify that for the following two rows in the output, the
<use>%values are less than 50%:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
[...]
/dev/sda3 <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /
[...]
/home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data| |
If the disk usage is over 50%, do not proceed with the rest of the steps and contact Metaswitch technical support. |
-
Exit the TSN by running:
$ exitUpload the configuration
The new configuration written during the pre-maintenance window steps, is required to change the schema that is in use.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig upload-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t mmt-<gsm|cdma> -i ~/yamls --vm-version-source this-rvtconfigVerify that the configuration has uploaded successfully
-
Verify that the output after the command has completed running includes the following sentence:
Wrote config for version <version>, deployment ID <deployment-id>, and group ID <group-id>-
Exit the SIMPL VM by running:
$ exit-
Use SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) to access each of the MMTs. -
From the home directory, run the command:
$ report-initconf statusuntil the following is displayed in the output:
status=vm_converged| |
If after 15 minutes, the status of the VMs is not converged, proceed to Rollback. |
Test the new tables
-
Perform a test call to force a registration.
| |
If the test call does not succeed, proceed to Rollback. |
Exit the maintenance window
Take the deployment out of maintenance window mode.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>-
verify the command output includes the following:
Maintenance window has been terminated. The VMs will resume running scheduled tasks as per their configured schedules.
Rollback
This section describes the steps for rolling back the change of primary key for MMT nodes. These steps are expected to take 30 minutes to complete.
Truncate the registrations_v2 and assocuris_v2 tables on Cassandra
The existing registrations_v2 and assocuris_v2 tables take up some space on disk. Truncate these tables to ensure free disk space is over 50%. Truncation must be run on one TSN node.
-
Use SSH to access the TSN as the primary user (
sentinel). -
Start the Cassandra CLI by running the command:
$ cqlsh-
Truncate the tables by running the command:
TRUNCATE opencloud_thirdparty_reg.REGISTRATIONDATA_V2; TRUNCATE opencloud_thirdparty_reg.ASSOCURIS_V2; -
Verify that there are no messages printed to the console after running the
TRUNCATEcommand. -
Exit the Cassandra CLI by running:
$ exit| |
If the TRUNCATE command fails, run the next command (nodetool clearsnapshot), before attempting to run the TRUNCATE command and the nodetool command again. |
Clear snapshots on all TSN nodes
-
SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) into each of the TSNs sequentially and run the command:
$ nodetool clearsnapshot opencloud_thirdparty_reg --allVerify that the truncation has been successful
-
Run the command:
$ df -h-
Verify that for the following two rows in the output, the
<use>%values are less than 50%:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
[...]
/dev/sda3 <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /
[...]
/home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data| |
If the disk usage is over 50%, do not proceed with the rest of the steps and contact Metaswitch technical support. |
-
Exit the TSN by running:
$ exitUpload the config
The backup config, which was taken during the pre-maintenance window steps, is required to change the schema that is in use.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Copy the backup over
~/yamls:cp -f ~/yamls-rollback/* ~/yamls/ -
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig upload-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t mmt-<gsm|cdma> -i ~/yamls --vm-version-source this-rvtconfigVerify that the configuration has uploaded successfully
-
Verify that the output after the command has completed running includes the following sentence:
Wrote config for version <version>, deployment ID <deployment-id>, and group ID <group-id>-
Exit the SIMPL VM by running:
$ exit-
Use SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) to access each of the MMTs. -
From the home directory, run the command:
$ report-initconf statusuntil the following is displayed in the output:
status=vm_converged| |
If after 15 minutes, the status of the VMs is not converged, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Test the rollback
-
Perform a test call to force a registration.
| |
If the test call does not succeed, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Exit the maintenance window
Take the deployment out of maintenance window mode.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path> $ ./rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id> -
verify the command output includes the following:
Maintenance window has been terminated. The VMs will resume running scheduled tasks as per their configured schedules.
Change the schema for SMO nodes
The default schema uses the first-party REGISTER callID field as a part of the primary key. RFC 3261 Section 10.2 states that User Equipment (UE) should use the same callID for the duration of the time it is registered. As the specification allows UE to use different CALLID values for the same registration, this requires proper handling.
As the callID is a part of the primary key, one row is used per unique callID, which may result in multiple rows representing the same logical registration. In cases where a significant proportion of UE on the network do not reuse their callID significantly more disk space is required to hold registration records. This contributes to the disk space for registration records being unpredictable under some circumstances.
The alternate schema uses the IMS private identity (hereafter deviceID) in place of callID in the schema. Per 3gpp 24.229 specification this must be set on all REGISTER attempts. As the deviceID does not change from registration attempt to registration attempt, the size of the database is more predictable.
See Data Schema for details of the Registrar schemas.
The following sections provide instructions for switching to the alternate schema on the SMO node. The required tables already exist on the TSN. You will change SMO configuration to use the alternate tables.
Impacts
During the change of the schema, the system may be affected as follows:
-
There will be an increase in the number of HSS queries. This is because the third-party registrations serve as a cache, and in their absence, devices can only be verified through queries to the HSS. After the procedure is complete, the number of HSS queries should gradually return to the pre-maintenance window level.

The speed at which the number of HSS queries returns to normal depends on the registration validity period. It can be very quick or fairly slow. It is anticipated to be very quick on average. -
When you run the
TRUNCATEcommand, disk usage will not drop immediately. Disk usage will only drop after thenodetool clearsnapshotcommand is run. This is because theTRUNCATEcommand moves the data to a snapshot instead of deleting. The snapshot is only removed when thenodetool clearsnapshotcommand is run.
| |
If you encounter any impacts that are not listed, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Pre-maintenance window steps for changing the Cassandra schema
Before entering the maintenance window you need to take some steps to get prepared. Performing these beforehand ensures that changing the Cassandra schema is a smooth exercise. Some steps can be done well in advance. Other steps need to bedone immediately before entering the maintenance window, as they are a final check to ensure everything is ready for the change.
Pre-maintenance window steps that can be done in advance
Verify the deployed SMO version
Make sure that the SMO VMs have already been upgraded to at least the maintenance version of RVT 4.1-1-1.0.0. The configuration changes that are being made will only work if the SMO is at least this version.
Create file with commands to run
There are commands that will need to be run in preparation for and during the Cassandra schema change. These commands requires specific arguments that need to be prepared beforehand. Creating a file of commands ready to be copy/pasted and run beforehand ensures smooth running of the steps. Placeholder values are of the form <…>. <a|b> means a choice of either a or b. For example, mmt-<gsm|cdma> means mmt-gsm or mmt-cdma.
The file of commands can be stored anywhere that is convenient.
Many of the commands are rvtconfig commands. Further information can be found in the rvtconfig reference.
Determine the following arguments:
-
tsn-mgmt-address- The management IP address of at least one TSN node. The TSN management IP addresses can be found in theTSNsection of the SDF. If multiple addresses are used, they should be formatted as-c <address1> <address2>…. -
deployment-id- This can be found in the SDF under the keydeployment-id. -
site-id- The site-id of the site you are changing config for. This can be found in the SDF assite-id. -
group-id- The group-id of the SMO vnf,RVT-smo.<site-id>. -
sdf-path- The path to the SDF file on your SIMPL VM. -
rvtconfig-path- The path to the rvtconfig on your SIMPL VM. This is expected to be something like:/home/admin/.local/share/csar/smo/<version>/resources
If Cassandra authentication is enabled, then two additional arguments will be required for every rvtconfig command.
-
cds-username- Username to authenticate with Cassandra. You can find it in the SDF undercassandra-username. -
cds-password-secret-name- Password identifier to authenticate with Cassandra. You can find it in the SDF undercassandra-password-id.
They are added in the format --cds-username <cds-username> --cds-password-secret-name <cds-password-secret-name> as the last two arguments to every rvtconfig command.
Create a text file containing all the subsequent commands with substitutions completed.
Take a backup of the current configuration
In case you need to roll back later, prepare a copy of the current configuration. Otherwise, you may have to recreate your configuration files manually.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path> $ rvtconfig dump-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> --group-id <group-id> --vm-version-source this-rvtconfig --output-dir ~/yamls-rollback
--output-diris the output directory for thervtconfig dump-configcommand. Any easily accessible directory can be chosen and the command will create the directory if it does not exist. The recommendation is to maintain~/yamls-rollback, as this value is referenced in the rollback procedure. In the event that a different folder is used, substitute that value for~/yamls-rollbackin the rollback procedure.
Create the new configuration file
The new configuration needs to be written for upload. The configuration points to change are located in the smo-overrides.yaml file in ~/yamls. Create the file if it does not exist.
SMO configuration change
| |
Contact Metaswitch technical support for assistance with writing the new configuration. |
| |
Yaml uses semantic whitespace. The resulting file must be valid yaml that rvtconfig can accept. |
If smo-overrides.yaml does not exist, create it with the following content:
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''
profile-tables:
- name: RegistrarConfigurationTable
profiles:
- name: 'Metaswitch::::'
present: true
attributes:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'If smo-overrides.yaml exists and does not contain the string RegistrarConfigurationTable, insert the following contents immediately below the line profile-tables::
- name: RegistrarConfigurationTable
profiles:
- name: 'Metaswitch::::'
present: true
attributes:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'If smo-overrides.yaml exists and contains the string RegistrarConfigurationTable, insert the following into the attributes key of RegistrarConfigurationTable:
- name: usePrivateIdAsRegistrarDataPrimaryKey
content: 'true'Pre-maintenance window steps to be done immediately prior to entering the maintenance window
| |
Before performing these steps, ensure that you have: |
-
A file with all the commands that need to be run for changing the Cassandra schema. The commands will have all the required arguments substituted.
-
Two sets of
.yamlconfiguration files - the new configuration (~/yamls), the current config (~/yamls-rollback). -
Verified that the deployment consists of the right version of the VMs.
Compare live configuration on SMOs with configuration on SIMPL
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Verify that the directory
/tmp/checkdiffdoes not exist. If the directory does exist, remove it. -
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig compare-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t smo -i ~/yamls-rollback --output-dir /tmp/checkdiff --vm-version-source this-rvtconfig| |
--output-dir is the output directory for the rvtconfig compare-config command. The command will create the directory if it does not exist and will return an error if the directory does exist. |
-
Verify that the command completes with:
No differences found in yaml files.
Uploading this configuration will have no effect unless secrets, certificates or licenses have changed, or --reload-resource-adaptors is specified.If the output returned does not include "No differences found in yaml files.", contact Metaswitch technical support.
Perform health checks on SMOs in the deployment
The deployment needs to be in a healthy state. To verify that the deployment is healthy, run the following tests.
Enter the maintenance window
If all the healthchecks above pass, start a maintenance window and then run through the steps for changing the Cassandra schema. To enter a maintenance window:
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig enter-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>Procedure
This section describes the steps for changing the primary key for SMO nodes. These steps are expected to take 30 minutes to complete.
| |
Before beginning these steps, ensure that the placeholder values in commands listed here have been substituted with the required values. Placeholder values are of the form <…>. |
Truncate the registrations and assocuris tables on Cassandra
The existing registrations and assocuris tables take up some space on disk. Truncate these tables to ensure free disk space is over 50%. Truncation must be run on one TSN node.
-
Use SSH to access the TSN as the primary user (
sentinel). -
Start the Cassandra CLI by running the command:
$ cqlsh-
Truncate the tables by running the command:
TRUNCATE opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg.REGISTRATIONDATA;
TRUNCATE opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg.ASSOCURIS;-
Verify that there are no messages printed to the console after running the TRUNCATE command.
-
Exit the Cassandra CLI by running:
$ exit| |
If the TRUNCATE command fails, run the next command (nodetool clearsnapshot), before attempting to run the TRUNCATE command and the nodetool command again. |
Clear snapshots on all TSN nodes
-
SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) into each of the TSNs sequentially and run the command:
$ nodetool clearsnapshot opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg --allVerify that the truncation has been successful
-
Run the command:
$ df -h-
Verify that for the following two rows in the output, the
<use>%values are less than 50%:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
[...]
/dev/sda3 <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /
[...]
/home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data| |
If the disk usage is over 50%, do not proceed with the rest of the steps and contact Metaswitch technical support. |
-
Exit the TSN by running:
$ exitUpload the configuration
The new configuration written during the pre-maintenance window steps, is required to change the schema that is in use.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig upload-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t smo -i ~/yamls --vm-version-source this-rvtconfigVerify that the configuration has uploaded successfully
-
Verify that the output after the command has completed running includes the following sentence:
Wrote config for version <version>, deployment ID <deployment-id>, and group ID <group-id>-
Exit the SIMPL VM by running:
$ exit-
Use SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) to access each of the SMOs. -
From the home directory, run the command:
$ report-initconf statusuntil the following is displayed in the output:
status=vm_converged| |
If after 15 minutes, the status of the VMs is not converged, proceed to Rollback. |
Test the new tables
-
Perform a test SMS to force a registration.
| |
If the test SMS does not succeed, proceed to Rollback. |
Exit the maintenance window
Take the deployment out of maintenance window mode.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id>-
verify the command output includes the following:
Maintenance window has been terminated. The VMs will resume running scheduled tasks as per their configured schedules.
Rollback
This section describes the steps for rolling back the change of primary key for SMO nodes. These steps are expected to take 30 minutes to complete.
Truncate the registrations_v2 and assocuris_v2 tables on Cassandra
The existing registrations_v2 and assocuris_v2 tables take up some space on disk. Truncate these tables to ensure free disk space is over 50%. Truncation must be run on one TSN node.
-
Use SSH to access the TSN as the primary user (
sentinel). -
Start the Cassandra CLI by running the command:
$ cqlsh-
Truncate the tables by running the command:
TRUNCATE opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg.REGISTRATIONDATA_V2; TRUNCATE opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg.ASSOCURIS_V2; -
Verify that there are no messages printed to the console after running the
TRUNCATEcommand. -
Exit the Cassandra CLI by running:
$ exit| |
If the TRUNCATE command fails, run the next command (nodetool clearsnapshot), before attempting to run the TRUNCATE command and the nodetool command again. |
Clear snapshots on all TSN nodes
-
SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) into each of the TSNs sequentially and run the command:
$ nodetool clearsnapshot opencloud_ipsmgw_thirdparty_reg --allVerify that the truncation has been successful
-
Run the command:
$ df -h-
Verify that for the following two rows in the output, the
<use>%values are less than 50%:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
[...]
/dev/sda3 <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /
[...]
/home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data <size> <used> <avail> `<use>%` /home/sentinel/cassandra-ramdisk/data| |
If the disk usage is over 50%, do not proceed with the rest of the steps and contact Metaswitch technical support. |
-
Exit the TSN by running:
$ exitUpload the config
The backup config, which was taken during the pre-maintenance window steps, is required to change the schema that is in use.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Copy the backup over
~/yamls:cp -f ~/yamls-rollback/* ~/yamls/ -
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path>
$ ./rvtconfig upload-config -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -t smo -i ~/yamls --vm-version-source this-rvtconfigVerify that the configuration has uploaded successfully
-
Verify that the output after the command has completed running includes the following sentence:
Wrote config for version <version>, deployment ID <deployment-id>, and group ID <group-id>-
Exit the SIMPL VM by running:
$ exit-
Use SSH as the primary user (
sentinel) to access each of the SMOs. -
From the home directory, run the command:
$ report-initconf statusuntil the following is displayed in the output:
status=vm_converged| |
If after 15 minutes, the status of the VMs is not converged, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Test the rollback
-
Perform a test SMS to force a registration.
| |
If the test SMS does not succeed, contact Metaswitch technical support. |
Exit the maintenance window
Take the deployment out of maintenance window mode.
-
Use SSH to access the SIMPL VM.
-
Run the command:
$ cd <rvtconfig-path> $ ./rvtconfig leave-maintenance-window -c <tsn-mgmt-address> -d <deployment-id> -S <site-id> -
verify the command output includes the following:
Maintenance window has been terminated. The VMs will resume running scheduled tasks as per their configured schedules.
RVT service centralization and continuity configuration
This section describes how to set up the service centralization and continuity (SCC) services.
Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS)
What it does
Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS) is a component of the terminating SCC AS that determines whether a call should be delivered over the circuit-switched (CS) or the packet-switched (PS) network. It adjusts the SIP signaling as required to deliver the call over the CS or PS network.
Routing mode
T-ADS supports several different modes which determine how it will prioritize its attempts to connect to the CS and/or PS networks. The mode to use for any given call is not determined by T-ADS configuration, but instead by a parameter on the Route header of the incoming SIP INVITE request. The parameter’s name is oc-tads-routing. It can have the following values:
| Parameter value | Behavior |
|---|---|
ps-cs |
T-ADS first attempts to connect the call over the PS network, and falls back to the CS network if that fails. |
cs-ps |
T-ADS first attempts to connect the call over the CS network, and falls back to the PS network if that fails. |
ps-only |
T-ADS only attempts to connect the call over the PS network. |
cs-only |
T-ADS only attempts to connect the call over the CS network. |
parallel |
T-ADS forks the call and attempts to connect the call over the CS and PS networks simultaneously; the first fork to be successfully answered is selected. |
If the parameter is absent, the ps-cs behavior is used.
All modes other than parallel are collectively known as "sequential" modes.
| |
Route header parameters can be set in the subscriber’s initial filter criteria (iFC) on the HSS. |
Request disposition
In one particular case, the Request-Disposition header (defined in RFC 3841) can alter the behavior selected by the oc-tads-routing parameter. If the Request-Disposition header contains the value no-fork and does not also contain the value redirect, then:
-
ps-csandparalleluse theps-onlybehavior -
cs-psuses thecs-onlybehavior.
CS routing
When T-ADS attempts to route the call over the CS network, it will generate a CS Domain Routing Number (CSRN). This number is used in the Request-URI of the outbound INVITE request. There are a few options for how T-ADS should generate the CSRN.
The basic number can be taken from any of the following numbers:
-
Correlation Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number (C-MSISDN), which is retrieved from the HSS
-
Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN), which is retrieved from the HLR (for GSM networks only)
-
Temporary Local Directory Number (TLDN), which is retrieved from the HLR (for CDMA networks only).
An optional prefix can be specified that will be added to that number to create the final CSRN.
Routing via the I-CSCF
When routing to the CS network, it may be desirable to send the outbound INVITE request directly to the I-CSCF, bypassing the S-CSCF and thus any further IMS services that it might try to invoke. This can be configured with the cs-routing-via-icscf field.
PS routing
T-ADS supports three different modes for determining where to route requests to the PS network. It may route to:
-
the subscriber’s IMS public identity
-
the SIP instance(s) that are recorded in
pub-gruuinformation in the subscriber’s registration data -
the SIP instance(s) that are recorded in
pub-gruuandPathinformation in the subscriber’s registration data.
Both modes that use SIP instances can result in multiple different attempts to connect the call over the PS network (one attempt for each acceptable SIP instance).
Route validation and voice over PS support
Unless there is an oc-blindpsrouting parameter present on the Route header of the initial INVITE request for a call, T-ADS will do additional validation on each PS route before deciding to use it.
The method for doing this validation depends on the setting for voice-over-ps-support.
If voice over PS support is required, the route will be validated by explicitly asking the HSS if voice over PS is supported for that route. If voice over PS support is not required, the route will be validated by checking access network information in the subscriber’s registration data.
When querying the HSS for voice over PS support, there are several different options for which subscriber identity to query the information for. The option to use varies depending on the network. The options are listed here.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
IMPU |
The IMS public identity |
MSISDN |
The C-MSISDN |
IMPU_IMPI |
A combination of the IMS public and private identities |
MSISDN_IMPI |
A combination of the C-MSISDN and the IMS private identity |
Voice over Wi-Fi
By default, T-ADS will select PS routes that go through the PS cellular network. The system also supports PS routes that go through the internet and Wi-Fi. You can configure this with the wlan-allowed field.
Deciding on a route
This section describes the approach T-ADS uses to decide whether a particular routing attempt has been successful. The routing mode determines the order in which routes are attempted (or whether they should all be attempted at the same time in the case of parallel mode). It is important to note that even if a particular route receives a SIP error response, T-ADS may still determine it was a successful routing attempt and forward the response to the caller, thus ending the call.
In sequential routing modes
Usually, a route is selected and T-ADS completes once a non-100 SIP response is received from a connection attempt on that route (which is true even if the response is an error response that will cause the call to be terminated). A route is usually only rejected if no response is received within the maximum wait time period specified in the tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds setting. However, there are exceptions to this:
-
If a provisional SIP response is received that has an SDP body with a disabled audio stream and the subscriber is known to have multiple devices on the current route, the response will be ignored and the maximum wait time will be reset.
-
If a SIP error response with a 488 status code is received, the route is rejected.*
-
If attempting a PS route and a SIP error response is received with a status code matching a code in
ps-fallback-response-codes, the route is rejected.*
* If all PS routes have been exhausted and the error response has an SDP body with no PSTN audio streams, the call will be terminated instead.
When a route is rejected, T-ADS aborts the connection attempt and attempts to connect the call on the next available route. If all available routes have been rejected, the call is terminated.
In parallel routing mode
The first route to receive a SIP success response is selected. If all routes respond with a SIP error response or the maximum wait time period specified in the parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds setting is exceeded, the call is terminated.
As a special case when the companion device service is in use, if a 486 Busy SIP response is received from any route it is possible to end the call immediately. You can configure this with the release-all-legs-on-busy setting.
Interactions with other services
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
If an attempt to connect the call over the CS network fails, it is possible that communication forwarding could be triggered twice; the first time downstream of the SCC AS in the CS core network, the second time in the IMS core upstream in the MMTel AS.
T-ADS can be configured to suppress communication forwarding services in the CS network. It does this by imposing a limit on the number of times the call may be forwarded, then indicating that the limit has been reached. SIP Diversion headers are used to send this information to the CS network, with limit parameters used to set the limit. One of the following methods is used to indicate that the limit has been reached:
-
including a pair of
Diversionheaders that each have acounterparameter which, between the two, sums to the diversion limit, or -
including a number of
Diversionheaders that matches the limit.
For configuration instructions, see Suppress call forwarding services in the CS network.
For details of how to suppress forwarding in the MMTel AS, see Communications Diversion (CDIV).
Companion device
The companion device service may force T-ADS to ignore the requested routing mode and use parallel instead. Restrictions imposed by the Request-Disposition header will still apply in this case.
The companion device service may also provide its own set of CSRNs for T-ADS to use when attempting to connect the call over the CS network.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to T-ADS in the sentinel-volte/tads section.
What you need
-
❏ The source for generating the CSRN for CS delivery; one of:
C-MSISDN,MSRN, orTLDN. -
❏ The source for generating potential PS routes; one of:
IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY,SIP_INSTANCE, orPATH_FROM_SIP_INSTANCE. -
❏ If checking for Voice Over PS support before routing over PS to a subscriber, the identity to use when querying the HSS; one of:
IMPU,MSISDN,IMPU_IMPI, orMSISDN_IMPI -
❏ Whether or not calls outbound to the CS network should bypass the S-CSCF and go directly to the I-CSCF.
-
❏ Whether or not calls are allowed to be delivered over a Wi-Fi network.
-
❏ What error code to send to the caller if the call is terminated due to no routes being found.
If using the parallel routing mode:
-
❏ The maximum time to wait for a call to be answered.
-
❏ Whether or not to abort the call if any routing attempt receives a 486 Busy response.
If using any sequential routing modes:
-
❏ The maximum time to wait for a response during a particular routing attempt.
-
❏ Any SIP error codes that you would like to trigger an attempt on the next available route, instead of ending the call.
Setting up CS routing behavior
I want to…
Generate the CSRN from the C-MSISDN when routing to the CS network
| |
Ensure that HSS integration has been configured. |
In the tads section, set address-source-for-scc-tads to CMSISDN:
address-source-for-scc-tads: CMSISDNRelated section: CS routing
Generate the CSRN from the MSRN when routing to the CS network
| |
Ensure that HLR integration has been configured. |
| |
Be aware that the MSRN is only available on GSM networks. |
In the tads section, set address-source-for-scc-tads to MSRN:
address-source-for-scc-tads: MSRNRelated section: CS routing
Generate the CSRN from the TLDN when routing to the CS network
| |
Ensure that HLR integration has been configured. |
Be aware that the TLDN is only available on CDMA networks.
In the tads section, set address-source-for-scc-tads to TLDN:
address-source-for-scc-tads: TLDNRelated section: CS routing
Include a number prefix (steering digits) on the generated CSRN
In this example 00 is used as the prefix.
In the tads section, set csrn-prefix to "00":
csrn-prefix: "00"Related section: CS routing
Prevent T-CSI information from being requested from the HLR
| |
This is only relevant on GSM networks when using the MSRN to generate the CSRN. |
In the tads section, in sri-requests-to-hlr, set set-suppress-tcsi-flag to true:
sri-requests-to-hlr:
set-suppress-tcsi-flag: truePrevent announcement information from being requested from the HLR
This is only relevant on GSM networks when using the MSRN to generate the CSRN.
In the tads section, in sri-requests-to-hlr, set set-suppress-announcement-flag to true:
sri-requests-to-hlr:
set-suppress-announcement-flag: trueRoute calls to the CS network directly through the I-CSCF
| |
Ensure that I-CSCF integration has been configured. |
In the tads section, set cs-routing-via-icscf to true:
cs-routing-via-icscf: trueRelated section: Routing via the I-CSCF
Route calls to the CS network through the S-CSCF
In the tads section, set cs-routing-via-icscf to false:
cs-routing-via-icscf: falseRelated section: Routing via the I-CSCF
Suppress call forwarding services in the CS network
In the tads section, ensure that the suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion section is present and not commented out.
suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion:
use-diversion-counter-parameter: true
cs-domain-diversion-limit: 1-
Set
use-diversion-counter-parameterto:-
trueto indicate that the limit has been reached using the counter parameter on the SIPDiversionheader, or -
falseto indicate that the limit has been reached using the number ofDiversionheaders present.
-
-
Set
cs-domain-diversion-limitto the maximum number of times you want to indicate that call forwarding was allowed (note that no matter what this setting is, T-ADS will still indicate that the limit has been reached).
Related section: Interaction with call forwarding
Allow call forwarding services in the CS network
In the tads section, remove or comment out the entire suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion section.
# suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion:
# use-diversion-counter-parameter: true
# cs-domain-diversion-limit: 1Related section: Interaction with call forwarding
Setting up PS routing behaviour
I want to…
Route the PS attempt to the subscriber’s IMS public identity
In the tads section, set tads-identity-for-terminating-device:
tads-identity-for-terminating-device: IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITYRelated section: PS routing
Route PS attempts to the SIP instance of the terminating device(s)
In the tads section, set tads-identity-for-terminating-device:
tads-identity-for-terminating-device: SIP_INSTANCERelated section: PS routing
Route PS attempts to the SIP instance path of the terminating device(s)
In the tads section, set tads-identity-for-terminating-device:
tads-identity-for-terminating-device: PATH_FROM_SIP_INSTANCERelated section: PS routing
Check that a subscriber has support for Voice Over PS before attempting to route over the PS network
| |
Ensure that HSS integration has been configured. |
In the tads section, ensure that the voice-over-ps-support section is present and not commented out.
voice-over-ps-support:
request-user-identity-type: IMPUSet which subscriber identity to use when querying the HSS for the voice over PS support information. See request-user-identity-type for the list of options.
Related section: Route validation and voice over PS support
Skip the check that the subscriber has voice over PS support before attempting to route the call over the PS network
In the tads section, remove or comment out the entire voice-over-ps-support section.
# voice-over-ps-support:
# request-user-identity-type: IMPURelated section: Route validation and voice over PS support
Setting up route selection behavior
I want to…
Change the SIP response code used to end the call if no valid route to the called party can be found
In this example the call will be ended with a 410 Gone response.
In the tads section, set end-session-error-code:
end-session-error-code: 410End all companion device connection attempts if any one of them returns a 486 Busy response
In the tads, on-parallel-routing section, set release-all-legs-on-busy:
release-all-legs-on-busy: trueRelated section: Deciding on a route in parallel routing mode
Change the maximum time to wait to get a final response from any parallel connection attempt
This example sets the maximum wait time to 15 seconds.
In the tads , on-parallel-routing section, set parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds to the desired value in milliseconds:
parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 15000Related section: Deciding on a route in parallel routing mode
Try the next available route if a PS attempt results in a particular SIP response status code or codes
| |
A 488 response will always cause the next available route to be attempted, and does not need to be included in this field. |
This example lists 408, 480, and 481 as the codes that should trigger the next routing attempt.
In the tads, on-sequential-routing section, set ps-fallback-response-codes with the list of desired response codes:
ps-fallback-response-codes: [ 408, 480, 481 ]Related section: Deciding on a route in sequential routing modes
Change the maximum time to wait for a response before trying the next route
| |
This setting is only relevant when using a sequential routing mode and is subject to the provisional response condition described in Deciding on a route in sequential routing modes. |
In the tads, on-sequential-routing section, set tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds to the value in milliseconds:
tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 5000Access transfer
What it does
Access transfer is a Rhino VoLTE TAS SCC service that is responsible for managing the handover of a call from a packet switched (PS) network to a circuit switched (CS) network when a subscriber moves out of PS network coverage. It works by replacing the existing access leg (that is, the SIP leg between the Rhino VoLTE TAS and the served user) with a new one.
Access transfer is initiated on receipt of a new initial INVITE request that has a Request-URI which aligns with either the configured ATU-STI or STN-SR. Initially this request is not directly associated with the call it applies to, and initially may not even be processed by the same Rhino VoLTE TAS node that is handling the original call. Information in the new INVITE request is used to correlate it with the original call so that it can be injected into that call, where it is used to establish the new access leg.
Supported cases
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) for PS to CS transfer of sessions in the following cases:
-
a single active session with media anchored in the Access Transfer Gateway (eSRVCC)
-
a single active session with media not anchored in the Access Transfer Gateway (standard SRVCC)
-
a single alerting session (aSRVCC)
-
a single originating session in the pre-alerting state (bSRVCC).
If a device initiates access transfer while it has multiple sessions in progress (for example, if the subscriber has someone on hold while talking on another call), only the most recently active session will be transferred. All other sessions are treated as superfluous and are ended as part of the transfer procedure.
Enabling access transfer
Access transfer is not enabled through configuration. Instead, it is enabled per-call if both of the following requirements are met:
-
The served subscriber’s registration data indicates that their device has
UE-SRVCC-Capability. -
The served subscriber has an assigned C-MSISDN in the HSS.
There are additional requirements for alerting and pre-alerting access transfer. These take the form of media feature tags in the SIP Contact header from the subscriber. For the calling subscriber this head will be checked on the initial INVITE request, for the called subscriber the first SIP 18x response will be checked. To enable alerting access transfer there must be a +g.3gpp.srvcc-alerting tag, and for pre-alerting access transfer there must be a +g.3gpp.ps2cs-srvcc-orig-pre-alerting tag. Note that pre-alerting access transfer is only applicable to the calling subscriber.
Access Transfer Control Function
Access Transfer Control Function (ATCF) is a signalling anchor that is used for eSRVCC procedures. It is responsible for initiating access transfer procedures in the Rhino VoLTE TAS by sending a INVITE request using the ATU-STI as the Request-URI.
To determine where to send access transfer requests, the ATCF must know the ATU-STI to use for a given subscriber. The Rhino VoLTE TAS is responsible for notifying the ATCF of the ATU-STI, which it does by sending it in a SIP MESSAGE request when the subscriber registers with the network. The maximum time that the Rhino VoLTE TAS should wait for a response to the MESSAGE request can be configured in the atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds field.
STN-SR and ATU-STI
The STN-SR (Session Transfer Number for SRVCC) and ATU-STI (Access Transfer Update - Session Transfer Identifier) serve the same purpose of identifying that an incoming request is for access transfer. The main difference between the two is that they are used to trigger different versions of the access transfer procedure.
The STN-SR is used for access transfer as defined in the Rel-8 3GPP specifications, where signalling is not anchored in the ATCF, therefore the Rhino VoLTE TAS receives the transfer request directly from the MSC (Mobile Switching Center, part of the CS core network). It takes the form of a number prefix on the Request-URI of the incoming access transfer request. The only requirement for picking an STN-SR is that it must cause messages to be delivered to the Rhino VoLTE TAS. When a subscriber registers with the network, the Rhino VoLTE TAS will update their STN-SR in the HSS to match what is configured here.
The ATU-STI is used for access transfer, as defined in the Rel-10 3GPP specifications, where signalling is anchored in the ATCF, therefore the transfer request comes from the ATCF. It is a fixed URI that is used as the Request-URI on access transfer requests. As the Rhino VoLTE TAS tells the ATCF what ATU-STI to use for a subscriber, the only requirement for its value is that it resolves to the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to access transfer in the sentinel-volte/scc/service-continuity section.
What you need
-
❏ The STN-SR that will trigger Rel-8 access transfer.
-
❏ Optionally, a custom timeout period to wait for a response from the ATCF when updating the ATU-STI for a subscriber.
Setting up access transfer
I want to…
Set the STN-SR for triggering Rel-8 access transfer
In the service-continuity section, set stn-sr with the desired number prefix:
stn-sr: "123456"Related section: STN-SR and ATU-STI
Change how long to wait for the ATCF to respond to a request to update a subscriber’s ATU-STI
In the service-continuity section, set atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds with the desired time period, in milliseconds:
atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds: 5000Related section: Access Transfer Control Function
Reorigination
What it does
Reorigination enables CS calls to be processed in the SCC-AS. SS7 triggers received by the Rhino VoLTE TAS are forwarded to a number within a pre-defined range, which causes the call to be rerouted into the IMS. The SCC-AS then acts as a B2BUA between the I-CSCF and the subscriber’s assigned S-CSCF.
Routing through the I-CSCF
The SCC-AS will add a CSCF address to the route header of the outgoing INVITE message. This address can be either the calling party’s S-CSCF address retrieved from the HSS, or it can be the I-CSCF address configured in i-cscf-uri.
Anti-fraud measures
To guard against fraud, the P-Asserted-Identity from the incoming INVITE can be compared to the normalized calling party number from the InitialDP. If they do not match, the request is rejected with a 403 response.
The P-Visited-Network-Information header
The SCC-AS will add a P-Visited-Network-Information header to the outgoing INVITE. It is recommended that this is set according to IR.65, section 6.2.1, that is, that the format for this is epc.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org if the version followed is 12 or less, or ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org if a later version is used. The values of <MCC> and <MNC> are extracted from the triggering SS7 message.
The IP Multimedia Routing Number pool
The number used as the interchange between the SS7 and IP networks (the IMRN) must belong to a pre-allocated, reserved range of values. These numbers must be reserved to prevent overlap with numbers in use by subscribers. The pre-allocated range must be configured within the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
The pool of values does not need to be overly large, as values will only be reserved for the time between the receipt of the SS7 trigger and the processing of the INVITE. As an approximation, with normal error rates and a 20 ms interval between IMRN reservation (on the SS7 end) and IMRN return-to-pool, a range of 1000 values will accommodate 50,000 calls per second. Adjust the pool sizings to meet network requirements accordingly.
The simple-imrn-pool defines the digit string, with the cdma-imrn-formation and gsm-imrn-formation sections defining the protocol-specific digit formatting details.
Bypass reorigination for unregistered subscribers
If a subscriber is not registered in the IMS network, reorigination from SS7 to IMS can be skipped to avoid unnecessary processing. This bypass can be enabled for all unregistered subscribers, or for only non-roaming subscribers (to support terminating charging of roaming subscribers through the IMS).
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to reorigination in the sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation section.
What you need
-
❏ The expected format of the
P-Visited-Network-Informationheader. -
❏ The range of numbers available to be used as the IMRN.
-
❏ The expected format of the IMRN.
Setting up reorigination
I want to…
Use the configured I-CSCF address and prevent the HSS from being queried
To include the configured I-CSCF address in the route header of the outgoing INVITE, in the service-centralisation section, set use-direct-icscf-routing:
use-direct-icscf-routing: trueRelated section: Routing through the I-CSCF
Set the format of the PVNI header to the later standard
To set the P-Visited-Network-Information header template to the later format, in the service-centralisation section, set generated-pvni-template:
generated-pvni-template: "ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org"Related section: The P-Visited-Network-Information header
Reject messages sent to an IMRN where the P-Asserted-Identity does not match the recorded calling party digits
To enable comparing the P-Asserted-Identity header to the normalized calling party number, in the service-centralisation section, set police-originating-requests:
police-originating-requests: trueRelated section: Anti-fraud measures
Set a 1000 element IMRN range
To create a 1000 element range with 10-digit numbers from 5550000000 to 5550000999, in the service-centralisation section, set the values in simple-imrn-pool as follows:
simple-imrn-pool:
minimum-correlation-id: 5550000000
maximum-correlation-id: 5550000999
number-of-digits-in-correlation-id: 10Related section: The IP Multimedia Routing Number pool
Configure the CDMA responses sent in error conditions
In CDMA networks, the responses sent in error conditions are configured in the scc-cdma-actions section.
scc-cdma-actions:
action-on-unsupported-trigger: accessDeniedReason_terminationDenied
action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number: accessDeniedReason_busy
default-failure-action: accessDeniedReason_serviceDeniedTo configure the error response:
-
when an invalid SS7 trigger is received, set the
action-on-unsupported-trigger -
when an internal error occurred and the Rhino VoLTE TAS could not generate an IMRN, set the
action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number -
on other errors, set the
default-failure-action.
Set the format of the GSM IMRN
In GSM networks, the non-digitstring section of the IMRN is configured in the scc-gsm-service-centralisation, gsm-imrn-formation section.
gsm-imrn-formation:
routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed: true
nature: NATIONAL
numbering-plan: ISDNTo configure the GSM IMRN information:
-
set
routing-to-internal-network-number-allowedastrue. -
set
natureasNATIONAL -
set
numbering-planasISDN
Set the format of the CDMA IMRN
In CDMA networks, the non-digitstring section of the IMRN is configured in the scc-cdma-service-centralisation, cdma-imrn-formation section.
cdma-imrn-formation:
imrn-type-of-digits: DIALED_OR_CALLED_PARTY_NUMBER
imrn-nature-of-number: INTERNATIONAL
imrn-numbering-plan: TELEPHONYTo configure the CDMA IMRN information, set:
-
imrn-type of digitsasDIALED_OR_CALLED_PARTY_NUMBER -
imrn-nature of numberasINTERNATIONAL -
imrn-numbering planasTELEPHONY.
Bypass terminating reorigination for unregistered subscribers on GSM networks
In GSM networks, the terminating reorigination trigger can be bypassed for subscribers that are not registered in the IMS.
To enable this, in the scc-gsm-service-centralisation section, set bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered:
bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered: trueBypass terminating reorigination for unregistered, non-roaming subscribers on GSM networks
In GSM networks, the terminating reorigination bypass can be enabled for all unregistered subscribers, or for only non-roaming subscribers.
To bypass reorigination for unregistered subscribers while still reoriginating roaming traffic, in the scc-gsm-service-centralisation section, set bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered and always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming:
This will result in only unregistered, non-roaming subscribers bypassing reorigination. Registered subscribers and roaming subscribers will still reoriginate to the IMS.
bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered: true
always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming: trueBypass reorigination for unregistered subscribers on CDMA networks
In CDMA networks, to bypass reorigination for subscribers that are not registered in the IMS, in the scc-cdma-service-centralisation section, set bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered:
bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered: trueRVT MMTel configuration
This section describes how to configure MultiMedia Telephony (MMTel) services.
- Announcements
- Announcements on call failure
- PSAP callback
- Dial plan enforcement (DPE)
- MMTel privacy settings
- Conference (CONF)
- Call barring
- Communication Waiting (CW)
- Communication Hold (HOLD)
- Communications Diversion (CDIV)
- Voicemail forwarding
- Companion device
- Vertical service codes (VSC)
- International Call Management
- Location based dialing (LBD)
- Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT)
- Flexible Alerting (FA)
- Session transfer to own device
Announcements
What it does
Defines the announcements that are available to be played by the MMTel services.
The announcements themselves are played on the Media Resource Function (MRF) node, which should already be provisioned with the announcements before they are configured here.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to announcements in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement section.
What you need
-
❏ The SIP: or Tel: URI of the media server (MRF) that plays the announcements.
-
❏ Details of the announcements available on that media server:
-
❏ their URI
-
❏ their mime type
-
❏ which locales are available for each announcement.
-
-
❏ Details of how those announcements will be used:
-
❏ Whether to repeat the announcement:
-
❏ and if so, the maximum number of times to repeat
-
❏ and the delay between repetitions.
-
-
❏ Whether or not the announcement can be interrupt by user actions.
-
❏ Whether or not the media stream should be forced to be one way between the MRF and the user during the announcement.
-
❏ Whether to suspend charging while the announcement is playing.
-
❏ Whether to end the call if the announcement cannot be played.
-
Setting up the MRF connection
I want to…
Specify the address of the MRF to use for announcements
In the mmtel, announcement section, set announcements-media-server-uri.
announcements-media-server-uri: sip:annc-audio@mrf-announcements:5260;lr;transport=tcpChange the timeout when signaling the MRF
The default timeout is 1000 ms.
To set a new value, in the mmtel, announcement section, ensure that the announcements-no-response-timeout-milliseconds parameter is present and not commented out. Set the desired value, in milliseconds.
announcements-no-response-timeout-milliseconds: 1500Setting up each announcement
I want to…
Repeat an announcement indefinitely until interrupted by user actions
For the desired announcement in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list:
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: -1
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false-
Set the
repeatvalue to-1, which will send arepeat=foreverparameter to the MRF. -
Set interruptable to
true.
Let the MRF determine how often to repeat the announcement
For the desired announcement in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list, set the repeat value to 0, so it is not sent to the MRF.
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 0
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: falseLet the MRF determine the delay between announcement repetitions
For the desired announcement in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list, set the delay-milliseconds value to 0, so it is not sent to the MRF.
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 0
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: falseLet the MRF determine the duration of the announcement
For the desired announcement in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list, set the duration-milliseconds value to 0, so it is not sent to the MRF.
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 0
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: falseLet the MRF determine the media type of the announcement
For the desired announcement in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list, comment out or delete the mimetype entry.
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
# mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: falseReuse an existing announcement which does not suspend charging, but suspend charging
Duplicate an entire announcement definition in the mmtel, announcement section, announcements list, then change the appropriate values in the new announcement.
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 201
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring - uncharged"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: true-
Change the
idof the copy to a previously unused value, for example,201. -
Change the
descriptionas appropriate. -
Change
suspend-chargingtotrue.
Announcements on call failure
What it does
When a call fails with an error response code (a SIP response code in the range 400 … 699), an announcement may be played to the caller, and the status code may be changed to 487 to hide the true status code.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to call failure announcements in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/ section.
What you need
-
❏ A status code for which you want to play an announcement.
-
❏ The announcement ID of the announcement you wish to play.
-
❏ Whether you want to hide the true status code.
-
❏ Default handling of error codes.
Setting up each announcement
I want to…
Play an announcement when a call fails with a response code 404
Within the mmtel, announcement section, error-code-announcements list, add a new error code announcement entry like this:
error-code-announcements:
- error-code: 404
announcement-id: 24
end-call-with-487-response: false-
Ensure that
error-code-announcementslist is present and not commented out. -
Add a new announcement. Set the values to the following:
-
error-codeto the SIP response code to play the announcement for. -
announcement-idto theidof the announcement to play. -
end-call-with-487-responsetofalseto end the call with the 404 response.
-
Play a default announcement for all other failure response codes
Within the mmtel, announcement section:
default-error-code-announcement:
announcement-id: 22
end-call-with-487-response: false-
Ensure that
default-error-code-announcementis present and not commented out. -
Set
announcement-idto theidof the announcement to play. -
Set
end-call-with-487-responseto:-
falseto end the call with the original response, or -
trueto force all other error codes to replaced with a487response.
-
Only play an announcement for the specified error codes
In the mmtel, announcement section, remove or comment out the entire default-error-code-announcement section.
#default-error-code-announcement:
# announcement-id: 22
# end-call-with-487-response: falsePlay an announcement when a call fails with a response code 488 and change it to a 487 response
Within the mmtel, announcement section, error-code-announcements list, add a new announcement entry like this:
error-code-announcements:
- error-code: 488
announcement-id: 22
end-call-with-487-response: true-
Ensure that
error-code-announcementslist is present and not commented out. -
Add a new announcement. Set the values to the following:
-
error-codeto488. -
announcement-idto theidof the announcement to play. -
end-call-with-487-responsetotrueto end the call with a487response.
-
Not play any announcements triggered solely by an error code
Directly under the mmtel, announcement section, completely remove or comment out both the default-error-code-announcement and error-code-announcements list sections.
announcement:
#default-error-code-announcement:
# announcement-id: 22
# end-call-with-487-response: false
#error-code-announcements:
# - error-code: 486
# announcement-id: 24
# end-call-with-487-response: false
# - error-code: 488
# announcement-id: 22
# end-call-with-487-response: truePlay the same announcement for all error codes except for 404, which has no announcement
In the mmtel, announcement section, set up a default-error-code-announcement as described in Play a default announcement for all other failure response codes, then set up an error-code-announcements list entry for error code 404 with disable-announcement set to true.
announcement:
default-error-code-announcement:
announcement-id: 22
end-call-with-487-response: false
error-code-announcements:
- error-code: 404
# announcement-id: 24
disable-announcement: true
end-call-with-487-response: false-
Ensure that
default-error-code-announcementexists and plays the desired announcement, as above. -
Ensure that
error-code-announcementslist exists and is not commented out. -
Add an entry for the
error-code. -
Remove or comment out its
announcement-id. -
Add
disable-announcement, with the value set totrue.
PSAP callback
What it does
Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP) callback is a service that helps emergency services call back a subscriber after an emergency call has ended. On the Rhino VoLTE TAS, the PSAP callback service ensures that none of a subscriber’s terminating MMTel TAS services (for example, Incoming Call Barring) hinder the callback attempt.
PSAP callback detection
There are two mechanisms available for detecting when a PSAP callback could be occurring:
-
direct notification from the Emergency Call Session Control Function (E-CSCF), or
-
analysis of the Priority header on incoming initial INVITE requests.
Both mechanisms can be used simultaneously. If either mechanism indicates a PSAP callback attempt, then the call will be handled as such.
E-CSCF notification
The Rhino VoLTE TAS can be configured to receive SIP MESSAGE requests from the E-CSCF when a subscriber calls an emergency number. If this behavior is enabled, upon receiving a such a request, the TAS makes a record of the subscriber’s identity that expires after a period of time determined by the expiry-time-seconds configuration field. Until the record expires, all incoming calls to the subscriber are handled as if they are a PSAP callback attempt and many MMTel services will be disabled.
Depending on network requirements, the SIP MESSAGE from the E-CSCF can either be allowed to continue on to its next destination, or the Rhino VoLTE TAS can stop the MESSAGE and generate a final response to the E-CSCF.
Interactions with other services
MMTel terminating services in general
The PSAP callback service’s purpose is to bypass any terminating MMTel TAS services that could potentially prevent emergency services from calling back a subscriber.
When a call is handled as a PSAP callback, the following terminating MMTel services are disabled:
-
Announcements
-
All types of call barring
-
Communication diversion
-
Voicemail forwarding
-
Explicit communication transfer
-
Communication hold
The following terminating MMTel services remain active for PSAP callbacks:
-
Session transfer to own device
-
Flexible alerting
-
Privacy (OIP and TIR)
-
Communication waiting
Online charging
Online charging is handled as a special case. The Rhino VoLTE TAS continues to communicate with the online charging server as normal for the duration of the call, but if the subscriber requires credit to receive the call and it cannot be allocated, the call is still allowed to continue.
Companion device
Certain functions of the companion device service that could interfere with emergency calls are disabled when an emergency call is detected:
-
When a companion device initiates an emergency call, its undisclosed identity will not be hidden.
-
When a PSAP callback attempt is made to the undisclosed identity, the companion device service will not block the call.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to PSAP callback in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/psap-callback section.
What you need
-
❏ Whether or not to use the
Priorityheader to detect PSAP callback attempts. -
❏ Whether or not to use the notifications from the E-CSCF to detect PSAP callback attempts.
If using notifications from the E-CSCF:
-
❏ How long after receiving a notification from the E-CSCF to handle incoming calls for a subscriber as PSAP callbacks.
-
❏ Whether or not to forward the notification onwards after processing it.
Setting up PSAP callback
I want to…
Use the Priority header to detect PSAP callbacks
In the psap-callback section, set use-priority-header to true:
use-priority-header: trueRelated section: PSAP callback detection
Disable use of the Priority header to detect PSAP callbacks
In the psap-callback section, set use-priority-header to false:
use-priority-header: falseRelated section: PSAP callback detection
Use notifications from the E-CSCF to detect PSAP callbacks
In the psap-callback section, add a sip-message-options section:
sip-message-options:
expiry-time-seconds: 86400
terminate-message: true-
The
expiry-time-secondsfield must be set to the period of time in seconds that incoming calls for a subscriber should be treated as PSAP callback attempts. -
The
terminate-messagefield must be set to indicate whether the notification message should be answered by the Rhino VoLTE TAS or forwarded on.
Related section: PSAP callback detection
Disable use of notifications from the E-CSCF to detect PSAP callbacks
In the psap-callback section, remove or comment out the sip-message-options section:
# sip-message-options:
# expiry-time-seconds: 86400
# terminate-message: trueRelated section: PSAP callback detection
Change how long after receiving an E-CSCF notification that incoming calls for a subscriber should be handled as PSAP callbacks
In the sip-message-options section, set the expiry-time-seconds to the desired time period in seconds:
expiry-time-seconds: 10000Related section: E-CSCF notification
Forward E-CSCF notifications onwards to their destination after processing them
In the sip-message-options section, set the terminate-message to false.
terminate-message: falseRelated section: E-CSCF notification
Not forward E-CSCF notifications onwards and instead send a final response for them
In the sip-message-options section, set the terminate-message to true.
terminate-message: trueRelated section: E-CSCF notification
Dial plan enforcement (DPE)
What it does
The dial plan enforcement (DPE) service ensures that a subscriber has dialed a valid number before allowing a call to proceed.
Number analysis
The service works by confirming that the length of the dialed number is within an expected range. The allowed range can vary based on prefixes that the service detects on the number.
For example, the configuration for the service might specify that:
-
a number starting with
087can be between 4 and 9 digits long (not including the prefix itself), and -
all other numbers must be between 4 and 7 digits long.
In this case:
-
12345678would be rejected by the DPE service for having more than 7 digits, but -
08712345678would be allowed since the087prefix means the number can have up to 9 digits after the prefix.
The service may be configured to detect any number of different prefixes with different ranges for each one. If a single number has multiple potential prefix matches, the service will choose the longest matching prefix.
There is a special case for numbers that are in international format. If one begins with either the configured national-prefix or the configured international-prefix, then the DPE service is bypassed. All other international format numbers will be subject to the same enforcement checks as non-international numbers. See the Number normalization section for information about configuring the national and international prefixes.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the DPE service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
MMTel privacy settings
MMTel privacy is a set of services that allow for a calling party identity to be presented and/or restricted.
-
The Originating Identity Restriction (OIR) service adjusts the privacy restrictions for the originating user to restrict its identity.
-
The Originating Identity Presentation (OIP) service enforces the privacy presentation restrictions of the originating user to the terminating user.
-
The Terminating Identity Restriction (TIR) service adjusts the privacy restrictions for the terminating user.
-
The Terminating Identity Presentation (TIP) service enforces the privacy presentation restrictions of the terminating user to the originating user.
These services are subscriber specific and are configured in the HSS inside the MMTel-Services XML document for the subscriber.
System wide defaults are configured for OIR and OIP services using declarative configuration for when the subscriber’s services are not defined/active in the MMTel-Services XML document. No configuration is required for TIR and TIP services.
Originating Identification Restriction (OIR)
What it does
Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) service enables the originating user to prevent presentation of its identity to the terminating user. This allows the network to insert a privacy header field into the originating user’s SIP messages.
The declarative configuration for the OIR applies calling party identity restriction rules network wide for all OIR subscribed parties. Whether the OIR service is active and if it may diverge from this network default is determined by how the subscribers involved are provisioned in the MMTel Services document. The OIR service depends on the originating user’s provisioned settings for OIR.
Setting identity restrictions
The OIR service adjusts the privacy header of the originating party’s outgoing requests. The privacy header designates to the OIP service what should be removed from the request before it reaches the terminating user. The OIP service configuration determines how the privacy header is interpreted and used to remove identifying information.
The provisioned OIR settings for the originating user stored in the HSS MMTel Service document take precedence where relevant. Otherwise, the default network configuration given in the declarative configuration of the Rhino VoLTE TAS is used for all OIR subscribers.
The provided table OIR configurability describes how the user’s provisioned settings and the network wide configuration interact with each other.
| Configurable option | Network configurable options | Subscriber configurable options |
|---|---|---|
When identity restriction occurs for an OIR subscriber |
||
Specific details of when identity restriction occurs are given in 3GPP 24.607 Section 4.5.2.4 |
||
Mode |
|
N/A |
Temporary Mode Default Action |
N/A |
For when temporary mode is active:
|
What is restricted by OIR on a subscriber’s outgoing requests |
||
Presentation Restriction |
|
|
User Policy |
|
N/A |
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to OIR in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/privacy/originating-identification-restriction section.
What you need
-
❏ Whether to set the default presentation restriction for an OIR subscriber to:
-
restrict all private information (
Privacy:header), or -
only restrict the identity (
Privacy:id) of the originating party.
-
-
❏ Whether to set the default OIR subscriber’s OIR user policy to:
-
anonymize the
fromheader in the originating party’s requests, -
restrict all user data in a request (
Privacy:user) and anonymize thefromin the originating party’s requests, or -
to specify no default user policy.
-
You will also need to configure the OIP service as well to enforce these identity restrictions to the terminating user.
Setting up subscriber data
There are subscriber provisioned restriction rules configured in the HSS inside the MMTel-Services XML document for the subscriber.
The presentation-restriction-type subscriber defined restriction rule directly overrides the network’s default configuration.
Setting up service codes
The Rhino VoLTE TAS standard deployment includes service code actions for subscribers to activate OIR.
| Display name | Action |
|---|---|
Set Dialled Caller ID Restriction Type |
Used to override the OIR service’s There are 3 valid values: * * * |
For more information, see Vertical service codes.
Setting up OIR
I want to…
Restrict only network defined user identity information for OIR subscribers
| |
If a subscriber has provisioned the presentation-restriction-type in the MMTel Services Document, their setting will override this configuration. |
In the privacy, originating-identification-restriction section, set presentation-restriction-type to ONLY_IDENTITY:
presentation-restriction-type: ONLY_IDENTITYRestrict all network defined private user information for OIR subscribers
| |
If a subscriber has provisioned the presentation-restriction-type in the MMTel Services Document, their setting will override this configuration. |
In the privacy, originating-identification-restriction section, set presentation-restriction-type to ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION:
presentation-restriction-type: ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATIONAnonymize the from for OIR subscribers by default
In the privacy, originating-identification-restriction section, set user-policy to ANONYMIZE_FROM:
user-policy: ANONYMIZE_FROMRemove all user configurable identifying information for OIR subscribers
| |
This includes anonymizing the from header for OIR subscribers. |
In the privacy, originating-identification-restriction section, set user-policy to ADD_USER_PRIVACY:
user-policy: ADD_USER_PRIVACYOriginating Identification Presentation (OIP)
What it does
Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) service allows the terminating user to receive identity information from the originating user. The OIP service removes and anonymizes headers based on the originating user’s SIP message privacy header.
The declarative configuration for the OIP applies calling party identity presentation rules network wide for all OIP subscribed subscribers. Whether the OIP service is active and if it may diverge from this network default is determined by how the subscribers are provisioned in the MMTel Services document. The OIP service depends on the terminating user’s provisioned settings for OIP.
Applying identification presentation rules
The OIP service uses the privacy header on the originating user’s requests and responses to decide what is presented to the terminating subscriber.
If the privacy header field is set to:
-
id, the privacy header will not be removed. The Rhino VoLTE TAS does not anonymize anything, the S-CSCF would remove theP-Asserted-Identityheader. -
header, all headers containing private information are anonymized per RFC 3323 Section 5.1. -
user, all user configurable headers are anonymized per RFC 3323 Section 5.3.
There are other privacy headers supported, they are enforced as per RFC 3323.
Also, if the terminating subscriber does not subscribe to the OIP service, then:
-
any
P-Asserted-IdentityorPrivacyheader is removed from the originating user’s request -
if
anonymize-from-headeris set true, thefromheader is anonymized
Interactions with other services
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to OIP in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/privacy/originating-identification-presentation section.
What you need
-
❏ Whether to anonymize the originating user’s
fromheader when OIP is not active for a subscriber. -
❏ Whether to allow the History-Info header to be deleted when using OIP.
You will also need to configure the OIR service as well to determine how the privacy header may be pre-processed when OIR is active.
Setting up subscriber data
There are subscriber provisioned OIP settings configured in the HSS inside the MMTel-Services XML document for the subscriber.
Setting up OIP
I want to…
Anonymize the from header for non-active OIP subscribers
In the originating-identification-presentation, originating-identification-presentation section, set anonymize-from-header to true:
anonymize-from-header: trueAllow deletion of the History-Info header
In the originating-identification-presentation, originating-identification-presentation section, set allow-history-info-header-deletion to true:
allow-history-info-header-deletion: trueConference (CONF)
What it does
The ad-hoc conferencing (CONF) functionality in Rhino VoLTE TAS allows a subscriber to add multiple parties to a voice or video session. The conference is initiated by a subscriber (the conference moderator) making a call toward the conference factory Public Service Identity (PSI). The Rhino VoLTE TAS will process this call and begin a session with the media server (MRFC/MRFP). As the moderator adds more participants to the conference, the Rhino VoLTE TAS instructs the media server to join or mix the media of the new participant with the conference session media. The moderator controls the conference, and sessions are terminated when the moderator disconnects.
Participants 'subscribe' to the conference to be notified of changes, such as members joining or leaving. Each subscription is valid for a specified length of time.
Operators can control whether the MRF is contacted directly from the Rhino VoLTE TAS, or whether the I-CSCF is added to the route header of messages sent to the MRF.
Conference media
Every conference participant establishes signaling and media sessions with the media server, facilitated by the Rhino VoLTE TAS. The specifics of the media sessions (and of the message flows used during conferencing) are dependent on the endpoints in use and on the MRF itself, so there are a number of configuration options to control details of the conference media settings. Operators can also control value-add features such as the maximum number of conference participants and whether video-conferencing is allowed.
Interactions with other services
Each participant’s session is treated by the Rhino VoLTE TAS as a regular call, subject to normal call processing in addition to conference treatment. This means that standard Rhino VoLTE TAS functionality, such as access transfer, mid-call announcements, and hold-and-resume functionality, are all supported during conferencing.
Configuration
What you need
-
❏ The URI of the conference MRF.
-
❏ A list of conference factory PSIs to use in addition to the PSIs defined in 3GPP TS 23.003.
-
❏ The vendor of the Media Server Markup Language in use.
-
❏ Whether the
rootelement in the MSML is a child of theselectorelement or of thevideolayoutelement. -
❏ The maximum number of participants in the call.
-
❏ Whether video conferences are allowed.
Setting up conferencing
| |
Ensure that conferencing media server integration has been configured. |
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to conferencing in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/conferencing section.
I want to…
Set the URI of the Media Resource Function
In the conferencing section, set conference-mrf-uri to the URI:
conference-mrf-uri: sip:mrf@mrfhost.example.com:5060Route messages to the MRF via the IMS
In the conferencing section, set route-to-mrf-via-ims to true:
route-to-mrf-via-ims: trueSet the MSML schema vendor name
In the conferencing section, set msml-vendor to the vendor name:
msml-vendor: DialogicAttach the MSML root element as a child of videolayout
In the conferencing section, set root-on-selector to false:
root-on-selector: falseAdd a conference PSI alias
In the conferencing section, add the conference PSI alias to the list of conference-factory-psi-aliases:
conference-factory-psi-aliases:
- sip:conf-factory@ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.comSet the maximum number of participants in a conference
In the conferencing section, set maximum-participants:
maximum-participants: 4Allow video-conferencing
In the conferencing section, set allow-video-conference-calls to true:
allow-video-conference-calls: trueSet the default expiry time on conference subscriptions
In the subscription section, set default-subscription-expiry-seconds:
default-subcription-expiry-seconds: 1800Set the minimum allowed subscription time
In the subscription section, set min-subscription-expiry-seconds:
min-subscription-expiry-seconds: 10Notify participants about subscription changes every 10 seconds
In the subscription section, set polling-interval-seconds:
polling-interval-seconds: 10Call barring
What it does
Call barring is a set of MMTel services that conditionally bar calls using a combination of system-wide and per subscriber rules.
-
Incoming Call Barring (ICB) bars incoming calls based on per subscriber rules written using common-policy schema (for example, a subscriber may set up Do Not Disturb, to bar all calls).
-
Anonymous Call Rejection (ACR) bars incoming calls from anonymous callers.
-
-
Outgoing Call Barring (OCB) bars outgoing calls based on per subscriber rules written using common-policy schema.
-
Operator Determined Barring (ODB) is a fixed set of barring conditions, each enabled or not per subscriber.
-
Operator Specific Barring (OSB) is a subset of ODB containing four rules each enabled or not per subscriber, but where the system-wide conditions and actions are configured using common-policy schema. Additionally, the action when these rules trigger may be augmented to retarget the call, with an ability to disable charging, and/or use a rule-specific announcement in this case.
-
Prefix barring uses dialed number rules to either explicitly allow or bar an outgoing call, or to effectively force a match condition for some of the ODB conditions, including the OSB rules.
-
Announcements may be set to be played to the caller when a call is barred.
Interactions with other services
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
Call barring for incoming calls is applied before MMTel CDIV, so any barred incoming call will not be subject to forwarding.
However, an inbound call which is not barred but then forwarded will have outbound barring processing applied to the outbound forwarded call.
Vertical service codes with XCAP data update
Vertical service codes in combination with XCAP data update may change subscriber data, affecting subscriber ICB and OCB rules, and enabling or disabling ODB rules for a subscriber.
ODB rules may prevent changes to subscriber data, both via vertical service codes with XCAP data update, and when using XCAP directly from user equipment.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to call barring in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring section.
What you need
-
❏ Whether the system should process or ignore international and international-exHC barring rules based on the reliability of determining that an incoming call is international.
-
❏ The ID of an optional announcement to play when an incoming call is barred due to an anonymous caller.
-
❏ The ID of an optional announcement to play when an incoming call is barred otherwise.
-
❏ The ID of an optional announcement to play when an outgoing call is barred.
-
❏ For up to four operator specific barring rules:
-
❏ The common policy ruleset which defines the conditions and action for the rule.
-
❏ Whether to retarget the call and if so:
-
❏ the URL target
-
❏ the ID of an optional announcement to play
-
❏ whether to disable charging.
-
-
Setting up announcements
Call barring configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcements that should be played. The details of those announcements should be configured beforehand. For details about how to do this, see Announcements.
Setting up call barring
I want to…
Enable ODB
In the hss-queries-enabled section, set odb to true:
odb: trueDisable ODB
In the hss-queries-enabled section, set odb to false:
odb: falseSetting up incoming call barring
I want to…
Use the same announcement for all incoming barred calls
In the incoming-communication-barring, announcement section, set the same announcement ID for both announcements:
announcement:
announcement-id: 21
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 21Use a different announcement for barred incoming anonymous calls
In the incoming-communication-barring, announcement section, set separate announcement IDs for the two announcements:
announcement:
announcement-id: 21
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 22For barred incoming calls, only play an announcement when it is anonymously barred
In the incoming-communication-barring, announcement section, remove or comment out the announcement-id.
announcement:
# announcement-id: 21
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 22For barred incoming calls, only play an announcement when it is not anonymously barred
In the incoming-communication-barring, announcement section, remove or comment out the anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id.
announcement:
announcement-id: 21
# anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 22Enable evaluation of incoming international barring rules
In the incoming-communication-barring section, set international-rules-active to true.
international-rules-active: trueSetting up outbound call barring
I want to…
Play an announcement for barred outgoing calls
In the outgoing-communication-barring, announcement section, set the announcement-id:
announcement:
announcement-id: 20Not play an announcement for barred outgoing calls
In the outgoing-communication-barring section, delete or comment out the whole announcement section.
# announcement:
# announcement-id: 20Bar a suspended subscriber from making any calls, redirecting them to a specific number
-
Ensure ODB is enabled. See Enable ODB above.
-
Choose an OSB rule number to use.
(considering what types are spare and the desired priority of this and existing rules)
-
Ensure this OSB rule is disabled for all subscribers.
out of scope of this document
-
Set the OSB rule to:
-
bar all outbound calls
-
retarget any outbound call to the call center
-
optionally set up a specific announcement to play to the subscriber before retargeting the call
-
disable online charging for the call.
-
-
In the
operator-communication-barringsection, for the selected rule, underoperator-barring-rules, add the following (this example for type1 OSB rule):
operator-communication-barring:
operator-barring-rules:
type1:
rule: # Bar outgoing calls
<cp:ruleset
xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy"
>
<cp:rule id="bar-outgoing--enabled-when-out-of-credit">
<cp:conditions>
<outgoing/>
</cp:conditions>
<cp:actions>
<allow>false</allow>
</cp:actions>
</cp:rule>
</cp:ruleset>
retarget:
retarget-uri: sip:payments@pay.your.bill.com
disable-online-charging-on-retarget: true
announcement:
announcement-id: 23-
Enable this OSB rule in subscriber data for suspended subscribers.
out of scope of this document
Setting up prefix based barring
Prefix based barring provides a mechanism for an operator to augment the implicit or explicit condition of a MMTel OCB barring rule, so that the rule will also apply when the called party number matches some prefix with optional length criteria.
Because the same prefix can be treated differently (for example, depending on whether it is national or international), and multiple prefixes may all need to be treated the same way, the configuration is split into a list of prefixes and a list of classifications.
Each prefix has a list of classifications that may apply.
Each classification has further predicates to see if the classification is applicable to the call (minimum-number-length, maximum-number-length and match-international). If it is, the classification specifies the barring treatment of that call, and can optionally override the normal barring announcements.
Prefix barring interactions with other OCB features
There are different types of OCB rules, in the following overall order of priority:
-
Prefix based
OperatorAllow -
Operator-specific ODB rules that allow a call, regardless whether applied by matching their defined condition, or by prefix based treatment
-
Prefix based
OperatorBar -
Operator-specific ODB rules that bar a call, regardless whether applied by matching their defined condition, or by prefix based treatment
-
Prefix based premium-rate communication barring
-
Standard ODB rules
-
OCB rules
Within rules of the same type, an allow action will always take precedence over a barring or retargeting action.
If multiple operator-specific ODB rules apply and have conflicting retarget or barring actions, then the rule with the lower number will take precedence. (There are four slots available for operator-specific ODB rules, numbered one through four).
I want to…
Treat 90077xxxxx numbers as premium rate entertainment for barring purposes and use a custom announcement when barred
In outgoing-prefix-barring, add a classification and map that prefix to it. In this case we use the maximum value for maximum-number-length to prevent this barring rule being circumvented by overdialing.
outgoing-prefix-barring:
prefixes:
- prefix: '90077'
classifications:
- 'premium rate entertainment'
classifications:
- name: 'premium rate entertainment'
minimum-number-length: 10
maximum-number-length: 20
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'PremiumRateEntertainment'
announcement:
announcement-id: 27Treat all other 9007xxxxxx numbers as premium rate information services for barring purposes
In outgoing-prefix-barring, extend the above scenario by adding a new prefix and a new classification. This works because a call will match the longest prefix.
outgoing-prefix-barring:
prefixes:
- prefix: '90077'
classifications:
- 'premium rate entertainment'
- prefix: '9007'
classifications:
- 'premium rate info'
classifications:
- name: 'premium rate entertainment'
minimum-number-length: 10
maximum-number-length: 20
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'PremiumRateEntertainment'
- name: 'premium rate info'
minimum-number-length: 10
maximum-number-length: 20
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'PremiumRateInformation'Bar all calls to 8xx numbers without playing an announcement, but with no prefix barring handling for calls to 801
In outgoing-prefix-barring, we need to be explicit about all the 80x prefixes excluding 801, and all the remaining 8x prefixes, mapping them all to the same classification.
outgoing-prefix-barring:
prefixes:
- prefix: '800'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '802'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '803'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '804'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '805'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '806'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '807'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '808'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '809'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '81'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '82'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '83'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '84'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '85'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '86'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '87'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '88'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
- prefix: '89'
classifications:
- 'barred shortcodes'
classifications:
- name: 'barred shortcodes'
minimum-number-length: 3
maximum-number-length: 3
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'OperatorBar'
disable-ocb-announcement: trueOverride any other barring rules to always allow calls to one specific number
In outgoing-prefix-barring, add a classification with barring-treatment set to OperatorAllow and matching exact number length, and map this from the complete number to that classification.
outgoing-prefix-barring:
prefixes:
- prefix: '900123456'
classifications:
- 'explicit allowed 9 digit numbers'
classifications:
- name: 'explicit allowed 9 digit numbers'
minimum-number-length: 9
maximum-number-length: 9
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'OperatorAllow'Bar calls to 60000 whether or not the call is international
In outgoing-prefix-barring, add two classifications, one for national and one for international, but otherwise the same, then map the prefix to both classifications.
outgoing-prefix-barring:
prefixes:
- prefix: '60000'
classifications:
- 'bar me'
- 'bar me - intl'
classifications:
- name: 'bar me'
minimum-number-length: 5
maximum-number-length: 5
match-international: false
barring-treatment: 'OperatorBar'
- name: 'bar me - intl'
minimum-number-length: 5
maximum-number-length: 5
match-international: true
barring-treatment: 'OperatorBar'Communication Waiting (CW)
What it does
MMTel Communication Waiting (CW) is a service that alerts the subscriber when a new call arrives while a call is already in progress. The called party can accept, ignore, or reject the call. If accepted, the existing call can be put on hold.
This service can also play an announcement to the caller. See Announcements.
Interactions with other services
Call barring
The MMTel call barring services always take precedence over call waiting. If an incoming call is barred, the call will be terminated without waiting. See Call barring.
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
The MMTel CDIV takes precedence over communication waiting. If the called subscriber is already on a call, the call will be forwarded without waiting. See Communications Diversion (CDIV).
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to call waiting in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-waiting section.
What you need
-
❏ The ID of the announcement to play to the caller.
-
❏ The time in seconds to give the called party to answer the call before giving up and tearing down the call.
Setting up call waiting
I want to…
Play an announcement to the caller that the call is waiting
Call waiting configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcement to be played. The details of that announcement should be configured beforehand. For details about how to do this, see Announcements.
-
If it is not already present, add an
announcementsection directly undercommunication-waiting.
communication-waiting:
announcement:-
In the
announcementsection, set theannouncement-idto the ID for the desired announcement:
announcement-id: 24Change the number of seconds to give the called party to answer the call
In the communication-waiting section, set timer-seconds to the desired limit:
timer-seconds: 30Communication Hold (HOLD)
What it does
MMTel Communication Hold (HOLD) is a service that lets a user suspend reception of the media stream(s) of an established IP multimedia session, and resume the media stream(s) at a later time.
This service provides a way for the operator to:
-
restrict bandwidth for held calls
-
play announcements to the held party
-
determine how media streams for the holding party are handled while an announcement to the held party is in progress.
Bandwidth controls
Bandwidth controls allow the Rhino VoLTE TAS to restrict the bandwidth available to media streams to the holding party for the duration of the hold. The call hold service allows you to set three different bandwidth parameters. The values for all of these parameters are set in kilobits per second.
| Parameter | Config field | Description |
|---|---|---|
AS |
Sets the bandwidth available for application specific data. It is safe to set this to 0. |
|
RS |
Sets the bandwidth available for RTCP (Real-time Transport Control Protocol) for participants that are sending data. This should be set high enough to allow RTCP messages to continue while the call is on hold. |
|
RR |
Sets the bandwidth available for RTCP for participants that are not sending data. This should be set high enough to allow RTCP messages to continue while the call is on hold. |
Announcements
The call hold service can play an announcement to the party that has been put on hold. Call hold configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcement that should be played. For instructions on how to configure the details of the announcement, see announcements.
Media handling during announcement
While an announcement to the held party is in progress, there are three options on how to deal with the media streams to the holding party. The behavior is configured in the holding-party-media-mode field with the following options.
| Field value | Behavior |
|---|---|
NO_HOLD |
No change is made to the media streams to the holding party. |
BLACK_HOLE_ONLY |
The media streams to the holding party are directed to a black hole IP address ( |
FULL_HOLD |
The media streams to the holding party are put on a two-way hold for the duration of the announcement. |
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to call hold in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-hold section.
Setting up call hold
I want to…
Set the bandwidth for held media streams
In the communication-hold section, change the values, in kilobits per second, of the bandwidth-adjustment parameters.
bandwidth-adjustment:
b-as-parameter: 0
b-rr-parameter: 500
b-rs-parameter: 500Related section: Bandwidth controls
Play an announcement to the held party that the call is on hold
-
If it is not already present, add an
announcementsection in thecommunication-holdsection.
communication-hold:
announcement:-
In the
communication-hold,announcementsection, set theannouncement-idto the ID for the desired announcement:
announcement-id: 25Related section: Announcements
Leave media streams to the holding party unchanged while an announcement is in progress
In the communication-hold section, set the holding-party-media-mode to NO_HOLD.
holding-party-media-mode: NO_HOLDRelated section: Media handling during announcement
Direct media streams to the holding party to a black hole IP address while an announcement is in progress
In the communication-hold section, set the holding-party-media-mode to BLACK_HOLE_ONLY.
holding-party-media-mode: BLACK_HOLE_ONLYRelated section: Media handling during announcement
Put media streams to the holding party on a two-way hold while an announcement is in progress
In the communication-hold section, set the holding-party-media-mode to FULL_HOLD.
holding-party-media-mode: FULL_HOLDRelated section: Media handling during announcement
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
What it does
MMTel Communications Diversion (CDIV) is a service that redirects incoming calls according to rules set by the network operator and/or the subscriber. Each of these rules specifies the particular condition or conditions that should trigger it, and the destination to forward to when the rule is triggered. The rules are subscriber specific and are therefore configured in the HSS rather than the Rhino VoLTE TAS.
Forwarding rules
Each forwarding rule must correspond to one of five different types of forwarding. Each forwarding type is triggered under different circumstances. The types are:
| Name | Acronym | Trigger Condition |
|---|---|---|
Communication Forwarding Unconditional |
CFU |
Triggers immediately upon receipt of an incoming call. |
Communication Forwarding on Busy user |
CFB |
Receipt of a |
Communication Forwarding on no Reply |
CFNR |
A |
Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable |
CFNRc |
Receipt of a SIP response with any of these status codes: |
Communication Forwarding on Not Logged-in |
CFNL |
Receipt of an incoming call when the called party is not currently registered on the network. |
Additional conditions
In addition to the basic types above, additional conditions can be placed on forwarding rules:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
media |
Makes a forwarding rule conditional on the specific media types appearing in the SDP for the call. |
validity |
Makes a forwarding rule conditional on the date and time the call is received. |
Forwarding action
In addition to its conditions, each forwarding rule should have a forward-to action. This action contains a number of parameters that detail how to handle forwarding when the rule’s conditions are met. The supported fields are:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
target |
The URI to forward to. |
notify-caller |
Determines whether to send a |
reveal-identity-to-caller |
Determines whether the identity of the forward-to target should be revealed to the calling party. |
reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller |
Determines whether the identity of the original called party should be revealed to the calling party. |
reveal-identity-to-target |
Determines whether the identity of the original called party should be revealed to the forward-to target. |
Communication Deflection
Communication Deflection (CD) is another type of MMTel call forwarding that, unlike the others, is not triggered through forwarding rules. Instead it is triggered by receipt of a 302 Moved Temporarily SIP response from the called party. For this type of forwarding, the response itself contains the destination to forward to.
No reply timer
As described above, CFNR is triggered after a 180 Ringing response, either by a 408 Request Timeout response or by the no reply timer expiring. The no reply timer is started on receipt of the 180 Ringing response, and expires after a period of time derived from either:
-
the
communication-forwarding-on-no-reply-timersetting in subscriber HSS configuration (this option takes priority) or -
the period of time specified in global configuration in the
no-reply-timeout-secondsfield.
Forwarding limits
The number of times that a single call can be forwarded can be limited with the max-diversions field.
If the limit is reached, there are several options for how to handle the call. This is configured in the max-diversion-action field. The options are:
| Option | Behaviour |
|---|---|
REJECT |
Terminates the call. |
DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION |
Makes a final attempt to forward the call to the destination given in the |
DELIVER_TO_SUBSCRIBERS_VOICEMAIL_SERVER |
Makes a final attempt to forward the call to the subscriber’s specified voicemail server. This option requires that the subscriber’s voicemail server URI has been set in their Metaswitch-TAS-Services document in the HSS. |
It is also possible to specify a list of known URIs in the diversion-limit-exempt-uris field that can be forwarded to, even when the forwarding limit is reached.
Interactions with other services
Call barring
The MMTel call barring service always takes precedence over call forwarding. If an incoming call is barred, the call will be terminated without forwarding.
Voicemail forwarding
Voicemail forwarding is closely related to the MMTel call forwarding service. There are certain situations that can trigger either service, for example, if the called party is already on a call. In such cases MMTel call forwarding takes precedence, and will evaluate the provisioned forwarding rules for the called party. Voicemail forwarding will be triggered if there are no forwarding rules that result in the call being forwarded.
| |
There are certain situations where the MMTel call forwarding service may be suppressed, for example, when routing to a CS network where MSC is expected to handle call forwarding. In these situations the Voicemail Forwarding service will also be suppressed. |
Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS)
If T-ADS attempts to connect the call over the circuit switched (CS) network and the attempt fails, it is possible that call forwarding could be triggered twice. The first time for call forwarding behavior in the CS core network, the second time for MMTel call forwarding.
For this reason it is possible to disable MMTel call forwarding for calls that are terminating in a CS network, see below.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to call forwarding in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/call-diversion/mmtel-call-diversion section.
What you need
-
❏ The maximum limit for the number of forwards that should be allowed for a single call.
-
❏ The preferred option for handling a call that has reached the maximum number of forwards.
-
❏ Any URIs that can be forwarded to, even when forwarding limits have been reached.
-
❏ Optionally, a default URI to forward to if a rule without an explicit target is triggered.
-
❏ The default length of time to allow the call to ring before triggering CFNR.
-
❏ Whether MMTel call forwarding should be disabled for calls that terminate in a CS network.
-
❏ Whether subscribers' forwarding rules should take precedence over the operator’s rules.
-
❏ Whether CFNRc should be allowed to trigger after the call starts ringing.
-
❏ Any SIP response status codes that should trigger CFNRc besides the standard ones.
-
❏ Whether an
origtag should be added to outbound forwarded SIPINVITErequests. -
❏ Whether a
hi-target-paramof typempshould be included in the History-Info for a forwarded message.
Setting up subscriber data
Both subscriber and operator defined forwarding rules, along with a subscriber specific setting for the no reply timer are configured in the HSS inside the MMTel-Services XML document for the subscriber.
You can find a detailed description of what this configuration looks like in the 3GPP technical specification for the MMTel call forwarding service, see section 4.9 of 3GPP TS 24.604.
Not all of the rule conditions listed in the technical specification are supported by the Rhino VoLTE TAS. Only the following conditions may be used: busy, not-registered, cp:validity, media, no-answer, rule-deactivated, and not-reachable.
Similarly there are also forward-to action parameters listed in the specification that are not supported by the Rhino VoLTE TAS. The following parameters may be used: target, notify-caller, reveal-identity-to-caller, reveal-served-user-identity-to-caller, and reveal-identity-to-target.
Setting up call forwarding
I want to…
Set the limit for how many times a call can be forwarded
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set max-diversions to the desired limit:
max-diversions: 10Reject calls that exceed the forwarding limit
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set max-diversion-action to reject the call:
max-diversion-action: REJECTForward calls that exceed the forwarding limit to a fixed URI
-
In the
mmtel-call-diversionsection, setmax-diversion-actionto deliver the call to a fixed destination:
max-diversion-action: DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION-
In the
mmtel-call-diversionsection, setmax-diversion-fixed-destinationto the desired SIP or tel URI:
max-diversion-fixed-destination: tel:+123456789Allow forwarding to special URIs even when forwarding limits have been reached
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, add the desired SIP and/or tel URIs to the list of diversion-limit-exempt-uris:
diversion-limit-exempt-uris:
- sip:voicemail@example.com
- tel:+123456789Add to the set of SIP error response codes that trigger the CFNRc
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, add the desired codes to the list of additional-not-reachable-status-codes:
additional-not-reachable-status-codes:
- 404
- 480Allow CFNRc to still be triggered after receiving an 180 Ringing response
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set allow-not-reachable-during-alerting:
allow-not-reachable-during-alerting: trueSet a default destination to use if a subscriber’s forwarding rule does not specify a destination
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set default-target-uri to the desired SIP or tel URI:
default-target-uri: sip:default-target@example.comSet the default timeout for triggering CFNR
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set no-reply-timeout-seconds to the desired timeout:
no-reply-timeout-seconds: 15Disable the MMTel call forwarding service when the call is being delivered over a circuit-switched network
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain to true:
suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain: trueAllow the subscriber’s forwarding rules to override the operator’s rules
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set prefer-subscriber to true:
prefer-subscriber: truePlay an announcement to the caller when the call is forwarded
MMTel call forwarding configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcement to be played. The details of that announcement should be configured beforehand. For details about how to do this, see Announcements.
-
If it is not already present, add an
announcementsection directly undercall-diversion.
call-diversion:
announcement:-
In the
announcementsection, set theannouncement-idto the ID for the desired announcement:
announcement-id: 12Add the 'orig' tag to the Route header of forwarded SIP INVITE requests
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set add-orig-tag to true:
add-orig-tag: truePrevent the 'orig' tag from being added to the Route header of forwarded SIP INVITE requests
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set add-orig-tag to false:
add-orig-tag: falseInclude a 'hi-target-param' of type 'mp' in the History-Info header that is added to forwarded SIP INVITE requests
In the mmtel-call-diversion section, set add-mp-param to true:
add-mp-param: trueVoicemail forwarding
What it does
When enabled for a subscriber, the voicemail forwarding service can forward an incoming call to a voicemail server. Depending on the selected configuration, this can happen under any of these conditions:
-
The call has waited longer than a specified timeout for a successful response.
-
The called subscriber is unavailable and has no provisioned diversion rules for the MMTel call forwarding service.
-
The called subscriber has provisioned diversion rules, but none of them cause the call to be forwarded.
-
The called subscriber uses online charging and credit cannot be allocated.
For details about diversion rules, see Communications Diversion (CDIV).
The URI of the voicemail server to forward to is provisioned per subscriber. It is possible to allow a subscriber to choose their own voicemail server.
The voicemail forwarding configuration includes a list of URIs for known voicemail servers on the network.
| |
If a subscriber’s chosen voicemail server does not appear in this list, it can change which announcement they will hear before the call is forwarded. It can also potentially disable voicemail forwarding when credit cannot be allocated. |
The voicemail forwarding service only runs on the terminating instance of the Rhino VoLTE TAS, and can be triggered at any time during call setup.
Voicemail forwarding can be used with the Metaswitch Voicemail Server. See the VMS product documentation for details of how to set up the server.
Playing announcements
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports playing an operator specified announcement to the calling party before forwarding to voicemail. If a subscriber’s voicemail server is on the list of known voicemail servers, the announcement can be specified for voicemail forwarding. If not, the standard Communications Diversion (CDIV) announcement will play instead.
These announcements are distinct from any announcement that the voicemail server itself might play to the calling party.
Forwarding to voicemail without credit
If the subscriber is using Diameter Ro based online charging and they will be charged for the incoming call, forwarding to voicemail can be invoked if credit could not be allocated. The policy for when this is allowed is part of the Voicemail Forwarding configuration.
Voicemail service codes
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports a subscriber dialing a service code (for example *123) to retrieve voicemail by forwarding the originating call to their configured voicemail server. This function uses the same voicemail server URI in subscriber config as the voicemail forwarding service, but it runs on the originating Rhino VoLTE TAS instance.
There is also support for setting up a service code that a subscriber can use to set their voicemail server URI (if they are permitted to do so).
Interactions with other services
Call barring
The MMTel call barring services (ICB and OCB) always take precedence over voicemail forwarding. If barring is triggered, the call will be terminated without forwarding to voicemail.
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
Voicemail forwarding is closely related to the MMTel CDIV service. There are certain situations that can trigger either service, for example, if the called subscriber is already on a call. In such cases MMTel call forwarding takes precedence, and will evaluate the provisioned diversion rules for the called subscriber. Voicemail forwarding will be triggered if there are no diversion rules that result in the call being forwarded.
If a subscriber is allowed to provision their own diversion rules for the MMTel call forwarding service, they can use that functionality to forward the call to their own voicemail server. This is true even when they are not permitted to choose their own voicemail server for the voicemail forwarding service.
| |
There are certain situations where the MMTel CDIV service may be suppressed, for example, when routing to a CS network where MSC is expected to handle call forwarding. In these situations the voicemail forwarding service will also be suppressed. |
Online charging
When using online charging, voicemail forwarding can be configured to activate when credit cannot be allocated for the call (for any reason). If this behavior is triggered, voicemail forwarding will finalize the online charging session. After this, there will be no further communication with the online charging system.
Configuration
What you need
-
❏ The wait time for a call to be successfully connected before it is forwarded to voicemail.
-
❏ A list of URIs for known voicemail servers on the network.
-
❏ Whether to allow forwarding to voicemail if credit cannot be allocated for a subscriber that uses online charging. If allowed, forwarding can either be restricted to URIs on the known voicemail servers list or permitted for any URI.
-
❏ Optionally, the ID of the announcement to be played before forwarding to any of the known voicemail servers.
-
❏ Subscriber configuration set up with the Metaswitch-TAS-Services section enabled and the voicemail server URI field populated.
Setting up announcements
Voicemail forwarding configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcement that should be played. The details of that announcement should be configured beforehand. For details about how to do this, see Announcements.
Setting up subscriber configuration
All subscribers using the Voicemail Forwarding service need to be configured with a voicemail server URI in the Metaswitch-TAS-Services section of their subscriber profile. Further information on configuring the subscriber data for the voicemail forwarding service is given in Forward to voicemail subscriber data.
| |
For standard Rhino VoLTE TAS deployments, the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document is disabled. This must be enabled to activate voicemail forwarding using subscriber data. |
Setting up service codes
The Rhino VoLTE TAS standard deployment includes service code actions for subscribers to retrieve voicemail and update their voicemail server URI (if permitted to do so).
| Display name | Action |
|---|---|
Connect Subscriber To Voicemail Provider |
Execute dialing for voicemail. |
Set Default Forward Voicemail Server Number |
Update the default forward voicemail number for the subscriber data ( |
For more information, see Vertical service codes.
Setting up voicemail forwarding
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to voicemail forwarding in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/call-diversion/forward-to-voicemail section.
I want to…
Activate voicemail forwarding
Ensure the entire forward-to-voicemail section is present and not commented out in the configuration file.
forward-to-voicemail:
voicemail-uris:
- sip:vms1@example.com
- sip:vms2@example.com
forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds: 0
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: NEVER_ALLOWSet time to forward calls to voicemail after processing the initial INVITE
In the forward-to-voicemail section, set forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds:
forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds: 30Disable forwarding to voicemail due to timeout
In the forward-to-voicemail section, set forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds to 0:
forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds: 0Disallow forwarding to voicemail if unable to allocate credit to the subscriber
| |
This only applies to subscribers using Diameter Ro based online charging. |
In the forward-to-voicemail section, set forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit to never allow forwarding:
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: NEVER_ALLOWAllow forwarding to voicemail regardless of being able to allocate credit to subscriber
| |
This only applies to subscribers using Diameter Ro based online charging. |
In the forward-to-voicemail section, set forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit to always allow forwarding:
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: ALWAYS_ALLOWAllow forwarding to a known voicemail server regardless of the credit status of a subscriber using online charging
| |
This only applies to subscribers using Diameter Ro based online charging. |
In the forward-to-voicemail section, set the following:
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: ALLOW_ONLY_FOR_WELL_KNOWN_SERVERS
voicemail-uris:
- sip:vms1@example.com-
Set
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credittoALLOW_ONLY_FOR_WELL_KNOWN_SERVERS -
Add the URI of the voicemail server to the list of
voicemail-uris.
Play a voicemail announcement (announcement id=7) to the calling party when voicemail forwarding occurs
-
In the
forward-to-voicemailsection, setvoicemail-uris:
voicemail-uris:
- sip:vms1@example.com-
In the
call-diversion,announcementsection, setvoicemail-announcement-id:
voicemail-announcement-id: 7Play the default forwarding announcement to the calling party when voicemail forwarding occurs
In the call-diversion, announcement section, remove or comment out voicemail-announcement-id:
# voicemail-announcement-id: 7Related section: Communications Diversion (CDIV)
Companion device
What it does
Companion devices are VoLTE UEs that are linked to a primary device such as a smart phone. Smart watches are a common type of companion device. The companion device service enables companion devices to share a phone number with the primary device. This means:
-
calls to the shared number will cause both devices to ring, and
-
calls from the companion device will appear to come from the shared number.
This type of service is sometimes referred to as "One Number", "Multi-SIM", or "Multi-Device".
The companion device will still have its own number called the "undisclosed identity". Depending on service configuration, it may still be possible to use this number to contact the companion device, but the Rhino VoLTE TAS will always attempt to hide and replace it with the shared number.
The companion device service can function for devices connecting over both packet switched (PS) and circuit switched (CS) networks.
Outbound calls
For outbound calls, the companion device will usually use the shared number to identify itself. However, if it uses its undisclosed identity instead, the companion device service will replace it with the shared number before allowing the call to proceed.
Inbound calls
When an incoming call is targeted at the shared number, the companion device service will force the T-ADS service to use parallel routing mode. This ensures that both the primary and companion device will ring at the same time, regardless of whether they are connected to a PS or CS network. When the subscriber answers the call on either device, the other device will stop ringing.
When companion devices are in use, T-ADS may use special handling if one of the devices indicates the subscriber is busy. If the release-all-legs-on-busy field in the T-ADS configuration is set to true, a single busy response from either device will cause the call to be terminated. If the field is false, T-ADS will wait for a response from the other device as per normal behavior.
The companion device service can also be configured to block incoming calls to the undisclosed identity.
Companion device provisioning
Per-subscriber companion device data is provisioned in two places:
-
IMS subscription data in the HSS, and
-
the
Metaswitch-TAS-Servicesdocument stored in HSS transparent data.
Provisioning of IMS subscription data is not done using the Rhino VoLTE TAS. Contact your HSS provider for more information.
| |
For standard Rhino VoLTE TAS deployments, the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document is disabled. This must be enabled to activate the companion device service. |
Further information on configuring the companion device service subscriber data is given in the managing companion device subscriber data page.
Interactions with other services
Terminating Access Domain Selection (T-ADS)
When a companion device is in use, the companion device service will force the T-ADS service to use its parallel routing mode. However, restrictions imposed by the Request-Disposition header will still apply. See Request disposition in the T-ADS section for details.
The companion device service may also provide CS routing numbers (CSRNs) for the T-ADS service to use on its CS network connection attempts.
CAP charging
If CAP charging is in use, on inbound calls there will be a separate session between the Rhino VoLTE TAS and the service control point (SCP) providing the charging service for each forked PS and CS leg for each device. The leg that is answered by the called subscriber will be charged, and the other legs will be recorded as zero length calls with the SCP.
PSAP callback
Certain functions of the companion device service that could interfere with emergency calls are disabled when an emergency call is detected:
-
When a companion device initiates an emergency call, its undisclosed identity will not be hidden.
-
When a PSAP callback attempt is made to the undisclosed identity, the companion device service will not block the call.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the companion device service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
Vertical service codes (VSC)
What it does
The vertical service code (VSC) service provides support for carrying out a wide variety of actions based on the number dialed by a subscriber.
Number analysis
The VSC service is capable of invoking other services based on matching either a prefix on the dialed number or the full number.
In the event that there are multiple possible matches for the same number, the longest match takes priority. So for example, if two VSC prefixes were specified:
-
520to hide the caller’s identity for this call, and -
52to reveal the caller’s identity for this call.
For the dialed number 5205551234, the caller’s identity would be hidden for the call. This also means that a full number match will always take precedence over any possible prefix match.
When a prefix is found on a dialed number, it can optionally be stripped from the number before invoking its corresponding service. Using the numbers for the privacy example above, this would cause 5205551234 to become 5551234 on the outbound leg of the call.
It is also possible to seek further matches in the remaining part of a number after a prefix has been matched. This can be done regardless of whether the prefix is stripped from the outbound number. So if 1234 was a full number vertical service code that invoked the Location based dialing service to call a nearby visitor information center, then again using the numbers from the privacy example above, a caller dialing 5201234 would call the information center and have their identity hidden.
Vertical service codes are only supported for numbers in the network’s home country. If a dialed number is in international format but has the home country code, it will be removed prior to matching.
Service code actions
The Rhino VoLTE TAS comes preconfigured with a number of actions that can be assigned to a vertical service code. It is also possible to set up an announcement to be played before the action is carried out.
The available actions are:
-
Enable identity restriction for the current call.
-
Disable identity restriction for the current call.
-
Enable identity restriction permanently.
-
Disable identity restriction permanently.
-
Enable identity presentation.
-
Disable identity presentation.
-
Enable call forwarding for busy and no answer.
-
Disable call forwarding for busy and no answer.
-
Enable unconditional forwarding to specified number.
-
Disable unconditional forwarding.
-
Enable busy call forwarding to specified number.
-
Disable busy call forwarding.
-
Enable no answer call forwarding to specified number.
-
Disable no answer call forwarding.
-
Enable not logged in call forwarding to specified number.
-
Disable not logged in call forwarding.
-
Enable not reachable call forwarding to specified number.
-
Disable not reachable call forwarding.
-
Enable the call forwarding service.
-
Disable the call forwarding service.
-
Execute location based dialling.
-
Connect the subscriber to their voicemail server.
-
Set the subscriber’s voicemail server number.
-
Continue searching for more service codes.
-
Stop searching for more service codes.
-
Strip this service code and continue searching for others.
-
Strip this service code and stop searching for others.
-
Reject the call with 603 decline response.
It is also possible to create custom actions. For guidance on how to do this, contact Metaswitch support.
Interactions with other services
The VSC service finds a service code in a dialed number, so it can have broad reaching effects that can impact other services.
There are two key points to note:
-
The VSC service can be used to invoke other services outside of their usual operating procedures or to override their usual behavior.
-
When the VSC service strips a prefix from a dialed number, other services that analyze the dialed number will not see that prefix. This is different from most services that manipulate the outbound dialed number, and is of particular note for the call barring service.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the VSC service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
International Call Management
What it does
The International Call Management service provides support for barring and playing announcements for international calls based on the format of the dialed digits, and the identified country of the destination address.
Outbound calls can be barred if a call is determined to be international and the international dialing prefix is not explicitly present in the dialed digits. An announcement can be played before the call is barred. Additionally, if a call is determined to be international a pre-call announcement can be played to the calling party. The default options can be overridden based on the destination country.
| |
The |
Restrictions
The destination country can only be identified if the country uses the North American Numbering Plan (ie international prefix is 1). Countries outside the NANP will be treated with the default handling.
Interactions with other services
Roaming and international status determination
If North American Numbering Plan (NANP) analysis is enabled, the details determined by NANP will be used to establish the international and roaming status of the call (by comparing the access network country code, the home network country code, and the destination country code).
Call Barring
The MMTel Outgoing call barring service (OCB) always takes precedence over international call management. If barring is triggered, the call will be terminated without playing an international call management announcement.
Number translation services in general
International Call Management looks at the original dialed number as received by the RVT when doing its analysis. This means that changes to the number by services that provide number translation (such as Location Based Dialing) will not be considered by this service.
Configuration
The example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml show example configuration relevant to international call management in the sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management and sentinel-volte/mmtel/north-american-numbering-plan sections.
What you need
-
❏ Whether the system should bar international calls dialed without an international prefix.
-
❏ Optionally, the ID of the announcement to be played before barring calls.
-
❏ Optionally, the ID of the announcement to be played before international calls are connected.
-
❏ Optionally, per-country overrides for the above, along with the 2 digit upper case ISO country code for countries to be overridden.
Setting up announcements
International Call Management configuration only needs the announcement ID of the announcement that should be played. The details of that announcement should be configured beforehand. For details about how to do this, see Announcements.
I want to…
Bar and play an announcement to international calls dialed without the international call prefix
In the default-international-call-management section, set bar-calls-with-missing-prefix to true and set bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id to the ID of the selected announcement.
international-call-management:
default-international-call-management:
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: true
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 200Play an announcement before international calls
In the default-international-call-management section, set international-call-announcement-id to the ID of the selected announcement.
international-call-management:
default-international-call-management:
international-call-announcement-id: 200Bar international calls dialed without the international call prefix, except calls to Canada
In the north-american-numbering-plan-analysis section, set enable-nanp-analysis to true.
In the default-international-call-management section, set bar-calls-with-missing-prefix to true.
Ensure the call-management-by-country-code list is present and uncommented.
Add a list item with an iso-country-code of CA and a bar-calls-with-missing-prefix value of false.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis:
enable-nanp-analysis: true
international-call-management:
default-international-call-management:
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: true
call-management-by-country-code:
- iso-country-code: "CA"
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: falsePlay an announcement before international calls, except calls to Canada
In the north-american-numbering-plan-analysis section, set enable-nanp-analysis to true.
In the default-international-call-management section, set international-call-announcement-id to the ID of the selected announcement.
Ensure the call-management-by-country-code list is present and uncommented.
Add a list item with an iso-country-code of CA. Ensure that the international-call-announcement-id within the country code list is unset.
The unset value in the CA profile will not fall back to the default value - a missing international-call-announcement-id at any level means that no announcement will be played at that level.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis:
enable-nanp-analysis: true
international-call-management:
default-international-call-management:
international-call-announcment-id: 200
call-management-by-country-code:
- iso-country-code: "CA"Allow international calls dialed without the international call prefix, except calls to the US,
In the north-american-numbering-plan-analysis section, set enable-nanp-analysis to true.
In the default-international-call-management section, set bar-calls-with-missing-prefix to false.
Ensure the call-management-by-country-code list is present and uncommented.
Add a list item with an iso-country-code of US and a bar-calls-with-missing-prefix value of true.
Add a bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id and an international-call-announcement-id if desired.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis:
enable-nanp-analysis: true
international-call-management:
default-international-call-management:
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: false
call-management-by-country-code:
- iso-country-code: "US"
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: true
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 101
international-call-announcement-id: 102Location based dialing (LBD)
What it does
Location based dialing (LBD) is a service that allows a subscriber to dial a number that redirects to a different number depending on the subscriber’s location.
LBD is invoked when the Vertical service codes service detects that a subscriber has dialed a number that requires it. When invoked, LBD retrieves the dialed number and attempts to determine the subscriber’s location. Using this information, it consults a database to get a new number. If one is found, the call will be redirected to it.
If the service can’t determine the subscriber’s location or the database doesn’t have an entry for their location, the service can instead take any of the following actions:
-
play an announcement to the subscriber
-
end the call
-
redirect the call to a default destination.
Subscriber data
Per-subscriber location based dialing service data is provisioned in the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document stored in HSS transparent data.
| |
For standard Rhino VoLTE TAS deployments, the Metaswitch-TAS-Services document is disabled. This must be enabled to activate the location based dialing service. |
Further information on configuring the location based dialing service subscriber data is given in Location based dialing subscriber data.
Interactions with other services
Vertical service codes (VSC)
LBD depends on the vertical service code service to identify when a number requiring LBD has been dialed.
Call barring
Call barring operates based on the original number dialed by the subscriber, not the new number targeted by the LBD service.
International Call Management
When it does number analysis the International Call Management service will look at the original dialed number, not the new number targeted by the LBD service. This means that if the LBD service directs the call to an international number, International Call Management may bar the call if the original number was not dialed with a country code.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the location based dialing service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT)
What it does
Explicit Communication Transfer (ECT) is an MMTel service that enables a party involved in a communication to transfer their role to a third party.
For this service there are three actors involved:
-
The transferor initiates the call transfer
-
The transferee is the other party on the call
-
The transfer target is the party that replaces the transferor in a call transfer.
The transferor invokes the ECT and the transferee replies back accordingly to transfer to the transfer target. The Rhino VoLTE TAS processes these messages to handle the call transfer while maintaining charging.
The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s ECT service supports either a consultative transfer or a blind transfer:
-
A consultative transfer is where the transferor has consultative communication with the transfer target before a transfer. This may involve an existing session between the transferor and transfer target before a call transfer.
-
A blind transfer is where the transferor has no consultative communication with the transfer target. The transferor invokes a call transfer with no current session between the transferor and the transfer target.
The Rhino VoLTE TAS supports a response timeout for requests generated by the transfer service.
If the parties' dialog is interrupted or removed during a call transfer, the Rhino VoLTE TAS’s ECT service initiates a new dialog to continue the transfer using third party call control procedures.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the ECT service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
Flexible Alerting (FA)
What it does
The MMTel Flexible Alerting (FA) service allows the creation of a group of member identities bound to a single number, called the Pilot Number.
When a call to the pilot number is identified, the service will alert all the members of the group and the caller is bound to the first member of the group that answers the call.
When a member answers the call with 200 (OK), the service cancels all other sessions towards the other members and finishes the call setup procedures between the calling party and the member that answered.
The service can be set to alert the group members:
-
sequentially - sequentially alerts the group members in order, with each member sending a final response or timing out before the next is alerted.
-
in parallel - alerts all the group members at once.
3GPP defines flexible alerting in TS 24.239 and the flexible alerting subscriber data schema is defined in TS 24.239 and TS 29.364.
Group members
The group of identities that may be contacted by the Flexible Alerting feature is called the FA Group.
There can be two types of FA Group:
-
single-user - one user, who may have one or more devices.
-
multiple-users - more than one user. An example would be the devices of more than person in the same office.
Interactions with other services
CAP charging
If CAP charging is in use, on inbound calls there will be a separate session between the Rhino VoLTE TAS and the service control point (SCP) providing the charging service for each forked PS and CS leg for each device. The leg that is answered by the called subscriber will be charged, and the other legs will be recorded as zero length calls with the SCP.
PSAP callback
Certain functions of the flexible alerting service that could interfere with emergency calls are disabled when an emergency call is detected:
-
When a PSAP callback attempt is made to the undisclosed identity, the flexible alerting service will not block the call.
Communications Diversion (CDIV)
Communication Forwarding Unconditional (CFU)
If CFU is active for the Pilot Identity, the procedures will be applied and no group member will be alerted.
Communication Forwarding on Busy user (CFB)
If CFB is active for the Pilot Identity, the procedures will be applied if the pilot number is considered busy.
The definition of Busy for the pilot number depends on the group type:
-
For single-user, when one member is busy the pilot number is busy.
-
For multiple-uses all group members have to be busy for the pilot number to be considered busy.
Communication Forwarding on no Reply (CFNR) and Communication Forwarding on Subscriber Not Reachable (CFNRc)
If the FA Pilot Identity is considered in a state of CFNR or CFNRc, the procedures for those MMTel services will be applied.
The pilot number is considered in a state of:
-
No Replywhen all group members are in a state of no reply. -
Not Reachablewhen all group members are in a state of not reachable.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the flexible alerting service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
Session transfer to own device
What it does
The Rhino VoLTE TAS allows a subscriber to transfer an active call from their current active registered device (UE1) to another of their registered devices (UE2). This active call is maintained while the communication session between the A and B party’s devices has changed. Sessions can be transferred between devices that share the same IMS Public User Identity (IMPU). This service is supported for either originating or terminating users.
In the originating case, The A party subscriber can initiate a session transfer during an active session by pulling the call on to the UE2 device. For example, the calling party may transfer a call from a phone (UE1) to a tablet (UE2).
The Rhino VoLTE TAS verifies that the UE2 device is configured for a session transfer for the A party subscriber. If the configuration is verified, then the Rhino VoLTE TAS pulls the UE2 device into the call with the B party. Once the connection has been established, the UE1 device is disconnected from the session.
The service makes an SDP remote update on the existing called leg to guarantee SDP integrity and correctness on all involved dialogs.
The terminating case is also supported. This would be where the B party subscriber can use another registered device with the same IMPU to pull the call. The service makes an SDP remote update on the existing calling leg to ensure SDP integrity.
Configuration
Currently, the declarative configuration for the session transfer to own device service is only available through low-level overrides, which require the guidance of Metaswitch support.
To configure the service, contact your Metaswitch customer care representative.
| |
Full declarative configuration support for this service may become available in a later version. |
RVT XCAP
What it does
The Rhino VoLTE TAS XCAP server is a web application that implements the XCAP (XML Configuration Access Protocol) towards the UE, and supports the XML schemas for user and operator data defined in TS 29.364. It stores and retrieves this information in the HSS using Sh Transparent Data, according to TS 29.364.
A subscriber can use the XCAP Ut interface from their UE to retrieve and modify their MMTel call settings, such as diversion and blocking, stored in the HSS.
Configuration
For configuration details, see XCAP domains.
Shared configuration
The XCAP server takes the rest of its configuration from some of the shared system configuration files.
Number analysis
To validate that all URIs updated via XCAP are normalizable, the XCAP server uses:
-
the number normalization configuration from
number-analysis-config.yaml, and -
the country dialing code from
home-network-config.yaml.
Additionally, when a UE updates call diversion rules, the XCAP server checks the target URIs against the list of non-provisionable URIs from number-analysis-config.yaml.
BSF and NAF configuration
The BSF (Bootstrapping Server Function) and NAF (Network Application Function) must be configured to allow UEs to authenticate requests to the XCAP server. See RVT Authentication Gateway for details.
To configure any parts of the XCAP server not mentioned here, contact Metaswitch support.
XCAP domains
The list of domains in the mag-vmpool-config.yaml file is the complete set of domains that the XCAP server should handle for UEs making XCAP requests in the network.
How it works
The XCAP domains specified in the mag-vmpool-config.yaml file are used by initconf to generate or validate the XCAP and BSF certificates. For the BSF certificate, the domains are the configured XCAP ones with the initial xcap. prefix replaced with bsf..
If a custom BSF and/or XCAP certificate was provided (see REM certificates) then initconf will validate that the certificate(s) apply to all the configured domains. If a custom BSF or XCAP certificate was not provided, initconf will generate a self-signed certificate that applies to all the configured domains.
Configuration
The xcap-domains field lists the domains for which the Rhino VoLTE TAS XCAP server will accept requests, as shown in the Example for mag-vmpool-config.yaml
You will likely have at least one domain per mcc-mnc in your network, as configured in the PLMN IDs for my network.
Setting up XCAP domains configuration
I want to …
Specify a set of domains the Rhino VoLTE TAS XCAP server will accept request for
To configure the Rhino VoLTE TAS XCAP server to accept request for a set of domains, in the mag-virtual-machine-pool section, set the xcap-domains list to a list of domain names.
xcap-domains:
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc123.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.org
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc124.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.orgRVT Authentication Gateway
The Authentication Gateway is responsible for handling general authentication architecture (GAA) behavior in the Rhino VoLTE TAS. There are two main components of the Authentication Gateway:
-
the bootstrap security function (BSF)
-
the network application function (NAF) filter
Configuration for the BSF is limited to setting up the Diameter Zh connection to the home subscriber server (HSS). For information about this, see the Diameter Zh interface section of the HSS integration instructions.
NAF filter
What it does
In the Rhino VoLTE TAS, the purpose of the network application function (NAF) authentication filter is to verify a subscriber’s identity before allowing them to view or modify their subscriber configuration using XCAP.
The NAF filter is part of the 3GPP specified general authentication architecture (GAA).
Service information
The configuration for the NAF filter includes a number of settings that provide information about the service it’s providing.
-
The
service-typeis a number that identifies the type of service the NAF filter is providing within the GAA. Recognized values for this setting are defined in Annex B of 3GPP TS 29.109. The default value for the NAF filter is0, which indicates an "unspecific service". -
The
service-idis a number that uniquely identifies the exact service the NAF filter is providing within an operator’s network. The value that should be used is operator specific, but must match the service ID in the subscriber’s Generic Bootstrapping Architecture User Security Settings (GUSS) in the HSS. -
The
naf-groupis a name that identifies the group that the NAF filter instance is a part of. The group name is decided by the operator and it is optional to use this field. The NAF group provides an additional layer of control on top of the service type and ID over what part of the GUSS is used by the NAF filter instance.
Cassandra database
The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s implementation of the NAF filter differs from the 3GPP specification in the way that it communicates with the Bootstrap Security Function (BSF). Rather than communicating directly using the Diameter Zn interface, a Cassandra database is used as an intermediary. This allows the BSF and NAF nodes to be stateless, making it easy to scale out horizontally.
The NAF filter also uses a Cassandra database to track all nonce values that are currently in use; see Nonce values for details. The Cassandra keyspace to use for nonce storage must be specified in the nonce-cassandra-keyspace field.
Nonce values
When generating an authentication challenge for the subscriber’s handset, the NAF filter must create a nonce value to include as part of it. This nonce value is one part of the mechanism used by the handset to verify its identity in subsequent messages. For this reason, the NAF filter must keep track of the values used for each subscriber for each authentication challenge.
Nonce values are tracked in a Cassandra database. This allows the NAF filter to operate statelessly, meaning that if there are multiple NAF filter nodes in use, messages from a given subscriber do not always need to go to the same node. The Cassandra keyspace to use must be specified in the nonce-cassandra-keyspace field.
Normally, a single nonce should never be used more than once, but to avert the need to send a new challenge every time the handset wants to send a message, a separate nonce count number is included in each message. This allows the same nonce to be reused up to a number of times determined by the reuse-count field. The count starts at 1 in the first message and is incremented in each subsequent message.
A nonce can become invalid under a number of circumstances, if this happens the subscriber’s handset must restart authentication procedures. The nonce will become invalid when any of the following conditions are met:
-
Too much time has passed since the nonce was generated. The time period can be configured in the
lifetime-millisecondsfield. -
The IP address of the subscriber’s handset changes.
-
The nonce count exceeds the maximum count configured in the
reuse-countfield. -
A message with the same nonce and nonce-count as a previous message is received.
Configuration
What you need
-
❏ The service type for the NAF filter.
-
❏ The service ID for the NAF filter.
-
❏ Optionally, the name of the group that the NAF filter instance is a part of.
-
❏ The Cassandra keyspace to use for storing nonce values.
-
❏ The maximum amount of time a nonce should remain valid.
-
❏ The maximum number of times a nonce can be reused by incrementing the nonce count.
Setting up the NAF filter
I want to…
Set the service type
In the naf-filter section, set the service-type to the desired value:
service-type: 1Related section: Service information
Set the service ID
In the naf-filter section, set the service-id to the desired value:
service-id: 2Related section: Service information
Set the NAF group name
In the naf-filter section, set the naf-group to the desired value:
naf-group: "nafgroup1"Related section: Service information
Change the number of times a single nonce can be reused by incrementing the nonce count
In the nonce-options section, set reuse-count to the required maximum:
reuse-count: 100Related section: Nonce values
Change how long a single nonce will remain valid after it is created
In the nonce-options section, set lifetime-milliseconds to the required time period in milliseconds:
lifetime-milliseconds: 180000Related section: Nonce values
Enable debug logging
| |
Never enable debug logging on production systems. |
In the naf-filter section, set debug-logging-enabled to true:
debug-logging-enabled: trueDisable debug logging
In the naf-filter section, set debug-logging-enabled to false:
debug-logging-enabled: falseRVT IP Short Message Gateway (IP-SM-GW)
What it does
The IP Short Message Gateway (IP-SM-GW) translates SMS traffic between GSM and LTE networks.
The Rhino VoLTE TAS IP-SM-GW is based on 3GPP TS 24.341, and implements suitable SMS interworking as part of GSMA IR.92 version 9.0.
| |
The IP-SM-GW only supports MAP-based SS7 protocols. CDMA networks are not supported. |
MO and MT
The IP-SM-GW handles both Mobile Originating (MO) and Mobile Terminating (MT) messages. In MO scenarios, the short message is received over a packet-switched (PS) network and submitted to a Short Message Service Center (SMSC) over a circuit-switched (CS) network. In MT scenarios, the short message is received from a Gateway Message Switching Center (GMSC) and delivered to the subscriber over either the PS or CS network.
Charging
The IP-SM-GW can control Diameter Ro charging for both MO and MT scenarios. The IP-SM-GW acts as the Charging Trigger Function, and uses Immediate Event Charging. Charging can be enabled separately for each of MO, PS MT, and CS MT traffic scenarios.
Routing modes
The IP-SM-GW supports four different modes which determine how it will prioritize its attempts to deliver MT traffic.
| Parameter value | Behavior |
|---|---|
PS_THEN_CS |
Try packet-switched network first, then fall back to the circuit-switched network. |
CS_THEN_PS |
Try circuit-switched network first, then fall back to the packet-switched network. |
PS_ONLY |
Only try delivery over the packet-switched network. |
CS_ONLY |
Only try delivery over the circuit-switched network. |
In the case of the CS_THEN_PS and PS_THEN_CS modes, message delivery can be controlled further through the use of avoidance codes, which allow you to avoid fallback based on the response to the initial delivery attempt.
PS fallback avoidance codes
When PS delivery fails, the CP-Cause parameter in the resulting RP-Error is checked against the entries in the avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs list. The numeric causes and their meanings can be found in TS 24.011 Section 8. If the CP-Cause received is present in the configured list, CS delivery will not be attempted.
The table below lists the avoidance values.
| Cause | Value |
|---|---|
UNASSIGNED_NUMBER |
1 |
OPERATOR_DETERMINED_BARRING |
8 |
CALL_BARRED |
10 |
RESERVED |
11 |
SHORT_MESSAGE_TRANSFER_REJECTED |
21 |
MEMORY_CAPACITY_EXCEEDED |
22 |
DESTINATION_OUT_OF_ORDER |
27 |
UNIDENTIFIED_SUBSCRIBER |
28 |
FACILITY_REJECTED |
29 |
UNKNOWN_SUBSCRIBER |
30 |
NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER |
38 |
TEMPORARY_FAILURE |
41 |
CONGESTION |
42 |
RESOURCES_UNAVAILABLE |
47 |
REQUESTED_FACILITY_NOT_SUBSCRIBED |
50 |
REQUESTED_FACILITY_NOT_IMPLEMENTED |
69 |
INVALID_SHORT_MESSAGE_REFERENCE_VALUE |
81 |
INVALID_MESSAGE |
95 |
INVALID_MANDATORY_INFORMATION |
96 |
MESSAGE_TYPE_NONEXISTENT_OR_NOT_IMPLEMENTED |
97 |
MESSAGE_NOT_COMPATIBLE_WITH_SHORT_MESSAGE_PROTOCOL_STATE |
98 |
INFORMATION_ELEMENT_NONEXISTENT_OR_NOT_IMPLEMENTED |
99 |
PROTOCOL_ERROR |
111 |
INTERWORKING |
127 |
CS fallback avoidance codes
When CS delivery fails, the SM-EnumeratedDeliveryFailureCause parameter in the error response is checked against the entries in the avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps list. The numeric causes and their meanings can be found in TS 29.002 Section 17.7.7 Error data types. If the value is present in the list, PS delivery will not be attempted. The values of the avoidance codes used when avoiding fallback from CS to PS are listed below.
| Cause | Value |
|---|---|
|
0 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
UE reachability notifications
The IP-SM-GW supports UE Reachability Notifications in the case where an MT message sent over a PS network cannot be delivered due to the UE becoming unavailable. In this situation, the IP-SM-GW will request a notification from the HSS in the event that the UE comes back online. When this notification is received from the HSS, the IP-SM-GW will notify the HLR that UE is ready for SM delivery.
Multiple sites and geo-redundancy
The IP-SM-GW can be deployed at multiple geographically distributed sites. To configure full geographic redundancy including cross-site failover, contact support.
Networking considerations
The IP-SM-GW interfaces with network elements from a variety of different vendors. A number of configuration options are available to control the interactions with these elements, particularly the HLR and MSCs.
Modifying SCCP-layer addressing
When accepting an OpenRequest, the SCCP responder address in the OpenAccept will, by default, be set to the value of the SCCP called party in the OpenRequest. If use-gt-as-calling-party is set to true, and if the received sccp-called-party contains a global title, the responder address will be modified in the following way:
-
the Translation Type is set to 0
-
the Routing Indicator will be set to gt
-
the Point Code will be unset
-
the National indicator will be set to false.
This is useful when the inbound sccp-called-party has been modified by a network element to use PC/SSN routing, but GT routing is required for establishing the TCAP dialog.
Use allow listing for incoming SCCP global titles
The IP-SM-GW can filter incoming SCCP messages on global title prefix, to help control the network elements permitted to initiate CS connections.
Suppress HLR interaction
The IP-SM-GW supports the suppression of all HLR interactions. This removes the CS capability and dependencies from the product, allowing it to work as a purely PS to PS platform.
Content size threshold
During MO message delivery, the IP-SM-GW will either include the ForwardSM in the TC-BEGIN message, or send the ForwardSM separately. This determination is configurable based on message content size.
Setting DeliveryNotIntended during SMMA flows
When the IP-SM-GW sends a SendRoutingInfoForSM request to the HLR which is not part of an MT delivery flow, the DeliveryNotIntended flag may be used to indicate that the HLR should not expect follow-up messages. This should be adjusted based on HLR capabilities.
Configuration
Example IP-SM-GW configuration can be found in the example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml and in the example for hlr-config.yaml.
What you need
-
❏ The number of geographically distributed sites in use.
-
❏ The SCCP addressing format in use.
-
❏ The externally-visible global title of the SMO cluster.
-
❏ The domain to use for outgoing SIP messages.
-
❏ Whether all HLR interaction should be suppressed.
-
❏ The PLMN ID ranges in use.
-
❏ The MT message delivery order, and any fallback avoidance codes.
-
❏ A DNS record pointing at all SMO node signalling interfaces.
-
❏ The Ro charging configuration in use.
Setting up network integration
Initial configuration
Network integration must be configured before further configuration of the system can take place.
1. Adjust the georedundancy setting to suit your deployment
In the georedundancy section, uncomment the georedundancy and total-sites lines, and set total-sites to 2.
# The number of IPSMGW sites
total-sites: 2| |
To configure full geographic redundancy, including cross-site failover, contact support. |
Related section: Multiple sites and geo-redundancy
2. Configure the SCCP address format used when connecting to an SMSC.
The template-smsc-address is used to specify the non-digit string portions of the SMSC’s SCCP address, which MT CS messages will be sent to.
In the map-messaging section, set the template-smsc-address as appropriate for your network.
template-smsc-address: "type=C7,ri=gt,digits=0,ssn=8,national=false,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,gti=4,tt=0"3. Set the SCCP address used as the calling party address in SS7 messages initiated by the IP-SM-GW.
In the map-messaging section, set the originating-address as appropriate for your network.
originating-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=148"| |
If the originating-address contains a pc= parameter, that parameter’s value must be the same as the point-code value in sgc-config.yaml. See M3UA interface configuration. |
4. Set the address that GMSCs will use to contact the IP-SM-GW
The ipsmgw-as-msc-address is the address that the IP-SM-GW will return to the GMSC during the SendRoutingInformation phase of the MT message procedure, so that subsequent messages will be delivered to the IP-SM-GW. TCAP messages with this address should be routeable to an IP-SM-GW node.
In the map-messaging section, set the ipsmgw-as-msc-address to an address which will route to the IP-SM-GW.
ipsmgw-as-msc-address: "address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN"5. Configure how to determine the address of the HLR
When processing MT messages, the IP-SM-GW can determine the address of an HLR in two ways. The HLR address can be fixed and set in the hlr section of hlr-config.yaml, or alternatively the MSISDN of the called party can be used as the digit portion of the HLR address.
-
If you are using a fixed HLR address:
In hlr-config.yaml, confirm that the hlr-address is set correctly.
hlr-address: "type=C7,ri=gt,digits=123456789,ssn=8,national=false,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,gti=4,tt=0"In sentinel-ipsmgw.yaml, in the map-messaging section, set use-msisdn-as-hlr-address to false.
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: false-
If you are using dynamic routing for the HLR address:
In hlr-config.yaml, in the hlr section, ensure that the hlr-address field is set to use global title addressing.
hlr-address: "type=C7,ri=gt,digits=0,ssn=8,national=false,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,gti=4,tt=0"In sentinel-ipsmgw.yaml, in the map-messaging section, set use-msisdn-as-hlr-address to true.
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: true6. Configure the terminating SIP URI domain
Outbound SIP messages generated by the IP-SM-GW require a configured value to use as the domain portion of the SIP URI. Set this to a network-appropriate SIP domain.
Set the terminating-domain value to an appropriate SIP domain.
terminating-domain: example.comI want to…
Deploy the IP-SM-GW in an environment without an HLR
In hlr-config.yaml, in the hlr section, ensure that the hlr-address field is set to the default value.
hlr-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=6"In sentinel-ipsmgw.yaml, set delivery_order to PS_ONLY. In sentinel-ipsmgw.yaml, in the map-messaging section, set suppress-hlr-interaction to true.
map-messaging:
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: true
delivery-order: PS_THEN_CSRelated sections: Suppress HLR interaction, HLR integration
Prefer GT addressing for SCCP calling party in OpenResponse messages
In the map-messaging section, set the use-gt-as-calling-party value to true.
use-gt-as-calling-party: trueRelated section: Modifying SCCP-layer addressing
Send ForwardSM messages with 120 characters in a separate TCAP message
In the map-messaging section, set the sms-content-size-threshold value to 119.
sms-content-size-threshold: 119Related section: Content size threshold
Disable the delivery-not-intended flag in SendRoutingInformationForSM requests
In the map-messaging section, set the sri-sm-delivery-not-intended value to false.
sri-sm-delivery-not-intended: falseRelated section: Setting DeliveryNotIntended during SMMA flows
Set the PLMN ID used when generating correlation IMSIs
The PLMN ID used when generating correlation IMSIs must be part of the Home Network PLMN ID set. See Set the PLMN IDs for my network for details.
Setting up Mobile Terminating scenarios
I want to…
Attempt delivery over PS first, falling back to CS unless there are network problems
First, reference the table in PS fallback avoidance codes to determine the numeric codes relevant to the fallback avoidance scenarios. In this case, codes 42 and 38 are appropriate (CONGESTION and NETWORK_OUT_OF_ORDER respectively).
Set the delivery-order to PS_THEN_CS. In the fallback-settings section, set avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs to a list containing these values:
delivery-order: PS_THEN_CS
fallback-settings:
avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs:
- 42
- 38Related section: :Routing modes
Attempt delivery over CS first, falling back to PS unless there are network problems
First, reference the table in CS fallback avoidance codes to determine the numeric codes relevant to the fallback avoidance scenarios. In this case, code 4 is appropriate (sc_Congestion).
Set the delivery-order to CS_THEN_PS. In the fallback-settings section, set avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps to a list containing 4.
delivery-order: CS_THEN_PS
fallback-settings:
avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps:
- 4Related section: Routing modes
Subscribe to UE reachability notifications
In the ue-reachability-notifications section, set the notification-host parameter to an appropriate hostname value. This hostname must be configured in DNS to point at the signalling IPs of all SMO nodes in the cluster.
notification-host: smo.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgRelated section: UE reachability notifications
Setting up charging
I want to…
Configure charging for MO and MT PS traffic
In the charging-options section, uncomment and configure the diameter-ro section.
# You must also specify the per-node-diameter-ro configuration in smo-vmpool-config.yaml
diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-realm: metaswitch.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1-
The
diameter-ro-releaseof Diameter Ro to use. -
The Diameter
origin-realmfor the Rhino VoLTE TAS. -
The Diameter
destination-realmfor the online charging system. -
A Diameter
destination-peerslist that correspond to OCS servers. There must be at least one entry, and for each entry the following values must be set:-
the
destination-hostnamefor the OCS server -
the
portfor the OCS server -
the
protocol-transportto use with the OCS server. -
the
metricto use for this OCS server peer.
-
In the charging-options section, set mt-ps-enabled and mo-ps-enabled to true.
mt-ps-enabled: true
mt-cs-enabled: false
mo-ps-enabled: trueIn smo-vmpool-config.yaml, you must ensure that all per-node-diameter-ro sections are present and not commented out.
# Uncomment this if diameter-ro is enabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: smo1.smo.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgRelated section: Charging
= RVT USSD over IM CN subsystem (USSI) :indexpage: :sortorder: 80 :toc: macro :toclevels: 4 :toc-title: On this page
== What it does
The Rhino VoLTE TAS acts as a gateway for USSI (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data over IM CN subsystem) messages. SIP messages containing USSD payloads are processed by the Rhino VoLTE TAS and forwarded to the HLR over the MAP protocol. Responses are then encoded back into SIP and sent to the invoking subscriber.
This feature is enabled alongside the IP-SM-GW, and will be present if that service is configured.
Aside from network integration, the only configuration possible for USSI is to reject all incoming traffic.
| |
The USSI only supports MAP-based SS7 protocols. CDMA networks are not supported. |
== Configuration
The example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml shows example configuration relevant to USSI in the sentinel-ipsmgw/map-messaging and sentinel-ipsmgw/ussi sections.
=== What you need
-
❏ The text of the USSI rejection message, if disabling the service.
=== Initial configuration
As the USSI service runs alongside the IP-SM-GW, the IP-SM-GW service must be configured following the instructions in Initial configuration.
=== Setting up USSI ==== I want to… ===== Reject all USSI messages
Uncomment the entire ussi block.
ussi:
reject-all-with-default-message:
language: "en"
message: "USSD messages are not supported - check your balance on example.com"RVT declarative configuration reference
This reference follows the same structure as the high level configuration files.
- node-type choice
- snmp
- sgc
- routing
- custom-data
- common
- home-network
- hlr
- icscf
- number-analysis
- sas
- sentinel-volte
- scc
- mmtel
- registrar
- sis
- hlr-connectivity-origin
- charging
- session-refresh
- system
node-type choice
The VM node type.
Context
The context of node-type choice within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mag deployment-config:mag-virtual-machine-pool (in mag-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:naf-filter (in naf-filter-config.yaml) deployment-config:bsf (in bsf-config.yaml) mmt-cdma mmt-gsm shcm deployment-config:shcm-virtual-machine-pool (in shcm-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:shcm-service (in shcm-service-config.yaml) tsn smo deployment-config:smo-virtual-machine-pool (in smo-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:sentinel-ipsmgw (in sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml) infra
A Choice between one of the following:
mag
See mag for details of this node and its descendants.
mmt-cdma
See mmt-cdma for details of this node and its descendants.
mmt-gsm
See mmt-gsm for details of this node and its descendants.
shcm
See shcm for details of this node and its descendants.
tsn
See tsn for details of this node and its descendants.
smo
See smo for details of this node and its descendants.
infra
See infra for details of this node and its descendants.
mag
Configure MAG node(s).
Context
The context of mag within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mag deployment-config:mag-virtual-machine-pool (in mag-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:naf-filter (in naf-filter-config.yaml) deployment-config:bsf (in bsf-config.yaml)
mag-virtual-machine-pool
See mag-virtual-machine-pool for details of this node and its descendants.
naf-filter
See naf-filter for details of this node and its descendants.
bsf
See bsf for details of this node and its descendants.
mag-virtual-machine-pool
Context
The context of mag-virtual-machine-pool within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mag deployment-config:mag-virtual-machine-pool (in mag-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 xcap-domains list additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role rem-auth list username real-name password role virtual-machines list vm-id diameter-zh-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rem-debug-logging-enabled
The Management and Authentication Gateway (MAG) virtual machine pool.
This node and its descendants are configured in mag-vmpool-config.yaml.
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
cassandra-contact-points list
Explicit list of Cassandra contact points. This should only be specified for testing or special use cases. When left unspecified, the Cassandra contact points will be automatically determined from the TSN VM pool IP addresses.
List Structure
management.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone signaling.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone
The keys are management.ipv4 and signaling.ipv4.
management.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the management interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
signaling.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
xcap-domains list
The list of domains used to generate or validate XCAP and BSF certificates. For the BSF certificate, the domains are derived from these XCAP ones with the initial xcap. prefix replaced with bsf..
Each domain must start with the string 'xcap.'.
| |
Metaswitch support should be contacted for advice on how changes to this value can be made to take effect. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
Type List of domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
Internet domain names are only loosely specified. Section 3.5 of RFC 1034 recommends a syntax (modified in Section 2.1 of RFC 1123). The pattern above is intended to allow for current practice in domain name use, and some possible future expansion. It is designed to hold various types of domain names, including names used for A or AAAA records (host names) and other records, such as SRV records. Note that Internet host names have a stricter syntax (described in RFC 952) than the DNS recommendations in RFCs 1034 and 1123, and that systems that want to store host names in schema nodes using the domain-name type are recommended to adhere to this stricter standard to ensure interoperability.
The encoding of DNS names in the DNS protocol is limited to 255 characters. Since the encoding consists of labels prefixed by a length bytes and there is a trailing NULL byte, only 253 characters can appear in the textual dotted notation.
The description clause of schema nodes using the domain-name type MUST describe when and how these names are resolved to IP addresses. Note that the resolution of a domain-name value may require to query multiple DNS records (e.g., A for IPv4 and AAAA for IPv6). The order of the resolution process and which DNS record takes precedence can either be defined explicitly or may depend on the configuration of the resolver.
Domain-name values use the US-ASCII encoding. Their canonical format uses lowercase US-ASCII characters. Internationalized domain names MUST be A-labels as per RFC 5890.
- Reference
-
RFC 952: DoD Internet Host Table Specification
RFC 1034: Domain Names - Concepts and Facilities
RFC 1123: Requirements for Internet Hosts — Application
and Support
RFC 2782: A DNS RR for specifying the location of services
(DNS SRV)
RFC 5890: Internationalized Domain Names in Applications
(IDNA): Definitions and Document Framework
- Values
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
xcap\..*
additional-rhino-jvm-options list
Additional JVM options to use when running Rhino. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
name
Name of the JVM option. Do not include '-D'.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
value
Value for the JVM option.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
rhino-auth list
List of Rhino users and their plain text passwords.
Must contain at least 1 element.
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration. |
- Default value
-
'view'
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to REM configuration. Also has access to the HSS Subscriber Provisioning REST API. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to REM configuration. Note: Rhino write permissions are controlled by the Rhino credentials used to connect to Rhino, NOT the REM credentials. |
- Default value
-
'em-user'
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
List Structure
vm-id string diameter-zh-origin-host domain-name scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string rhino-node-id rhino-node-id-type scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string
The key is vm-id.
The values of diameter-zh-origin-host must be unique.
The values of rhino-node-id must be unique.
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
diameter-zh-origin-host
The origin host to use when sending Diameter Zh requests from this node to the HSS.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
scheduled-sbb-cleanups
Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules. If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rhino-node-id
The Rhino node identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type rhino-node-id-type
- Description
-
The Rhino node identifier type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 32767
scheduled-rhino-restarts
Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rem-debug-logging-enabled
Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
naf-filter
Context
The context of naf-filter within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mag deployment-config:naf-filter (in naf-filter-config.yaml) service-type service-id naf-group force-auth-on-paths list cassandra-connectivity reconnection-policy reconnection-interval-seconds reconnection-initial-delay-seconds reconnection-max-delay-seconds socket-connect-timeout-milliseconds socket-read-timeout-milliseconds socket-keepalive socket-reuse-address socket-linger-seconds socket-tcp-nodelay socket-receive-buffer-size-bytes socket-send-buffer-size-bytes lb-recipe lb-latency-aware-exclusion-threshold lb-latency-aware-scale use-ssl nonce-options reuse-count lifetime-milliseconds cache-capacity storage-mechanism nonce-cassandra-keyspace debug-logging-enabled intercept-tomcat-errors http-version
The Network Address Function (NAF) filter configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in naf-filter-config.yaml.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../common depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../naf-filter.
../home-network has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../naf-filter.
Conditional node ../number-analysis depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../naf-filter.
Conditional node ../home-network depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../naf-filter.
service-type
Identifies the type of service the NAF filter is providing. Recognized values for this setting are defined in Annex B of 3GPP TS 29.109. Affects which settings are selected from the GUSS.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
0
service-id
An operator specific identifier that uniquely identifies the service the NAF filter is providing within the network. Affects which settings are selected from the GUSS.
Type uint16
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
0
naf-group
Identifies the group that the NAF filter belongs to. Affects which settings are selected from the GUSS.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
- Default value
-
''
force-auth-on-paths list
A list of URL path prefixes for which authentication should always be enforced, even for requests from trusted entities.
Type List of string
- Values
-
a string
cassandra-connectivity
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Cassandra connectivity configuration for the NAF filter
Container Structure
reconnection-policy reconnection-interval-seconds reconnection-initial-delay-seconds reconnection-max-delay-seconds socket-connect-timeout-milliseconds socket-read-timeout-milliseconds socket-keepalive socket-reuse-address socket-linger-seconds socket-tcp-nodelay socket-receive-buffer-size-bytes socket-send-buffer-size-bytes lb-recipe lb-latency-aware-exclusion-threshold lb-latency-aware-scale use-ssl
reconnection-policy
The reconnection policy: 'constant' or 'exponential'.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../reconnection-interval-seconds depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../reconnection-policy.
Conditional node ../reconnection-initial-delay-seconds depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../reconnection-policy.
Conditional node ../reconnection-max-delay-seconds depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../reconnection-policy.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The time between reconnect attempts is constant. |
|
The time between reconnect attempts increases exponentially to an upper limit. |
- Default value
-
'constant'
reconnection-interval-seconds
The reconnection interval (in seconds) to be used when the reconnection policy is set to 'constant'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../reconnection-policy = 'constant'.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 5 to 60
- Default value
-
10
reconnection-initial-delay-seconds
The initial reconnection delay (in seconds) to be used when the reconnection policy is set to 'exponential'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../reconnection-policy = 'exponential'.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 24
- Default value
-
1
reconnection-max-delay-seconds
The longest permitted interval (in seconds) between reconnect attempts when the reconnection policy is set to 'exponential'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../reconnection-policy = 'exponential'.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 16 to 128
- Default value
-
32
socket-connect-timeout-milliseconds
The socket connection timeout (in milliseconds).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
4000
socket-read-timeout-milliseconds
The socket read timeout (in milliseconds).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
4000
socket-keepalive
The socket 'keepalive' option value. 'true' will enable the sending of keepalive messages. 'false' disables the sending of these messages. A value of 'not-set' indicates that the operating system default should be used.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable the 'keepalive' socket option. |
|
Disable the 'keepalive' socket option. |
|
Use the operating system default value for the 'keepalive' socket option. |
- Default value
-
'not-set'
socket-reuse-address
The socket 'reuse-address' option value. 'true' enables this option which allows reuse of the local address provided that there is no active socket already bound to the address. 'false' disables this option. A value of 'not-set' indicates that the operating system default should be used.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable the 'reuse-address' socket option. |
|
Disable the 'reuse-address' socket option. |
|
Use the operating system default value for 'reuse-address'. |
- Default value
-
'not-set'
socket-linger-seconds
If set to a value greater than '0' activates the 'linger' socket option. When activated, a close or shutdown of a socket will not return until all queued messages have been sent or the timeout (in seconds) has expired.
Setting this to '0' disables the 'linger' socket option.
A value of '-1' uses the operating system default.
Type int32
- Value
-
a number in the range -1 or more
- Default value
-
-1
socket-tcp-nodelay
A value of 'true' disables Nagle’s algorithm. All messages will be sent immediately. A value of 'false' enables Nagle’s algorithm. When Nagle’s algorithm is enabled the operating system may temporarily queue outbound data pending the arrival of further data to the same destination. This can reduce network overhead when many small TCP messages are generated by an application. A transmission delay of up to 500ms may occur as a result.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
socket-receive-buffer-size-bytes
The socket receive buffer size (in bytes). A value of '-1' uses the operating system default.
Type int32
- Value
-
a number in the range -1 or more
- Default value
-
-1
socket-send-buffer-size-bytes
The socket send buffer size (in bytes). A value of '-1' uses the operating system default.
Type int32
- Value
-
a number in the range -1 or more
- Default value
-
-1
lb-recipe
The load balancing recipe.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use round robin load balancing. |
|
Use data center (DC) aware round robin load balancing. |
|
Use latency aware round robin load balancing. |
|
Use latency and data center (DC) aware round robin load balancing. |
|
Use the default load balancing mechanism. |
- Default value
-
'use-default'
lb-latency-aware-exclusion-threshold
The load balancing latency aware exclusion threshold.
Type decimal64
- Value
-
a number with up to 1 decimal digits in the range 0.0, 1.0 or more
- Default value
-
0.0
lb-latency-aware-scale
The load balancing latency aware scale.
Type decimal64
- Value
-
a number with up to 1 decimal digits in the range 0.0 or more
- Default value
-
0.0
use-ssl
The SSL implementation to use. 'none' means do not use SSL.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use the JDK’s SSL implementation. |
|
Use Netty’s SSL implementation. |
|
Do not use SSL. |
- Default value
-
'none'
reuse-count
The maximum number of times a nonce can be reused by incrementing the nonce count.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
100
lifetime-milliseconds
The time that a nonce remains valid for after being generated (in milliseconds).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
180000
cache-capacity
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The capacity of the nonce cache. This setting is only relevant when using the local storage mechanism.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 or more
- Default value
-
100000
storage-mechanism
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The storage mechanism to use for the nonce cache.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use Cassandra storage. |
|
Use local storage. |
- Default value
-
'local'
nonce-cassandra-keyspace
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The Cassandra keyspace for the nonce cache. This setting is only relevant when using the Cassandra storage mechanism.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
- Default value
-
'opencloud_nonce_info'
debug-logging-enabled
Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
intercept-tomcat-errors
OBSOLETE in RVT 4.1 series and later. Whether to let NGINX replace Tomcat errors with default errors. Use only on advice of your Customer Care Representative.
| |
Metaswitch support should be contacted for advice on how changes to this value can be made to take effect. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
http-version
HTTP version to use on the Ub (BSF) and Ua/Ut (NAF) interfaces.
| |
Metaswitch support should be contacted for advice on how changes to this value can be made to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use HTTP version 1.0. |
|
Use HTTP version 1.1. |
- Default value
-
'1.1'
bsf
Context
The context of bsf within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mag deployment-config:bsf (in bsf-config.yaml) zh-diameter destination-realm origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric debug-logging-enabled
The Bootstrap Security Function (BSF) configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in bsf-config.yaml.
destination-realm
The Diameter destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
origin-realm
The Diameter origin realm.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-peers list
Diameter destination peer(s).
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
protocol-transport enumeration destination-hostname domain-name port port-number metric uint32
The key is destination-hostname.
protocol-transport
The combined Diameter protocol and transport.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over tcp |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp. IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported. |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are provisioned. |
- Default value
-
'aaa'
destination-hostname
The destination hostname.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
The destination port number.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3868
metric
The metric to use for this peer. Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric, traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
1
mmt-cdma
Context
The context of mmt-cdma within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mmt-cdma deployment-config:mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool (in mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
Configure MMT CDMA node(s).
mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool
MMT CDMA virual machine pool configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml.
Container Structure
deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../sentinel-volte depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool.
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
cassandra-contact-points list
A list of Cassandra contact points. These should normally not be specified as this option is intended for testing and/or special use cases.
List Structure
management.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone signaling.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone
The keys are management.ipv4 and signaling.ipv4.
management.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the management interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
signaling.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
additional-rhino-jvm-options list
Additional JVM options to use when running Rhino. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
name
Name of the JVM option. Do not include '-D'.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
value
Value for the JVM option.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
rhino-auth list
List of Rhino users and their plain text passwords.
Must contain at least 1 element.
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration. |
- Default value
-
'view'
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
List Structure
vm-id string per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host domain-name per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host domain-name scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string rhino-node-id rhino-node-id-type scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string
The key is vm-id.
The values of rhino-node-id must be unique.
The values of per-node-diameter-ro/diameter-ro-origin-host must be unique.
The values of per-node-diameter-rf/diameter-rf-origin-host must be unique.
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
per-node-diameter-ro
Configuration for Diameter Ro.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'.
Container Structure
diameter-ro-origin-host
The Diameter Ro origin host.
The value that will be used for the Origin-Host AVP when sending messages to the OCS
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
per-node-diameter-rf
Configuration for Diameter Rf.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/rf-charging.
Container Structure
diameter-rf-origin-host
The Diameter Rf origin host.
The value that will be used for the Origin-Host AVP when sending messages to the CDF
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
scheduled-sbb-cleanups
Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules. If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rhino-node-id
The Rhino node identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type rhino-node-id-type
- Description
-
The Rhino node identifier type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 32767
scheduled-rhino-restarts
Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
mmt-gsm
Context
The context of mmt-gsm within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice mmt-gsm deployment-config:mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool (in mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
Configure MMT GSM node(s).
mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool
MMT GSM virual machine pool configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml.
Container Structure
deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../sentinel-volte depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool.
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
cassandra-contact-points list
Explicit list of Cassandra contact points. This should only be specified for testing or special use cases. When left unspecified, the Cassandra contact points will be automatically determined from the TSN VM pool IP addresses.
List Structure
management.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone signaling.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone
The keys are management.ipv4 and signaling.ipv4.
management.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the management interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
signaling.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
additional-rhino-jvm-options list
Additional JVM options to use when running Rhino. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
name
Name of the JVM option. Do not include '-D'.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
value
Value for the JVM option.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
rhino-auth list
List of Rhino users and their plain text passwords.
Must contain at least 1 element.
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration. |
- Default value
-
'view'
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
List Structure
vm-id string per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host domain-name per-node-diameter-rf diameter-rf-origin-host domain-name scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string rhino-node-id rhino-node-id-type scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string
The key is vm-id.
The values of rhino-node-id must be unique.
The values of per-node-diameter-ro/diameter-ro-origin-host must be unique.
The values of per-node-diameter-rf/diameter-rf-origin-host must be unique.
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
per-node-diameter-ro
Configuration for Diameter Ro.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'ro' or ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro' or ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'.
Container Structure
diameter-ro-origin-host
The Diameter Ro origin host.
The value that will be used for the Origin-Host AVP when sending messages to the OCS
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
per-node-diameter-rf
Configuration for Diameter Rf.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/rf-charging.
Container Structure
diameter-rf-origin-host
The Diameter Rf origin host.
The value that will be used for the Origin-Host AVP when sending messages to the CDF
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
scheduled-sbb-cleanups
Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules. If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rhino-node-id
The Rhino node identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type rhino-node-id-type
- Description
-
The Rhino node identifier type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 32767
scheduled-rhino-restarts
Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
shcm
Configure ShCM node(s).
Context
The context of shcm within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice shcm deployment-config:shcm-virtual-machine-pool (in shcm-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:shcm-service (in shcm-service-config.yaml)
shcm-virtual-machine-pool
See shcm-virtual-machine-pool for details of this node and its descendants.
shcm-service
See shcm-service for details of this node and its descendants.
shcm-virtual-machine-pool
Context
The context of shcm-virtual-machine-pool within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice shcm deployment-config:shcm-virtual-machine-pool (in shcm-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id diameter-sh-origin-host scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
ShCM virtual machine pool configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in shcm-vmpool-config.yaml.
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
cassandra-contact-points list
A list of Cassandra contact points. These should normally not be specified as this option is intended for testing and/or special use cases.
List Structure
management.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone signaling.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone
The keys are management.ipv4 and signaling.ipv4.
management.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the management interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
signaling.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
additional-rhino-jvm-options list
Additional JVM options to use when running Rhino. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
name
Name of the JVM option. Do not include '-D'.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
value
Value for the JVM option.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
rhino-auth list
List of Rhino users and their plain text passwords.
Must contain at least 1 element.
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration. |
- Default value
-
'view'
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
List Structure
vm-id string diameter-sh-origin-host domain-name scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string rhino-node-id rhino-node-id-type scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string
The key is vm-id.
The values of diameter-sh-origin-host must be unique.
The values of rhino-node-id must be unique.
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
diameter-sh-origin-host
Diameter Sh origin host.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
scheduled-sbb-cleanups
Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules. If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rhino-node-id
The Rhino node identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type rhino-node-id-type
- Description
-
The Rhino node identifier type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 32767
scheduled-rhino-restarts
Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
shcm-service
Context
The context of shcm-service within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice shcm deployment-config:shcm-service (in shcm-service-config.yaml) diameter-sh destination-realm origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric health-check-user-identity additional-client-addresses list diameter-request-timeout-milliseconds cassandra-locking backoff-time-milliseconds backoff-limit hold-time-milliseconds caching service-indications list service-indication cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds data-references-subscription-allowed list data-reference cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds data-references-subscription-not-allowed list data-reference cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds debug-logging-enabled
ShCM service configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in shcm-service-config.yaml.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../common depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../shcm-service.
destination-realm
The Diameter destination realm.
| |
Changing this value will require consistent changes to external systems also. Changing this value will converge automatically. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
origin-realm
The Diameter origin realm.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-peers list
Diameter destination peer(s).
| |
Adding or removing entries in this list will require consistent changes to external systems also. Adding or removing entries in this list will converge automatically. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
protocol-transport enumeration destination-hostname domain-name port port-number metric uint32
The key is destination-hostname.
protocol-transport
The combined Diameter protocol and transport.
| |
Changing this value will require consistent changes to external systems also. Changing this value will converge automatically. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over tcp |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp. IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported. |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are provisioned. |
- Default value
-
'aaa'
destination-hostname
The destination hostname.
| |
Changing this value will require consistent changes to external systems also. Changing this value will converge automatically. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
The destination port number.
| |
Changing this value will require consistent changes to external systems also. Changing this value will converge automatically. |
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3868
metric
The metric to use for this peer. Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric, traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.
| |
Changing this value will require consistent changes to external systems also. Changing this value will converge automatically. |
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
1
health-check-user-identity
The health check user identity. This should match a test user configured in the HSS.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-uri-type
- Description
-
The SIP URI type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.*
additional-client-addresses list
Optional list of additional allowed ShCM client IP addresses. These addresses may access the ShCM API port, in addition to TAS and REM nodes which automatically have access.
Type List of ipv4-address
- Description
-
The ipv4-address type represents an IPv4 address in dotted-quad notation.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Values
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|2[0-4][0-9]|25[0-5])\.){3}([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1[0-9][0-9]|2[0-4][0-9]|25[0-5])(%[\p{N}\p{L}]+)?
diameter-request-timeout-milliseconds
The Diameter request timeout (in milliseconds).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 909 to 27273
- Default value
-
5000
backoff-time-milliseconds
The time (in milliseconds) to backoff before re-attempting to obtain the lock in Cassandra.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 50 to 5000
- Default value
-
5000
backoff-limit
The limit of times to backoff and re-attempt to obtain a lock in Cassandra.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 10
- Default value
-
5
hold-time-milliseconds
The time (in milliseconds) to hold a lock in Cassandra.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1000 to 30000
- Default value
-
12000
caching
Caching configuration.
Container Structure
service-indications list service-indication cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds data-references-subscription-allowed list data-reference cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds data-references-subscription-not-allowed list data-reference cache-strategy cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds
service-indications list
Service indications.
List Structure
service-indication string cache-strategy cache-strategy-type cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds uint32
The key is service-indication.
cache-strategy
Cache strategy.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../cache-parameters depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../cache-strategy.
Type cache-strategy-type
- Description
-
The type used to define the caching strategy.
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Do not use a cache. |
|
Use a simple cache. |
|
Use a subscription cache. |
- Default value
-
'subscription-cache'
cache-parameters
Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'.
Container Structure
cache-validity-time-seconds
Cache validity time (in seconds).
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 172800
data-references-subscription-allowed list
List of data references for which subscription is permitted, and their caching strategy configuration
List Structure
data-reference enumeration cache-strategy cache-strategy-type cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds uint32
The key is data-reference.
data-reference
The data reference.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
IMS public identity |
|
S-CSCF Name |
|
Initial filter criteria |
|
Service level trace info |
|
IP address secure binding information |
|
Service priority level |
|
Extended priority |
cache-strategy
The cache strategy.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../cache-parameters depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../cache-strategy.
Type cache-strategy-type
- Description
-
The type used to define the caching strategy.
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Do not use a cache. |
|
Use a simple cache. |
|
Use a subscription cache. |
- Default value
-
'subscription-cache'
cache-parameters
Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'.
Container Structure
cache-validity-time-seconds
/shcm-service/caching/data-references-subscription-allowed/cache-parameters/cache-validity-time-seconds
Cache validity time (in seconds).
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 172800
data-references-subscription-not-allowed list
List of data references for which subscription is not permitted, and their caching strategy configuration.
List Structure
data-reference enumeration cache-strategy enumeration cache-parameters cache-validity-time-seconds uint32
The key is data-reference.
data-reference
The data reference.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Charging information |
|
MS-ISDN |
|
PSI activation |
|
DSAI |
|
SMS registration info |
|
TADS information |
|
STN SR |
|
UE SRV CC capability |
|
CSRN |
|
Reference location information |
cache-strategy
The cache strategy.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../cache-parameters depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../cache-strategy.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Do not use a cache. |
|
Use a simple cache. |
- Default value
-
'simple-cache'
cache-parameters
Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'.
Container Structure
cache-validity-time-seconds
/shcm-service/caching/data-references-subscription-not-allowed/cache-parameters/cache-validity-time-seconds
Cache validity time (in seconds).
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 172800
tsn
Context
The context of tsn within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice tsn deployment-config:tsn-virtual-machine-pool (in tsn-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix virtual-machines list vm-id scheduled-cassandra-repairs scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
Configure TSN node(s).
tsn-virtual-machine-pool
The pool of TSN virtual machines.
This node and its descendants are configured in tsn-vmpool-config.yaml.
Container Structure
deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix virtual-machines list vm-id scheduled-cassandra-repairs scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
scheduled-cassandra-repairs
Repair Cassandra on specified schedules, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, Cassandra repairs will be scheduled on the leader node every day at 02:00.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
smo
Configure SMO node(s).
Context
The context of smo within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice smo deployment-config:smo-virtual-machine-pool (in smo-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-config:sentinel-ipsmgw (in sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml)
smo-virtual-machine-pool
See smo-virtual-machine-pool for details of this node and its descendants.
sentinel-ipsmgw
See sentinel-ipsmgw for details of this node and its descendants.
smo-virtual-machine-pool
Context
The context of smo-virtual-machine-pool within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice smo deployment-config:smo-virtual-machine-pool (in smo-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled cassandra-contact-points list management.ipv4 signaling.ipv4 additional-rhino-jvm-options list name value rhino-auth list username password role virtual-machines list vm-id per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host sip-local-uri scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day rhino-node-id scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week monthly day-of-month time-of-day multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week time-of-day monthly monthly list day-of-month time-of-day
SMO VM pool configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in smo-vmpool-config.yaml.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../sgc depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../smo-virtual-machine-pool.
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled
Whether Sentinel IPSMGW will be installed and enabled on SMO nodes.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../rhino-auth depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled.
Conditional node ../additional-rhino-jvm-options depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled.
Conditional node ../../sentinel-ipsmgw depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../smo-virtual-machine-pool/sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
cassandra-contact-points list
A list of Cassandra contact points. These should normally not be specified as this option is intended for testing and/or special use cases.
List Structure
management.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone signaling.ipv4 ipv4-address-no-zone
The keys are management.ipv4 and signaling.ipv4.
management.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the management interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
signaling.ipv4
The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.
This node is mandatory.
Type ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
additional-rhino-jvm-options list
Additional JVM options to use when running Rhino. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
Conditional
This list is only valid when ../sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled = 'true'.
name
Name of the JVM option. Do not include '-D'.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
value
Value for the JVM option.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
rhino-auth list
List of Rhino users and their plain text passwords.
Conditional
This list is only valid when ../sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled = 'true'.
Must contain at least 1 element.
username
The user’s username. Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 3 to 16 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]+
password
The user’s password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using the deployment’s 'secret-private-key'.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+
role
The user’s role.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration. |
|
Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration. |
- Default value
-
'view'
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
List Structure
vm-id string per-node-diameter-ro diameter-ro-origin-host domain-name sip-local-uri sip-uri-type scheduled-sbb-cleanups scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string rhino-node-id rhino-node-id-type scheduled-rhino-restarts scheduling-rule choice single-schedule frequency choice daily weekly day-of-week enumeration monthly day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string multiple-schedule frequency-list choice weekly weekly list day-of-week enumeration time-of-day string monthly monthly list day-of-month uint8 time-of-day string
The key is vm-id.
The values of per-node-diameter-ro/diameter-ro-origin-host must be unique.
The values of sip-local-uri must be unique.
vm-id
The unique virtual machine identifier.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
per-node-diameter-ro
Configuration for Diameter Ro.
If sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled is set to false, omit this.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../sentinel-ipsmgw/charging-options/diameter-ro.
Container Structure
diameter-ro-origin-host
The Diameter Ro origin host.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
sip-local-uri
SIP URI for this node.
If sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled is set to false, specify an arbitrary placeholder value here.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-uri-type
- Description
-
The SIP URI type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.*
scheduled-sbb-cleanups
Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules. If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
rhino-node-id
Rhino node identifier.
If sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled is set to false, specify an arbitrary placeholder value here.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type rhino-node-id-type
- Description
-
The Rhino node identifier type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 32767
scheduled-rhino-restarts
Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes. If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a scheduled Cassandra repair.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
scheduling-rule choice
Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.
A Choice between one of the following:
frequency choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry format is deprecated.
A Choice between one of the following:
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
frequency-list choice
Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
A Choice between one of the following:
weekly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-week
The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Every Monday. |
|
Every Tuesday. |
|
Every Wednesday. |
|
Every Thursday. |
|
Every Friday. |
|
Every Saturday. |
|
Every Sunday. |
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
monthly list
A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month and times of day to run the scheduled task
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
day-of-month
The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th) on which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 28
time-of-day
The time of day (24hr clock in the system’s timezone) at which to run the scheduled task.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]
sentinel-ipsmgw
Context
The context of sentinel-ipsmgw within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice smo deployment-config:sentinel-ipsmgw (in sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml) georedundancy total-sites map-messaging template-smsc-address originating-address ipsmgw-as-msc-address use-msisdn-as-hlr-address suppress-hlr-interaction use-gt-as-calling-party sms-content-size-threshold sri-sm-delivery-not-intended discard-inform-sc force-sm-rp-pri invoke-timeout-milliseconds terminating-domain sip-transport delivery-order charging-options mt-ps-enabled mt-cs-enabled mo-ps-enabled diameter-ro diameter-ro-release realm-choice choice single-realm destination-realm multiple-realms destination-realms list destination-realm charging-function-address peers list origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric cdr max-size-bytes max-cdrs max-interval-milliseconds registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled ue-reachability-notifications subscription-expiry-time-seconds correlation-ra-plmnid mcc mnc fallback-settings fallback-timer-milliseconds avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs list avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps list sccp-allowlist list routing-info-cassandra-ttl-seconds ussi reject-all-with-default-message language message debug-logging-enabled
IPSMGW configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../smo-virtual-machine-pool/sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled = 'true'.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../common depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
../home-network has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
Conditional node ../icscf depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
Conditional node ../hlr depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
Conditional node ../home-network depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
georedundancy
Geo-redundancy configuration.
- When present
-
Enables geo-redundancy for IPSMGW.
Container Structure
total-sites
The number of geo-redundant sites.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 2 to 32
template-smsc-address
The 'digits' parameter value in this template is replaced by the value of that parameter from the received SMSC address to create a return address to the SMSC.
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
originating-address
The SCCP address used as the calling party address in SS7 messages initiated by the IP-SM-GW.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
ipsmgw-as-msc-address
The ipsmgw-as-msc-address is the address that the IP-SM-GW will return to the GMSC during the SendRoutingInformation phase of the MT message procedure, so that subsequent messages will be delivered to the IP-SM-GW. TCAP messages with this address should be routeable to an IP-SM-GW node.
This node is mandatory.
Type ss7-address-string-type
- Description
-
The SS7 address string type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*address=.and matching.=.(,.=.)*
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address
Indicates if 'hlr/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR address, or have its digits replaced with the MSISDN of the subscriber.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
suppress-hlr-interaction
If true, no MAP messages will be sent to the HLR. Useful in LTE-only networks. Can only be set to true when 'delivery-order' is 'PS_ONLY'
This node is mandatory.
Data Validation Constraint
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
'suppress-hlr-interaction' can only be 'true' when 'delivery-order' is set to 'PS_ONLY' |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
use-gt-as-calling-party
When accepting an OpenRequest, the SCCP responder address in the OpenAccept will, by default, be set to the value of the SCCP called party in the OpenRequest. If UseGtAsCallingParty is set to true, and if the received sccp-called-party contains a global title, then the global title will be used.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
sms-content-size-threshold
If the length of the message content falls within the configured maximum then send the ForwardSM as part of the TC-BEGIN. As a special case a configured max size of 0 disables this functionality regardless of the actual content length.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
sri-sm-delivery-not-intended
If true, specify the SmDeliveryNotIntended flag when performing an SRI for SM IMSI-only query (i.e. during SMMA callflows).
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
discard-inform-sc
If true, discard outbound InformSC components from requests sent to the HLR.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
force-sm-rp-pri
If true, force Sm_RP_PRI to be set to true in SendRoutingInfoForSM requests sent to the HLR.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
invoke-timeout-milliseconds
Timeout (in milliseconds) when invoking MAP operations.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
4500
terminating-domain
Domain defined by the operator to compose SIP URIs from the MSISDN.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
sip-transport
The SIP transport to use for IPSMGW’s own SIP URI in outbound requests.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
TCP. |
|
UDP. |
- Default value
-
'udp'
delivery-order
The delivery order for mobile-terminating messages.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
../map-messaging/suppress-hlr-interaction has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../../delivery-order.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Try IMS network first, then circuit-switched network second. |
|
Try circuit-switched network first, then IMS network second. |
|
Only try delivery over the IMS network. |
|
Only try delivery over the circuit-switched network. |
charging-options
Message charging options.
Container Structure
mt-ps-enabled mt-cs-enabled mo-ps-enabled diameter-ro diameter-ro-release realm-choice choice single-realm destination-realm multiple-realms destination-realms list destination-realm charging-function-address peers list origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric cdr max-size-bytes max-cdrs max-interval-milliseconds registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled
mt-ps-enabled
Whether charging is enabled for mobile-terminating PS messages.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mt-ps-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
mt-cs-enabled
Whether charging is enabled for mobile-terminating CS messages.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mt-cs-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
mo-ps-enabled
Whether charging is enabled for mobile-originating PS messages.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mo-ps-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
diameter-ro
Diameter Ro configuration.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../mt-ps-enabled = 'true' or ../mt-cs-enabled = 'true' or ../mo-ps-enabled = 'true'.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../../smo-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-ipsmgw/charging-options/diameter-ro.
diameter-ro-release
The Diameter Ro release to use.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Release V8d0 |
|
Release V960 |
|
Release Va00 |
|
Release Vb80 |
|
Release Vcb0 |
- Default value
-
'Vcb0'
realm-choice choice
Whether to use a single realm or multiple realms.
A Choice between one of the following:
destination-realm
The Diameter destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-realms list
List of Diameter destination realms.
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
destination-realm domain-name charging-function-address string peers list string
The key is destination-realm.
destination-realm
The destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
charging-function-address
The value that must appear in a P-Charging-Function-Addresses header in order to select this destination realm. If omitted, this will be the same as the destination-realm value.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
peers list
List of Diameter peers for the realm.
Must contain at least 1 element.
Type List of string
- Values
-
a string
origin-realm
The Diameter origin realm.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-peers list
Diameter destination peer(s).
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
protocol-transport enumeration destination-hostname domain-name port port-number metric uint32
The key is destination-hostname.
protocol-transport
The combined Diameter protocol and transport.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over tcp |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp. IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported. |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are provisioned. |
- Default value
-
'aaa'
destination-hostname
The destination hostname.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
The destination port number.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3868
metric
The metric to use for this peer. Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric, traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
1
max-size-bytes
Approximate maximum size in bytes before a new CDR file is started. After a CDR is written, the total file size is compared to MaxSize. If the current file size is larger, it is completed. If set to 0, no size-based rollover is done.
Type uint64
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
100000000
max-cdrs
Number of records to be written to a CDR file before a new file is started. If set to 0, no record-based rollover is done.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
0
max-interval-milliseconds
The length of time (in milliseconds) before time-based file rollover. If a CDR file is used for more than max-interval-milliseconds without being rolled over due to record- or size-based limits, it is completed anyway. If set to 0, no time-based rollover is done.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0, 1000 or more
- Default value
-
0
registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled
'true' enables the creation of Registrar audit CDRs, 'false' disables.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
ue-reachability-notifications
Settings regarding UE reachability subscriptions.
- When present
-
Enables UE reachability notifications.
Container Structure
subscription-expiry-time-seconds
The UE reachability subscription expiry time (in seconds).
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
correlation-ra-plmnid
The PLMNID used by the correlation RA to generate MT correlation IMSIs when the routing info for the terminating subscriber cannot be determined. Must match one of the PLMNIDs defined in the home network configuration.
mnc
The Mobile Network Code (MNC).
This node is mandatory.
Type leafref
- Value
-
one of /home-network/home-plmn-ids[mcc = current()/../mcc/mncs]
fallback-timer-milliseconds
Timeout (in milliseconds) before attempting message delivery fallback.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
5000
avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs list
List of error codes which will prevent fallback from PS to CS.
Type List of uint32
- Values
-
a number in the range 0 or more
avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps list
List of error codes which will prevent fallback from CS to PS.
Type List of uint32
- Values
-
a number in the range 0 or more
sccp-allowlist list
List of allowed GT prefixes. If non-empty, then requests from any GT originating addresses not on the list will be rejected. If empty, then all requests will be allowed. Requests from non-GT addresses are always allowed.
Type List of string
- Values
-
a string
routing-info-cassandra-ttl-seconds
Timeout (in seconds) that routing info is stored in Cassandra.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
120
reject-all-with-default-message
Should all USSI messages be rejected with a default message.
- When present
-
Reject all USSI messages with a default message
language
The language that will be set in the USSI response message.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 2 matching
[a-zA-Z]*
message
The text that will be set in the USSI response message.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
infra
Context
The context of infra within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
node-type choice infra deployment-config:infra-virtual-machine-pool (in infra-vmpool-config.yaml) deployment-id site-id node-type-suffix virtual-machines list vm-id
Configure infrastructure node(s).
infra-virtual-machine-pool
The infrastructure node virtual machine pool.
This node and its descendants are configured in infra-vmpool-config.yaml.
Container Structure
deployment-id
The deployment identifier. Used to form a unique VM identifier within the VM host.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type deployment-id-type
- Description
-
Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and 20 characters in length, inclusive.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}
site-id
Site ID for the site that this VM pool is a part of.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type site-id-type
- Description
-
Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more digits 0-9.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
DC[0-9]+
node-type-suffix
Suffix to add to the node type when deriving the group identifier. Should normally be left blank.
| |
This value should never be changed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this value to take effect. |
Type node-type-suffix-type
- Description
-
Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a' through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9]* - Default value
-
''
virtual-machines list
Configured virtual machines.
| |
This list should not have entries added or removed for an existing live deployment. The deployment must be deleted and redeployed for a change to this list to take effect. |
snmp
SNMP configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in snmp-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Always.
Context
The context of snmp within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:snmp (in snmp-config.yaml) v1-enabled v2c-enabled v3-enabled trap_type community v3-authentication agent-details notifications sgc
v1-enabled
Enables the use of SNMPv1 if set to 'true'. Note that support for SNMPv1 is deprecated and SNMP v2c should be used instead. Use of v1 is limited to Rhino only and may cause some Rhino statistics to fail to appear correctly or not at all. Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv1.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
v2c-enabled
Enables the use of SNMPv2c if set to 'true'. Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv2c.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../agent-details depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../community depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/system-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/sgc-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../trap_type depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/rhino-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v2c-enabled.
Conditional node ../sgc/v2c-port depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v2c-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
v3-enabled
Enables the use of SNMPv3 if set to 'true'. Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv3.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../v3-authentication depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../v3-enabled.
Conditional node ../sgc/v3-port depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v3-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/rhino-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v3-enabled.
Conditional node ../agent-details depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../v3-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/sgc-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v3-enabled.
Conditional node ../notifications/system-notifications-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../v3-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
trap_type
Configure the notification type to use when SNMPv2c is enabled.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../v2c-enabled = 'true'.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Generate TRAP type notifications. |
|
Generate INFORM type notifications. |
- Default value
-
'trap'
community
The SNMPv2c community name.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../v2c-enabled = 'true'.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
- Default value
-
'clearwater'
v3-authentication
See v3-authentication for details of this node and its descendants.
agent-details
See agent-details for details of this node and its descendants.
notifications
See notifications for details of this node and its descendants.
sgc
See sgc for details of this node and its descendants.
v3-authentication
Context
The context of v3-authentication within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:snmp (in snmp-config.yaml) v3-authentication username authentication-protocol authentication-key privacy-protocol privacy-key
SNMPv3 authentication configuration. Only used when 'v3-enabled' is set to 'true'.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../v3-enabled = 'true'.
authentication-protocol
The authentication mechanism to use.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
SHA |
|
MD5 message digest. |
- Default value
-
'SHA'
authentication-key
The authentication key.
This node is mandatory.
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string with length 8 or more
privacy-protocol
The privacy mechanism to use.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Data Encryption Standard (DES) |
|
Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES). |
|
128 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). |
|
192 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). |
|
256 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). |
- Default value
-
'AES128'
agent-details
Context
The context of agent-details within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:snmp (in snmp-config.yaml) agent-details location contact
The configurable SNMP agent details. The VM ID is used as the agent’s name, and the human readable node description from the metadata is used as the description.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../v3-enabled = 'true'.
location
The physical location of the SNMP agent.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
notifications
Context
The context of notifications within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
Notification configuration.
Data Validation Constraints
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
You must specify whether to enable system notifications. If enabled, you must also specify at least one system notification target. |
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
You must specify whether to enable Rhino notifications. If enabled, you must also specify at least one Rhino notification target. |
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
You must specify whether to enable SGC notifications. If enabled, you must also specify at least one SGC notification target. |
system-notifications-enabled
Specifies whether or not system SNMP v2c/3 notifications are enabled. System notifications are: high memory and CPU usage warnings, and system boot notifications.
If you use MetaView Server to monitor your platform, then it is recommended to set this to 'false'.
This node is mandatory.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'.
Related Constraints
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as system-notifications-enabled.
Conditional node ../targets/send-system-notifications depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../system-notifications-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
rhino-notifications-enabled
Specifies whether or not Rhino SNMP v2c/3 notifications are enabled.
Applicable only when there is a Rhino node in your deployment and SNMPv2c and/or SNMPv3 are enabled.
This node is mandatory.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../targets/send-rhino-notifications depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../rhino-notifications-enabled.
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as rhino-notifications-enabled.
Conditional node ../categories depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../rhino-notifications-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
sgc-notifications-enabled
Specifies whether or not OCSS7 SGC SNMP v2c/3 notifications are enabled.
Applicable only when there is an SMO or an SGC node in your deployment and SNMPv2c and/or SNMPv3 are enabled.
This node is mandatory.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'.
Related Constraints
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as sgc-notifications-enabled.
Conditional node ../targets/send-sgc-notifications depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../sgc-notifications-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
targets list
The list of SNMP notification targets.
Note that you can specify targets even if not using Rhino or system notifications - the targets are also used for the disk and service monitor alerts.
List Structure
version enumeration host host port port-number send-rhino-notifications boolean send-system-notifications boolean send-sgc-notifications boolean
The keys are version and host and port.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as targets.
version
The SNMP notification version to use for this target.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
SNMPv1 |
|
SNMPv2c |
|
SNMPv3 |
host
The target host.
Type host
- Description
-
The host type represents either an IP address or a DNS domain name.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
- ip-address
-
The ip-address type represents an IPv4 address in dotted-quad notation or an IPv6 address in full, mixed, shortened, and shortened-mixed notation.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- or domain-name
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
port
The target port, normally 162.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
send-rhino-notifications
Specifies whether or not to send Rhino SNMP v2c/3 notifications to this target.
Can only be specified if ../rhino-notifications-enabled is true.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../rhino-notifications-enabled = 'true'.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
send-system-notifications
Specifies whether or not to send system SNMP v2c/3 notifications to this target.
Can only be specified if ../system-notifications-enabled is true.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../system-notifications-enabled = 'true'.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
send-sgc-notifications
Specifies whether or not to send SGC SNMP v2c/3 notifications to this target.
Can only be specified if ../sgc-notifications-enabled is true.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../sgc-notifications-enabled = 'true'.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
categories list
Rhino notification categories to enable or disable.
Conditional
This list is only valid when ../rhino-notifications-enabled = 'true'.
category
Notification category.
If you are using MetaView Server, only the alarm-notification category of Rhino SNMP notifications is supported. Therefore, all other notification categories should be disabled.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Alarm related notifications. |
|
Log related notifications. |
|
Log rollover notifications. |
|
Resource adaptor entity state change notifications. |
|
Service state change notifications. |
|
SLEE state change notifications. |
|
Trace notifications. |
|
Usage notifications. |
sgc
Context
The context of sgc within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:snmp (in snmp-config.yaml) sgc v2c-port v3-port
SGC-specific SNMP configuration.
v2c-port
The port to bind to for v2c SNMP requests.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../v2c-enabled = 'true'.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
11100
v3-port
The port to bind to for v3 SNMP requests.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../v3-enabled = 'true'.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
11101
sgc
OCSS7 SGC configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in sgc-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on SMO and SGC nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sgc-virtual-machine-pool or ../smo-virtual-machine-pool.
Context
The context of sgc within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) hazelcast sgcenv sgc-properties m3ua remote global-title outbound matchers translations list rewriters list
hazelcast
See hazelcast for details of this node and its descendants.
sgcenv
See sgcenv for details of this node and its descendants.
sgc-properties
See sgc-properties for details of this node and its descendants.
m3ua
See m3ua for details of this node and its descendants.
hazelcast
Context
The context of hazelcast within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) hazelcast backup-count password
Cluster-wide Hazelcast configuration.
backup-count
Hazelcast 'backup-count' parameter.
Leave unset to automatically derive this value from the number of VMs deployed. This is recommended to prevent data loss.
If it must be set, set the variable to 'number of nodes - 1' to avoid data loss.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 6
password
The optional Hazelcast cluster password.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type secret
- Description
-
A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).
- Value
-
a string
sgcenv
Context
The context of sgcenv within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) sgcenv jmx-port
Values to be placed in the sgcenv configuration file.
jmx-port
The port to bind to for JMX service, used by the CLI and MXBeans.
The SGC’s jmx-host will be set to localhost
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
10111
sgc-properties
Context
The context of sgc-properties within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) sgc-properties properties list name value
Values to be placed in the SGC.properties configuration file.
- When present
-
This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.
properties list
List of name,value property pairs.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
name
Property name.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
m3ua
M3UA configuration.
local-port
The port to bind for this local M3UA endpoint.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
2905
per-node-local-port list
Allows the 'local-port' to be overridden on a per-node basis. Only required for deployments where each SGC cluster member needs to have its local M3UA endpoint listen on a different port to the other members.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
node-index
The index of the node within the cluster. '1' is the first node, '2' is the second, and so on.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type int16
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 or more
local-port
The port to bind for this node’s local M3UA endpoint.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
point-code
This SGC cluster’s signaling point code.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type ss7-point-code-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SS7 point code. When ANSI variant is in use, specify this in network-cluster-member format, such as 1-2-3, where each element is between 0 and 255. When ITU variant is in use, specify this as an integer between 0 and 16383. Note that for ITU you will need to quote the integer, as this field takes a string rather than an integer.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(([0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9]-){2}[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9])|([0-1]?[0-9]{1,4})
sccp-variant
The SCCP variant to configure this SGC to use.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
ITU-T SCCP |
|
ANSI SCCP |
- Default value
-
'ITU'
national
The value of the 'national indicator' SCCP address indicator bit for SCMG messages sent by this node.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Uses the SCCP variant to determine the best |
|
Set the |
|
Set the |
- Default value
-
'AUTO'
network-indicator
The value of the 'network indicator' field in M3UA messages generated by this cluster.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Set the M3UA 'network indicator' field to the value |
|
Set the M3UA 'network indicator' field to the value |
|
Set the M3UA 'network indicator' field to the value |
|
Set the M3UA 'network indicator' field to the value |
- Default value
-
'INTERNATIONAL'
remote
See remote for details of this node and its descendants.
global-title
See global-title for details of this node and its descendants.
remote
Context
The context of remote within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua remote peers list id remote-ips list node-index ips list port state-maintenance-role conn-type is-ipsp asp-id application-servers list as-id daud-on-asp-ac application-servers list id traffic-maintenance-role routing-context routes default-priority dpc-ids list id priority precond-ssns list dpcs list id dpc network-appearance muss mss pudt cpcs list dpc ssns list
Remote M3UA configuration.
peers list
Connection configuration.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
List Structure
id string remote-ips list node-index int16 ips list ipv4-address-no-zone port port-number state-maintenance-role enumeration conn-type enumeration is-ipsp boolean asp-id uint32 application-servers list as-id string daud-on-asp-ac boolean
The key is id.
id
Unique connection identifier.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
remote-ips list
Remote IP configuration to connect this SGC cluster to this remote peer.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
node-index
The index of the SMO node that hosts the SGC that will be connected to this IP set. '1' is the first SMO node, '2' is the second, and so on. '-1' indicates that all SGC nodes in the cluster will use this remote IP set.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type int16
- Value
-
a number in the range -1, 1 or more
ips list
The remote IP address(es) that belong to this IP set.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
Type List of ipv4-address-no-zone
- Description
-
An IPv4 address without a zone index.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Values
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9\.]*
port
The remote port for this M3UA association.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
2905
state-maintenance-role
The role to perform in M3UA state maintenance.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The SGC takes an active role in M3UA state maintenance. |
|
The SGC takes a passive role in M3UA state maintenance. |
- Default value
-
'active'
conn-type
The connection type to establish: client or server.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The SGC connects to the remote peer. |
|
The SGC waits for a connection from the remote peer. |
- Default value
-
'client'
is-ipsp
true if the SGC is an IPSP, otherwise false.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
asp-id
The ASP identifier to use in ASP-UP/DOWN messages.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
application-servers list
The application servers to which this connection belongs.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
as-id
The AS to which this connection belongs, as identified by that application server’s id field.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
daud-on-asp-ac
Send DAUD when the ASP goes ACTIVE in this AS.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
application-servers list
Application server configuration.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
List Structure
id string traffic-maintenance-role enumeration routing-context uint32 routes default-priority uint8 dpc-ids list id string priority uint8 precond-ssns list uint8
The key is id.
id
Uniquely identifies this list entry.
Not referred to anywhere else in the configuration. Any unique value is permitted.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
traffic-maintenance-role
The traffic-maintenance role to assume in this application server.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Assume an active traffic-maintenance role. |
|
Assume a passive traffic-maintenance role. |
- Default value
-
'active'
routing-context
The routing context of this application server. No value specified means null.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
default-priority
The default priority to apply to any routes in this application server where a specific priority has not been configured.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
dpc-ids list
A list of DPCs that may be accessible from this application server.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
id
The DPC identifier applicable to this route.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
priority
This DPC’s priority. Overrides any value configured in ../default-priority
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
precond-ssns list
This application server will not become active until there is at least one connected TCAP stack for each SSN specified here.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type List of uint8
- Values
-
a number in the range 0 or more
dpcs list
Configured DPCs.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
id
An identifier used to reference this DPC from an application server’s routing configuration.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
dpc
The destination point code.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type ss7-point-code-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SS7 point code. When ANSI variant is in use, specify this in network-cluster-member format, such as 1-2-3, where each element is between 0 and 255. When ITU variant is in use, specify this as an integer between 0 and 16383. Note that for ITU you will need to quote the integer, as this field takes a string rather than an integer.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(([0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9]-){2}[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9])|([0-1]?[0-9]{1,4})
network-appearance
The network appearance.
Absent means null. 0 and null have different meanings in the network.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
muss
The MUSS.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
mss
The MSS.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
pudt
The preferred unitdata message type.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use UDT messages where possible. |
|
Use XUDT messages even if the data would fit within a UDT message. |
- Default value
-
'UDT'
cpcs list
Notify the specified destination point code if the local SSN status changes.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
dpc
The destination point code to inform if the monitored SSN changes state.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type ss7-point-code-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SS7 point code. When ANSI variant is in use, specify this in network-cluster-member format, such as 1-2-3, where each element is between 0 and 255. When ITU variant is in use, specify this as an integer between 0 and 16383. Note that for ITU you will need to quote the integer, as this field takes a string rather than an integer.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(([0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9]-){2}[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9])|([0-1]?[0-9]{1,4})
global-title
Global title configuration.
Context
The context of global-title within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua global-title inbound list id addrinfo is-prefix natofaddr numplan ssn trtype outbound matchers translations list rewriters list
inbound list
The set of inbound global title translations to apply.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
id
Uniquely identifies this list entry.
Not referred to anywhere else in the configuration. Any unique value is permitted.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
addrinfo
The address information to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
is-prefix
true if the addrinfo should be considered a prefix. false if the addrinfo must be an exact match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
natofaddr
The nature of address to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
numplan
The numbering plan to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
ssn
The local Sub-System Number (SSN) to route matches towards.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
trtype
The translation type to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
outbound
See outbound for details of this node and its descendants.
outbound
Outbound global title configuration.
Context
The context of outbound within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua global-title outbound matchers translations list rewriters list
matchers
See matchers for details of this node and its descendants.
translations list
See translations list for details of this node and its descendants.
rewriters list
See rewriters list for details of this node and its descendants.
matchers
Context
The context of matchers within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua global-title outbound matchers defaults natofaddr numplan trtype rules list id use-defaults addrinfo is-prefix natofaddr numplan trtype translations list
Outbound global title matchers.
defaults
Default values to apply to matchers if use-default is set to True or is unset in an individual matcher.
natofaddr
The nature of address to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
numplan
The numbering plan to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
trtype
The translation type to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
rules list
List of outbound global title matchers to configure.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
List Structure
id string use-defaults boolean addrinfo string is-prefix boolean natofaddr uint8 numplan uint8 trtype uint8 translations list string
The key is id.
id
Uniquely identifies this list entry. Not referred to anywhere else in the configuration. Any unique value is permitted.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
use-defaults
If set to true (or unset) use any defaults in the ../defaults section when creating matchers. If set to false then only the values specified here will be used.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
addrinfo
The address information to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
is-prefix
true if the ‘addrinfo’ should be considered a prefix. false if the ‘addrinfo’ must be an exact match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
natofaddr
The nature of address to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
numplan
The numbering plan to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
trtype
The translation type to match.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
translations list
Context
The context of translations list within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua global-title outbound translations list id dpc prefer-local priority rewriter-id
The set of outbound global title translations available to matchers.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
id string dpc ss7-point-code-type prefer-local boolean priority uint16 rewriter-id string
The key is id.
id
The unique identifier of this translation. Referred to by one or more outbound matchers.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
dpc
The destination point code to route matching messages to.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type ss7-point-code-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SS7 point code. When ANSI variant is in use, specify this in network-cluster-member format, such as 1-2-3, where each element is between 0 and 255. When ITU variant is in use, specify this as an integer between 0 and 16383. Note that for ITU you will need to quote the integer, as this field takes a string rather than an integer.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(([0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9]-){2}[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9])|([0-1]?[0-9]{1,4})
prefer-local
true if routes local to this SGC node are preferred over routes via other SGC cluster members, otherwise false
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
priority
The translation priority.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint16
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
rewriters list
Context
The context of rewriters list within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sgc (in sgc-config.yaml) m3ua global-title outbound rewriters list id addrinfo gtencoding gti natofaddr numplan route-on ssn trtype
The rules specifying which SCCP address parameters to alter when this replace-gt rule is activated.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
id
Identifier used to reference this replace-gt rule in outbound and inbound translations.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
addrinfo
The replacement address digits.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type string
- Value
-
a string
gtencoding
The replacement GT encoding.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
gti
The replacement global title indicator.
ITU-T SCCP valid values: 1-4.
ANSI SCCP valid values: 1-2.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
natofaddr
The replacement nature of address.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
numplan
The replacement numbering plan.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
route-on
The action to perform on the routing indicator when this replace-gt rule is activated.
| |
See 'Reconfiguring the SGC' in 'Rhino VoLTE TAS Configuration and Management Guide' for how to activate changes to this value. |
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Set to route on Sub-System Number (SSN). |
|
Set to route on Global Title (GT). |
|
Leave the routing indicator unchanged. |
routing
Context
The context of routing within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:routing (in routing-config.yaml) routing-rules list name target interface gateway node-types list
Routing configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in routing-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Always.
routing-rules list
The list of routing rules.
List Structure
name string target union interface traffic-type gateway ip-address node-types list enumeration
The key is name.
The values of target must be unique.
target
The target for the routing rule. Can be either an IP address or a block of IP addresses.
This node is mandatory.
Type union
- Value
-
- ip-address
-
The ip-address type represents an IPv4 address in dotted-quad notation or an IPv6 address in full, mixed, shortened, and shortened-mixed notation.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- or ip-prefix
-
The ip-prefix type represents an IPv4 prefix (eg 192.168.0.0/24) or an IPv6 prefix similarly.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
interface
The interface to use to connect to the specified endpoint. This must be one of the allowed traffic types, corresponding to the interface carrying the traffic type.
This node is mandatory.
Type traffic-type
- Description
-
The name of the traffic type.
- Value
-
- signaling-traffic-type
-
The name of the signaling traffic type.
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Internal signaling traffic. |
|
Diameter signaling traffic. |
|
SS7 signaling traffic. |
|
SIP signaling traffic. |
|
HTTP signaling traffic. |
|
Applies to custom VMs only. Custom signaling traffic. |
|
Applies to custom VMs only. Second custom signaling traffic. |
- or multihoming-signaling-traffic-type
-
The name of the multihoming signaling traffic type.
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Second Diameter signaling traffic. |
|
Second SS7 signaling traffic. |
- or enumeration
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Management traffic. |
|
Cluster traffic. |
|
Access traffic. |
gateway
The IP address of the gateway to route through.
This node is mandatory.
Type ip-address
- Description
-
The ip-address type represents an IPv4 address in dotted-quad notation or an IPv6 address in full, mixed, shortened, and shortened-mixed notation.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
node-types list
The node-types this routing rule applies to.
Type List of enumeration
- Values
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Apply this routing rule to the shcm nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the mag nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the mmt-gsm nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the mmt-cdma nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the smo nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the tsn nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the max nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the rem nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the sgc nodes. |
|
Apply this routing rule to the custom nodes. |
custom-data
Context
The context of custom-data within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:custom-data (in custom-config-data.yaml) custom-config
Custom configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in custom-config-data.yaml.
- When present
-
Always.
common
Context
The context of common within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:common (in common-config.yaml) platform-operator-name
Common configuration. Used on MAG, MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, ShCM, and MAX nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in common-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MAG, MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, ShCM, and MAX nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sentinel-volte or ../sentinel-ipsmgw or ../naf-filter or ../shcm-service or ../max-service.
home-network
Context
The context of home-network within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:home-network (in home-network-config.yaml) home-domain home-network-country-dialing-code home-network-iso-country-code home-plmn-ids list mcc mncs list
Home network configuration. Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in home-network-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sentinel-volte or ../sentinel-ipsmgw or ../naf-filter.
Data Validation Constraint
|
Validation Error: |
'home-domain' must be specified for MMT configuration. |
home-domain
Identifier for the home network.
Should match the value in the SIP: p-visited-network-id header inserted by the S-CSCF or P-CSCF.
Used for determining whether a call is roaming or not.
- Reference
-
RFC 3455 section 4.3
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as home-domain.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[a-zA-Z0-9@.:_/-]+
home-network-country-dialing-code
The home network country dialing code.
This node is mandatory.
Type number-string
- Description
-
A type that permits a non-negative integer value.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 4
home-network-iso-country-code
The home network ISO country code.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 2 matching
[A-Z]*
mcc
The Mobile Country Code (MCC).
This node is mandatory.
Type number-string
- Description
-
A type that permits a non-negative integer value.
- Value
-
a string with length 3
hlr
Context
The context of hlr within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:hlr (in hlr-config.yaml) hlr-address
Home Location Register configuration. Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in hlr-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sentinel-volte or ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
hlr-address
The HLR SCCP address. This is typically in the form of a Global Title
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
icscf
Context
The context of icscf within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:icscf (in icscf-config.yaml) i-cscf-uri
Interrogating Call Service Control Function configuration. Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in icscf-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and SMO nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sentinel-volte or ../sentinel-ipsmgw.
i-cscf-uri
The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF).
For MMT, the Conf and ECT features will automatically add an 'lr' parameter to it. The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the I-CSCF.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-uri-type
- Description
-
The SIP URI type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.*
number-analysis
Number analysis configuration. Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and MAG nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in number-analysis-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MMT GSM, MMT CDMA, and MAG nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../sentinel-volte or ../naf-filter.
Context
The context of number-analysis within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:number-analysis (in number-analysis-config.yaml) normalization non-provisionable-uris list assume-sip-uris-are-phone-numbers
normalization
See normalization for details of this node and its descendants.
non-provisionable-uris list
List of URIs that cannot be provisioned.
Type List of union
- Values
-
- sip-or-tel-uri-type
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
- or phone-number-type
-
A type that represents a phone number.
a string with length 0 or more matching
+?[*0-9]+
normalization
Context
The context of normalization within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:number-analysis (in number-analysis-config.yaml) normalization international-prefix min-normalizable-length national-prefix network-dialing-code normalize-to
Normalization configuration.
international-prefix
The international prefix. 1 to 5 digits in length.
This node is mandatory.
Type dialing-code-type
- Description
-
A type that represents a dialing code.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 5
min-normalizable-length
The minimum normalizable length.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 31
national-prefix
The national prefix. 1 to 5 digits in length.
This node is mandatory.
Type dialing-code-type
- Description
-
A type that represents a dialing code.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 5
network-dialing-code
The network dialing code. 1 to 3 digits in length.
This node is mandatory.
Type dialing-code-type
- Description
-
A type that represents a dialing code.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 3
normalize-to
The format to normalize to when comparing numbers, sending outgoing requests and checking whether numbers are normalizable.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Normalize to international format. |
|
Normalize to national format. |
- Default value
-
'international'
sas
Context
The context of sas within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sas (in sas-config.yaml) enabled sas-connection system-type system-version servers list
SAS configuration.
This node and its descendants are configured in sas-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Always.
Data Validation Constraint
enabled
'true' enables the use of SAS, 'false' disables.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../sas-connection depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
sas-connection
Configuration for connecting to SAS.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../enabled = 'true'.
Container Structure
system-type
The SAS system type. Only valid for custom nodes. Defaults to the image name if not specified.
Related Constraint
../.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as sas-connection/system-type.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 255 matching
[a-zA-Z0-9.\-_@:"', ]+
system-version
The SAS system version. Defaults to the VM version if not specified.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
sentinel-volte
Sentinel VoLTE configuration. Used on MMT GSM and MMT CDMA nodes.
This node and its descendants are configured in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml or sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Used on MMT GSM and MMT CDMA nodes.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool or ../mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool.
Context
The context of sentinel-volte within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) session-replication-enabled scc service-centralisation simple-imrn-pool scc-gsm-service-centralisation scc-cdma-service-centralisation tads mmtel announcement hss-queries-enabled conferencing international-and-roaming north-american-numbering-plan-analysis international-call-management call-diversion mmtel-call-diversion forward-to-voicemail announcement communication-hold communication-waiting privacy psap-callback communication-barring incoming-communication-barring outgoing-communication-barring operator-communication-barring operator-barring-rules outgoing-prefix-barring vertical-service-codes registrar sis hlr-connectivity-origin charging session-refresh debug-logging-enabled
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../icscf depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
Conditional node ../home-network depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
Conditional node ../hlr depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
Conditional node ../common depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
Conditional node ../number-analysis depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
../home-network has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../sentinel-volte.
session-replication-enabled
When enabled, SIP dialogs and charging sessions can be failed over to other cluster nodes if the original node fails.
Set to 'true' to enable session replication. Set to 'false' to disable.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
scc
See scc for details of this node and its descendants.
mmtel
See mmtel for details of this node and its descendants.
registrar
See registrar for details of this node and its descendants.
sis
See sis for details of this node and its descendants.
hlr-connectivity-origin
See hlr-connectivity-origin for details of this node and its descendants.
charging
See charging for details of this node and its descendants.
session-refresh
See session-refresh for details of this node and its descendants.
scc
SCC configuration.
Context
The context of scc within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc scc-mobile-core-type fetch-cmsisdn-source udr-included-identities service-continuity atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds stn-sr service-centralisation simple-imrn-pool scc-gsm-service-centralisation scc-cdma-service-centralisation tads
Data Validation Constraint
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
When |
scc-mobile-core-type
The SCC mobile core type: 'GSM' or 'CDMA'.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../../hlr-connectivity-origin/cdma depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../tads/sri-requests-to-hlr depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../../charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
../tads/address-source-for-scc-tads has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../../scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../../mmtel/determine-roaming-from-hlr depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../service-centralisation/scc-gsm-service-centralisation depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../../registrar/data-storage-type depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
Conditional node ../../hlr-connectivity-origin/gsm depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
GSM |
|
CDMA |
fetch-cmsisdn-source
The fetch Correlation Mobile Station ISDN (CMS-ISDN) source. If set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN', udr-included-identities MUST be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as fetch-cmsisdn-source.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
MS-ISDN |
|
Extended MS-ISDN |
- Default value
-
'MSISDN'
udr-included-identities
Defines which IMS user identities to include in outgoing user data requests. Can be either 'IMPU' or 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'. Must be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI' if fetch-cmsisdn-source is set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as udr-included-identities.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
IMPU |
|
IMPU_AND_IMPI |
atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds
The Access Transfer Control Function (ATCF) update timeout
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
2000
stn-sr
The Session Transfer Number for SRVCC (STN-SR).
This node is mandatory.
Type number-string
- Description
-
A type that permits a non-negative integer value.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9]+
service-centralisation
See service-centralisation for details of this node and its descendants.
tads
See tads for details of this node and its descendants.
service-centralisation
SCC Service Centralisation Configuration.
Context
The context of service-centralisation within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc service-centralisation inbound-ss7-address use-direct-icscf-routing generated-pvni-template police-originating-requests simple-imrn-pool scc-gsm-service-centralisation scc-cdma-service-centralisation
inbound-ss7-address
The originating SCCP address.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
use-direct-icscf-routing
If 'true', the configured I-CSCF URI will be added to the route header of the reoriginated INVITE. If 'false', the HSS will be queried for the S-CSCF URI to use for the subscriber.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
generated-pvni-template
A template string for the P-Visited-Network-Information header generated in the reorigination, where {mnc} and {mcc} are replaced with the MNC and MCC respectively.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
police-originating-requests
Police incoming originating requests, and reject attempts to hijack the call.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
simple-imrn-pool
See simple-imrn-pool for details of this node and its descendants.
scc-gsm-service-centralisation
See scc-gsm-service-centralisation for details of this node and its descendants.
scc-cdma-service-centralisation
See scc-cdma-service-centralisation for details of this node and its descendants.
simple-imrn-pool
Context
The context of simple-imrn-pool within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc service-centralisation simple-imrn-pool minimum-correlation-id maximum-correlation-id number-of-digits-in-correlation-id
Simple IMRN pool config for mainline case.
Data Validation Constraint
|
Validation Error: |
When configuring simple-imrn-pool config, minimum-correlation-id must be less than maximum-correlation-id. |
minimum-correlation-id
The minimum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to maximum-correlation-id.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as minimum-correlation-id.
Type uint64
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 999999999999999999
maximum-correlation-id
The maximum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to (10^18-1).
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as maximum-correlation-id.
Type uint64
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 999999999999999999
scc-gsm-service-centralisation
Context
The context of scc-gsm-service-centralisation within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc service-centralisation scc-gsm-service-centralisation gsm-imrn-formation routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed nature numbering-plan bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming
SCC GSM Service Centralisation Configuration.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-gsm-service-centralisation/gsm-imrn-formation/routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed
If set to 'true', routing to an internal network number is allowed.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
nature
The type of call. Used when forwarding a call.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Subscriber |
|
Unknown |
|
National |
|
International |
|
Network specific |
|
Network routing national |
|
Network routing network specific |
|
Network routing with call directory |
numbering-plan
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-gsm-service-centralisation/gsm-imrn-formation/numbering-plan
The numbering plan to be used when forwarding a call.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Spare 0 |
|
ISDN |
|
Spare 2 |
|
Data |
|
Telex |
|
National 5 |
|
National 6 |
|
Spare 7 |
bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-gsm-service-centralisation/bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered
If true, reorigination is skipped if the subscriber is not registered in the IMS network.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-gsm-service-centralisation/always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming
If true, roaming terminating sessions will always be reoriginated (regardless of IMS registration).
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
scc-cdma-service-centralisation
Context
The context of scc-cdma-service-centralisation within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc service-centralisation scc-cdma-service-centralisation scc-cdma-actions action-on-unsupported-trigger action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number default-failure-action cdma-imrn-formation imrn-type-of-digits imrn-nature-of-number imrn-numbering-plan bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered
SCC CDMA Service Centralisation Configuration.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'.
action-on-unsupported-trigger
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/scc-cdma-actions/action-on-unsupported-trigger
Action to take when an unexpected trigger is received.
This node is mandatory.
Type action
- Description
-
SCC CDMA actions
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Access Denied - Not Used |
|
Access Denied - Unassigned Directory Number |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Inactive |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Busy |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Termination Denied |
|
Access Denied, Reason - No Page Response |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Unavailable |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By MS |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By The System |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Type Mismatch |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Denied |
|
Allow Call To Continue |
action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/scc-cdma-actions/action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number
Action to take when there is a failure generating a routing number.
This node is mandatory.
Type action
- Description
-
SCC CDMA actions
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Access Denied - Not Used |
|
Access Denied - Unassigned Directory Number |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Inactive |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Busy |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Termination Denied |
|
Access Denied, Reason - No Page Response |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Unavailable |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By MS |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By The System |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Type Mismatch |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Denied |
|
Allow Call To Continue |
default-failure-action
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/scc-cdma-actions/default-failure-action
Default action to take on error.
This node is mandatory.
Type action
- Description
-
SCC CDMA actions
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Access Denied - Not Used |
|
Access Denied - Unassigned Directory Number |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Inactive |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Busy |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Termination Denied |
|
Access Denied, Reason - No Page Response |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Unavailable |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By MS |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By The System |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Type Mismatch |
|
Access Denied, Reason - Service Denied |
|
Allow Call To Continue |
imrn-type-of-digits
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/cdma-imrn-formation/imrn-type-of-digits
The type of digits used in the generated IMRN.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Dialed Number or Called Party Number |
|
Calling Party Number |
|
Caller Interaction |
|
Routing Number |
|
Billing Number |
|
Destination Number |
|
LATA |
|
Carrier Number |
imrn-nature-of-number
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/cdma-imrn-formation/imrn-nature-of-number
The nature field of the IMRN generated.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
National |
|
International |
imrn-numbering-plan
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/cdma-imrn-formation/imrn-numbering-plan
The numbering plan field of the IMRN generated.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Unknown Numbering Plan |
|
ISDN Numbering |
|
Telephony Numbering (ITU-T E.164, E.163) |
|
Data Numbering (ITU-T X.121) |
|
Telex Numbering (ITU-T F.69) |
|
Maritime Mobile Numbering |
|
Land Mobile Numbering (ITU-T E.212) |
|
Private Numbering Plan (service provider defined) |
|
SS7 Point Code and Subsystem Number |
|
Internet Protocol Address |
bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered
/sentinel-volte/scc/service-centralisation/scc-cdma-service-centralisation/bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered
If true, reorigination is skipped if the subscriber is not registered in the IMS network.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
tads
Context
The context of tads within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) scc tads csrn-prefix address-source-for-scc-tads voice-over-ps-support request-user-identity-type wlan-allowed tads-identity-for-terminating-device end-session-error-code cs-routing-via-icscf on-sequential-routing tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds ps-fallback-response-codes list on-parallel-routing parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds release-all-legs-on-busy sri-requests-to-hlr set-suppress-tcsi-flag set-suppress-announcement-flag suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion use-diversion-counter-parameter cs-domain-diversion-limit
TADS configuration.
address-source-for-scc-tads
Which value should be used for routing TADS requests to. Valid values are 'CMSISDN', 'MSRN' (GSM only), and 'TLDN' (CDMA only)
This node is mandatory.
Data Validation Constraints
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
'address-source-for-scc-tads' cannot be set to 'MSRN' when 'scc-mobile-core-type' is set to 'cmda'. |
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
'address-source-for-scc-tads' cannot be set to 'TLDN' when’scc-mobile-core-type' is set to 'gsm' |
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../../hlr-connectivity-origin depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../scc/tads/address-source-for-scc-tads.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use the Correlation Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number (CMSISDN) for SCC TADS. |
|
Use the Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) for SCC TADS. Only valid when the scc-mobile-core-type is 'gsm'. |
|
Use the Temporary Local Directory Number (TLDN) for SCC TADS. Only valid when the scc-mobile-core-type is 'cdma'. |
voice-over-ps-support
Configuration for voice over PS support.
- When present
-
Indicates that voice over PS support is required.
Container Structure
request-user-identity-type
The user identity type to use in requests.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The IMS Public ID user identity type. |
|
The MS-ISDN user identity type. |
|
The IMPU IMPI user identity type. |
|
The MS-ISDN IMPI user identity type. |
wlan-allowed
Set to 'true' if W-LAN is allowed. Set to 'false' to disallow.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
tads-identity-for-terminating-device
The identity of the terminating device that TADS will send the request to.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Send TADS requests to the IMS public identity of the terminating device |
|
Send TADS requests to the 'sip.instance' of the terminating device |
|
Send TADS requests to the 'path' header within the 'sip.instance' of the terminating device |
- Default value
-
'IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY'
end-session-error-code
The SIP response code that is returned when a session is ended due to an error.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 400 to 699
- Default value
-
480
cs-routing-via-icscf
When enabled INVITE requests destined for the CS network will be sent directly via the I-CSCF, bypassing the S-CSCF.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds
Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a potentially better forked response.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 500 to 5000
ps-fallback-response-codes list
List of SIP response codes that will trigger attempts of more routes after a PS attempt.
Type List of sip-status-code
- Description
-
SIP response status code type.
- Values
-
a number in the range 400 to 699
parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds
Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a final response.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 30000
release-all-legs-on-busy
When enabled TADS will end all parallel forks on the first busy response (486).
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
sri-requests-to-hlr
Configuration for SRI requests sent to the HLR
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
Container Structure
set-suppress-tcsi-flag
If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR the feature will set the suppress T-CSI flag on the request
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
set-suppress-announcement-flag
If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR on a terminating call the feature will set the 'Suppression of Announcement' flag on the request.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion
When present, requests destined to the CS domain will contain a Diversion header to suppress call diversion in the CS domain side of the call.
- When present
-
Suppress call diversion in CS domain
Container Structure
use-diversion-counter-parameter
When true, use diversion counter parameter, otherwise use number of headers.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
mmtel
Configuration for MMTel services.
Context
The context of mmtel within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel announcement hss-queries-enabled determine-roaming-from-hlr conferencing international-and-roaming north-american-numbering-plan-analysis international-call-management call-diversion mmtel-call-diversion forward-to-voicemail announcement communication-hold communication-waiting privacy psap-callback communication-barring incoming-communication-barring outgoing-communication-barring operator-communication-barring operator-barring-rules outgoing-prefix-barring vertical-service-codes
announcement
See announcement for details of this node and its descendants.
hss-queries-enabled
See hss-queries-enabled for details of this node and its descendants.
determine-roaming-from-hlr
Determines whether location information from the GSM HLR should be used to determine the roaming status of the subscriber.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../hlr-connectivity-origin depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../mmtel/determine-roaming-from-hlr.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
conferencing
See conferencing for details of this node and its descendants.
international-and-roaming
See international-and-roaming for details of this node and its descendants.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis
See north-american-numbering-plan-analysis for details of this node and its descendants.
international-call-management
See international-call-management for details of this node and its descendants.
call-diversion
See call-diversion for details of this node and its descendants.
communication-hold
See communication-hold for details of this node and its descendants.
communication-waiting
See communication-waiting for details of this node and its descendants.
privacy
See privacy for details of this node and its descendants.
psap-callback
See psap-callback for details of this node and its descendants.
communication-barring
See communication-barring for details of this node and its descendants.
vertical-service-codes
See vertical-service-codes for details of this node and its descendants.
announcement
Context
The context of announcement within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel announcement announcements-media-server-uri announcements-no-response-timeout-milliseconds announcements list id description announcement-url delay-milliseconds duration-milliseconds repeat mimetype interruptable suspend-charging end-session-on-failure enforce-one-way-media locale default-error-code-announcement announcement-id end-call-with-487-response error-code-announcements list error-code disable-announcement announcement-id end-call-with-487-response
Configuration for SIP announcements.
announcements-media-server-uri
The URI of the media server used to play announcements.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
announcements-no-response-timeout-milliseconds
The maximum time to wait (in milliseconds) for the media server to respond before cancelling an announcement.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 or more
- Default value
-
1000
announcements list
A list containing the configuration for each announcement that the system can play.
List Structure
id uint32 description string announcement-url string delay-milliseconds uint32 duration-milliseconds uint32 repeat int32 mimetype string interruptable boolean suspend-charging boolean end-session-on-failure boolean enforce-one-way-media boolean locale string
The key is id.
Data Validation Constraint
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
'interruptable' must be set to 'true' if 'repeat' is set to '-1'. |
id
The ID for this announcement.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 or more
announcement-url
The file URL of this announcement on the media server.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
delay-milliseconds
The delay interval (in milliseconds) between repetitions of this announcement.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
duration-milliseconds
The maximum duration (in milliseconds) of this announcement.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
repeat
How many times the media server should repeat this announcement. A value of -1 will cause the announcement to repeat continuously until it is interrupted.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as repeat.
Type int32
- Value
-
a number in the range -1 or more
mimetype
The MIME content type for this announcement, e.g audio/basic, audio/G729, audio/mpeg, video/mpeg.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
interruptable
Determines whether this announcement can be interrupted. This only applies to announcements played after the call is established.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as interruptable.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
suspend-charging
Determines whether online charging should be suspended while this announcement is in progress. This only applies to announcements played after the call is established.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
end-session-on-failure
Determines whether the session should be terminated if this announcement fails to play. This only applies to announcements played during call setup.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
enforce-one-way-media
Determines whether to enforce one-way media from the media server to the party hearing the announcement. This only applies to announcements played after the call is established.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
default-error-code-announcement
Configuration for the default announcement that is played when an error response is received during call setup.
- When present
-
Enable default error code announcement
Container Structure
announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to be played to the calling party when an error response is received during call setup.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
end-call-with-487-response
Determines whether the call should be ended with a 487 error code rather than the error code that triggered the announcement.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
error-code-announcements list
A list containing configuration for assigning specific announcements for specific SIP error response codes received during call setup.
List Structure
error-code uint16 disable-announcement boolean announcement-id announcement-id-type end-call-with-487-response boolean
The key is error-code.
error-code
The SIP error response code that this entry applies to.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint16
- Value
-
a number in the range 400 to 699
disable-announcement
If set to 'true', no announcement will be played for this error code, overriding any default error code announcement that has been set.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../announcement-id depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../disable-announcement.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement-id
ID of the announcement to play when this error code is received.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../disable-announcement = 'false'.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
hss-queries-enabled
Context
The context of hss-queries-enabled within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel hss-queries-enabled odb metaswitch-tas-services
Configuration for enabling optional queries for certain types of subscriber data in the HSS.
odb
Determines whether the HSS will be queried for operator determined barring (ODB) subscriber data.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../hss-queries-enabled/odb.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
conferencing
Context
The context of conferencing within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel conferencing conference-mrf-uri route-to-mrf-via-ims msml-vendor enable-scc-conf-handling root-on-selector conference-factory-psi-aliases list maximum-participants allow-video-conference-calls conference-view-removal-delay-milliseconds subscription default-subscription-expiry-seconds min-subscription-expiry-seconds polling-interval-seconds
Configuration for the MMTel conferencing service.
conference-mrf-uri
The URI for the Media Resource Function (MRF) used for conferencing.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-uri-type
- Description
-
The SIP URI type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.*
route-to-mrf-via-ims
Set to 'true' to add the I-CSCF to the 'route' header of messages towards the MRF. Set to 'false' and the messages will be routed directly to the MRF from the TAS.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
msml-vendor
The Media Server Markup Language (MSML) vendor, for Conferencing.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Dialogic |
|
Radisys |
enable-scc-conf-handling
Determines the SIP signaling used to draw conference participants from their consulting call into the conference call. When 'false' the 3GPP standard conferencing signaling will be used, when 'true' a more reliable method based on SCC access transfer procedures will be used instead.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
root-on-selector
Determines where the root element is placed when generating MSML. When 'false' it will be placed directly on the video layout element, when 'true' its will be set on the selector element on the video layout element.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
conference-factory-psi-aliases list
A list of conference factory PSIs to use in addition to the standard conference factory PSIs, as per TS 23.003, which are: - 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.<HOME-DOMAIN>' - 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org' - 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ics.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org' Within values '<HOME-DOMAIN>' matches the value defined for /home-network/home-domain. Within values, if both '<MCC>' and '<MNC>' are used in an entry, they will match any MCC/MNC pair defined in /home-network/home-plmn-ids.
Type List of sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Values
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
maximum-participants
The maximum number of participants that are allowed in a single conference call.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 3 or more
allow-video-conference-calls
Set to 'true' to allow video to be used in conference calls.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
conference-view-removal-delay-milliseconds
Delay (in milliseconds) after a conference ends before conference view information in cleaned up.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
default-subscription-expiry-seconds
Time (in seconds) for a subscription to last if the SUBSCRIBE message doesn’t contain an Expires header.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3600
min-subscription-expiry-seconds
Minimum time (in seconds) that a subscription is allowed to last for. SUBSCRIBE requests with an Expires value lower than this are rejected.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
5
international-and-roaming
Context
The context of international-and-roaming within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel international-and-roaming non-international-format-number-is-national end-call-if-no-visited-network use-mcc-specific min-length
Configuration for determining international and roaming status.
non-international-format-number-is-national
Set to 'true' to treat non-international numbers (no leading '+') as national. Set to 'false' to disable this behaviour.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
end-call-if-no-visited-network
Set to 'true' to end the call if no visited network can be determined. Set to 'false' to allow the call to proceed.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
use-mcc-specific
Set to 'true' to determine international status using different configuration for each access network MCC. Set to 'false' to use the default configuration.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis
Context
The context of north-american-numbering-plan-analysis within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel north-american-numbering-plan-analysis enable-nanp-analysis
Configuration for analysing numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan.
enable-nanp-analysis
Whether to analyse numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan, using this to determine location information.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../international-call-management/call-management-by-country-code depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../north-american-numbering-plan-analysis/enable-nanp-analysis.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
international-call-management
Context
The context of international-call-management within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel international-call-management default-international-call-management bar-calls-with-missing-prefix bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id international-call-announcement-id call-management-by-country-code list iso-country-code bar-calls-with-missing-prefix bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id international-call-announcement-id
Configuration for barring and announcements of calls determined to be international.
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/default-international-call-management/bar-calls-with-missing-prefix
Whether calls dialed without the international prefix are barred.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/default-international-call-management/bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to play when calls dialed without the international prefix are barred.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix = 'true'.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
international-call-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/default-international-call-management/international-call-announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to play to the calling party when an international call is made.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
call-management-by-country-code list
The configuration of international NANP calls by destination country. Only available if North American Numbering Plan analysis is enabled.
Conditional
This list is only valid when ../../north-american-numbering-plan-analysis/enable-nanp-analysis = 'true'.
List Structure
iso-country-code string bar-calls-with-missing-prefix boolean bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id announcement-id-type international-call-announcement-id announcement-id-type
The key is iso-country-code.
iso-country-code
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/call-management-by-country-code/iso-country-code
The determined ISO country code of the called party if within the NANP.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 2 matching
[A-Z]*
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/call-management-by-country-code/bar-calls-with-missing-prefix
Whether to bar calls to this destination that were dialled without an international prefix.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/call-management-by-country-code/bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to play if calls to this destination were barred.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix = 'true'.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
international-call-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/international-call-management/call-management-by-country-code/international-call-announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to play before international calls to this destination are connected.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
call-diversion
Configuration for the MMTel call diversion service.
Context
The context of call-diversion within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel call-diversion mmtel-call-diversion forward-to-voicemail announcement
mmtel-call-diversion
See mmtel-call-diversion for details of this node and its descendants.
forward-to-voicemail
See forward-to-voicemail for details of this node and its descendants.
announcement
See announcement for details of this node and its descendants.
mmtel-call-diversion
Context
The context of mmtel-call-diversion within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel call-diversion mmtel-call-diversion max-diversions max-diversion-action max-diversion-fixed-destination no-reply-timeout-seconds add-orig-tag diversion-limit-exempt-uris list suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain prefer-subscriber default-target-uri additional-not-reachable-status-codes list allow-not-reachable-during-alerting add-mp-param
Configuration for the MMTel call diversion service.
max-diversions
Maximum number of diversions that may be made while attempting to establish a session.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
max-diversion-action
Action to take when the maximum number of diversions is exceeded.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../max-diversion-fixed-destination depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../max-diversion-action.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Reject the call. |
|
Direct the call to the address specified in max-diversion-fixed-destination. |
|
Direct the call to the subscriber’s voicemail server. |
max-diversion-fixed-destination
The address to deliver communication to when the maximum number of diversions is exceeded and ../max-diversion-action is set to 'DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../max-diversion-action = 'DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION'.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
no-reply-timeout-seconds
Time to wait (in seconds) for a reply before diverting due to a no reply rule. This value is the network default, and can be overridden in subscriber data.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 5 to 180
add-orig-tag
Set to 'true' to add an 'orig' tag to the Route header when diverting a call.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
diversion-limit-exempt-uris list
List of URIs may still be diverted to after the max diversions limit has been reached.
Type List of sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Values
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain
Set to 'true' to suppress call diversion behaviour for calls terminating in the CS domain.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
prefer-subscriber
Set to 'true' to have subscriber configuration take precedence over operator configuration.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
default-target-uri
The address to forward to if an operator or subscriber forward-to rule has no target specified.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
additional-not-reachable-status-codes list
List of response codes that can trigger a 'not-reachable' diversion rule (in addition to those outlined in the MMTel call diversion specification). The following status codes cannot be used: 1xx, 2xx, 302, 404, 408, 486, 487.
Type List of sip-status-code
- Description
-
SIP response status code type.
- Values
-
a number in the range 300 to 301, 303 to 399, 400 to 403, 405 to 407, 409 to 485, 488 to 699
allow-not-reachable-during-alerting
Set to 'true' to allow diversion rules with 'not-reachable' conditions to be triggered after a 180 response has been received from the called party.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
forward-to-voicemail
Context
The context of forward-to-voicemail within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel call-diversion forward-to-voicemail voicemail-uris list forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit
Configuration for forwarding to a subscriber’s voicemail server.
- When present
-
Enable forwarding to a subscriber’s configured voicemail server if all other connection attempts fail.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../announcement/voicemail-announcement-id depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../forward-to-voicemail.
voicemail-uris list
List of URIs for which a voicemail-specific announcement will be played (if specified) and for which forwarding to without allocated credit will be allowed (if enabled).
Type List of sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Values
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds
Maximum amount of time to wait (in seconds) for a call to be successfully connected before executing default forward to voicemail behaviour (if enabled). Set to '0' to disable the timer.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit
Determines whether to allow forwarding to voicemail when credit cannot be allocated for a call. Only applies when using Diameter Ro based online charging.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'ro' or ../../../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro' or ../../../../charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Never forward to voicemail when credit has not been allocated. |
|
Allow forwarding to voicemail when credit has not been allocated if address matches a known voicemail server. |
|
Always allow forwarding to voicemail when credit has not been allocated. |
announcement
Context
The context of announcement within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel call-diversion announcement announcement-id voicemail-announcement-id
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
voicemail-announcement-id
The ID of the announcement to be played when forwarding to a recognized voicemail server.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../forward-to-voicemail.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
communication-hold
Context
The context of communication-hold within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-hold bandwidth-adjustment b-as-parameter b-rr-parameter b-rs-parameter holding-party-media-mode announcement announcement-id
Configuration for the MMTel communication hold service.
bandwidth-adjustment
Configuration for adjusting the bandwidth of responses when sessions are Held and Resumed.
Parameter definitions: 3GPP TS 24.610 Rel 12.6.0 section 4.5.2.4.
- When present
-
Bandwidth adjustment is enabled.
Container Structure
b-as-parameter
The value to set for the 'b=AS:' parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
b-rr-parameter
The value to set for the 'b=RR:' parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
b-rs-parameter
The value to set for the 'b=RS:' parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
holding-party-media-mode
Determines how media streams for the holding party are handled while an announcement to the held party is in progress.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The passive party is not put on hold during the announcement, media streams are left as they were. |
|
SDP is renegotiated with the passive party so that for the duration of the announcement, all media streams are directed to a black hole IP. |
|
SDP is renegotiated with the passive party so that for the duration of the announcement, all media streams are directed to a black hole IP; and additionally the passive party is put on hold by setting the stream status to |
- Default value
-
'FULL_HOLD'
announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
communication-waiting
Context
The context of communication-waiting within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-waiting timer-seconds announcement announcement-id
Configuration for the MMTel communication waiting service.
timer-seconds
The maximum time (in seconds) that the communication waiting service will wait for the call to be answered before abandoning it. Default value is 0, which means the timer does not apply.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 0, 30 to 120
announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
privacy
Context
The context of privacy within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel privacy originating-identification-presentation anonymize-from-header allow-history-info-header-deletion originating-identification-restriction presentation-restriction-type user-policy
Configuration for the MMTel privacy services.
originating-identification-presentation
Configuration for the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) feature.
Container Structure
anonymize-from-header
If set to 'true', this typically means that:
-
OIP is authorized for the large majority of subscribers, and that:
-
The OIP active flag is either not present in the subscriber’s data (therefore defaulting to true), or the OIP flag is present in the subscriber’s data (typically set to true).
-
This also implies that the ../../originating-identification-restriction/user-policy is set to 'NONE'.
If set to 'false', this typically means that:
-
OIP is not 'active' or 'authorized' yet the operator desires the called party to see the calling party.
-
This implies that the ../../originating-identification-restriction/user-policy would be set to 'ANONYMIZE_FROM' or 'ADD_USER_PRIVACY'.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
allow-history-info-header-deletion
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/privacy/originating-identification-presentation/allow-history-info-header-deletion
If 'true', allows History-Info header deletion.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
originating-identification-restriction
Configuration for the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) feature.
Container Structure
presentation-restriction-type
Controls the presentation restriction type, influencing what value will be present in the Privacy header.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Privacy header is set to 'Privacy:id'. |
|
The Privacy header is set to 'Privacy:header'. |
- Default value
-
'ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION'
psap-callback
Context
The context of psap-callback within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel psap-callback use-priority-header sip-message-options expiry-time-seconds terminate-message
Configuration for PSAP callback service.
use-priority-header
If set to 'true', use the contents of the Priority header in the initial INVITE to determine whether the session is a PSAP callback.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
sip-message-options
Configuration for the SIP MESSAGE mechanism for determining whether a session is a PSAP callback.
- When present
-
Use the SIP MESSAGE mechanism to determine whether session is a PSAP callback.
Container Structure
expiry-time-seconds
When a SIP MESSAGE notifying that a PSAP call has taken place, this is the time (in seconds) after receiving that MESSAGE that sessions for the identified user are assumed to be a PSAP callback.
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
communication-barring
Configuration for MMTel communication barring service.
Context
The context of communication-barring within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring incoming-communication-barring outgoing-communication-barring operator-communication-barring operator-barring-rules outgoing-prefix-barring
incoming-communication-barring
See incoming-communication-barring for details of this node and its descendants.
outgoing-communication-barring
See outgoing-communication-barring for details of this node and its descendants.
operator-communication-barring
See operator-communication-barring for details of this node and its descendants.
incoming-communication-barring
Context
The context of incoming-communication-barring within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring incoming-communication-barring international-rules-active announcement announcement-id anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id
Configuration for incoming communication barring.
international-rules-active
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/international-rules-active
If 'false', incoming call barring will ignore International and International-exHC rules. This is because it is not possible to accurately determine whether the calling party is international in all circumstances.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/incoming-communication-barring/announcement/anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id
The ID for a different announcement that can be played if the call is barred because it is from an anonymous user.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
outgoing-communication-barring
Context
The context of outgoing-communication-barring within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring outgoing-communication-barring announcement announcement-id
Configuration for outgoing communication barring.
announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/outgoing-communication-barring/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
operator-communication-barring
Configuration for operator communication barring.
Context
The context of operator-communication-barring within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring operator-communication-barring operator-barring-rules outgoing-prefix-barring
operator-barring-rules
See operator-barring-rules for details of this node and its descendants.
outgoing-prefix-barring
See outgoing-prefix-barring for details of this node and its descendants.
operator-barring-rules
Context
The context of operator-barring-rules within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring operator-communication-barring operator-barring-rules type1 rule retarget retarget-uri disable-online-charging-on-retarget announcement announcement-id type2 rule retarget retarget-uri disable-online-charging-on-retarget announcement announcement-id type3 rule retarget retarget-uri disable-online-charging-on-retarget announcement announcement-id type4 rule retarget retarget-uri disable-online-charging-on-retarget announcement announcement-id
Configuration for operator barring rules.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../../hss-queries-enabled/odb = 'true'.
type1
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1
The Type1 operator barring rule.
- When present
-
Enable type1 operator barring rule
Container Structure
rule
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/rule
This node is mandatory.
Type XML data as specified.
retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/retarget
Should the call be retargeted if this barring rule matches.
- When present
-
Indicates that the call should be retargeted when this rule matches.
Container Structure
retarget-uri
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/retarget/retarget-uri
The URI to retarget this call to if the barring rule matches.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
disable-online-charging-on-retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/retarget/disable-online-charging-on-retarget
Should charging be disabled when we retarget.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/retarget/announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type1/retarget/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
type2
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2
The Type2 operator barring rule.
- When present
-
Enable type2 operator barring rule
Container Structure
rule
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/rule
This node is mandatory.
Type XML data as specified.
retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/retarget
Should the call be retargeted if this barring rule matches.
- When present
-
Indicates that the call should be retargeted when this rule matches.
Container Structure
retarget-uri
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/retarget/retarget-uri
The URI to retarget this call to if the barring rule matches.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
disable-online-charging-on-retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/retarget/disable-online-charging-on-retarget
Should charging be disabled when we retarget.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/retarget/announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type2/retarget/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
type3
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3
The Type3 operator barring rule.
- When present
-
Enable type3 operator barring rule
Container Structure
rule
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/rule
This node is mandatory.
Type XML data as specified.
retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/retarget
Should the call be retargeted if this barring rule matches.
- When present
-
Indicates that the call should be retargeted when this rule matches.
Container Structure
retarget-uri
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/retarget/retarget-uri
The URI to retarget this call to if the barring rule matches.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
disable-online-charging-on-retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/retarget/disable-online-charging-on-retarget
Should charging be disabled when we retarget.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/retarget/announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type3/retarget/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
type4
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4
The Type4 operator barring rule.
- When present
-
Enable type4 operator barring rule
Container Structure
rule
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/rule
This node is mandatory.
Type XML data as specified.
retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/retarget
Should the call be retargeted if this barring rule matches.
- When present
-
Indicates that the call should be retargeted when this rule matches.
Container Structure
retarget-uri
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/retarget/retarget-uri
The URI to retarget this call to if the barring rule matches.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-or-tel-uri-type
- Description
-
A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.
- Value
-
- sip-uri-type
-
The SIP URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
sip:.* - or tel-uri-type
-
The Tel URI type.
a string with length 0 or more matching
tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+
disable-online-charging-on-retarget
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/retarget/disable-online-charging-on-retarget
Should charging be disabled when we retarget.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/retarget/announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/operator-barring-rules/type4/retarget/announcement/announcement-id
The announcement to be played.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
outgoing-prefix-barring
Context
The context of outgoing-prefix-barring within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel communication-barring operator-communication-barring outgoing-prefix-barring prefixes list prefix classifications list classifications list name minimum-number-length maximum-number-length match-international barring-treatment disable-ocb-announcement announcement announcement-id
Configuration for outgoing prefix barring.
- When present
-
Outgoing prefix barring is configured
prefixes list
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/prefixes
The list of prefixes to match against, and their corresponding classifications to be used for outgoing barring.
prefix
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/prefixes/prefix
The prefix to match against for outgoing barring.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
classifications list
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/prefixes/classifications
The classification(s) to apply when this prefix is matched.
Type List of leafref
- Values
-
one of ../../classifications/name
classifications list
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications
The list of classifications that can be applied for a prefix match.
List Structure
name string minimum-number-length uint8 maximum-number-length uint8 match-international boolean barring-treatment enumeration disable-ocb-announcement boolean announcement announcement-id announcement-id-type
The key is name.
Data Validation Constraints
|
Validation Error: |
'minimum-number-length' must be less than or equal to 'maximum-number-length'. |
|
|
|
|
Validation Error: |
'disable-ocb-announcement' must be omitted or set to 'false' if an outgoing prefix barring announcement is specified. |
name
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/name
The name for this barring classification.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[^\t\n\r]+
minimum-number-length
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/minimum-number-length
The minimum length the number must be to match this classification.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as minimum-number-length.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 20
maximum-number-length
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/maximum-number-length
The maximum length the number can be to match this classification.
This node is mandatory.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as maximum-number-length.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 20
match-international
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/match-international
When true, the normalized number must be international and not within the Home Country Code to match this classification.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
barring-treatment
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/barring-treatment
How to handle a call that this classification applies to.
This node is mandatory.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Treat call as a Type1 operator barring rule. |
|
Treat call as a Type2 operator barring rule. |
|
Treat call as a Type3 operator barring rule. |
|
Treat call as a Type4 operator barring rule. |
|
Allow call to proceed. |
|
Bar the call. |
|
Treat call as premium rate information. |
|
Treat call as premium rate entertainment. |
disable-ocb-announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/disable-ocb-announcement
Disables the 'outgoing-call-barring' announcement. Cannot be 'true' when an announcement is specified.
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as disable-ocb-announcement.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
announcement
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/announcement
Should an announcement be played
- When present
-
Enables announcements
Container Structure
Related Constraint
.. has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as announcement.
announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/mmtel/communication-barring/operator-communication-barring/outgoing-prefix-barring/classifications/announcement/announcement-id
The ID of an announcement to play instead of the usual 'outgoing-call-barring' announcement.
This node is mandatory.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
vertical-service-codes
Context
The context of vertical-service-codes within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) mmtel vertical-service-codes xcap-data-update host port use-https base-uri auid document success-response-status-code failure-response-status-code failure-announcement announcement-id
Configuration for vertical service codes.
host
Hostname of XCAP server to send HTTP requests to.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Port of XCAP server to send HTTP requests to. Can be omitted to use the default port for the protocol port.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
use-https
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Indicates whether or not to use HTTP over TLS to connect to the XCAP server.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
base-uri
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Base URI of XCAP server.
Type uri
- Description
-
The uri type represents a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) as defined by STD 66.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string
auid
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. XCAP application unique identifier to use in request URI.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
document
Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. XCAP document to use in request URI.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
success-response-status-code
Response status code to use following a successful HTTP response.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-status-code
- Description
-
SIP response status code type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 100 to 699
failure-response-status-code
Response status code to use following a failure HTTP response.
This node is mandatory.
Type sip-status-code
- Description
-
SIP response status code type.
- Value
-
a number in the range 100 to 699
failure-announcement
An announcement be played if the update fails.
- When present
-
Enables announcement on failure
Container Structure
registrar
Context
The context of registrar within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) registrar data-storage-type user-identity-type-for-stn-sr-request include-private-id-in-stn-sr-request
Registrar configuration.
data-storage-type
Data storage type.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
HSS cache data storage. |
|
Cassandra data storage. |
- Default value
-
'cassandra'
user-identity-type-for-stn-sr-request
The type of user identity to use when creating Sh requests for the STN-SR.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The user’s CMS ISDN. |
|
The user’s public ID. |
- Default value
-
'PUBLIC_ID'
sis
Context
The context of sis within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) sis unavailable-peer-list-timer-milliseconds failover-timer-milliseconds
SIS configuration.
unavailable-peer-list-timer-milliseconds
The duration for which a server will be blocked after a failure is detected. This avoids the RA trying to use the server immediately after a failure, when it is most likely just going to fail again. After this time has passed the failed server may be tried again on subsequent client transactions. If a server specifies a Retry-After duration in a 503 response, that value will be used instead.
Type uint64
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
60000
failover-timer-milliseconds
Specifies the duration of the failover timer. If this timer expires before any responses were received, the RA treats this as a transport error and tries sending the request to the next available server. This timer should be set to a value smaller than the default Timer B and Timer F timers (32s) so that failures can be detected promptly. A value of zero disables this timer.
Type uint64
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
4000
hlr-connectivity-origin
Context
The context of hlr-connectivity-origin within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) hlr-connectivity-origin originating-address gsm mlc-address use-msisdn-as-hlr-address msc-originating-address cdma market-id switch-number map-invoke-timeout-milliseconds
Origin HLR connectivity configuration.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../scc/tads/address-source-for-scc-tads != 'CMSISDN' or ../mmtel/determine-roaming-from-hlr = 'true' or ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/originating-tdp or ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/terminating-tdp.
originating-address
The originating SCCP address. This often is a Point Code and SSN, where the SSN is typically 145 or 146
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
gsm
HLR connectivity configuration specific to GSM.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
Container Structure
mlc-address
The MLC SCCP address. This is the logical address of the originator, i.e. this service. Typically a Global Title.
This node is mandatory.
Type ss7-address-string-type
- Description
-
The SS7 address string type.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*address=.and matching.=.(,.=.)*
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address
Indicates if 'hlr/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR address, or have its digits replaced with the MSISDN of the subscriber.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
msc-originating-address
Originating SCCP address when acting as an MSC, used when establishing the MAP dialog. Will default to the value of 'originating-address' when not present. Typically used to set a different originating SSN when sending a SendRoutingInformation message to the HLR.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
cdma
HLR connectivity configuration specific to CDMA.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'.
Container Structure
market-id
The market ID (MarketID). Forms part of the Mobile Switching Center Identification (MSCID)
- Reference
-
X.S0004-550-E v3.0 2.161
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 65535
switch-number
The switch number (SWNO). Forms part of the Mobile Switching Center Identification (MSCID)
- Reference
-
X.S0004-550-E v3.0 2.161
This node is mandatory.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range up to 255
charging
Context
The context of charging within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) charging gsm-online-charging-type cdma-online-charging-enabled ro-charging diameter-ro continue-session-on-ocs-failure diameter-ro-release realm-choice choice single-realm destination-realm multiple-realms destination-realms list destination-realm charging-function-address peers list origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric charging-announcements low-credit-announcements call-setup-announcement-id mid-call-announcement-id charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds out-of-credit-announcements call-setup-announcement-id mid-call-announcement-id rf-charging diameter-rf diameter-rf-release destination-realm origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric cap-charging imssf imcsi-fetching originating-tdp terminating-tdp charging-gt format unknown-location only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming scf-address cdr interim-cdrs write-cdrs-in-filesystem write-cdr-on-sdp-change interim-cdrs-period-seconds session-cdrs-enabled registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled registrar-cdr-stream-name
Charging configuration
gsm-online-charging-type
The online charging type. Only valid when 'scc-mobile-core-type' is 'gsm'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../../mmtel/call-diversion/forward-to-voicemail/forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type.
Conditional node ../cap-charging depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../gsm-online-charging-type.
Conditional node ../ro-charging depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../gsm-online-charging-type.
Conditional node ../../../mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/gsm-online-charging-type.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use Diameter Ro charging. |
|
Use CAMEL Application Part (CAP) charging. |
|
Use both Diameter Ro and CAMEL Application Part (CAP) charging. |
|
Disable online charging. |
- Default value
-
'ro'
cdma-online-charging-enabled
Set to 'true' to enable online charging. Set to 'false' to disable. Only valid when 'scc-mobile-core-type' is 'cdma'.
Conditional
This leaf is only valid when ../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'.
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../../../mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled.
Conditional node ../ro-charging depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../cdma-online-charging-enabled.
Conditional node ../../mmtel/call-diversion/forward-to-voicemail/forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../../charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled.
Conditional node ../../../mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-ro depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
ro-charging
Ro charging configuration. Used when 'cdma-online-charging-type' is set to 'true' or when 'gsm-online-charging-type' is set to 'ro' or 'cap-ro'.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'ro' or ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro' or ../cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'.
Container Structure
diameter-ro continue-session-on-ocs-failure diameter-ro-release realm-choice choice single-realm destination-realm multiple-realms destination-realms list destination-realm charging-function-address peers list origin-realm destination-peers list protocol-transport destination-hostname port metric charging-announcements low-credit-announcements call-setup-announcement-id mid-call-announcement-id charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds out-of-credit-announcements call-setup-announcement-id mid-call-announcement-id
continue-session-on-ocs-failure
Set to 'true' to permit sessions to continue if there is an OCS (Online Charging System) failure.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
diameter-ro-release
The Diameter Ro release to use.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Release V8d0 |
|
Release V960 |
|
Release Va00 |
|
Release Vb80 |
|
Release Vcb0 |
- Default value
-
'Vcb0'
realm-choice choice
Whether to use a single realm or multiple realms.
A Choice between one of the following:
destination-realm
The Diameter destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-realms list
List of Diameter destination realms.
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
destination-realm domain-name charging-function-address string peers list string
The key is destination-realm.
destination-realm
The destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
charging-function-address
The value that must appear in a P-Charging-Function-Addresses header in order to select this destination realm. If omitted, this will be the same as the destination-realm value.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
peers list
List of Diameter peers for the realm.
Must contain at least 1 element.
Type List of string
- Values
-
a string
origin-realm
The Diameter origin realm.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-peers list
Diameter destination peer(s).
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
protocol-transport enumeration destination-hostname domain-name port port-number metric uint32
The key is destination-hostname.
protocol-transport
The combined Diameter protocol and transport.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over tcp |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp. IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported. |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are provisioned. |
- Default value
-
'aaa'
destination-hostname
The destination hostname.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
The destination port number.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3868
metric
The metric to use for this peer. Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric, traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
1
call-setup-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging/charging-announcements/low-credit-announcements/call-setup-announcement-id
Announcement ID to be played during call setup if the subscriber has low credit.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
mid-call-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging/charging-announcements/low-credit-announcements/mid-call-announcement-id
Announcement ID to be played during a call if the subscriber has low credit.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds
/sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging/charging-announcements/low-credit-announcements/charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds
The delay (in milliseconds) for issuing a credit check after a call is connected with low balance (0 indicates immediate reauth).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
call-setup-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging/charging-announcements/out-of-credit-announcements/call-setup-announcement-id
Announcement ID to be played during call setup if the subscriber is out of credit.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
mid-call-announcement-id
/sentinel-volte/charging/ro-charging/charging-announcements/out-of-credit-announcements/mid-call-announcement-id
Announcement ID to be played during a call if the subscriber is out of credit.
Type announcement-id-type
- Description
-
The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP announcement IDs from '/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.
- Value
rf-charging
Rf charging configuration. Presence enables Rf charging.
- When present
-
Enables Rf charging.
Data Validation Constraint
|
Validation Error: |
'interim-cdrs' section must be present when 'rf-charging' is present. |
Related Constraints
Conditional node ../../../mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-rf depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/rf-charging.
Conditional node ../../../mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool/virtual-machines/per-node-diameter-rf depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../../../sentinel-volte/charging/rf-charging.
diameter-rf-release
The Diameter Rf release to use.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Release V8d0 |
|
Release V960 |
|
Release Va00 |
|
Release Vb80 |
|
Release Vcb0 |
- Default value
-
'Vcb0'
destination-realm
The Diameter destination realm.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
origin-realm
The Diameter origin realm.
| |
A restart is required for changes to this value to take effect. |
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
destination-peers list
Diameter destination peer(s).
Must contain at least 1 element.
List Structure
protocol-transport enumeration destination-hostname domain-name port port-number metric uint32
The key is destination-hostname.
protocol-transport
The combined Diameter protocol and transport.
Type enumeration
- Value
-
one of the following
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over tcp |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp. IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported. |
|
The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are provisioned. |
- Default value
-
'aaa'
destination-hostname
The destination hostname.
This node is mandatory.
Type domain-name
- Description
-
The domain-name type represents a DNS domain name. The name SHOULD be fully qualified whenever possible.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a string with length 1 to 253 matching
((([a-zA-Z0-9_]([a-zA-Z0-9\-]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.)*([a-zA-Z0-9]([a-zA-Z0-9\-_]){0,61})?[a-zA-Z0-9]\.?)|\.
port
The destination port number.
Type port-number
- Description
-
The port-number type represents a 16-bit port number of an Internet transport-layer protocol such as UDP, TCP, DCCP, or SCTP.
See RFC 6991 for full details.
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
3868
metric
The metric to use for this peer. Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric, traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
1
cap-charging
CAP charging configuration. Used when 'gsm-online-charging-type' is set to 'cap' or 'cap-ro'.
Conditional
This container is only valid when ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap' or ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro'.
originating-tdp
The requested Trigger Detection Point for originating calls, which determines whether T_CSI or O_CSI is requested from the HLR. Values of '2' or '3' will request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other values are not valid.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../../../../hlr-connectivity-origin depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/originating-tdp.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 2, 3, 12
terminating-tdp
The requested Trigger Detection Point for terminating calls, which determines whether T_CSI or O_CSI is requested from the HLR. Values of '2' or '3' will request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other values are not valid.
Related Constraint
Conditional node ../../../../../hlr-connectivity-origin depends on this node. The Conditional expression refers to this node as ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/terminating-tdp.
Type uint8
- Value
-
a number in the range 2, 3, 12
charging-gt
Configuration for the charging GT (global title) that is sent to the SCP.
Container Structure
format
The format template to use when creating Charging GTs (global title). It must be a digit string except for tokens ('{iso}', '{mcc}', '{mnc}') which are substituted in.
This node is mandatory.
Type string
- Value
-
a string
unknown-location
The Charging GT (global title) to use when one could not be generated because the user’s location could not be determined.
This node is mandatory.
Type number-string
- Description
-
A type that permits a non-negative integer value.
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
[0-9]+
only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming
/sentinel-volte/charging/cap-charging/imssf/charging-gt/only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming
Should terminating charging only be applied if the served user is roaming internationally.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
scf-address
The SCCP address of the GSM charging SCP.
This node is mandatory.
Type sccp-address-type
- Description
-
A type representing an SCCP address in string form. The basic form of an SCCP address is:
type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,…where
<variant>isA7for ANSI-variant SCCP orC7for ITU-variant SCCP, and<address type>is one ofgtorpcssn(for an address specified by Global Title (GT), or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).The
<parameter>options are:-
Point code:
pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI) or integer (ITU) format> -
Subsystem number:
ssn=<subsystem number 0-255> -
Global title address digits:
digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9> -
Nature of address:
nature=<nature>where<nature>isunknown,international,national, orsubscriber -
Numbering plan:
numbering=<numbering>where<numbering>isunknown,isdn,generic,data,telex,maritime-mobile,land-mobile,isdn-mobile, orprivate -
Global title translation type:
tt=<integer 0-255> -
National indicator:
national=<true or false>.parameternames are separated from their values by an equals sign, and all<parameter>=<value>pairs are separated by commas. Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.Only the
ssnandnationalparameters are mandatory; the others are optional, depending on the details of the address - see below.Note carefully the following:
-
For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=true, unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network. -
For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify
national=false. -
All SCCP addresses across the deployment’s configuration must use the same variant (
A7orC7). -
Be sure to update the SGC’s SCCP variant in
sgc-config.yamlto match the variant of the addresses.
For PC/SSN addresses (with
ri=pcssn), you need to specify the point code and SSN. For GT addresses (withri=gt), you must specify the global title digits and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
-
nature of address only
-
translation type only
-
numbering plan and translation type
-
nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
-
type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true -
type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=trueSome valid ITU address examples are:
-
type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0, digits=123456,national=false -
type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false
-
- Value
-
a string with length 0 or more matching
(.,)*type=(A|C)7.and matching(.,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).and matching(.,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].and matching.=.(,.=.)*
interim-cdrs
Interim CDR configuration. Presence enables Interim CDRs.
- When present
-
Enables interim CDRs.
Container Structure
Related Constraint
../../rf-charging has a Data Validation Constraint which references this node. The validation expression refers to this node as ../cdr/interim-cdrs.
write-cdrs-in-filesystem
'true' means that CDRs are written locally by the application. CDRs are written via Diameter Rf if the Sentinel VoLTE configuration value 'rf-charging' is present.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
write-cdr-on-sdp-change
Indicates whether or not to write CDRs on SDP changes.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
interim-cdrs-period-seconds
The maximum duration (in seconds) between timer driven interim CDRs.
Setting this to zero will disable timer based interim CDRs.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
300
session-cdrs-enabled
'true' enables the creation of session CDRs, 'false' disables.
This node is mandatory.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled
'true' enables the creation of Registrar audit CDRs, 'false' disables.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
false
session-refresh
Context
The context of session-refresh within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte (in sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml and sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml) session-refresh timer-interval-seconds refresh-period-seconds refresh-with-update-if-allowed max-call-duration-seconds
Session Refresh configuration.
timer-interval-seconds
The interval (in seconds) of the periodic timer used to check whether a session needs refreshing.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
30
refresh-period-seconds
Period of no activity for leg to refresh (in seconds).
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 0 or more
- Default value
-
570
refresh-with-update-if-allowed
Whether the session should be refreshed using UPDATE requests, when the endpoint allows UPDATE requests.
Otherwise sessions are refreshed using re-INVITE requests.
Type boolean
- Value
-
'true' or 'false'
- Default value
-
true
system
Context
The context of system within the schema tree is shown. Italicised links are to other pages.
deployment-config:system (in system-config.yaml) networking core receive-buffer-size-default receive-buffer-size-max send-buffer-size-default send-buffer-size-max sctp rto-min rto-initial rto-max sack-timeout hb-interval path-max-retransmissions association-max-retransmissions
OS-level parameters.
This node and its descendants are configured in system-config.yaml.
- When present
-
Always (but not all settings may be relevant on all nodes).
receive-buffer-size-default
Default socket receive buffer size.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 65536 to 16777216
- Units
-
bytes
- Default value
-
512000
receive-buffer-size-max
Maximum socket receive buffer size.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 65536 to 16777216
- Units
-
bytes
- Default value
-
2048000
send-buffer-size-default
Default socket send buffer size.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 65536 to 16777216
- Units
-
bytes
- Default value
-
512000
send-buffer-size-max
Maximum socket send buffer size.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 65536 to 16777216
- Units
-
bytes
- Default value
-
2048000
rto-min
Round trip estimate minimum. Used in SCTP’s exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 10 to 5000
- Units
-
milliseconds
- Default value
-
50
rto-initial
Round trip estimate initial value. Used in SCTP’s exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 10 to 5000
- Units
-
milliseconds
- Default value
-
300
rto-max
Round trip estimate maximum. Used in SCTP’s exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 10 to 5000
- Units
-
milliseconds
- Default value
-
1000
sack-timeout
Timeout within which the endpoint expects to receive a SACK message.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 50 to 5000
- Units
-
milliseconds
- Default value
-
100
hb-interval
Heartbeat interval. The longer the interval, the longer it can take to detect that communication with a peer has been lost.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 50 to 30000
- Units
-
milliseconds
- Default value
-
1000
path-max-retransmissions
Maximum number of retransmissions on one path before communication via that path is considered to be lost.
Type uint32
- Value
-
a number in the range 1 to 20
- Default value
-
5
Example configuration and schemas
- Example configuration YAML files
- Example for snmp-config.yaml
- Example for routing-config.yaml
- Example for system-config.yaml
- Example for bsf-config.yaml
- Example for naf-filter-config.yaml
- Example for common-config.yaml
- Example for home-network-config.yaml
- Example for tsn-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for number-analysis-config.yaml
- Example for sas-config.yaml
- Example for shcm-service-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml
- Example for hlr-config.yaml
- Example for icscf-config.yaml
- Example for sgc-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml
- Example for mag-overrides.yaml
- Example for shcm-overrides.yaml
- Example for mmt-cdma-overrides.yaml
- Example for mmt-gsm-overrides.yaml
- Example for smo-overrides.yaml
- Example for mag-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for shcm-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for smo-vmpool-config.yaml
- YANG schemas
- snmp-configuration.yang
- routing-configuration.yang
- system-configuration.yang
- traffic-type-configuration.yang
- bsf-configuration.yang
- naf-filter-configuration.yang
- common-configuration.yang
- home-network-configuration.yang
- number-analysis-configuration.yang
- sas-configuration.yang
- shcm-service-configuration.yang
- sentinel-volte-configuration.yang
- hlr-configuration.yang
- icscf-configuration.yang
- sgc-configuration.yang
- sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration.yang
- vm-types.yang
Example configuration YAML files
The Rhino VoLTE TAS’s example YAML configuration consists of the following YAML files.
![]() Download the configuration as a package.
Download the configuration as a package.
- Example for snmp-config.yaml
- Example for routing-config.yaml
- Example for system-config.yaml
- Example for bsf-config.yaml
- Example for naf-filter-config.yaml
- Example for common-config.yaml
- Example for home-network-config.yaml
- Example for tsn-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for number-analysis-config.yaml
- Example for sas-config.yaml
- Example for shcm-service-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml
- Example for hlr-config.yaml
- Example for icscf-config.yaml
- Example for sgc-config.yaml
- Example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml
- Example for mag-overrides.yaml
- Example for shcm-overrides.yaml
- Example for mmt-cdma-overrides.yaml
- Example for mmt-gsm-overrides.yaml
- Example for smo-overrides.yaml
- Example for mag-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for shcm-vmpool-config.yaml
- Example for smo-vmpool-config.yaml
Example for snmp-config.yaml
deployment-config:snmp:
# Enable SNMP v1 (not recommended)
v1-enabled: false
# Enable SNMP v2c
v2c-enabled: true
# Enable SNMP v3
v3-enabled: false
# SNMP Community. Required for SNMP v2c
community: clearwater
# SNMP agent details
agent-details:
location: Unknown location
contact: support.contact@invalid.com
# SNMP Notifications
notifications:
# Enable Rhino SNMP Notifications
rhino-notifications-enabled: true
# Enable System SNMP Notifications
system-notifications-enabled: true
# Enable SGC SNMP Notifications
sgc-notifications-enabled: true
# SNMP notification targets. Normally this is the address of your MVS
targets:
- version: v2c
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 162
# Enable different SNMP notification categories
categories:
- category: alarm-notification
enabled: true
- category: log-notification
enabled: false
- category: log-rollover-notification
enabled: false
- category: resource-adaptor-entity-state-change-notification
enabled: false
- category: service-state-change-notification
enabled: false
- category: slee-state-change-notification
enabled: false
- category: trace-notification
enabled: false
- category: usage-notification
enabled: falseExample for routing-config.yaml
# This file is optional. If you do not use any custom routing rules,
# you can omit this file from the configuration bundle uploaded to CDS.
deployment-config:routing:
routing-rules: []
# To create routing rules, populate the routing-rules list as shown in the example below.
# routing-rules:
# - name: Example
#
## The target for the routing rule.
## Can be either an IP address or a block of addresses (e.g. 10.0.0.0/8).
# target: 8.8.8.8
#
## The interface to use.
## Can be one of 'management', 'diameter', 'ss7', 'sip', 'internal', 'access', 'cluster',
## 'diameter-multihoming' or 'ss7_multihoming'.
# interface: management
#
## The IP address of the gateway to route through.
# gateway: 0.0.0.0
#
# The node types this routing rule applies to.
# If ommitted, this routing rule will be attempt to apply itself to all node types.
# node-types:
# - tsn
# - mag
#
# - name: Example2
## ...Example for system-config.yaml
# This file contains OS-level settings.
# This file is optional. Unless your Metaswitch Customer Care Representative
# has recommended that you override some settings within this file,
# omit this file from the configuration bundle uploaded to CDS.
deployment-config:system:
networking: {}
# To populate settings, remove the "{}" and fill in the appropriate keys and values.
# For example:
#
# deployment-config:system:
# networking:
# sctp:
# hb-interval: 1000Example for bsf-config.yaml
# This file contains the configuration for the BSF
deployment-config:bsf:
# the Zh interface is between the BSF and the HSS only
# It is a Diameter interface
# the Destination realm and peers are configured in this file
# As each Virtual Machine needs to have an origin host, the Zh origin host is present
# in the MAG VM Pool file rather than this file.
# I.e, each virtual machine is defined in the MAG VM pool file, with its own origin host
zh-diameter:
origin-realm: opencloud.com
destination-realm: opencloud.com
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: hss.opencloud.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for naf-filter-config.yaml
# This file contains the configuration for the NAF
#nothing is mandatory as the defaults are always suitable
deployment-config:naf-filter:
service-type: 0
service-id: 0
# By default the naf group is the empty string, but it can be set to something like nafgroup1
naf-group: ""
nonce-options:
reuse-count: 500
nonce-cassandra-keyspace: opencloud_nonce_info
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for common-config.yaml
# This file contains configuration common to the deployment
deployment-config:common:
# Platform operator name. Can contain letters, numbers, - and _.
platform-operator-name: MetaswitchExample for home-network-config.yaml
# This file contains configuration for the home network.
deployment-config:home-network:
# Home domain.
home-domain: metaswitch.com
# Home network country dialing code.
home-network-country-dialing-code: "64"
# Two letter ISO country code for the home network.
home-network-iso-country-code: NZ
# Home PLMN IDs.
home-plmn-ids:
- mcc: "001"
mncs:
- "01"
- "001"Example for tsn-vmpool-config.yaml
# this file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a TSN Cluster
deployment-config:tsn-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-tsn-1
- vm-id: example-tsn-2
- vm-id: example-tsn-3Example for number-analysis-config.yaml
# This config is used for translating from the subscriber format.
# It is used in CDIV and XCAP.
deployment-config:number-analysis:
normalization:
# The international prefix of the home network.
international-prefix: "00"
# Any number shorter than this will not be normalized.
min-normalizable-length: 0
# The national prefix of the home network.
national-prefix: "0"
# The network dialing code of the home network.
network-dialing-code: "6"
# Whether to normalize to international or national format.
normalize-to: international
# When calling the following numbers, any call forwarding rules related to the call are ignored.
non-provisionable-uris:
- "tel:111"
- "sip:111@example.com"Example for sas-config.yaml
deployment-config:sas:
# Whether SAS is enabled ('true') or disabled ('false')
enabled: true
# Parameters for connecting to SAS
sas-connection:
# List of SAS servers. Either IP addresses or DNS hostnames.
# SAS servers can also be discovered from MDM, so if both this VM and SAS are connected
# to MDM, these do not have to be specified.
servers:
- 10.10.10.10
- 10.10.10.11Example for shcm-service-config.yaml
# Service configuration for the Sh Cache Microservice
deployment-config:shcm-service:
##
## Diameter Sh Configuration
##
diameter-sh:
# The origin realm to use when sending messages.
origin-realm: opencloud.com
# The value to use as the destination realm.
destination-realm: opencloud
# The HSS destination peers.
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: hss.opencloud.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
# The user identity that is put in the diameter message to the HSS when a health check is performed
health-check-user-identity: sip:shcm-health-check@example.com
##
## Advanced settings - don't change unless specifically instructed
## by a Metaswitch engineer
##
# The request timeout (milliseconds) the Sh RA should use
diameter-request-timeout-milliseconds: 5000
##
## Cassandra locking configuration
##
cassandra-locking:
# The time (in milliseconds) to wait before retrying to acquire the cassandra lock. Limited to 50-5000.
backoff-time-milliseconds: 200
# The number of times to retry to acquire the cassandra lock. Limited to 1-10.
backoff-limit: 5
# The time (in milliseconds) to hold the cassandra lock. Limited to 1000-30000.
hold-time-milliseconds: 12000
##
## Caching strategy
## Every setting has both no-cache or simple-cache options, and for most settings
## subscription-cache is also available.
##
## no-cache:
## The cache functionality will not be used; every read and write will
## always query the HSS for the requested information. Subscription is
## not applicable.
## simple-cache:
## Results from HSS queries will be cached. Updates will always write
## through to the HSS. The cache will not receive updates from the HSS.
## subscription-cache:
## Results from HSS queries will be cached. Updates will always write
## through to the HSS. ShCM will subscribe to data changes in the HSS and
## cache entries will be updated if the data is modified in the HSS.
##
## Recommendation:
## Don't change the default settings below.
## However, some HSS's don't support subscriptions and for these simple-cache
## should be used.
##
## If a Cassandra database isn't available for caching then no-cache can be
## used for test purposes.
##
caching:
##
## Caching strategy: one of `no-cache, simple-cache, subscription-cache`
##
service-indications:
# Caching configuration for MMTel-Services
- service-indication: mmtel-services
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for ims-odb-information
- service-indication: ims-odb-information
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for opencloud-3rd-party-registrar
- service-indication: opencloud-3rd-party-registrar
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for metaswitch-tas-services
- service-indication: metaswitch-tas-services
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
data-references-subscription-allowed:
# Caching configuration for ims-public-identity
- data-reference: ims-public-identity
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for s-cscfname
- data-reference: s-cscfname
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for initial-filter-criteria
- data-reference: initial-filter-criteria
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for service-level-trace-info
- data-reference: service-level-trace-info
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for ip-address-secure-binding-information
- data-reference: ip-address-secure-binding-information
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for service-priority-level
- data-reference: service-priority-level
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
# Caching configuration for extended-priority
- data-reference: extended-priority
cache-strategy: subscription-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 86400
##
## Caching strategy: one of `no-cache, simple-cache`
##
data-references-subscription-not-allowed:
# Caching configuration for charging-information
- data-reference: charging-information
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for msisdn
- data-reference: msisdn
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for psi-activation
- data-reference: psiactivation
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for dsai
- data-reference: dsai
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for sms-registration-info
- data-reference: sms-registration-info
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for tads-information
- data-reference: tads-information
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for stn-sr
- data-reference: stn-sr
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for ue-srvcc-capability
- data-reference: ue-srvcc-capability
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for csrn
- data-reference: csrn
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# Caching configuration for reference-location-information
- data-reference: reference-location-information
cache-strategy: simple-cache
cache-parameters:
cache-validity-time-seconds: 3600
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for sentinel-volte-cdma-config.yaml
# This file contains the configuration for Sentinel VoLTE that is not already in a shared file.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte:
# Whether session replication is enabled.
session-replication-enabled: true
# SCC configuration.
scc:
# Whether this deployment is 'gsm' or 'cdma'.
scc-mobile-core-type: cdma
# Whether to retrieve the MSISDN from 'MSISDN' or 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'.
# If set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN', udr-included-identities MUST be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
fetch-cmsisdn-source: MSISDN
# Defines which IMS user identities to include in outgoing user data requests.
# Can be either 'IMPU' or 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
# Must be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI' if fetch-cmsisdn-source is set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'.
udr-included-identities: IMPU_AND_IMPI
# Service continuity configuration.
# This configuration is irrelevant for CDMA, but it is still required to be present.
service-continuity:
# Time (in milliseconds) to wait before we consider the ATCF update has failed.
atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds: 2000
# STN-SR.
stn-sr: "6421999999"
# Service Centralisation configuration.
service-centralisation:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
# Note that using this also requires setting 'sccp-variant: ANSI' in sgc-config.yaml.
inbound-ss7-address: type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=987654,national=true
# Add the I-CSCF to the route header of the reoriginated invite.
use-direct-icscf-routing: true
# A template string for the P-Visited-Network-Information header generated in the reorigination,
# where {mnc} and {mcc} are replaced with the MNC and MCC respectively.
# IR 65 versions 12 or earlier define this to be epc.ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org,
# while later versions define this as ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org.
generated-pvni-template: "epc.ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org"
# Police incoming originating requests, and reject attempts to hijack the call. Enabled by default.
police-originating-requests: true
# Simple IMRN pool config for mainline case.
simple-imrn-pool:
# The minimum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to maximum-correlation-id.
minimum-correlation-id: "0"
# The maximum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to (10^18-1).
maximum-correlation-id: "999"
# The number of digits the correlation ID should have.
# Minimum of number of digits in maximum-correlation-id to 18 maximum.
number-of-digits-in-correlation-id: 10
# CDMA specific configuration.
scc-cdma-service-centralisation:
# CDMA actions to be taken.
scc-cdma-actions:
# Action to take when an unexpected trigger is received.
action-on-unsupported-trigger: accessDeniedReason_terminationDenied
# Action to take when there is a failure generating a routing number.
action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number: accessDeniedReason_busy
# Default action to take on error.
default-failure-action: accessDeniedReason_serviceDenied
# Config for IMRN formation.
cdma-imrn-formation:
# The type of digits field of the IMRN generated.
imrn-type-of-digits: DIALED_OR_CALLED_PARTY_NUMBER
# The nature field of the IMRN generated.
imrn-nature-of-number: INTERNATIONAL
# The numbering plan field of the IMRN generated.
imrn-numbering-plan: TELEPHONY
# If true, reorigination is skipped if the subscriber is not registered in the IMS network.
bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered: true
# TADS configuration.
tads:
# (Optional) prefix to append to the CMSISDN, MSRN or TLDN when forming a CSRN.
# csrn-prefix:
# By default SCC TADS Routing uses the 'CMSISDN' from the HSS,
# but it can also be configured to use the 'TLDN' from the HLR.
# Valid values are 'CMSISDN' and 'TLDN'.
address-source-for-scc-tads: TLDN
# If true, the HSS must be queried for voice over PS support as part of
# the decision to attempt to route via PS.
voice-over-ps-support:
# Specifies which identities will be used for the voice over PS support
# request to the HSS.
# One of 'IMPU', 'MSISDN', 'IMPU_IMPI' and 'MSISDN_IMPI'.
request-user-identity-type: IMPU
# Allow WLAN access.
wlan-allowed: false
# The identity of the terminating device that TADS will send the request to.
# One of 'IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY', 'SIP_INSTANCE', and 'PATH_FROM_SIP_INSTANCE'
tads-identity-for-terminating-device: IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY
# The SIP response code that is returned when a session is ended due to an error.
end-session-error-code: 480
# When enabled INVITE requests destined for the CS network will be sent directly via
# the I-CSCF, bypassing the S-CSCF.
cs-routing-via-icscf: true
# Configuration for TADS sequential routing
on-sequential-routing:
# Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a potentially better forked response.
tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 5000
# List of SIP response codes that will trigger attempts of more routes after a PS attempt.
ps-fallback-response-codes: []
# Configuration for TADS parallel routing
on-parallel-routing:
# Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a final response.
parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 20000
# When enabled TADS will end all parallel forks on the first busy response (486).
release-all-legs-on-busy: false
# When present, requests destined to the CS domain will contain a Diversion header to
# suppress call diversion in the CS domain side of the call.
# suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion:
#
# # When true, use diversion counter parameter, otherwise use number of headers.
# use-diversion-counter-parameter: true
#
# # The configured diversion limit in the CS network to suppress further call diversion.
# cs-domain-diversion-limit: 1
# Configuration for MMTel services.
mmtel:
announcement:
# Media server URI, used when playing announcements
# This is distinct from mrf-uri for Conferencing
announcements-media-server-uri: sip:annc-audio@localhost:5260;lr;transport=tcp
# Each announcement needs to be configured with the following:
# id - The announcement ID that is used to correlate between services and the
# announcement that will be played.
# description - A human readable string that indicates what the announcement is for.
# announcement-url - The URL to the file on the MRF that will be played.
# duration-milliseconds - The maximum duration of the announcement (in milliseconds).
# repeat - The number of times the announcement will be repeated.
# delay-milliseconds - The delay between repeated announcements (in milliseconds).
# mimetype - The MimeType of the announcement to be played.
# interruptable - Whether or not the announcement can be interrupt by user actions.
# end-session-on-failure - Whether or not the current session should be ended if there
# is an error while playing the announcement.
# enforce-one-way-media - Whether or not the media stream should be forced to be one
# way between the MRF and the user during the announcement.
# suspend-charging - Whether or not charging should be suspended while the
# announcement is being played.
announcements:
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 21
description: "MMTel - Incoming Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_icb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 22
description: "MMTel - Anonymous Call Rejection"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_acr.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 21000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 23
description: "MMTel - Call Diversion"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_cdiv.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 5000
repeat: 1
delay-milliseconds: 0
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 24
description: "MMTel - Call Waiting"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_cw.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 600000
repeat: 500
delay-milliseconds: 10000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 25
description: "MMTel - Call Hold (Hold)"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_hold_hold.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 10000
repeat: 500
delay-milliseconds: 10000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 100
description: "OCS - Low Balance"
announcement-url: "file://charging_low.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 4000
repeat: 1
delay-milliseconds: 0
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 101
description: "OCS - Insufficient Balance"
announcement-url: "file://charging_insuf.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 102
description: "OCS - Out Of Credit"
announcement-url: "file://charging_out.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 9000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
# Default error code announcement config.
# Presence determines whether an announcement should be played to the calling party on receipt
# of any error code not explicitly listed in the error-code-announcements configuration.
# default-error-code-announcement:
# # ID of the announcement to be played on an error response.
# announcement-id: 22
# # Whether the call should be ended with a 487 response rather than the error code that
# # triggered this announcement.
# end-call-with-487-response: false
# Config for whether or not an announcement should be played to calling party on particular error codes
# error-code-announcements:
# # Each announcement is configured with the following:
# # error-code - The SIP error response code that should trigger this announcement.
# # announcement-id - The announcement ID that is to be used for this error code.
# # Cannot be specified when disable-announcement is set to true.
# # disable-announcement - Optional. If set to true, no announcement
# # will be played for the specified error code, overriding any default error
# # code announcement that may have been specified. If set to true, then
# # announcement-id must not be specified.
# # end-call-with-487-response - Once the announcement is finished should the call be
# # ended with a 487 response or the original error that triggered this announcement.
# - error-code: 486
# announcement-id: 24
# end-call-with-487-response: false
# - error-code: 488
# announcement-id: 22
# end-call-with-487-response: true
# - error-code: 489
# disable-announcement: true
# end-call-with-487-response: true
# Support for enabling or disabling specific HSS queries.
hss-queries-enabled:
# Whether to query for Operator Determined Barring Information (IMS-ODB-Information).
odb: false
# Whether to query for Metaswitch TAS Services (Metaswitch-TAS-Services).
metaswitch-tas-services: false
# Configuration for conferencing.
conferencing:
# The URI of the Media Resource Function used for Conferencing.
# This is distinct from the media-server-uri used for Announcements
# The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the MRF.
conference-mrf-uri: sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060;transport=tcp
# Should messages to the MRF be routed via the IMS, or are they allowed to be routed
# direcectly from the TAS to MRF.
route-to-mrf-via-ims: false
# The MMTel Conference MSML Schema Vendor Name.
# Used by the Conf feature to determine mapper selection
# when creating MSML documents for interaction with the MRF.
# 'Dialogic' or 'Radisys'.
msml-vendor: Radisys
# Whether to use the Re-INVITE based three-party conference flow.
enable-scc-conf-handling: true
# Decides whether the 'root' element will be a child of the 'selector' element,
# otherwise will be a child of 'videolayout'
root-on-selector: true
# A list of conference factory PSIs to use in addition to the standard conference
# factory PSIs, as per TS 23.003. They are as follows:
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.<HOME-DOMAIN>"
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org"
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ics.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org"
conference-factory-psi-aliases: []
# Maximum number of participants that are allowed in each conference call.
maximum-participants: 3
# Should video be allowed during conference calls
allow-video-conference-calls: false
# Delay (in milliseconds) after a conference ends before ConferenceView profiles are
# removed.
conference-view-removal-delay-milliseconds: 0
# Conferencing event subscription configuration.
subscription:
# Value to be used if the SUBSCRIBE message doesn't contain an Expires header.
default-subscription-expiry-seconds: 3600
# SUBSCRIBE requests with an Expires value lower than this are rejected.
min-subscription-expiry-seconds: 5
# Frequency of polls for changes to conference view.
polling-interval-seconds: 5
# Configuration for determining international and roaming status
international-and-roaming:
# Treat non-international format numbers as national.
non-international-format-number-is-national: false
# End call if no visited network.
end-call-if-no-visited-network: false
# Minimum length of destination address to set international
# and roaming status for. Destination addresses less than this
# length will not have international or roaming status set.
min-length: 0
# Configuration for analysing numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis:
# Whether to analyse numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan, using
# this to determine location information.
enable-nanp-analysis: false
# Configuration for barring and announcements of calls determined to be international
international-call-management:
# The default handling of calls determined to be international
default-international-call-management:
# Whether calls dialed without the international prefix are barred.
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: false
# The ID of the announcement to play when calls dialed without the international
# prefix are barred.
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 102
# The ID of the announcement to play to the calling party when an international
# call is made.
# international-call-announcement-id: 101
# The configuration of international NANP calls by destination
# country. Only available if North American Numbering Plan
# analysis is enabled.
# call-management-by-country-code:
# The determined ISO country code of the called party if within the NANP.
# - iso-country-code: "CA"
# Whether to bar calls to this destination that were dialled without an international prefix
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: true
# The ID of the announcement to play if calls to this destination were barred
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 102
# The ID of the announcement to play to the caller before international calls to this
# destination are connected
# international-call-announcement-id: 102
# Configuration for the communication hold feature.
communication-hold:
# Parameters for Hold response processing. If one is specified, then all should be.
# Their presence indicates bandwidth should be adjusted when a session is Held and Resumed.
# Default values taken from 3GPP TS 24.610 Rel 12.6.0 section 4.5.2.4.
bandwidth-adjustment:
# The value of the "b=AS:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-as-parameter: 0
# The value of the "b=RR:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-rr-parameter: 800
# The value of the "b=RS:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-rs-parameter: 800
# Should an announcement be played when a session is held.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when a session is held.
announcement-id: 25
# Determines how media streams for the holding party are handled while an announcement
# to the held party is in progress. Can be set to NO_HOLD, BLACK_HOLE_ONLY, or FULL_HOLD.
holding-party-media-mode: NO_HOLD
# Configuration for the communication waiting feature.
communication-waiting:
# Should an announcement be played to a calling user when communication waiting is
# applied.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when communication waiting is applied.
announcement-id: 24
# Time (in seconds) for the communication waiting timer.
timer-seconds: 0
# Configuration for privacy features.
privacy:
# Configuration for the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) feature.
originating-identification-presentation:
# When set to true, the from header of the originating INVITE will be
# anonymized if the OIP feature is not active for the subscriber.
#
# If set to 'true', this typically means that:
# - OIP is authorized for the large majority of subscribers, and that;
# - The OIP active flag is either not present in the subscriber's data
# (therefore defaulting to true), or the OIP flag is present in the
# subscriber's data (typically set to true).
# - This also implies that the OIR user-policy is set to 'None'.
#
# If set to 'false', this typically means that:
# - OIP is not 'active' or 'authorized' yet the operator desires the
# called party to see the calling party.
# - This implies that the OIR user-policy would be set to
# ANONYMIZE_FROM or ADD_USER_PRIVACY.
anonymize-from-header: true
# If true, allows History-Info header deletion.
allow-history-info-header-deletion: false
# Configuration for the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) feature.
originating-identification-restriction:
# Can be one of two values: ONLY_IDENTITY, and ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION.
# Use of ONLY_IDENTITY means the Privacy header is set to Privacy:id.
# Use of ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION means the Privacy header is set to Privacy:header.
presentation-restriction-type: ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION
# The user policy for OIR. Must be one of NONE, ANONYMIZE_FROM, and ADD_USER_PRIVACY.
user-policy: NONE
# Configuration for PSAP callback functionality.
psap-callback:
# Use the contents of the Priority header in the initial INVITE
# to determine whether the session is a PSAP callback.
use-priority-header: false
# Configuration for the SIP MESSAGE mechanism for determining PSAP callbacks.
# Presence determines whether the mechanism is used or not.
sip-message-options:
# For use when use-sip-message is set to true.
# When a SIP MESSAGE notifying that a PSAP call has taken place, this is the time
# (in seconds) after receiving that MESSAGE that sessions for the identified user are
# assumed to be a PSAP callback.
expiry-time-seconds: 86400
# For use when use-sip-message is set to true.
# If set to true, SIP MESSAGEs notifying a PSAP call will be terminated at the MMTel,
# otherwise they are propagated through the network.
terminate-message: true
# Configuration for call diversion (CDIV)
call-diversion:
# Play announcement on diversion.
announcement:
announcement-id: 23
# voicemail-announcement-id: 23
# Standard MMTel call diversion configuration
mmtel-call-diversion:
# Maximum number of diversions that may be made while
# attempting to establish a session.
max-diversions: 20
# Action to take when the maximum number of diversions is exceeded.
max-diversion-action: REJECT
# Address to divert to when max-diversions limit is reached and
# max-diversion-action is set to DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION.
# max-diversion-fixed-destination: sip:no-reply@example.com
# Time to wait (in seconds) for a reply before diverting due to a no reply rule.
# This value is the network default, and can be overridden in subscriber data.
no-reply-timeout-seconds: 20
# Whether to add orig tag when diverting a call.
add-orig-tag: true
# URIs allowed to be re-targeted to in case of max-diversions limit being reached.
# diversion-limit-exempt-uris:
# - sip:user@example.com
# Whether diversion should be suppressed if call terminates in CS domain.
suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain: false
# Whether subscriber configuration should take precedence over operator
# configuration.
prefer-subscriber: false
# Address to forward to if operator or subscriber forward-to rule has no target
# specified.
# default-target-uri: sip:user@example.com
# Additional response codes that will trigger CDIV Not-Reachable (in addition to
# those outlined in the MMTel CDIV specification).
# additional-not-reachable-status-codes:
# - 488
# Whether to allow CDIV rules with not-reachable conditions to be triggered after
# a 180 response has been received from the called-party.
allow-not-reachable-during-alerting: false
# Whether to add 'hi-target-param' of type 'mp' to the 'hi-entry' added by a
# diversion.
add-mp-param: false
# Configuration for forwarding to a voicemail server
# If present, enables forwarding to subscriber's voicemail server if all other
# connection attempts fail.
# forward-to-voicemail:
#
# # URIs of voicemail servers for which a voicemail-specific announcement may be
# # played (if specified) and for which forwarding to without allocated credit
# # can be allowed (if enabled).
# voicemail-uris:
# - sip:vms1@example.com
# - sip:vms2@example.com
#
# # Time to wait (in seconds) for a call to be successfully connected before
# # forwarding to voicemail (if enabled) or 0 to disable timer.
# forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds: 0
#
# # When to allow forwarding to voicemail when out of credit.
# # Only applies when using 'ro' for online charging
# forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: NEVER_ALLOW
# Configuration for communication barring
communication-barring:
# Configuration for incoming communication barring
incoming-communication-barring:
# Should an announcement be played when an incoming call is barred.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when an incoming call is barred.
announcement-id: 21
# (Optional) A different announcement can be played if the call is barred
# because it is from an anonymous user.
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 22
# If false, incoming call barring will ignore International and International-exHC
# rules. This is because it is not possible to accurately determine whether the
# calling party is international in all circumstances.
international-rules-active: false
# # Configuration for outgoing communication barring
# outgoing-communication-barring:
#
# # Should an announcement be played when an outgoing call is barred.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played when an outgoing call is barred.
# announcement-id: 20
# Configuration for operator communication barring
# operator-communication-barring:
# The set of operator barring rules that can be applied.
# (Optional) Only required if '../hss-queries-enabled/odb' is 'true'.
# operator-barring-rules:
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type1'
# type1:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar domain "example.com"
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="blacklist-domain">
# <cp:conditions>
# <cp:identity>
# <many domain="example.com" />
# </cp:identity>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type2'
# type2:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar international calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="bar-international">
# <cp:conditions>
# <international/>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type3'
# type3:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar roaming calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="bar-roaming">
# <cp:conditions>
# <roaming/>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type4'
# type4:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Allow audio calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="allow-audio">
# <cp:conditions>
# <media>audio</media>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>true</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
# Outgoing prefix barring configuration
# outgoing-prefix-barring:
#
# # The list of prefixes to match against when doing prefix barring
# prefixes:
#
# # The prefix barring rule for prefix '87'
# - prefix: '87'
# # List of the classifications to apply when the above prefix is matched.
# # Must refer to the name of a defined classification.
# classifications:
# - 'Operator Bar'
#
# # The list of classifications that can be applied to a prefix match
# classifications:
#
# # A barring configuration called 'Operator Bar'.
# - name: 'Operator Bar'
#
# # The minimum length of dialled digits to match against
# minimum-number-length: 5
#
# # The maximum length of dialled digits to match against
# maximum-number-length: 8
#
# # When true, the normalized number must be international and not
# # within the Home Country Code to match this classification.
# match-international: false
#
# # The barring treatment to apply if this condition matches.
# # Valid values are: 'OSBType1', 'OSBType2', 'OSBType3', 'OSBType4',
# # 'OperatorAllow', 'OperatorBar', 'PremiumRateInformation',
# # and 'PremiumRateEntertainment'.
# barring-treatment: 'OperatorBar'
#
# # Disables the outgoing-call-barring (OCB) announcement.
# # Cannot be specified alongside a prefix barring announcement.
# #disable-ocb-announcement: true
#
# # Should a different announcement be used rather than the one
# # from 'outgoing-communication-barring/announcement'
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement ID to use instead of the one from
# # `outgoing-communication-barring/announcement/announcement-id`
# announcement-id: 20
# Configuration for Vertical Service Codes
vertical-service-codes:
# Configuration for Vertical Service Codes XCAP Data Update feature
xcap-data-update:
# Internally-accessible hostname of the XCAP server.
host: xcap.internal.example
# SIP status code to respond with following a successful HTTP response.
success-response-status-code: 603
# SIP status code to respond with following an unsuccessful HTTP response.
failure-response-status-code: 409
# Whether an announcement should be played on failure.
# failure-announcement:
# # ID of the announcement to play on failure.
# announcement-id: 23
# Configuration for the SIS.
sis:
# RFC3263 unavailable peer list timer (milliseconds).
unavailable-peer-list-timer-milliseconds: "60000"
# RFC3263 failover timer (milliseconds).
failover-timer-milliseconds: "4000"
# Origin configuration for this application when connecting to the HLR.
# The actual HLR SCCP address (destination) is in the hlr-configuration.yaml file
# Uncomment this section if using the TLDN for SCC TADS Routing
hlr-connectivity-origin:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
originating-address: type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true
# The timeout value for opening the MAP dialog with the HLR (in milliseconds).
map-invoke-timeout-milliseconds: 5000
# CDMA specific configuration.
cdma:
# The market ID value to be used in the MSCID set on outgoing CDMA requests to the HLR
market-id: 1
# The switch number value to be used in the MSCID set on outgoing CDMA requests to the HLR
switch-number: 1
# Charging configuration
charging:
# Whether to enable online charging
# If disabled, then you must also remove or comment out the ro-charging section below.
cdma-online-charging-enabled: true
# When not using Diameter Ro, comment out the contents of this file down to the <<<< END ro-charging
# Also you must remove the lines from mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
ro-charging:
diameter-ro:
# The Diameter Ro release to use.
diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
# The origin realm to use when sending messages.
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
# The value to use as the destination realm.
destination-realms:
- destination-realm: metaswitch.com
peers:
- peer.metaswitch.com
# The Diameter Ro destination peers.
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
# Whether the session is permitted to continue if there is an OCS failure.
continue-session-on-ocs-failure: false
charging-announcements:
# Config for low balance announcements
low-credit-announcements:
# Low balance announcement ID to be used during call setup.
call-setup-announcement-id: 100
# Low balance announcement ID to be used after call setup.
mid-call-announcement-id: 100
# The delay (in milliseconds) before a another credit check should happen after a
# low balance announcement has occurred.
charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds: 30000
# Config for out of credit announcements.
out-of-credit-announcements:
# Out of credit announcement ID to be used during call setup.
call-setup-announcement-id: 101
# Out of credit announcement ID to be used after call setup.
mid-call-announcement-id: 102
# <<<< END ro-charging
# Whether to enable connections to Diameter Rf peer through the Diameter Rf Control RA.
# If present, Rf is enabled. Comment out to disable Rf.
# When not using Diameter Rf, comment out the contents of this file down to the <<<< END rf-charging
# Also you must remove the lines from mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
# rf-charging:
#
# diameter-rf:
#
# # The Diameter Rf release to use.
# diameter-rf-release: Vcb0
#
# # The origin realm to use when sending messages.
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The value to use as the destination realm.
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The Diameter Rf destination peers.
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: sctp
# metric: 1
# <<<< END rf-charging
# Configuration for CDRs
cdr:
# If present, interim CDRs are enabled. If Diameter Rf has been enabled, this is required.
interim-cdrs:
# Enable CDRs to go to the local filesystem
# Diameter Rf is selected separately
write-cdrs-in-filesystem: true
# Indicates whether or not to write CDRs on SDP changes.
write-cdr-on-sdp-change: true
# The maximum duration (in seconds) between timer driven interim CDRs.
# Setting this to zero will disable timer based interim CDRs.
interim-cdrs-period-seconds: 300
# Enable session CDRs.
session-cdrs-enabled: true
# Configuration for the Session Refresh feature.
session-refresh:
# The interval of the periodic timer (in seconds).
timer-interval-seconds: 30
# Period of no activity for leg tp refresh (in seconds).
refresh-period-seconds: 570
# Whether the session should be refreshed using UPDATE requests,
# as long as the endpoint allows UPDATE requests.
refresh-with-update-if-allowed: true
# Maximum allowed duration of a call (in seconds).
max-call-duration-seconds: 86400
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for sentinel-volte-gsm-config.yaml
# This file contains the configuration for Sentinel VoLTE that is not already in a shared file.
deployment-config:sentinel-volte:
# Whether session replication is enabled.
session-replication-enabled: true
# SCC configuration.
scc:
# Whether this deployment is 'gsm' or 'cdma'.
scc-mobile-core-type: gsm
# Whether to retrieve the MSISDN from 'MSISDN' or 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'.
# If set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN', udr-included-identities MUST be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
fetch-cmsisdn-source: MSISDN
# Defines which IMS user identities to include in outgoing user data requests.
# Can be either 'IMPU' or 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
# Must be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI' if fetch-cmsisdn-source is set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'.
udr-included-identities: IMPU_AND_IMPI
# Service continuity configuration.
service-continuity:
# Time (in milliseconds) to wait before we consider the ATCF update has failed.
atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds: 2000
# STN-SR.
stn-sr: "6421999999"
# Service Centralisation configuration.
service-centralisation:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
inbound-ss7-address: type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=123456,national=false
# Add the I-CSCF to the route header of the reoriginated invite.
use-direct-icscf-routing: true
# A template string for the P-Visited-Network-Information header generated in the reorigination,
# where {mnc} and {mcc} are replaced with the MNC and MCC respectively.
# IR 65 versions 12 or earlier define this to be epc.ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org,
# while later versions define this as ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org.
generated-pvni-template: "epc.ims.mnc{mnc}.mcc{mcc}.3gppnetwork.org"
# Police incoming originating requests, and reject attempts to hijack the call. Enabled by default.
police-originating-requests: true
# Simple IMRN pool config for mainline case.
simple-imrn-pool:
# The minimum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to maximum-correlation-id.
minimum-correlation-id: "0"
# The maximum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to (10^18-1).
maximum-correlation-id: "999"
# The number of digits the correlation ID should have.
# Minimum of number of digits in maximum-correlation-id to 18 maximum.
number-of-digits-in-correlation-id: 10
# GSM specific configuration.
scc-gsm-service-centralisation:
# Config for IMRN formation.
gsm-imrn-formation:
# Whether routing to an internal network number is allowed or not.
routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed: true
# The type of call, with several possible values. Used when forwarding a call.
nature: NATIONAL
# The numbering plan to be used when forwarding a call.
numbering-plan: ISDN
# If true, reorigination is skipped for terminating sessions if the subscriber
# is not registered in the IMS network.
bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered: true
# If true, roaming terminating sessions will always be reoriginated (regardless
# of ims registration)
always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming: false
# TADS configuration.
tads:
# (Optional) prefix to append to the CMSISDN, MSRN or TLDN when forming a CSRN.
# csrn-prefix:
# By default SCC TADS Routing uses the 'CMSISDN' from the HSS,
# but it can also be configured to use the 'MSRN' from the HLR.
# Valid values are 'CMSISDN' and 'MSRN'.
address-source-for-scc-tads: CMSISDN
# If true, the HSS must be queried for voice over PS support as part of
# the decision to attempt to route via PS.
voice-over-ps-support:
# Specifies which identities will be used for the voice over PS support
# request to the HSS.
# One of 'IMPU', 'MSISDN', 'IMPU_IMPI' and 'MSISDN_IMPI'.
request-user-identity-type: IMPU
# Allow WLAN access.
wlan-allowed: false
# The identity of the terminating device that TADS will send the request to.
# One of 'IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY', 'SIP_INSTANCE', and 'PATH_FROM_SIP_INSTANCE'
tads-identity-for-terminating-device: IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY
# The SIP response code that is returned when a session is ended due to an error.
end-session-error-code: 480
# When enabled INVITE requests destined for the CS network will be sent directly via
# the I-CSCF, bypassing the S-CSCF.
cs-routing-via-icscf: true
# Configuration for TADS sequential routing
on-sequential-routing:
# Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a potentially better forked response.
tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 5000
# List of SIP response codes that will trigger attempts of more routes after a PS attempt.
ps-fallback-response-codes: []
# Configuration for TADS parallel routing
on-parallel-routing:
# Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a final response.
parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds: 20000
# When enabled TADS will end all parallel forks on the first busy response (486).
release-all-legs-on-busy: false
# Configuration for SRI requests sent to the HLR
sri-requests-to-hlr:
# If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR the feature will set the suppress T-CSI flag on the request
set-suppress-tcsi-flag: false
# If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR on a terminating call the feature
# will set the 'Suppression of Announcement' flag on the request.
set-suppress-announcement-flag: false
# When present, requests destined to the CS domain will contain a Diversion header to
# suppress call diversion in the CS domain side of the call.
# suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion:
#
# # When true, use diversion counter parameter, otherwise use number of headers.
# use-diversion-counter-parameter: true
#
# # The configured diversion limit in the CS network to suppress further call diversion.
# cs-domain-diversion-limit: 1
# Configuration for MMTel services.
mmtel:
announcement:
# Media server URI, used when playing announcements
# This is distinct from mrf-uri for Conferencing
announcements-media-server-uri: sip:annc-audio@localhost:5260;lr;transport=tcp
# Each announcement needs to be configured with the following:
# id - The announcement ID that is used to correlate between services and the
# announcement that will be played.
# description - A human readable string that indicates what the announcement is for.
# announcement-url - The URL to the file on the MRF that will be played.
# duration-milliseconds - The maximum duration (in milliseconds) of the announcement.
# repeat - The number of times the announcement will be repeated.
# delay-milliseconds - The delay (in milliseconds) between repeated announcements.
# mimetype - The MimeType of the announcement to be played.
# interruptable - Whether or not the announcement can be interrupt by user actions.
# end-session-on-failure - Whether or not the current session should be ended if there
# is an error while playing the announcement.
# enforce-one-way-media - Whether or not the media stream should be forced to be one
# way between the MRF and the user during the announcement.
# suspend-charging - Whether or not charging should be suspended while the
# announcement is being played.
announcements:
- id: 20
description: "MMTel - Outgoing Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_ocb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 21
description: "MMTel - Incoming Call Barring"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_icb.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 22
description: "MMTel - Anonymous Call Rejection"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_acr.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 21000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 23
description: "MMTel - Call Diversion"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_cdiv.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 5000
repeat: 1
delay-milliseconds: 0
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 24
description: "MMTel - Call Waiting"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_cw.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 600000
repeat: 500
delay-milliseconds: 10000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 25
description: "MMTel - Call Hold (Hold)"
announcement-url: "file://mmtel_hold_hold.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 10000
repeat: 500
delay-milliseconds: 10000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 100
description: "OCS - Low Balance"
announcement-url: "file://charging_low.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 4000
repeat: 1
delay-milliseconds: 0
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 101
description: "OCS - Insufficient Balance"
announcement-url: "file://charging_insuf.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 13000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: false
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
- id: 102
description: "OCS - Out Of Credit"
announcement-url: "file://charging_out.3gp"
duration-milliseconds: 9000
repeat: 2
delay-milliseconds: 1000
mimetype: "audio/3gpp"
interruptable: true
end-session-on-failure: false
enforce-one-way-media: false
suspend-charging: false
# Default error code announcement config.
# Presence determines whether an announcement should be played to the calling party on receipt
# of any error code not explicitly listed in the error-code-announcements configuration.
# default-error-code-announcement:
# # ID of the announcement to be played on an error response.
# announcement-id: 22
# # Whether the call should be ended with a 487 response rather than the error code that
# # triggered this announcement.
# end-call-with-487-response: false
# Config for whether or not an announcement should be played to calling party on particular error codes
# error-code-announcements:
# # Each announcement is configured with the following:
# # error-code - The SIP error response code that should trigger this announcement.
# # announcement-id - The announcement ID that is to be used for this error code.
# # Cannot be specified when disable-announcement is set to true.
# # disable-announcement - Optional. If set to true, no announcement
# # will be played for the specified error code, overriding any default error
# # code announcement that may have been specified. If set to true, then
# # announcement-id must not be specified.
# # end-call-with-487-response - Once the announcement is finished should the call be
# # ended with a 487 response or the original error that triggered this announcement.
# - error-code: 486
# announcement-id: 24
# end-call-with-487-response: false
# - error-code: 488
# announcement-id: 22
# end-call-with-487-response: true
# - error-code: 489
# disable-announcement: true
# end-call-with-487-response: true
# Support for enabling or disabling specific HSS queries.
hss-queries-enabled:
# Whether to query for Operator Determined Barring Information (IMS-ODB-Information).
odb: false
# Whether to query for Metaswitch TAS Services (Metaswitch-TAS-Services).
metaswitch-tas-services: false
# When the roaming status is unknown the HLR can be used to try to determine the roaming status
# of a subscriber by sending an ATI query to it.
determine-roaming-from-hlr: true
# Configuration for conferencing.
conferencing:
# The URI of the Media Resource Function used for Conferencing.
# This is distinct from the media-server-uri used for Announcements
# The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the MRF.
conference-mrf-uri: sip:mrf@mrfhost.example:5060;transport=tcp
# Should messages to the MRF be routed via the IMS, or are they allowed to be routed
# direcectly from the TAS to MRF.
route-to-mrf-via-ims: false
# The MMTel Conference MSML Schema Vendor Name.
# Used by the Conf feature to determine mapper selection
# when creating MSML documents for interaction with the MRF.
# 'Dialogic' or 'Radisys'.
msml-vendor: Radisys
# Whether to use the Re-INVITE based three-party conference flow.
enable-scc-conf-handling: true
# Decides whether the 'root' element will be a child of the 'selector' element,
# otherwise will be a child of 'videolayout'
root-on-selector: true
# A list of conference factory PSIs to use in addition to the standard conference
# factory PSIs, as per TS 23.003. They are as follows:
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.<HOME-DOMAIN>"
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org"
# "sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ics.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org"
conference-factory-psi-aliases: []
# Maximum number of participants that are allowed in each conference call.
maximum-participants: 3
# Should video be allowed during conference calls
allow-video-conference-calls: false
# Delay (in milliseconds) after a conference ends before ConferenceView profiles are
# removed.
conference-view-removal-delay-milliseconds: 0
# Conferencing event subscription configuration.
subscription:
# Value to be used if the SUBSCRIBE message doesn't contain an Expires header.
default-subscription-expiry-seconds: 3600
# SUBSCRIBE requests with an Expires value lower than this are rejected.
min-subscription-expiry-seconds: 5
# Frequency of polls for changes to conference view.
polling-interval-seconds: 5
# Configuration for determining international and roaming status
international-and-roaming:
# Treat non-international format numbers as national.
non-international-format-number-is-national: false
# End call if no visited network.
end-call-if-no-visited-network: false
# Use different configuration for each access network MCC.
# Set to false to use the default configuration.
use-mcc-specific: false
# Minimum length of destination address to set international
# and roaming status for. Destination addresses less than this
# length will not have international or roaming status set.
min-length: 0
# Configuration for analysing numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan.
north-american-numbering-plan-analysis:
# Whether to analyse numbers according to the North American Numbering Plan, using
# this to determine location information.
enable-nanp-analysis: false
# Configuration for barring and announcements of calls determined to be international
international-call-management:
# The default handling of calls determined to be international
default-international-call-management:
# Whether calls dialed without the international prefix are barred.
bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: false
# The ID of the announcement to play when calls dialed without the international
# prefix are barred.
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 102
# The ID of the announcement to play to the calling party when an international
# call is made.
# international-call-announcement-id: 101
# The configuration of international NANP calls by destination
# country. Only available if North American Numbering Plan
# analysis is enabled.
# call-management-by-country-code:
# The determined ISO country code of the called party if within the NANP.
# - iso-country-code: "CA"
# Whether to bar calls to this destination that were dialled without an international prefix
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix: true
# The ID of the announcement to play if calls to this destination were barred
# bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id: 102
# The ID of the announcement to play to the caller before international calls to this
# destination are connected
# international-call-announcement-id: 102
# Configuration for the communication hold feature.
communication-hold:
# Parameters for Hold response processing. If one is specified, then all should be.
# Their presence indicates bandwidth should be adjusted when a session is Held and Resumed.
# Default values taken from 3GPP TS 24.610 Rel 12.6.0 section 4.5.2.4.
bandwidth-adjustment:
# The value of the "b=AS:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-as-parameter: 0
# The value of the "b=RR:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-rr-parameter: 800
# The value of the "b=RS:" parameter to use when processing a Hold response.
b-rs-parameter: 800
# Should an announcement be played when a session is held.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when a session is held.
announcement-id: 25
# Determines how media streams for the holding party are handled while an announcement
# to the held party is in progress. Can be set to NO_HOLD, BLACK_HOLE_ONLY, or FULL_HOLD.
holding-party-media-mode: NO_HOLD
# Configuration for the communication waiting feature.
communication-waiting:
# Should an announcement be played to a calling user when communication waiting is
# applied.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when communication waiting is applied.
announcement-id: 24
# Time (in seconds) for the communication waiting timer.
timer-seconds: 0
# Configuration for privacy features.
privacy:
# Configuration for the Originating Identification Presentation (OIP) feature.
originating-identification-presentation:
# When set to true, the from header of the originating INVITE will be
# anonymized if the OIP feature is not active for the subscriber.
#
# If set to 'true', this typically means that:
# - OIP is authorized for the large majority of subscribers, and that;
# - The OIP active flag is either not present in the subscriber's data
# (therefore defaulting to true), or the OIP flag is present in the
# subscriber's data (typically set to true).
# - This also implies that the OIR user-policy is set to 'None'.
#
# If set to 'false', this typically means that:
# - OIP is not 'active' or 'authorized' yet the operator desires the
# called party to see the calling party.
# - This implies that the OIR user-policy would be set to
# ANONYMIZE_FROM or ADD_USER_PRIVACY.
anonymize-from-header: true
# If true, allows History-Info header deletion.
allow-history-info-header-deletion: false
# Configuration for the Originating Identification Restriction (OIR) feature.
originating-identification-restriction:
# Can be one of two values: ONLY_IDENTITY, and ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION.
# Use of ONLY_IDENTITY means the Privacy header is set to Privacy:id.
# Use of ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION means the Privacy header is set to Privacy:header.
presentation-restriction-type: ALL_PRIVATE_INFORMATION
# The user policy for OIR. Must be one of NONE, ANONYMIZE_FROM, and ADD_USER_PRIVACY.
user-policy: NONE
# Configuration for PSAP callback functionality.
psap-callback:
# Use the contents of the Priority header in the initial INVITE
# to determine whether the session is a PSAP callback.
use-priority-header: false
# Configuration for the SIP MESSAGE mechanism for determining PSAP callbacks.
# Presence determines whether the mechanism is used or not.
sip-message-options:
# For use when use-sip-message is set to true.
# When a SIP MESSAGE notifying that a PSAP call has taken place, this is the time
# (in seconds) after receiving that MESSAGE that sessions for the identified user are
# assumed to be a PSAP callback.
expiry-time-seconds: 86400
# For use when use-sip-message is set to true.
# If set to true, SIP MESSAGEs notifying a PSAP call will be terminated at the MMTel,
# otherwise they are propagated through the network.
terminate-message: true
# Configuration for call diversion (CDIV)
call-diversion:
# Play announcement on diversion.
announcement:
announcement-id: 23
# voicemail-announcement-id: 23
# Standard MMTel call diversion configuration
mmtel-call-diversion:
# Maximum number of diversions that may be made while
# attempting to establish a session.
max-diversions: 20
# Action to take when the maximum number of diversions is exceeded.
# Must be one of:
# REJECT, DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION, DELIVER_TO_SUBSCRIBERS_VOICEMAIL_SERVER
max-diversion-action: REJECT
# Address to divert to when max-diversions limit is reached and
# max-diversion-action is set to DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION.
# max-diversion-fixed-destination: sip:no-reply@example.com
# Time to wait (in seconds) for a reply before diverting due to a no reply rule.
# This value is the network default, and can be overridden in subscriber data.
no-reply-timeout-seconds: 20
# Whether to add orig tag when diverting a call.
add-orig-tag: true
# URIs allowed to be re-targeted to in case of max-diversions limit being reached.
# diversion-limit-exempt-uris:
# - sip:user@example.com
# Whether diversion should be suppressed if call terminates in CS domain.
suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain: false
# Whether subscriber configuration should take precedence over operator
# configuration.
prefer-subscriber: false
# Address to forward to if operator or subscriber forward-to rule has no target
# specified.
# default-target-uri: sip:user@example.com
# Additional response codes that will trigger CDIV Not-Reachable (in addition to
# those outlined in the MMTel CDIV specification).
# additional-not-reachable-status-codes:
# - 488
# Whether to allow CDIV rules with not-reachable conditions to be triggered after
# a 180 response has been received from the called-party.
allow-not-reachable-during-alerting: false
# Whether to add 'hi-target-param' of type 'mp' to the 'hi-entry' added by a
# diversion.
add-mp-param: false
# Configuration for forwarding to a voicemail server
# If present, enables forwarding to subscriber's voicemail server if all other
# connection attempts fail.
# forward-to-voicemail:
#
# # URIs of voicemail servers for which a voicemail-specific announcement may be
# # played (if specified) and for which forwarding to without allocated credit
# # can be allowed (if enabled).
# voicemail-uris:
# - sip:vms1@example.com
# - sip:vms2@example.com
#
# # Time to wait (in seconds) for a call to be successfully connected before
# # forwarding to voicemail (if enabled) or 0 to disable timer.
# forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds: 0
#
# # When to allow forwarding to voicemail when out of credit.
# # Only specified when using 'ro' for online charging.
# # Must be one of:
# # NEVER_ALLOW, ALLOW_ONLY_FOR_WELL_KNOWN_SERVERS, ALWAYS_ALLOW
# forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit: NEVER_ALLOW
# Configuration for communication barring
communication-barring:
# Configuration for incoming communication barring
incoming-communication-barring:
# Should an announcement be played when an incoming call is barred.
announcement:
# The announcement to be played when an incoming call is barred.
announcement-id: 21
# (Optional) A different announcement can be played if the call is barred
# because it is from an anonymous user.
anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id: 22
# If false, incoming call barring will ignore International and International-exHC
# rules. This is because it is not possible to accurately determine whether the
# calling party is international in all circumstances.
international-rules-active: false
# # Configuration for outgoing communication barring
# outgoing-communication-barring:
#
# # Should an announcement be played when an outgoing call is barred.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played when an outgoing call is barred.
# announcement-id: 20
# Configuration for operator communication barring
# operator-communication-barring:
# The set of operator barring rules that can be applied.
# (Optional) Only required if '../hss-queries-enabled/odb' is 'true'.
# operator-barring-rules:
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type1'
# type1:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar domain "example.com"
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="blacklist-domain">
# <cp:conditions>
# <cp:identity>
# <many domain="example.com" />
# </cp:identity>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type2'
# type2:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar international calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="bar-international">
# <cp:conditions>
# <international/>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type3'
# type3:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Bar roaming calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="bar-roaming">
# <cp:conditions>
# <roaming/>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>false</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
#
# # Operator barring rule for 'Type4'
# type4:
#
# # The barring rule to be applied
# rule: # Allow audio calls
# <cp:ruleset xmlns="http://uri.etsi.org/ngn/params/xml/simservs/xcap"
# xmlns:cp="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:common-policy">
# <cp:rule id="allow-audio">
# <cp:conditions>
# <media>audio</media>
# </cp:conditions>
# <cp:actions>
# <allow>true</allow>
# </cp:actions>
# </cp:rule>
# </cp:ruleset>
#
# # Should the call be redirected when barred by this rule.
# retarget:
#
# # The URI to redirect the barred call to.
# retarget-uri: sip:retarget@retargethost.example:5060
#
# # Should an announcement be played when the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement to be played if the call is barred by this rule.
# announcement-id: 20
#
# # If we retarget the call, should online charging be disabled.
# disable-online-charging-on-retarget: false
# Outgoing prefix barring configuration
# outgoing-prefix-barring:
#
# # The list of prefixes to match against when doing prefix barring
# prefixes:
#
# # The prefix barring rule for prefix '87'
# - prefix: '87'
# # List of the classifications to apply when the above prefix is matched.
# # Must refer to the name of a defined classification.
# classifications:
# - 'Operator Bar'
#
# # The list of classifications that can be applied to a prefix match
# classifications:
#
# # A barring configuration called 'Operator Bar'.
# - name: 'Operator Bar'
#
# # The minimum length of dialled digits to match against
# minimum-number-length: 5
#
# # The maximum length of dialled digits to match against
# maximum-number-length: 8
#
# # When true, the normalized number must be international and not
# # within the Home Country Code to match this classification.
# match-international: false
#
# # The barring treatment to apply if this condition matches.
# # Valid values are: 'OSBType1', 'OSBType2', 'OSBType3', 'OSBType4',
# # 'OperatorAllow', 'OperatorBar', 'PremiumRateInformation',
# # and 'PremiumRateEntertainment'.
# barring-treatment: 'OperatorBar'
#
# # Disables the outgoing-call-barring (OCB) announcement.
# # Cannot be specified alongside a prefix barring announcement.
# #disable-ocb-announcement: true
#
# # Should a different announcement be used rather than the one
# # from 'outgoing-communication-barring/announcement'
# announcement:
#
# # The announcement ID to use instead of the one from
# # `outgoing-communication-barring/announcement/announcement-id`
# announcement-id: 20
# Configuration for Vertical Service Codes
vertical-service-codes:
# Configuration for Vertical Service Codes XCAP Data Update feature
xcap-data-update:
# Internally-accessible hostname of the XCAP server.
host: xcap.internal.example
# SIP status code to respond with following a successful HTTP response.
success-response-status-code: 603
# SIP status code to respond with following an unsuccessful HTTP response.
failure-response-status-code: 409
# Whether an announcement should be played on failure.
# failure-announcement:
# # ID of the announcement to play on failure.
# announcement-id: 23
# Configuration for the third party registrar.
registrar:
# The registrar can either use the HSS (hsscache) or Cassandra (cassandra) for data storage.
data-storage-type: cassandra
# The type of user identity to use when creating Sh requests for the STN-SR.
user-identity-type-for-stn-sr-request: PUBLIC_ID
# Whether the user's IMS Private ID should be included in Sh requests for the STN-SR.
include-private-id-in-stn-sr-request: false
# Configuration for the SIS.
sis:
# RFC3263 unavailable peer list timer (milliseconds).
unavailable-peer-list-timer-milliseconds: "60000"
# RFC3263 failover timer (milliseconds).
failover-timer-milliseconds: "4000"
# Origin configuration for this application when connecting to the HLR.
# The actual HLR SCCP address (destination) is in the hlr-configuration.yaml file
hlr-connectivity-origin:
# The SCCP address of the Sentinel VoLTE AS.
originating-address: type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=147,national=false
# The timeout value for opening the MAP dialog with the HLR (in milliseconds).
map-invoke-timeout-milliseconds: 5000
# GSM specific configuration.
gsm:
# The address of the MLC (Sentinel).
mlc-address: address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN
# Indicates if 'hlr-config/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR address, or have
# its digit's replaced with the MSISDN of the subscriber.
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: true
# Originating SCCP address when acting as an MSC, used when
# establishing the MAP dialog. Will default to the value of
# 'originating-address' when not present. Typically used to set a
# different originating SSN when sending a SendRoutingInformation
# message to the HLR.
# msc-originating-address: type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=148,national=false
# Charging configuration
charging:
# Online charging type to use. One of 'ro', 'cap', 'cap-ro', and 'disabled'.
# If ro is chosen, the peers should be configured in the diameter-ro section below.
# If cap or disabled is chosen, then you must also remove or comment out the
# diameter-ro section below.
# If cap-ro is chosen, then both the diameter-ro and camel sections should be updated
gsm-online-charging-type: ro
# When not using Diameter Ro, comment out the contents of this file down to the <<<< END ro-charging
# Also you must remove the lines from mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
ro-charging:
diameter-ro:
# The Diameter Ro release to use.
diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
# The origin realm to use when sending messages.
origin-realm: metaswitch.com
# The value to use as the destination realm.
destination-realms:
- destination-realm: metaswitch.com
peers:
- peer.metaswitch.com
# The Diameter Ro destination peers.
destination-peers:
- destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
port: 3868
protocol-transport: aaa
metric: 1
# Whether the session is permitted to continue if there is an OCS failure.
continue-session-on-ocs-failure: false
charging-announcements:
# Config for low balance announcements
low-credit-announcements:
# Low balance announcement ID to be used during call setup.
call-setup-announcement-id: 100
# Low balance announcement ID to be used after call setup.
mid-call-announcement-id: 100
# The delay (in milliseconds) before a another credit check should happen after a
# low balance announcement has occurred.
charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds: 30000
# Config for out of credit announcements.
out-of-credit-announcements:
# Out of credit announcement ID to be used during call setup.
call-setup-announcement-id: 101
# Out of credit announcement ID to be used after call setup.
mid-call-announcement-id: 102
# <<<< END ro-charging
# Whether to enable connections to Diameter Rf peer through the Diameter Rf Control RA.
# If present, Rf is enabled. Comment out to disable Rf.
# When not using Diameter Rf, comment out the contents of this file down to the <<<< END rf-charging
# Also you must remove the lines from mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
# rf-charging:
#
# diameter-rf:
#
# # The Diameter Rf release to use.
# diameter-rf-release: Vcb0
#
# # The origin realm to use when sending messages.
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The value to use as the destination realm.
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The Diameter Rf destination peers.
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: sctp
# metric: 1
# <<<< END rf-charging
# When not using CAP charging, comment out the contents of this file down to the <<<< END cap-charging
# cap-charging:
#
# # Configuration for the IM-SSF.
# imssf:
# # When using CAP charging and GSM, the IMCSI can be fetched from the HLR and provided to the IMSSF
# # in the originating and/or terminating case.
# # Comment out the whole section to disable for both originating and terminating calls.
# imcsi-fetching:
# # The requested Trigger Detection Point for originating calls, which determines whether
# # T_CSI or O_CSI is requested from the HLR.
# # Values of '2' or '3' will request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other values
# # are not valid.
# # Comment out to disable for originating calls.
# originating-tdp: 2
#
# # The requested Trigger Detection Point for terminating calls, which determines whether
# # T_CSI or O_CSI is requested from the HLR.
# # Values of '2' or '3' will request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other values
# # are not valid.
# # Comment out to disable for terminating calls.
# terminating-tdp: 12
#
# # Configuration for the charging GT (global title) that is sent to the SCP.
# charging-gt:
# # The format template to use when creating Charging GTs (global title). It must
# # be a digit string except for tokens ('{iso}', '{mcc}', '{mnc}) which are
# # substituted in.
# format: "6422142{iso}"
#
# # The Charging GT (global title) to use when one could not be generated because
# # the user’s location could not be determined.
# unknown-location: "64221429090"
#
# # The SCCP address of the GSM charging SCP.
# scf-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=6,ssn=156"
# <<<< END cap-charging
# Configuration for CDRs
cdr:
# If present, interim CDRs are enabled. If Diameter Rf has been enabled, this is required.
interim-cdrs:
# Enable CDRs to go to the local filesystem
# Diameter Rf is selected separately
write-cdrs-in-filesystem: true
# Indicates whether or not to write CDRs on SDP changes.
write-cdr-on-sdp-change: true
# The maximum duration (in seconds) between timer driven interim CDRs.
# Setting this to zero will disable timer based interim CDRs.
interim-cdrs-period-seconds: 300
# Enable session CDRs.
session-cdrs-enabled: true
# Configuration for the Session Refresh feature.
session-refresh:
# The interval of the periodic timer (in seconds).
timer-interval-seconds: 30
# Period of no activity for leg tp refresh (in seconds).
refresh-period-seconds: 570
# Whether the session should be refreshed using UPDATE requests,
# as long as the endpoint allows UPDATE requests.
refresh-with-update-if-allowed: true
# Maximum allowed duration of a call (in seconds).
max-call-duration-seconds: 86400
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for hlr-config.yaml
# This file contains Home Location Register (HLR) configuration.
# This file must be present alongside the other Rhino VoLTE TAS YAML configuration files on the
# SIMPL server, regardless of whether the HLR is enabled or disabled.
deployment-config:hlr:
hlr-address: "type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=6,national=false"Example for icscf-config.yaml
# This file contains Interrogating Call Service Control Function (I-CSCF) configuration.
deployment-config:icscf:
# The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function.
# For MMT, the Conf and ECT features will automatically add an "lr" parameter to it.
# The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or the IP address of the I-CSCF.
i-cscf-uri: sip:icscf@icscfhost.example:5060Example for sgc-config.yaml
# This file contains configuration for the OCSS7 SGC.
deployment-config:sgc:
sgcenv:
# The port to bind to for JMX service, used by the CLI and MXBeans.
jmx-port: 10111
hazelcast:
# If omitted, backup-count defaults to N-1, where N is number of SMO nodes.
# Don't uncomment, unless support instructs you to.
# backup-count: 1
password: xxxxxxxx
# Only change SGC properties if support instructs you to
#sgc-properties:
# properties:
# - name: com.cts.ss7.shutdown.gracefulWait
# value: '30000'
m3ua:
# The default port to bind for this local M3UA endpoint.
local-port: 2905
# # Normally each node in an SGC cluster will use the same port for its local M3UA endpoint.
# # However, some configurations require that each node uses a different local port.
# # Uncomment and configure if required. For 'node-index', '1' is the first SMO node, '2' the
# # second and so on. Any nodes not configured here will use the global default 'local-port'
# # above.
# per-node-local-port:
# - node-index: 2
# local-port: 2906
# - node-index: 3
# local-port: 2907
# The SCCP variant to configure this SGC to use.
# Can be either: ITU or ANSI
sccp-variant: ITU
# This cluster's signaling point code.
# If specifying a single integer (for ITU point codes), be sure to quote it
# along with all other point codes in this file.
point-code: "5"
remote:
peers:
- id: 'STP-1'
remote-ips:
# The index of the SMO node that hosts the SGC that will be
# connected to this IP set. '1' is the first SMO node,
# '2' is the second, and so on. '-1' indicates that all
# SGC nodes in the cluster will use this remote IP set.
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.14.144.71
- 10.14.144.134
# The remote port for this M3UA association.
port: 2906
# The AS to which this connection belongs.
application-servers:
- as-id: 'NN-AS'
- id: 'STP-2'
remote-ips:
- node-index: -1
ips:
- 10.14.144.81
- 10.14.144.144
port: 2906
application-servers:
- as-id: 'NN-AS'
application-servers:
- id: 'NN-AS'
routes:
default-priority: 5
# The DPC identifiers applicable to this route.
dpc-ids:
- id: 'alias-2-233-3'
- id: 'NN-AS2'
routes:
default-priority: 0
# The DPC identifiers applicable to this route.
dpc-ids:
- id: 'alias-2-233-3'
precond-ssns:
- 2
- 3
dpcs:
- id: 'alias-2-233-3'
dpc: "5963"
# maximum unsegmented SCCP message size to send to this
# destination as a single unsegmented message
muss: 252
# maximum user data length per segment to send to this
# destination
mss: 245
cpcs:
- dpc: "5963"
# The local SSNs to monitor.
ssns:
- 8
- 146
global-title:
# For this example:
# Match everything and send to the single alias point code.
outbound:
matchers:
defaults:
natofaddr: 0
numplan: 7
trtype: 129
rules:
- id: '1'
is-prefix: false
translations:
- 'all'
translations:
- id: 'all'
dpc: "5963"
priority: 5
# # Example rewriter would take all translation rules that
# # use the 'example' rewriter, replace the digits with
# # '123456', and set translated messages to route on the SSN.
# rewriters:
# - id: 'example'
# addrinfo: '123456'
# route-on: 'SSN'
# Inbound translation has only matching rules.
# If an address is matched, it is sent to the
# configured SSN
inbound:
- id: 'to-sentinel-volte-gsm'
addrinfo: '123456'
is-prefix: false
natofaddr: 4
numplan: 1
trtype: 0
ssn: 146
- id: 'to-sentinel-volte-cdma'
addrinfo: '987654'
is-prefix: false
trtype: 0
ssn: 146Example for sentinel-ipsmgw-config.yaml
# This file contains the configuration for Sentinel IPSMGW that is not already in a shared file.
deployment-config:sentinel-ipsmgw:
# Geo-redundancy configuration.
# Comment out, or remove this section to disable geo-redundancy.
# georedundancy:
# # The number of IPSMGW sites
# total-sites: 2
# MAP messaging configuration
map-messaging:
# Template SMSC address. The digits are replaced by those of the received SMSC address.
template-smsc-address: type=C7,ri=gt,digits=0,ssn=8,national=false,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0
# IPSMGW SCCP address.
originating-address: type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=5,ssn=148,national=false
# IPSMGW as msc address.
ipsmgw-as-msc-address: "address=653333333,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numberingPlan=ISDN"
# Indicates if 'hlr-config/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR address, or have its
# digits replaced with the MSISDN of the subscriber.
use-msisdn-as-hlr-address: false
# If true, no MAP messages will be sent to the HLR.
# Can only be set to true when 'delivery-order' is 'PS_ONLY'
suppress-hlr-interaction: false
# When accepting an OpenRequest, the SCCP responder address in theOpenAccept will, by
# default, be set to the value of the SCCP called party in the OpenRequest.
# If `UseGtAsCallingParty` is set to true, and if the received sccp-called-party contains a
# global title, then the global title will be used.
use-gt-as-calling-party: false
# If the length of the message content falls within the configured maximum then send the
# ForwardSM as part of the TC-BEGIN.
# As a special case a configured max size of 0 disables this functionality regardless of the
# actual content length.
sms-content-size-threshold: 0
# If true, specify the SmDeliveryNotIntended flag when performing an SRI for SM IMSI-only
# query (i.e. during SMMA callflows).
sri-sm-delivery-not-intended: false
# The domain name used in SIP URIs on IPSMGW-generated outbound requests.
terminating-domain: metaswitch.com
# The delivery order for mobile-terminating messages.
# Choices are PS_THEN_CS, CS_THEN_PS, PS_ONLY or CS_ONLY.
# PS stands for "packet-switched network" (i.e. IMS network).
# CS stands for "circuit-switched network".
delivery-order: PS_THEN_CS
# Charging options.
charging-options:
# Whether to enable charging for mobile-terminating PS messages.
mt-ps-enabled: false
# Whether to enable charging for mobile-terminating CS messages.
mt-cs-enabled: false
# Whether to enable charging for mobile-originating PS messages.
mo-ps-enabled: false
# Only required if one of the charging options is enabled.
# You must also specify the per-node-diameter-ro configuration in smo-vmpool-config.yaml
# diameter-ro:
# # The Diameter Ro release to use.
# diameter-ro-release: Vcb0
#
# # The origin realm to use when sending messages.
# origin-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The value to use as the destination realm.
# destination-realm: metaswitch.com
#
# # The Diameter Ro destination peers.
# destination-peers:
# - destination-hostname: peer.metaswitch.com
# port: 3868
# protocol-transport: aaa
# metric: 1
# Presence enables UE reachability notifications.
ue-reachability-notifications:
# Reachability notification subscription expiry time (in seconds).
subscription-expiry-time-seconds: 3600
# MCC/MNC used by the Correlation RA to generate a Correlation IMSI when the terminating
# subscriber's routing info cannot be determined. Must match one of the PLMNIDs in
# the home network configuration.
correlation-ra-plmnid:
mcc: "001"
mnc: "01"
# Fallback control for message delivery.
fallback-settings:
# Timeout (in milliseconds) before falling back to the other network type.
fallback-timer-milliseconds: 5000
# List of error codes which will prevent fallback from PS to CS.
avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs:
- 22
# List of error codes which will prevent fallback from CS to PS.
avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps: []
# SCCP allowed GT prefixes.
sccp-allowlist: []
# Configuration for USSI functions
# ussi:
#
# # Should all USSI messages be rejected with a default message.
# # Remove or comment out this section to allow USSI messages to be processed.
# reject-all-with-default-message:
#
# # The language of the message to be sent in the USSI response
# language: "en"
#
# # The message to be sent in the USSI response
# message: "Please visit www.example.com"
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for mag-overrides.yaml
# This file contains low-level Rhino configuration.
# Use only on advice of your Customer Care representative.
# If this file is not in use, you don't have to upload it to CDS.
rhino-config:config-bundle:
format: partial
schema-version: '1.0'
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''Example for shcm-overrides.yaml
# This file contains low-level Rhino configuration.
# Use only on advice of your Customer Care representative.
# If this file is not in use, you don't have to upload it to CDS.
rhino-config:config-bundle:
format: partial
schema-version: '1.0'
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''Example for mmt-cdma-overrides.yaml
# This file contains low-level Rhino configuration.
# Use only on advice of your Customer Care representative.
# If this file is not in use, you don't have to upload it to CDS.
rhino-config:config-bundle:
format: partial
schema-version: '1.0'
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''Example for mmt-gsm-overrides.yaml
# This file contains low-level Rhino configuration.
# Use only on advice of your Customer Care representative.
# If this file is not in use, you don't have to upload it to CDS.
rhino-config:config-bundle:
format: partial
schema-version: '1.0'
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''Example for smo-overrides.yaml
# This file contains low-level Rhino configuration.
# Use only on advice of your Customer Care representative.
# If this file is not in use, you don't have to upload it to CDS.
rhino-config:config-bundle:
format: partial
schema-version: '1.0'
rhino-config:rhino-configuration:
namespaces:
- name: ''Example for mag-vmpool-config.yaml
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "MAG cluster"
# there are some pieces of software on this VM type that require clustering and
# knowing each other's IP addresses, for example Rhino
deployment-config:mag-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
xcap-domains:
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc123.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.org
- xcap.site1.ims.mnc124.mcc530.pub.3gppnetwork.org
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
# Define one or more REM users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# each REM user maps to a Rhino user, when REM logs into Rhino
rem-auth:
- username: remreadonly
real-name: REM read only user
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-mag-1
rhino-node-id: 101
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag1.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mag-2
rhino-node-id: 102
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag2.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mag-3
rhino-node-id: 103
diameter-zh-origin-host: mag3.mag.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# DO NOT ENABLE IN PRODUCTION
# Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during acceptance testing
rem-debug-logging-enabled: falseExample for mmt-cdma-vmpool-config.yaml
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "MMT cluster"
# there are some pieces of software on this VM type that require clustering and
# knowing each other's IP addresses, for example Rhino
deployment-config:mmt-cdma-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-mmt-cdma-1
rhino-node-id: 201
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mmt-cdma-2
rhino-node-id: 202
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt2.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt2.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mmt-cdma-3
rhino-node-id: 203
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt3.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt3.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgExample for mmt-gsm-vmpool-config.yaml
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "MMT cluster"
# there are some pieces of software on this VM type that require clustering and
# knowing each other's IP addresses, for example Rhino
deployment-config:mmt-gsm-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-mmt-gsm-1
rhino-node-id: 201
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt1.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mmt-gsm-2
rhino-node-id: 202
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt2.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt2.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-mmt-gsm-3
rhino-node-id: 203
# Remove this if diameter-ro is disabled
per-node-diameter-ro:
diameter-ro-origin-host: mmt3.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
# Remove this if diameter-rf is disabled
# per-node-diameter-rf:
# diameter-rf-origin-host: mmt3.mmt.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgExample for shcm-vmpool-config.yaml
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise a "ShCM group"
deployment-config:shcm-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vApp parameter
site-id: DC1
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-shcm-1
diameter-sh-origin-host: shcm1.shcm.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
rhino-node-id: 101
- vm-id: example-shcm-2
diameter-sh-origin-host: shcm2.shcm.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
rhino-node-id: 102Example for smo-vmpool-config.yaml
# This file describes the pool of Virtual Machines that comprise an "SMO cluster"
# there are some pieces of software on this VM type that require clustering and
# knowing each other's IP addresses, for example Rhino and the OCSS7 SGC.
deployment-config:smo-virtual-machine-pool:
# needs to match the deployment_id vapp parameter
deployment-id: example
# needs to match the site_id vapp parameter
site-id: DC1
# Whether sentinel-ipsmgw should be enabled and installed on the smo node.
# If set to false, ipsmgw will not be installed and no other sentinel-ipsmgw config
# should be specified.
sentinel-ipsmgw-enabled: true
# Define one or more Rhino users and give their passwords in plain-text.
# Passwords will be encrypted by 'rvtconfig upload-config' before this file is uploaded to CDS.
# This user is a read-only user, they can log in and see things in Rhino but do not have permission to change configuration
# it is discouraged to log into Rhino to modify configuration using REM, instead the declarative configuration system should be used
rhino-auth:
- username: readonly
password: xxxxxxxx
virtual-machines:
- vm-id: example-smo-1
rhino-node-id: 301
# Uncomment this if diameter-ro is enabled
# per-node-diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-origin-host: smo1.smo.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
sip-local-uri: sip:smo1@mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-smo-2
rhino-node-id: 302
# Uncomment this if diameter-ro is enabled
# per-node-diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-origin-host: smo2.smo.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
sip-local-uri: sip:smo2@mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
- vm-id: example-smo-3
rhino-node-id: 303
# Uncomment this if diameter-ro is enabled
# per-node-diameter-ro:
# diameter-ro-origin-host: smo3.smo.site1.mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.org
sip-local-uri: sip:smo3@mnc123.mcc530.3gppnetwork.orgYANG schemas
The YANG schema used to validate the YAML configuration consists of the following sub-schemas:
- snmp-configuration.yang
- routing-configuration.yang
- system-configuration.yang
- traffic-type-configuration.yang
- bsf-configuration.yang
- naf-filter-configuration.yang
- common-configuration.yang
- home-network-configuration.yang
- number-analysis-configuration.yang
- sas-configuration.yang
- shcm-service-configuration.yang
- sentinel-volte-configuration.yang
- hlr-configuration.yang
- icscf-configuration.yang
- sgc-configuration.yang
- sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration.yang
- vm-types.yang
snmp-configuration.yang
module snmp-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/snmp-configuration";
prefix "snmp";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "SNMP configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping snmp-configuration-grouping {
leaf v1-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enables the use of SNMPv1 if set to 'true'. Note that support for SNMPv1
is deprecated and SNMP v2c should be used instead. Use of v1 is limited
to Rhino only and may cause some Rhino statistics to fail to appear
correctly or not at all. Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv1.";
}
leaf v2c-enabled {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Enables the use of SNMPv2c if set to 'true'.
Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv2c.";
}
leaf v3-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enables the use of SNMPv3 if set to 'true'.
Set to 'false' to disable SNMPv3.";
}
leaf trap_type {
when "../v2c-enabled = 'true'";
type enumeration {
enum trap {
description "Generate TRAP type notifications.";
}
enum inform {
description "Generate INFORM type notifications.";
}
}
default trap;
description "Configure the notification type to use when SNMPv2c is enabled.";
}
leaf community {
when "../v2c-enabled = 'true'";
type string;
default "clearwater";
description "The SNMPv2c community name.";
}
container v3-authentication {
when "../v3-enabled = 'true'";
leaf username {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The SNMPv3 user name.";
}
leaf authentication-protocol {
type enumeration {
enum SHA {
description "SHA";
}
enum MD5 {
description "MD5 message digest.";
}
}
default SHA;
description "The authentication mechanism to use.";
}
leaf authentication-key {
type vmt:secret {
length "8 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "The authentication key.";
}
leaf privacy-protocol {
type enumeration {
enum DES {
description "Data Encryption Standard (DES)";
}
enum 3DES {
description "Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES).";
}
enum AES128 {
description "128 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).";
}
enum AES192 {
description "192 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).";
}
enum AES256 {
description "256 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).";
}
}
default AES128;
description "The privacy mechanism to use.";
}
leaf privacy-key {
type vmt:secret {
length "8 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "The privacy key.";
}
description "SNMPv3 authentication configuration. Only used when 'v3-enabled' is set
to 'true'.";
}
container agent-details {
when "../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../v3-enabled= 'true'";
// agent name is the VM ID
// description is the human-readable node description from the metadata
leaf location {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The physical location of the SNMP agent.";
}
leaf contact {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The contact email address for this SNMP agent.";
}
description "The configurable SNMP agent details. The VM ID is used as the agent's
name, and the human readable node description from the metadata is used
as the description.";
}
container notifications {
leaf system-notifications-enabled {
when "../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Specifies whether or not system SNMP v2c/3 notifications are enabled.
System notifications are: high memory and CPU usage warnings,
and system boot notifications.
If you use MetaView Server to monitor
your platform, then it is recommended to set this to 'false'.";
}
must "system-notifications-enabled = 'false'
or (count(targets[send-system-notifications = 'true']) > 0)" {
error-message "You must specify whether to enable system notifications.
If enabled, you must also specify "
+ "at least one system notification target.";
}
leaf rhino-notifications-enabled {
when "../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Specifies whether or not Rhino SNMP v2c/3 notifications are enabled.
Applicable only when there is a Rhino node in your deployment
and SNMPv2c and/or SNMPv3 are enabled.";
}
must "rhino-notifications-enabled = 'false'
or count(targets[send-rhino-notifications = 'true']) > 0" {
error-message "You must specify whether to enable Rhino notifications.
If enabled, you must also specify "
+ "at least one Rhino notification target.";
}
leaf sgc-notifications-enabled {
when "../../v2c-enabled = 'true' or ../../v3-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Specifies whether or not OCSS7 SGC SNMP v2c/3 notifications are
enabled.
Applicable only when there is an SMO or an SGC node in your deployment
and SNMPv2c and/or SNMPv3 are enabled.";
}
must "sgc-notifications-enabled = 'false'
or count(targets[send-sgc-notifications = 'true']) > 0" {
error-message "You must specify whether to enable SGC notifications.
If enabled, you must also specify "
+ "at least one SGC notification target.";
}
list targets {
key "version host port";
leaf version {
type enumeration {
enum v1 {
description "SNMPv1";
}
enum v2c {
description "SNMPv2c";
}
enum v3 {
description "SNMPv3";
}
}
description "The SNMP notification version to use for this target.";
}
leaf host {
type ietf-inet:host;
description "The target host.";
}
leaf port {
type ietf-inet:port-number;
// 'port' is a key and YANG ignores the default value of any keys, hence we
// cannot set a default '162' here.
description "The target port, normally 162.";
}
leaf send-rhino-notifications {
when "../../rhino-notifications-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
default true;
description "Specifies whether or not to send Rhino SNMP v2c/3 notifications
to this target.
Can only be specified if ../rhino-notifications-enabled is true.";
}
leaf send-system-notifications {
when "../../system-notifications-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
default true;
description "Specifies whether or not to send system SNMP v2c/3 notifications
to this target.
Can only be specified if ../system-notifications-enabled is true.";
}
leaf send-sgc-notifications {
when "../../sgc-notifications-enabled = 'true'";
type boolean;
default true;
description "Specifies whether or not to send SGC SNMP v2c/3 notifications
to this target.
Can only be specified if ../sgc-notifications-enabled is true.";
}
description "The list of SNMP notification targets.
Note that you can specify targets even if not using Rhino or system
notifications - the targets are also used for the disk and
service monitor alerts.";
}
list categories {
when "../rhino-notifications-enabled = 'true'";
key "category";
leaf category {
type enumeration {
enum alarm-notification {
description "Alarm related notifications.";
}
enum log-notification {
description "Log related notifications.";
}
enum log-rollover-notification {
description "Log rollover notifications.";
}
enum resource-adaptor-entity-state-change-notification {
description "Resource adaptor entity state change notifications.";
}
enum service-state-change-notification {
description "Service state change notifications.";
}
enum slee-state-change-notification {
description "SLEE state change notifications.";
}
enum trace-notification {
description "Trace notifications.";
}
enum usage-notification {
description "Usage notifications.";
}
}
description "Notification category.
If you are using MetaView Server, only the `alarm-notification`
category of Rhino SNMP notifications is supported.
Therefore, all other notification categories should be disabled.";
}
leaf enabled {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to enable this category. Set to 'false' to disable.";
}
description "Rhino notification categories to enable or disable.";
}
description "Notification configuration.";
}
container sgc {
leaf v2c-port {
when "../../v2c-enabled = 'true'";
type ietf-inet:port-number;
default 11100;
description "The port to bind to for v2c SNMP requests.";
}
leaf v3-port {
when "../../v3-enabled = 'true'";
type ietf-inet:port-number;
default 11101;
description "The port to bind to for v3 SNMP requests.";
}
description "SGC-specific SNMP configuration.";
}
description "SNMP configuration.";
}
}routing-configuration.yang
module routing-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/routing-configuration";
prefix "routing";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import traffic-type-configuration {
prefix "traffic-type";
revision-date 2022-04-11;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Routing configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping routing-configuration-grouping {
list routing-rules {
key "name";
unique "target";
leaf name {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The name of the routing rule.";
}
leaf target {
type union {
type ietf-inet:ip-address;
type ietf-inet:ip-prefix;
}
mandatory true;
description "The target for the routing rule.
Can be either an IP address or a block of IP addresses.";
}
leaf interface {
type traffic-type:traffic-type;
mandatory true;
description "The interface to use to connect to the specified endpoint.
This must be one of the allowed traffic types,
corresponding to the interface carrying the traffic type.";
}
leaf gateway {
type ietf-inet:ip-address;
mandatory true;
description "The IP address of the gateway to route through.";
}
leaf-list node-types {
type enumeration {
enum shcm {
description "Apply this routing rule to the shcm nodes.";
}
enum mag {
description "Apply this routing rule to the mag nodes.";
}
enum mmt-gsm {
description "Apply this routing rule to the mmt-gsm nodes.";
}
enum mmt-cdma {
description "Apply this routing rule to the mmt-cdma nodes.";
}
enum smo {
description "Apply this routing rule to the smo nodes.";
}
enum tsn {
description "Apply this routing rule to the tsn nodes.";
}
enum max {
description "Apply this routing rule to the max nodes.";
}
enum rem {
description "Apply this routing rule to the rem nodes.";
}
enum sgc {
description "Apply this routing rule to the sgc nodes.";
}
enum custom {
description "Apply this routing rule to the custom nodes.";
}
}
description "The node-types this routing rule applies to.";
}
description "The list of routing rules.";
}
description "Routing configuration";
}
}system-configuration.yang
module system-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/system-configuration";
prefix "system";
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "OS-level parameters configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping system-configuration-grouping {
container networking {
container core {
leaf receive-buffer-size-default {
type uint32 {
range "65536 .. 16777216";
}
units "bytes";
default 512000;
description "Default socket receive buffer size.";
}
leaf receive-buffer-size-max {
type uint32 {
range "65536 .. 16777216";
}
units "bytes";
default 2048000;
description "Maximum socket receive buffer size.";
}
leaf send-buffer-size-default {
type uint32 {
range "65536 .. 16777216";
}
units "bytes";
default 512000;
description "Default socket send buffer size.";
}
leaf send-buffer-size-max {
type uint32 {
range "65536 .. 16777216";
}
units "bytes";
default 2048000;
description "Maximum socket send buffer size.";
}
description "Core network settings.";
}
container sctp {
leaf rto-min {
type uint32 {
range "10 .. 5000";
}
units "milliseconds";
default 50;
description "Round trip estimate minimum. "
+ "Used in SCTP's exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.";
}
leaf rto-initial {
type uint32 {
range "10 .. 5000";
}
units "milliseconds";
default 300;
description "Round trip estimate initial value. "
+ "Used in SCTP's exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.";
}
leaf rto-max {
type uint32 {
range "10 .. 5000";
}
units "milliseconds";
default 1000;
description "Round trip estimate maximum. "
+ "Used in SCTP's exponential backoff algorithm for retransmissions.";
}
leaf sack-timeout {
type uint32 {
range "50 .. 5000";
}
units "milliseconds";
default 100;
description "Timeout within which the endpoint expects to receive "
+ "a SACK message.";
}
leaf hb-interval {
type uint32 {
range "50 .. 30000";
}
units "milliseconds";
default 1000;
description "Heartbeat interval. The longer the interval, "
+ "the longer it can take to detect that communication with a peer "
+ "has been lost.";
}
leaf path-max-retransmissions {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. 20";
}
default 5;
description "Maximum number of retransmissions on one path before "
+ "communication via that path is considered to be lost.";
}
leaf association-max-retransmissions {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. 20";
}
default 10;
description "Maximum number of retransmissions to one peer before "
+ "communication with that peer is considered to be lost.";
}
description "SCTP-related settings.";
}
description "Network-related settings.";
}
description "OS-level parameters. It is advised to leave all settings at their defaults.";
}
}traffic-type-configuration.yang
module traffic-type-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/traffic-type-configuration";
prefix "traffic-type";
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Traffic type configuration schema.";
revision 2022-04-11 {
description "Initial revision";
reference "Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
typedef signaling-traffic-type {
type enumeration {
enum internal {
description "Internal signaling traffic.";
}
enum diameter {
description "Diameter signaling traffic.";
}
enum ss7 {
description "SS7 signaling traffic.";
}
enum sip {
description "SIP signaling traffic.";
}
enum http {
description "HTTP signaling traffic.";
}
enum custom-signaling {
description "Applies to custom VMs only.
Custom signaling traffic.";
}
enum custom-signaling2 {
description "Applies to custom VMs only.
Second custom signaling traffic.";
}
}
description "The name of the signaling traffic type.";
}
typedef multihoming-signaling-traffic-type {
type enumeration {
enum diameter-multihoming {
description "Second Diameter signaling traffic.";
}
enum ss7-multihoming {
description "Second SS7 signaling traffic.";
}
}
description "The name of the multihoming signaling traffic type.";
}
typedef traffic-type {
type union {
type signaling-traffic-type;
type multihoming-signaling-traffic-type;
type enumeration {
enum management {
description "Management traffic.";
}
enum cluster {
description "Cluster traffic.";
}
enum access {
description "Access traffic.";
}
}
}
description "The name of the traffic type.";
}
}bsf-configuration.yang
module bsf-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/bsf-configuration";
prefix "bsf";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "BSF configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping bsf-configuration-grouping {
// Zh is the interface between the BSF and the HSS
container zh-diameter {
uses vmt:diameter-configuration-grouping;
description "Diameter Zh configuration.";
}
// HTTP RA address and port is hardcoded since it has to match nginx.conf.
// Cassandra address and port is taken from the NAF filter config.
leaf debug-logging-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during
acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.";
}
description "The Bootstrap Security Function (BSF) configuration";
}
}naf-filter-configuration.yang
module naf-filter-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/naf-filter-configuration";
prefix "naf-filter";
import cassandra-configuration {
prefix "cassandra";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import extensions {
prefix "yangdoc";
revision-date 2020-12-02;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "NAF filter configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping naf-filter-configuration-grouping {
leaf service-type {
type uint8;
default 0;
description "Identifies the type of service the NAF filter is providing.
Recognized values for this setting are defined in Annex B of
3GPP TS 29.109. Affects which settings are selected from the GUSS.";
}
leaf service-id {
type uint16;
default 0;
description "An operator specific identifier that uniquely identifies the service the
NAF filter is providing within the network. Affects which settings
are selected from the GUSS.";
}
leaf naf-group {
type string;
default "";
description "Identifies the group that the NAF filter belongs to. Affects which
settings are selected from the GUSS.";
}
leaf-list force-auth-on-paths {
type string;
default "/rem/auth-check";
description "A list of URL path prefixes for which authentication should always be
enforced, even for requests from trusted entities.";
}
container cassandra-connectivity {
status obsolete;
uses cassandra:cassandra-connectivity-grouping;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Cassandra connectivity
configuration for the NAF filter";
}
container nonce-options {
uses nonce-options-grouping;
description "Settings for how the NAF filter handles nonce values";
}
leaf debug-logging-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during
acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.";
}
leaf intercept-tomcat-errors {
type boolean;
default false;
status obsolete;
description "OBSOLETE in RVT 4.1 series and later.
Whether to let NGINX replace Tomcat errors with default errors.
Use only on advice of your Customer Care Representative.";
yangdoc:change-impact "contact";
}
leaf http-version {
type enumeration {
enum 1.0 {
description "Use HTTP version 1.0.";
}
enum 1.1 {
description "Use HTTP version 1.1.";
}
}
default 1.1;
description "HTTP version to use on the Ub (BSF) and Ua/Ut (NAF) interfaces.";
yangdoc:change-impact "contact";
}
description "The Network Application Functions (NAF) filter configuration.";
}
grouping nonce-options-grouping {
leaf reuse-count {
type uint32;
default 100;
description "The maximum number of times a nonce can be reused by incrementing the
nonce count.";
}
leaf lifetime-milliseconds {
type uint32;
default 180000;
description "The time that a nonce remains valid for after being generated
(in milliseconds).";
}
leaf cache-capacity {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. max";
}
default 100000;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The capacity of the nonce cache.
This setting is only relevant when using the local storage mechanism.";
}
leaf storage-mechanism {
type enumeration {
enum cassandra {
description "Use Cassandra storage.";
}
enum local {
description "Use local storage.";
}
}
default local;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The storage mechanism to use for
the nonce cache.";
}
leaf nonce-cassandra-keyspace {
type string;
default "opencloud_nonce_info";
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. The Cassandra keyspace for the nonce
cache. This setting is only relevant when using the Cassandra storage
mechanism.";
}
description "Nonce option configuration.";
}
}common-configuration.yang
module common-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/common-configuration";
prefix "common";
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Common configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping common-configuration-grouping {
leaf platform-operator-name {
type string {
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+";
}
mandatory true;
description "The platform operator name.";
}
description "Common configuration.";
}
}home-network-configuration.yang
module home-network-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/home-network-configuration";
prefix "home-network";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Home network configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping home-network-configuration-grouping {
leaf home-domain {
type string {
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9@.:_/-]+";
}
description "Identifier for the home network.
Should match the value in the SIP: p-visited-network-id header inserted by
the S-CSCF or P-CSCF.
Used for determining whether a call is roaming or not.";
reference "RFC 3455 section 4.3";
}
leaf home-network-country-dialing-code {
type vmt:number-string {
length "1 .. 4";
}
mandatory true;
description "The home network country dialing code.";
}
leaf home-network-iso-country-code {
type string {
length "2";
pattern "[A-Z]*";
}
description "The home network ISO country code.";
}
list home-plmn-ids {
key "mcc";
leaf mcc {
type vmt:number-string {
length "3";
}
mandatory true;
description "The Mobile Country Code (MCC).";
}
leaf-list mncs {
type vmt:number-string {
length "2..3";
}
min-elements 1;
description "The list of Mobile Network Codes (MNCs).";
}
description "The home Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) identifiers.";
}
description "The home network configuration.";
}
}number-analysis-configuration.yang
module number-analysis-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/number-analysis-configuration";
prefix "number-analysis";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Number analysis configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
typedef dialing-code-type {
type string {
pattern '[0-9]+';
}
description "A type that represents a dialing code.";
}
grouping number-analysis-configuration-grouping {
container normalization {
leaf international-prefix {
type dialing-code-type {
length "1 .. 5"; // from http://www.idd.com.au/international-dialling-codes.php
}
mandatory true;
description "The international prefix. 1 to 5 digits in length.";
}
leaf min-normalizable-length {
type uint8 {
range "0 .. 31";
}
mandatory true;
description "The minimum normalizable length.";
}
leaf national-prefix {
type dialing-code-type {
length "1 .. 5";
}
mandatory true;
description "The national prefix. 1 to 5 digits in length.";
}
leaf network-dialing-code {
type dialing-code-type {
length "1 .. 3";
}
mandatory true;
description "The network dialing code. 1 to 3 digits in length.";
}
leaf normalize-to {
type enumeration {
enum international {
description "Normalize to international format.";
}
enum national {
description "Normalize to national format.";
}
}
default international;
description "The format to normalize to when comparing numbers, sending outgoing
requests and checking whether numbers are normalizable.";
}
description "Normalization configuration.";
}
leaf-list non-provisionable-uris {
type union {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
type vmt:phone-number-type;
}
description "List of URIs that cannot be provisioned.";
}
leaf assume-sip-uris-are-phone-numbers {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Set to 'true' to attempt to extract phone numbers from SIP URIs
even if they don't contain the 'user=phone' parameter.
Set to 'false' to disable this behaviour.";
}
description "Number analysis configuration.";
}
}sas-configuration.yang
module sas-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/sas-configuration";
prefix "sas";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "SAS configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping sas-configuration-grouping {
leaf enabled {
type boolean;
default true;
description "'true' enables the use of SAS, 'false' disables.";
}
container sas-connection {
when "../enabled = 'true'";
leaf system-type {
type string {
length "1..255";
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9.\\-_@:\"', ]+";
}
description "The SAS system type.
Only valid for custom nodes.
Defaults to the image name if not specified.";
}
leaf system-version {
type string;
description "The SAS system version.
Defaults to the VM version if not specified.";
}
leaf-list servers {
type union {
type ietf-inet:ipv4-address-no-zone;
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
}
min-elements 1;
description "The list of SAS servers to send records to.";
}
description "Configuration for connecting to SAS.";
}
description "SAS configuration.";
}
grouping sas-instance-configuration-grouping {
leaf system-name {
type string {
length "1..64";
}
description "The SAS system name.
Defaults to a string containing the deployment ID, system type,
and the node ID (or the VM index for unclustered nodes)
if not specified.";
}
description "SAS instance configuration.";
}
}shcm-service-configuration.yang
module shcm-service-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/shcm-service-configuration";
prefix "shcm-service";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix inet;
revision-date 2013-07-15;
}
import extensions {
prefix "yangdoc";
revision-date 2020-12-02;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "ShCM service configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
typedef cache-strategy-type {
type enumeration {
enum no-cache {
description "Do not use a cache.";
}
enum simple-cache {
description "Use a simple cache.";
}
enum subscription-cache {
description "Use a subscription cache.";
}
}
description "The type used to define the caching strategy.";
}
grouping shcm-service-configuration-grouping {
container diameter-sh {
uses vmt:diameter-configuration-grouping;
description "Diameter Sh configuration.";
yangdoc:change-impact "external";
yangdoc:change-impact "converges";
}
leaf health-check-user-identity {
type vmt:sip-uri-type;
mandatory true;
description "The health check user identity.
This should match a test user configured in the HSS.";
}
leaf-list additional-client-addresses {
type inet:ipv4-address;
description "Optional list of additional allowed ShCM client IP addresses.
These addresses may access the ShCM API port,
in addition to TAS and REM nodes
which automatically have access.";
}
leaf diameter-request-timeout-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "909 .. 27273";
}
default 5000;
description "The Diameter request timeout (in milliseconds).";
}
container cassandra-locking {
leaf backoff-time-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "50 .. 5000";
}
default 5000;
description "The time (in milliseconds) to backoff before re-attempting to obtain
the lock in Cassandra.";
}
leaf backoff-limit {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. 10";
}
default 5;
description "The limit of times to backoff and re-attempt to obtain a lock in
Cassandra.";
}
leaf hold-time-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "1000 .. 30000";
}
default 12000;
description "The time (in milliseconds) to hold a lock in Cassandra.";
}
description "Cassandra locking configuration.";
}
grouping cache-parameters-group {
description "Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.";
leaf cache-validity-time-seconds {
type uint32 {
range "1..172800";
}
mandatory true;
description "Cache validity time (in seconds).";
}
}
container caching {
list service-indications {
key "service-indication";
leaf service-indication {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "Service indication.";
}
leaf cache-strategy {
type cache-strategy-type;
default "subscription-cache";
description "Cache strategy.";
}
container cache-parameters {
when "../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'";
uses "cache-parameters-group";
description "Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.";
}
description "Service indications.";
}
list data-references-subscription-allowed {
key "data-reference";
leaf data-reference {
type enumeration {
enum ims-public-identity {
description "IMS public identity";
}
enum s-cscfname {
description "S-CSCF Name";
}
enum initial-filter-criteria {
description "Initial filter criteria";
}
enum service-level-trace-info {
description "Service level trace info";
}
enum ip-address-secure-binding-information {
description "IP address secure binding information";
}
enum service-priority-level {
description "Service priority level";
}
enum extended-priority {
description "Extended priority";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The data reference.";
}
leaf cache-strategy {
type cache-strategy-type;
default "subscription-cache";
description "The cache strategy.";
}
container cache-parameters {
when "../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'";
uses "cache-parameters-group";
description "Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.";
}
description "List of data references for which subscription is permitted, and
their caching strategy configuration";
}
list data-references-subscription-not-allowed {
key "data-reference";
leaf data-reference {
type enumeration {
enum charging-information {
description "Charging information";
}
enum msisdn {
description "MS-ISDN";
}
enum psiactivation {
description "PSI activation";
}
enum dsai {
description "DSAI";
}
enum sms-registration-info {
description "SMS registration info";
}
enum tads-information {
description "TADS information";
}
enum stn-sr {
description "STN SR";
}
enum ue-srvcc-capability {
description "UE SRV CC capability";
}
enum csrn {
description "CSRN";
}
enum reference-location-information {
description "Reference location information";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The data reference.";
}
leaf cache-strategy {
type enumeration {
enum no-cache {
description "Do not use a cache.";
}
enum simple-cache {
description "Use a simple cache.";
}
}
default "simple-cache";
description "The cache strategy.";
}
container cache-parameters {
when "../cache-strategy != 'no-cache'";
uses "cache-parameters-group";
description "Parameters describing the configuration for this cache.";
}
description "List of data references for which subscription is not permitted,
and their caching strategy configuration.";
}
description "Caching configuration.";
}
leaf debug-logging-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during
acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.";
}
description "ShCM service configuration.";
}
}sentinel-volte-configuration.yang
module sentinel-volte-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/sentinel-volte-configuration";
prefix "volte";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import diameter-rf-configuration {
prefix "rf";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import diameter-ro-configuration {
prefix "ro";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import privacy-configuration {
prefix "privacy";
revision-date 2020-05-04;
}
import extensions {
prefix "yangdoc";
revision-date 2020-12-02;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Sentinel VoLTE configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping sentinel-volte-configuration-grouping {
leaf session-replication-enabled {
type boolean;
default true;
description "When enabled, SIP dialogs and charging sessions can be failed over to
other cluster nodes if the original node fails.
Set to 'true' to enable session replication. Set to 'false' to disable.";
yangdoc:change-impact "restart";
}
container scc {
must "fetch-cmsisdn-source != 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'
or udr-included-identities = 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'" {
error-message "When `fetch-cmsisdn-source` is set to `EXTENDED_MSISDN`,"
+ " `udr-included-identities` MUST be set to `IMPU_AND_IMPI`.";
}
leaf scc-mobile-core-type {
type enumeration {
enum "gsm" {
description "GSM";
}
enum "cdma" {
description "CDMA";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The SCC mobile core type: 'GSM' or 'CDMA'.";
}
leaf fetch-cmsisdn-source {
type enumeration {
enum "MSISDN" {
description "MS-ISDN";
}
enum "EXTENDED_MSISDN" {
description "Extended MS-ISDN";
}
}
default "MSISDN";
description "The fetch Correlation Mobile Station ISDN (CMS-ISDN) source.
If set to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN', `udr-included-identities` MUST
be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.";
}
leaf udr-included-identities {
type enumeration {
enum "IMPU" {
description "IMPU";
}
enum "IMPU_AND_IMPI" {
description "IMPU_AND_IMPI";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "Defines which IMS user identities to include in outgoing user data
requests. Can be either 'IMPU' or 'IMPU_AND_IMPI'.
Must be set to 'IMPU_AND_IMPI' if `fetch-cmsisdn-source` is set
to 'EXTENDED_MSISDN'";
}
container service-continuity {
leaf atcf-update-timeout-milliseconds {
type uint32;
default 2000;
description "The Access Transfer Control Function (ATCF) update timeout";
}
leaf stn-sr {
type vmt:number-string;
mandatory true;
description "The Session Transfer Number for SRVCC (STN-SR).";
}
description "Service continuity configuration.";
}
container service-centralisation {
leaf inbound-ss7-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The originating SCCP address.";
yangdoc:change-impact "restart";
}
leaf use-direct-icscf-routing {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If 'true', the configured I-CSCF URI will be added to the route
header of the reoriginated INVITE. If 'false', the HSS will be
queried for the S-CSCF URI to use for the subscriber.";
}
leaf generated-pvni-template {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "A template string for the P-Visited-Network-Information header
generated in the reorigination, where {mnc} and {mcc} are
replaced with the MNC and MCC respectively.";
}
leaf police-originating-requests {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Police incoming originating requests, and reject attempts to
hijack the call.";
}
container simple-imrn-pool {
must "minimum-correlation-id < maximum-correlation-id" {
error-message "When configuring simple-imrn-pool config,"
+ " minimum-correlation-id must be less than"
+ " maximum-correlation-id.";
}
leaf minimum-correlation-id {
type uint64 {
range "0 .. 999999999999999999";
}
mandatory true;
description "The minimum correlation ID value used in the cluster.
0 to maximum-correlation-id.";
}
leaf maximum-correlation-id {
type uint64 {
range "0 .. 999999999999999999";
}
mandatory true;
description "The maximum correlation ID value used in the cluster. 0 to
(10^18-1).";
}
leaf number-of-digits-in-correlation-id {
type uint8 {
range "1 .. 18";
}
mandatory true;
description "The number of digits the correlation ID should have.
Minimum of number of digits in maximum-correlation-id
to 18 maximum.";
}
description "Simple IMRN pool config for mainline case.";
}
container scc-gsm-service-centralisation {
when "../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
container gsm-imrn-formation {
leaf routing-to-internal-network-number-allowed {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If set to 'true', routing to an internal network number is
allowed.";
}
leaf nature {
type enumeration {
enum "SUBSCRIBER" {
description "Subscriber";
}
enum "UNKNOWN" {
description "Unknown";
}
enum "NATIONAL" {
description "National";
}
enum "INTERNATIONAL" {
description "International";
}
enum "NETWORK_SPECIFIC" {
description "Network specific";
}
enum "NETWORK_ROUTING_NATIONAL" {
description "Network routing national";
}
enum "NETWORK_ROUTING_NETWORK_SPECIFIC" {
description "Network routing network specific";
}
enum "NETWORK_ROUTING_WITH_CALLED_DIRECTORY" {
description "Network routing with call directory";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The type of call. Used when forwarding a call.";
}
leaf numbering-plan {
type enumeration {
enum "SPARE_0" {
description "Spare 0";
}
enum "ISDN" {
description "ISDN";
}
enum "SPARE_2" {
description "Spare 2";
}
enum "DATA" {
description "Data";
}
enum "TELEX" {
description "Telex";
}
enum "NATIONAL_5" {
description "National 5";
}
enum "NATIONAL_6" {
description "National 6";
}
enum "SPARE_7" {
description "Spare 7";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The numbering plan to be used when forwarding a call.";
}
description "GSM IMRN formation configuration.";
}
leaf bypass-terminating-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If true, reorigination is skipped if the subscriber
is not registered in the IMS network.";
}
leaf always-term-reoriginate-if-served-user-is-roaming {
type boolean;
default false;
description "If true, roaming terminating sessions will always be
reoriginated (regardless of IMS registration).";
}
description "SCC GSM Service Centralisation Configuration.";
}
container scc-cdma-service-centralisation {
when "../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'";
container scc-cdma-actions {
typedef action {
type enumeration {
enum "accessDenied_notUsed" {
description "Access Denied - Not Used";
}
enum "accessDenied_unassignedDirectoryNumber" {
description "Access Denied - Unassigned Directory Number";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_inactive" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Inactive";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_busy" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Busy";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_terminationDenied" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Termination Denied";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_noPageResponse" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - No Page Response";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_unavailable" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Unavailable";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_serviceRejectedByMS" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By MS";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_serviceRejectedByTheSystem" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Service Rejected By The
System";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_serviceTypeMismatch" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Service Type Mismatch";
}
enum "accessDeniedReason_serviceDenied" {
description "Access Denied, Reason - Service Denied";
}
enum "allowCallToContinue" {
description "Allow Call To Continue";
}
}
description "SCC CDMA actions";
}
leaf action-on-unsupported-trigger {
type action;
mandatory true;
description "Action to take when an unexpected trigger is received.";
}
leaf action-on-failed-to-allocate-routing-number {
type action;
mandatory true;
description "Action to take when there is a failure generating a
routing number.";
}
leaf default-failure-action {
type action;
mandatory true;
description "Default action to take on error.";
}
description "SCC CDMA actions configuration.";
}
container cdma-imrn-formation {
leaf imrn-type-of-digits {
type enumeration {
enum "DIALED_OR_CALLED_PARTY_NUMBER" {
description "Dialed Number or Called Party Number";
}
enum "CALLING_PARTY_NUMBER" {
description "Calling Party Number";
}
enum "CALLER_INTERACTION" {
description "Caller Interaction";
}
enum "ROUTING_NUMBER" {
description "Routing Number";
}
enum "BILLING_NUMBER" {
description "Billing Number";
}
enum "DESTINATION_NUMBER" {
description "Destination Number";
}
enum "LATA" {
description "LATA";
}
enum "CARRIER" {
description "Carrier Number";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The type of digits used in the generated IMRN.";
}
leaf imrn-nature-of-number {
type enumeration {
enum "NATIONAL" {
description "National";
}
enum "INTERNATIONAL" {
description "International";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The nature field of the IMRN generated.";
}
leaf imrn-numbering-plan {
type enumeration {
enum "UNKNOWN" {
description "Unknown Numbering Plan";
}
enum "ISDN" {
description "ISDN Numbering";
}
enum "TELEPHONY" {
description "Telephony Numbering (ITU-T E.164, E.163)";
}
enum "DATA" {
description "Data Numbering (ITU-T X.121)";
}
enum "TELEX" {
description "Telex Numbering (ITU-T F.69)";
}
enum "MARITIME_MOBILE" {
description "Maritime Mobile Numbering";
}
enum "LAND_MOBILE" {
description "Land Mobile Numbering (ITU-T E.212)";
}
enum "PRIVATE" {
description "Private Numbering Plan (service provider defined)";
}
enum "PC_SSN" {
description "SS7 Point Code and Subsystem Number";
}
enum "IP_ADDRESS" {
description "Internet Protocol Address";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The numbering plan field of the IMRN generated.";
}
description "CDMA IMRN formation configuration.";
}
leaf bypass-forwarding-if-served-user-not-ims-registered {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If true, reorigination is skipped if the subscriber
is not registered in the IMS network.";
}
description "SCC CDMA Service Centralisation Configuration.";
}
description "SCC Service Centralisation Configuration.";
}
container tads {
leaf csrn-prefix {
type string;
description "The Circuit Switched Routing Number (CSRN) prefix.";
}
leaf address-source-for-scc-tads {
type enumeration {
enum "CMSISDN" {
description "Use the Correlation Mobile Station International
Subscriber Directory Number (CMSISDN) for SCC TADS.";
}
enum "MSRN" {
description "Use the Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN) for SCC TADS.
Only valid when the scc-mobile-core-type is 'gsm'.";
}
enum "TLDN" {
description "Use the Temporary Local Directory Number (TLDN) for SCC
TADS. Only valid when the scc-mobile-core-type is
'cdma'.";
}
}
must "(. != 'MSRN' and ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma')
or ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'" {
error-message "'address-source-for-scc-tads' cannot be set to 'MSRN' when"
+ " 'scc-mobile-core-type' is set to 'cmda'.";
}
must "(. != 'TLDN' and ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm')
or ../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'" {
error-message "'address-source-for-scc-tads' cannot be set to 'TLDN' when"
+ "'scc-mobile-core-type' is set to 'gsm'";
}
mandatory true;
description "Which value should be used for routing TADS requests to. Valid
values are 'CMSISDN', 'MSRN' (GSM only), and 'TLDN' (CDMA only)";
}
container voice-over-ps-support {
presence "Indicates that voice over PS support is required.";
leaf request-user-identity-type {
type enumeration {
enum "IMPU" {
description "The IMS Public ID user identity type.";
}
enum "MSISDN" {
description "The MS-ISDN user identity type.";
}
enum "IMPU_IMPI" {
description "The IMPU IMPI user identity type.";
}
enum "MSISDN_IMPI" {
description "The MS-ISDN IMPI user identity type.";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The user identity type to use in requests.";
}
description "Configuration for voice over PS support.";
}
leaf wlan-allowed {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Set to 'true' if W-LAN is allowed. Set to 'false' to disallow.";
}
leaf tads-identity-for-terminating-device {
type enumeration {
enum "IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY" {
description "Send TADS requests to the IMS public identity of the
terminating device";
}
enum "SIP_INSTANCE" {
description "Send TADS requests to the 'sip.instance' of the
terminating device";
}
enum "PATH_FROM_SIP_INSTANCE" {
description "Send TADS requests to the 'path' header within the
'sip.instance' of the terminating device";
}
}
default "IMS_PUBLIC_IDENTITY";
description "The identity of the terminating device that TADS will send the
request to.";
}
leaf end-session-error-code {
type uint32 {
range "400 .. 699";
}
default 480;
description "The SIP response code that is returned when a session is ended
due to an error.";
}
leaf cs-routing-via-icscf {
type boolean;
default true;
description "When enabled INVITE requests destined for the CS network will be
sent directly via the I-CSCF, bypassing the S-CSCF.";
}
container on-sequential-routing {
leaf tads-timer-max-wait-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "500 .. 5000";
}
mandatory true;
description "Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a potentially better forked
response.";
}
leaf-list ps-fallback-response-codes {
type vmt:sip-status-code {
range "400 .. 699";
}
description "List of SIP response codes that will trigger attempts of more
routes after a PS attempt.";
}
description "Configuration for TADS sequential routing";
}
container on-parallel-routing {
leaf parallel-timer-max-wait-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "0 .. 30000";
}
mandatory true;
description "Time to wait (in milliseconds) for a final response.";
}
leaf release-all-legs-on-busy {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "When enabled TADS will end all parallel forks on the first
busy response (486).";
}
description "Configuration for TADS parallel routing";
}
container sri-requests-to-hlr {
when "../../scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
leaf set-suppress-tcsi-flag {
type boolean;
default false;
description "If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR the feature
will set the suppress T-CSI flag on the request";
}
leaf set-suppress-announcement-flag {
type boolean;
default false;
description "If enabled, when sending an SRI request to the HLR on a
terminating call the feature will set the
'Suppression of Announcement' flag on the request.";
}
description "Configuration for SRI requests sent to the HLR";
}
container suppress-cs-domain-call-diversion {
presence "Suppress call diversion in CS domain";
leaf use-diversion-counter-parameter {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "When true, use diversion counter parameter, otherwise use
number of headers.";
}
leaf cs-domain-diversion-limit {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "The configured diversion limit in the CS network to suppress
further call diversion.";
}
description "When present, requests destined to the CS domain will contain a
Diversion header to suppress call diversion in the CS domain
side of the call.";
}
description "TADS configuration.";
}
description "SCC configuration.";
}
container mmtel {
container announcement {
leaf announcements-media-server-uri {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
mandatory true;
description "The URI of the media server used to play announcements.";
}
leaf announcements-no-response-timeout-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. max";
}
default 1000;
description "The maximum time to wait (in milliseconds) for the media server
to respond before cancelling an announcement.";
}
list announcements {
must "repeat > '-1' or interruptable = 'true'" {
error-message "'interruptable' must be set to 'true' if 'repeat' is set to
'-1'.";
}
key "id";
leaf id {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "The ID for this announcement.";
}
leaf description {
type string;
description "A description of what this announcement is used for.";
}
leaf announcement-url {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The file URL of this announcement on the media server.";
}
leaf delay-milliseconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The delay interval (in milliseconds) between repetitions
of this announcement.";
}
leaf duration-milliseconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The maximum duration (in milliseconds) of this announcement.";
}
leaf repeat {
type int32 {
range "-1 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "How many times the media server should repeat this
announcement. A value of -1 will cause the announcement
to repeat continuously until it is interrupted.";
}
leaf mimetype {
type string;
description "The MIME content type for this announcement, e.g audio/basic,
audio/G729, audio/mpeg, video/mpeg.";
}
leaf interruptable {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Determines whether this announcement can be interrupted. This
only applies to announcements played after the call is
established.";
}
leaf suspend-charging {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Determines whether online charging should be suspended while
this announcement is in progress. This only applies to
announcements played after the call is established.";
}
leaf end-session-on-failure {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Determines whether the session should be terminated if this
announcement fails to play. This only applies to
announcements played during call setup.";
}
leaf enforce-one-way-media {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Determines whether to enforce one-way media from the media
server to the party hearing the announcement. This only applies
to announcements played after the call is established.";
}
leaf locale {
type string;
description "The language/language variant used in the announcement.";
}
description "A list containing the configuration for each announcement that
the system can play.";
}
container default-error-code-announcement {
presence "Enable default error code announcement";
leaf announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
mandatory true;
description "The ID of the announcement to be played to the calling party
when an error response is received during call setup.";
}
leaf end-call-with-487-response {
type boolean;
description "Determines whether the call should be ended with a 487
error code rather than the error code that triggered the
announcement.";
}
description "Configuration for the default announcement that is played when
an error response is received during call setup.";
}
list error-code-announcements {
key error-code;
leaf error-code {
type uint16 {
range "400..699";
}
mandatory true;
description "The SIP error response code that this entry applies to.";
}
leaf disable-announcement {
type boolean;
default false;
description "If set to 'true', no announcement will be played for this
error code, overriding any default error code announcement
that has been set.";
}
leaf announcement-id {
when "../disable-announcement = 'false'";
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "ID of the announcement to play when this error code is
received.";
}
leaf end-call-with-487-response {
type boolean;
description "Determines whether to use the original received error code,
or a 487 error code to end the call after the announcement.";
}
description "A list containing configuration for assigning specific
announcements for specific SIP error response codes received during
call setup.";
}
description "Configuration for SIP announcements.";
}
container hss-queries-enabled {
leaf odb {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Determines whether the HSS will be queried for operator
determined barring (ODB) subscriber data.";
}
leaf metaswitch-tas-services {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Determines whether the HSS will be queried for Metaswitch TAS
services subscriber data.";
}
description "Configuration for enabling optional queries for certain types of
subscriber data in the HSS.";
}
leaf determine-roaming-from-hlr {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
type boolean;
default true;
description "Determines whether location information from the GSM HLR should be
used to determine the roaming status of the subscriber.";
}
container conferencing {
leaf conference-mrf-uri {
type vmt:sip-uri-type;
mandatory true;
description "The URI for the Media Resource Function (MRF) used for
conferencing.";
}
leaf route-to-mrf-via-ims {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to add the I-CSCF to the 'route' header of messages
towards the MRF. Set to 'false' and the messages will be routed
directly to the MRF from the TAS.";
}
leaf msml-vendor {
type enumeration {
enum Dialogic {
description "Dialogic";
}
enum Radisys {
description "Radisys";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The Media Server Markup Language (MSML) vendor, for Conferencing.";
}
leaf enable-scc-conf-handling {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Determines the SIP signaling used to draw conference participants
from their consulting call into the conference call. When 'false'
the 3GPP standard conferencing signaling will be used, when 'true'
a more reliable method based on SCC access transfer procedures will
be used instead.";
}
leaf root-on-selector {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Determines where the root element is placed when generating MSML.
When 'false' it will be placed directly on the video layout
element, when 'true' its will be set on the selector element on
the video layout element.";
}
leaf-list conference-factory-psi-aliases {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
description "A list of conference factory PSIs to use in addition to the
standard conference factory PSIs, as per TS 23.003, which are:
- 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.<HOME-DOMAIN>'
- 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ims.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org'
- 'sip:mmtel@conf-factory.ics.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.3gppnetwork.org'
Within values '<HOME-DOMAIN>' matches the value defined for
/home-network/home-domain.
Within values, if both '<MCC>' and '<MNC>' are used in an entry,
they will match any MCC/MNC pair defined in
/home-network/home-plmn-ids.";
}
leaf maximum-participants {
type uint8 {
range "3 .. max";
}
mandatory true;
description "The maximum number of participants that are allowed in a single
conference call.";
}
leaf allow-video-conference-calls {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to allow video to be used in conference calls.";
}
leaf conference-view-removal-delay-milliseconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "Delay (in milliseconds) after a conference ends before
conference view information in cleaned up.";
}
container subscription {
leaf default-subscription-expiry-seconds {
type uint32;
default 3600;
description "Time (in seconds) for a subscription to last if the SUBSCRIBE
message doesn't contain an Expires header.";
}
leaf min-subscription-expiry-seconds {
type uint32;
default 5;
description "Minimum time (in seconds) that a subscription is allowed to
last for. SUBSCRIBE requests with an Expires value lower than
this are rejected.";
}
leaf polling-interval-seconds {
type uint32;
default 5;
description "Interval (in seconds) between of polls for changes to the
conference view.";
}
description "Configuration for conference event subscriptions.";
}
description "Configuration for the MMTel conferencing service.";
}
container international-and-roaming {
leaf non-international-format-number-is-national {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Set to 'true' to treat non-international numbers (no leading '+')
as national. Set to 'false' to disable this behaviour.";
}
leaf end-call-if-no-visited-network {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Set to 'true' to end the call if no visited network can be
determined. Set to 'false' to allow the call to proceed.";
}
leaf use-mcc-specific {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Set to 'true' to determine international status using different
configuration for each access network MCC.
Set to 'false' to use the default configuration.";
}
leaf min-length {
type uint8 {
range "0 .. 31";
}
mandatory true;
description "Minimum length that the destination address must be before doing
a check for international and roaming status.";
}
description "Configuration for determining international and roaming status.";
}
container north-american-numbering-plan-analysis {
leaf enable-nanp-analysis {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Whether to analyse numbers according to the North American
Numbering Plan, using this to determine location information.";
}
description "Configuration for analysing numbers according to the North American
Numbering Plan.";
}
container international-call-management {
container default-international-call-management {
leaf bar-calls-with-missing-prefix {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Whether calls dialed without the international prefix are
barred.";
}
leaf bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id {
when "../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix = 'true'";
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID of the announcement to play when calls dialed without
the international prefix are barred.";
}
leaf international-call-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID of the announcement to play to the calling party when an
international call is made.";
}
description "The default handling of calls determined to be international.";
}
list call-management-by-country-code {
when "../../north-american-numbering-plan-analysis/enable-nanp-analysis
= 'true'" ;
key iso-country-code;
leaf iso-country-code {
type string {
length "2";
pattern "[A-Z]*";
}
description "The determined ISO country code of the called party if
within the NANP.";
}
leaf bar-calls-with-missing-prefix {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Whether to bar calls to this destination that were dialled
without an international prefix.";
}
leaf bar-calls-with-missing-prefix-announcement-id {
when "../bar-calls-with-missing-prefix = 'true'";
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID of the announcement to play if calls to this destination
were barred.";
}
leaf international-call-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID of the announcement to play before international calls
to this destination are connected.";
}
description "The configuration of international NANP calls by destination
country. Only available if North American Numbering Plan
analysis is enabled.";
}
description "Configuration for barring and announcements of calls determined to be
international.";
}
container call-diversion {
uses vmt:feature-announcement {
refine "announcement/announcement-id" {
mandatory false;
}
augment "announcement" {
leaf voicemail-announcement-id {
when "../../forward-to-voicemail";
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID of the announcement to be played when forwarding
to a recognized voicemail server.";
}
description "Add voicemail-specific announcement.";
}
}
container mmtel-call-diversion {
leaf max-diversions {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "Maximum number of diversions that may be made while attempting
to establish a session.";
}
leaf max-diversion-action {
type enumeration {
enum REJECT {
description "Reject the call.";
}
enum DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION {
description "Direct the call to the address specified in
max-diversion-fixed-destination.";
}
enum DELIVER_TO_SUBSCRIBERS_VOICEMAIL_SERVER {
description "Direct the call to the subscriber's voicemail
server.";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "Action to take when the maximum number of diversions is
exceeded.";
}
leaf max-diversion-fixed-destination {
when "../max-diversion-action = 'DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION'";
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
description "The address to deliver communication to when the maximum
number of diversions is exceeded and ../max-diversion-action
is set to 'DELIVER_TO_FIXED_DESTINATION'.";
}
leaf no-reply-timeout-seconds {
type uint8 {
range "5 .. 180";
}
mandatory true;
description "Time to wait (in seconds) for a reply before diverting due to
a no reply rule. This value is the network default, and can
be overridden in subscriber data.";
}
leaf add-orig-tag {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Set to 'true' to add an 'orig' tag to the Route header when
diverting a call.";
}
leaf-list diversion-limit-exempt-uris {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
description "List of URIs may still be diverted to after the max diversions
limit has been reached.";
}
leaf suppress-for-cs-terminating-domain {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to suppress call diversion behaviour for calls
terminating in the CS domain.";
}
leaf prefer-subscriber {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to have subscriber configuration take
precedence over operator configuration.";
}
leaf default-target-uri {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
description "The address to forward to if an operator or subscriber
forward-to rule has no target specified.";
}
leaf-list additional-not-reachable-status-codes {
type vmt:sip-status-code {
range "300..301|303..399|400..403|405..407|409..485|488..699";
}
description "List of response codes that can trigger a 'not-reachable'
diversion rule (in addition to those outlined in the MMTel
call diversion specification). The following status codes
cannot be used: 1xx, 2xx, 302, 404, 408, 486, 487.";
}
leaf allow-not-reachable-during-alerting {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to allow diversion rules with 'not-reachable'
conditions to be triggered after a 180 response has been
received from the called party.";
}
leaf add-mp-param {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Set to 'true' to add a 'hi-target-param' of type 'mp' to the
History-Info header entry added by a diversion.";
}
description "Configuration for the MMTel call diversion service.";
}
container forward-to-voicemail {
presence "Enable forwarding to a subscriber's configured voicemail server if
all other connection attempts fail.";
leaf-list voicemail-uris {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
description "List of URIs for which a voicemail-specific announcement will
be played (if specified) and for which forwarding to
without allocated credit will be allowed (if enabled).";
}
leaf forward-to-voicemail-timeout-seconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "Maximum amount of time to wait (in seconds) for a call to be
successfully connected before executing default forward to
voicemail behaviour (if enabled). Set to '0' to disable
the timer.";
}
leaf forward-to-voicemail-without-ocs-credit {
when "../../../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'ro'
or ../../../../charging/gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro'
or ../../../../charging/cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'";
type enumeration {
enum NEVER_ALLOW {
description "Never forward to voicemail when credit has not been
allocated.";
}
enum ALLOW_ONLY_FOR_WELL_KNOWN_SERVERS {
description "Allow forwarding to voicemail when credit has not been
allocated if address matches a known voicemail
server.";
}
enum ALWAYS_ALLOW {
description "Always allow forwarding to voicemail when credit has
not been allocated.";
}
}
description "Determines whether to allow forwarding to voicemail when
credit cannot be allocated for a call. Only applies when using
Diameter Ro based online charging.";
}
description "Configuration for forwarding to a subscriber's voicemail server.";
}
description "Configuration for the MMTel call diversion service.";
}
container communication-hold {
uses vmt:feature-announcement;
container bandwidth-adjustment {
presence "Bandwidth adjustment is enabled.";
leaf b-as-parameter {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The value to set for the 'b=AS:' parameter to use when
processing a Hold response.";
}
leaf b-rr-parameter {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The value to set for the 'b=RR:' parameter to use when
processing a Hold response.";
}
leaf b-rs-parameter {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The value to set for the 'b=RS:' parameter to use when
processing a Hold response.";
}
description "Configuration for adjusting the bandwidth of responses when
sessions are Held and Resumed.
Parameter definitions: 3GPP TS 24.610 Rel 12.6.0 section 4.5.2.4.";
}
leaf holding-party-media-mode {
type enumeration {
enum NO_HOLD {
description "The passive party is not put on hold during the
announcement, media streams are left as they were.";
}
enum BLACK_HOLE_ONLY {
description "SDP is renegotiated with the passive party so that for
the duration of the announcement, all media streams
are directed to a black hole IP.";
}
enum FULL_HOLD {
description "SDP is renegotiated with the passive party so that for
the duration of the announcement, all media streams
are directed to a black hole IP; and additionally the
passive party is put on hold by setting the stream
status to `sendonly` or `inactive`.";
}
}
default FULL_HOLD;
description "Determines how media streams for the holding party are handled
while an announcement to the held party is in progress.";
}
description "Configuration for the MMTel communication hold service.";
}
container communication-waiting {
uses vmt:feature-announcement;
leaf timer-seconds {
type uint8 {
range "0 | 30 .. 120";
}
mandatory true;
description "The maximum time (in seconds) that the communication waiting
service will wait for the call to be answered before abandoning
it. Default value is 0, which means the timer does not apply.";
}
description "Configuration for the MMTel communication waiting service.";
}
container privacy {
uses privacy:privacy-config-grouping;
description "Configuration for the MMTel privacy services.";
}
container psap-callback {
leaf use-priority-header {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If set to 'true', use the contents of the Priority header in
the initial INVITE to determine whether the session is a
PSAP callback.";
}
container sip-message-options {
presence "Use the SIP MESSAGE mechanism to determine whether session is a PSAP
callback.";
leaf expiry-time-seconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "When a SIP MESSAGE notifying that a PSAP call has taken
place, this is the time (in seconds) after receiving that
MESSAGE that sessions for the identified user are assumed
to be a PSAP callback.";
}
leaf terminate-message {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If set to true, SIP MESSAGEs notifying a PSAP call will be
terminated at the MMTel, otherwise they are propagated
through the network.";
}
description "Configuration for the SIP MESSAGE mechanism for determining
whether a session is a PSAP callback.";
}
description "Configuration for PSAP callback service.";
}
container communication-barring {
container incoming-communication-barring {
uses vmt:feature-announcement {
refine "announcement/announcement-id" {
mandatory false;
}
augment "announcement" {
leaf anonymous-call-rejection-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "The ID for a different announcement that can be played
if the call is barred because it is from an anonymous
user.";
}
description "Add new fields to announcement.";
}
}
leaf international-rules-active {
type boolean;
default false;
description "If 'false', incoming call barring will ignore International
and International-exHC rules. This is because it is not
possible to accurately determine whether the calling party
is international in all circumstances.";
}
description "Configuration for incoming communication barring.";
}
container outgoing-communication-barring {
uses vmt:feature-announcement;
description "Configuration for outgoing communication barring.";
}
container operator-communication-barring {
container operator-barring-rules {
when "../../../hss-queries-enabled/odb = 'true'";
container type1 {
uses operator-barring-rule;
presence "Enable type1 operator barring rule";
description "The Type1 operator barring rule.";
}
container type2 {
uses operator-barring-rule;
presence "Enable type2 operator barring rule";
description "The Type2 operator barring rule.";
}
container type3 {
uses operator-barring-rule;
presence "Enable type3 operator barring rule";
description "The Type3 operator barring rule.";
}
container type4 {
uses operator-barring-rule;
presence "Enable type4 operator barring rule";
description "The Type4 operator barring rule.";
}
description "Configuration for operator barring rules.";
}
container outgoing-prefix-barring {
presence "Outgoing prefix barring is configured";
list prefixes {
key "prefix";
leaf prefix {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The prefix to match against for outgoing barring.";
}
leaf-list classifications {
type leafref {
path "../../classifications/name";
}
description "The classification(s) to apply when this prefix
is matched.";
}
description "The list of prefixes to match against, and their
corresponding classifications to be used for outgoing
barring.";
}
list classifications {
must 'minimum-number-length <= maximum-number-length' {
error-message "'minimum-number-length' must be less than or equal
to 'maximum-number-length'.";
}
must "not(announcement and disable-ocb-announcement = 'true')" {
error-message "'disable-ocb-announcement' must be omitted or
set to 'false' if an outgoing prefix barring
announcement is specified.";
}
key "name";
leaf name {
type string {
pattern '[^\t\n\r]+';
}
mandatory true;
description "The name for this barring classification.";
}
leaf minimum-number-length {
type uint8 {
range "1 .. 20";
}
mandatory true;
description "The minimum length the number must be to match
this classification.";
}
leaf maximum-number-length {
type uint8 {
range "1 .. 20";
}
mandatory true;
description "The maximum length the number can be to match
this classification.";
}
leaf match-international {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "When true, the normalized number must be international
and not within the Home Country Code to match this
classification.";
}
leaf barring-treatment {
type enumeration {
enum OSBType1 {
description "Treat call as a Type1 operator barring rule.";
}
enum OSBType2 {
description "Treat call as a Type2 operator barring rule.";
}
enum OSBType3 {
description "Treat call as a Type3 operator barring rule.";
}
enum OSBType4 {
description "Treat call as a Type4 operator barring rule.";
}
enum OperatorAllow {
description "Allow call to proceed.";
}
enum OperatorBar {
description "Bar the call.";
}
enum PremiumRateInformation {
description "Treat call as premium rate information.";
}
enum PremiumRateEntertainment {
description "Treat call as premium rate entertainment.";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "How to handle a call that this classification applies
to.";
}
leaf disable-ocb-announcement {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Disables the 'outgoing-call-barring' announcement.
Cannot be 'true' when an announcement is specified.";
}
uses vmt:feature-announcement {
refine "announcement/announcement-id" {
description "The ID of an announcement to play instead of the
usual 'outgoing-call-barring' announcement.";
}
}
description "The list of classifications that can be applied for a
prefix match.";
}
description "Configuration for outgoing prefix barring.";
}
description "Configuration for operator communication barring.";
}
description "Configuration for MMTel communication barring service.";
}
container vertical-service-codes {
container xcap-data-update {
leaf host {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "Hostname of XCAP server to send HTTP requests to.";
}
leaf port {
type ietf-inet:port-number;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Port of XCAP server to
send HTTP requests to. Can be omitted to use the default port
for the protocol port.";
}
leaf use-https {
type boolean;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Indicates whether or not
to use HTTP over TLS to connect to the XCAP server.";
}
leaf base-uri {
type ietf-inet:uri;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. Base URI of XCAP
server.";
}
leaf auid {
type string;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. XCAP application unique
identifier to use in request URI.";
}
leaf document {
type string;
status obsolete;
description "Obsolete in RVT 4.1 series and later. XCAP document to use in
request URI.";
}
leaf success-response-status-code {
type vmt:sip-status-code;
mandatory true;
description "Response status code to use following a successful HTTP
response.";
}
leaf failure-response-status-code {
type vmt:sip-status-code;
mandatory true;
description "Response status code to use following a failure HTTP
response.";
}
container failure-announcement {
presence "Enables announcement on failure";
leaf announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
mandatory true;
description "The ID of the announcement to be played.";
}
description "An announcement be played if the update fails.";
}
description "Configuration for service codes that execute XCAP data updates.";
}
description "Configuration for vertical service codes.";
}
description "Configuration for MMTel services.";
}
container registrar {
leaf data-storage-type {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
type enumeration {
enum hsscache {
description "HSS cache data storage.";
}
enum cassandra {
description "Cassandra data storage.";
}
}
default cassandra;
description "Data storage type.";
}
leaf user-identity-type-for-stn-sr-request {
type enumeration {
enum CMSISDN {
description "The user's CMS ISDN.";
}
enum PUBLIC_ID {
description "The user's public ID.";
}
}
default PUBLIC_ID;
description "The type of user identity to use when creating Sh requests for the
STN-SR.";
}
leaf include-private-id-in-stn-sr-request {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Whether the user's IMS Private ID should be included in Sh requests
for the STN-SR.";
}
description "Registrar configuration.";
}
container sis {
leaf unavailable-peer-list-timer-milliseconds {
type uint64;
default 60000;
description "The duration for which a server will be blocked after a failure is
detected. This avoids the RA trying to use the server immediately
after a failure, when it is most likely just going to fail again.
After this time has passed the failed server may be tried again on
subsequent client transactions. If a server specifies a Retry-After
duration in a 503 response, that value will be used instead.";
}
leaf failover-timer-milliseconds {
type uint64;
default 4000;
description "Specifies the duration of the failover timer. If
this timer expires before any responses were received, the
RA treats this as a transport error and tries sending the request to
the next available server. This timer should be set to a value smaller
than the default Timer B and Timer F timers (32s) so that failures can
be detected promptly. A value of zero disables this timer.";
}
description "SIS configuration.";
}
container hlr-connectivity-origin {
when "../scc/tads/address-source-for-scc-tads != 'CMSISDN'
or ../mmtel/determine-roaming-from-hlr = 'true'
or ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/originating-tdp
or ../charging/cap-charging/imssf/imcsi-fetching/terminating-tdp";
leaf originating-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The originating SCCP address. This often is a Point Code and SSN,
where the SSN is typically 145 or 146";
}
container gsm {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
description "HLR connectivity configuration specific to GSM.";
leaf mlc-address {
type vmt:ss7-address-string-type;
mandatory true;
description "The MLC SCCP address. This is the logical address
of the originator, i.e. this service. Typically a Global Title.";
}
leaf use-msisdn-as-hlr-address {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Indicates if 'hlr/hlr-address' should be used as the actual
HLR address, or have its digits replaced with the MSISDN of
the subscriber.";
}
leaf msc-originating-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
description "Originating SCCP address when acting as an MSC, used when
establishing the MAP dialog. Will default to the value of
'originating-address' when not present. Typically used to set a
different originating SSN when sending a SendRoutingInformation
message to the HLR.";
}
}
container cdma {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'";
description "HLR connectivity configuration specific to CDMA.";
leaf market-id {
type uint32 {
range "0..65535";
}
mandatory true;
description "The market ID (MarketID).
Forms part of the Mobile Switching Center Identification (MSCID)";
reference "X.S0004-550-E v3.0 2.161";
}
leaf switch-number {
type uint32 {
range "0..255";
}
mandatory true;
description "The switch number (SWNO).
Forms part of the Mobile Switching Center Identification (MSCID)";
reference "X.S0004-550-E v3.0 2.161";
}
}
leaf map-invoke-timeout-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "250 .. 45000";
}
default 5000;
description "The Message Application Part (MAP) invoke timeout (in milliseconds).";
}
description "Origin HLR connectivity configuration.";
}
container charging {
leaf gsm-online-charging-type {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'gsm'";
type enumeration {
enum ro {
description "Use Diameter Ro charging.";
}
enum cap {
description "Use CAMEL Application Part (CAP) charging.";
}
enum cap-ro {
description "Use both Diameter Ro and CAMEL Application Part (CAP)
charging.";
}
enum disabled {
description "Disable online charging.";
}
}
default ro;
description "The online charging type. Only valid when 'scc-mobile-core-type' is
'gsm'.";
}
leaf cdma-online-charging-enabled {
when "../../scc/scc-mobile-core-type = 'cdma'";
type boolean;
default true;
description "Set to 'true' to enable online charging. Set to 'false' to disable.
Only valid when 'scc-mobile-core-type' is 'cdma'.";
}
container ro-charging {
when "../gsm-online-charging-type = 'ro'
or ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro'
or ../cdma-online-charging-enabled = 'true'";
container diameter-ro {
uses ro:diameter-ro-configuration-grouping;
leaf continue-session-on-ocs-failure {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Set to 'true' to permit sessions to continue if there is an
OCS (Online Charging System) failure.";
}
description "Diameter Ro configuration.";
}
container charging-announcements {
container low-credit-announcements {
leaf call-setup-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "Announcement ID to be played during call setup if the
subscriber has low credit.";
}
leaf mid-call-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "Announcement ID to be played during a call if the
subscriber has low credit.";
}
leaf charging-reauth-delay-milliseconds {
type uint32;
description "The delay (in milliseconds) for issuing a credit check
after a call is connected with low balance (0 indicates
immediate reauth).";
}
description "Configuration for low credit announcements.";
}
container out-of-credit-announcements {
leaf call-setup-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "Announcement ID to be played during call setup if the
subscriber is out of credit.";
}
leaf mid-call-announcement-id {
type vmt:announcement-id-type;
description "Announcement ID to be played during a call if the
subscriber is out of credit.";
}
description "Configuration for out of credit announcements.";
}
description "Configuration for charging related announcements.";
}
description "Ro charging configuration. Used when 'cdma-online-charging-type' is
set to 'true' or when 'gsm-online-charging-type' is set to 'ro' or
'cap-ro'.";
}
container rf-charging {
must "../cdr/interim-cdrs" {
error-message "'interim-cdrs' section must be present when 'rf-charging' is"
+ " present.";
}
presence "Enables Rf charging.";
container diameter-rf {
uses rf:diameter-rf-configuration-grouping;
description "Diameter Rf configuration.";
}
description "Rf charging configuration. Presence enables Rf charging.";
}
container cap-charging {
when "../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap'
or ../gsm-online-charging-type = 'cap-ro'";
container imssf {
container imcsi-fetching {
leaf originating-tdp {
type uint8 {
range "2 | 3 | 12";
}
description "The requested Trigger Detection Point for originating
calls, which determines whether T_CSI or O_CSI is
requested from the HLR. Values of '2' or '3' will
request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other
values are not valid.";
}
leaf terminating-tdp {
type uint8 {
range "2 | 3 | 12";
}
description "The requested Trigger Detection Point for terminating
calls, which determines whether T_CSI or O_CSI is
requested from the HLR. Values of '2' or '3' will
request the O_CSI, '12' will request the T_CSI, other
values are not valid.";
}
description "IM-CSI fetching configuration.";
}
container charging-gt {
leaf format {
type string {
pattern '(\d*({iso})*({mcc})*({mnc})*)+';
}
mandatory true;
description "The format template to use when creating Charging GTs
(global title). It must be a digit string except for
tokens ('{iso}', '{mcc}', '{mnc}') which are
substituted in.";
}
leaf unknown-location {
type vmt:number-string;
mandatory true;
description "The Charging GT (global title) to use when one could not
be generated because the user’s location could not be
determined.";
}
leaf only-charge-terminating-call-if-international-roaming {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Should terminating charging only be applied if the served
user is roaming internationally.";
}
description "Configuration for the charging GT (global title) that is sent
to the SCP.";
}
leaf scf-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The SCCP address of the GSM charging SCP.";
}
description "IM-SSF configuration.";
}
description "CAP charging configuration. Used when 'gsm-online-charging-type' is
set to 'cap' or 'cap-ro'.";
}
container cdr {
container interim-cdrs {
presence "Enables interim CDRs.";
leaf write-cdrs-in-filesystem {
type boolean;
default true;
description "'true' means that CDRs are written locally by the application.
CDRs are written via Diameter Rf if the Sentinel VoLTE
configuration value 'rf-charging' is present.";
}
leaf write-cdr-on-sdp-change {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Indicates whether or not to write CDRs on SDP changes.";
}
leaf interim-cdrs-period-seconds {
type uint32;
default 300;
description "The maximum duration (in seconds) between timer driven interim
CDRs.
Setting this to zero will disable timer based interim CDRs.";
}
description "Interim CDR configuration. Presence enables Interim CDRs.";
}
leaf session-cdrs-enabled {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "'true' enables the creation of session CDRs, 'false' disables.";
}
leaf registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "'true' enables the creation of Registrar audit CDRs, 'false'
disables.";
}
leaf registrar-cdr-stream-name {
type string;
default 'registrar-cdr-stream';
description "CDR stream to write Registrar audit CDRs to.";
}
description "CDR configuration.";
}
description "Charging configuration";
}
container session-refresh {
leaf timer-interval-seconds {
type uint32;
default 30;
description "The interval (in seconds) of the periodic timer used to check whether
a session needs refreshing.";
}
leaf refresh-period-seconds {
type uint32;
default 570;
description "Period of no activity for leg to refresh (in seconds).";
}
leaf refresh-with-update-if-allowed {
type boolean;
default true;
description "Whether the session should be refreshed using UPDATE requests,
when the endpoint allows UPDATE requests.
Otherwise sessions are refreshed using re-INVITE requests.";
}
leaf max-call-duration-seconds {
type uint32;
default 86400;
description "Maximum allowed duration of a call (in seconds).";
}
description "Session Refresh configuration.";
}
leaf debug-logging-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during
acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.";
}
description "The Sentinel VoLTE configuration.";
}
grouping operator-barring-rule {
anyxml rule {
mandatory true;
description "";
}
container retarget {
presence "Indicates that the call should be retargeted when this rule matches.";
leaf retarget-uri {
type vmt:sip-or-tel-uri-type;
mandatory true;
description "The URI to retarget this call to if the barring rule matches.";
}
uses vmt:feature-announcement;
leaf disable-online-charging-on-retarget {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Should charging be disabled when we retarget.";
}
description "Should the call be retargeted if this barring rule matches.";
}
description "Operator barring rule";
}
}hlr-configuration.yang
module hlr-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/hlr-configuration";
prefix "hlr";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "HLR configuration schema.";
revision 2020-06-01 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping hlr-configuration-grouping {
leaf hlr-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The HLR SCCP address.
This is typically in the form of a Global Title";
}
description "HLR configuration.";
}
}icscf-configuration.yang
module icscf-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/icscf-configuration";
prefix "icscf";
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "I-CSCF configuration schema.";
revision 2020-06-01 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping icscf-configuration-grouping {
leaf i-cscf-uri {
type vmt:sip-uri-type;
mandatory true;
description "The URI of the Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF).
For MMT, the Conf and ECT features will automatically add an 'lr'
parameter to it. The hostname part should either be a resolvable name or
the IP address of the I-CSCF.";
}
description "I-CSCF configuration.";
}
}sgc-configuration.yang
module sgc-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/sgc-configuration";
prefix "sgc";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import hazelcast-configuration {
prefix "hazelcast";
}
import m3ua-configuration {
prefix "m3ua";
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "SGC configuration schema.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping sgc-configuration-grouping {
container hazelcast {
uses hazelcast:hazelcast-configuration-grouping;
description "Cluster-wide Hazelcast configuration.";
}
container sgcenv {
uses sgcenv-configuration-grouping;
description "Values to be placed in the sgcenv configuration file.";
}
container sgc-properties {
presence "This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.";
uses sgc-properties-configuration-grouping;
description "Values to be placed in the SGC.properties configuration file.";
}
container m3ua {
uses m3ua:m3ua-configuration-grouping;
description "M3UA configuration.";
}
description "SGC configuration.";
}
grouping sgcenv-configuration-grouping {
leaf jmx-port {
type ietf-inet:port-number;
default 10111;
description "The port to bind to for JMX service, used by the CLI and MXBeans.
The SGC's jmx-host will be set to localhost";
}
description "Values to be placed in the sgcenv configuration file.";
}
grouping sgc-properties-configuration-grouping {
list properties {
key "name";
leaf name {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "Property name.";
}
leaf value {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "Property value.";
}
description "List of name,value property pairs.";
}
description "Values to be placed in the SGC.properties configuration file.";
}
}sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration.yang
module sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration";
prefix "ipsmgw";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import vm-types {
prefix "vmt";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import diameter-ro-configuration {
prefix "ro";
revision-date 2019-11-29;
}
import extensions {
prefix "yangdoc";
revision-date 2020-12-02;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Sentinel IPSMGW configuration schema.";
revision 2020-06-01 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
grouping sentinel-ipsmgw-configuration-grouping {
container georedundancy {
presence "Enables geo-redundancy for IPSMGW.";
leaf total-sites {
type uint32 {
range '2 .. 32';
}
mandatory true;
description "The number of geo-redundant sites.";
}
// Site ID is derived from site-id in the vmpool config
description "Geo-redundancy configuration.";
}
container map-messaging {
leaf template-smsc-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The 'digits' parameter value in this template
is replaced by the value of that parameter from the
received SMSC address to create a return address to the SMSC.";
}
leaf originating-address {
type vmt:sccp-address-type;
mandatory true;
description "The SCCP address used as the calling party address in SS7 messages
initiated by the IP-SM-GW.";
yangdoc:change-impact "restart";
}
leaf ipsmgw-as-msc-address {
type vmt:ss7-address-string-type;
mandatory true;
description "The ipsmgw-as-msc-address is the address that the IP-SM-GW will
return to the GMSC during the SendRoutingInformation phase of the
MT message procedure, so that subsequent messages will be delivered
to the IP-SM-GW. TCAP messages with this address should be
routeable to an IP-SM-GW node.";
}
leaf use-msisdn-as-hlr-address {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Indicates if 'hlr/hlr-address' should be used as the actual HLR
address, or have its digits replaced with the MSISDN of the
subscriber.";
}
leaf suppress-hlr-interaction {
type boolean;
must ". = 'true' and ../../delivery-order = 'PS_ONLY' or . = 'false'" {
error-message "'suppress-hlr-interaction' can only be 'true' when"
+ " 'delivery-order' is set to 'PS_ONLY'";
}
mandatory true;
description "If true, no MAP messages will be sent to the HLR. Useful in LTE-only
networks. Can only be set to true when 'delivery-order' is 'PS_ONLY'";
}
leaf use-gt-as-calling-party {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "When accepting an OpenRequest, the SCCP responder address in the
OpenAccept will, by default, be set to the value of the SCCP called
party in the OpenRequest. If `UseGtAsCallingParty` is set to true,
and if the received sccp-called-party contains a global title, then
the global title will be used.";
}
leaf sms-content-size-threshold {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "If the length of the message content falls within the configured
maximum then send the ForwardSM as part of the TC-BEGIN. As a
special case a configured max size of 0 disables this functionality
regardless of the actual content length.";
}
leaf sri-sm-delivery-not-intended {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "If true, specify the SmDeliveryNotIntended flag when performing an SRI
for SM IMSI-only query (i.e. during SMMA callflows).";
}
leaf discard-inform-sc {
type boolean;
default true;
description "If true, discard outbound InformSC components from requests sent to
the HLR.";
}
leaf force-sm-rp-pri {
type boolean;
default true;
description "If true, force Sm_RP_PRI to be set to true in SendRoutingInfoForSM
requests sent to the HLR.";
}
description "IPSMGW address configuration.";
}
leaf invoke-timeout-milliseconds {
type uint32;
default 4500;
description "Timeout (in milliseconds) when invoking MAP operations.";
}
leaf terminating-domain {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "Domain defined by the operator to compose SIP URIs from the MSISDN.";
}
leaf sip-transport {
type enumeration {
enum tcp {
description "TCP.";
}
enum udp {
description "UDP.";
}
}
default udp;
description "The SIP transport to use for IPSMGW's own SIP URI in
outbound requests.";
}
leaf delivery-order {
type enumeration {
enum PS_THEN_CS {
description "Try IMS network first, then circuit-switched network second.";
}
enum CS_THEN_PS {
description "Try circuit-switched network first, then IMS network second.";
}
enum PS_ONLY {
description "Only try delivery over the IMS network.";
}
enum CS_ONLY {
description "Only try delivery over the circuit-switched network.";
}
}
mandatory true;
description "The delivery order for mobile-terminating messages.";
}
container charging-options {
leaf mt-ps-enabled {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Whether charging is enabled for mobile-terminating PS messages.";
}
leaf mt-cs-enabled {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Whether charging is enabled for mobile-terminating CS messages.";
}
leaf mo-ps-enabled {
type boolean;
mandatory true;
description "Whether charging is enabled for mobile-originating PS messages.";
}
container diameter-ro {
when "../mt-ps-enabled = 'true'
or ../mt-cs-enabled = 'true'
or ../mo-ps-enabled = 'true'";
uses ro:diameter-ro-configuration-grouping;
description "Diameter Ro configuration.";
}
container cdr {
leaf max-size-bytes {
type uint64;
default 100000000;
description "Approximate maximum size in bytes before a new CDR file is
started. After a CDR is written, the total file size is
compared to MaxSize. If the current file size is larger, it is
completed. If set to 0, no size-based rollover is done.";
}
leaf max-cdrs {
type uint32;
default 0;
description "Number of records to be written to a CDR file before a new file is
started. If set to 0, no record-based rollover is done.";
}
leaf max-interval-milliseconds {
type uint32 {
range "0 | 1000 .. max";
}
default 0;
description "The length of time (in milliseconds) before time-based file
rollover. If a CDR file is used for more than
max-interval-milliseconds without being rolled over due to
record- or size-based limits, it is completed anyway. If set to
0, no time-based rollover is done.";
}
leaf registrar-audit-cdrs-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "'true' enables the creation of Registrar audit CDRs, 'false'
disables.";
}
description "CDR configuration.";
}
description "Message charging options.";
}
container ue-reachability-notifications {
presence "Enables UE reachability notifications.";
leaf subscription-expiry-time-seconds {
type uint32;
mandatory true;
description "The UE reachability subscription expiry time (in seconds).";
}
description "Settings regarding UE reachability subscriptions.";
}
container correlation-ra-plmnid {
leaf mcc {
type leafref {
path "/home-network/home-plmn-ids/mcc";
}
mandatory true;
description "The Mobile Country Code (MCC).";
}
leaf mnc {
type leafref {
path "/home-network/home-plmn-ids[mcc = current()/../mcc]/mncs";
}
mandatory true;
description "The Mobile Network Code (MNC).";
}
description "The PLMNID used by the correlation RA to generate MT correlation IMSIs
when the routing info for the terminating subscriber cannot be
determined. Must match one of the PLMNIDs defined in the
home network configuration.";
}
container fallback-settings {
leaf fallback-timer-milliseconds {
type uint32;
default 5000;
description "Timeout (in milliseconds) before attempting message delivery
fallback.";
}
leaf-list avoidance-codes-ps-to-cs {
type uint32;
description "List of error codes which will prevent fallback from PS to CS.";
}
leaf-list avoidance-codes-cs-to-ps {
type uint32;
description "List of error codes which will prevent fallback from CS to PS.";
}
description "Delivery fallback settings.";
}
leaf-list sccp-allowlist {
type string;
description "List of allowed GT prefixes.
If non-empty, then requests from any GT originating addresses not on the
list will be rejected. If empty, then all requests will be allowed.
Requests from non-GT addresses are always allowed.";
}
leaf routing-info-cassandra-ttl-seconds {
type uint32;
default 120;
description "Timeout (in seconds) that routing info is stored in Cassandra.";
}
container ussi {
container reject-all-with-default-message {
presence "Reject all USSI messages with a default message";
leaf language {
type string {
length "2";
pattern "[a-zA-Z]*";
}
mandatory true;
description "The language that will be set in the USSI response message.";
}
leaf message {
type string;
mandatory true;
description "The text that will be set in the USSI response message.";
}
description "Should all USSI messages be rejected with a default message.";
}
description "USSI configuration.";
}
leaf debug-logging-enabled {
type boolean;
default false;
description "Enable extensive logging for verification and issue diagnosis during
acceptance testing. Must not be enabled in production.";
}
description "IPSMGW configuration.";
}
}vm-types.yang
module vm-types {
yang-version 1.1;
namespace "http://metaswitch.com/yang/tas-vm-build/vm-types";
prefix "vm-types";
import ietf-inet-types {
prefix "ietf-inet";
}
import extensions {
prefix "yangdoc";
revision-date 2020-12-02;
}
organization "Metaswitch Networks";
contact "rvt-schemas@metaswitch.com";
description "Types used by the various virtual machine schemas.";
revision 2019-11-29 {
description
"Initial revision";
reference
"Metaswitch Deployment Definition Guide";
}
typedef rhino-node-id-type {
type uint16 {
range "1 .. 32767";
}
description "The Rhino node identifier type.";
}
typedef sgc-cluster-name-type {
type string;
description "The SGC cluster name type.";
}
typedef deployment-id-type {
type string {
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9-]{1,20}";
}
description "Deployment identifier type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a'
through 'z', the digits '0' through '9' and hyphens. Must be between 1 and
20 characters in length, inclusive.";
}
typedef site-id-type {
type string {
pattern "DC[0-9]+";
}
description "Site identifier type. Must be the letters DC followed by one or more
digits 0-9.";
}
typedef node-type-suffix-type {
type string {
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9]*";
}
description "Node type suffix type. May only contain upper and lower case letters 'a'
through 'z' and the digits '0' through '9'. May be empty.";
}
typedef trace-level-type {
type enumeration {
enum off {
description "The 'off' trace level.";
}
enum severe {
description "The 'severe' trace level.";
}
enum warning {
description "The 'warning level.";
}
enum info {
description "The 'info' trace level.";
}
enum config {
description "The 'config' trace level.";
}
enum fine {
description "The 'fine' trace level.";
}
enum finer {
description "The 'finer' trace level.";
}
enum finest {
description "The 'finest' trace level.";
}
}
description "The Rhino trace level type";
}
typedef sip-uri-type {
type string {
pattern 'sip:.*';
}
description "The SIP URI type.";
}
typedef tel-uri-type {
type string {
pattern 'tel:\+?[-*#.()A-F0-9]+';
}
description "The Tel URI type.";
}
typedef sip-or-tel-uri-type {
type union {
type sip-uri-type;
type tel-uri-type;
}
description "A type allowing either a SIP URI or a Tel URI.";
}
typedef number-string {
type string {
pattern "[0-9]+";
}
description "A type that permits a non-negative integer value.";
}
typedef phone-number-type {
type string {
pattern '\+?[*0-9]+';
}
description "A type that represents a phone number.";
}
typedef sccp-address-type {
type string {
pattern "(.*,)*type=(A|C)7.*";
pattern "(.*,)*ri=(gt|pcssn).*";
pattern "(.*,)*ssn=[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9].*";
pattern ".*=.*(,.*=.*)*";
}
description "A type representing an SCCP address in string form.
The basic form of an SCCP address is:
`type=<variant>,ri=<address type>,<parameter>=<value>,...`
where `<variant>` is `A7` for ANSI-variant SCCP or `C7` for ITU-variant SCCP,
and `<address type>` is one of `gt` or `pcssn`
(for an address specified by Global Title (GT),
or Point Code (PC) and Subsystem Number (SSN), respectively).
The `<parameter>` options are:
- Point code: `pc=<point code in network-cluster-member (ANSI)
or integer (ITU) format>`
- Subsystem number: `ssn=<subsystem number 0-255>`
- Global title address digits: `digits=<address digits, one or more 0-9>`
- Nature of address: `nature=<nature>` where `<nature>` is
`unknown`, `international`, `national`, or `subscriber`
- Numbering plan: `numbering=<numbering>` where `<numbering>` is
`unknown`, `isdn`, `generic`, `data`, `telex`, `maritime-mobile`,
`land-mobile`, `isdn-mobile`, or `private`
- Global title translation type: `tt=<integer 0-255>`
- National indicator: `national=<true or false>`.
`parameter` names are separated from their values by an equals sign,
and all `<parameter>=<value>` pairs are separated by commas.
Do not include any whitespace anywhere in the address.
Only the `ssn` and `national` parameters are mandatory; the others are optional,
depending on the details of the address - see below.
Note carefully the following:
- For ANSI addresses, ALWAYS specify `national=true`,
unless using ITU-format addresses in an ANSI-variant network.
- For ITU addresses, ALWAYS specify `national=false`.
- All SCCP addresses across the deployment's configuration
must use the same variant (`A7` or `C7`).
- Be sure to update the SGC's SCCP variant in `sgc-config.yaml`
to match the variant of the addresses.
---
For PC/SSN addresses (with `ri=pcssn`), you need to specify
the point code and SSN.
For GT addresses (with `ri=gt`), you must specify the global title digits
and SSN in addition to the fields listed below (choose one option).
There are two options for ANSI GT addresses:
- translation type only
- numbering plan and translation type.
There are four options for ITU GT addresses:
- nature of address only
- translation type only
- numbering plan and translation type
- nature of address with either or both of numbering plan and translation type.
---
Some valid ANSI address examples are:
- `type=A7,ri=pcssn,pc=0-0-5,ssn=147,national=true`
- `type=A7,ri=gt,ssn=146,tt=8,digits=12012223333,national=true`
Some valid ITU address examples are:
- `type=C7,ri=pcssn,pc=1434,ssn=147,national=false`
- `type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=146,nature=INTERNATIONAL,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,
digits=123456,national=false`
- `type=C7,ri=gt,ssn=148,numbering=ISDN,tt=0,digits=0778899,national=false`";
}
typedef ss7-point-code-type {
type string {
pattern "(([0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9]-){2}[0-2]?[0-9]?[0-9])|"
+ "([0-1]?[0-9]{1,4})";
}
description "A type representing an SS7 point code.
When ANSI variant is in use, specify this in network-cluster-member format,
such as 1-2-3, where each element is between 0 and 255.
When ITU variant is in use, specify this as an integer between 0 and 16383.
Note that for ITU you will need to quote the integer,
as this field takes a string rather than an integer.";
}
typedef ss7-address-string-type {
type string {
pattern "(.*,)*address=.*";
pattern ".*=.*(,.*=.*)*";
}
description "The SS7 address string type.";
}
typedef sip-status-code {
type uint16 {
range "100..699";
}
description "SIP response status code type.";
}
typedef secret {
type string;
description "A secret, which will be automatically encrypted using the secrets-private-key
configured in the Site Definition File (SDF).";
}
grouping cassandra-contact-point-interfaces {
leaf management.ipv4 {
type ietf-inet:ipv4-address-no-zone;
mandatory true;
description "The IPv4 address of the management interface.";
}
leaf signaling.ipv4 {
type ietf-inet:ipv4-address-no-zone;
mandatory true;
description "The IPv4 address of the signaling interface.";
}
description "Base network interfaces: management and signaling";
}
grouping day-of-week-grouping {
leaf day-of-week {
type enumeration {
enum Monday {
description "Every Monday.";
}
enum Tuesday {
description "Every Tuesday.";
}
enum Wednesday {
description "Every Wednesday.";
}
enum Thursday {
description "Every Thursday.";
}
enum Friday {
description "Every Friday.";
}
enum Saturday {
description "Every Saturday.";
}
enum Sunday {
description "Every Sunday.";
}
}
description "The day of the week on which to run the scheduled task.";
}
description "Grouping for the day of the week.";
}
grouping day-of-month-grouping {
leaf day-of-month {
type uint8 {
range "1..28";
}
description "The day of the month (from the 1st to the 28th)
on which to run the scheduled task.";
}
description "Grouping for the day of the month.";
}
grouping frequency-grouping {
choice frequency {
case daily {
// empty
}
case weekly {
uses day-of-week-grouping;
}
case monthly {
uses day-of-month-grouping;
}
description "Frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: running a scheduled task in the single-entry
format is deprecated.";
}
uses time-of-day-grouping;
description "Grouping for frequency options for running a scheduled task.
Note: This field is deprecated. Use the options in
frequency-list-grouping instead.";
}
grouping frequency-list-grouping {
choice frequency-list {
case weekly {
list weekly {
key "day-of-week";
uses day-of-week-grouping;
uses time-of-day-grouping;
description "A list of schedules that specifies the days of the week
and times of day to run the scheduled task";
}
}
case monthly {
list monthly {
key "day-of-month";
uses day-of-month-grouping;
uses time-of-day-grouping;
description "A list of schedules that specifies the days of the month
and times of day to run the scheduled task";
}
}
description "Frequency options for running a scheduled task.";
}
description "Grouping for frequency options for a task scheduled multiple times.";
}
grouping time-of-day-grouping {
leaf time-of-day {
type string {
pattern "([0-1][0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]";
}
mandatory true;
description "The time of day (24hr clock in the system's timezone)
at which to run the scheduled task.";
}
description "Grouping for specifying the time of day.";
}
grouping scheduled-task {
choice scheduling-rule {
case single-schedule {
uses frequency-grouping;
}
case multiple-schedule {
uses frequency-list-grouping;
}
description "Whether the scheduled task runs once or multiple times per interval.";
}
description "Grouping for determining whether the scheduled task runs once
or multiple times per interval.
Note: Scheduling a task once per interval is deprecated.
Use the options in frequency-list-grouping instead
to schedule a task multiple times per interval.";
}
grouping rvt-vm-grouping {
uses rhino-vm-grouping;
container scheduled-sbb-cleanups {
presence "This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.";
uses scheduled-task;
description "Cleanup leftover SBBs and activities on specified schedules.
If omitted, SBB cleanups will be scheduled for every day at 02:00.";
}
description "Parameters for a Rhino VoLTE TAS (RVT) VM.";
}
grouping rhino-vm-grouping {
leaf rhino-node-id {
type rhino-node-id-type;
mandatory true;
description "The Rhino node identifier.";
}
container scheduled-rhino-restarts {
presence "This container is optional, but has mandatory descendants.";
uses scheduled-task;
description "Restart Rhino on a specified schedule, for maintenance purposes.
If omitted, no Rhino restarts will be enabled.
Note: Please ensure there are no Rhino restarts within one hour of a
scheduled Cassandra repair.";
}
description "Parameters for a VM that runs Rhino.";
}
grouping rhino-auth-grouping {
leaf username {
type string {
length "3..16";
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9]+";
}
description "The user's username.
Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.";
}
leaf password {
type secret {
length "8..max";
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+";
}
description "The user's password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using
the deployment's 'secret-private-key'.";
}
leaf role {
type enumeration {
enum admin {
description "Administrator role. Can make changes to Rhino configuration.";
}
enum view {
description "Read-only role. Cannot make changes to Rhino configuration.";
}
}
default view;
description "The user's role.";
}
description "Configuration for one Rhino user.";
}
grouping rem-auth-grouping {
leaf username {
type string {
length "3..16";
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9]+";
}
description "The user's username.
Must consist of between 3 and 16 alphanumeric characters.";
}
leaf real-name {
type string;
description "The user's real name.";
}
leaf password {
type secret {
length "8..max";
pattern "[a-zA-Z0-9_@!$%^/.=-]+";
}
description "The user's password. Will be automatically encrypted at deployment using
the deployment's 'secret-private-key'.";
}
leaf role {
type enumeration {
enum em-admin {
description "Administrator role. Can make changes to REM configuration.
Also has access to the HSS Subscriber Provisioning REST API.";
}
enum em-user {
description "Read-only role. Cannot make changes to REM configuration.
Note: Rhino write permissions are controlled by the Rhino
credentials used to connect to Rhino, NOT the REM credentials.";
}
}
default em-user;
description "The user's role.";
}
description "Configuration for one REM user.";
}
grouping diameter-multiple-realm-configuration-grouping {
uses diameter-common-configuration-grouping;
choice realm-choice {
case single-realm {
leaf destination-realm {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "The Diameter destination realm.";
}
}
case multiple-realms {
list destination-realms {
key "destination-realm";
min-elements 1;
leaf destination-realm {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "The destination realm.";
}
leaf charging-function-address {
type string;
description "The value that must appear in a P-Charging-Function-Addresses
header in order to select this destination realm. If omitted,
this will be the same as the destination-realm value.";
}
leaf-list peers {
type string;
min-elements 1;
description "List of Diameter peers for the realm.";
}
description "List of Diameter destination realms.";
}
}
description "Whether to use a single realm or multiple realms.";
}
description "Diameter configuration supporting multiple realms.";
}
grouping diameter-configuration-grouping {
uses diameter-common-configuration-grouping;
leaf destination-realm {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "The Diameter destination realm.";
}
description "Diameter configuration using a single realm.";
}
grouping diameter-common-configuration-grouping {
leaf origin-realm {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "The Diameter origin realm.";
yangdoc:change-impact "restart";
}
list destination-peers {
key "destination-hostname";
min-elements 1;
leaf protocol-transport {
type enumeration {
enum aaa {
description "The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA)
protocol over tcp";
}
enum aaas {
description "The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting with Secure
Transport (AAAS) protocol over tcp.
IMPORTANT: this protocol is currently not supported.";
}
enum sctp {
description "The Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA)
protocol over Stream Control Transmission Protocol
(SCTP) transport. Will automatically be configured
multi-homed if multiple signaling interfaces are
provisioned.";
}
}
default aaa;
description "The combined Diameter protocol and transport.";
}
leaf destination-hostname {
type ietf-inet:domain-name;
mandatory true;
description "The destination hostname.";
}
leaf port {
type ietf-inet:port-number;
default 3868;
description "The destination port number.";
}
leaf metric {
type uint32;
default 1;
description "The metric to use for this peer.
Peers with lower metrics take priority over peers
with higher metrics. If all peers have the same metric,
traffic is round-robin load balanced over all peers.";
}
description "Diameter destination peer(s).";
}
description "Diameter configuration.";
}
typedef announcement-id-type {
type leafref {
path "/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id";
}
description "The announcement-id type, limits use to be one of the configured SIP
announcement IDs from
'/sentinel-volte/mmtel/announcement/announcements/id'.";
}
grouping feature-announcement {
container announcement {
presence "Enables announcements";
leaf announcement-id {
type announcement-id-type;
mandatory true;
description "The announcement to be played.";
}
description "Should an announcement be played";
}
description "Configuration for announcements.";
}
}