This document details basic procedures for system administrators managing, maintaining, configuring, and deploying OpenCloud’s IM-SSF Module.
IM-SSF provides protocol translation from SIP to ETSI INAP CS1 and CAP v1/v2/v3 with the Service Interaction SLEE (SIS).
Topics
-
About the IM-SSF — IM-SSF features; and how it is triggered, looks up subscription information, classifies the call as originating or terminating, and runs the BCSM
-
Configuring the IM-SSF — configuring general properties, subscription information, and user interface
-
IM-SSF Statistics — parameter sets related to originating and terminating BCSMs, charging and writing call detail records, looking up subscription information, user interaction, and routing to the called party
-
IM-SSF Alarms — alarm types and descriptions
-
Using the IM-SSF — how to include the IM-SSF in a service composition, support more than one IM-SSF use in a service composition, override the IM-SSF method for classifying originating or terminating access tracing in the IM-SSF, support IM-SSF acting as an assisting SSF for announcements, and use rate limiting with the IM-SSF.
For more information
-
The IM-SSF SIS Module Changelog
-
Documentation on the Service Interaction SLEE (SIS)
About the IM-SSF
The IM-SSF module provides support for protocol translation from SIP to ETSI INAP CS1 and CAP v1/v2/v3.
Support for translation into other SS7 protocols are part of the IM-SSF module roadmap.
The IM-SSF module implements most of the features of the IMS specification (3gpp 23.278 'IM CN Interworking'), plus some additional features (such as support for ETSI INAP CS1).
| |
Standalone IM-SSF
The IM-SSF is also available as a dedicated standalone product. Contact your OpenCloud sales representative for more details. |
Below are tables outlining features related to 3gpp 23.278, plus additional features of the IM-SSF.
Features related to 3gpp 23.278
| Feature supported | Description |
|---|---|
|
CAPv1, CAPv2, CAPv3 |
supports CAMEL phase 1, 2, and 3 |
|
Call Control |
supports messages such as |
|
Charging |
supports |
|
User Interaction |
supports |
|
O-IM-CSI, VT-IM-CSI |
supports both originating and terminating subscription information |
| Feature NOT supported | Description |
|---|---|
|
CAP v4 |
does not yet support CAMEL phase 4 |
|
D-IM-CSI |
does not yet support dialed subscription information |
|
|
does not yet include a method for translating |
Additional features
| Feature supported | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
INAP |
The IM-SSF provides the same set of features for various INAP variants as it does for CAMEL. INAP variants currently supported are: ETSI INAP CS1, Ericsson INAP CS1 (optional), and Ericsson INAP CS1+ (optional).
|
||
|
Multiple media servers |
The IM-SSF uses lookup tables (which can support many entries) to map the parameters received from the SCP to the address of the media server to use. Can also provision a default media server. |
||
|
Configurable routing to the media server |
Some operators prefer the IM-SSF to route directly to the media server; others prefer the route to go back through the S-CSCF. Routing method is configurable per media server. Can also define default routing behaviour. |
||
|
Per-CSI-tracing |
Can enable detail tracing per CSI using an additional field in the CSI data stored in the IM-SSF. If per-CSI tracing is enabled, then the IM-SSF will generate more trace output whenever that CSI is applied to an incoming |
||
|
Ability to override per-MSISDN lookup of CSI |
The IM-SSF uses the MSISDN (extracted from the |
||
|
Ability to override method for classifying the trigger and originating or terminating |
The IM-SSF looks for a parameter in the incoming |
| |
See Using the IM-SSF for more details on using the additional IM-SSF features. See IM-SSF in Action for details on how IM-SSF istriggered, looks up subscription information, classifies the call as originating or terminating, and runs the BCSM. |
IM-SSF in Action
:sortorder:2
The IM-SSF is a protocol translator that mediates between a SIP session with the SIS and a CAP or INAP session with an external SCP.
Below is an outline of how IM-SSF is triggered, looks up subscription information, classifies the call as originating or terminating, and runs the BCSM.
INVITE triggers a composition that invokes IM-SSF
The process starts when …
1 |
…the SIS receives an 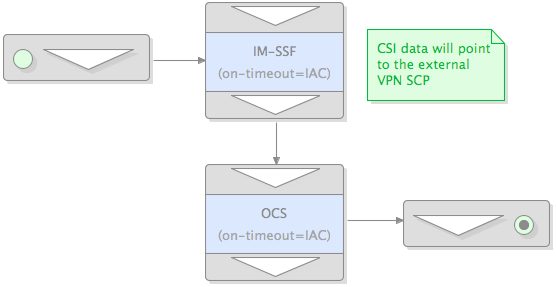
|
|---|---|
2 |
The SIS forwards the
|
3 |
IM-SSF uses a key to look up subscription information
If the INVITE has an "OC-IM-TDP" header, then the IM-SSF will use the value of the header for the subscription information, skipping the lookup with a key.
To look up subscription information, IM-SSF first checks to see if the INVITE has an "IM-CSI-Key"header. If so, IM-SSF will use the value of theheader as the key to lookup subscription information. Otherwise, it will:
1 |
Get the destination MSISDN from the |
||
|---|---|---|---|
2 |
|||
3 |
If the call is originating:
|
||
4 |
If the call is terminating:
|
| |
If IM-SSF fails to locate any subscription information for the call, it rejects the INVITE. |
| |
Getting an MSISDN from a SIP URI
If the IM-SSF cannot extract an MSISDN, it rejects the |
Classifying the call as originating or terminating
To classify a call as originating or terminating, the IM-SSF first checks to see if the INVITE includes an "IM-Access-Override" header. If the value of theheader is:
-
orig— IM-SSF applies originating treatment -
term— IM-SSF applies terminating treatment -
otherwise, the IM-SSF checks the parameters in the topmost Routeheader (see below).
| |
The IM-SSF is configured with the parameter to look for (RqdParameter) and the expected parameter value (RqdParameterVal) that tells the IM-SSF if the call is originating access. RqdParameterVal may be empty, indicating that presence of the parameter is enough to classify the call as originating.{ocpanel} |
| |
You can define the parameter the IM-SSF looks for using the sis-console command configure-originating-access. See General IM-SSF Configuration for more details. |
Inspecting the Routeheader
The IM-SSF inspects the topmost Routeheader and checks each parameter:
if (RqdParameterVal is Empty) then if (param == RqdParameter) then call is *originating*, else call is *terminating* else if (param == RqdParameter and paramVal == RqdParameterVal) then call is *originating* else call is *terminating*
In the following example, we can see an incoming INVITE that includes a parameter mode with expected value originating in the topmost route (in this case, the IM-SSF should be configured: configure-originating-access mode originating).
INVITE sip:1453800888888@ims1.operator.com SIP/2.0 To: <sip:1453800888888@ims1.operator.com;user=phone> From: <sip:+886230050000@ims1.operator.com;user=phone>;tag=snl_0008395652_NSN_CLIENT Call-ID: NSNSIP-c2421c0a-c4421c0a-1-11-1254881719-108155-1254989874 CSeq: 1235 INVITE ... Route: <sip:6N0j0Hg5C+O3p0hBLp~usAFA@172.28.81.7:5060;oc-node=101;lr;transport=udp;mode=originating>, ... ...
Running the BCSM
The IM-SSF executes the IM-BCSM following description 3gpp 23.278. An important aspect of this process is the subscription information it uses for the call. The subscription information tells the IM-SSF, among other things, the address of the external SCP to contact, the ServiceKey to use in the InitialDP message and how to respond in failure scenarios. The following tables explain the fields in both O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI.
Properties common to both O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Msisdn |
The unique id of the subscriber. This field is a string that is normally a digit sequence. It may, however, be a string that corresponds to the |
getGsmSCFAddress |
The SCCP address of the external SCF. |
ServiceKey. |
The service key to include in the |
DefaultCallHandling |
Indicates whether the IP multimedia session shall be released or continued in case of error in the IM-SSF to gsmSSF dialogue. One of ( |
CAMELCapabilityHandling |
Indicates the phase of CAMEL which is asked by the gsmSCF for the service. One of ( |
CSIActiveStatus |
Whether the CSI is active or not. |
TraceEnabled |
Whether detailed tracing should be done, if tracer level is |
O-IM-CSI
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Trigger Detection Points |
|
CollectedInfo |
One of ( |
AnalyzedInformation |
One of ( Note that this TDP is only relevant for INAP. |
RouteSelectFailure |
One of ( |
VT-IM-CSI
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Trigger Detection Points |
|
TerminatingAttemptAuthourised |
One of ( |
TBusy |
One of ( |
TNOAnswer |
One of ( |
| |
See Configuring IM-SSF Subscription Information for the sis-console commands to use for managing the subscription information. |
Configuring the IM-SSF
The SIS administration interface is extended with a set of commands during the IM-SSF installation process.
If you use the sis-console help command to list the help categories, you will see three new categories:
[Rhino@localhost (#25)] help Available command categories: auditing Manage Rhino's auditing subsystem ... imssf IM-SSF management operations imssf-csi IM-SSF subscription information management operations imssf-ui IM-SSF user interaction management operations ... Enter help <category name | command name substring> for a list of available commands
The first is related to general configuration properties, the second is related to subscription information, and the third is related to user-interaction configuration.
General IM-SSF Configuration
This command category supports general administration tasks such as activating the IM-SSF, or configuring the SCP timeout.
| |
Type help imssf at the sis-console to see a list of commands related to general IM-SSF configuration. |
Display the current configuration
imssf-displaygeneralcfg
Command |
imssf-displaygeneralcfg
Display general configuration of the IM-SSF
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display the current general configuration: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displaygeneralcfg IM-SSF Configuration Data addPAssertIDHeader : false autoPopulateInitialDP : false bNumberPrefixListForOAccess : 0800,0900 confirmedInviteErrorResponse : 487 ... |
Determine originating or terminating access and triggering
imssf-configurebnumberprefixes
Command |
imssf-configurebnumberprefixes <prefixes>
Provision the prefixes the IM-SSF will use to check the B number
for, to see if it will be used to lookup O-CSI on an originating
trigger. E.g: '0800,0900'
|
|---|---|
Example |
To provision prefixes of 0800 and 0900: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configurebnumberprefixes 0800,0900 B Number prefixes now set to: 0800,0900 |
imssf-configureoriginatingaccess
Command |
imssf-configureoriginatingaccess <parameter-name> (<parameter-value>)
Configure the parameter the IM-SSF uses to classify an incoming
INVITE as originating access. Some operators use the presence of
a parameter only (i.e it is originating if the parameter is
there, otherwise terminating). Other operators always include a
parameter, and use a particular parameter value (i.e it is
originating or terminating depending on the parameter value).
|
|---|---|
Example |
To use a parameter of 'call' with value 'orig': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configureoriginatingaccess call orig Method to determine originating access updated: look for the parameter 'call' with value 'orig' |
Install location-related properties
imssf-configurecountrycode
Command |
imssf-configurecountrycode <country-code>
Set the coutry code
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the country code to 64: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configurecountrycode 64 Country code now set to: 64 |
imssf-configureinternationaldiallingprefix
Command |
imssf-configureinternationaldiallingprefix <idd>
Set the international dialling prefix
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the international dialing prefix to 00: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configureinternationaldiallingprefix 00 International dialling prefix now set to: 00 |
imssf-configurescptimeout
Command |
imssf-configurescptimeout <timeout>
Set the SCP response timeout (in ms). The IM-SSF
treats the SCP as failed if it does not respond
to an InitialDP within this timeout
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the SCP timeout to .5s: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configurescptimeout 500 SCP timeout set to 500ms |
Configure SIP error-response codes
imssf-configuresiperrorresponsecodes
Command |
imssf-configuresiperrorresponsecodes <confirmed INVITE error code>
<unconfirmed INVITE error code>
<unconfirmed INVITE, after early media, error code>
Configure the sip error response codes to use when send an error
response in relation to the incoming INVITE. SIP error response
codes can be provisioned for three scenarios: for a confirmed
INVITE, for an unconfirmed INVITE and for an unconfirmed INVITE
where early media has played. Some operators prefer to use the
same error response code in all situations, some prefer to
distinguish the case where early media is involved
|
|---|---|
Example |
To use 'Request Terminated' for unconfirmed INVITEs and 'Not Acceptable' for confirmed INVITEs: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configuresiperrorresponsecodes 487 606 606 Sip error response codes configured Confirmed INVITE : 487 Unconfirmed INVITE : 606 Unconfirmed INVITE, after early media: 606 |
Enable optional features
imssf-enableaddpassertidheader
Command |
imssf-enableaddpassertidheader <true/false>
Enable the automatic additional of P-Assert-ID headers if
the From address is changed by the IM-SSF
|
|---|---|
Example |
To enable this feature: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-enableaddpassertidheader true Adding of a P-Assert-ID header if the From address changes has been turned on |
imssf-enableautopopulateinitialdp
Command |
imssf-enableautopopulateinitialdp <true/false>
Turn on the auto-populate-initialDP feature
|
|---|---|
Example |
To enable this feature: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-enableautopopulateinitialdp true The auto-populate-initialDP features has been turned on |
imssf-configureautopopulateinitialdpdefaults
Command |
imssf-configureautopopulateinitialdpdefaults <msc address> <mcc>
<mnc> <location number>
Set the default values to apply for the autopopulated feauture.
These defaults are all related to CAMEL. MscAddress is the
address string to include in the MSCAddress parameter in CAMEL
triggers. MCC (mobile country code) and MNC (mob network code)
are used build a default imsi and in location related paramters.
Location number is the address string used in the LocationNumber
parameter.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the default values related to auto-populating InitialDPs: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configureautopopulateinitialdpdefaults 6413456768 530 4 64495750394 The auto-populate-initialDP related defaults have been set: CAP MSC Address : 6413456768 MCC : 530 MNC : 4 Location Address: 64495750394 |
imssf-enableupdatefromdisplayname
Command |
imssf-enableupdatefromdisplayname <true/false>
Enable update of the From address display name based on the
Connect received from the SCP
|
|---|---|
Example |
To enable this feature: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-enableupdatefromdisplayname true Update of the From address display name based on response from the SCP has been turned on |
Configuring IM-SSF Subscription Information
The IM-SSF includes a table of subscription information that dictates which SCP is triggered for an initial INVITE.
There are two types of subscription information:
-
O-IM-CSIfor originating access -
VT-IM-CSIfor terminating access.
| |
Type help imssf-csi at the sis-console to see a list of commands related to subscription information. |
Originating subscription information (O-IM-CSI)
imssf-addoimcsi
Command |
imssf-addoimcsi <msisdn> <gscSCFAddress> <servicekey> <defaultCallHandling>
<camelCapabilityHandling> <csiActive (true/false)>
<traceEnabled (true/false)> <collectedInfoTriggerStatus>
<analyzedInfoTriggerStatus> <routeSelectFailureTriggerStatus>
Add a new O-IM-CSI for a subscriber (as identified by the msisdn
parameter).
camelCapabilityHandling = [CAPv2 (2), CAPv3 (3), CAPv4 (4),
ESTI INAP CS1 (5)]
triggerStatus = [Int (0), N&C (1), Trn (2), Unset (9)]
defaultCallHandling = [Continue (2), Release (1)]
|
|---|---|
Example |
To add O-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addoimcsi 21599374 type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 2 5 true true 0 2 2 Added O-IM-CSI for 21599374 |
imssf-removeoimcsi
Command |
imssf-removeoimcsi <msisdn>
Remove the O-IM-CSI for a subscriber
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove O-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removeoimcsi 21599374 Removed O-IM-CSI for 21599374 |
imssf-updateoimcsi
Command |
imssf-updateoimcsi <msisdn> <gscSCFAddress> <servicekey>
<defaultCallHandling> <camelCapabilityHandling>
<csiActive (true/false)> <traceEnabled (true/false)>
<collectedInfoTriggerStatus> <analyzedInfoTriggerStatus>
<routeSelectFailureTriggerStatus>
Change the O-IM-CSI for a subscriber (as identified by the msisdn
parameter).
camelCapabilityHandling = [CAPv2 (2), CAPv3 (3), CAPv4 (4),
ESTI INAP CS1 (5)]
triggerStatus = [Int (0), N&C (1), Trn (2), Unset (9)]
defaultCallHandling = [Continue (2), Release (1)]
|
|---|---|
Example |
To update O-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374, and change the protocol from INAP to CAPv2: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-updateoimcsi 21599378 type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 2 2 true true 0 2 2 Updated O-IM-CSI for 21599378 [Rhino@localhost (#2)] imssf-displayimcsi 21599378 IM-CSI for 21599378 CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- VT-IM-CSI 21599378 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599378 CAPv2 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] 2 rows |
Terminating subscription information (VT-IM-CSI)
imssf-addvtimcsi
`
Command |
imssf-addvtimcsi <msisdn> <gscSCFAddress> <servicekey>
<defaultCallHandling> <camelCapabilityHandling>
<csiActive (true/false)> <traceEnabled (true/false)>
<terminatingAttemptAuthTriggerStatus> <tBusyTriggerStatus>
<tNoAnswerTriggerStatus>
Add a new VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber (as identified by the
msisdn parameter).
camelCapabilityHandling = [CAPv2 (2), CAPv3 (3), CAPv4 (4),
ESTI INAP CS1 (5)]
triggerStatus = [Int (0), N&C (1), Trn (2), Unset (9)]
defaultCallHandling = [Continue (2), Release (1)]
|
|---|---|
Example |
To add VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addvtimcsi 21599374 type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 2 5 true true 0 2 2 Added VT-IM-CSI for 21599374 |
imssf-removevtimcsi
Command |
imssf-removevtimcsi <msisdn>
Remove the VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removevtimcsi 21599374 Removed VT-IM-CSI for 21599374 |
imssf-updatevtimcsi
Command |
imssf-updatevtimcsi <msisdn> <gscSCFAddress> <servicekey>
<defaultCallHandling> <camelCapabilityHandling>
<csiActive (true/false)> <traceEnabled (true/false)>
<terminatingAttemptAuthTriggerStatus> <tBusyTriggerStatus>
<tNoAnswerTriggerStatus>
Change the VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber (as identified by the
msisdn parameter).
camelCapabilityHandling = [CAPv2 (2), CAPv3 (3), CAPv4 (4),
ESTI INAP CS1 (5)]
triggerStatus = [Int (0), N&C (1), Trn (2), Unset (9)]
defaultCallHandling = [Continue (2), Release (1)]
|
|---|---|
Example |
To update VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599374, and change the protocol from INAP to CAPv2: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-updatevtimcsi 21599378 type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 2 2 true true 0 2 2 Updated VT-IM-CSI for 21599378 [Rhino@localhost (#2)] imssf-displayimcsi 21599378 IM-CSI for 21599378 CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- VT-IM-CSI 21599378 CAPv2 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599378 CAPv2 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] 2 rows |
Displaying subscription information
imssf-displayallcsi
Command |
imssf-displayallcsi <include O-IM-CSI (true/false)>
<include VT-IM-CSI (true/false)>
Inspect the O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI for all subscribers
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all O and VT IM-CSI records: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayallcsi true true CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- O-IM-CSI 21599376 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599374 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] VT-IM-CSI 21599378 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599378 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] VT-IM-CSI 21599376 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] 5 rows |
imssf-displayallocsi
Command |
imssf-displayallocsi
Inspect the O-IM-CSI for all subscribers
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all O-IM-CSI records: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayallocsi CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers --------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- O-IM-CSI 21599376 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599374 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599378 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] 3 rows |
imssf-displayallvtcsi
Command |
imssf-displayallvtcsi
Inspect the VT-IM-CSI for all subscribers
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all VT-IM-CSI records: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayallvtcsi CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- --------------------------------------------- VT-IM-CSI 21599378 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] VT-IM-CSI 21599376 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] 2 rows |
imssf-displayimcsi
Command |
imssf-displayimcsi <msisdn>
Inspect the O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI for a subscriber
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all CSI for a subscriber with MSISDN of 21599374: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayimcsi 21599374 IM-CSI for 21599374 CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- VT-IM-CSI 21599374 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599374 ESTI INAP CS1 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 true [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] 2 rows |
Tracing
imssf-enabletracing
Command |
imssf-enabletracing <msisdn> <traceEnabled (true/false)>
Enable tracing for a subscriber
|
|---|---|
Example |
To disable tracing for a subscriber with MSISDN 21599378: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-enabletracing 21599378 false Set per session tracing for 21599378 to false [Rhino@localhost (#24)] imssf-displayimcsi 21599378 IM-CSI for 21599378 CSI type msisdn camelCapabilityHandling csiActiveStatus defaultCallHandling gsmSCFAddress serviceKey traceEnabled triggers ---------- --------- ------------------------ ---------------- -------------------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------- ----------------------------------------------- VT-IM-CSI 21599378 CAPv2 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 false [TAttemptAuth=Int, TBusy=Trn, TNoAnswer=Trn] O-IM-CSI 21599378 CAPv2 true Continue type=c7,ri=pcssn,pc=2,ssn=224 55 false [CollectedInfo=Int, AnalyzedInfo=Trn, RSF=Trn] 2 rows |
Configuring IM-SSF User Interaction
The IM-SSF includes support for translating user-interaction requests by SCPs into equivalent requests to media servers in the IMS network.
For example, if an SCP requests that a particular announcement should be played with a PlayAnnouncement message containing an InformationToSend.SEND_INBAND_INFO, then the IM-SSF will map this to a corresponding INVITE to a media server with an appropriate play-URL.
| |
Type help imssf-ui at the sis-console to see a list of commands related to user interaction. |
User-interaction defaults
imssf-displayuigeneralconfiguration
Command |
imssf-displayuigeneralconfiguration
Display general IM-SSF configuration related to user interaction
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display the general user-interaction related configuration: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayuigeneralconfiguration General UI configuration Default: Media Server Address : mediaserver.local.net:1234 Default: Route Direct : false IpRoutingAddress Format : 'IPAddress,CorrelationID,ScfID', corrID length = 4 digits, scfID length = 2 digits |
imssf-configuredefaultmediaserveraddress
Command |
imssf-configuredefaultmediaserveraddress <host:port>
Provision the default address used for media server by the IM-SSF. The media
server is used as a part of user interaction.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To provision the default media server to use: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configuredefaultmediaserveraddress mediaserver.local.net:1234 Set default media server address mediaserver.local.net:1234 |
imssf-configuredefaultmediaserverrouting
Command |
imssf-configuredefaultmediaserverrouting <true/false>
Configure the default routing behaviour of the IM-SSF - whether it routes back
to the S-CSCF, or directly to the media server.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To configure the IM-SSF so that it does not route to the media server directly by default: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configuredefaultmediaserverrouting false Set default media server route-direct to false |
imssf-configureassistingsspiproutingaddressformat
Command |
imssf-configureassistingsspiproutingaddressformat <ICS|ICS|CIS|CSI|SIC|SCI>
<CorrelationID-length> <ScfID-length>
Configure how the IM-SSF should parse the assistingSSPIPRoutingAddress in
an EstablishTemporaryConnection message, in the case that correlation ID
and scf ID are encoding in this parameter. The first parameter defines the
layout of the assistingSSPIPRoutingAddress Address (I=IpAddress,
C=CorrelationID, S=ScfID)
|
|---|---|
Example |
To define the layout of the assistingSSPIPRoutingAddress as IpAddress/CorrelationID/ScfID, with correlation ID of 4 digits and and ScfID of 2 digits: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-configureassistingsspiproutingaddressformat ICS 4 2 Set assistingSSPIPRoutingAddress format to: 'IPAddress,CorrelationID,ScfID', with correlation ID of 4 digits and scf ID of 2 digits |
Media server address maps
The IM-SSF maintains a table of media server configuration properties that are mapped from the IP addresses provided by the SCP. This means the IM-SSF can support a number of different media servers if required. The IM-SSF will use default values if a mapping for an SCP-supplied address provided has not been provisioned.
imssf-addmediaserveraddressmapping
Command |
imssf-addmediaserveraddressmapping <SS7Address> <media-server host:port>
<route-direct (true/false)>
Add an entry into the media server address map. This map is a lookup
table of the ss7 address provided by the SCP to the ip address
(+ other configuration properties). The IM-SSF looks in this table
during user-interaction processing. If no entry is found, then the
defaults are applied.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To add a media server address mapping for '5421784584575': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addmediaserveraddressmapping 5421784584575 mediasever2.local.net:1234 true Added media server address mapping for 5421784584575 |
imssf-removemediaserveraddressmapping
Command |
imssf-removemediaserveraddressmapping <SS7Address>
Remove an entry from the media server address map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove a media server address mapping for 5421784584797: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removemediaserveraddressmapping 5421784584797 Removed media server address mapping for 5421784584797 |
imssf-displaymediaserveraddressmapping
Command |
imssf-displaymediaserveraddressmapping
Display the media server address map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all media server address mappings: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displaymediaserveraddressmapping CldPN MediaServerHostPort RouteDirect ----------- --------------------------- ------------ 5421784584797 mediasever3.local.net:1234 true 5421784584575 mediasever2.local.net:1234 true 2 rows |
Message announcement maps
The IM-SSF maintains a translation table to map announcement-related properties received by the SCP into equivalent properties that are provided to a media server. These commands support tasks related to managing this mapping.
imssf-addmessageannouncementmapping
Command |
imsssfaddmessageannouncementmapping <key> <scheme> <mimetype>
<announcementURL> <locale>
Add an entry into the message announcement map. This map is a lookup
table of a key (derived from the message ID) to properties used to
build the play URL sent to the media server
|
|---|---|
Example |
To add a message announcement mapping for 'msg-50': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addmessageannouncementmapping msg-50 sips audio/mpeg3 file://message50.mp3 en_NZ Added Message mapping for msg-50 |
imssf-removemessageannouncementmapping
Command |
imssf-removemessageannouncementmapping <key>
Remove an entry from the message announcement map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove a message mapping for msg-50: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removemessageannouncementmapping msg-50 Removed message mapping for msg-50 |
imssf-displaymessageannouncementmapping
Command |
imssf-displaymessageannouncementmapping
Display the tone announcement map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all provisioned message mappings: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displaymessageannouncementmapping MsgKey AnnouncementURL MimeType Scheme locale ------- --------------------- ------------ ------- ------- msg-60 file://message60.mp3 audio/mpeg3 sips en_NZ msg-50 file://message50.mp3 audio/mpeg3 sips en_NZ 2 rows |
Building the message 'key'
The key of the message announcement map is derived from the message ID provided by the SCP. We apply the following rules to build a message 'key':
MessageID
| Message type | Key | Example |
|---|---|---|
ID_ELEMENTARY_MESSAGE_ID |
msg-<eID.MessageID> |
msg-<ID> |
ID_ELEMENTARY_MESSAGE_IDS |
msg-<eIDs.MessageIDs[0]>(-<eIDs.MessageIDs[x]>)* |
msg-<ID1>-<ID2>-...-<IDn> |
ID_TEXT |
msg-<tID.MessageContent> |
msg-<msg content> |
ID_VARIABLE_MESSAGE |
msg-<vID.ElementaryMessageID>(-<*VariablePartKey*(vParts[x])>)* |
msg-<vpart1>-<vpart2>-...-<vpartn> |
Tone announcement maps
The IM-SSF maintains a translation table to map tone-related properties received by the SCP into equivalent properties that are provided to a media server. These commands support tasks related to managing this mapping.
imssf-addtoneannouncementmapping
Command |
imssf-addtoneannouncementmapping <toneID> <scheme> <mimetype> <toneURL>
Add an entry into the tone announcement map. This map is a lookup
table of a ToneID to properties used to build the play URL sent to
the media server
|
|---|---|
Example |
To add a tone mapping for Tone with ID '60': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addtoneannouncementmapping 60 sips audio/mpeg3 file://tone60.mp3 Added Tone mapping for 60 |
imssf-removetoneannouncementmapping
Command |
imssf-removetoneannouncementmapping <toneID>
Remove an entry from the tone announcement map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove a Tone mapping for Tone with ID 60: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removetoneannouncementmapping 60 Removed tone mapping for 60 |
imssf-displaytoneannouncementmapping
Command |
imssf-displaytoneannouncementmapping
Display the tone announcement map.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all tone announcement mappings: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displaytoneannouncementmapping
ToneID MimeType Scheme ToneURL
------- ------------ ------- ------------------
60 audio/mpeg3 sips file://tone60.mp3
50 audio/mpeg3 sips file://tone50.mp3
2 rows
|
Acting as an Assisting-SSP
If the IM-SSF received an EstablishTemporaryConnection message from an SCP it will act as the assisting SSP and send the SCP an AssistRequestInstructions message on a second dialog. These commands allow the administrator to influence the properties of the AssistRequestInstructions message the IM-SSF will send.
-
IPAvailableis used for INAP protocols and is an OCTET string that has operator-specific encoding and length. -
IPSSPCapabilitiesis used for CAMEL protocols and is a OCTET string that has operator-specific encoding and length of 4.
In some cases the EstablishTemporaryConnection message may contain enough information for the IM-SSF to contact a media server directly, instead of acting as an assisting SSP and initiating the second dialog with AssistRequestInstructions. In these cases the default assisting SSF behaviour can be disabled using imssf-disableassistingssfbehaviour, and the IM-SSF will contact the media server immediately based on the information in the EstablishTemporaryConnection.
imssf-addariipavailable
Command |
imssf-addariipavailable <assistingSSPRoutingAddress> <ipavailable (hexEncodedString)>
Configuree the AssistRequestInstructions IpAvailable to use when the IM-SSF is
acting as an assisting SSF related to an assistingSSPRoutingAddress provided by
the SCP in an EstablishTemporaryConnection.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the IPAvailable parameter to use when acting as the assisting SSP '5421784584575': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addariipavailable 5421784584575 71 Added ARI Ip Available for 5421784584575 of '71' |
imssf-addariipsspcapabilities
Command |
imssf-addariipsspcapabilities <assistingSSPRoutingAddress>
<ipsspcapabilities (hexEncodedString)>
Configure the AssistRequestInstructions IpSSPCapabilities to use
when the IM-SSF is acting as an assisting SSF related to an
assistingSSPRoutingAddress provided by the SCP in an
EstablishTemporaryConnection.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To set the IPSSPCapabilities parameter to use when acting as the assisting SSP '5421784584797': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-addariipsspcapabilities 5421784584797 93 Added ARI IP SSP Capabilities for 5421784584575 of '93' |
imssf-removeariproperties
Command |
imssf-removeariproperties <assistingSSPRoutingAddress>
Remove all AssistRequestInstructions related properties associated with an
assistingSSPRoutingAddress provided by the SCP
|
|---|---|
Example |
To remove IPSSPCapabilities and IPAvailable configured for the IM-SSF when acting as the assisting SSP '5421784584575': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-removeariproperties 5421784584575 Removed ARI SSP Capabilities for 5421784584575 |
imssf-enableassistingssfbehaviour
Command |
imssf-enableassistingssfbehaviour <assistingSSPRoutingAddress>
Instruct the IM-SSF that assisting SSF behaviour is enabled for this
assistingSSPRoutingAddress. When an EstablishTemporaryConnection
request is received for this address, the IM-SSF will use
AssistRequestInstructions, and will wait for instructions before
contacting the SIP media server.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To enable assisting SSF behaviour for the assisting SSP address '5421784584575': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-enableassistingssfbehaviour 5421784584575 Enabled Assisting-SSF behaviour for 5421784584575 |
imssf-disableassistingssfbehaviour
Command |
imssf-disableassistingssfbehaviour <assistingSSPRoutingAddress>
Instruct the IM-SSF that assisting SSF behaviour is disabled for
this assistingSSPRoutingAddress. When an EstablishTemporaryConnection
request is received for this address, the IM-SSF will not use
AssistRequestInstructions, and will contact the SIP media server
immediately instead.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To disable assisting SSF behaviour for the assisting SSP address '5421784584575': [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-disableassistingssfbehaviour 5421784584575 Disabled Assisting-SSF behaviour for 5421784584575 |
imssf-displayariproperties
Command |
imssf-displayariproperties
Display all AssistRequestInstructions related properties.
|
|---|---|
Example |
To display all ARI related properties: [Rhino@localhost (#1)] imssf-displayariproperties
AssistingSSPIPRoutingAddress AssistingSSFBehaviourNotRequired HasIPAvailable HasIPSSPCapabilities IPAvailable IPSSPCapabilities
----------------------------- --------------------------------- --------------- --------------------- ------------ ------------------
5421784584797 false false true 93
5421784584575 false true false 71
2 rows
|
IM-SSF Statistics
The IM-SSF defines parameter sets related to: originating and terminating BCSMs, charging and writing call detail records, looking up subscription information, user interaction, and routing to the called party.
| |
You can list the statistics parameter sets using the $ ./rhino-stats -l SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>]. See Usage in the Rhino Administration and Deployment Guide for more details about usage statistics. |
O_BCSM and T_BCSM statistic parameter sets
The IM-SSF defines a parameter set with these statistics for originating and terminating BCSMs.
| Counter | Description |
|---|---|
failedToInitialiseEnv |
a failure to initialise the components environment in setSbbContext |
rolledBackTransactions |
transactions that are rolledback |
sBBExceptionThrown |
how often sbbExecptionThrown is called by Rhino |
numberOfTriggers |
the number of triggers for this type of BCSM translator |
csiNotActive |
how often CSI used for the session is marked as not active |
triggerNotArmed |
how often CSI used for the session does not have the relevant trigger armed |
failedToBuildSCCPAddress |
failures to build an SCCP address for the external SCP from CSI data |
unsupportedProtocol |
triggers by way of procotols that are not supported |
failedToCreateOutboundSCPDialog |
failures to create a dialog to the external SCP |
defaultCallHandlingRelease |
how often CSI default call handling of Release is used |
defaultCallHandlingContinue |
how often CSI default call handling of Continue is used |
tssfExpiredOnInitialSCPResponse |
how often the Tssf timer expires waiting for a response from the extenal SCP to the InitialDP |
tssfExpiredOnEventReportSCPResponse |
how often the Tssf timer expires waiting for a response from the extenal SCP to an event report |
failedToSendMessageToSCP |
how often we fail to send a message to the SCP due to the underlying dialog being in an invalid state (such as closed) |
| |
Paremeter sets
SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=O_BCSM,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].(default) SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=T_BCSM,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].(default) |
Charging statistic parameter set
These counters are related to the IM-SSF writing call detail records.
| Counter | Description |
|---|---|
failedToInitialiseEnv |
a failure to initialise the components environment in setSbbContext |
rolledBackTransactions |
transactions that are rolledback |
sBBExceptionThrown |
how often sbbExecptionThrown is called by Rhino |
failedToWriteDR |
number of CDRs not written due to a failure on write |
cDRNotEnabled |
number of CDRs not written as the CDR RA is not enabled |
callFailedCDR |
number of CDRs written for a failed call |
callSuccessCDR |
number of CDRs written for a successful call |
zeroDurationCallCDR |
number of CDRs written that have a call duration of 0ms |
This sample statistic is the call duration of sessions processed by the IM-SSF. You can monitor the miniumum, maximum, and median call duration with this statistic.
| Sample | Description |
|---|---|
chargedCallDuration |
sample of the call duration |
| |
Parameter set
SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=Charging,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].(default) |
ProfileBasedCSIReader statistic parameter set
These parameters are related to looking up subscription information for an incoming trigger.
| Counter | Description |
|---|---|
failedToInitialiseEnv |
a failure to initialise the components environment in setSbbContext |
rolledBackTransactions |
transactions that are rolledback |
sBBExceptionThrown |
how often sbbExecptionThrown is called by Rhino |
noOImCsi |
how often there is no O-IM-CSI for the incoming session |
noVtImCsi |
how often there is no VT-IM-CSI for the incoming session |
| |
Parameter set
SLEE -Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=ProfileBasedCSIReader,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].(default) |
RouteToMediaNode statistic parameter set
These statistics are related to the IM-SSF supporting user interaction and routing to the media server to play announcements.
| Counter | Description |
|---|---|
failedToInitialiseEnv |
a failure to initialise the components environment in setSbbContext |
rolledBackTransactions |
transactions that are rolledback |
sBBExceptionThrown |
how often sbbExecptionThrown is called by Rhino |
failedToForwardInvite |
how often the IM-SSF fails to forward the initial INVITE |
useDefaultMediaServerAddress |
how often we use the configured default address for the media server |
failedToRouteToMediaNodeNo​DefaultMediaServerAddress |
how many times we fail to route to the media server because no default address is configured |
failedToRouteToMediaNodeNo​MessageAnnoucementMapping |
how many times we fail to route to the media server because no mapping is configured for the Msg ID For InformationToSend.SEND_INBAND_INFO |
failedToRouteToMediaNodeNo​ToneAnnoucementMapping |
how many times we fail to route to the media server because no mapping is configured for the Tone ID For InformationToSend.SEND_TONE |
noMediaServerAddressMappingForSS7Address |
how many times there is no configured mapping for the SS7 address from a ConnectToResource or EstablishTemporaryConnection |
noIPCapabilitiesForSS7Address |
how many times there are no IP capabilities configured for an EstablishTemporaryConnection |
| |
Parameter set
SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=RouteToMediaNode,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>]. |
RouteToDestination
This statistic is related to any exceptional failure to send the INVITE to destination party.
| Counter | Description |
|---|---|
failedToInitialiseEnv |
a failure to initialise the components environment in setSbbContext |
rolledBackTransactions |
transactions that are rolledback |
sBBExceptionThrown |
how often sbbExecptionThrown is called by Rhino |
failedToForwardInvite |
how often the IM-SSF fails to forward the initial INVITE |
| |
Parameter set
SLEE-Usage.Services.ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].SbbID[name=RouteToDestination,vendor=OpenCloud,version=<version>].(default) |
IM-SSF Alarms
The IM-SSF may raise the following two alarms:
| Alarm Type | Alarm Instance ID | Alarm level | Description | Raised if… |
|---|---|---|---|---|
UnlicensedComponent |
imssf_management |
CRITICAL |
IM-SSF is not active. Check that there is a valid license for Rhino-IM-SSF, and that resource adaptor entity imssf_management has been activated. |
…the IM-SSF is triggered by the SIS, but the IM-SSF is not licensed. |
opencloud.imssf.Alarm |
FailedToWriteCDR |
CRITICAL |
Failed to write a CDR. |
…the IM-SSF fails to write a call detail record. |
| |
Threshold-based alarms
You can define your own custom alarms using Rhino’s threshold based alarm feature — see Threshold Alarms in the Rhino Administration and Deployment Guide. |
Using the IM-SSF
Below are instructions for using the IM-SSF
Including the IM-SSF in a service composition
Before you can use the IM-SSF in a service composition you must create a service reference in your SIS SIP instance. Use the sis-console command createlocalserviceref to do this (see 1 Creating Local Service References):
[Rhino@localhost (#1)] createlocalserviceref sis-sip IM-SSF "name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=1.4" Created service reference IM-SSF for local SLEE service ServiceID[name=IM-SSF,vendor=OpenCloud,version=1.4]
Supporting more than one IM-SSF use in a service composition
The O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI tables are keyed on the MSISDN field (this field is actually of type String, so we can use things other than digit sequences as a key if we wish). The IM-SSF will also recognise a proprietary header: IM-CSI-KEY that it will use in place of the subscriber’s MSISDN when selecting an appropriate CSI.
So, one can define O-IM-CSI and VT-IM-CSI with the MSISDN field = <some string that corresponds to a service> and use a SIS signaling interceptor to add a header to the initial INVITE with IM-CSI-KEY: <some string that corresponds to a service>. The IM-SSF removes this header so we do not propagate it forward.
In the following example, we can see a fragment of an INVITE message that uses the IM-CSI-KEY header with the value to use as the CSI key of VPN.
INVITE tel:+351210999999 SIP/2.0 From: <tel:+351210900000>;tag=1 To: <tel:+351210999999> ... CSeq: 8511 INVITE ... IM-CSI-KEY: VPN
Overriding the IM-SSF method for classifying originating or terminating access
The IMSSF uses parameters in the route header to determine whether to use originating or terminating access. However, some use cases require an alternate method to classify the call as originating or terminating treatment. The IMSSF can recognise a proprietary header to decide how to treat the call.
The header is called IM-Access-Override, with valid values of orig and term. If this header exists, then the route is ignored and the value of the header is used instead.
If the values provided are not orig or term, the IM-SSF falls back onto the default behaviour.
The IM-SSF also removes this header so we do not propagate it forward.
One can use a SIS signaling interceptor to perform any ad-hoc determination of originating or terminating access, and add an IM-Access-Override header.
Tracing in the IM-SSF
The IM-SSF supports a per-CSI tracing option that will generate detailed output of messages sent and received, and generate a flow-trace output. You may configure this feature with the sis-console command imssfenabletracing (see Configuring IM-SSF Subscription Information).
Support for IM-SSF acting as an assisting SSF for announcements
The IM-SSF supports ETC/ARI for announcements. It acts as an assisting SSP when it receives an ETC, by opening a second dialog to the SCP and issuing an ARI on it. The properties of the ARI can be configured using the sis-console, with commands such as imssfaddariipavailable and imssfaddariipsspcapabilities (see Configuring IM-SSF User Interaction).
These commands let you manage a lookup table of assistSSPIPRoutingAddres → AssistRequestInstructions properties.
| IP Capabilities Profile Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
AssistingSSPIPRoutingAddress |
As provided in the ETC. |
IncludeIPSSPCapabilities |
Whether to include this in the ARI. iPSSPCapabilities:
|
IPSSPCapabilities |
The hex-encoded string that corresponds to the byte[]. |
IncludeIPAvailable |
Whether to include this in the ARI. iPAvailable:
|
IPAvailable |
The hex-encoded string that corresponds to the byte[]. |
If there is no entry in the IP-capabilities table, then the IM-SSF will use defaults of IPSSPCapabilities(supported=(IPRoutingAddress, VoiceBack)).
See the CGIN RA javadoc and the INAP and CAP specs for the layout of the byte[].
Correlation ID and Scf ID
The EstablishTemporaryConnection operation may either include a correlation ID and scfID as separate parameters, or it may encode them as a part of the AssistingSSPIPRoutingAddress parameter. This encoding is operator-specific, so the IM-SSF includes configuration options for controlling how this decoding is achieved.
Use the sis-console command imssfconfigureassistingsspiproutingaddressformat to configure how the IM-SSF should decode the AssistingSSPIPRoutingAddress parameter.
| |
The IM-SSF ignores the ScfID
Rather than use the ScfID to query a lookup table for the SCCP address of the SCP, the IM-SSF uses the CSI data it already has. That is, it assumes that the ARI should go to the same SCP that it sent the InitialDP to. |
Rate limiting the IM-SSF
The IM-SSF defines a custom rate limiter endpoint, imssf-triggers. By default this limiter endpoint is not associated with a limiter. You can create a limiter in the SIS using the sis-console, and associate it with the IM-SSF limiter endpoint if you wish.
[Rhino@localhost (#0)] listlimiterendpoints RAEntity/imssf-cdr/Input RAEntity/imssf_management/Input RAEntity/imssf_management/imssf-triggers RAEntity/sis-cap/Input RAEntity/sis-cap/inbound RAEntity/sis-inap/Input RAEntity/sis-inap/inbound RAEntity/sis-sip/Input RAEntity/sis-sip/inbound
IM-SSF SIS Module Changelog
3.1.12 - 2025-08-18
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.12
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.14
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.18
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.16
3.1.11 - 2025-04-16
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.11
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.13
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.17
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.15
-
Update the io.netty libraries to 4.1.118.Final
3.1.10 - 2025-01-27
-
Generate InitialDP/Location-Info/CellGlobalId with the MCC/MNC values provided by optional
OC-MCCandOC-MNCheaders. (#1876288) -
Fixed a bug to prevent IMSSF to forward
PRACK(received on upstream leg for previously sent 1xx-rel response) to already-torn-down downstream leg as initial request. (#1874118) -
Ensure that Reason headers in an incoming CANCEL request are copied to the corresponding outgoing CANCEL request. (#1902760)
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.10
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.12
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.16
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.14
-
Update the com.google.protobuf:protobuf-java library to 3.25.5
-
Update the io.netty libraries to 4.1.115.Final
| |
This version of Netty introduces new default DNS resolver behaviour when deploying on Rhino versions 3.1.13 and earlier. If you experience issues, please set the following Java system property to restore the old behaviour: io.netty.resolver.dns.tryCnameOnAddressLookups=true. Rhino versions 3.1.14 and later have this property set by default. |
3.1.9 - 2024-10-17
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.9
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.11
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.15
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.13
3.1.8 - 2024-07-12
Improvements
-
Fixed a bug stopping the IMSSF from handling calls to and from numbers with parameters in the user side of the SIP URI. (#1306954)
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.8
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.10
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.13
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.10
3.1.7 - 2024-02-29
New Features
-
Support for running on Java 17 (tested with the Microsoft build of OpenJDK 17). Existing support for Java 11 is unchanged.
Dependency Updates
-
Update the CGIN dependency to 3.1.6
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 4.1.7
-
Update the SIP dependency to 3.1.9
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.8
3.1.6 - 2024-01-25
Dependency Updates
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.7
-
Update the netty libraries to 4.1.103.Final
3.1.5 - 2023-11-13
Improvements
-
In a call diversion scenario, the vlr-address and the msc-address on the InitialDP for the terminating leg towards the diverted-to user are now set in the same way they would be on an ordinary terminating leg. (#894007)
-
Previously, these were set as the same values as would be set on an originating call.
-
The change means that for the terminating leg towards the diverted-to user, the InitialDP will:
-
have the vlr-address taken from the OC-Charging-GT header
-
have no msc-address present on the InitialDP
-
-
Dependencies
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.6
-
Update org.yaml:snakeyaml to 2.0 (#740859)
-
Update com.google.protobuf:protobuf-java to 3.19.6 (#740851)
3.1.4 - 2023-07-18
-
Fix an
IllegalStateExceptionthat occurs becauseRouteToMediaNodeSbbretrieves the wrongelementaryMessageIDparameter from aPlayAnnouncement(Request). (#398395) -
Make IM-SSF receive ActivityEndEvents. If the event is ending the last SipSession leg then IM-SSF now terminates charging. (#633380)
3.1.2 - 2022-12-21
Bug fixes
-
Fix an issue identified in P-Asserted-Identity header handling.
-
If Additional Calling Party Number present in Connect an the outbound INVITE would include an additional P-Asserted-Identity header. (#393069)
-
-
Fix an issue that meant Open Refuse events were not processed by the IM-SSF service. (#366598)
Dependencies
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.2
3.1.1 - 2022-10-13
| |
Release versions now have three components, not four. This release requires Rhino 3.1 or later. |
New features
-
IM-SSF now uses SNMP Static OIDs (added in Rhino 3.1). For more information see Static OID introduction.
Dependencies
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.2.1
-
All open source libraries used by this resource adaptor have been updated to the latest available version, including:
-
Netty to 4.1.70.Final.
-
Guava to 30.1.1-jre.
-
3.0.0.6 - 2021-11-18
Bug fixes
-
Fix issues identified in IM-SSF when handling SIP error responses during call setup. (VOLTE-10023)
-
Only generate ERBCSM 'routeSelectFailure' for an initial INVITE error response.
-
Handle SIP requests for follow on legs after initial INVITE error response.
-
Dependencies
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.0.0.7
3.0.0.4 - 2021-06-10
Bug fixes
-
Fix a bug where the IM-SSF would attempt (and fail) to change the BCSM state when receiving a SIP error response for a non-INVITE request while the call was active. (VOLTE-9760)
-
Fix a bug where the IM-SSF would attempt to send a SIP message on a dialog that no longer existed. (VOLTE-9715)
Dependencies
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.0.0.3
3.0.0.3 - 2021-05-10
-
Add SAS tracing for CAP messages. (VOLTE-9704)
-
Call IDs in log messages now appear alongside other logging context information rather than immediately before the actual message. (VOLTE-9679)
-
Update the SIS dependency to 3.0.0.2
3.0.0.0 - 2020-10-08
-
This release is built on and requires JDK 11. It requires Rhino 3.0 or later releases.
Bug fixes
-
Avoid sending a second PRACK to the MRF in precondition flows. (VOLTE-8433)
-
Fix issue with copying URI flag parameters between requests. (PRX-287)
2.7.0.3 - 2020-06-19
-
Update the Diameter dependency to 3.1.3.1
-
Update the Easysip dependency to 1.7.2
2.7.0.0 - 2019-10-24
-
Add support for active call failover. This allows SIP traffic for calls transiting the IM-SSF to continue on a different node after the original node goes down. Note that CAP translation will not continue on the new node as the dialog to the SCP cannot be recovered by the new node. (VOLTE-7780)
-
Fixed NullPointerException when forwarding CANCEL requests. (VOLTE-8330)
-
Corrected setting of pre-arranged end in some dialog close cases. (PRX-286)
2.6.2.6 - 2019-10-15
-
Fixed problem where ETCFailed was being incorrectly sent in response to CTR when MRF call failed (VOLTE-8328)
-
Improve sending CANCEL request error handling (VOLTE-8330)
-
Update SIS dependency to 2.6.2.10
2.6.2.5 - 2019-08-30
-
Disarm noAnswer event is cleared after Answer (PRX-284)
-
UPDATE error responses after call answered are forwarded (PRX-285)
-
Update SIS dependency to 2.6.2.9
-
Update http-ratype dependency to 2.5.0.1
-
Update rhino dependency to 2.6.2.6
2.6.2.4 - 2019-06-14
-
Fixed forwarding of responses resulting from a downstream forking proxy. (VOLTE-7411)
-
The
Request-Disposition: no-forkheader is no longer added to initial requests. (VOLTE-7815) -
Update Rhino dependency to 2.6.2.3